Efficacy of Tamoxifen Metabolites in Combination with Colistin and Tigecycline in Experimental Murine Models of Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Activity
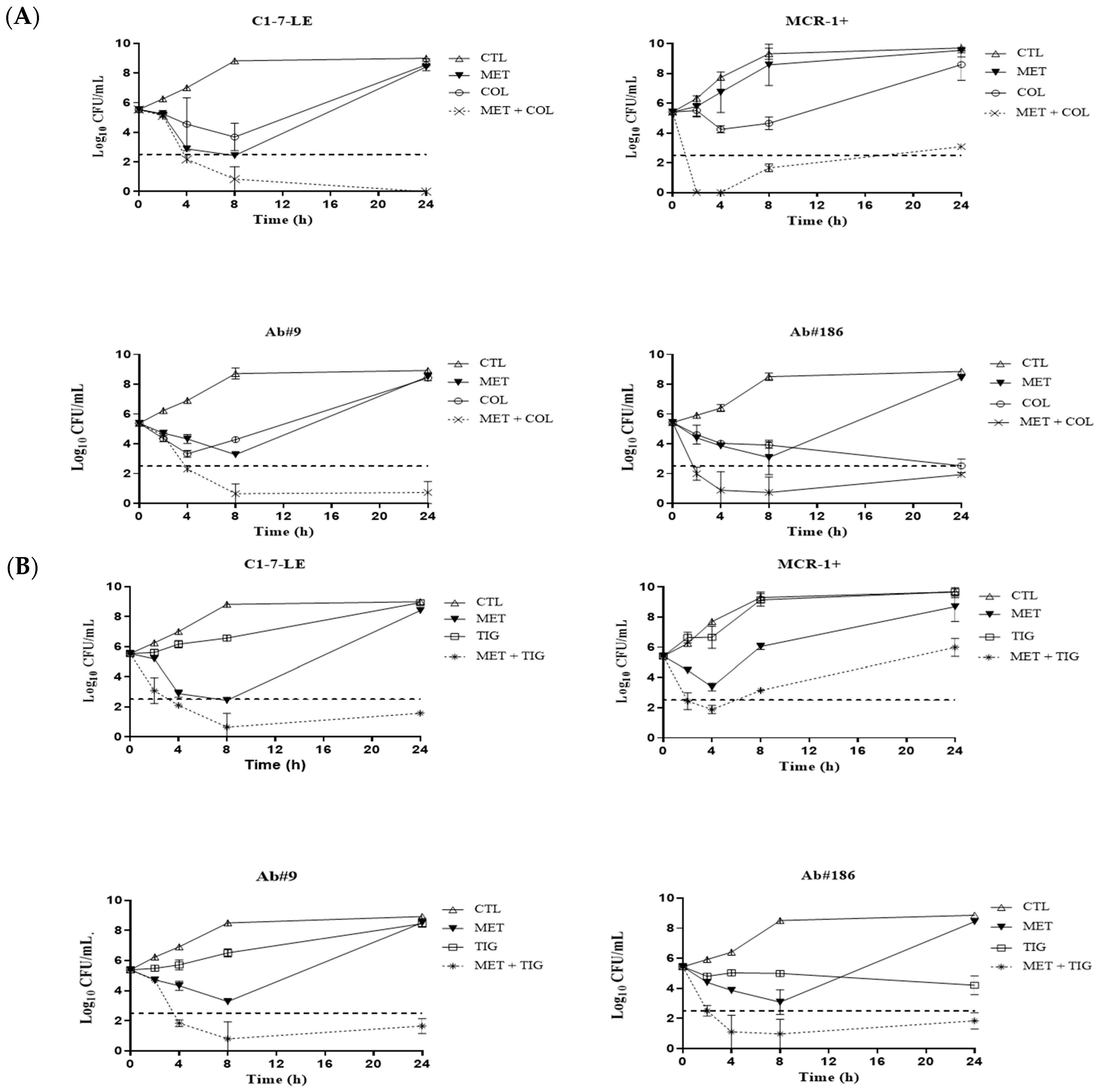
2.2. Time–Kill Curves
2.3. In Vivo Studies
2.3.1. Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD)
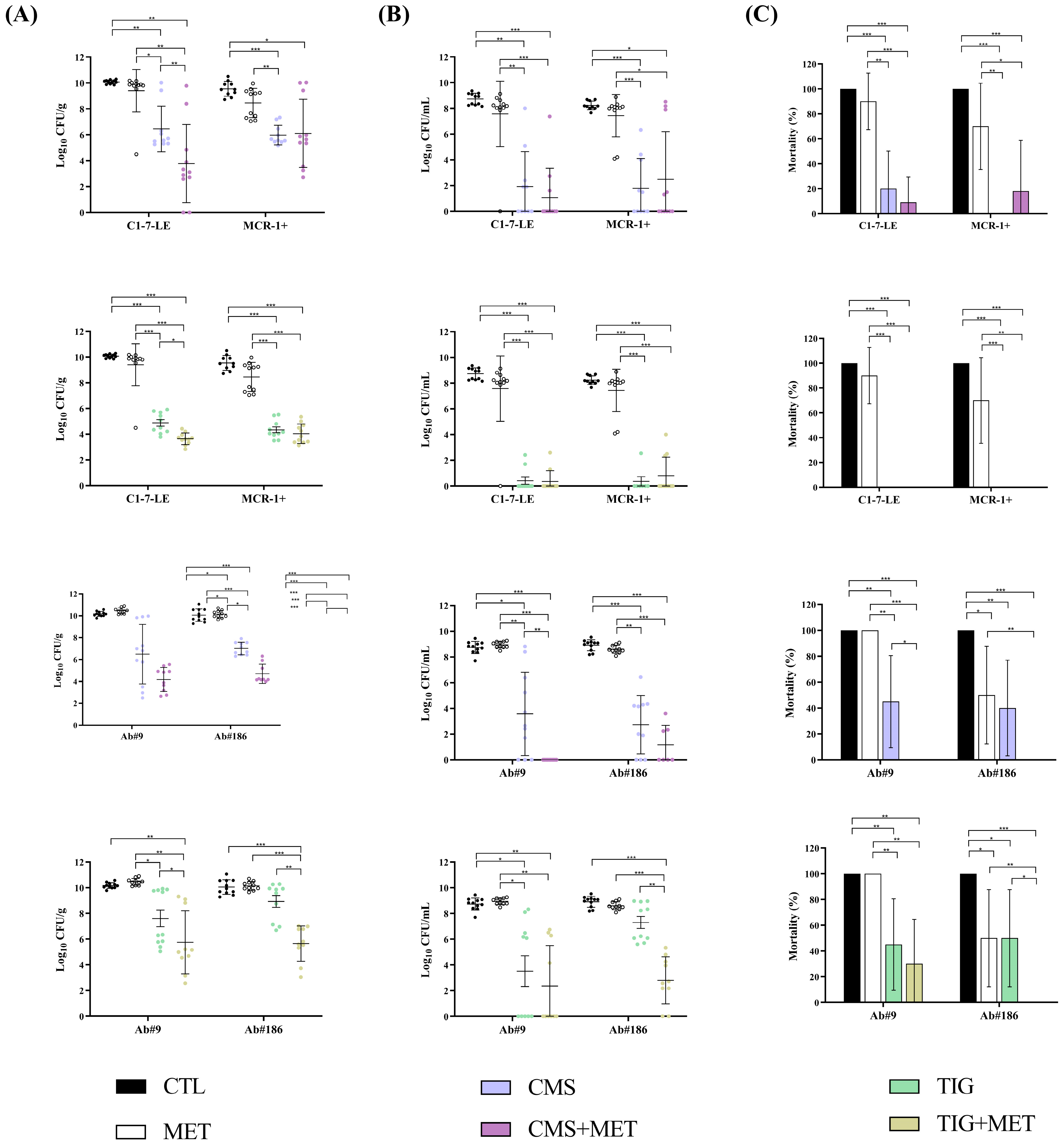
2.3.2. Efficacy of the Metabolite Mix Combinations in the Peritoneal Sepsis Model
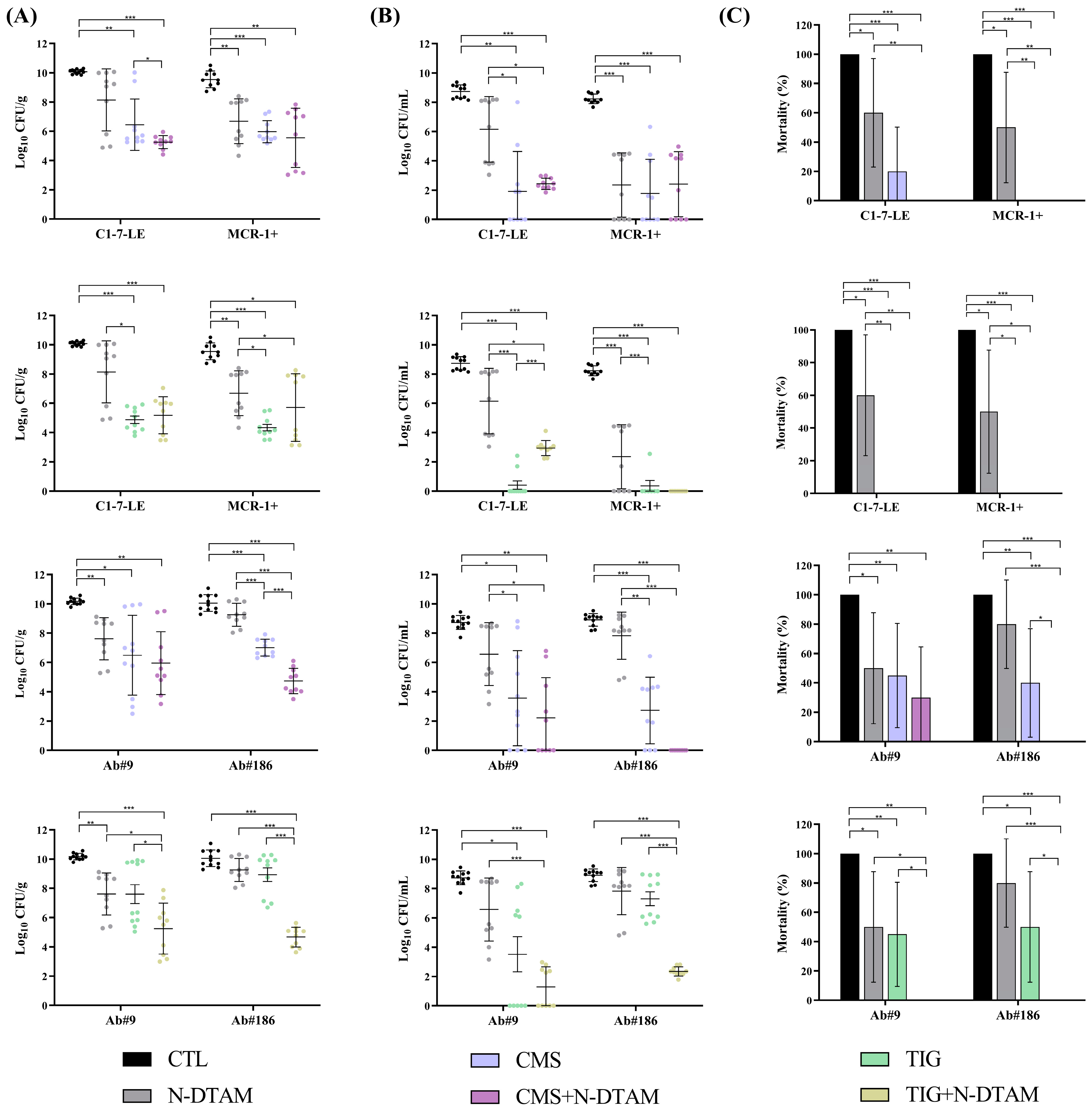
2.3.3. Efficacy of Metabolite Mix and N-Desmethyltamoxifen Combinations in the Experimental Pneumonia Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tamoxifen, Tamoxifen Metabolites, and Antimicrobial Agents
4.2. Bacterial Strains
4.3. In Vitro Studies
4.3.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3.2. Time–Kill Assays
4.4. In Vivo Studies
4.4.1. Animals
4.4.2. Toxicity Studies
4.4.3. Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD)
4.4.4. Peritoneal Sepsis Model
4.4.5. Pneumonia Model
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO (World Health Organization). Global Research Agenda for Antimicrobial Resistance in Human Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655, Erratum in Lancet 2022, 400, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwakoti, S.; Subedi, A.; Sharma, A.; Baral, R.; Bhattarai, N.R.; Khanal, B. Incidence and outcomes of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria infections in intensive care unit from Nepal- a prospective cohort study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos, V.; Cabañero-Navalón, M.D.; Salavert Lletí, M. Resistance to beta-lactams in Gram-negative bacilli: Relevance and potential therapeutic alternatives. Rev. Española Quimioter. 2022, 35 (Suppl. 2), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuntayaporn, P.; Thirapanmethee, K.; Chomnawang, M.T. An Update of Mobile Colistin Resistance in Non-Fermentative Gram-Negative Bacilli. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 882236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompkins, K.; van Duin, D. Treatment for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales infections: Recent advances and future directions. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 2053–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC/WHO (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and World Health Organization). Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe. 2023. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/Antimicrobial%20resistance%20surveillance%20in%20Europe%202023%20-%202021%20data.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- WHO (World Health Organization). Antimicrobial Resistance Fact Sheet; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Lai, C.C.; Ko, W.C.; Hsueh, P.R. Geographical patterns of in vitro susceptibilities to tigecycline and colistin among worldwide isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Data from the Antimicrobial Testing Leadership and Surveillance (ATLAS) programme, 2016–2021. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto Tiz, D.; Bagnoli, L.; Rosati, O.; Marini, F.; Sancineto, L.; Santi, C. FDA-Approved Small Molecules in 2022: Clinical Uses and Their Synthesis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Mounts, P.; Hurlburt, E.; Pfaffle, A.; Poggio, E.C. Taurolidine/Heparin Lock Solution and Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection in Hemodialysis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Control, Phase 3 Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.P.; Chen, J.Y. Conjugation of antimicrobial peptides to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 259, 115680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiesh, B.M.; Nazzal, M.A.; Abdelhaq, A.I.; Abutaha, S.A.; Zyoud, S.H.; Sabateen, A. Impact of an antibiotic stewardship program on antibiotic utilization, bacterial susceptibilities, and cost of antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Thirapanmethee, K.; Khuntayaporn, P.; Chomnawang, M.T. CRISPR-Based Gene Editing in Acinetobacter baumannii to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, K.; Poh, C.L. The Promising Potential of Reverse Vaccinology-Based Next-Generation Vaccine Development over Conventional Vaccines against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Y. Repurposing 9-Aminoacridine as an Adjuvant Enhances the Antimicrobial Effects of Rifampin against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0447422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domalaon, R.; Ammeter, D.; Brizuela, M.; Gorityala, B.K.