Genomic Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (OXA-23) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-2) Causing Hospital-Acquired Infections in Dogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.2. Comparative Genomics
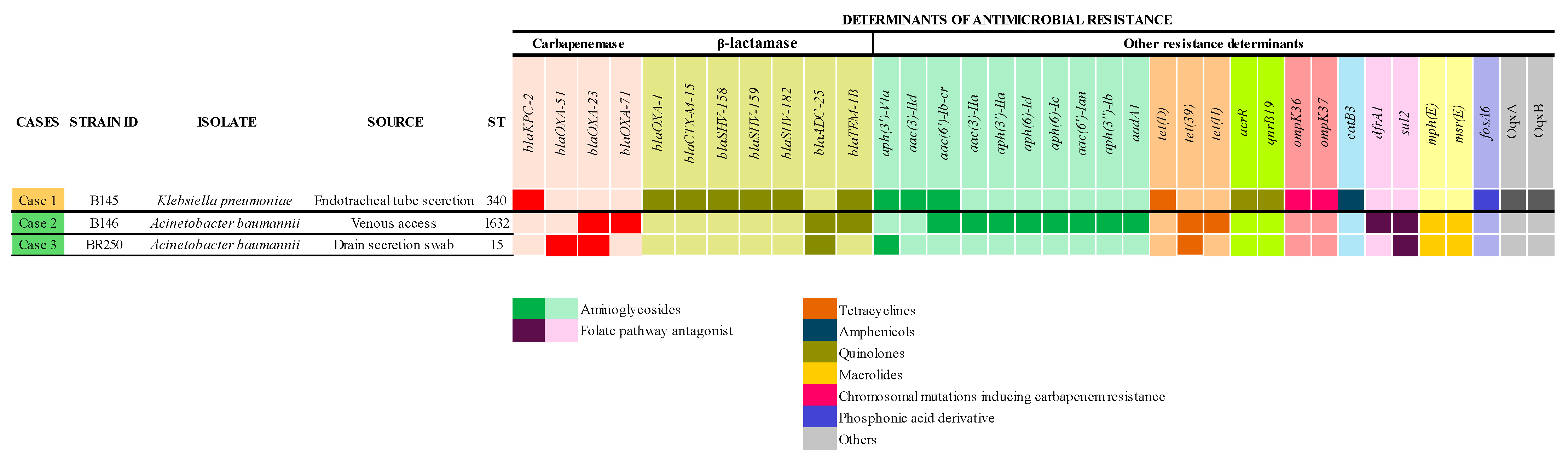
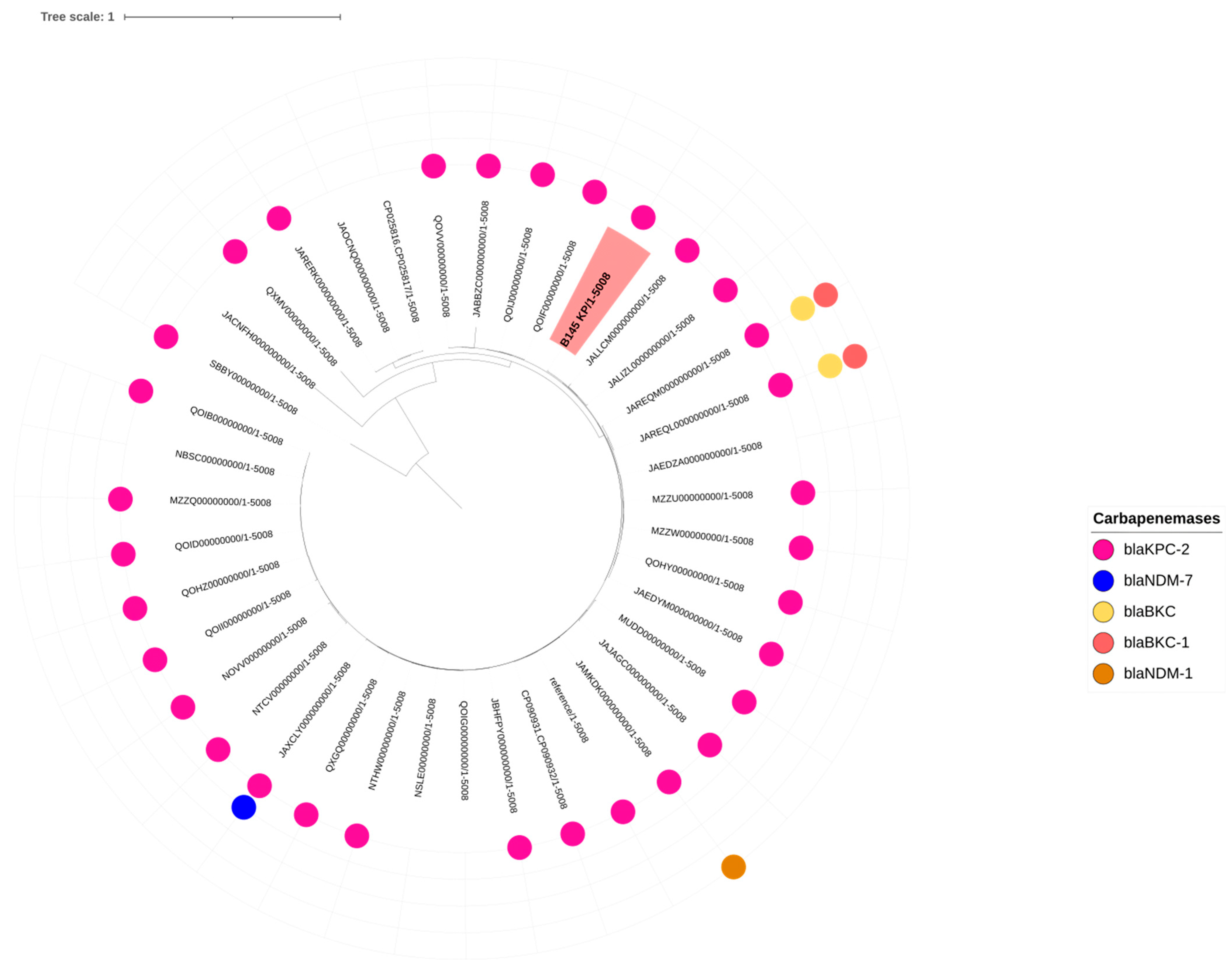
2.2.1. Presence and Type of Carbapenemase Genes
2.2.2. Other Determinants of Antimicrobial Resistance
2.2.3. Mobile Genetic Elements
2.2.4. MLST, KL-Typing, OCL-Typing and SNP Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Case 1
4.2. Case 2
4.3. Case 3
4.4. Bacterial Culture, Identification and Antimicrobial Resistance Tests
4.5. Whole Genome Sequencing and Comparative Genomics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jian, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A Challenge in the Intensive Care Unit. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1045206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čiginskienė, A.; Dambrauskienė, A.; Rello, J.; Adukauskienė, D. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Due to Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Risk Factors and Mortality Relation with Resistance Profiles, and Independent Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality. Medicina 2019, 55, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.M.; Cao, J.; Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Wu, W.; Zhao, L.; Malani, P.N.; Rao, K.; Bachman, M.A. Molecular Epidemiology of Colonizing and Infecting Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. mSphere 2016, 1, e00261-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachanon, R.; Khine, N.O.; Phumthanakorn, N.; Wongsurawat, T.; Niyomtham, W.; Chatsuwan, T.; Hampson, D.J.; Prapasarakul, N. Genomic Characterization of Carbapenem and Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Humans and Dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1386496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Paterson, D. Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 074–084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouza, E. The Role of New Carbapenem Combinations in the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, iv38–iv45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Carrara, E.; Retamar, P.; Tängdén, T.; Bitterman, R.; Bonomo, R.A.; De Waele, J.; Daikos, G.L.; Akova, M.; Harbarth, S.; et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) Guidelines for the Treatment of Infections Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli (Endorsed by European Society of Intensive Care Medicine). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WOAH. WOAH List of Antimicrobial Agents of Veterinary Importance 2025; WOAH: Paris, France, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Gentilini, F.; Turba, M.E.; Pasquali, F.; Mion, D.; Romagnoli, N.; Zambon, E.; Terni, D.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D.; Parisi, A.; et al. Hospitalized Pets as a Source of Carbapenem-Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, A.; Châtre, P.; Ponsin, C.; Saras, E.; Boulouis, H.-J.; Keck, N.; Haenni, M.; Madec, J.-Y. Clonal Spread of Acinetobacter baumannii Sequence Type 25 Carrying BlaOXA-23 in Companion Animals in France. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01881-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, C.; Klotz, P.; Leidner, U.; Stamm, I.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Göttig, S.; Semmler, T.; Scheufen, S. OXA-23 and ISAba1-OXA-66 Class D β-Lactamases in Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Companion Animals. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobmeyer, L.; Semmler, T.; Stamm, I.; Ewers, C. Genomic Analysis of Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Carrying OXA-23 and OXA-58 Genes from Animals Reveals ST1 and ST25 as Major Clonal Lineages. