Investigation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravesical Tigecycline Administration in Rats with Cystitis Induced by Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR), Tigecycline-Sensitive Acinetobacter baumannii Strain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Microbiological Findings
2.2. Histopathological Findings
2.3. Cytogenetic Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Bacterial Cystitis Model
4.3. Study Groups
4.4. Sacrifice and Sample Collection
4.5. Microbiological and Histopathological Examination
4.6. Cytogenetic Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manack, A.; Motsko, S.P.; Haag-Molkenteller, C.; Dmochowski, R.R.; Goehring, E.L., Jr.; Nguyen-Khoa, B.-A.; Jones, J.K. Epidemiology and healthcare utilization of neurogenic bladder patients in a US claims database. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyndaele, J.J. Complications of intermittent catheterization: Their prevention and treatment. Spinal Cord. 2002, 40, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tural, M.; Ozluk, O.; Unal, I.; Ciftci, H.; Atahan, O. Intravesical antibiotic treatment in patients with recurrent urinary tract infections. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, B.; Akbal, C.; Tinay, I.; Ozkanli, S.; Erdem, M.R.; Yagci, C. The efficacy of intravesical fosfomycin in patients with recurrent urinary tract infections. Urol. J. 2020, 17, 346–352. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Kozminski, M.; Wang, S.C.; Faerber, G.J.; McGuire, E.J.; Bloom, D.A.; Ritchey, M.L. Intravesical instillation of gentamicin sulfate: In Vitro, rat, canine, and human studies. Urology 1994, 43, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannek, J. Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections in neurourology. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welk, B.; Munday, C.; Burton, J.; Baverstock, R.J. Fosfowash: Early proof of concept study investigating intravesical fosfomycin for recurrent urinary tract infections. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2021, 15, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wood, G.C.; Chapman, J.L.; Boucher, B.A.; Mueller, E.W.; Fabian, T.C.; Croce, M.A. Tobramycin bladder irrigation for treating a urinary tract infection in a critically ill patient. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 1318–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.M.; Wood, G.C.; Hickerson, W.L. Linezolid bladder irrigation as adjunctive treatment for a vancomycin resistant Enterococcus faecium catheter-associated urinary tract infection. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, R.R.; Philpot, C.; Morley, J.E. Continuous bladder irrigation with vancomycin for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1996, 44, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés González, J.R.; Ortiz Lara, G.E.; Arratia Maqueo, J.A.; Gómez Guerra, L.S. Continous bladder irrigation with amikacin as adjuvant treatment for emphysematous cystitis. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2007, 60, 1.218-1.220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abrams, P.; Hashim, H.; Tomson, C.; Macgowan, A.; Skews, R.; Warren, K. The use of intravesical gentamicin to treat recurrent urinary tract infections in lower urinary tract dysfunction. