Abstract
Background/Objectives: Motile aeromonads are ubiquitous aquatic Gram-negative opportunistic pathogens with environmental, animal, aquatic, and human health implications. Methods: Motile aeromonads were isolated from village pond water samples (n = 100) of the Hisar district of Haryana state in India. Selective isolation and enumeration were followed by biochemical and genotypic identification using gyrB gene; evaluation of seven putative virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance studies and determination of extended spectrum beta lactamase (ESBL) and AmpC beta lactamase (ACBL) enzyme-producing abilities took place. Results: The viable counts of motile aeromonads varied from 1.6 × 102 CFU/mL to 1.2 × 108 CFU/mL. Six species of Aeromonas were identified with high prevalence of A. veronii (74.7%), followed by A. caviae (8.9%), A. hydrophila (7.6), A. jandaei (5%), A. sobria (2.5%), and A. dhakensis (1.3%). PCR amplification of seven genes related to virulence indicated that the majority of the isolates were positive for enolase (eno, 98%), cytotoxic enterotoxin (act, 88%), and hemolysin (asa1, 86%). Many isolates were also positive for type III secretion system inner membrane component (ascV, 53%), ADP-ribosylating toxin (aexT, 47%), and extracellular hemolysin (ahh1, 4%). The antimicrobial resistance (AMR) profile of the isolated Aeromonas isolates indicated the high resistance observed to nalidixic acid (40.2%), cefoxitin (33%), and imipenem (6.2%). In addition, the occurrence of 10.3% ESBL, 32% ACBL, and 29.9% multi-drug resistant (MDR) isolates is alarming. Phylogenetic analysis of gyrB sequences of A. veronii isolates (n = 59) together with GenBank sequences of A. veronii from different geographical regions of the world indicated high genotypic diversity. Conclusions: the village aquaculture ponds in Hisar district have a high occurrence of MDR A. veronii, A. hydrophila, and A. caviae, posing significant animal and public health concern.
1. Introduction
Members of the genus Aeromonas are Gram-negative, rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic bacteria that are unique to aquatic environments [1]. Many common species are considered to be emerging pathogens that not only infect aquatic organisms such as fish, but also act as opportunistic pathogens for humans and animals [2]. Given their abundance in freshwater lakes and ponds, they are of immense economic importance in pisciculture. Diseases such as furunculosis, hemorrhagic septicemia or motile Aeromonas septicemia, hemorrhagic enteritis, epizootic ulcerative syndrome, red sore disease, tail and fin rot, and lethargy are reported in fish [3]. A few of the important Aeromonas spp., viz., Aeromonas caviae, Aeromonas veronii, Aeromonas hydrophila, and Aeromonas dhakensis, are frequently associated with opportunistic infections, such as septicemia, gastroenteritis, and cutaneous infections, in immunocompromised individuals [4]. Therefore, the identification of Aeromonas spp. is important for understanding disease ecology.
However, the identification of motile aeromonads has its own set of intricacies. The motile aeromonads group is composed of 32 species and 12 validly published subspecies [5]. Formerly placed in the family Vibrionaceae, the genus Aeromonas taxonomy was revised in 1986 to create a new family, Aeromonadaceae, based on the results of 5S rRNA, 16S rRNA, and rRNA-DNA hybridization approaches [6]. However, phenotypic biochemical methods as well as molecular 16S rRNA processing pose challenges and are not sufficiently discriminatory for species identification due to the variable behavior of motile aeromonad strains [7,8,9]. Due to existing heterogeneity within the group, the phylogeny of housekeeping genes, mainly that of gyrB, a type II DNA topoisomerase encoding the β-subunit of DNA gyrase, has been considered an appropriate indicator for bacterial systematics [9,10].
The pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. is a function of its virulence-encoding genes, which assist the bacterium in colonizing, overwhelming the host immune system and establishing infection. These include various extracellular enzymes, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), pore-forming aerolysin, hemolytic toxins, cytotoxic and cytotonic enterotoxins, the type III secretion system (T3SS), and associated effectors [3,11]. Therefore, in view of the increased one health significance, it is important to understand the genotypic basis of these factors for characterizing the pathogenic potential of aeromonads.
Freshwater fish farming, arguably considered to be a sustaining component of the aquaculture industry, is thought to support income and employment in developing countries [12]. Bacterial infections associated with poor water quality are some of the challenges confronting freshwater aquaculture. For a long time, antimicrobial agents and chemotherapies have been primarily employed to control bacterial diseases caused by aeromonads [13]. The most widely utilized antimicrobials in the aquaculture industry are tetracyclines, enrofloxacin, erythromycin, amoxicillin, sulfonamides, oxolinic acid, oxytetracycline, chloramphenicol, and florfenicol [14]. The lack of uniform antimicrobial standards in aquatic environments is the prime reason for their frequent overuse and exploitation in fish culture [15], especially because antimicrobials may be easily available as over-the-counter medications and may be used off label [16]. Antimicrobial residues may be retained in fish fecal matter and uneaten food, where subsequent entry of these antibiotics into the aquatic environment and selective genome mutations in bacteria can lead to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). In this regard, motile aeromonads, ubiquitous in natural water bodies, can be considered good indicators of antimicrobial resistance, water quality, and sewage pollution, which has been well documented by various studies [17,18,19,20].
The water quality of natural ponds deteriorates due to organic and inorganic sewage effluent, defecation by domestic animals, solid waste disposal by locals, and poor drainage and mismanagement. Deterioration in water quality can be indicated by specific physicochemical parameters, which predispose the fish towards infection by such opportunistic pathogens [21]. Among these parameters, the most important are increased pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), temperature, salinity, turbidity, water electrical conductivity (EC), and decreased dissolved oxygen (DO) [16,22].
Our study highlights the importance of inland aquaculture pond systems as the ecological compartments of the environment, which, on account of their role as endpoint of organic wastes from humans and animals, may act as local epicentres of AMR evolution and dissemination, affecting the integrity of the aquaculture food chain, as well as animal and human health. The world is in the midst of a silent pandemic of antimicrobial resistance. The global action plan on AMR emphasized the gathering of evidence of an antimicrobial resistance base through surveillance and research. This study aims to address the aquatic environmental surveillance on AMR in village pond waters used for aquaculture, animal husbandry, and humans in the northern region of Haryana (India) for the first time. Therefore, to understand the prevalence of motile aeromonads in village pond waters used for aquaculture in this region, their species-level identification and antimicrobial resistance profile were investigated in natural freshwater village ponds in/around the Hisar district (Haryana, India). The physicochemical parameters of the pond water samples were evaluated. The Aeromonas spp. bacterial isolates were identified by phenotypic and biochemical testing and at the molecular level using gyrB sequencing. The genetic traits associated with the virulence of motile aeromonads isolated from pond water were also evaluated. The identified isolates were subjected to antimicrobial resistance profiling using a set of antimicrobial agents.
2. Results
One hundred pond water samples were collected from 66 village aquaculture ponds in the regions in/around Hisar (Haryana, India). Physicochemical characterization was performed on the water samples, and aeromonad bacteria were isolated from the water samples.
2.1. Water Quality Parameters
The physicochemical water quality parameters were measured in the examined pond water samples (n = 100), for which the range obtained is given in Table 1. The parameters of temperature (29–34 °C), pH (6.8–9.0), salinity (0.1–0.3 ppt), and dissolved oxygen (2.9–8.0 ppm) did not exhibit marked variations from the reference range [23,24,25]. Two of the evaluated parameters, TDS and EC, exceeded the desired values for some ponds, with the highest values being 2440 ppm and 3641 µs/cm, respectively.

Table 1.
Physicochemical parameters of pond water samples.
2.2. Prevalence and Diversity of Aeromonas Species in the Fish Culture Ponds
Large, smooth, and honey-yellow colonies on SAA consisting of Gram-negative, pleomorphic rod-shaped bacteria were tentatively identified as Aeromonas species [26]. A total of 100 Gram-negative, oxidase-, and catalase-positive colonies were selected and isolated as putative members of the genus Aeromonas from all 100 pond water samples and cryopreserved as glycerol stocks until further analysis. The counts of motile aeromonads recovered using SAA varied from 1.6 × 102 CFU/mL to 1.2 × 108 CFU/mL in the sampled pond waters.
For phenotypic confirmation, these 100 isolates were subjected to further biochemical tests, and the presumed motile aeromonads exhibited reactions characteristic of the genus Aeromonas spp. (Supplementary Table S2). The isolates produced positive reactions to catalase, oxidase, and D-glucose, while variable reactions were observed using citrate, malonate, lactose, and sucrose. None of the presumptive aeromonads were able to produce H2S gas or urease enzyme. β- and α-haemolysis were demonstrated by 58.8% and 37.1% of the isolates, respectively, on 5% sheep blood agar (SBA), while only 4.1% of the isolates were non-haemolytic. Most of the isolates had fermentative properties (75.3%) and were all motile (88.7). The majority (99%) of the isolates could utilize glucose in the medium as their energy source, while only 36.1% of the isolates could metabolize lactose/sucrose present in the medium. Further, 69.1% of the total isolates showed gas production from D-glucose utilization. On the other hand, 56.7% and 7.2% of the isolates could use citrate and malonate as their carbon and energy sources, respectively. Finally, 87.6% of the isolates could breakdown the amino acid tryptophan into indole and were considered indole-positive (Supplementary Table S2).
