Detection and Preliminary Genomic Characterization of Poultry-Derived Salmonella enterica from Southern Kazakhstan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
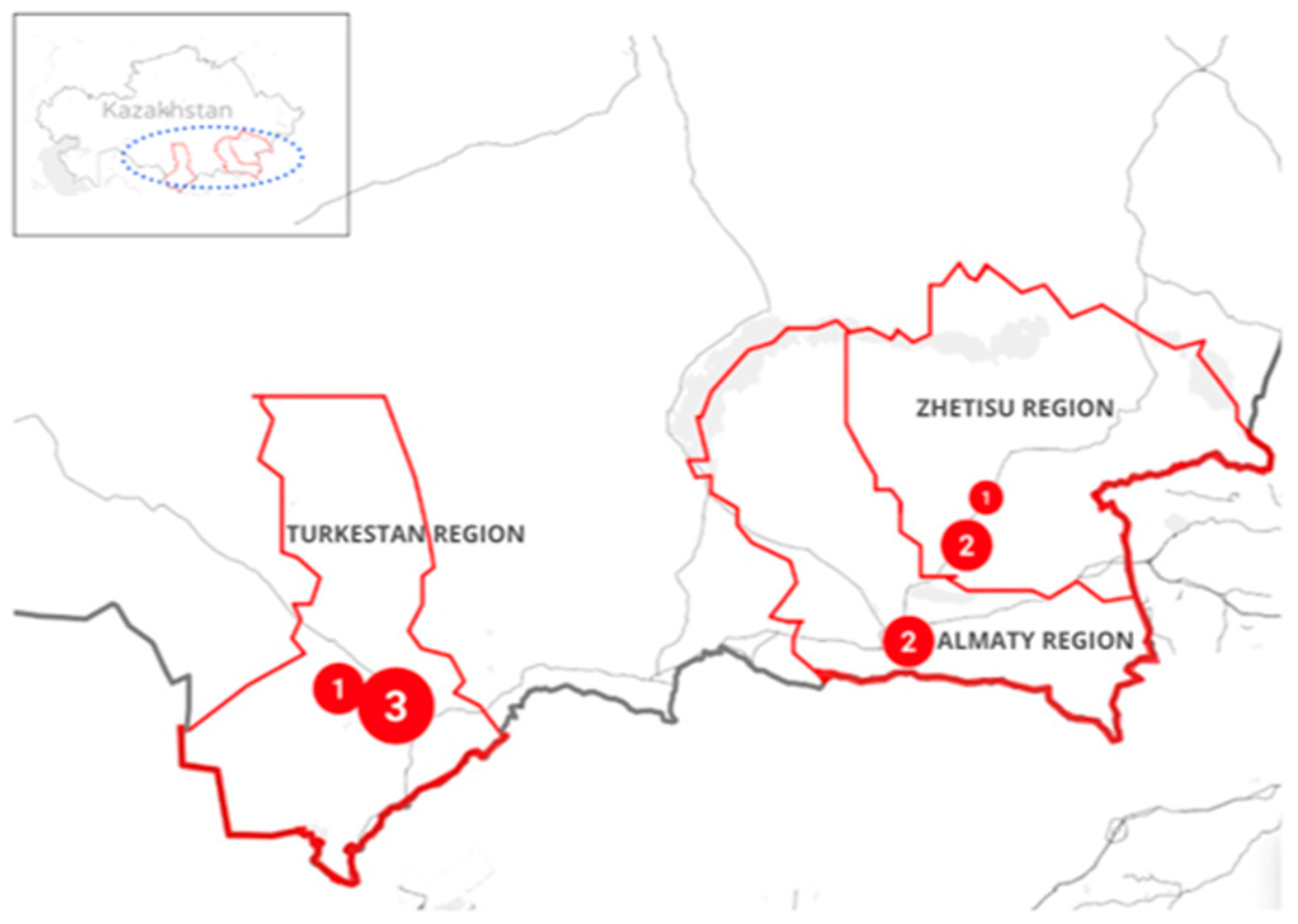
2.1. Sampling Yield
2.2. Culture and Preliminary Identification
2.3. Microscopy and Biochemical Profile
2.4. Serology (Slide Agglutination)
2.5. Molecular Identification (Real-Time PCR)
2.6. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.7. Genotypic AMR Determinants (Conventional PCR)
2.8. Whole-Genome Sequencing and In Silico AMR
2.9. In Silico Serotyping and MLST
2.10. Phylogenetic Placement
2.11. Mapping of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling and Ethics
4.2. Case Selection and Sampling
4.3. Bacterial Isolation
4.4. Microscopic Examination
4.5. Molecular Identification (Real-Time PCR)
4.6. Slide Agglutination Serology
4.7. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.8. AMR Gene Screening (Conventional PCR)
4.9. Whole-Genome Sequencing and De Novo Assembly
4.10. In Silico Serotyping and MLST
4.11. Genotypic AMR Prediction
4.12. Selection of Publicly Available Reference Genomes
4.13. SNP Calling and Recombination Masking
4.14. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.15. AMR Gene Presence/Absence Visualization
4.16. Statistical Analysis
4.17. Use of Generative AI
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | antimicrobial resistance |
| AST | antimicrobial susceptibility testing |
| bp | base pairs |
| CFU | colony-forming units |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| Ct | cycle threshold |
| ECOFF | epidemiological cut-off value |
| EnteroBase | public bacterial population genomics platform |
| GC | guanine–cytosine content |
| Gubbins | recombination-aware phylogeny software |
| iTOL | Interactive Tree Of Life (phylogeny visualization) |
| IQ-TREE | maximum-likelihood phylogenetic inference software |
| MHA | Mueller–Hinton agar |
| MLST | multilocus sequence typing |
| N50 | assembly N50 (contiguity metric) |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PlasmidFinder | database/tool for plasmid replicons |
| PointFinder | database/tool for chromosomal AMR mutations |
| PubMLST | public MLST database |
| qPCR | real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| QRDR | quinolone resistance–determining region |
| QUAST | genome assembly quality assessment tool |
| ResFinder | database/tool for acquired AMR genes |
| SeqSero2 | WGS-based Salmonella serotyping software |
| SNP | single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| Snippy | bacterial variant calling pipeline |
| SPAdes | de novo genome assembler |
| ST | sequence type |
| WGS | whole-genome sequencing |
| ZOI | zone of inhibition |
References