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Repurposed Antimicrobial Combination Therapy: Tobramycin-Ciprofloxacin Hybrid Augments Activity of the Anticancer Drug Mitomycin C Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró-Canturri, A.; Ayerbe-Algaba, R.; Del Toro, R.; Mejías, M.E.; Pachón, J.; Smani, Y. Potential Tamoxifen Repurposing to Combat Infections by Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin-Fenton, D.P.; Damkier, P.; Lash, T.L. Metabolism and transport of tamoxifen in relation to its effectiveness: New perspectives on an ongoing controversy. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.J.; Thorn, C.F.; Desta, Z.; Flockhart, D.A.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB summary: Tamoxifen pathway, pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2013, 23, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA (Food Drug Administration) Nolvadex. Professional Information Brochure. 1998. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/1998/17970.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Miró-Canturri, A.; Ayerbe-Algaba, R.; Vila-Domínguez, A.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Pachón, J.; Smani, Y. Repurposing of the Tamoxifen Metabolites to Combat Infections by Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazuria, R.; Kerscher, B.; Huber, K.E.; Hoover, J.L.; Lundberg, C.V.; Hansen, J.U.; Sordello, S.; Renard, S.; Aranzana-Climent, V.; Hughes, D.; et al. Variability of murine bacterial pneumonia models used to evaluate antimicrobial agents. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 988728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallart, E.; Guerin, F.; Amoura, A.; Le Scouarnec, M.; Hamon, A.; El Meouche, I.; Chau, F.; Lefort, A.; Fantin, B.; Cattoir, V.; et al. Impact of the phenotypic expression of temocillin resistance in Escherichia coli on temocillin efficacy in a murine peritonitis model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, dkae072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Pichardo, C.; Llanos, A.C.; Pachón, J. Activity of tigecycline (GAR-936) against Acinetobacter baumannii strains, including those resistant to imipenem. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4479–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E.; Labrador-Herrera, G.; Cebrero-Cangueiro, T.; Díaz, C.; Smani, Y.; Del Palacio, J.P.