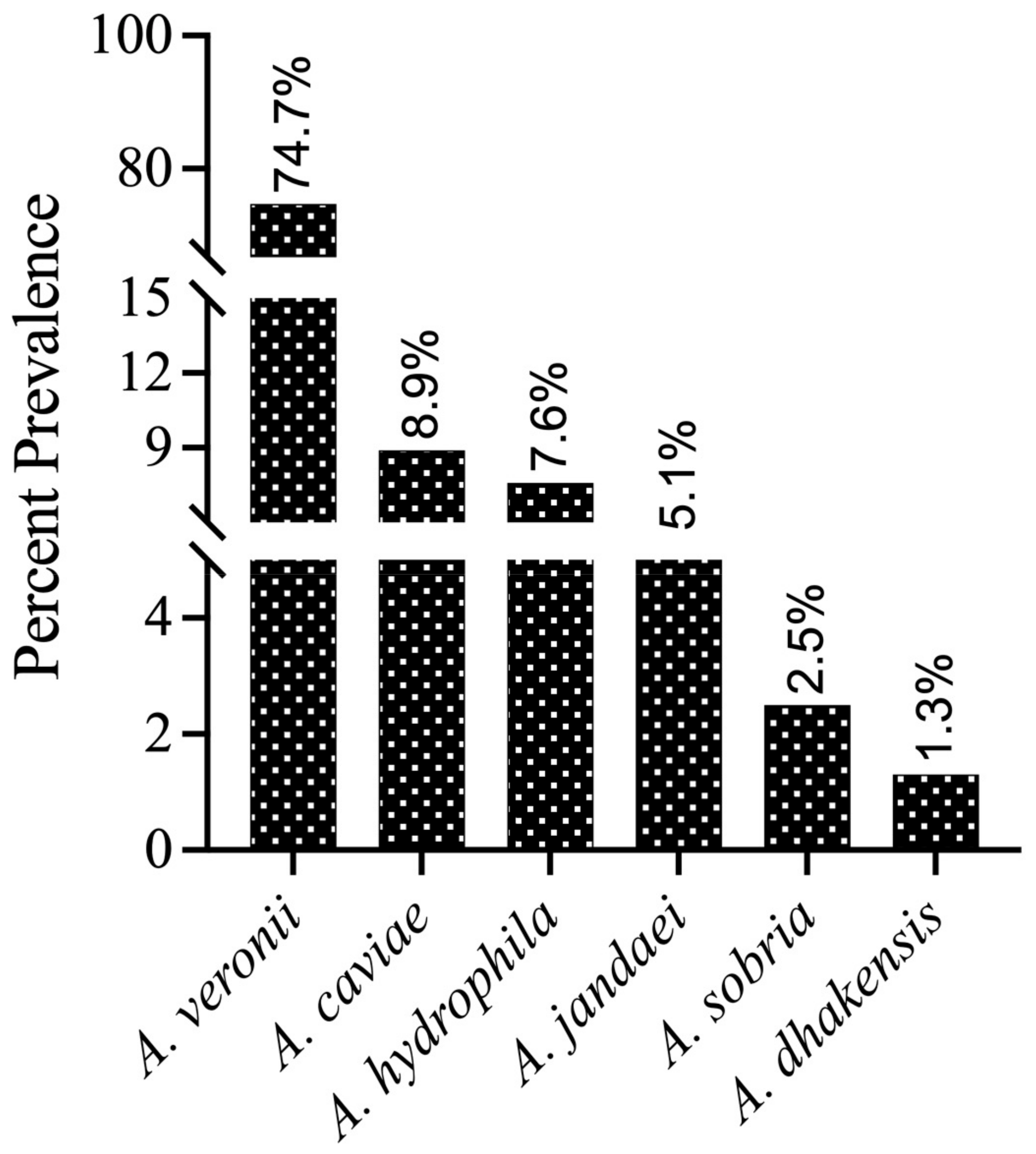
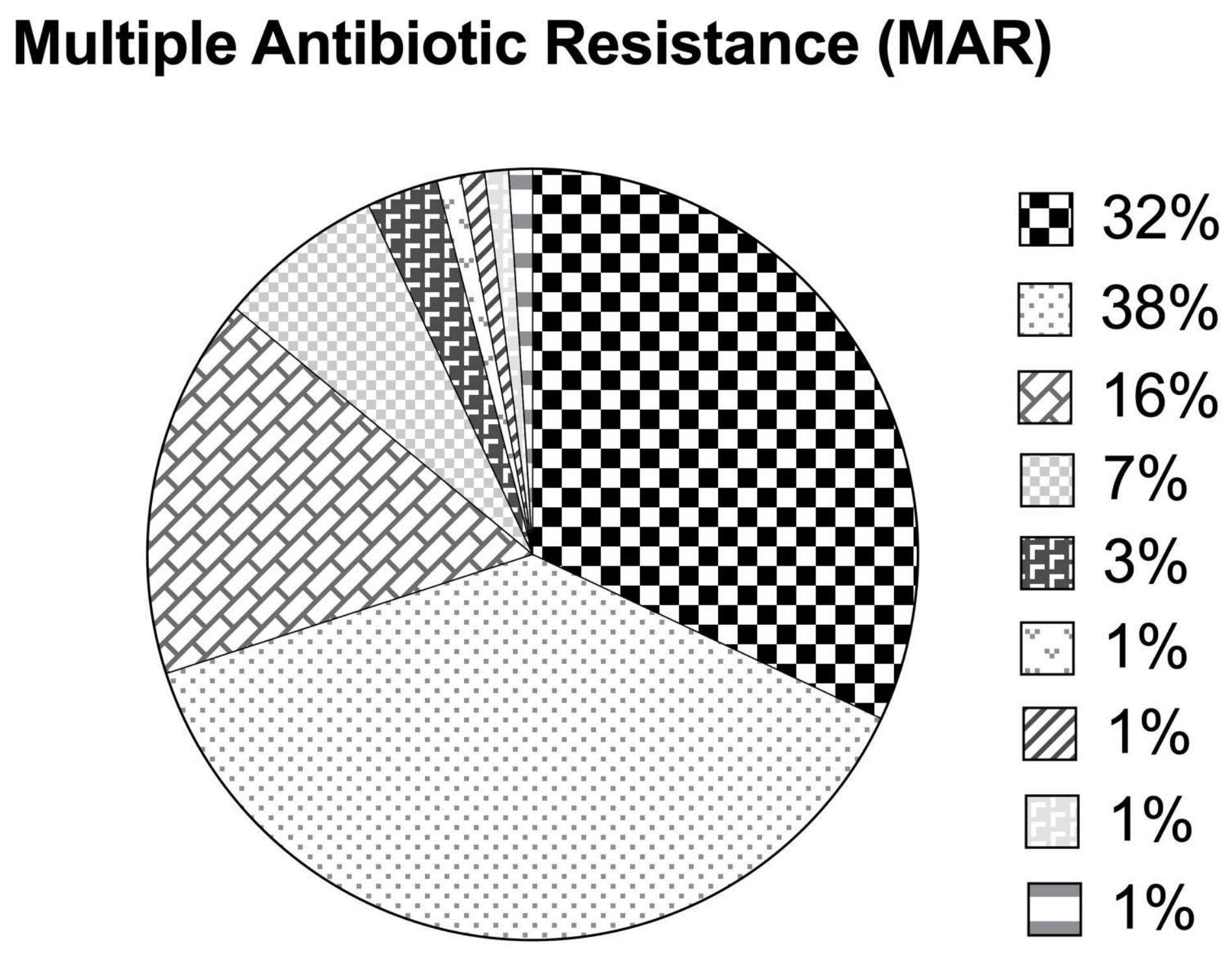
For species-level identification, these isolates (n = 100) were further analyzed by PCR amplification of the housekeeping gene gyrB. BLAST analysis of the gyrB sequences revealed that 79 isolates were most closely related to Aeromonas genus members in the NCBI database (percent identity between species ranging from 98.04 to 100%). The gyrB sequences of 79 isolates were deposited in the NCBI GenBank database, and the accession numbers were assigned (Supplementary Table S3). The submitted sequences belonged to six different Aeromonas species (Figure 1), which included A. veronii (n = 59), A. caviae (n = 7), A. hydrophila (n = 6), A. jandaei (n = 4), A. sobria (n = 2), and A. dhakensis (n = 1). Additionally, some isolates were not grouped into any cluster with known Aeromonas species strains, and these isolates need further investigation using more than one gene or other approaches. Therefore, these isolates were provisionally considered as “Aeromonas spp.” (n = 18). In addition to Aeromonas spp., our gyrB gene sequencing also identified three isolates as Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Pseudomonas alcaliphila, and Pseudomonas sediminis (one isolate each), which may belong to the normal fish microbiota or the aquatic ecosystem and are reported as fish pathogens under stress conditions [27]. Therefore, these three isolates were discontinued for the current study and only 97 isolates were taken up for further analysis. As an outcome of this survey, the phylogenetic relationships of the predominant species, A. veronii strains, were determined using gyrB gene sequences from 59 total Indian (NCVTC) isolates in this study, along with 19 other A. veronii strains from GenBank (representing various countries and hosts).
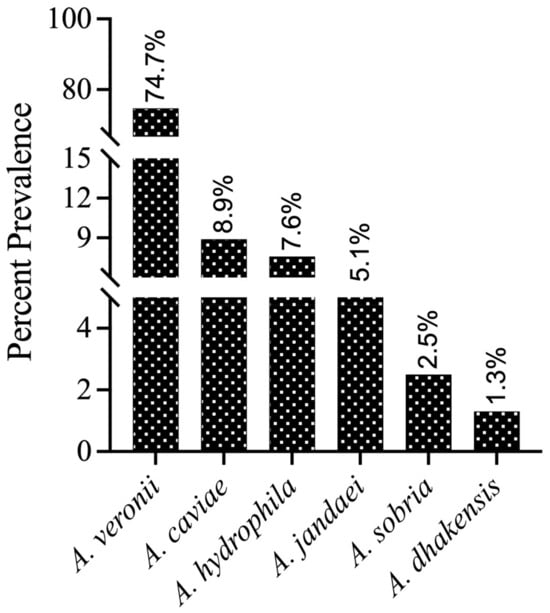
Figure 1.
Prevalence (%) of different Aeromonas species in the fish culture ponds confirmed by gyrB gene sequencing and submitted to NCBI (n = 79).