- Castro-Vargas, R.E.; Herrera-Sánchez, M.P.; Rodríguez-Hernández, R.; Rondón-Barragán, I.S. Antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella isolated from poultry: A global overview. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2070–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e08113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijnacker, R.; Dallman, T.J.; Tijsma, A.S.L.; Hawkins, G.; Larkin, L.; Kotila, S.M.; Amore, G.; Amato, E.; Suzuki, P.M.; Denayer, S.; et al. An international outbreak of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis linked to eggs from Poland: A microbiological and epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Tang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Xue, L.; Zhang, Y. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella from retail raw chicken in China. Foods 2022, 11, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Su, J. Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Diseased Poultry in Northern China between 2014 and 2018. Pathogens 2020, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Plasmids and the spread of resistance. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozwandowicz, M.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Fischer, J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B.; Guerra, B.; Mevius, D.J.; Hordijk, J. Plasmids carrying antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Park, J.H.; Kang, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeong, M.H. Emergence of pESI-like megaplasmid in Salmonella Infantis from broiler chickens in Korea. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 290, 110500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.B.; Lee, Y.J. Genomic analysis of pESI-like megaplasmid in Salmonella Infantis from the poultry industry in Korea. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 307, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendybayeva, A.; Mussabekova, A.; Nurkadilova, D.; Aikynbayeva, G.; Uzakov, Y. Antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from poultry products in northern Kazakhstan. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; Agama Study Group; Achtman, M. The EnteroBase user’s guide, with case studies on Salmonella transmissions, Yersinia pestis phylogeny, and Escherichia core genomic diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EnteroBase User’s Guide. Available online: https://enterobase.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH); United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). One Health Joint Plan of Action (2022–2026): Working Together for the Health of Humans, Animals, Plants and the Environment; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; 86p, ISBN 978-92-4-005913-9. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240059139 (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI Standard VET01; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 4th ed.; CLSI Supplement VET08; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, CLSI Supplement M100, 34th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union One Health 2019 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Biswas, S.; Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Li, X.; Fang, W.; Yue, M. Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium Isolates Recovered From the Food Chain Through National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System Between 1996 and 2016. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, F.; Pitondo-Silva, A.; Oliveira, M.A.; Falcão, J.P. Molecular epidemiology and virulence markers of Salmonella Infantis isolated over 25 years in São Paulo State, Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 19, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezal, E.H.; Sabol, A.; Khan, M.A.; Ali, N.; Stefanova, R.; Khan, A.A. Isolation and molecular characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis from poultry house and clinical samples during 2010. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiky, N.A.; Sarker, M.S.; Khan, M.S.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.A.; Sobur, M.A.; Rahman, M.T. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from chicken at wet markets in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.Y.; You, L.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, D. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular genotyping of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis clinical isolates from Guizhou province of Southwestern China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.N.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, D.; Hu, D. Serotypes, antibiotic resistance, and virulence genes of Salmonella in children with diarrhea. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacan Sever, N.; Akan, M. Molecular analysis of virulence genes of Salmonella Infantis isolated from chickens and turkeys. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaltabadi, F.R.; Ehsani, P.; Ebrahimi, R.M.; Khaledi, A. Molecular detection, virulence genes, biofilm formation, and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis isolated from poultry and clinical samples. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2018, 11, e69504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.H.; Zhou, X.; Addwebi, T.; Davis, M.A.; Orfe, L.; Call, D.R.; Guard, J.; Besser, T.E. Cell invasion of poultry-associated Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolates is associated with pathogenicity, motility and proteins secreted by the type III secretion system. Microbiology 2011, 157, 1428–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; den Bakker, H.C.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Lane, C.; Lauer, A.C.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. SeqSero2: Rapid and improved Salmonella serotype determination using whole-genome sequencing data. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01746-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utrarachkij, F.; Nakajima, C.; Siripanichgon, K.; Suthienkul, O.; Suzuki, Y. Genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance pattern of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis clinical isolates in Thailand. J. Infect. Chemother. 2016, 22, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendybayeva, A.M.; Ryshchanova, R.M.; Seilkhanova, R.O. Models of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella. Innov. Food Saf. 2021, 33, 14–21. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Sørensen, G.; Löfström, C.; Battisti, A.; Szabo, I.; Wasyl, D.; Slowey, R.; Zhao, S.; Brisabois, A.; Kornschober, C.; et al. Cross-border transmission of Salmonella Choleraesuis var. Kunzendorf in European pigs and wild boar: Infection, genetics, and evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasmin, R.; Gulig, P.A.; Parveen, S. Detection of virulence plasmid-encoded genes in Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Kentucky isolates recovered from commercially processed chicken carcasses. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qu, D.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Cui, S.; Shi, Y.; Xi, M.; Sheng, M.; Zhi, S.; Meng, J. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella serovars in retail meats of marketplace in Shaanxi, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skyberg, J.A.; Logue, C.M.; Nolan, L.K. Virulence genotyping of Salmonella spp. with multiplex PCR. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asten, A.J.A.M.; van Dijk, J.E. Distribution of “classic” virulence factors among Salmonella spp. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 44, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Al-Khaldi, S.F.; Branham, W.S.; Han, T.; Fuscoe, J.C.; Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Spayd, S.; Xu, J.; Fang, H.; et al. Microarray analysis of virulence gene profiles in Salmonella serovars from food/food animal environment. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2011, 5, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, J.; Edwards, D.J.; Dimovski, K.; Hiley, L.; Billman-Jacobe, H.; Hogg, G.; Holt, K.E. Evidence of microevolution of Salmonella Typhimurium during a series of egg-associated outbreaks linked to a single chicken farm. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawiec, M.; Kuczkowski, M.; Kruszewicz, A.G.; Wieliczko, A. Prevalence and genetic characteristics of Salmonella in free-living birds in Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, A.; Baghbani-Arani, F.; Ahmadiyan, S.; Farahani, R.K.; Ehsani, P.; Ebrahimi-Rad, M.; Moulana, Z. Multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis in Salmonella isolates as an effective molecular subtyping method. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffatellu, M.; Wilson, R.P.; Chessa, D.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.; Tran, Q.T.; Lawhon, S.; Khare, S.; Adams, L.G.; Bäumler, A.J. SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 contribute to Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium invasion of epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıçam İnce, S.; Akan, M. Molecular characterization of virulence genes in poultry-originated Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium. Ankara Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2024, 71, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain-Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Bacteriological Analytical Manual (BAM), Chapter 5: Salmonella; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food/bacteriological-analytical-manual-bam-chapter-5-salmonella (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars, 9th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institut Pasteur: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 6579-1:2017/Amd 1:2020; Microbiology of the Food Chain-Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella-Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp.; Amendment 1: Broader Range of Incubation Temperatures, Minor Changes and Corrections. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- EUCAST (The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing). MIC and Zone Diameter Distributions and ECOFFs (Epidemiological Cut-Off Values); EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2025; Available online: https://www.eucast.org/mic_distributions_and_ecoffs (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Colom, K.; Pérez, J.; Alonso, R.; Fernández-Aranguiz, A.; Lariño, E.; Cisterna, R. Simple and reliable multiplex PCR assay for detection of blaTEM, blaSHV and blaOXA-1 genes in Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 223, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, N.; Fagan, E.J.; Ellington, M.J. Multiplex PCR for rapid detection of genes encoding CTX-M extended-spectrum β-lactamases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.K.; Martin, I.; Alfa, M.; Mulvey, M. Multiplex PCR for the detection of tetracycline resistant genes. Mol. Cell. Probes 2001, 15, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, K.; Wachino, J.; Suzuki, S.; Arakawa, Y. Plasmid-mediated qnrD encoding a novel quinolone resistance determinant in Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3074–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronvall, G.; Hagelberg, A. Numerical evaluation of minimal biochemical test combinations for the identification of Entero-bacteriaceae species. Apmis 2002, 110, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreten, V.; Boerlin, P. A new sulfonamide resistance gene (sul3) in Escherichia coli is widespread in the pig population of Switzerland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butaye, P.; Michael, G.B.; Schwarz, S.; Barrett, T.J.; Brisabois, A.; White, D.G. The clonal spread of multidrug-resistant non-typhi Salmonella serotypes. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkenany, R.M.; Eladl, A.H.; El-Shafei, R.A. Genetic characterisation of class 1 integrons among multidrug-resistant Salmonella serotypes in broiler chicken farms. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgharpour, F.; Marashi, S.M.A.; Moulana, Z. Molecular detection of class 1, 2 and 3 integrons and some antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella Infantis isolates. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2018, 10, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Bioinformatics: Cambridge, UK, 2010; Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes de novo assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. mlst: Scan Contig Files Against PubMLST Typing Schemes. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/mlst (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Public Health Agency of Canada, National Microbiology Laboratory (PHAC-NML). staramr: Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Genome Assemblies; Public Health Agency of Canada, National Microbiology Laboratory: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2023. Available online: https://github.com/phac-nml/staramr (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Slotta, D.J.; Tolstoy, I.; Tyson, G.H.; Zhao, S.; Hsu, C.-H.; McDermott, P.F.; et al. Validating the AMRFinder tool and resistance gene database by using antimicrobial resistance genotype–phenotype correlations in a collection of isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00483-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherchame, E.; Ilango, G.; Cadel-Six, S. Retrieving good-quality Salmonella genomes from the GenBank database using a Python tool, SalmoDEST. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2022, 16, 11779322221080264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croucher, N.J.; Page, A.J.; Connor, T.R.; Delaney, A.J.; Keane, J.A.; Bentley, S.D.; Parkhill, J.; Harris, S.R. Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole-genome sequences using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, M.; Sanderson, K.E.; Spieth, J.; Clifton, S.W.; Latreille, P.; Courtney, L.; Porwollik, S.; Ali, J.; Dante, M.; Du, F.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2. Nature 2001, 413, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.-Y. ggtree: An R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-H.; Su, L.-H.; Chu, C.; Chia, J.-H.; Wu, T.-L.; Lin, T.-Y.; Lee, Y.-S. Detection of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium phage types DT102, DT104 and U302 by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2354–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
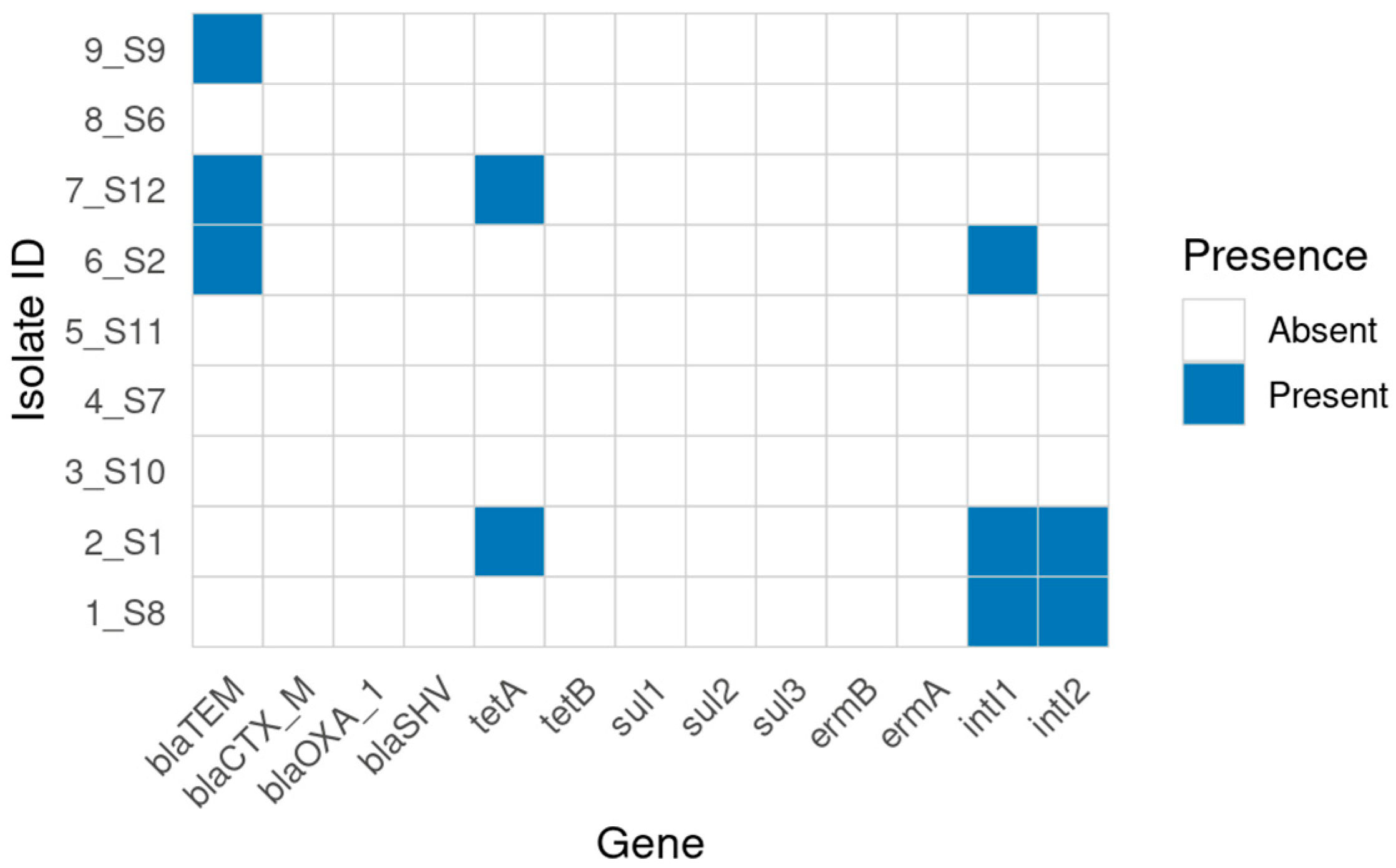
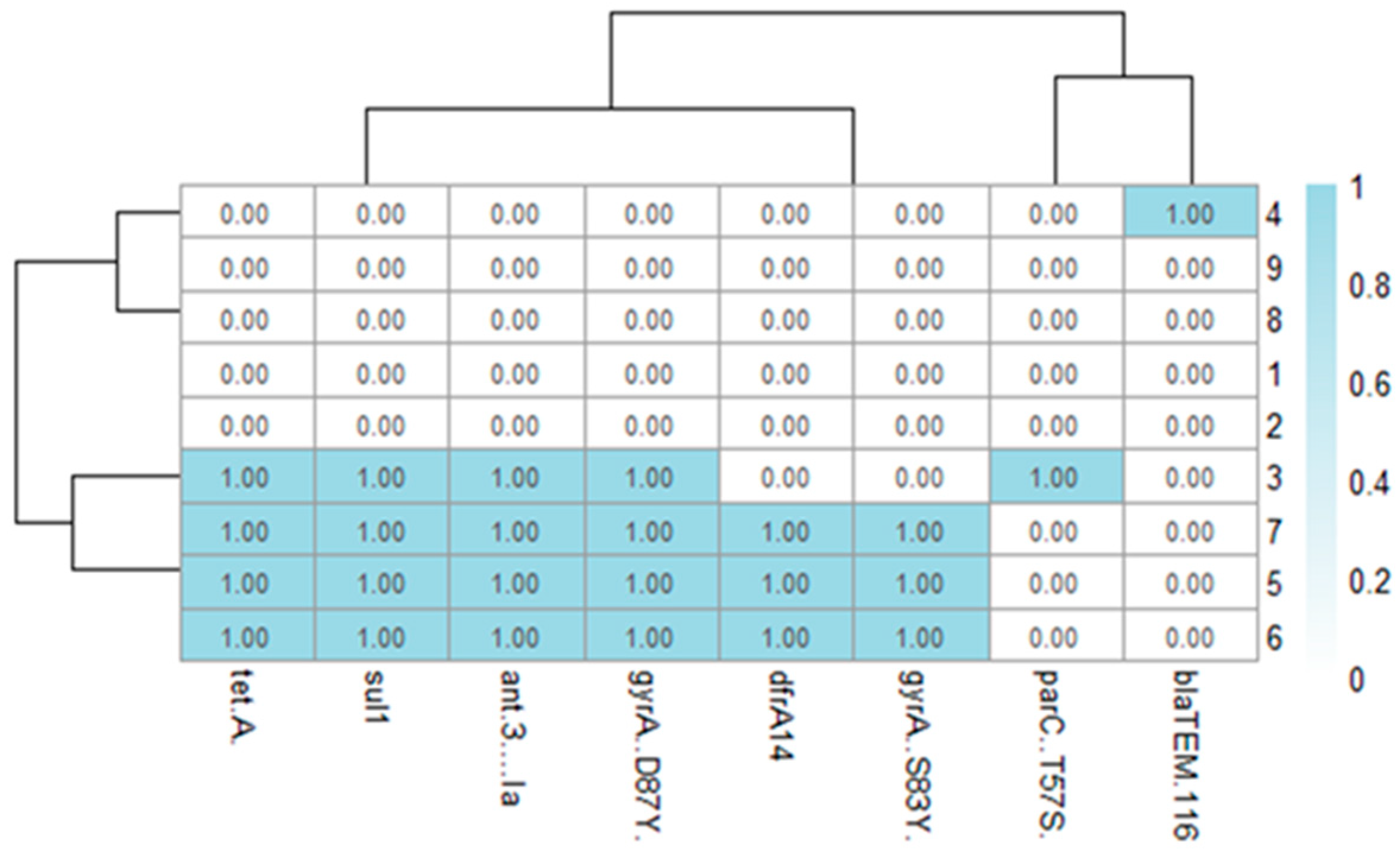
| ID | AMP/β-Lactamase (blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaOXA-1, blaSHV) | CHL | GEN | SXT/Sulfonamide (sul1, sul2, sul3) | TET (tetA/tetB) | Integrons (intI1, intI2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1_S8 | R/- | S/- | R/- | R/- | - | intI1+, intI2+ |
| 2_S1 | R/- | I/- | R/- | R/- | tet A+ | intI1+, intI2+ |
| 3_S10 | I/- | S/- | R/- | R/- | - | - |
| 4_S7 | I/- | S/- | R/- | R/- | - | - |
| 5_S11 | R/- | I/- | R/- | R/- | - | - |
| 6_S2 | R/blaTEM+ | S/- | R/- | R/- | - | - |
| 7_S12 | R/blaTEM+ | S/- | I/- | R/- | tet A+ | - |
| 8_S6 | R/- | S/- | R/- | R/- | - | intI1+, intI2+ |
| 9_S9 | R/blaTEM+ | S/- | R/- | S/- | - | - |
| Sample ID | Predicted Antigenic Profile | Predicted Serotype | MLST Type | Sample Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salm-Otar-1_S8 | 9:g,m | Enteritidis | 11 | Localized flushing |
| Salm-Otar-2_S1 | 9:g,m | Enteritidis | 11 | Chicken droppings |
| Salm-Otar-3_S10 | 7:r:1.5 | Infantis | 32 | Chicken droppings |
| Salm-Otar-4_S7 | 9:g,m | Enteritidis | 11 | Localized flushing |
| Salm-Otar-5_S11 | 7:r:1.5 | Infantis | 32 | Fallen bird |
| Salm-Otar-6_S2 | 7:r:1.5 | Infantis | 32 | Fallen bird |