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Pascual, A.; Pachón, J.; Conejo, M.C. Efficacy of Colistin and Its Combination With Rifampin in Vitro and in Experimental Models of Infection Caused by Carbapenemase-Producing Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichardo, C.; Pachón-Ibañez, M.E.; Docobo-Perez, F.; López-Rojas, R.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Garcia-Curiel, A.; Pachon, J. Efficacy of tigecycline vs. imipenem in the treatment of experimental Acinetobacter baumannii murine pneumonia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watashi, K.; Inoue, D.; Hijikata, M.; Goto, K.; Aly, H.H.; Shimotohno, K. Anti-hepatitis C virus activity of tamoxifen reveals the functional association of estrogen receptor with viral RNA polymerase NS5B. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 32765–32772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, S.; Luo, D.; Li, L.; Ye, Q.; Li, R.T.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Yang, H.; Deng, Y.Q.; Cheng, G. Tamoxifen and clomiphene inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection by suppressing viral entry. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Janabi, A. Repurposing of Tamoxifen Against the Oral Bacteria. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 18, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.S.; Kim, S.; Podder, B.; Jyoti, M.A.; Nam, K.W.; Lee, B.E.; Song, H.Y. Anti-Mycobacterial Activity of Tamoxifen Against Drug-Resistant and Intra-Macrophage Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, A.J.; Drozda, A.A.; Blader, I.J. Drug Repurposing Screening Identifies Novel Compounds That Effectively Inhibit Toxoplasma gondii Growth. mSphere 2016, 1, e00042-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, J.; Yildiz, A.; Young, A.H.; Taylor, M.J. Tamoxifen for bipolar disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramenko, N.; Vellieux, F.; Brábek, J.; Dvořánková, B.; Rösel, D.; Kaplánek, R.; Lacina, L.; Smetana, K., Jr.; Tesař, A.; Jakubek, M.; et al. Estrogen Receptor Modulators in Viral Infections Such as SARS-CoV-2: Therapeutic Consequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corriden, R.; Hollands, A.; Olson, J.; Derieux, J.; Lopez, J.; Chang, J.T.; Gonzalez, D.J.; Nizet, V. Tamoxifen augments the innate immune function of neutrophils through modulation of intracellular ceramide. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.D.; Karr, J.P.; Murphy, G.P. Effect of tamoxifen citrate on a murine renal cell adenocarcinoma. Oncology 1983, 40, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbach, J.L.; Wang, A.W.; Hawisher, D.; Cauvi, D.M.; Lizardo, R.E.; Rosas, J.; Reyes, T.; Escobedo, O.; Bickler, S.W.; Coimbra, R.; et al. Why Antibiotic Treatment Is Not Enough for Sepsis Resolution: An Evaluation in an Experimental Animal Model. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00664-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behjati, S.; Frank, M.H. The effects of tamoxifen on immunity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3076–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunakom, S.; Otani, H.; Udwary, D.W.; Doering, D.T.; Mouncey, N.J. Cytochromes P450 involved in bacterial RiPP biosyntheses. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 50, kuad005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Du, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Qu, Z.; Han, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Qi, F.; Yao, Q.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into Interactions between Bacterial Class I P450 Enzymes and Redox Partners. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9992–10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Deng, S.; Wen, W.; Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Zhong, G.; Li, J.; Ting, W.J.; Fu, B. Molecular typing, and integron and associated gene cassette analyses in Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from clinical samples. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracquadanio, S.; Bonomo, C.; Marino, A.; Bongiorno, D.; Privitera, G.F.; Bivona, D.A.; Mirabile, A.; Bonacci, P.G.; Stefani, S. Acinetobacter baumannii and Cefiderocol, between Cidality and Adaptability. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0234722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karah, N.; Sundsfjord, A.; Towner, K.; Samuelsen, Ø. Insights into the global molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible clones of Acinetobacter baumannii. Drug Resist. Updates 2012, 15, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrador-Herrera, G.; Pérez-Pulido, A.J.; Álvarez-Marín, R.; Casimiro-Soriguer, C.S.; Cebrero-Cangueiro, T.; Morán-Barrio, J.; Pachón, J.; Viale, A.M.; Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E. Virulence