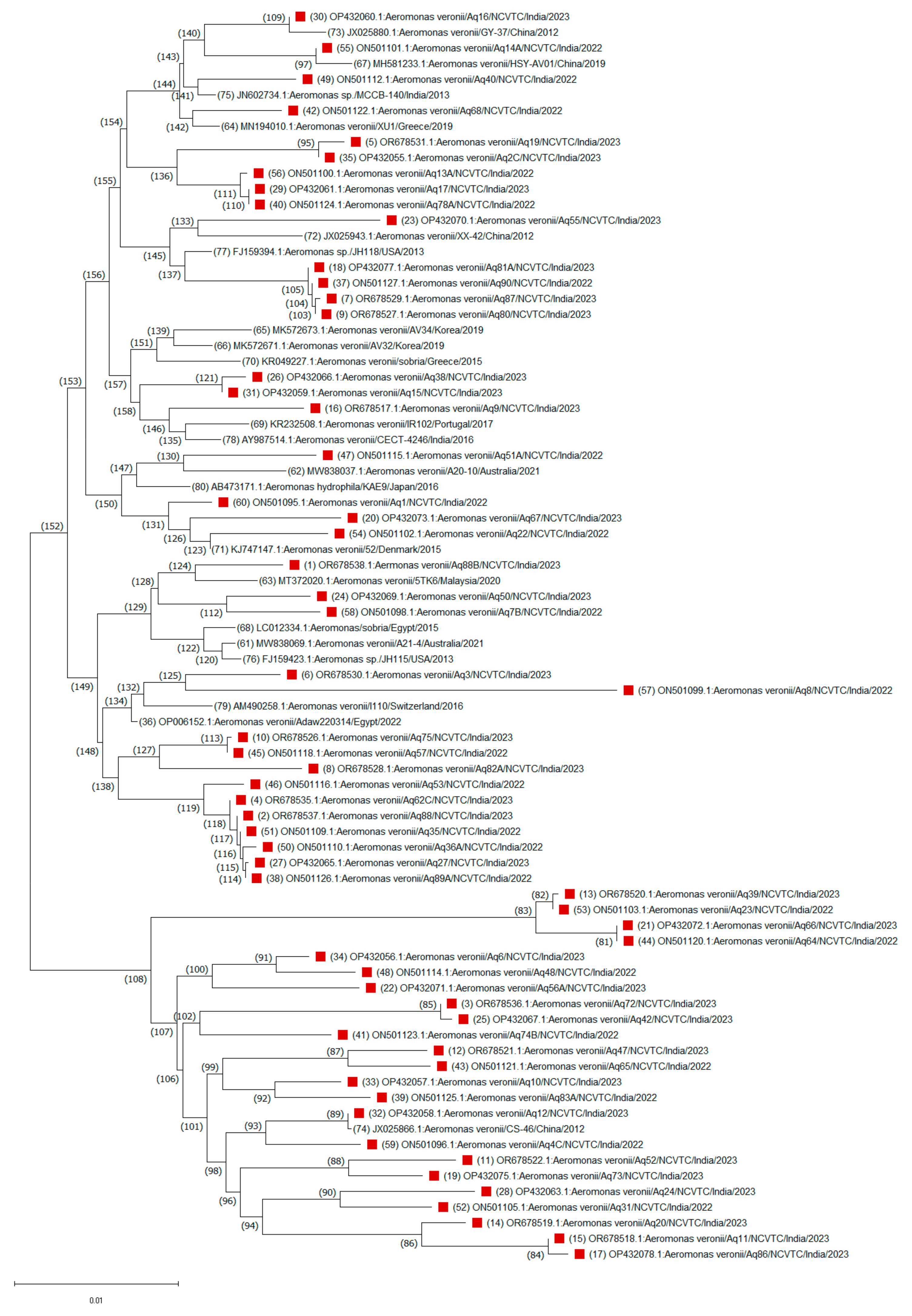
A consensus phylogenetic tree with bootstrap support was constructed to illustrate the evolutionary relationships of these A. veronii sequences based on a dataset of 1190 nucleotide positions (Figure 2). The evolutionary relationships of other Aeromonas species isolated from this study were also drawn (Supplementary Figure S2). Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that the A. veronii isolates were grouped into two highly conserved branches, corresponding to two major clades. One major clade, comprising 53 isolates, was divided into two distinct subgroups, suggesting a greater degree of genetic similarity among these isolates. The smaller subgroup (node ID 60) consisted of 19 isolates, primarily from India, along with one isolate each from Switzerland (I110/2016) and Egypt (Adaw220314/2022). This clustering pattern suggests that ecological niches, rather than geographical origin, are key determinants of evolutionary relationships among A. veronii isolates. In contrast, the larger subgroup (node ID 34) consisted of 34 isolates, including 20 from India and 14 from 10 other countries. One minor branch (node ID 46) grouped an Indian isolate with a U.S. isolate (H-1159/2013), possibly indicating a common origin. Another notable subgroup (node ID 6) clustered an Indian isolate (Aq55) with isolates from China, Australia, Spain, Korea, and Portugal, showing global clustering patterns. Isolates Aq88 and 5TK6 from India and Malaysia, respectively, branched with an Australian isolate (A21-4/2021) under node ID 58, while isolates Aq15 and Aq38 clustered with a Japanese isolate (AAr1218/2018) under node ID 43. A minor clade (node ID 94) consisted primarily of 25 Indian isolates, with only two isolates from other countries. For instance, isolates Aq31 and Aq24 clustered closely with a Japanese isolate (WL4-118/2015), while Aq12 formed a distinct branch with a Chinese isolate (CS-46/2012) under node ID 74. This analysis suggests close evolutionary distances among these isolates, highlighting the diversity within A. veronii species.
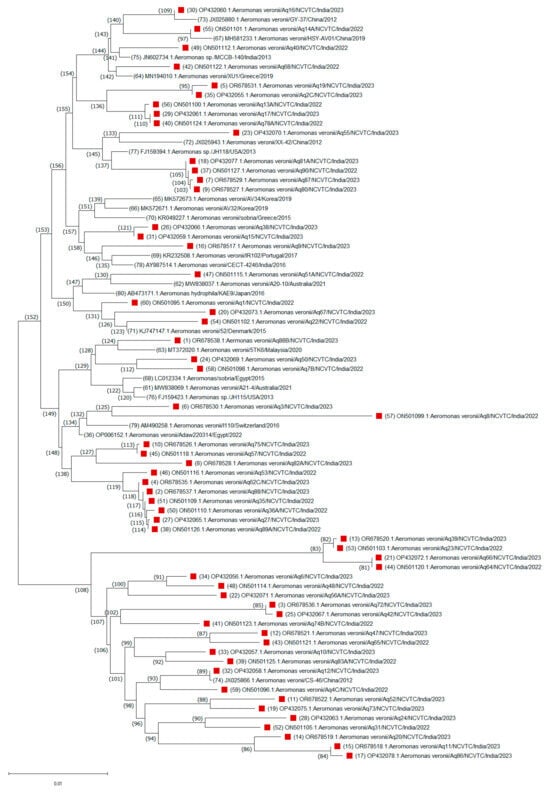
Figure 2.
Unrooted neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees based on the gyrB gene sequences of a total of 79 (59 strains from this study, red blocks and the remaining are 19 strains from GenBank) Aeromonas veronii strains. Evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method. The percentages of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together based on 1000 bootstrap replicates are shown adjacent to branches. Sequence accession numbers are in parentheses.
2.3. Virulence Gene Characteristics
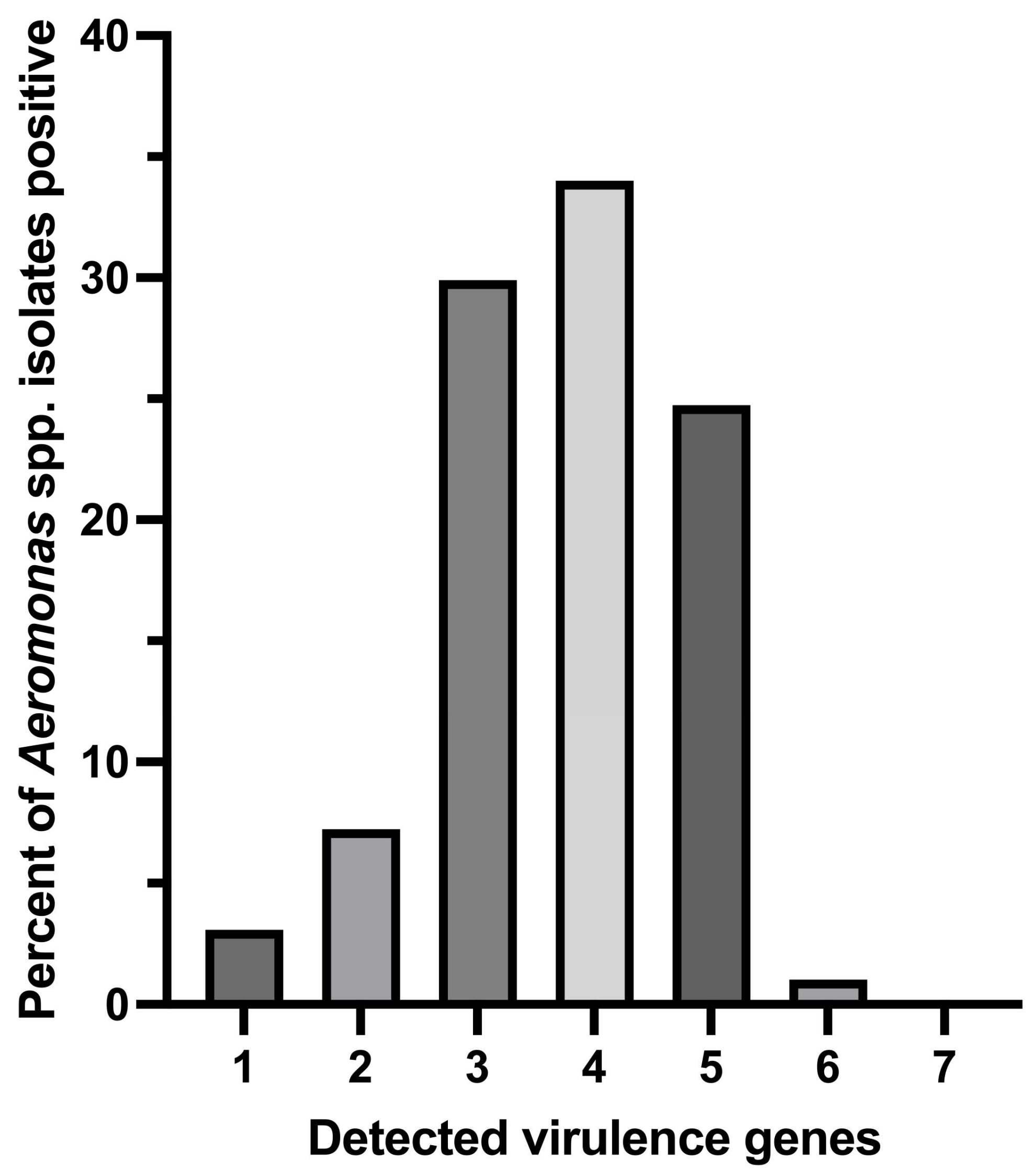
Among the 97 genotypically confirmed Aeromonas isolates, a greater number of the isolates (34.02%; 33/97) were found to carry 4 out of 7 virulence genes, followed by 24.74% (24/97), 29.9% (29/97), 7.22% (7/97), and 3.09% (3/97) of the isolates carrying 5, 3, 2, and 1 screened virulence gene (s), respectively (Figure 3). One isolate of A. hydrophila (1.03%; 1/97) was detected to carry as many as 6 out of the 7 tested virulence genes.