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalenhoef, J.E.; van Nieuwkoop, C.; Menken, P.H.; Bernards, S.T.; Elzevier, H.W.; van Dissel, J.T. Intravesical gentamicin treatment for recurrent urinary tract infections caused by multidrug resistant bacteria. J. Urol. 2019, 201, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoor, W.; Ferguson, D.; Mashni, S.; Creelman, L.; Reeves, D.; Minevich, E.; Reddy, P.; Sheldon, C. Safety of Gentamicin Bladder Irrigations in Complex Urological Cases. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieuwkoop, C.; den Exter, P.L.; Elzevier, H.W.; Hartigh, J.D.; van Dissel, J.T. Intravesical gentamicin for recurrent urinary tract infection in patients with intermittent bladder catheterisation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.; He, C.; Bevins, J.; Clemens, J.Q.; Stoffel, J.T.; Cameron, A.P. Gentamicin bladder instillations decrease symptomatic urinary tract infections in neurogenic bladder patients on intermittent catheterization. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2017, 11, E350–E354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlini, A.B.; Merlini, R.H.; de Abreu, B.N.; Bergamasco, M.D.D.D. Current Options for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. In Acinetobacter baumannii—The Rise of a Resistant Pathogen [Internet]; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/1167210 (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Greer, N.D. Tigecycline (Tygacil): The first in the glycylcycline class of antibiotics. Proc. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. 2006, 19, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Ko, K.S. Tigecycline Heteroresistance and Resistance Mechanism in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nix, D.E.; Matthias, K.R. Should tigecycline be considered for urinary tract infections? A pharmacokinetic re-evaluation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1311–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, B.A. Pharmacokinetic considerations regarding the efficacy of tigecycline in serious infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48 (Suppl. 1), S58–S64. [Google Scholar]
- Doğan, E.; Gültekin, F.A.; Avci, A.; Gülenç, M. Investigation of genotoxic and oxidative effects of tigecycline in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalem, M.; Ayar, G.; Özkan, A.; Bağci, C. Evaluation of the genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of tigecycline in cultured human peripheral lymphocytes. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zupanič Pajnič, I.; Mahne, K.; Ravnik-Glavač, M. Genotoxicity of tigecycline evaluated by comet assay in human lymphocytes. Acta. Med. Mediter. 2016, 32, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar]
- ResearchGate [Internet]. Investigation of the Antibiotic Susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from Clinical Samples. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/314550134_Investigation_of_the_Antibiotic_Susceptibility_of_Acinetobacter_baumannii_Strains_Isolated_from_Clinical_Samples (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- CoLab [Internet]. Investigation of Antimicrobial Resistance Rates of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains from Nosocomial Infections. Available online: https://colab.ws/articles/10.5222%2Fankem.2013.007 (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Tamma, P.D.; Heil, E.L.; Justo, J.A.; Mathers, A.J.; Satlin, M.J.; Bonomo, R.A. Infectious Diseases Society of America 2024 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, ciae403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, M.J.; Jin, S.J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, B.H.; Koh, W.J.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.H. Intravesical colistin delivery for the treatment of multidrug-resistant urinary tract infections: An experimental study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105841. [Google Scholar]
