Nebulized Antibiotics for Preventing and Treating Gram-Negative Respiratory Infections in Critically Ill Patients: An Overview of Reviews
Abstract
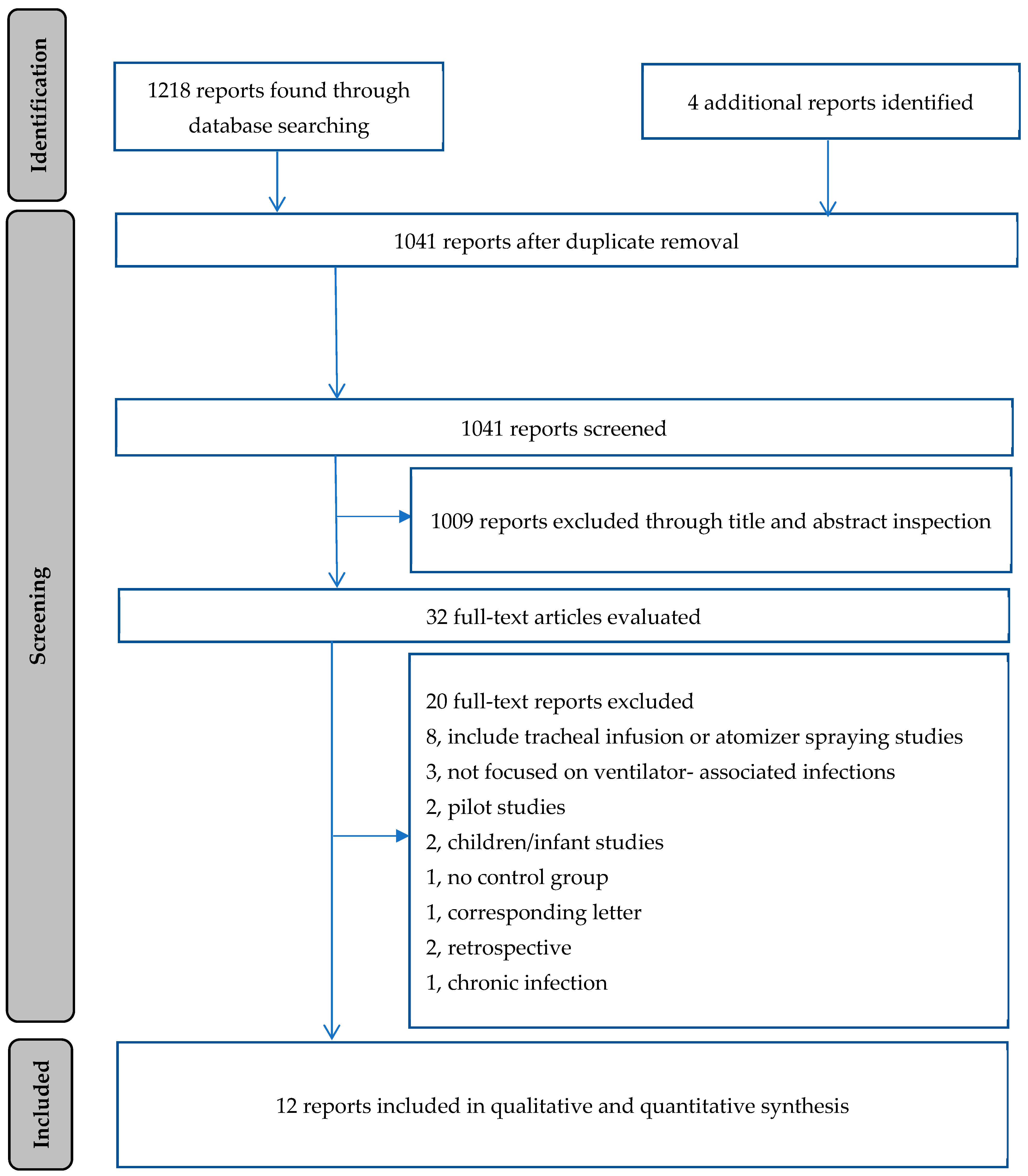
1. Introduction
Background
2. Results
2.1. Prevention Assessment
2.2. Treatment Assessment
2.3. Methodological Quality Evaluation
2.4. Outcomes—Effects of Interventions
2.5. Clinical Response
2.6. Bacterial Response and Eradication
2.7. Mortality
2.8. Other Clinical Outcomes
2.9. VAT Treatment
2.10. Adverse Effects
2.11. Certainty of Evidence
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
4.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
4.1.3. Definitions
4.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
4.3. Study Selection
4.4. Data Extraction
4.5. Methodological Quality and Risk of Bias Assessment
4.6. Data Analysis
4.7. Certainty of Evidence Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMSTAR | Assessment of Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews |
| CCA | Corrected Covered area |
| DTR | Difficult-to-treat resistant |
| GNB | Gram-negative bacteria |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation |
| IV | Intravenous |
| PDR | Pandrug resistant |
| VAP | Ventilator-associated pneumonia |
| VARI | Ventilator-associated respiratory tract infections |
| VAT | Ventilator-associated tracheobronchitis |
| XDR | Extensively drug resistant |
References
- Rello, J.; Lisboa, T.; Koulenti, D. Respiratory infections in patients undergoing mechanical ventilation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papazian, L.; Klompas, M.; Luyt, C.E. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in adults: A narrative review. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 888–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koulenti, D.; Arvaniti, K.; Judd, M.; Lalos, N.; Tjoeng, I.; Xu, E.; Armaganidis, A.; Lipman, J. Ventilator-Associated Tracheobronchitis: To Treat or Not to Treat? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nseir, S.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Makris, D.; Jaillette, E.; Karvouniaris, M.; Valles, J.; Zakynthinos, E.; Artigas, A. Impact of appropriate antimicrobial treatment on transition from ventilator-associated tracheobronchitis to ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Povoa, P.; Rodríguez, A.; Curcio, D.; Suarez, D.; Mira, J.P.; Cordero, M.L.; Lepecq, R.; Girault, C.; Candeias, C.; et al. Incidence and prognosis of ventilator-associated tracheobronchitis (TAVeM): A multicentre, prospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar]
- Karvouniaris, M.; Makris, D.; Manoulakas, E.; Zygoulis, P.; Mantzarlis, K.; Triantaris, A.; Chatzi, M.; Zakynthinos, E. Ventilator-associated tracheobronchitis increases the length of intensive care unit stay. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 800–808. [Google Scholar]
- Kalil, A.C.; Metersky, M.L.; Klompas, M.; Muscedere, J.; Sweeney, D.A.; Palmer, L.B.; Napolitano, L.M.; O’Grady, N.P.; Bartlett, J.G.; Carratalà, J.; et al. Management of Adults With Hospital-acquired and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia: 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e61–e111. [Google Scholar]
- Melsen, W.G.; Rovers, M.M.; Koeman, M.; Bonten, M.J.M. Estimating the attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia from randomized prevention studies. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Alnimr, A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Predictive Microbiology and Evidence-Based Therapy. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 1527–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Stoian, M.; Andone, A.; Rareș Bândilă, S.; Onișor, D.; Ștefan Laszlo, S.; Lupu, G. Mechanical Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era: A Critical Challenge in the Intensive Care Units. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kadri, S.S.; Adjemian, J.; Lai, Y.L.; Spaulding, A.B.; Ricotta, E.; Prevots, D.R.; Palmore, T.N.; Rhee, C.; Klompas, M.; Dekker, J.P.; et al. Difficult-to-Treat Resistance in Gram-negative Bacteremia at 173 US Hospitals: Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Prevalence, Predictors, and Outcome of Resistance to All First-Line Agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar]