Figure 3.
Distribution of multiple virulence gene indices of Aeromonas species isolates positive for tested virulence genes.
On average, enolase (eno, 97.9%) was the most frequently detected virulence gene in Aeromonas species, followed by cytotoxic enterotoxin (act, 88.7%) and hemolysin (asa1, 85.6%), which had nearly similar detection frequencies (Table 2). AscV (a type III secretion system inner membrane component) was detected at a lower frequency of 51.6%, followed by the occurrence of the ADP ribosylating toxin gene aexT at 45.4%. The least frequent gene was the extracellular hemolysin gene ahh1, with a 4.12% prevalence. In contrast, the heat-stable cytotonic enterotoxin gene ast was not detected in any of the 97 isolates.

Table 2.
Detection frequency of different virulence genes among Aeromonas species isolates.
The dendrogram obtained by clustering Aeromonas isolates on the basis of the presence or absence of different virulence genes was depicted by the formation of two different clusters (shown with different colors) (Supplementary Figure S1) which further delineated into two major groups and two minor groups, revealing virulence-mediated heterogeneity in the species. Both the major groups were dominated by A. veronii isolates. Either the isolates were positive for asa/act/ascV/eno/aexT (shown in purple and red) or for asa/act/eno (shown in blue). One of the two minor clusters (shown in black) clustered together the A. veronii isolates positive for asa/act/eno/aexT genes. Furthermore, the fourth minor cluster (shown in green) was highly variable in composition, accounting for most of the A. hydrophila strains, along with the A. caviae and A. jandaei isolates. Most of the A. hydrophila and A. sobria isolates were found to harbor the virulence genes asa1/ast/ascV/eno, whereas all A. jandaei were positive for asa1/ascV/eno/aexT. Further, most of the A. caviae isolates were positive for asa1/act/eno and A. dhakensis isolate was found to harbor asa1/eno genes. The cluster dendrogram revealed the characteristic species-wise distribution of each Aeromonas species and that the different species belonged to different groups/clusters (e.g., A. hydrophila), with few exceptions where the number of isolates was low (e.g., A. jandaei and A. caviae) (Supplementary Figure S1).
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns
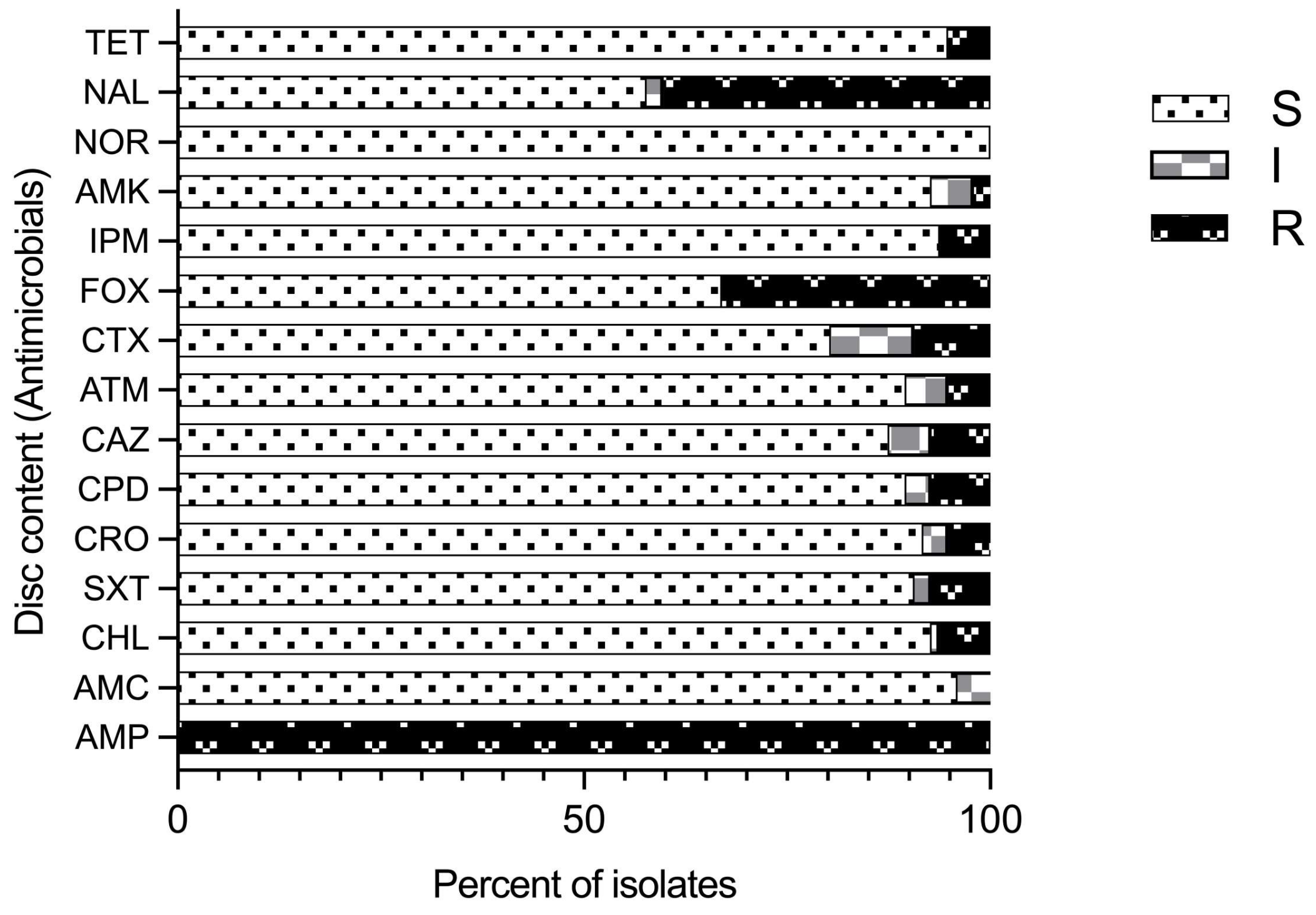
Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of 97 isolates identified as Aeromonas species by the sequencing of the gyrB gene using 15 common antimicrobial agents (8 classes) was performed by disc diffusion assay (Figure 4). Variable susceptibility patterns to all the tested antimicrobial agents were recorded (Figure 4; Supplementary Table S4) except ampicillin (AMP), for which all the isolates were resistant. Further, all of the isolates were susceptible to norfloxacin (NOR). Resistance to imipenem was observed in five A. veronii isolates (8.47%) and one A. caviae isolate (14.29%). Five isolates (5.2%) were resistant to tetracycline (three A. hydrophila, one A. veronii, and one Aeromonas spp. isolate). Resistance to nalidixic acid (NAL) and cefoxitin (FOX) was observed in 40.2% and 33% of the total 97 isolates, respectively. Resistance to cefoxitin, which is a cephamycin, second-generation cephalosporin, was found in 83.3% A. hydrophila and 57.1% A. caviae isolates followed by 27.1% A. veronii isolates. Similarly, high resistance to nalidixic acid and synthetic quinolones was observed in 66.7% A. hydrophila isolates, followed by 57.1% A. caviae and 35.6% A. veronii isolates. Therefore, proportionally more A. hydrophila and A. caviae isolates than A. veronii isolates were resistant to cefoxitin and nalidixic acid, possibly because of the significant difference in the number of isolates. Further, all isolates expressed variable degrees of resistance to imipenem (IPM), cefotaxime (CTX), aztreonam (ATM), chloramphenicol (CHL), ceftazidime (CAZ), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT), tetracycline (TET), and amoxiclav (AMX) at frequencies less than 10%.
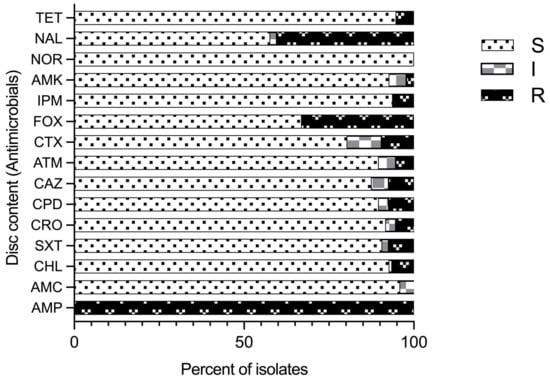
Figure 4.
Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern for Aeromonas species isolates for different antimicrobials tested and their classes: tetracycline (TET); nalidixic acid (NAL); norfloxacin (NOR); amikacin (AMK); imipenem (IPM); cefoxitin (FOX); cefotaxime (CTX); aztreonam (ATM); ceftazidime (CAZ); cefpodoxime (CPD); ceftriaxone (CRO); trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT); chloramphenicol (CHL); amoxicillin-CA (AMC); and ampicillin (AMP); (R–resistant; I–intermediate; and S–sensitive).
Furthermore, synergy-based examination of phenotypically and genotypically confirmed Aeromonas isolates for the production of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) and AmpC β-lactamase (ACBL) was performed. The results reveal that in total, 10.3% isolates (n = 10) were extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producers, comprising largely A. veronii (7.21%, n = 7), with A. hydrophila (5.15%), A. caviae (2.06%), A. dhakensis (1.03%), and others also included in the group. On the other hand, 34.02% isolates (n = 33) were ampC β-lactamase producers, dominated by A. veronii (16.5%, n = 16), followed by A. hydrophila (5.15%, n = 5) and A. caviae (4.12%, n = 4). Additionally, one A. dhakensis isolate was ESBL-positive, while no A. jandaei or A. sobria showed ACBL production.
