Evaluation of Amlodipine and Imipramine Efficacy to Treat Galleria mellonella Infection by Biofilm-Producing and Antimicrobial-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. S. aureus Virulence and Infective Dose of Bacteria
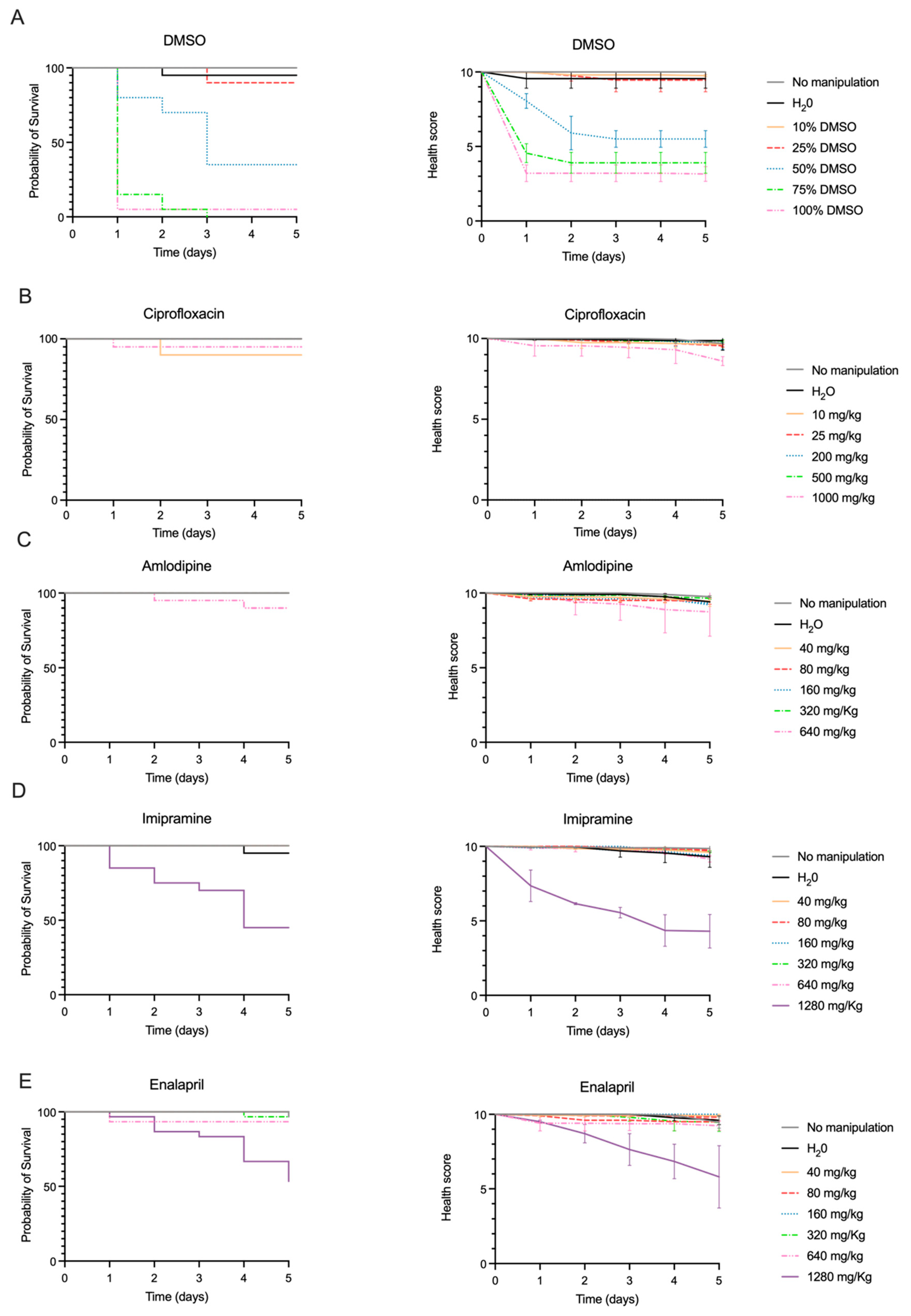
2.2. Drug Toxicity
2.3. Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin to Counteract G. mellonella Infection by S. aureus
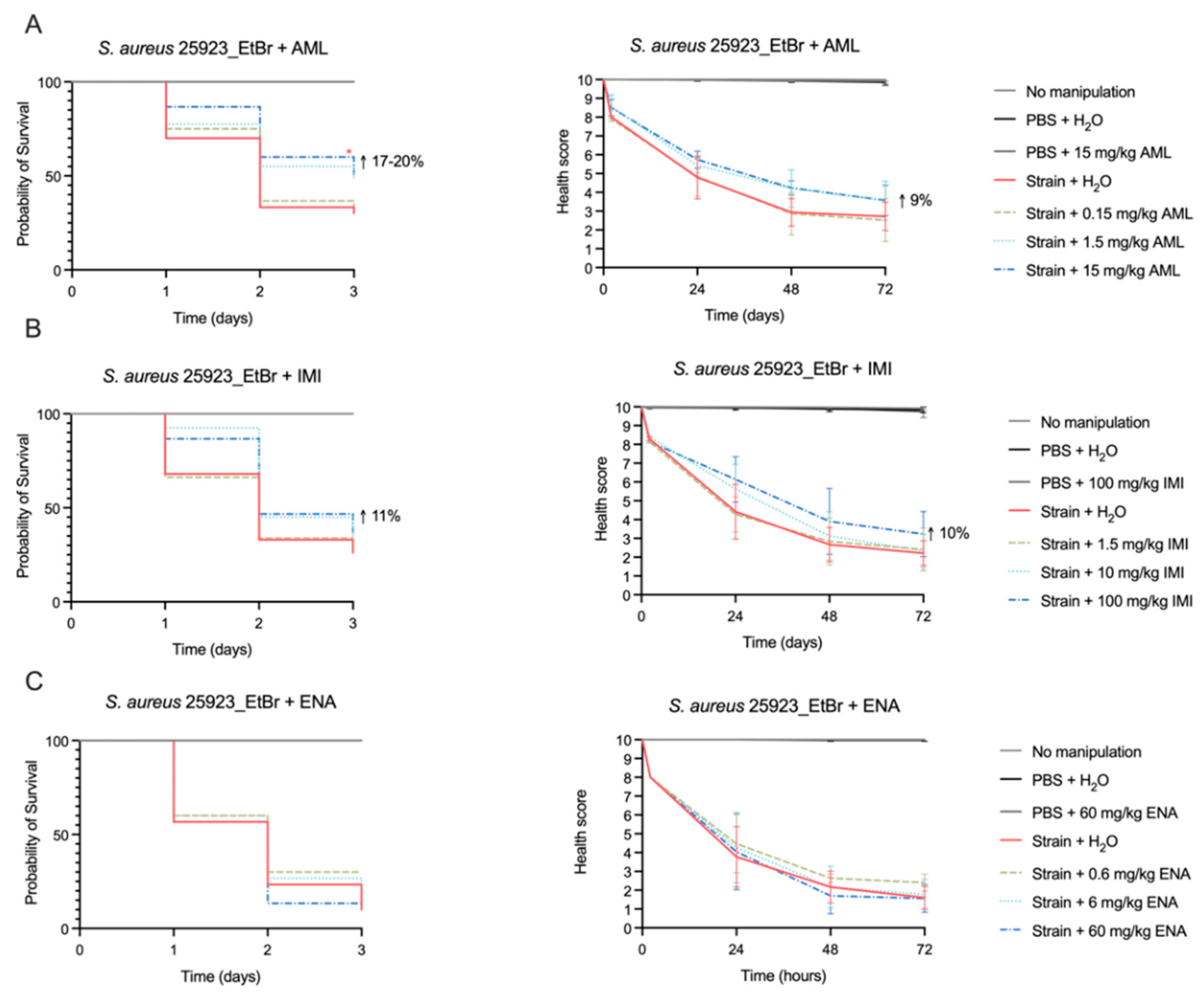
2.4. Efficacy of Amlodipine and Imipramine to Treat G. mellonella Infection by S. aureus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Antimicrobials and Candidate Drugs
4.2. Previous in Silico Drug Repurposing Study
4.3. Galleria mellonella Colony
4.4. Determination of the Infective Dose of Bacteria
4.5. Evaluation of Drug Toxicity in G. mellonella
4.6. Drug Efficacy Assays in G. mellonella
4.7. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | directory of open access journals |
| AML | amlodipine |
| CIP | ciprofloxacin |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ENA | enalapril |
| EtBr | ethidium bromide |
| IMI | imipramine |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
References
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.M.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An overview of basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 400, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L.; Couto, I. Multidrug Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: An Update. Open. Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Tanwar, M.; Singh, T.P.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P. An escape from ESKAPE pathogens: A comprehensive review on current and emerging therapeutics against antibiotic resistance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Rosato, A.E.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Couto, I. Impact of efflux in the development of multidrug resistance phenotypes in Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.; Richmond, G.E.; Piddock, L.J. Multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Abrantes, P.; Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Couto, I. Occurrence and Variability of the Efflux Pump Gene norA across the Staphylococcus Genus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, G.W. Multidrug efflux pumps of Gram-positive bacteria. Drug Resist. Updates 2016, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmidis, C.; Schindler, B.D.; Jacinto, P.L.; Patel, D.; Bains, K.; Seo, S.M.; Kaatz, G.W. Expression of multidrug resistance efflux pump genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2012, 40, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeaux, D.; Ghigo, J.M.; Beloin, C. Biofilm-related infections: Bridging the gap between clinical management and fundamental aspects of recalcitrance toward antibiotics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 510–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alav, I.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. Role of bacterial efflux pumps in biofilm formation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2003–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z. Efflux pumps as potential targets for biofilm inhibition. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1315238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.C.; Saavedra, M.J.; Simões, L.C.; Simões, M. Combinatorial approaches with selected phytochemicals to increase antibiotic efficacy against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.; Andrade, M.; Bento, M.; Viveiros, M.; Rodrigues, L.; Couto, I.; Costa, S.S. New candidate drugs for repurposing as efflux inhibitors and antibiofilm agents against antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Infections, Perth, Australia, 19–21 August 2024; Available online: https://icmsmeetings.eventsair.com/isssi-2024/speakers (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Knox, C.; Wilson, M.; Klinger, C.M.; Franklin, M.; Oler, E.; Wilson, A.; Pon, A.; Cox, J.; Chin, N.E.L.; Strawbridge, S.A.; et al. DrugBank 6.0: The DrugBank Knowledgebase for 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1265–D1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, G.; Rouillon, A.; Cattoir, V.; Donnio, P.Y. Galleria mellonella as a Suitable Model of Bacterial Infection: Past, Present and Future. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 782733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, G.; Dixon, A.; Kavanagh, K. Utilization of Galleria mellonella larvae to characterize the development of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Microbiology 2019, 165, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.R.; Stoneham, C.A.; Schuelein, R.; Newton, H.; Oates, C.V.; Hartland, E.L.; Schroeder, G.N.; Frankel, G. The Dot/Icm effector SdhA is necessary for virulence of Legionella pneumophila in Galleria mellonella and A/J mice. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2598–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Andérico, L.; Admella, J.; Fernandes, R.; Torrents, E. Monitoring Gene Expression during a Galleria mellonella Bacterial Infection. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, L.; Duxbury, S.; Pawlowska, B.; Ho, H.L.; Haynes, K.; Bates, S. Galleria mellonella as a host model to study Candida glabrata virulence and antifungal efficacy. Virulence 2017, 8, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatek, M.; Sheehan, G.; Kavanagh, K. Galleria mellonella: The Versatile Host for Drug Discovery, In Vivo Toxicity Testing and Characterising Host-Pathogen Interactions. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, M.; McCormack, A.; Parcell, B.J.; Coote, P.J. Combination Therapy with Ciprofloxacin and Pentamidine against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Assessment of In Vitro and In Vivo Efficacy and the Role of Resistance-Nodulation-Division (RND) Efflux Pumps. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, I.; Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Martins, M.; Amaral, L. Efflux-mediated response of Staphylococcus aureus exposed to ethidium bromide. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.; Oliveira, K.; Morais, C.; Abrantes, P.; Pomba, C.; Rosato, A.E.; Couto, I.; Costa, S.S. Virulence Potential of Bio-film-Producing Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus coagulans Causing Skin Infections in Companion Animals. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrine, M.; Andrade, M.; Neves, J.; Mandomando, I.; Couto, I.; Costa, S.S. Exploring the virulence potential of Staphylococcus aureus CC121 and CC152 lineages related to paediatric community-acquired bacteraemia in Manhiça, Mozambique. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignasiak, K.; Maxwell, A. Galleria mellonella (greater wax moth) larvae as a model for antibiotic susceptibility testing and acute toxicity trials. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.; Piccioni, M.; Felicetti, T.; De Marco, S.; Manfroni, G.; Pagiotti, R.; Nocchetti, M.; Cecchetti, V.; Pietrella, D. Investigation on the effect of known potent S. aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors on the staphylococcal biofilm formation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 44280–44293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Vega, A.; Bernstein, L.R.; Mandujano-Tinoco, E.A.; García-Contreras, S.J.; García-Contreras, R. Drug repurposing as an alternative for the treatment of recalcitrant bacterial infections. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suay-García, B.; Alemán-López, P.A.; Bueso-Bordils, J.I.; Falcó, A.; Antón-Fos, G.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. New solvent options for in vivo assays in the Galleria mellonella larvae model. Virulence 2019, 10, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, M.L. Ciprofloxacin derivatives and their antibacterial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 1999, 2, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklerov, J.H.; Levine, B.; Ingwersen, K.M.; Aronica-Pollack, P.A.; Fowler, D. Two cases of fatal amlodipine overdose. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCS Inchem. Available online: https://www.inchem.org/documents/pims/pharm/imiprami.htm#SectionTitle:4.2%20Therapeutic%20dosage (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Barbosa, A.D.; Sá, L.G.; Neto, J.B.; Rodrigues, D.S.; Cabral, V.P.; Moreira, L.E.; Aguiar, I.G.; Santos, H.S.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Marinho, E.S.; et al. Activity of amlodipine against Staphylococcus aureus: Association with oxacillin and mechanism of action. Future Microbiol. 2023, 18, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, A.A.; Ahmed, W.; Bhat, R.S.; Bradley, E.K.; Ekins, S.; Nagaraja, V. Targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis topoisomerase I by small-molecule inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Khader, R.; Felix, L.O.; Frate, M.; Mylonakis, E.; Meschwitz, S.; Fuchs, B.B. A Substituted Diphenyl Amide Based Novel Scaffold Inhibits Staphylococcus aureus Virulence in a Galleria mellonella Infection Model. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 723133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussmann, M.; Obermueller, M.; Karer, M.; Kriz, R.; Chen, R.Y.; Hohl, L.; Schneider, L.; Burgmann, H.; Traby, L.; Vossen, M.G. Synergistic Effect of Cefazolin Plus Fosfomycin Against Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo in an Experimental Galleria mellonella Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 685807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallorini, M.; Marinacci, B.; Pellegrini, B.; Cataldi, A.; Dindo, M.L.; Carradori, S.; Grande, R. Immunophenotyping of hemocytes from infected Galleria mellonella larvae as an innovative tool for immune profiling, infection studies and drug screening. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.S.; Lopes, E.; Azzali, E.; Machado, D.; Coelho, T.; da Silva, P.E.; Viveiros, M.; Pieroni, M.; Couto, I. An experimental model for the rapid screening of compounds with potential use against mycobacteria. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2016, 14, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorjão, A.L.; Oliveira, L.D.; Scorzoni, L.; Figueiredo-Godoi, L.M.A.; Cristina, A.; Prata, M.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Junqueira, J.C. From moths to caterpillars: Ideal conditions for Galleria mellonella rearing for in vivo microbiological studies. Virulence 2018, 9, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, J.M.; Adenwalla, N.; Wiles, S.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella larvae as an infection model for group A Streptococcus. Virulence 2013, 4, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Loh, J.M.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella infection models for the study of bacterial diseases and for antimicrobial drug testing. Virulence 2016, 7, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, X. On the Calculation of TCID50 for Quantitation of Virus Infectivity. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Category | Description | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Activity | No activity | 0 |
| Minimal activity on stimulation | 1 | |
| Active when stimulated | 2 | |
| Active without stimulation | 3 | |
| Cocoon formation | No cocoon | 1 |
| Partial cocoon | 0.5 | |
| Full cocoon | 0 | |
| Melanization | Complete melanization (black) | 0 |
| Dark spots on brown larva | 0 | |
| ≥3 spots/segments on beige larva | 2 | |
| <3 spots/segments on beige larva | 3 | |
| No melanization | 4 | |
| Survival | Dead | 0 |
| Alive | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade, M.; Neves, J.; Bento, M.; Marques, J.; Seabra, S.G.; Silveira, H.; Rodrigues, L.; Armada, A.; Viveiros, M.; Couto, I.; et al. Evaluation of Amlodipine and Imipramine Efficacy to Treat Galleria mellonella Infection by Biofilm-Producing and Antimicrobial-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14020183
Andrade M, Neves J, Bento M, Marques J, Seabra SG, Silveira H, Rodrigues L, Armada A, Viveiros M, Couto I, et al. Evaluation of Amlodipine and Imipramine Efficacy to Treat Galleria mellonella Infection by Biofilm-Producing and Antimicrobial-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(2):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14020183
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade, Mariana, Joana Neves, Maria Bento, Joana Marques, Sofia G. Seabra, Henrique Silveira, Liliana Rodrigues, Ana Armada, Miguel Viveiros, Isabel Couto, and et al. 2025. "Evaluation of Amlodipine and Imipramine Efficacy to Treat Galleria mellonella Infection by Biofilm-Producing and Antimicrobial-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" Antibiotics 14, no. 2: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14020183
APA StyleAndrade, M., Neves, J., Bento, M., Marques, J., Seabra, S. G., Silveira, H., Rodrigues, L., Armada, A., Viveiros, M., Couto, I., & Costa, S. S. (2025). Evaluation of Amlodipine and Imipramine Efficacy to Treat Galleria mellonella Infection by Biofilm-Producing and Antimicrobial-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics, 14(2), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14020183






