Interactions Between Iron Metabolism and the Endocannabinoid System in Bacterial Infections
Abstract
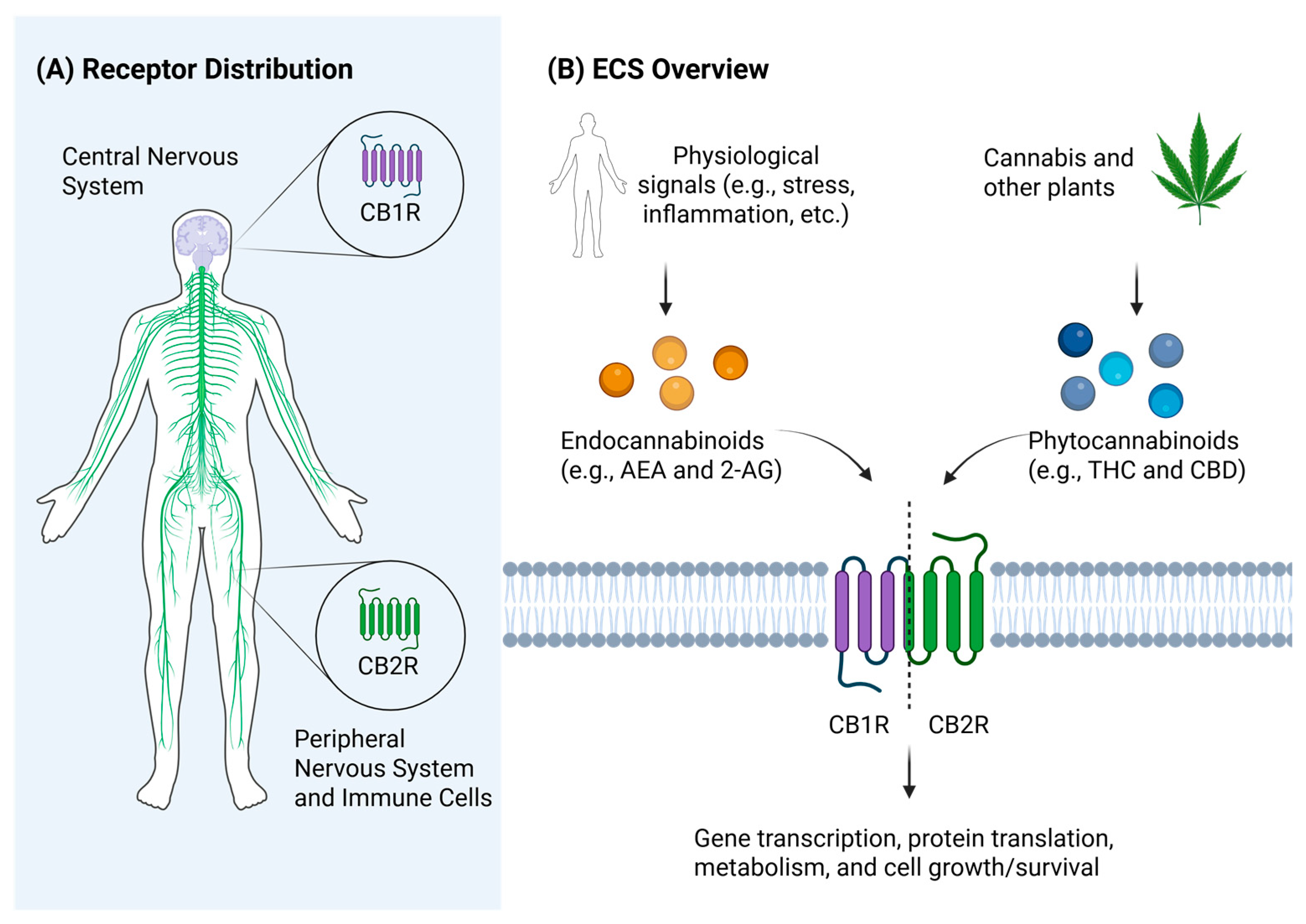
1. Introduction
2. Antibiotic Effects of Iron Chelators
3. Antibiotic Effects of Cannabinoids
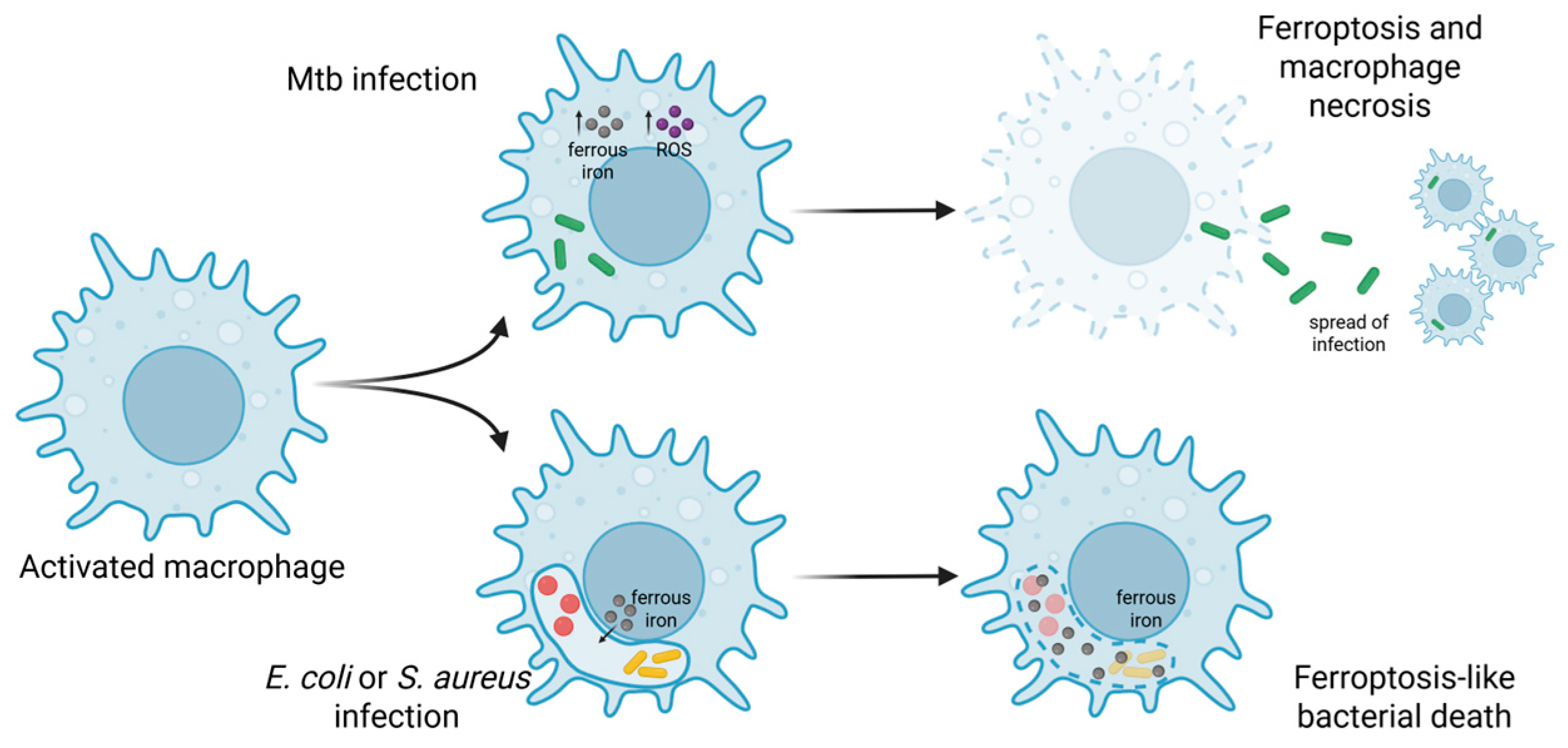
4. Potential Interactions and Synergies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Munk, P.; Njage, P.; van Bunnik, B.; McNally, L.; Lukjancenko, O.; Röder, T.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.; Pedersen, S.K.; Kjeldgaard, J.; et al. Global Monitoring of Antimicrobial Resistance Based on Metagenomics Analyses of Urban Sewage. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, A.N.; Zhu, S.; Cooper, N.; Little, P.; Tarrant, C.; Hickman, M.; Yao, G.; Karunasagar, I. The Economic Burden of Antibiotic Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Aguilar, G.R.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis with Forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudenda, S.; Chabalenge, B.; Daka, V.; Mfune, R.L.; Salachi, K.I.; Mohamed, S.; Mufwambi, W.; Kasanga, M.; Matafwali, S.K. Global Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2023, 14, 271–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegreness, M.; Shoresh, N.; Damian, D.; Hartl, D.; Kishony, R. Accelerated Evolution of Resistance in Multidrug Environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13977–13981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Rigol, S. A Brief History of Antibiotics and Select Advances in Their Synthesis. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antibacterial Products in Clinical Development for Priority Pathogens; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Belete, T.M. Novel Targets to Develop New Antibacterial Agents and Novel Alternatives to Antibacterial Agents. Hum. Microbiome J. 2019, 11, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaplewski, L.; Bax, R.; Clokie, M.; Dawson, M.; Fairhead, H.; Fischetti, V.A.; Foster, S.; Gilmore, B.F.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Harper, D.; et al. Alternatives to Antibiotics—A Pipeline Portfolio Review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ni, W. Cefiderocol for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Systematic Review of Currently Available Evidence. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 896971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaschella, C.; Nai, A.; Silvestri, L. Iron Metabolism and Iron Disorders Revisited in the Hepcidin Era. Haematologica 2020, 105, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frawley, E.R.; Fang, F.C. The Ins and Outs of Bacterial Iron Metabolism. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezari, S.; Haghi, S.M.; Norouzkhani, N.; Sahebnazar, B.; Vosoughian, F.; Akbarzadeh, D.; Islampanah, M.; Naghsh, N.; Abbasalizadeh, M.; Deravi, N. Iron Chelators in Treatment of Iron Overload. J. Toxicol. 2022, 2022, 4911205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.; Arora, G.; Dickson, K.; Lehmann, C. Iron Chelation in Local Infection. Molecules 2021, 26, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, K.P.; Skaar, E.P. A Battle for Iron: Host Sequestration and Staphylococcus Aureus Acquisition. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbina, S.; Gill, A.; Mathew, S.; Abbasi, U.