- Karvouniaris, M.; Almyroudi, M.P.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Blot, S.; Paramythiotou, E.; Tsigou, E.; Koulenti, D. Novel Antimicrobial Agents for Gram-Negative Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Sole-Lleonart, C.; Rouby, J.-J.; Chastre, J.; Blot, S.; Poulakou, G.; Luyt, C.-E.; Riera, J.; Palmer, L.; Pereira, J.; et al. Use of nebulized antimicrobials for the treatment of respiratory infections in invasively mechanically ventilated adults: A position paper from the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 629–639. [Google Scholar]
- Karvouniaris, M.; Makris, D.; Triantaris, A.; Zakynthinos, E. Inhaled antibiotics for nosocomial pneumonia. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2012, 11, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, T.; Ramsey, B.W. Cystic Fibrosis: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes Aller, S.; Quittner, A.L.; Salathe, M.A.; Schmid, A. Assessing effects of inhaled antibiotics in adults with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis—Experiences from recent clinical trials. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 769–782. [Google Scholar]
- Rello, J.; Rouby, J.J.; Sole-Lleonart, C.; Chastre, J.; Blot, S.; Luyt, C.E.; Riera, J.; Vos, M.C.; Monsel, A.; Dhanani, J.; et al. Key considerations on nebulization of antimicrobial agents to mechanically ventilated patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 640–646. [Google Scholar]
- Boisson, M.; Jacobs, M.; Grégoire, N.; Gobin, P.; Marchand, S.; Couet, W.; Mimoz, O. Comparison of intrapulmonary and systemic pharmacokinetics of colistin methanesulfonate (CMS) and colistin after aerosol delivery and intravenous administration of CMS in critically ill patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 7331–7339. [Google Scholar]
- Boisson, M.; Grégoire, N.; Cormier, M.; Gobin, P.; Marchand, S.; Couet, W.; Mimoz, O. Pharmacokinetics of nebulized colistin methanesulfonate in critically ill patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boisson, M.; Mimoz, O.; Hadzic, M.; Marchand, S.; Adier, C.; Couet, W.; Gregoire, N. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and nebulized gentamicin in critically ill patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2830–2837. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Athanassa, Z.E.; Markantonis, S.L.; Fousteri, M.-Z.; Myrianthefs, P.M.; Boutzouka, E.G.; Tsakris, A.; Baltopoulos, G.E. Pharmacokinetics of inhaled colistimethate sodium (CMS) in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, D.P.; Dimopoulos, G.; Welte, T.; Luyt, C.E. Can we improve clinical outcomes in patients with pneumonia treated with antibiotics in the intensive care unit? Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Luyt, C.E.; Nicolau, D.P.; Pugin, J. Characteristics of an ideal nebulized antibiotic for the treatment of pneumonia in the intubated patient. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, M.; Fernandes, R.M.; Becker, L.A.; Pieper, D.; Hartling, L. Chapter V: Overviews of Reviews. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 6.4 (updated August 2023); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2023; Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Vounzoulaki, E.; Mantsiou, C.D.; Savvides, E.D.; Ntzani, E.E.; Haidich, A.-B. Global mapping of overviews of systematic reviews in healthcare published between 2000 and 2020: A bibliometric analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 137, 58–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Pamporis, K.; Vounzoulaki, E.; Karagiannis, T.; Haidich, A.-B. Types and associated methodologies of overviews of reviews in health care: A methodological study with published examples. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2023, 153, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sella, N.; Pettenuzzo, T.; De Cassai, A.; Zarantonello, F.; Congedi, S.; Bruni, A.; Garofalo, E.; Ocagli, H.; Gregori, D.; Longhini, F.; et al. Inhaled antibiotics for treating pneumonia in invasively ventilated patients in intensive care unit: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials with trial sequential analysis. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 387. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, X.; Jiang, M.; Huang, S.; Yang, M. Nebulized colistin as the adjunctive treatment for ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2023, 77, 154315. [Google Scholar]