role of the outer membrane protein CarO in carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 2020, 11, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recacha, E.; Machuca, J.; Díaz-Díaz, S.; García-Duque, A.; Ramos-Guelfo, M.; Docobo-Pérez, F.; Blázquez, J.; Pascual, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M. Suppression of the SOS response modifies spatiotemporal evolution, post-antibiotic effect, bacterial fitness and biofilm formation in quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Ledesma, M.; García-Quintanilla, M.; Martín-Peña, R.; Pulido, M.R.; Pachón, J.; McConnell, M.J. Phenotypic changes associated with Colistin resistance due to Lipopolysaccharide loss in Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 2018, 9, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 14.0. 2024. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Skłodowski, K.; Suprewicz, Ł.; Chmielewska-Deptuła, S.J.; Kaliniak, S.; Okła, S.; Zakrzewska, M.; Minarowski, Ł.; Mróz, R.; Daniluk, T.; Savage, P.B.; et al. Ceragenins exhibit bactericidal properties that are independent of the ionic strength in the environment mimicking cystic fibrosis sputum. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1290952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC (National Research Council). Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MLST | MIC/MBC (mg/L) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST | CC | COL | TIG | TAM | N-DTAM | HTAM | ENDX | MET | |
| C1-7-LE | 8671 | 131 | 0.12/0.12 | 0.12/0.12 | >256/>256 | 128/256 | 256/256 | 64/128 | 4/4 |
| MCR-1+ | 6108 | 405 | 4/8 | 0.5/0.5 | >256/>256 | 128/256 | 256/256 | 128/256 | 4/4 |
| Ab#9 | 672 | 672 | 0.06/0.12 | 0.12/0.12 | >256/>256 | 16/16 | 256/256 | 32/32 | 4/8 |
| Ab#186 | 208 | 92 | 0.25/0.5 | 4/4 | >256/>256 | 64/64 | 256/256 | 32/64 | 4/4 |
| Dose (mg/kg) and Administration Route | AUC0–24 (mg/L·min) | Cmax (mg/L) | T1/2 (min) | AUC0–24/MIC | Cmax/MIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMS (20, ip) | 13.65 | 2.87 | 3.82 | 227.5 (C1-7-LE) 3.4 (MCR-1+) 227.5 (Ab#9) 54.6 (Ab#186) | |
| TIG (5, sc) | 9.24 | 1.92 | 2.33 | 77 (C1-7-LE) 37.1 (MCR-1+) 77 (Ab#9) 2.31 (Ab#186) | |