The overall MAR index ranged from 0.07 to 0.73, with 29.9% of the isolates exhibiting a MAR index > 0.2 (Figure 5). Approximately 32.9%, 37.1%, 16.5%, 6.2%, and 3.1% of the isolates were resistant to 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 out of the 15 tested antimicrobial agents, respectively, while 1.03% of the isolates were each resistant to 6, 7, 8, and 11 antimicrobial agents having a high MAR index (0.4–0.7). The majority of the isolates were resistant to either one (33%), i.e., ampicillin or two antimicrobial agents (37.1%), i.e., ampicillin and nalidixic acid. Nearly 16.5% of the isolates in this study were on the verge of becoming high-risk sourced isolates (MAR index = 0.2). On the other hand, the highest MAR index of 0.73 was observed for an A. veronii isolate (resistant to 11 antimicrobial agents).
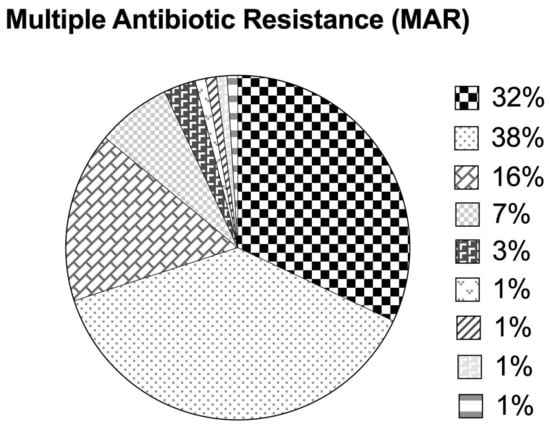
Figure 5.
Multiple antibiotic resistance indices based on antimicrobial susceptibility patterns among Aeromonas species isolates.
3. Discussion
The genus Aeromonas consists of Gram-negative rods that are ubiquitous in all types of aqueous environments. Consequently, several species of this genus, viz., A. hydrophila, A. salmonicida, A. veronii, A. jandaei, A. caviae, and A. bestiarum have been described as important fish pathogens [28]. These factors therefore constitute an important negative input as disease-causing limiting factors in sustainable fish farming worldwide. In view of the aquatic and public health importance of motile aeromonads, this study surveyed the prevalence of Aeromonas spp. in natural freshwater aquaculture village ponds in the Hisar district (Haryana, India).
Motile Aeromonas spp. were isolated from all 66 village aquaculture pond water samples. The genus Aeromonas is among the dominant bacteria inhabiting pond ecosystems and is a good indicator for assessing water quality [29]. A study in Egypt reported Aeromonas isolates in 12.5% of water samples [21]. Similarly, in Trinidad and Tobago, Aeromonas spp. were isolated from 60% of pond water samples [30]. The genus Aeromonas can be used almost synonymously with aquatic environments [3]. However, an exceptionally high rate of isolation of Aeromonas spp. from sampled pond water in our study also indicates that either contaminated water is sourced into ponds or that ponds become contaminated locally. The incidence of Aeromonas in wastewater has been reported to be high; moreover, the concentration of Aeromonas may be associated with terrestrial water effluents [31]. A variety of biomolecules, including proteins and lipids originating from the decomposition of dead flora, fauna, detritus, connective tissues, animal faeces and urine, etc., are present in earthen freshwater ponds [17]. In the current study, all the ponds had a freshwater canal system as a water source apart from seasonal rainwater. However, ponds also received additional drainage water from nearby residential sources, but no agricultural or other runoff was reported. The surveyed ponds were also commonly used for livestock and anthropogenic activities. This may be the reason for the detection of Aeromonas spp. in all the ponds, since aeromonads are carried in the fecal matter of domestic animals [32]. All the surveyed ponds also served as wallowing sites for water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis), which are important milch animals in this region, providing an easy gateway to constant exposure and interactions for the transmission of microbial contaminants and diseases, including those between aeromonads and humans. This finding is consistent with the strong associations of this genus with human infections [3]. They also reported that >85% of human Aeromonas infections are attributed to A. hydrophila, A. caviae, and A. veronii bv. sobria only. Researchers identified Aeromonas veronii as an established human pathogen [29]. This study, for the first time, reports the occurrence and identification of aeromonads in natural village aquaculture ponds in the sampled region of Haryana (India).
The quantitative data on the Aeromonas spp. inhabiting aquaculture ponds covered in this study varied from 1.6 × 102 CFU/mL to 1.2 × 108 CFU/mL. This level of Aeromonas corroborates (2.5 × 106 CFU/mL) with the previous data reported by Skwor and coworkers [29] from water samples of Lake Erie, USA, but is higher (101–103 CFU/mL) than the values noted by other authors [33] from earthen culture ponds of tilapia in the Philippines and the number of Aeromonas (2.1–2.6 × 106 CFU/mL) in the river water of Lotcha (West Bengal, India) [34]. A significant correlation has been reported between water temperature and total culturable Aeromonas spp. during the dry period at temperatures >25 °C [35]. Hisar district is located in an arid zone with a hot and dry climate. During most of the year (May to September), the average minimum diurnal temperature is >25 °C. In our study, which was performed during the months of June to Sept., the average water temperature was 32.3 °C (Table 1), which indicates a favorable environment for Aeromonas spp. growth and survival.
Most of the water physicochemical properties of all the ponds examined during the present study were within the range suitable for freshwater fish culture [23,24,25]. Furthermore, with these data, it can be inferred that a highest electrical conductivity observed for one sample (>2000 µS/cm) is still within the acceptable range (30–5000 µS/cm) [25]. However, monitoring the Aeromonas spp. load in such culture ponds is necessary, as are physicochemical parameters, which are integral components of pond management strategies for determining the quality of fish produced in ponds [33]. Sadique and workers reported that in addition to water temperature, no other physicochemical parameters (pH, DO, salinity, or TDS) were found to have any significant influence on the quantity of Aeromonas in water bodies [35].
We identified Aeromonas spp. isolates on the basis of gyrB sequence homology analysis in the NCBI database using the nBLAST tool. Consistent with previous findings, biochemical identification of aeromonads has limitations [1], as in the present study, a few phenotypically presumptively identified aeromonads were later identified as Pseudomonas spp. and Stenotrophomonas spp. through genetic gyrB characterization. The dominant species identified in this study included A. veronii, A. hydrophila, and A. caviae. This is similar to the findings of a study of freshwater lakes in Malaysia in which the dominant isolate was A. veronii, but they found A. jandaei to be the second most dominant species; however, rpoD sequencing was used for identification [36]. Among the Aeromonas spp. isolated from clinical cases, 95.4% were identified as containing only four species: Aeromonas caviae (37.26%), Aeromonas dhakensis (23.49%), Aeromonas veronii (21.54%), and Aeromonas hydrophila (13.07%) [37]. We also isolated one species of A. dhakensis from pond water, which was originally isolated from the stool of children with diarrhea and is considered more virulent than A. veronii, A. caviae, and A. hydrophila [38]. The A. veronii species is divided into two biovars, bv. sobria and bv. veronii, and the latter is considered more pathogenic [3]; however, in this study, we did not distinguish between A. veronii biovars.
The discrepancies in phenotypic and genotypic identification schemes at the species level complicate the taxonomy of the genus Aeromonas. Housekeeping genes such as gyrB and rpoD, which encode proteins related to DNA processing, are discriminatory phylogenetic markers, in contrast to the poor taxonomic resolution mediated by 16S rRNA in Aeromonas spp. [39]. Our study has the limitation of using only gyrB sequencing as a genetic marker for species identification; however, gyrB is the most frequent housekeeping gene used in the identification of motile aeromonads [39]. The gyrB gene has enough variable nucleotides and conserved positions and unique genetic codon usage, making it useful for species identification in Aeromonas spp. [40]. Furthermore, recent work suggested that even whole-genome-based multilocus phylogenetic analysis (MLPA) using six housekeeping genes may not be robust enough to identify certain strains of Aeromonas spp. Moreover, genomic approaches such as average nucleotide identity (ANI), in silico DNA—DNA hybridization (isDDH), and core genome phylogeny are essential for the correct identification of ambiguous Aeromonas strains [41].
The A. veronii strains detected in village aquaculture pond waters formed varying phylogroups on the basis of the gyrB gene. This indicates that strains have discernible variations and complex evolutionary histories. Tekedar and coworkers [42] reported a core genome phylogenetic tree for the 53 A. veronii genomes, which was characterized by the formation of two major clades further divided into multiple branches. The phylogenetic analysis in our study indicates the diversity of A. veronii isolates in village pond waters, which may belong to different ecological niches.
Aeromonas spp. strains are versatile opportunistic pathogens, in part complemented by multiple virulence-related factors [3]. In our study, various combinations of virulence factors within different strains of the same species were observed. On average, enolase (eno, 97.9%) was the most frequently detected virulence gene in the Aeromonas species isolated in our study, which is consistent with its almost complete prevalence reported previously [43] and high distribution (70%), as shown in another study [36]. In addition to its role in cell metabolism, enolase is involved in microbial diseases and autoimmunity [44], and promotes pathogen interactions, bacterial colonization, and pathogenesis [44,45]. In addition, the frequency of the cytotoxic enterotoxin gene encoding A. sobria hemolysin (act, 88.7%) was also high, and our findings corroborate those of others (ranging from 54 to 97%) [36,46,47]. Martino and coworkers [43] reported that the act and asa1 genes were present in all of their Aeromonas strains except A. media-A. caviae, similar to the high positivity exhibited by the Aeromonas isolates in our study. Cytotoxic enterotoxin (act) is a crucial virulence factor of this bacterium due to its association with hemolytic, cytotoxic, and enterotoxic nature [48]. Our estimates of gene ascV-positivity (51.6%) agree with the frequency (53.8%) determined by Rather and coworkers [47], whereas they contradict those of Khor and coworkers [36], who reported the complete absence of the ascV gene in their Aeromonas isolates. These findings demonstrate the pathogenic potential and one health importance of aeromonads prevalent in pond waters of Haryana (India), however, given the high genetic diversity of genus Aeromonas spp., and diversity within Aeromonas veronii isolates, as evidenced by phylogeny in our study, the approach of measuring frequency of the virulence gene by PCR may not be specific. A genomic approach for ascertaining virulence genes has been proposed (25). Although the role of Aeromonas spp. as a diahhoreal pathogen is uncertain, certain strains of Aeromonas may be implicated [37].