| Salm-Otar-7_S12 | 7:r:1.5 | Infantis | 32 | Cloacal swabs |
| Salm-Otar-8_S6 | 7:c:1.5 | Paratyphi C or Choleraesuis or Typhisuis | 68 | Dust sample from a private poultry farm |
| Salm-Otar-9_S9 | 7:c:1.5 | Paratyphi C or Choleraesuis or Typhisuis | 68 | Sample from shoe covers from a private poultry farm |
| Antibiotic Class | Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Size (bp) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-lactams | blaTEM | F: ATCAGTTGGGTGCACGAGTG R: ACGCTCACCGGCTCCAGA | 608 | [47] |
| blaOXA-1 | F: ATGAAAAACACAATACATATCAAC R: AAAGGACATTCACGCCTGTG | 768 | [47] | |
| blaCTX-M | F: TTTGCGATGTGCAGTACCAGTAA R: CCGCTGCCGGTCTTATC | 550 | [48] | |
| blaSHV | F: TCGCCTGTGTATTATCTCCC R: CGCAGATAAATCACCACAATG | 768 | [48] | |
| Tetracyc- lines | tetA | F: GGTTCACTCGAACGACGTCA R: CTGTCCGACAAGTTGCATGA | 577 | [49] |
| tetB | F: CATTAATAGGCGCATCGCTG R: TGAAGGTCATCGATAGCAGG | 930 | [50] | |
| Sulfonamides | sul1 | F: CTTCGATGAGAGCCGGCGGC R: GCAAGGCGGAAACCCCGCC | 432 | [51] |
| sul2 | F: GCGCTCAAGGCAGATGGCATT R: GCGTTTGATACCGGCACCCGT | 293 | [51] | |
| sul3 | F: CATTCTAGAAAACAGTCGTAGTTCG R: CATCTGCAGCTAACCTAGGGCTTTGGA | 789 | [52] | |
| Macrolides | ermB | F: GAAAAGGTACTCAACCAAATA R: AGTAACGGTACTTAAA TTGTTTAC | 636 | [53] |
| ermA | F: CTTCGATAGTTTATTAATATTAGT R: TCTAAAAAGCATGT AAAAGAA | 645 | [53] | |
| Integrons | IntI1 | F: CAGTGGACATAAGCCTGTTC R: CCCGAGGCATAGACTGTA | 160 | [54] |
| IntI2 | F: TTATTGCTGGGATTAGGC R: ACGGCTACCCTCTGTTATC | 233 | [55] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yespembetov, B.; Kirkimbayeva, Z.; Abdykalyk, A.; Akhmetova, A.; Shevtsov, A.; Syrym, N.; Alpysbayeva, S.; Sarmykova, M.; Abdimukhtar, A.; Anarbekova, A.; et al. Detection and Preliminary Genomic Characterization of Poultry-Derived Salmonella enterica from Southern Kazakhstan. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14121195
Yespembetov B, Kirkimbayeva Z, Abdykalyk A, Akhmetova A, Shevtsov A, Syrym N, Alpysbayeva S, Sarmykova M, Abdimukhtar A, Anarbekova A, et al. Detection and Preliminary Genomic Characterization of Poultry-Derived Salmonella enterica from Southern Kazakhstan. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(12):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14121195
Chicago/Turabian StyleYespembetov, Bolat, Zhumagul Kirkimbayeva, Akbope Abdykalyk, Assel Akhmetova, Alexandr Shevtsov, Nazym Syrym, Sabira Alpysbayeva, Makhpal Sarmykova, Azamat Abdimukhtar, Aktoty Anarbekova, and et al. 2025. "Detection and Preliminary Genomic Characterization of Poultry-Derived Salmonella enterica from Southern Kazakhstan" Antibiotics 14, no. 12: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14121195
APA StyleYespembetov, B., Kirkimbayeva, Z., Abdykalyk, A., Akhmetova, A., Shevtsov, A., Syrym, N., Alpysbayeva, S., Sarmykova, M., Abdimukhtar, A., Anarbekova, A., Yerzhigit, B., Shestakov, A., Kozhabergenov, N., Usserbayev, B., Bulatov, Y., & Toleukhan, A. (2025). Detection and Preliminary Genomic Characterization of Poultry-Derived Salmonella enterica from Southern Kazakhstan. Antibiotics, 14(12), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14121195