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Polyglycerol-Based Macromolecular Iron Chelator Adjuvants for Antibiotics To Treat Drug-Resistant Bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 37834–37844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.G.; Corey, B.W.; Si, Y.; Craft, D.W.; Zurawski, D.V. Antibacterial Activities of Iron Chelators against Common Nosocomial Pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5419–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-F.; Qiu, D.-H.; Kong, X.-L.; Hider, R.C.; Zhou, T. Synthesis and In-Vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of a High-Affinity Iron Chelator in Combination with Chloramphenicol. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Olaleye, E.D.; Kong, X.; Zhou, T.; Ma, Y.; Jurach, J.; Al Rugaie, O.; Hider, R.C.; Zhang, G.; Alsam, S.; et al. Macromolecular Iron-Chelators via RAFT-Polymerization for the Inhibition of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Growth. Polymer 2016, 87, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parquet, M.d.C.; Savage, K.A.; Allan, D.S.; Davidson, R.J.; Holbein, B.E. Novel Iron-Chelator DIBI Inhibits Staphylococcus Aureus Growth, Suppresses Experimental MRSA Infection in Mice and Enhances the Activities of Diverse Antibiotics in Vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.T.C.; Gumbau-Brisa, R.; Allan, D.S.; McDonald, R.; Ferguson, M.J.; Holbein, B.E.; Bierenstiel, M. DIBI, a 3-Hydroxypyridin-4-One Chelator Iron-Binding Polymer with Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconer, S.B.; Wang, W.; Gehrke, S.S.; Cuneo, J.D.; Britten, J.F.; Wright, G.D.; Brown, E.D. Metal-Induced Isomerization Yields an Intracellular Chelator That Disrupts Bacterial Iron Homeostasis. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.E.; Cilibrizzi, A.; Abbate, V.; Bruce, K.D.; Hider, R.C. Effect of Iron Chelation on Anti-Pseudomonal Activity of Doxycycline. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-H.; Kim, C.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.-Y. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Iron Chelators against Prevotella Intermedia. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekri, K.; Khoshdel, A.; Rasoulynezhad, M.; Kheiri, S.; Malekpour, A.; Zamanzad, B. In Vitro Effect of Iron Chelators on the Growth of Escherichia Coli, Staphylococcus Epidermidis, Staphylococcus Aureus, Yersinia Enterocolitica, and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Strains. J. Shahrekord Univ. Med. Sci. 2019, 21, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coraça-Huber, D.C.; Dichtl, S.; Steixner, S.; Nogler, M.; Weiss, G. Iron Chelation Destabilizes Bacterial Biofilms and Potentiates the Antimicrobial Activity of Antibiotics against Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, S.M.; Palmblad, J.; Tricta, F.; Temin, N.T.; Fradette, C.; Lin, L.; Rozova, A.; Sheth, S. Rates of Severe Neutropenia and Infection Risk in Patients Treated with Deferiprone: 28 Years of Data. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 5641–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbein, B.E.; Ang, M.T.C.; Allan, D.S.; Chen, W.; Lehmann, C. Iron-Withdrawing Anti-Infectives for New Host-Directed Therapies Based on Iron Dependence, the Achilles’ Heel of Antibiotic-Resistant Microbes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2789–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, M.; Béchet, M.; Blondeau, R. Comparison of the Main Siderophores Produced by Some Species of Streptomyces. Curr. Microbiol. 1995, 31, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.C.-F.; Chan, S.; Ho, P.-L.; Ha, S.