- Valachis, A.; Samonis, G.; Kofterides, D.P. The role of aerosolized colistin in the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Crit. Care. Med. 2015, 43, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri, F.G.; Nassar, A.P., Jr.; Gusmao-Flores, D.; Taniguchi, L.U.; Torres, A.; Ranzani, O.T. Nebulized antibiotics for ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.-X.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Qu, J.-M. Intravenous combined with aerosolised polymyxin versus intravenous polymyxin alone in the treatment of pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant pathogens: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé-Lleonart, C.; Rouby, J.J.; Blot, S.; Poulakou, G.; Chastre, J.; Palmer, L.B.; Bassetti, M.; Luyt, C.-E.; Pereira, J.M.; Riera, J.; et al. Nebulization of Antiinfective Agents in Invasively Mechanically Ventilated Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 890–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.P.; Huang, H.B.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Du, B. Amikacin nebulization for the adjunctive therapy of gram-negative pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardakas, K.Z.; Mavroudis, A.D.; Georgiou, M.; Falagas, M.E. Intravenous plus inhaled versus intravenous colistin monotherapy for lower respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2018, 76, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; He, L.-L.; Che, L.-Q.; Li, W.; Ying, S.M.; Chen, Z.-H.; Shen, H.-H. Aerosolized antibiotics for ventilator-associated pneumonia: A pairwise and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.J.; Shiroishi, M.S.; Siantz, E.; Wu, B.W.; Patino, C.M. The use of inhaled antibiotic therapy in the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia and tracheobronchitis: A systematic review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvouniaris, M.; Makris, D.; Zygoulis, P.; Triantaris, A.; Xitsas, S.; Mntzarlis, K.; Petinaki, E.; Zakynthinos, E. Nebulised colistin for ventilator-associated pneumonia prevention. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, S.; Barbier, F.; Demiselle, J.; Quenot, J.-P.; Herbrecht, J.-E.; Roux, D.; Lacherade, J.-C.; Landais, M.; Seguin, P.; Schnell, D.; et al. Inhaled Amikacin to Prevent Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2052–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Niu, J.; He, Z.; Fu, W.; Huang, Q.; Guan, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, R. Prophylactic antibiotics for preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia: A pairwise and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoa, F.C.C.; Cardinal-Fernandez, P.; Maia, I.S.; Reboredo, M.M.; Pinheiro, B.V. Effect of antibiotics administered via the respiratory tract in the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2018, 43, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Luo, R.; Wu, B.; Wang, F.; Song, H.; Chen, X. Effectiveness and safety of adjunctive inhaled antibiotics for ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Crit. Care 2021, 65, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeny, D.A.; Kalil, A.C. Why don’t we have more inhaled antibiotics to treat ventilator-associated pneumonia? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Mao, W. Efficacy and safety of intravenous combined with aerosolised polymyxin versus intravenous polymyxin alone in the treatment of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yang, X.; Tian, J.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Y. Antibiotic Treatment of Pulmonary Infections: An Umbrella Review and Evidence Map. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 680178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honore, P.M.; Perriens, E.; Blackman, S. Nebulized colistin as the adjunctive treatment for ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2024, 79, 154466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, N.A.; Awdallah, F.F.; Abbassi, M.M.; Sabri, N.A. Nebulized Versus IV Amikacin as Adjunctive Antibiotic for Hospital and Ventilator-Acquired Pneumonia Postcardiac Surgeries: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, B.; Nazarchuk, O.; Dmytriiev, D.; Bahniuk, N.; Melnychenko, M.; Dmytriiev, K. Adjunctive inhaled amikacin in infants with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia optimizes the complex antimicrobial therapy: Pilot study. Acta Biomed. 2023, 94, e2023084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angermair, S.; Deja, M.; Thronicke, A.; Grehn, C.; Akbari, N.; Uhrig, A.; Asgarpur, G.; Spies, C.; Treskatsch, S.; Schwarz, C. A prospective phase IIA multicenter double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of inhaled Tobramycin in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia (iToVAP). Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain. Med. 2023, 42, 101249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharathi, K.S.; Bhat, A.; Pruthi, G.; Simha, P.P. Randomized control study of nebulized colistin as an adjunctive therapy in ventilator-associated pneumonia in pediatric postoperative cardiac surgical population. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2022, 25, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, S.; Ramírez-Estrada, S.; Forero, C.G.; Gallego, M.; Soriano, J.B.; Cardinal-Fernández, P.A.; Ehrmann, S.; Rello, J. Safety and Efficacy of Devices Delivering Inhaled Antibiotics among Adults with Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis: A Systematic Review and a Network Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygun, F.; Aygun, F.D.; Varol, F.; Durak, C.; Cokugraş, H.; Camcioglu, Y.; Can, H. Can Nebulised Colistin Therapy Improve Outcomes in Critically Ill Children with Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Pneumonia? Antibiotics 2019, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pascale, G.; Pintaudi, G.; Lisi, L.; De Maio, F.; Cutuli, S.L.; Tanzarella, E.S.; Carelli, S.; Lombardi, G.; Cesarano, M.; Gennenzi, V.; et al. Use of High-Dose Nebulized Colistimethate in Patients with Colistin-Only Susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii VAP: Clinical, Pharmacokinetic and Microbiome Features. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrianopoulos, I.; Kazakos, N.; Lagos, N.; Maniatopoulou, T.; Papathanasiou, A.; Papathanakos, G.; Koulenti, D.; Toli, E.; Gartzonika, K.; Koulouras, V. Co-Administration of High-Dose Nebulized Colistin for Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteremic Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Impact on Outcomes. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendía, J.A.; Guerrero Patiño, D.; Zuluaga Salazar, A.F. Efficacy of adjunctive inhaled colistin and tobramycin for ventilator-associated pneumonia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lyu, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, P.; Albuainain, F.A.; Alamoudi, O.A.; Rochette, V.; Ehrmann, S. Prophylactic Antibiotics Delivered Via the Respiratory Tract to Reduce Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Systematic Review, Network Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.H.; Wu, J.Y.; Shiau, B.W.; Huang, P.Y.; Chuang, M.H.; Tsai, Y.W.; Liu, T.H.; Tang, H.J.; Lai, C.C. The preventive effect of inhaled antibiotic against ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 64, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Y. Effects of prophylactic nebulized antibiotics on the prevention of ICU-acquired pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ. 