The heat-stable cytotonic enterotoxin gene ast was not detected in any of the 97 isolates, which is consistent with the absence of this gene in other studies [13], while some studies reported the presence of this gene, although the frequency was low (1–6%) [36,46,47].
Being waterborne, Aeromonas strains are potential reservoirs of antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), as they can easily acquire and exchange certain ARGs [49]. To effectively monitor AMR in aquatic environments, numerous authors employed Aeromonas as an indicator organism [50]. A portion of the antimicrobial supplied (feed or water) prophylactically or therapeutically is transported through unmetabolized feces without complete breakdown [14]. These substances remain and accumulate in the environment of fish farming in high enough quantities to exert selective pressure on aquatic bacteria and act as “genetic fuel rods” or “hotspots” for the development of AMR in aquaculture systems.
All the Aeromonas isolates showed complete antimicrobial resistance (100%) to ampicillin (a β-lactam antibiotic). Various studies also reported similar results [16,46,51]. This is evident because aeromonads naturally produce chromosomal β-lactamases [52], indicating an abundance of the β-lactamase gene in the gene pool of microbes of the studied source [16]. Quinolones are the first-line medications advised against aeromonad infections, and the high level of quinolone resistance of Aeromonas spp. to these therapies found in this study is concerning. Moreover, 40.2% of the isolates were resistant to synthetic quinolone nalidixic acid (NA), which was mainly detected in A. hydrophila and A. caviae, followed by A. veronii and others. This finding is in line with earlier reports of plasmid- and chromosomal-mediated quinolone resistance in Aeromonas spp. [53]. The main elements causing resistance to quinolones (nalidixic acid) and flouroquinolones (norfloxacin) are related to chromosomal mutations in the drug target genes and plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes (PMQR) [54]. Aeromonas spp. or Vibrio spp. have been reported to be common environmental species detected to carry PMQR genes.
Resistance to cefoxitin, a second-generation cephalosporin, was found in 83.3% A. hydrophila and 57.1% A. caviae isolates followed by 27.1% A. veronii isolates and others. Resistance in Aeromonas spp. isolates was also observed against third-generation cephalosporins, with the most isolates resistant to cefotaxime, followed by ceftazidime, cefpodoxime, aztreonam, and ceftriaxone. Our findings corroborate those of Silva and coworkers [55] for the high resistance observed against cefoxitin (32%) attributed to carriage of the FOX gene (a member of the ampC gene family) [56]. A total of 10.3% of the isolates in our study produced the ESBL enzyme, which is lower than that reported in a study in Eastern India, in which 55% of Aeromonas spp. isolates were ESBL-positive; however, these isolates originated from bivalves sampled from sewage-fed wetlands [57]. However, this trend is a concern since the first report of plasmid-mediated ESBL resistance was from Aeromonas spp. [58], until a recent report, in which ESBL-resistant A. hydrophila strains were isolated from deep-stage infections in humans, which also exhibited carbapenem resistance [59]. In our study, as many as 6.2% of the isolates were carbapenem-resistant. The high ACBL resistance (32%) in aeromonads detected by the phenotypic method in our study matches the 34.02% rate of cefoxitin resistance, which may be due to the presence of mobile FOX AmpC beta-lactamases common in aeromonads [56]. Interestingly, although nalidixic acid resistance was present in 40.2% of the isolates, all of the isolates were fluoroquinolone-sensitive (100%), which is consistent with earlier findings [60]. In China, an A. punctata strain, resistant to nalidixic acid and susceptible to flouroquinolone, was isolated from wastewater [61]. Additionally, another study by Silva and coworkers [55] reported low resistance levels and greater efficiency against Aeromonas species isolates for amikacin (2.1%), which is within the range obtained in this study.
The isolates resistant to at least one antimicrobial agent from three or more antimicrobial drug classes used in the study were considered multidrug-resistant (MDR) isolates [17]. Multidrug resistance (MDR) was detected among the isolates, with 29.9% of the Aeromonas isolates being MDR. Of those, 7.2% of the isolates showed resistance to 5 or >5 tested antimicrobials, including an A. veronii isolate that was resistant to 11 antimicrobials and sensitive only to tetracycline, amoxiclav, amikacin, and norfloxacin. Isolates with a MAR index of 0.2 or greater than 0.2 are considered potential high-risk sources for the spread of drug-resistant strains [51]. A total of 29.9% of the isolates in our study had a MAR index greater than 0.2, indicating that they came from a source of contamination with a high risk of contamination where antimicrobials are often employed, all of which displayed MDR. The current study’s MAR index range (0.07 to 0.73) is also more comprehensive than that of earlier studies. The MAR index in aquaculture-borne aeromonads has been reported by [51] to range from 0.12 to 0.88.
Our findings support earlier research indicating that MDR Aeromonas strains are spreading in the environment [13,51]. This also has important health implications since the pond water used for aquaculture is sourced through canal waters, which might carry aeromonads through various sources and transmission routes, e.g., fertilizers of fecal origin, irrigation and surface water, and water for aquaculture [62].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling of Ponds and Isolation of Aeromonas spp.
4.1.1. Sources of Samples and Sample Collection
The village ponds, which are also used as reservoirs for pisciculture by village farmers, were used as sources of water samples. One hundred pond water samples were collected from 66 villages distributed in 4 blocks under the jurisdiction of the Hisar district (Haryana, India). Each sample was collected from a single pond. All the samplings were carried out in June to September 2020 during the early morning hours. Sub-superficial water samples were collected in undisturbed waters using 500 mL sterile bottles at a distance of 2–3 m from the pond bank and at a depth of 25–30 cm below the surface water level. After sampling, the surface of the bottles was immediately sterilized using a 70% alcohol swab. The collected samples were transported immediately to the laboratory on ice and stored at refrigeration (4 °C) until use. The samples were processed for bacterial isolation on the same day or within 24 h of sample collection.
4.1.2. Physicochemical Properties of Water
The pond water temperature was determined at the pond water site itself. For the determination of salinity, pH, DO, TDS, and EC, water samples were taken to the laboratory on ice within 1 h after collection and analysis. Salinity was measured with a handheld 0–32% salinity Brix refractometer with automatic temperature compensation (ATC). Total dissolved solids and pH were obtained using a TDS meter (Wellon digital TDS meter, Gujarat, India) with the electrode rinsed in distilled water before measurements to avoid any error. Conductivity was measured using a Labtronics Microprocessor COND-TDS-SAL Meter LT-51 (Haryana, India) (Siemens/centimeter, µS/cm). The dissolved oxygen content was determined using an Aquasol Dissolved oxygen test kit (North Tonawanda, NY, USA) (Code AEDO8).
4.1.3. Bacteriological Examination of Samples and Isolation of Aeromonas Species
For the selective isolation and enumeration of Aeromonas species, starch ampicillin agar (SAA) containing ampicillin, which is based on the color change due to acid production during fermentation caused by the growth of Aeromonas species, was used as the selective principle [26]. The pond water samples were subjected to serial decimal dilutions up to the fifth dilution (10−5) in chilled sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (pH = 7.2) in duplicate. The Petri plates were incubated at 28 °C for 18–24 h. Yellow to honey-colored colonies, which are typically 3–5 mm in diameter and presumed to be Aeromonas spp., were used for enumeration. These colonies showed an amylase-positive reaction (surrounded by a clear zone) upon flooding with 5 mL of Lugol iodine solution [26]. Morphologically representative isolates were selected and isolated as putative members of the genus Aeromonas and cryopreserved in nutrient broth (NB) supplemented with 80% glycerol (v/v) at −80 °C until further analysis.
Each of the isolates was given an identification tag by prefixing “Aq” followed by a digit, which represented the sample number. If more than 1 isolate was selected from any given sample, e.g., any morphologically variant colony, then it was represented by an additional alphabet in the capitals, such as A, B, etc., from the same sample, i.e., Aq1, Aq1A, Aq2, Aq2A, etc.
4.2. Phenotypic and Molecular Identification
4.2.1. Biochemical Testing
Each of the typical presumptive aeromonad colony types on the SAA plates was subjected to Gram staining and examined microscopically for shape and Gram reaction (Nikon Eclipse Microscope, Shinagawa, Japan). All Gram-negative rod-shaped isolates were sub-cultured on nutrient agar (NA) and subjected to cytochrome oxidase and catalase tests. Of the total representative Gram-negative, oxidase-, and catalase-positive colonies, 100 isolates were randomly selected for phenotypic confirmation, ensuring that from each pond water sample, one isolate was selected. Furthermore, the motility, utilization of citrate, malonate, glucose, lactose, and sucrose, hydrogen sulphide production, gas production from D-glucose, hemolysis on sheep blood agar (SBA), indole production, urease production, and oxidative–fermentative properties of the selected 100 putative Aeromonas isolates were tested via these secondary phenotypic tests. The strains were biochemically identified according to the biochemical scheme given previously [1].
4.2.2. Molecular Identification by gyrB Gene Sequencing
The genomic DNA from biochemically identified presumptive Aeromonas species (n = 100) was isolated using a Quick-DNA Fungal/Bacterial Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A PCR-amplified product (approximately 1100 bp fragment) of the gyrB gene was obtained using the following primers-gyrB_F: GGGGTCTACTGCTTCACCAA and gyrB_R: CTTGTCCGGGTTGTACTCGT [9]. The amplification reaction consisted of 12.5 µL of 2× DreamTaq Green PCR Master Mix (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 0.2 µL of 0.4 µM of each primer, and 2 µL of genomic DNA (~250 ng/µL) and was adjusted with nuclease-free water (Thermo Scientific) in a final reaction volume of 25 µL. The reaction was carried out in a PeqSTAR 2× Universal Gradient thermal cycler, Erlangen, Germany. The selection of primers, PCR conditions, and sequencing were performed as described in a previous report [9]. Amplified products were purified using a DNA Clean and ConcentratorTM-5 Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) before Sanger sequencing. The sequencing results were compared in a BLAST homology search with Aeromonas gene sequences submitted in the GenBank database.