-Y. Effects of Chelators (Deferoxamine, Deferiprone and Deferasirox) on the Growth of Klebsiella Pnemoniae AND Aeromonas Hydrophila Isolated from Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Patients. Hemoglobin 2009, 33, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, A.J.; Hannauer, M.; Welch, I.; Heinrichs, D.E. Deferoxamine Mesylate Enhances Virulence of Community-Associated Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, Y.; Kong, X.; Hider, R.C. Design of Iron Chelators with Therapeutic Application. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 6371–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombs, M.R.P.; Grant, T.; Greenshields, A.L.; Arsenault, D.J.; Holbein, B.E.; Hoskin, D.W. Inhibitory Effect of Iron Withdrawal by Chelation on the Growth of Human and Murine Mammary Carcinoma and Fibrosarcoma Cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbau-Brisa, R.; Ang, M.T.C.; Holbein, B.E.; Bierenstiel, M. Enhanced Fe3+ Binding through Cooperativity of 3-Hydroxypyridin-4-One Groups within a Linear Co-Polymer: Wrapping Effect Leading to Superior Antimicrobial Activity. BioMetals 2020, 33, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Nickerson, R.; Burton, L.; Stueck, A.; Holbein, B.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lehmann, C. The Hydroxypyridinone Iron Chelator DIBI Reduces Bacterial Load and Inflammation in Experimental Lung Infection. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokam, D.; Aali, M.; Dickson, K.; Scott, C.; Holbein, B.; Zhou, J.; Lehmann, C.; Hiebl, B.; Krüger-Genge, A.; Jung, F. The novel iron chelator, DIBI, attenuates inflammation and improves outcome in colon ascendens stent peritonitis-induced experimental sepsis. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2020, 76, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.L.; Ul-Haq, M.I.; Creagh, A.L.; Haynes, C.A.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Iron Binding and Iron Removal Efficiency of Desferrioxamine Based Polymeric Iron Chelators: Influence of Molecular Size and Chelator Density. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.L.; Ul-Haq, M.I.; Abbina, S.; Kalathottukaren, M.T.; Lai, B.F.; Hatef, A.; Unniappan, S.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. In Vivo Efficacy, Toxicity and Biodistribution of Ultra-Long Circulating Desferrioxamine Based Polymeric Iron Chelator. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, V.; Pramanik, A.; Gwinner, T.; Köberle, M.; Bohn, E. Sideromycins: Tools and Antibiotics. BioMetals 2009, 22, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möllmann, U.; Heinisch, L.; Bauernfeind, A.; Köhler, T.; Ankel-Fuchs, D. Siderophores as Drug Delivery Agents: Application of the “Trojan Horse” Strategy. BioMetals 2009, 22, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito-Horiyama, T.; Ishii, Y.; Ito, A.; Sato, T.; Nakamura, R.; Fukuhara, N.; Tsuji, M.; Yamano, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tateda, K. Stability of Novel Siderophore Cephalosporin S-649266 against Clinically Relevant Carbapenemases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4384–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shionogi Clinical Trials Study of Cefiderocol (S-649266) or Best Available Therapy for the Treatment of Severe Infections Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens (CREDIBLE-CR). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02714595 (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- Chanda, D.; Neumann, D.; Glatz, J.F.C. The Endocannabinoid System: Overview of an Emerging Multi-Faceted Therapeutic Target. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2019, 140, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.; Ranganath, T.; Fish, K.N.; Lewis, D.A.; Sweet, R.A. Cell Type Specific Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Distribution across the Human and Non-Human Primate Cortex. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiègue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carrière, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; LE Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Expression of Central and Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptors in Human Immune Tissues and Leukocyte Subpopulations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.S.; Angel, C.E.; Schwarcz, L.E.; Dunbar, P.R.; Glass, M. Detailed Characterisation of CB2 Receptor Protein Expression in Peripheral Blood Immune Cells from Healthy Human Volunteers Using Flow Cytometry. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillard, C.J. Circulating Endocannabinoids: From Whence Do They Come and Where Are They Going? Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pulgar, T.G.; Velasco, G.; Guzmán, M. The CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Is Coupled to the Activation of Protein Kinase B/Akt. Biochem. J. 2000, 347, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ji, Z.; Tsalkova, T.; Mei, F. Epac and PKA: A Tale of Two Intracellular CAMP Receptors. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, O.; Ganguly, D. Endocannabinoids in Immune Regulation and Immunopathologies. Immunology 2021, 164, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehle, J.; Schöne, B.; Bagheri, S.; Avraamidou, E.; Danisch, M.; Frank, I.; Pfeifer, P.; Bindila, L.; Lutz, B.; Lütjohann, D.; et al. Elevated Levels of 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Promote Atherogenesis in ApoE-/-Mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggirwar, S.B.; Khalsa, J.H. The Link between Cannabis Use, Immune System, and Viral Infections. Viruses 2021, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcinelli, S.D.; Cooper-Volkheimer, A.D.; Semenova, L.; Wu, E.; Richardson, A.; Ashokkumar, M.; Margolis, D.M.; Archin, N.M.; Rudin, C.D.; Murdoch, D.; et al. Impact of Cannabis Use on Immune Cell Populations and the Viral Reservoir in People with Hiv on Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Singh, S.; Niyogi, R.G.; Lamont, G.J.; Wang, H.; Lamont, R.J.; Scott, D.A. Marijuana-Derived Cannabinoids Trigger a CB2/PI3K Axis of Suppression of the Innate Response to Oral Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasim, K.; Haq, I.; Ashraf, M. Antimicrobial Studies of the Leaf of Cannabis sativa L. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 8, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Appendino, G.; Gibbons, S.; Giana, A.; Pagani, A.; Grassi, G.; Stavri, M.; Smith, E.; Rahman, M.M. Antibacterial Cannabinoids from Cannabis Sativa: A Structure−Activity Study. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.; Park, J.G.; Cho, K.-H.; Choi, P.; Kim, T.; Ham, J.; Lee, J. Assessment of Antiviral Potencies of Cannabinoids against SARS-CoV-2 Using Computational and in Vitro Approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, M.A.; El-Halfawy, O.M.; Gale, R.T.; Macnair, C.R.; Carfrae, L.A.; Zhang, X.; Jentsch, N.G.; Magolan, J.; Brown, E.D. Uncovering the Hidden Antibiotic Potential of Cannabis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.; Bail, S.; Friedl, S.M.; Jirovetz, L.; Buchbauer, G.; Wanner, J.; Denkova, Z.; Slavchev, A.; Stoyanova, A.; Geissler, M. Antimicrobial Activities of Single Aroma Compounds. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, M.C.S.; Vittorazzi, C.; Guimarães, A.C.; Martins, J.D.L.; Fronza, M.; Endringer, D.C.; Scherer, R. Effects of β-Caryophyllene and Murraya Paniculata Essential Oil in the Murine Hepatoma Cells and in the Bacteria and Fungi 24-h Time-Kill Curve Studies. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, F.A.; Souza, M.C.d.C.; Vermelho, L.L.R.; Vermelho, M.L.R.; Perciano, P.G.; Vargas, F.S.; Borges, A.P.B.; da Veiga-Junior, V.F.; Moreira, M.A.S. Use of β-Caryophyllene to Combat Bacterial Dental Plaque Formation in Dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo, C.-L.; Yang, S.-K.; Osman, M.-A.; Yuswan, M.H.; Loh, J.-Y.; Lim, W.-M.; Lim, S.-H.-E.; Lai, K.-S. Antibacterial Activity and Mode of Action of β-Caryophyllene on Bacillus Cereus. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, H.I.C.; Toyang, N.J.; McLaughlin, W. Potential of Cannabidiol for the Treatment of Viral Hepatitis. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, G.; Adorisio, S.; Delfino, D.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Recinella, L.; Leone, S.; D’antonio, M.; Zengin, G.; Acquaviva, A.; et al. Comparative Investigation of Composition, Antifungal, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Essential Oil from Three Industrial Hemp Varieties from Italian Cultivation. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.K.; de Freitas, B.S.; Garcia, R.C.L.; Monteiro, R.T.; Hallak, J.E.; Zuardi, A.W.; Crippa, J.A.S.; Schröder, N. Antiapoptotic Effects of Cannabidiol in an Experimental Model of Cognitive Decline Induced by Brain Iron Overload. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortora, C.; Di Paola, A.; Creoli, M.; Argenziano, M.; Martinelli, M.; Miele, E.; Rossi, F.; Strisciuglio, C. Effects of CB2 and TRPV1 Stimulation on Osteoclast Overactivity Induced by Iron in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Soriano-Castell, D.; Kepchia, D.; Duggan, B.M.; Currais, A.; Schubert, D.; Maher, P. Cannabinol Inhibits Oxytosis/Ferroptosis by Directly Targeting Mitochondria Independently of Cannabinoid Receptors. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 180, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.A.; Kumara, R.; Wetli, H.; Wessling-Resnick, M. Regulation of Divalent Metal Transporter-1 by Serine Phosphorylation. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 4243–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creoli, M.; Di Paola, A.; Tarallo, A.; Aziz, S.; Miele, E.; Martinelli, M.; Casertano, M.; Colucci, A.; Cenni, S.; Marrapodi, M.M.; et al. Effects of CB2 Receptor Modulation on Macrophage Polarization in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallelli, C.A.; Calcagnini, S.; Romano, A.; Koczwara, J.B.; de Ceglia, M.; Dante, D.; Villani, R.; Giudetti, A.M.; Cassano, T.; Gaetani, S. Modulation of the Oxidative Stress and Lipid Peroxidation by Endocannabinoids and Their Lipid Analogues. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.H.; Weyer-Nichols, C.E.; Garcia-Sanchez, J.I.; Wilson, K.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Blocks Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage Differentiation through Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Yong, V.W.; Xue, M. Anti-Oxidant Effects of Cannabidiol Relevant to Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1247550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Kavanagh, A.M.; Elliott, A.G.; Zhang, B.; Ramu, S.; Amado, M.; Lowe, G.J.; Hinton, A.O.; Pham, D.M.T.; Zuegg, J.; et al. The Antimicrobial Potential of Cannabidiol. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, D.; Shu, C.; Lian, F.; Fang, X. β-Caryophyllene Confers Cardioprotection by Scavenging Radicals and Blocking Ferroptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 18003–18012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Liu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Q. Pharmacological Inhibition of Ferroptosis as a Therapeutic Target for Sepsis-Associated Organ Damage. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 257, 115438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Huang, H.; Fan, S.; Zheng, B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Pi, J.; Xu, J.F. Ferroptosis: A Mixed Blessing for Infectious Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 992734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, E.P.; Costa, D.L.; Namasivayam, S.; Riteau, N.; Kamenyeva, O.; Mittereder, L.; Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Andrade, B.B.; Sher, A. A Major Role for Ferroptosis in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis–Induced Cell Death and Tissue Necrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Fang, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Gao, L. Ferroptotic Stress Promotes Macrophages against Intracellular Bacteria. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2266–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Stage | Iron Chelator | Target Pathogens | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-clinical | MRB20 | Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecium, Enterococcus faecalis | [18] |
| VK28 | Acinetobacter baumannii, S. aureus | [19] | |
| Apo6619 | A. baumannii, Escherichia coli | [19] | |
| ApoL1 | A. baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [19] | |
| Hexadentate hydroxypyridinone 7 | S. aureus, Providencia stuartii | [20] | |
| HPO–PGMA polymers | Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus (MRSA) | [21] | |
| DIBI | S. aureus, A. baumannii | [22,23] | |
| HPG–HBED-based macrochelators | S. aureus, MRSA | [18] | |
| Open merocyanine isomer | E. coli | [24] | |
| CP762 | P. aeruginosa | [25] | |
| Clinical (iron overload) | Deferoxamine | Prevotella intermedia, E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa | [26,27] |
| Deferasirox | P. intermedia, E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa | [26,27] | |
| Deferiprone | S. epidermidis, E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae | [19,27,28] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dickson, K.B.; Zhou, J.; Lehmann, C. Interactions Between Iron Metabolism and the Endocannabinoid System in Bacterial Infections. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060614
Dickson KB, Zhou J, Lehmann C. Interactions Between Iron Metabolism and the Endocannabinoid System in Bacterial Infections. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(6):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060614
Chicago/Turabian StyleDickson, Kayle Brenna, Juan Zhou, and Christian Lehmann. 2025. "Interactions Between Iron Metabolism and the Endocannabinoid System in Bacterial Infections" Antibiotics 14, no. 6: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060614
APA StyleDickson, K. B., Zhou, J., & Lehmann, C. (2025). Interactions Between Iron Metabolism and the Endocannabinoid System in Bacterial Infections. Antibiotics, 14(6), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060614