- Dray, E.V.; Clemens, J.Q. Recurrent urinary tract infections in patients with incomplete bladder emptying: Is there a role for intravesical therapy? Transl. Androl. Urol. 2017, 6 (Suppl. 2), S163–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chernyak, S.; Salamon, C. Intravesical Antibiotic Administration in the Treatment of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections: Promising Results from a Case Series. Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 26, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow-Fernández, P.; Rodríguez, C.F.; Cornejo-Juárez, P. Intravesical colistin irrigation to treat multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii urinary tract infection: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2012, 6, 426. Available online: http://www.jmedicalcasereports.com/content/6/1/426 (accessed on 12 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Goessens, W.H.F.; Mouton, J.W.; ten Kate, M.T.; Sörgel FKinzig, M.; Bakker-Woudenberg, I.A.J.M. The Therapeutic Effect of Tigecycline, Unlike That of Ceftazidime, Is Not Influenced by whether the Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain Produces Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases in Experimental Pneumonia in Rats. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, O.; Oztuna, V.; Colak, M.; Akdag, A.; Camdeviren, H. Comparison of the Efficacy of Tigecycline and Teicoplanin in an Experimental MethicillinResistant Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis Model. J. Chemother. 2008, 20, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robiyanto, R.; Zaidi, S.T.; Shastri, M.D.; Castelino, R.L.; Wanandy, S.T.; Jose, M.D.; Patel, R.P. Stability of Tigecycline in Different Types of Peritoneal Dialysis Solutions. Perit. Dial. Int. 2016, 36, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van der Weide, H.; Ten Kate, M.T.; Vermeulen-de Jongh, D.M.C.; Van der Meijden, A.; Wijma, R.A.; Boers, S.A.; Van Westreenen, M.; Hays, J.P.; Goessens, W.H.F.; Bakker-Woudenberg, I.A.J.M. Successful High-Dosage Monotherapy of Tigecycline in a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Pneumonia-Septicemia Model in Rats. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McGuire, E.J.; Savastano, J.A. Treatment of intractable bacterial cystitis with intermittent catheterization and antimicrobial instillation: Case report. J. Urol. 1987, 137, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, R.E.; Coelho, I.; Real, A.; França, L.; Araújo, A.; Pereira, T.; Catorze, N. Intra-Vesical Colistin for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Urinary Tract Infections. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2019, 6, 000996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Jin, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, C.; Li, J. Tigecycline-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in cultured human cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5533–5540. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, G.; Singla, S.; Mahajan, R.; Chhina, R.S.; Bansal, A.; Bansal, N. Local effects of high-dose intravesical antibiotics on urinary bladder histopathology in rats. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Dayana, K.; Manasa, M.R. Genotoxic evaluation of ceftriaxone by in vivo micronucleus test in albino mice. Int. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol 2018, 7, 1705–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.; Eke, D. The assessment of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of tetracycline antibiotic in human blood lymphocytes using CBMN and SCE analysis, In Vitro. Int. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 11, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambulkar, P.S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Ingole, I.V.; Pal, A.K. Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of antibacterial drug, ciprofloxacin, on human lymphocytes In Vitro. Nepal. Med. Coll. J. 2009, 11, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Imène, B.; Akram, M.M.; Eddine, M.S.; Ismahene, G.; Amarouayache, M.; Berredjem, M.; Berredjem, H. Antibacterial, Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Assessment of New Sulfonamide Derivatives. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İstifli, E.S.; Topaktaş, M. Cytogenetic genotoxicity of amoxicillin. Env. Mol. Mutagen. 2010, 51, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Musarrat, J. Tetracycline–Cu(II) photoinduced fragmentation of serum albumin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2002, 131, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Moullan, N.; Mouchiroud, L.; Wang, X.; Ryu, D.; Williams, E.G.; Mottis, A.; Jovaisaite, V.; Frochaux, M.V.; Quiros, P.M.; Deplancke, B.; et al. Tetracyclines Disturb Mitochondrial Function across Eukaryotic Models: A Call for Caution in Biomedical Research. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuşcu, F.; Öztürk, D.B.; Tütüncü, E.E.; Uslu, M.; Gürbüz, Y.; Gülen, G.; Şencan, İ. Çoğul Antibiyotik Dirençli Acinetobacter baumannii İzolatlarında Tigesiklin Duyarlılık Oranlarının E-Test® Yöntemiyle Araştırılması. Klimik Derg. 2009, 22, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Research C for DE and Tigecycline—Injection Products. FDA [Internet]. 26 January 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-resources/tigecycline-injection-products (accessed on 19 October 2024).


| 3rd Day of Treatment (6th Day of Infection) | p | 5th Day of Treatment (8th Day of Infection) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture-Negative | Culture-Positive | Culture-Negative | Culture-Positive | |||
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Untreated | 0 (0) | 6 (100) | 0.082 | 0 (0) | 6 (100) | 0.028 |
| Saline Solution | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | ||
| Low-Dose Tigecycline | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | ||
| High-Dose Tigecycline | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 5 (83.3) | 1 (16.7) | ||
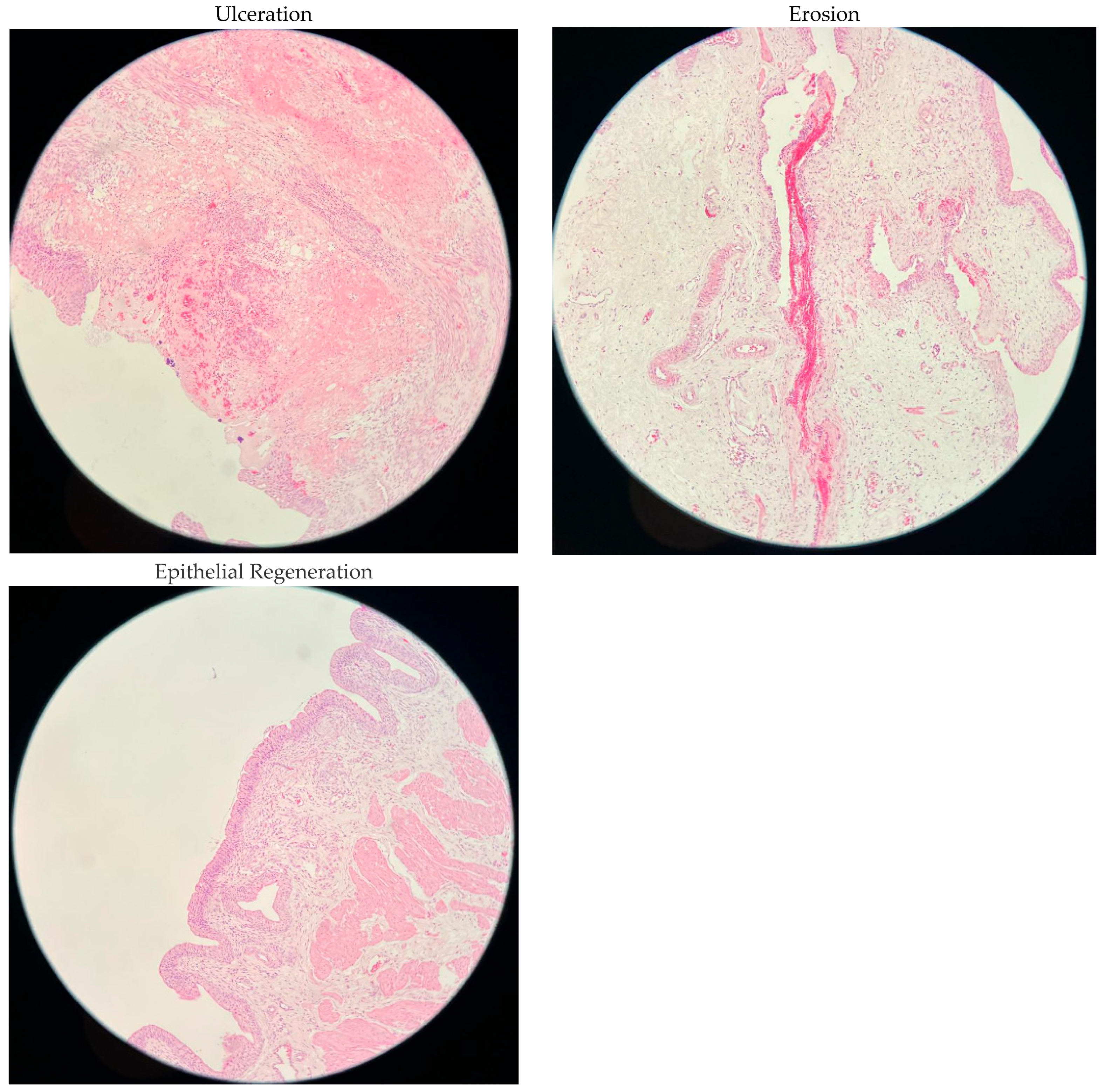
| Histopathological Findings | Percentage of Area | Study Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Saline Solution | Low-Dose Tigecycline | High-Dose Tigecycline | p | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Inflammation | 0% | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 0.029 |
| <25% | 1 (16.7) | 4 (66.7) | 4 (66.7) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| 25–50% | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| >50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (50) | ||
| Fibrosis | 0% | 4 (66.7) | 3 (50) | 3 (50) | 2 (33.3) | 0.308 |
| <25% | 2 (33.3) | 3 (50) | 3 (50) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| 25–50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | ||
| >50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| Vascular Proliferation | 0% | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 0.220 |