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.; LeCuyer, T.E.; Hendrix, G.K.; Burbick, C.R.; Jacob, M.E.; Byrne, B.A.; Olsen, K.; Mitchell, M.; Ceric, O.; Lin, R.; et al. Prevalence and Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales Isolated from Dog and Cat Faeces Submitted to Veterinary Laboratories in the USA. Zoonoses Public Health 2024, 71, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira Da Silva, J.; Menezes, J.; Fernandes, L.; Marques, C.; Costa, S.S.; Timofte, D.; Amaral, A.; Pomba, C. Dynamics of blaOXA-23 Gene Transmission in Acinetobacter Spp. from Contaminated Veterinary Environmental Surfaces: An Emerging One Health Threat? J. Hosp. Infect. 2024, 146, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartor, Y.H.; Ammar, A.M.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Hassan, K.A.; Shaker, A.; Elnahriry, S.S.; Nekouei, O.; Elsohaby, I. Emergence of Pandrug-Resistant Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales in Dogs and Cats: A Cross-Sectional Study in Egypt. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1318585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira Da Silva, J.; Menezes, J.; Mendes, G.; Santos Costa, S.; Caneiras, C.; Poirel, L.; Amaral, A.J.; Pomba, C. KPC-3-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 392 from a Dog’s Clinical Isolate in Portugal. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00893-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellera, F.P.; Fuga, B.; Fontana, H.; Esposito, F.; Cardoso, B.; Konno, S.; Berl, C.; Cappellanes, M.H.; Cortez, M.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Detection of IncN-pST15 One-health Plasmid Harbouring BlaKPC-2 in a Hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae CG258 Isolated from an Infected Dog, Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Díez, G.; Mengíbar, R.L.; Turrientes, M.-C.; Artigao, M.-R.B.; Gallifa, R.L.; Tello, A.M.; Pérez, C.F.; Santiago, T.A. Prevalence, Incidence and Risk Factors for Acquisition and Colonization of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase- and Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae from Dogs Attended at a Veterinary Hospital in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 92, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, R.; Daniels-Haardt, I.; Becker, K.; Mellmann, A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Mevius, D.; Schwarz, S.; Jurke, A. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Wildlife, Food-Producing, and Companion Animals: A Systematic Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.S.; Freire, M.P.; Cunha, M.P.V.; De Barcellos, T.A.F.; Bertani, A.M.D.J.; Dos Santos, C.A.; Chimara, E.; Nagamori, F.O.; Takagi, E.H.; Costa, S.F.; et al. Detection of Pandrug-Resistant ST15 Acinetobacter baumannii Causing Bloodstream Infection in an HSCT Patient in Brazil. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2691–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, T.P.G.; Carvalho, K.R.; De Oliveira Santos, I.C.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Asensi, M.D. Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Brazil (2008–2011): Countrywide Spread of OXA-23–Producing Clones (CC15 and CC79). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 79, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolentino, F.M.; Bueno, M.F.C.; Franscisco, G.R.; Barcelos, D.D.D.P.; Lobo, S.M.; Tomaz, F.M.M.B.; Da Silva, N.S.; De Andrade, L.N.; Casella, T.; Darini, A.L.D.C.; et al. Endemicity of the High-Risk Clone Klebsiella pneumoniae ST340 Coproducing QnrB, CTX-M-15, and KPC-2 in a Brazilian Hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, C.H.; Yamada, A.Y.; Souza, A.R.D.; Reis, A.D.; Santos, M.B.N.; Assis, D.B.D.; Carvalho, E.D.; Takagi, E.H.