| TAM (40, ip) | 152.78 | 0.16 | 746.34 | 0.30 (C1-7-LE) 0.30 (MCR-1+) 0.30 (Ab#9) 0.30 (Ab#186) | 3.1 × 10−4 (C1-7-LE) 3.1 × 10−4 (MCR-1+) 3.1 × 10−4 (Ab#9) 3.1 × 10−4 (Ab#186) |
| N-DTAM (40, ip) | 572.52 | 1.16 | 432.65 | 4.4 (C1-7-LE) 4.4 (MCR-1+) 35.8 (Ab#9) 8.9 (Ab#186) | 0.01 (C1-7-LE) 0.01 (MCR-1+) 0.07 (Ab#9) 0.02 (Ab#186) |
| N-DTAM (13.3, ip) | 250.91 | 0.63 | 314.73 | 1.96 (C1-7-LE) 1.96 (MCR-1+) 15.68 (Ab#9) 3.92 (Ab#186) | 4.9 × 10−3 (C1-7-LE) 4.9 × 10−3 (MCR-1+) 0.04 (Ab#9) 9.8 × 10−3 (Ab#186) |
| HTAM (13.3, ip) | 130.28 | 0.98 | 231.91 | 0.51 (C1-7-LE) 0.51 (MCR-1+) 0.51 (Ab#9) 0.51 (Ab#186) | 3.8 × 10−3 (C1-7-LE) 3.8 × 10−3 (MCR-1+) 3.8 × 10−3 (Ab#9) 3.8 × 10−3 (Ab#186) |
| ENDX (13.3, ip) | 169.65 | 0.73 | 321.96 | 2.65 (C1-7-LE) 1.33 (MCR-1+) 5.30 (Ab#9) 5.30 (Ab#186) | 0.01 (C1-7-LE) 5.7 × 10−3 (MCR-1+) 0.02 (Ab#9) 0.02 (Ab#186) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Espejo, S.; Vila-Domínguez, A.; Cebrero-Cangueiro, T.; Smani, Y.; Pachón, J.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E. Efficacy of Tamoxifen Metabolites in Combination with Colistin and Tigecycline in Experimental Murine Models of Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050386
Herrera-Espejo S, Vila-Domínguez A, Cebrero-Cangueiro T, Smani Y, Pachón J, Jiménez-Mejías ME, Pachón-Ibáñez ME. Efficacy of Tamoxifen Metabolites in Combination with Colistin and Tigecycline in Experimental Murine Models of Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(5):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050386
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Espejo, Soraya, Andrea Vila-Domínguez, Tania Cebrero-Cangueiro, Younes Smani, Jerónimo Pachón, Manuel E. Jiménez-Mejías, and María E. Pachón-Ibáñez. 2024. "Efficacy of Tamoxifen Metabolites in Combination with Colistin and Tigecycline in Experimental Murine Models of Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii" Antibiotics 13, no. 5: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050386
APA StyleHerrera-Espejo, S., Vila-Domínguez, A., Cebrero-Cangueiro, T., Smani, Y., Pachón, J., Jiménez-Mejías, M. E., & Pachón-Ibáñez, M. E. (2024). Efficacy of Tamoxifen Metabolites in Combination with Colistin and Tigecycline in Experimental Murine Models of Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics, 13(5), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050386