2024, 12, e18686, eCollection 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque Paz, D.; Chean, D.; Tattevin, P.; Bayeh, B.A.; Kouatchet, A.; Douillet, D.; Riou, J. Efficacy and safety of antibiotics targeting Gram-negative bacteria in nosocomial pneumonia: A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Ann. Intensive Care. 2024, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhoen, R.A.; Howes, D.; Maslove, D.M. Is Mortality a Useful Primary End Point for Critical Care Trials? Chest 2020, 158, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Niederman, M.S. Adjunctive Nebulized Antibiotics: What Is Their Place in ICU Infections? Front. Med. 2019, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalopoulos, A.; Fotakis, D.; Virtzili, S.; Vletsas, C.; Raftopoulou, S.; Mastora, Z.; Falagas, M.E. Aerosolized colistin as adjunctive treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia due to multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: A prospective study. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubin, B.K. Pediatric Aerosol Therapy: New Devices and New Drugs. Respir. Care 2011, 56, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Bihan, K.; Zahr, N.; Becquemin, M.H.; Lu, X.; Bertholon, J.-F.; Vezinet, C.; Arbelot, C.; Monsel, A.; Rouby, J.-J.; Langeron, O.; et al. Influence of diluent volume of colistimethate sodium on aerosol characteristics and pharmacokinetics in ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by MDR bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.X.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Pelingon, R.; Ramu, S.; Kavanagh, A.; Elliott, A.G.; Butler, M.S.; Montgomery, A.B.; Cooper, M.A. Mucin Binding Reduces Colistin Antimicrobial Activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5925–5931. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Luo, R.; Bodin, L.; Yang, J.; Zahr, N.; Aubry, A.; Golmard, J.-L.; Rouby, J.-J. Efficacy of high-dose nebulized colistin in ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii. Anesthesiology 2012, 117, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Solé-Lleonart, C.; Rouby, J.-J.; Chastre, J.; Poulakou, G.; Palmer, L.B.; Blot, S.; Felton, T.; Bassetti, M.; Luyt, C.-E.; Pereira, J.M.; et al. Intratracheal Administration of Antimicrobial Agents in Mechanically Ventilated Adults: An International Survey on Delivery Practices and Safety. Respir. Care 2016, 61, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Du, X.; Liu, X.; Chuan, L.; Jing, G.; Wang, Z.; Shu, W.; Ye, C.; et al. The utilization of aerosol therapy in mechanical ventilation patients: A prospective multicenter observational cohort study and a review of the current evidence. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1071. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, A.A.; Cuccia, A.D.; Smaldone, G.C. Reliability of vibrating mesh technology. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Monsel, A.; Roberts, J.A.; Pontikis, K.; Mimoz, O.; Rello, J.; Qu, J.; Rouby, J.J.; European Investigators Network for Nebulized Antibiotics in Ventiltor-associated Pneumonia. Nebulized Colistin in Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia and Tracheobronchitis: Historical Background, Pharmacokinetics and Perspectives. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanani, J.; Roberts, J.A.; Monsel, A.; Torres, A.; Kollef, M.; Rouby, J.J.; European Investigators Network for Nebulized Antibiotics inVentiltor-associated Pneumonia. Understanding the nebulization of antibiotics: The key role of lung microdialysis studies. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rouby, J.-J.; Xia, J.; Dhanani, J.; Li Bassi, G.; Monsel, A.; Torres, A.; on behalf of the European Investigators Network for Nebulized Antibiotics in Ventilator-associated Pneumonia (ENAVAP). Nebulized aminoglycosides for ventilator-associated pneumonia: Methodological considerations and lessons from experimental studies. J. Intensive Med. 2024, 5, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.B.; Velkov, T.; Nation, R.L.; Forrest, A.; Tsuji, B.T.; Bergen, P.P.; Li, J. Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of colistin and polymyxin B: Are we there yet? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmann, S.; Barbier, F.; Li, J. Aerosolized Antibiotic Therapy in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 730–736. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, M.; Gates, A.; Pieper, D.; Fernandez, R.M.; Tricco, A.C.; Moher, D.; Brennan, S.; Li, T.; Pollock, M.; Lunny, C.; et al. Reporting guideline for overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions: Development of the PRIOR statement. BMJ 2022, 378, e070849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunny, C.; Pieper, D.; Thabet, P.; Kanji, S. Managing overlap of primary study results across systematic reviews: Practical considerations for authors of overviews of reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Vounzoulaki, E.; Mantsiou, C.D.; Savvides, E.D.; Karakosta, C.; Diakonidis, T.; Tsapas, A.; Haidich, A.-B. Methods for depicting overlap in overviews of systematic reviews: An introduction to static tabular and graphical displays. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 132, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Diakonidis, T.; Mavromanoli, A.C.; Haidich, A.-B. ccaR: A package for assessing primary study overlap across systematic reviews in overviews. Res. Synth. Methods 2023, 14, 443–454. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Karakasis, P.; Pamporis, K.; Bouras, E.; Haidich, A.-B. amstar2Vis: An R package for presenting the critical appraisal of systematic reviews based on the items of AMSTAR 2. Res. Synth. Methods 2024, 15, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Sterne, J.A.C. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 6.4 (updated August 2023); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2023; Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Hernán, M.A.; McAleenan, A.; Reeves, B.C.; Higgins, J.P.T. Chapter 25: Assessing risk of bias in a non-randomized study. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 6.4 (updated August 2023); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2023; Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balshem, H.; Helfand, M.; Schunemann, H.J.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Vist, G.E.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Meerpohl, J.; Norris, S.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
| Author, Year (Ref) | Study Type | Included Studies | Studies/Patients, N | Bacteria Commonly Treated | Nebulization Strategy | Nebulized Drug | Daily Nebulized Dose, Range | Device | Primary Outcome | AMSTAR-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment studies | ||||||||||
| Sella, 2024 [29] | Meta-analysis | RCT | 11/1472 | NS | Adjunctive | Amikacin, colistin, polymyxin B, tobramycin | NS | variable | Microbiological eradication | Critically low |
| Zhang, 2023 [30] | Meta-analysis | RCT, observational | 10/950 | Ab, Kp, Pa | Adjunctive | Colistin | 2–12 MU | variable | Clinical response | Critically low |
| Valachis, 2015 [31] | Meta-analysis | Observational, RCT * | 8/724 | Ab, Kp, Pa | Adjunctive/substitutive § | Colistin | 2–5 MU | variable ¶ | Clinical response | Critically low |
| Zampieri 2015 [32] | Meta-analysis | RCT, observational | 12/885 | Ab, Kp, Pa | Adjunctive/substitutive § | Amikacin, colistin, tobramycin | 200–1200 mg 2–4 MU 200–600 mg | variable | Clinical cure | Critically low |
| Liu, 2015 [33] | Meta-analysis | Observational | 9/672 | Ab, Kp, Pa | Adjunctive/substitutive § | Colistin | 2–4 MU | NS | Multiple outcomes | Critically low |
| Russell, 2016 [38] | Systematic review | RCT | 6/305 | NS | Adjunctive | Amikacin, colistin, tobramycin | NS | NS | Clinical cure | Critically low |
| Sole-Lleonart, 2017 [34] | Meta-analysis | RCT, observational | 11/826 | NS | Adjunctive/substitutive § | Amikacin, colistin, gentamycin, tobramycin | NS | variable | Multiple outcomes | Critically low |
| Qin, 2021 [35] | Meta-analysis | RCT | 13/1733 | NS | Adjunctive | Amikacin | 800–1600 mg | variable | Clinical response | Critically low |
| Vardakas, 2018 [36] | Meta-analysis | Observational | 13/1135 | Ab, Kp, Pa | Adjunctive | Colistin | 2–6 MU | NS | All-cause mortality | Critically low |