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Tiba-Casas, M.R. Genomic Diversity of NDM-Producing Klebsiella Species from Brazil, 2013–2022. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, K.K.; Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Wyres, K.L.; Bachman, M.; Baker, S.; Barry, K.; Brisse, S.; Campino, S.; Chiaverini, A.; et al. Diversity, Functional Classification and Genotyping of SHV β-Lactamases in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K.; Jacoby, G.A. Updated Functional Classification of β-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robicsek, A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Jacoby, G.A.; Macielag, M.; Abbanat, D.; Hye Park, C.; Bush, K.; Hooper, D.C. Fluoroquinolone-Modifying Enzyme: A New Adaptation of a Common Aminoglycoside Acetyltransferase. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent Updates and New Developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Baena, Z.R.; Giannella, M.; Manissero, D.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Viale, P.; Lopes, S.; Wilson, K.; McCool, R.; Longshaw, C. Risk Factors for Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesudason, T. WHO Publishes Updated List of Bacterial Priority Pathogens. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE Pathogens: Antimicrobial Resistance, Epidemiology, Clinical Impact and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomba, C.; Endimiani, A.; Rossano, A.; Saial, D.; Couto, N.; Perreten, V. First Report of OXA-23-Mediated Carbapenem Resistance in Sequence Type 2 Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Associated with Urinary Tract Infection in a Cat. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1267–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebola, D.C.; Oguttu, J.W.; Kock, M.M.; Qekwana, D.N. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Dogs Presented at a Veterinary Academic Hospital in South Africa. Vet. World 2023, 16, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, S.; Moura, Q.; Cardoso, B.; Esposito, F.; Cerdeira, L.; Álvarez, E.; Barrera, E.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Gonzalez-Rocha, G.; Lincopan, N. Genomic Features of a Carbapenem-Resistant OXA-219-Positive Acinetobacter baumannii of International ST15 (CC15) from a Patient with Community-Onset Urinary Tract Infection in Chilean Patagonia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialek-Davenet, S.; Criscuolo, A.; Ailloud, F.; Passet, V.; Jones, L.; Delannoy-Vieillard, A.-S.; Garin, B.; Le Hello, S.; Arlet, G.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H.; et al. Genomic Definition of Hypervirulent and Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Groups. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-L.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Geographic Patterns of Acinetobacter baumannii and Carbapenem Resistance in the Asia-Pacific Region: Results from the Antimicrobial Testing Leadership and Surveillance (ATLAS) Program, 2012–2019. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 127, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, J.F.; Ward, M.E.; Woodford, N.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pike, R.; Livermore, D.M.; Pitt, T.L. The Role of ISAba1 in Expression of OXA Carbapenemase Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 258, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, S.J.; Hall, R.M. Does the Intrinsic oxaAb (blaOXA-51-like) Gene of Acinetobacter baumannii Confer Resistance to Carbapenems When Activated by ISAba1? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3518–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, C.A.; Pierrat, G.; Tenaillon, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bercot, B.; Jaouen, E.; Jacquier, H.; Birgy, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase Variants Resistant to Ceftazidime-Avibactam: An Evolutionary Overview. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e00447-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.T. Continuous Evolution: Perspective on the Epidemiology of Carbapenemase Resistance Among Enterobacterales and Other Gram-Negative Bacteria. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Global Spread of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budia-Silva, M.; Kostyanev, T.; Ayala-Montaño, S.; Bravo-Ferrer Acosta, J.; Garcia-Castillo, M.; Cantón, R.; Goossens, H.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Grundmann, H.; Reuter, S. International and Regional Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, I.; Chenouf, N.S.; Carvalho, J.A.; Castro, A.P.; Silva, V.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Enes Dapkevicius, M.D.L.N.; Igrejas, G.; Torres, C.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Harboring Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase Encoding Genes Isolated from Human Septicemias. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulou, A.; Voulgari, E.; Vrioni, G.; Xidopoulos, G.; Pliagkos, A.; Chatzipantazi, V.; Markou, F.; Tsakris, A. Imported Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing K. pneumoniae Clones in a Greek Hospital: Impact of Infection Control Measures for Restraining Their Dissemination. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2618–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Andini, R.; Zampino, R. Management of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, G.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Molecular Epidemiology and Drug Resistant Mechanism in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Pediatric Patients in Shanghai, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, M.; Costello, A.J.; Deshpande, L.M.; Jones, R.N. Expansion of Clonal Complex 258 KPC-2-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Latin American Hospitals: Report of the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1668–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a Key Trafficker of Drug Resistance Genes from Environmental to Clinically Important Bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.; Inoue, F.M.; Lobo, A.P.T.; Ibanes, A.S.; Tufik, S.; Kiffer, C.R.V. A Major Monoclonal Hospital Outbreak of NDM-1–Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST340 and the First Report of ST2570 in Brazil. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, C.A.M.; Pereira, P.S.; De Araujo, C.F.M.; Chagas, T.P.G.; Oliveira, J.C.R.; Buonora, S.N.; Albano, R.M.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Asensi, M.D. Multiclonal Expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Producing NDM-1 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01048-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenni, M.; Métayer, V.; Lupo, A.; Drapeau, A.; Madec, J.-Y. Spread of the BlaOXA-48/IncL Plasmid within and between Dogs in City Parks, France. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00403-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenni, M.; Boulouis, H.J.; Lagrée, A.C.; Drapeau, A.; Va, F.; Billet, M.; Châtre, P.; Madec, J.Y. Enterobacterales High-Risk Clones and Plasmids Spreading Bla ESBL/AmpC and Bla OXA-48 Genes within and between Hospitalized Dogs and Their Environment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, B.P.; Koong, J.; Wozniak, A.