4.2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of A. veronii Isolates
For evolutionary analysis, corresponding gyrB sequences of geographically distinct A. veronii strains (n = 19) were retrieved from NCBI. Evolutionary analyses were conducted using MEGA11 (https://www.megasoftware.net, accessed on 20 October 2023). The evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) was shown next to the branches. The tree was drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. All ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair (pairwise deletion option). These distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method and are expressed in terms of the number of base substitutions per site. The ME tree was constructed using the close neighbor interchange (CNI) algorithm at a search level of 1. The neighbor-joining algorithm was used to generate the initial tree. Codon positions included were 1st + 2nd + 3rd + noncoding, and all ambiguous positions were removed (pairwise deletion). The analysis involved 78 nucleotide sequences, with a total of 1190 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted using MEGA11 (v. 11.0.6) software. Likewise, evolutionary relationships of isolated species other than A. veronii were also drawn.
4.3. Genetic Traits of Potential Virulence Factors
The presence of 7 putative determinant genes of virulence, namely ahh1, asa1, act, ast, ascV, eno, and aexT, was screened in the Aeromonas spp. isolates through direct PCR amplification as reported previously by Martino and coworkers for determining Aeromonas spp. diversity from aquatic origins [43]. Details of their primers, expected product sizes, and PCR conditions are summarized in Supplementary Table S1.
The binary data obtained from the virulence gene detection patterns were used for calculating the pairwise genetic distance between isolates with the help of Nei’s standard genetic distance method [63]. Afterwards, agglomerative hierarchical clustering of the isolates was performed using Ward’s approach [64]. The number of clusters is chosen based on the Bayesian information criterion (BIC), i.e., 5. The clustering of isolates into different clusters is presented as a dendrogram (Supplementary Figure S1). Clustering analysis was performed using R and RStudio software (R version 4.3.10) with the help of the packages adegenet (exploratory analysis of genetic and genomic data), NAM, circle, and dendextend [65,66,67].
4.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
Antimicrobial susceptibility assays were performed by the disc diffusion method according to a standard procedure based on the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) document M45-Ed3 [68] using E. coli ATCC25922 as a reference strain. A panel of 15 antimicrobials belonging to the following 8 classes were used for the assay: class {Antimicrobial name, (abbreviation and disc content in µg)}: penicillin and beta-lactams {ampicillin (AMP/10); amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (AMC, 20/10)}; phenicols {chloramphenicol (CHL/30)}; folate pathway inhibitors {trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT, 1.25/23.75)}; cephems {ceftriaxone (CRO/30); cefpodoxime (CPD/10); ceftazidime (CAZ/30); aztreonam (ATM/30); cefotaxime (CTX/30); cefoxitin (FOX/30)}; carbapenem {imipenem (IPM/10)}; aminoglycosides {amikacin (AMK/30)}; flouroquinolone {norfloxacin (NOR/5); and quinolone {nalidixic acid (NAL/30)} and tetracyclines {tetracycline (TET/30)}. Colonies of isolates were incubated in nutrient broth (HiMedia). After achieving 0.5 MacFarland turbidity (Biosan Densitometer, Riga, Latvia), the bacterial suspension was inoculated on 100 mm diameter pre-dried Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA, HiMedia) plates using a sterile cotton swab, and immediately, the discs were transferred onto the plates. The inoculated plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. According to CLSI zone diameter interpretation criteria (CLSI M45-Ed3), zones of inhibition were recorded, and isolates were classified as sensitive (S), immediate (I), or resistant (R). In addition, the multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index was computed by dividing the number of antimicrobials to which the isolate was resistant by the total number of antimicrobials examined [13].
Furthermore, all the aeromonads that were resistant to CRO, CPD, ATM, CAZ, CTX, and FOX were screened for extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) (n = 10) and AmpC β-lactamase production (ACBL) (n = 33) using double disc synergy methods [69]. The double discs contained ceftazidime–clavulanic acid-combined discs (CAC-30/10 µg), cefotaxime–clavulanic acid-combined discs (CEC-30/10 µg), and cefoxitin–cloxacillin-combined discs (CXX-30/200 μg) for the ESBL and ACBL assays, respectively. Following incubation for 18–24 h at 37 °C, an increase of >5 mm and >4 mm in the zone around the combined disc compared to the corresponding disc alone was considered positive for ESBL and ACBL production, respectively.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed a potential risk of multidrug-resistant pathogenic aeromonad populations in the surface water of aquaculture ponds in the Hisar region of Haryana (India). Aeromonads were isolated from all the pond water samples. The dominant species with enterotoxigenic potential found in this study included A. veronii, A. hydrophila, and A. caviae. The number of aeromonads in pond water varied between 102 and 108 cfu/mL. Molecular identification of Aeromonas spp. by gyrB sequence revealed that 97% of the isolates were aeromonads, with A. veronii being the most dominant species, followed by A. caviae, A. hydrophila, A. jandaei, A. sobria, and A. dhakensis. The constructed phylogeny revealed the formation of major and minor clades, indicating genotypic diversity among the A. veronii isolates. Carriage of multiple-virulence genes was common among the Aeromonas isolates, and cluster analysis by dendrogram revealed multiple distinct clusters depicting virulence-mediated heterogeneity in the species. High antimicrobial resistance was detected against ampicillin (100%), nalidixic acid (40.2%), and cefoxitin (33%). Its resistance to third-generation cephalosporins indicates that ESBL resistance (10.3%) and ACBL resistance (34.02%) are emerging problems in aeromonads. The overall MAR of 0.07 to 0.73 and the prevalence of Aeromonas spp. with ESBL, ACBL, and carbapenem resistance are alarming. This study highlights that aquaculture pond waters in this region are infested with potentially pathogenic MDR strains of motile aeromonads, which has implications for one health, as aquaculture is an increasingly important source of aquatic dietary protein in form of fish and shrimp culture supplies. Furthermore, the sustainable growth of this sector is dependent on the health of the aquatic pond environment system, which is also used for animal husbandry, farm irrigation, and human use. This study underlines the importance of the surveillance of freshwater bodies to assess the level of pathogenic and drug resistance genotypes of Aeromonas spp. and importance of infection prevention and control (IPC) measures to control MDR motile aeromonads in water bodies used for aquaculture and other economic activity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics14030294/s1, Figure S1: Dendrogram of clustering groups based on virulence gene screening among Aeromonas isolates. (Note: AV—Aeromonas veronii; AH- Aeromonas hydrophila; AJ—Aeromonas jandaei; AC—Aeromonas caviae; AP—Aeromonas punctata; AS—Aeromonas sobria; AV bv S—Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria; AH s D—Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. dhakensis; A. sp—Aeromonas spp.); Figure S2: Unrooted neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees of different Aeromonas species based on their gyrB gene sequences (strains from this study are shown with red blocks and remaining are the strains from GenBank).; Table S1: Details of the primers used for screening virulence genes among Aeromonas isolates*; Table S2: Biochemical characteristics of different Aeromonas species isolated from the fish culture ponds; Table S3: Aeromonas isolates identification up to species level by gyrB sequences and GenBank Accession numbers; Table S4: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) assay for the different Aeromonas species isolates from the fish culture ponds.
Author Contributions
Field and laboratory work, A.N. guidance R.K.V. ’Conceptualization, methodology, project administration, supervision, draft reviewing, re-writing and editing, resources, funding acquisition, R.K.V.; Data curation and original draft preparation, A.N. and R.K.V.; Investigation, data analysis, reviewing and editing, T.A.; Field work extension, guidance, funding acquisition; reviewing and editing, R.V. and R.G.; Field work extension, guidance, resources, funding acquisition, reviewing and editing of manuscript, R.V. and R.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) (India) under a Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) to the first author under sanction letter no. 09/303(0297)/2019-EMR-I. The authors are grateful for support from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (Project ID: IXX11884), New Delhi (India). Funder(s) do not have any role in the conceptualization, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Nucleotide sequence data of the Aeromonas spp. isolates are accessioned and available in NCBI. Details are available in Table S3.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR); Director, National Research Centre on Equines, Hisar; and Dean, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, Haryana (India).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AMR | antimicrobial resistance |
| ESBL | extended-spectrum beta-lactamase |
| ACBL | AmpC beta lactamase |
| MDR | multidrug-resistant |
| SAA | starch ampicillin agar |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| ME | minimum evolution |
| CNI | close neighbor interchange |
| NCVTC | National Centre for Veterinary Type Cultures, Hisar, Haryana, India |
References
- Abbott, S.L.; Cheung, W.K.; Janda, J.M. The genus Aeromonas: Biochemical characteristics, atypical reactions, and phenotypic identification schemes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, P.J. Aeromonas species in disease of animals. In The Genus Aeromonas; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.L.; Shaw, J.G. Aeromonas spp. clinical microbiology and disease. J. Infect. 2011, 62, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parte, A.C.; Carbasse, J.S.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colwell, R.; MacDonell, M.; De Ley, J. Proposal to recognize the family Aeromonadaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1986, 36, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.; Abdelsalam, M.; Marouf, S.; Setta, A. Comparative analysis of virulence genes, antibiotic resistance and gyrB-based phylogeny of motile Aeromonas species isolates from Nile tilapia and domestic fowl. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, L.; Yáñez, M.A.; Chacon, M.R.; Aguilera-Arreola, M.G.; Catalán, V.; Figueras, M.J.; Martínez-Murcia, A.J. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas based on two housekeeping genes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, M.A.; Catalán, V.; Apráiz, D.; Figueras, M.J.; Martínez-Murcia, A.J. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Aeromonas based on gyrB gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Noureldin, E.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Fita, N.A. Molecular identification and epizootiology of Aeromonas veronii infection among farmed Oreochromis niloticus in Eastern Province, KSA. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 43, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C. Detection of three virulence genes alt, ahp and aerA in Aeromonas hydrophila and their relationship with actual virulence to zebrafish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhinh, D.T.; Le, D.V.; Van Van, K.; Giang, N.T.H.; Dang, L.T.; Hoai, T.D. Prevalence, virulence gene distribution and alarming the multidrug resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila associated with disease outbreaks in freshwater aquaculture. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manage, P.M. Heavy use of antibiotics in aquaculture; emerging human and animal health problems—A review. Sri Lanka J. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Harbottle, H. Antimicrobial drug resistance in fish pathogens. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Livestock and Companion Animals; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 501–520. [Google Scholar]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Mudryk, Z.J.; Perliński, P. Abundance and antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas isolated from the water of three carp ponds. Vet. Res. Commun. 2020, 44, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Fernandes, C.; Monteiro, S.; Cabecinha, E.; Teixeira, A.; Varandas, S.; Saavedra, M.J. The role of aquatic ecosystems (River Tua, Portugal) as reservoirs of multidrug-resistant Aeromonas spp. Water 2021, 13, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.R.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Quinolone resistant Aeromonas spp. as carriers and potential tracers of acquired antibiotic resistance in hospital and municipal wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, M.L.; Sousa-Santos, C.; Robalo, J.; Oliveira, M. The potential of Aeromonas spp. from wildlife as antimicrobial resistance indicators in aquatic environments. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.J.; Benet-Perelberg, A.; Naor, A.; Smirnov, M.; Ofek, T.; Nasser, A.; Minz, D.; Cytryn, E. Evidence of increased antibiotic resistance in phylogenetically-diverse Aeromonas isolates from semi-intensive fish ponds treated with antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, F.A.; Zahran, E.; El-Gawad, E.A.A.; El-Gohary, A.H.; Abdelhamid, F.M.; El-Mleeh, A.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Elsayed, M.M. Investigation of the prevalence, virulence genes, and antibiogram of motile Aeromonads isolated from Nile tilapia fish farms in Egypt and assessment of their water quality. Animals 2020, 10, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Zhu, Y.J.; Ringø, E.; Yang, D. Prevalence of Aeromonas hydrophila and Pseudomonas fluorescens and factors influencing them in different freshwater fish ponds. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2020, 19, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; p. 614. [Google Scholar]