| Xu, 2018 [37] | Meta-analysis | RCT, observational | 17/1367 | Ab, Kp, Pa | Adjunctive/substitutive § | Amikacin, colistin, tobramycin | 300–1750 mg 1–4 MU 240–600 mg | variable | Multiple outcomes | Critically low |
| Prevention studies † | ||||||||||
| Karvouniaris, 2015 [39] | RCT | NA | NA/ | NA | NA | Colistin | 500,000 iu TDS for the first 10 ICU days | jet nebulizer | 30-day VAP incidence | NA |
| Ehrmann, 2023 [40] | RCT | NA | NA/ | NA | NA | Amikacin | 20 mg/kg #, OD for 3 consecutive days | vibrating mesh nebulizer | 28-day VAP incidence | NA |
| Outcome | Nebulized Antibiotic | Pooled Effect Estimates (95% CI) | I2 Statistic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical response | Amikacin | RR 1.23 (1.13–1.34) | 47% |
| Colistin | OR 1.39 (0.87–2.20) | 56% | |
| Bacterial eradication | Amikacin | RR 1.51 (1.35–1.69) | 6% |
| Colistin | OR 2.21 (1.25–3.92) | 64% | |
| All-cause mortality | Amikacin | RR 1.17 (0.98–1.50) | 0% |
| Colistin | RR 0.94 (0.81–1.08) | 16% | |
| Pneumonia-associated mortality | Amikacin | RR 1.12 (0.82–1.52) | 0% |
| Colistin | OR 0.58 (0.34–0.96) | 46% | |
| Mechanical ventilation duration, days | Amikacin | MD −0.45 (−2.69 to 1.78) | 84% |
| Amikacin/colistin/tobramycin | SMD −0.10 (−1.22 to 1.00) | 96.5% | |
| ICU length of stay, days | Amikacin | MD −0.31 (−2.08 to 1.45) | 67% |
| Amikacin/colistin/tobramycin | SMD 0.14 (−0.46 to 0.73) | 89.2% | |
| Nephrotoxicity | Amikacin | RR 0.82 (0.60–1.12) | 2% |
| Colistin | OR 1.11 (0.69–1.80) | 23% | |
| Bronchospasm | Amikacin | RR 2.55 (1.40–4.66) | 0% |
| Colistin | OR 5.19 (1.05–25.52) | 0% |
| Outcome | Number of Reviews, n | CCA Percentage, % |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical response | 9 | 15.4 |
| Bacterial eradication | 7 | 16.7 |
| All-cause mortality | 8 | 18.4 |
| Pneumonia-associated mortality | 3 | 9.1 |
| Mechanical ventilation duration | 3 | 10 |
| ICU length of stay | 2 | 0 |
| Nephrotoxicity | 7 | 15.9 |
| Bronchospasm | 2 | 0 |
| Amikacin vs. Control | Colistin vs. Control | |
|---|---|---|
| Significance Level/Certainty of Evidence | ||
| Outcome | ||
| Clinical response | Significant/Moderate | Non-significant/Low–very low |
| Microbiological eradication | Significant/Low | Significant/Low–very low |
| All-cause mortality | Non-significant/Moderate | Non-significant/Low–very low |
| Infection-associated mortality | Non-significant/Moderate | Non-significant/Very low |
| Mechanical ventilation duration | Non-significant/Very low | Non-significant/Very low * |
| Length of ICU stay | Non-significant/Low | Non-significant/Very low |
| Nephrotoxicity | Non-significant/Moderate | Non-significant/Very low |
| Bronchospasm | Significant/Moderate | Significant/Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karvouniaris, M.; Koulenti, D.; Bougioukas, K.I.; Pagkalidou, E.; Paramythiotou, E.; Haidich, A.-B. Nebulized Antibiotics for Preventing and Treating Gram-Negative Respiratory Infections in Critically Ill Patients: An Overview of Reviews. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040370
Karvouniaris M, Koulenti D, Bougioukas KI, Pagkalidou E, Paramythiotou E, Haidich A-B. Nebulized Antibiotics for Preventing and Treating Gram-Negative Respiratory Infections in Critically Ill Patients: An Overview of Reviews. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(4):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040370
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarvouniaris, Marios, Despoina Koulenti, Konstantinos I. Bougioukas, Eirini Pagkalidou, Elizabeth Paramythiotou, and Anna-Bettina Haidich. 2025. "Nebulized Antibiotics for Preventing and Treating Gram-Negative Respiratory Infections in Critically Ill Patients: An Overview of Reviews" Antibiotics 14, no. 4: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040370
APA StyleKarvouniaris, M., Koulenti, D., Bougioukas, K. I., Pagkalidou, E., Paramythiotou, E., & Haidich, A.-B. (2025). Nebulized Antibiotics for Preventing and Treating Gram-Negative Respiratory Infections in Critically Ill Patients: An Overview of Reviews. Antibiotics, 14(4), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040370