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; To, J.; Garcia, P.; Hamidian, M. Genomic Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Recovered from Chilean Hospitals Reveals Lineages Specific to South America and Multiple Routes for Acquisition of Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02463-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodari, C.S.; Cayô, R.; Streling, A.P.; Lei, F.; Wille, J.; Almeida, M.S.; De Paula, A.I.; Pignatari, A.C.C.; Seifert, H.; Higgins, P.G.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Belonging to Major Endemic Clones in South America. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 584603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo-Capurro, A.; San Martín, I.; Quezada-Aguiluz, M.; Morales-León, F.; Domínguez-Yévenes, M.; Lima, C.A.; Esposito, F.; Cerdeira, L.; Bello-Toledo, H.; Lincopan, N.; et al. Evolutionary Dynamics of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Circulating in Chilean Hospitals. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.H.; Cunha, M.P.V.; De Barcellos, T.A.F.; Bueno, M.S.; Bertani, A.M.D.J.; Dos Santos, C.A.; Nagamori, F.O.; Takagi, E.H.; Chimara, E.; De Carvalho, E.; et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Characterisation of Antimicrobial Resistance in Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Hyperendemic Clones CC1, CC15, CC79 and CC25. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameranesi, M.M.; Paganini, J.; Limansky, A.S.; Moran-Barrio, J.; Salcedo, S.P.; Viale, A.M.; Repizo, G.D. Acquisition of Plasmids Conferring Carbapenem and Aminoglycoside Resistance and Loss of Surface-Exposed Macromolecule Structures as Strategies for the Adaptation of Acinetobacter baumannii CC104O/CC15P Strains to the Clinical Setting. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, F.K.S.F.; Dutra, V.; Nakazato, L.; Mello, C.M.; Pepato, M.A.; De Sousa, A.T.H.I.; Takahara, D.T.; Hahn, R.C.; Souto, F.J.D. Molecular Epidemiology of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection in Two Hospitals in Central Brazil: The Role of ST730 and ST162 in Clinical Outcomes. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, N.C.; Campos, T.L.; Rezende, A.M.; Docena, C.; Mendes-Marques, C.L.; De Sá Cavalcanti, F.L.; Wallau, G.L.; Rocha, I.V.; Cavalcanti, C.L.B.; Veras, D.L.; et al. Comparative Genomics of Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Strains from Brazil Reveals Polyclonal Dissemination and Selective Exchange of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Resistance Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.S.; De Araujo, C.F.M.; Seki, L.M.; Zahner, V.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Asensi, M.D. Update of the Molecular Epidemiology of KPC-2-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Brazil: Spread of Clonal Complex 11 (ST11, ST437 and ST340). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Belas, A.; Aboim, C.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Trigueiro, G.; Gama, L.T.; Pomba, C. Evidence of Sharing of Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains between Healthy Companion Animals and Cohabiting Humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01537-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, C.H.; Nastro, M.; Famiglietti, A. Carbapenemases in Acinetobacter baumannii. Review of Their Dissemination in Latin America. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2018, 50, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.; Rocha, L.; Sampaio, J.L.M.; Martins, A.F.; Barth, A.L. Emergence of OXA-72-Producing Acinetobacter Baumannii Belonging to High-Risk Clones (CC15 and CC79) in Different Brazilian States. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewnard, J.A.; Charani, E.; Gleason, A.; Hsu, L.Y.; Khan, W.A.; Karkey, A.; Chandler, C.I.R.; Mashe, T.; Khan, E.A.; Bulabula, A.N.H.; et al. Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries Avertible by Existing Interventions: An Evidence Review and Modelling Analysis. Lancet 2024, 403, 2439–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet. Antimicrobial Resistance: An Agenda for All. Lancet 2024, 403, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis with Forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.R.; Gales, A.C.; Laxminarayan, R.; Dodd, P.C. Antimicrobial Resistance: Addressing a Global Threat to Humanity. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukoubani, T.; Makris, D.; Daniil, Z.; Paraforou, T.; Tsolaki, V.; Zakynthinos, E.; Papanikolaou, J. The Role of Antimicrobial Resistance on Long-Term Mortality and Quality of Life in Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective Longitudinal 2-Year Study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance, to Guide Research, Development, and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance, 1st ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-92-4-009346-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zendri, F.; Isgren, C.M.; Devaney, J.; Schmidt, V.; Rankin, R.; Timofte, D. Resistome-Based Surveillance Identifies ESKAPE Pathogens as the Predominant Gram-Negative Organisms Circulating in Veterinary Hospitals. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1252216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoga, E.O.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F. Detection of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter species from Food-Producing Animals and Humans in Nigeria: Public Health Implications and One Health Control Measures. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 103, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwumere-Idolor, O.S.; Kperegbeyi, J.I.; Imonikebe, U.G.; Okoli, C.E.; Ajibo, F.E.; Njoga, E.O. Epidemiology of Multidrug-Resistant Zoonotic E. coli from Beef Processing and Retail Points in Delta State, Nigeria: Public Health Implications. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 224, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Hughes, J.M. Critical Importance of a One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance. EcoHealth 2019, 16, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, S.P.; Jarocki, V.M.; Seemann, T.; Cummins, M.L.; Watt, A.E.; Drigo, B.; Wyrsch, E.R.; Reid, C.J.; Donner, E.; Howden, B.P. Genomic Surveillance for Antimicrobial Resistance—A One Health Perspective. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, L.R.; Damborg, P.; Spohr, A.; Goericke-Pesch, S.; Langhorn, R.; Houser, G.; Willesen, J.; Schjærff, M.; Eriksen, T.; Møller Sørensen, T.; et al. Antibiotic Use Guidelines for Companion Animal Practice, 2nd ed.; The Danish Veterinary Association: Frederiksberg, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Weese, J.S.; Blondeau, J.; Boothe, D.; Guardabassi, L.G.; Gumley, N.; Papich, M.; Jessen, L.R.; Lappin, M.; Rankin, S.; Westropp, J.L.; et al. International Society for Companion Animal Infectious Diseases (ISCAID) Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Dogs and Cats. Vet. J. 2019, 247, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allerton, F.; Prior, C.; Bagcigil, A.; Broens, E.; Callens, B.; Damborg, P.; Dewulf, J.; Filippitzi, M.-E.; Carmo, L.; Gómez-Raja, J.; et al. Overview and Evaluation of Existing Guidelines for Rational Antimicrobial Use in Small-Animal Veterinary Practice in Europe. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UMN. Educational Resource Review: Handbook of Antimicrobial Stewardship in Companion Animal Veterinary Settings. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardefeldt, L.; Browning, G.; Bailey, K. Australian Veterinary Prescribing Guidelines 2017; Asia Pacific Centre for Animal Health and National Centre for Antimicrobial Stewardship: Parkville, VIC, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Assis, G.B.N.; Pereira, F.L.; Zegarra, A.U.; Tavares, G.C.; Leal, C.A.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Use of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry for the Fast Identification of Gram-Positive Fish Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-68440-104-8 [Print]/978-1-68440-105-5 [Electronic]. [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Bankevich, A.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Pyshkin, A.; Sirotkin, A.; Sirotkin, Y.; et al. Assembling Single-Cell Genomes and Mini-Metagenomes from Chimeric MDA Products. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 714–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Allesøe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A Novel Web Tool for WGS-Based Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Associated with Chromosomal Point Mutations in Bacterial Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Bortolaia, V.; Tansirichaiya, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Roberts, A.P.; Petersen, T.N. Detection of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella enterica Using a Newly Developed Web Tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E.; Wyres, K.L. Kaptive 2.0: Updated Capsule and Lipopolysaccharide Locus Typing for the Klebsiella pneumoniae Species Complex. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.Org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdeira, L.; Fernandes, M.R.; Francisco, G.R.; Bueno, M.F.C.; Ienne, S.; Souza, T.A.; De Oliveira Garcia, D.; Lincopan, N. Draft Genome Sequence of a Hospital-Associated Clone of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST340/CC258 Coproducing RmtG and KPC-2 Isolated from a Pediatric Patient. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e01130-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A Resource Combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D678–D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanon, I.P.; Campos, J.V.F.; Castro, Y.G.d.; Melo, I.M.S.d.; Aburjaile, F.F.; Brenig, B.; Azevedo, V.; Silva, R.O.S. Genomic Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (OXA-23) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-2) Causing Hospital-Acquired Infections in Dogs. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060584
Zanon IP, Campos JVF, Castro YGd, Melo IMSd, Aburjaile FF, Brenig B, Azevedo V, Silva ROS. Genomic Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (OXA-23) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-2) Causing Hospital-Acquired Infections in Dogs. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(6):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060584
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanon, Isabela Pádua, João Victor Ferreira Campos, Yasmin Gonçalves de Castro, Isadora Maria Soares de Melo, Flávia Figueira Aburjaile, Bertram Brenig, Vasco Azevedo, and Rodrigo Otávio Silveira Silva. 2025. "Genomic Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (OXA-23) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-2) Causing Hospital-Acquired Infections in Dogs" Antibiotics 14, no. 6: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060584
APA StyleZanon, I. P., Campos, J. V. F., Castro, Y. G. d., Melo, I. M. S. d., Aburjaile, F. F., Brenig, B., Azevedo, V., & Silva, R. O. S. (2025). Genomic Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (OXA-23) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-2) Causing Hospital-Acquired Infections in Dogs. Antibiotics, 14(6), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060584