- Saraswathy, R.; Muralidhar, M.; Sundaray, J.K.; Lalitha, N.; Kumararaja, P. Water Quality Management in Fish Hatchery and Grow-Out Systems. In Advances in Marine and Brackishwater Aquaculture; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, N.; Thomforde, H. Understanding Your Fish Pond Water Analysis Report; University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff: Pine Bluff, AR, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo, S.A.; Maxino, F.; Williams, A.C.; Buchanan, R.L.; Thayer, D.W. Starch-ampicillin agar for the quantitative detection of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 50, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, P.H.M.; Moreno, L.Z.; de Oliveira, C.H.; Gomes, V.T.M.; Silva, A.P.S.; Barbosa, M.R.F.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Balian, S.C.; Moreno, A.M. Main bacterial species causing clinical disease in ornamental freshwater fish in Brazil. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 66, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoai, T.D.; Trang, T.T.; Van Tuyen, N.; Giang, N.T.H.; Van Van, K. Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in channel catfish in Vietnam. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwor, T.; Shinko, J.; Augustyniak, A.; Gee, C.; Andraso, G. Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas veronii predominate among potentially pathogenic ciprofloxacin-and tetracycline-resistant Aeromonas isolates from Lake Erie. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Mutani, A.; Ramsubhag, A.; Adesiyun, A. Prevalence of bacterial pathogens and their anti-microbial resistance in tilapia and their pond water in Trinidad. Zoonoses Public Health 2008, 55, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwor, T.; Stringer, S.; Haggerty, J.; Johnson, J.; Duhr, S.; Johnson, M.; Seckinger, M.; Stemme, M. Prevalence of potentially pathogenic antibiotic-resistant Aeromonas spp. in treated urban wastewater effluents versus recipient riverine populations: A 3-year comparative study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02053-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Stickler, D.; Bryant, T. The incidence of virulence factors in mesophilic Aeromonas species isolated from farm animals and their environment. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 105, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakingking, R., Jr.; Palma, P.; Usero, R. Aeromonas load and species composition in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in earthen ponds in the Philippines. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4736–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Bahadur, M.; Barat, S. Isolation, identification and antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas spp. and Salmonella spp. from the fresh water loach, Lepidocephalichthys guntea and water of Terai River Lotchka, West Bengal, India. Zool. Pol. 2013, 58, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadique, A.; Neogi, S.B.; Bashar, T.; Sultana, M.; Johura, F.-T.; Islam, S.; Hasan, N.A.; Huq, A.; Colwell, R.R.; Alam, M. Dynamics, diversity, and virulence of Aeromonas spp. in homestead pond water in Coastal Bangladesh. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 692166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, W.C.; Puah, S.M.; Tan, J.A.M.A.; Puthucheary, S.; Chua, K.H. Phenotypic and genetic diversity of Aeromonas species isolated from fresh water lakes in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-L.; Lamy, B.; Ko, W.-C. Aeromonas dhakensis, an increasingly recognized human pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Martínez-Murcia, A. Phylogenetic analyses of the genus Aeromonas based on housekeeping gene sequencing and its influence on systematics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, H.; Watanabe, K.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Isono, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Harayama, S. Construction of the gyrB database for the identification and classification of bacteria. Genome Inform. 1998, 9, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- de Melo, B.S.T.; Mendes-Marques, C.L.; Campos, T.D.L.; Almeida, A.M.P.D.; Leal, N.C.; Xavier, D.E. High-resolution genome-wide analysis is essential for the identification of ambiguous Aeromonas strains. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekedar, H.C.; Arick, M.A.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Thrash, A.; Blom, J.; Lawrence, M.L.; Abdelhamed, H. Identification of antimicrobial resistance determinants in Aeromonas veronii strain MS-17-88 recovered from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.E.; Fasolato, L.; Montemurro, F.; Rosteghin, M.; Manfrin, A.; Patarnello, T.; Novelli, E.; Cardazzo, B. Determination of microbial diversity of Aeromonas strains on the basis of multilocus sequence typing, phenotype, and presence of putative virulence genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4986–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, V. Multifunctional α-enolase: Its role in diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2001, 58, 902–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Z. Applications of CRISPR/Cas9 technology in the treatment of lung cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Hamano, K.; Tsutsui, I.; Aue-Umneoy, D.; Ban, M.; Satomi, M. Occurrence, molecular characterization, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas spp. in marine species of shrimps cultured at inland low salinity ponds. Food Microbiol. 2015, 47, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, M.A.; Willayat, M.M.; Wani, S.A.; Hussain, S.A.; Shah, S.A. Enterotoxin gene profile and molecular epidemiology of Aeromonas species from fish and diverse water sources. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, J.; Pillai, L.; Fadl, A.A.; Galindo, C.L.; Erova, T.E.; Chopra, A.K. The type III secretion system and cytotoxic enterotoxin alter the virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 6446–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández–Montañez, Z.; López–Ramírez, M.P.; Delgado–Balbuena, L.; Dendooven, L.; Bello–López, J.M. Mesophilic strains of Aeromonas spp. can acquire the multidrug resistance plasmid pRAS1 in horizontal transfer experiments at low temperatures. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, M.; Tagaki, C.; Fukuda, A.; Okubo, T.; Boonla, C.; Suzuki, S.; Seki, K.; Takada, H.; Tamura, Y. Use of Aeromonas spp. as general indicators of antimicrobial susceptibility among bacteria in aquatic environments in Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanapala, P.M.; Kalupahana, R.S.; Kalupahana, A.W.; Wijesekera, D.; Kottawatta, S.A.; Jayasekera, N.K.; Silva-Fletcher, A.; Jagoda, S.d.S. Characterization and antimicrobial resistance of environmental and clinical Aeromonas species isolated from fresh water ornamental fish and associated farming environment in Sri Lanka. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayler, A.E.; Ayala, J.A.; Niumsup, P.; Westphal, K.; Baker, J.A.; Zhang, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Wiedemann, B.; Bennett, P.M.; Avison, M.B. Induction of β-lactamase production in Aeromonas hydrophila is responsive to β-lactam-mediated changes in peptidoglycan composition. Microbiology 2010, 156, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S.; Granier, S.A.; Larvor, E.; Jouy, E.; Cineux, M.; Wilhelm, A.; Gassilloud, B.; Le Bouquin, S.; Kempf, I.; Chauvin, C. Aeromonas diversity and antimicrobial susceptibility in freshwater—An attempt to set generic epidemiological cut-off values. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosikowska, U.; Stec, J.; Andrzejczuk, S.; Mendrycka, M.; Pietras-Ożga, D.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D. Plasmid-Mediated Fluoroquinolone Resistance Genes in Quinolone-Susceptible Aeromonas spp. Phenotypes Isolated From Recreational Surface Freshwater Reservoir. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 885360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Silva, A.D.S.; Barros, L.S.S.E.; Lima, D.D.V.; Velame, D.S. The Occurrence of Bacteria of the Genus Aeromonas spp. in Oreochromis niloticus (Tilapia) and in the Water of Amateur Sport Fish Ponds and Sensitiveness to Antimicrobials. Food Nutr. Sci. 2019, 10, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Ebmeyer, S.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.J. The mobile FOX AmpC beta-lactamases originated in Aeromonas allosaccharophila. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.; Das, B.K.; Kumari, P.; Dey, S.; Bera, A.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Roy, S. Prevalence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBLs) Producing Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Lamellidens marginalis (Lamark, 1819) of Sewage-Fed Wetland: A Phenotypic and Genotypic Approach. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maravić, A.; Skočibušić, M.; Šamanić, I.; Fredotović, Ž.; Cvjetan, S.; Jutronić, M.; Puizina, J. Aeromonas spp. simultaneously harbouring blaCTX-M-15, blaSHV-12, blaPER-1 and blaFOX-2, in wild-growing Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jia, X.; Jia, P.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Song, G.; Zhang, J.; et al. Emergence and clonal expansion of Aeromonas hydrophila ST1172 that simultaneously produces MOX-13 and OXA-724. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2024, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena-Román, M.; Inglis, T.J.J.; Henderson, B.; Riley, T.V.; Chang, B.J. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Aeromonas strains isolated from clinical and environmental sources to 26 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H. qnrVC-like gene located in a novel complex class 1 integron harboring the ISCR1 element in an Aeromonas punctata strain from an aquatic environment in Shandong Province, China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3471–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ); Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; et al. Role played by the environment in the emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) through the food chain. Efsa J. 2021, 19, e06651. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M. Genetic distance and molecular phylogeny. Popul. Genet. Fish. Manag. 1987, 193, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.H., Jr. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.; Xu, S.; Muir, W.M.; Rainey, K.M. NAM: Association studies in multiple populations. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3862–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, T. dendextend: An R package for visualizing, adjusting and comparing trees of hierarchical clustering. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3718–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. RA Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, J.H. Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria; Approved Guideline; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.J.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lee, M.F.; Lee, C.C.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, N.Y.; Chang, C.M.; Chen, P.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Yan, J.J. Bacteremia due to extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Aeromonas spp. at a medical center in Southern Taiwan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5813–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).