| <25% | 1 (16.7) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| 25–50% | 1 (16.7) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| >50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | ||
| Edema | 0% | 4 (66.7) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | 0.114 |
| <25% | 2 (33.3) | 3 (50) | 5 (83.3) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| 25–50% | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | 1 (16.7) | 2 (33.3) | ||
| >50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| Ulceration | 0% | 5 (83.3) | 5 (83.3) | 5 (83.3) | 3 (50) | 0.759 |
| <25% | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 2 (33.3) | ||
| 25–50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| >50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Erosion | 0% | 6 (100) | 4 (66.7) | 5 (83.3) | 6 (100) | 0.573 |
| <25% | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | ||
| 25–50% | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| >50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Epithelial Regeneration | 0% | 6 (100) | 4 (66.7) | 5 (83.3) | 4 (66.7) | 0.695 |
| <25% | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| 25–50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| >50% | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
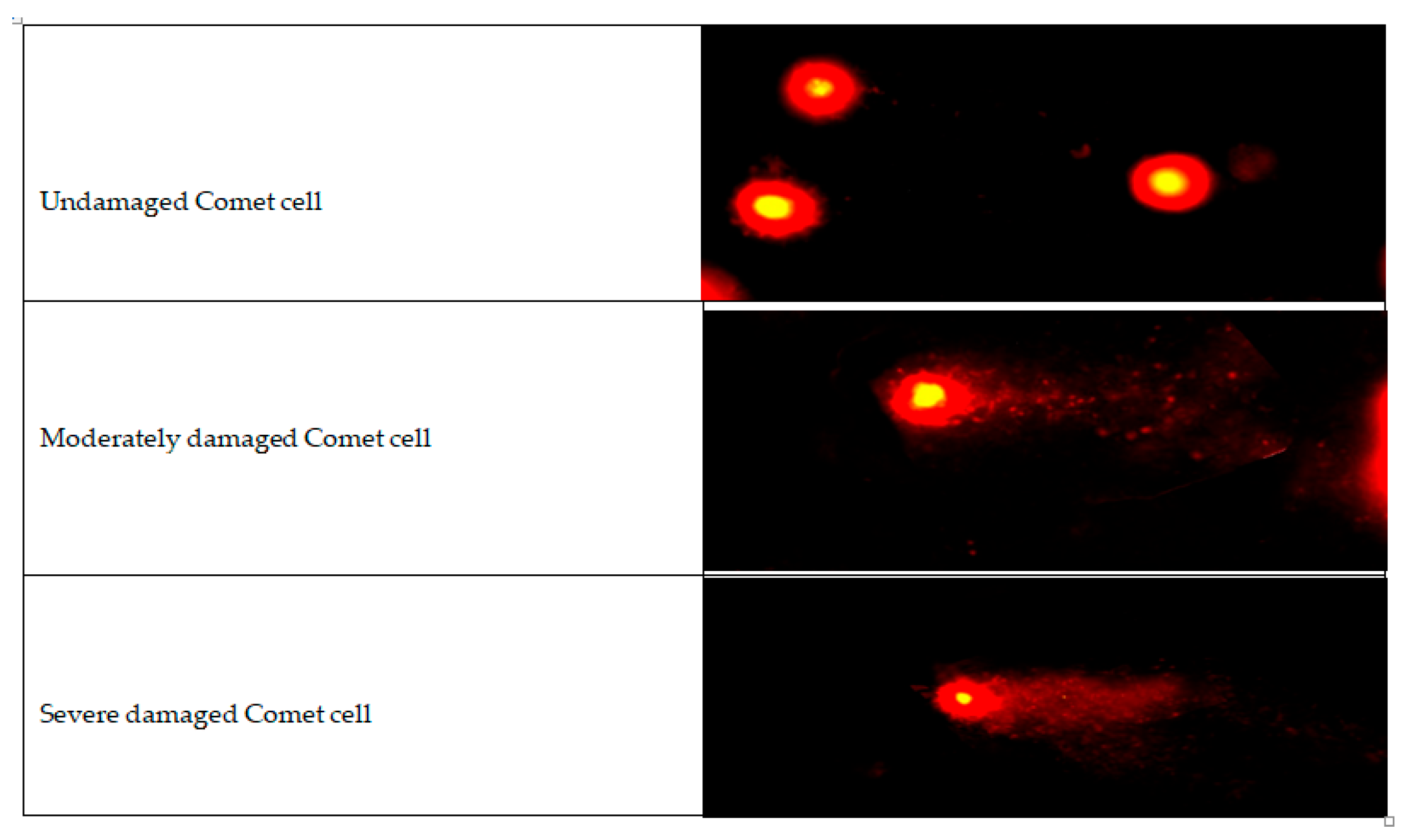
| Tail Length (µm) | Tail Moment | Tail Intensity (%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 13.13 ± 1.36 | 9.78 ± 1.25 | 229.31 ± 0.53 | <0.05 |
| Saline (SF) | 14.08 ± 1.55 | 10.69 ± 1.48 | 230.84 ± 0.61 | |
| Low-Dose TGC | 18.47 ± 1.88 | 15.61 ± 1.89 | 233.34 ± 0.71 | |
| High-Dose TGC | 21.24 ± 2.11 | 17.99 ± 2.12 | 233.89 ± 0.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yüksel, C.; Alıravcı, I.D.; Koşan, M.; Esen, S.; Yenice Aktaş, S.; Kaya Terzi, N.; Berber, A.A.; Alkan, S.; Kaya, S. Investigation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravesical Tigecycline Administration in Rats with Cystitis Induced by Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR), Tigecycline-Sensitive Acinetobacter baumannii Strain. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060611
Yüksel C, Alıravcı ID, Koşan M, Esen S, Yenice Aktaş S, Kaya Terzi N, Berber AA, Alkan S, Kaya S. Investigation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravesical Tigecycline Administration in Rats with Cystitis Induced by Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR), Tigecycline-Sensitive Acinetobacter baumannii Strain. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(6):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060611
Chicago/Turabian StyleYüksel, Cihan, Işıl D. Alıravcı, Murat Koşan, Sinem Esen, Sevinç Yenice Aktaş, Neslihan Kaya Terzi, Ahmet Ali Berber, Sevil Alkan, and Selçuk Kaya. 2025. "Investigation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravesical Tigecycline Administration in Rats with Cystitis Induced by Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR), Tigecycline-Sensitive Acinetobacter baumannii Strain" Antibiotics 14, no. 6: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060611
APA StyleYüksel, C., Alıravcı, I. D., Koşan, M., Esen, S., Yenice Aktaş, S., Kaya Terzi, N., Berber, A. A., Alkan, S., & Kaya, S. (2025). Investigation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravesical Tigecycline Administration in Rats with Cystitis Induced by Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR), Tigecycline-Sensitive Acinetobacter baumannii Strain. Antibiotics, 14(6), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060611







