Recurrent and Multidrug-Resistant UTI Treatments in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Retrospective Study from Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infection |
| rUTI | Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| BK | BK virus (polyomavirus) |
| MDRO | Multidrug-Resistant Organism |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| KTR | Kidney Transplant Recipient |
| AMR | Antimicrobial Resistance |
References
- Alangaden, G.J.; Thyagarajan, R.; Gruber, S.A.; Morawski, K.; Garnick, J.; El-Amm, J.M.; West, M.S.; Sillix, D.H.; Chandrasekar, P.H.; Haririan, A. Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: Current epidemiology and associated risk factors. Clin. Transplant. 2006, 20, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alangaden, G.J. Urinary tract infections in renal transplant recipients. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2007, 9, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veroux, M.; Giuffrida, G.; Corona, D.; Gagliano, M.; Scriffignano, V.; Vizcarra, D.; Tallarita, T.; Zerbo, D.; Virgilio, C.; Sciacca, A.; et al. Infective complications in renal allograft recipients: Epidemiology and outcome. Transplant. Proc. 2008, 40, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, M.; Pezeshgi, A.; Mahdiabadi, M.Z.; Sabzghabaei, F.; Hajishah, H.; Mahdavynia, S. Prevalence and risk factors of urinary tract infection in kidney recipients: A meta-analysis study. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.D.; Julian, K. Urinary tract infections in solid organ transplant recipients: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. The prevalence and predictive factors of urinary tract infection in patients undergoing renal transplantation: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Infect. Control 2016, 44, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzad, D.; Hakimeh, A.; Hossein, R.; Khaledi, A. A middle east systematic review and meta-analysis of bacterial urinary tract infection among renal transplant recipients; Causative microorganisms. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 148, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.H.G.; Nascimento, E.; Lasmar, M.F.; Fabreti-Oliveira, R.A. Effects of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infection on Clinical Outcome and Survival of Kidney Transplant Patients. Transplant. Proc. 2022, 54, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, N.S.; Hagopian, J.C.; Brennan, D.C.; Pottebaum, A.A.; Santos, C.A.; Gharabagi, A.; Horwedel, T.A. Effects of recurrent urinary tract infections on graft and patient outcomes after kidney transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasim, A.; Abu Jaffal, A.; Alyousef, A.A. Prevalence of Multidrug Resistance and Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Carriage of Clinical Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolates in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 3026851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zowawi, H.M. Antimicrobial resistance in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2016, 37, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zowawi, H.M.; Sartor, A.L.; Balkhy, H.H.; Walsh, T.R.; Al Johani, S.M.; Aljindan, R.Y.; Alfaresi, M.; Ibrahim, E.; Al-Jardani, A.; Al-Abri, S.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council: Dominance of OXA-48 and NDM Producers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3085–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeldah, M.M. Antimicrobial Resistance and Its Spread Is a Global Threat. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, M.; Pesce, F.; Schena, A.; Simone, S.; Castellano, G.; Gesualdo, L. Updates on urinary tract infections in kidney transplantation. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velioglu, A.; Guneri, G.; Arikan, H.; Asicioglu, E.; Tigen, E.T.; Tanidir, Y.; Tinay, I.; Yegen, C.; Tuglular, S. Incidence and risk factors for urinary tract infections in the first year after renal transplantation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizakos, M.; Nasioudis, D.; Mylonakis, E. Urinary tract infections caused by ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae in renal transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, e12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabkin, D.G.; Stifelman, M.D.; Birkhoff, J.; Richardson, K.A.; Cohen, D.; Nowygrod, R.; Benvenisty, A.I.; Hardy, M.A. Early catheter removal decreases incidence of urinary tract infections in renal transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 1998, 30, 4314–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, S.; Cimen, S.; Hurton, S.; Molinari, M. Risks and Benefits of Early Catheter Removal After Renal Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 2855–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werneburg, G.T. Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: Current Challenges and Future Prospects. Res. Rep. Urol. 2022, 14, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Hooton, T.M.; Naber, K.G.; Wullt, B.; Colgan, R.; Miller, L.G.; Moran, G.J.; Nicolle, L.E.; Raz, R.; Schaeffer, A.J.; et al. International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, e103–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, J.; Bartoletti, R.; Bruyère, F.; Cai, T.; Geerlings, S.; Köves, B.; Schubert, S.; Pilatz, A.; Veeratterapillay, R.; E Wagenlehner, F.M.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Urological Infections: Summary of the 2024 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A.E.; Norton, J.P.; Spivak, A.M.; Mulvey, M.A. Urinary Tract Infections: Current and Emerging Management Strategies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, J.D.D. Infections with Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Drugs 2010, 70, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamal, M.I.; Brahim, I.; Hisham, N.; Aladdin, R.; Mohammed, H.; Bahaaeldin, A. Recent updates of carbapenem antibiotics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 131, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Pan, Q.; Mo, C.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y.; Chen, L. Carbapenems vs alternative antibiotics for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infection. Medicine 2020, 99, e18769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Therapy of Complicated Urinary. 2012. Available online: https://swab.nl/exec/file/download/84 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Alshehri, A.A.; Aldali, J.A.; Abdelhamid, M.A.; Alanazi, A.A.; Alhuraiz, R.B.; Alanazi, L.Z.; Alshmrani, M.A.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Alrshoud, M.I.; Alharbi, R.F. Implementation of Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, M.A.; Nasser, S.A.; Rababa’h, A.M. A systematic review of Antimicrobial Stewardship Program implementation in Middle Eastern countries. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Chen, H.-P.; Lin, C.-W.; Tang, J.-J.; Hsu, T.-Y.; Weng, Y.-C.; Lee, Y.-M.; Wang, W.-S.; Lo, S.-S. Implementation and outcomes of an antimicrobial stewardship program: Effectiveness of education. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017, 80, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenlehner, F.M.E.; Vahlensieck, W.; Bauer, H.W.; Weidner, W.; Piechota, H.J.; Naber, K.G. Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2013, 65, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dason, S.; Dason, J.T.; Kapoor, A. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of recurrent urinary tract infection in women. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2011, 5, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Badr, A.; Al-Shaikh, G. Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections Management in Women: A Review. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2013, 13, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9 (Suppl. 3), S1–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert-Kay, S.A. Diagnosis and management of uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bono, M.J.; Leslie, S.W.; Reygaert, W.C. Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hooton, T.M. Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halskov, A.C.L.; Dagnæs-Hansen, J.; Stroomberg, H.V.; Sørensen, S.S.; Røder, A. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Renal Transplant Recipients. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2023, 52, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Tamimi, A.R.; Alotaibi, W.S.; Aljohani, R.M.; Aldharman, S.S.; Alharbi, N.M.; Khair, H.S. The Impact of Urinary Tract Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Six-Year Single-Center Experience. Cureus 2023, 15, e44458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
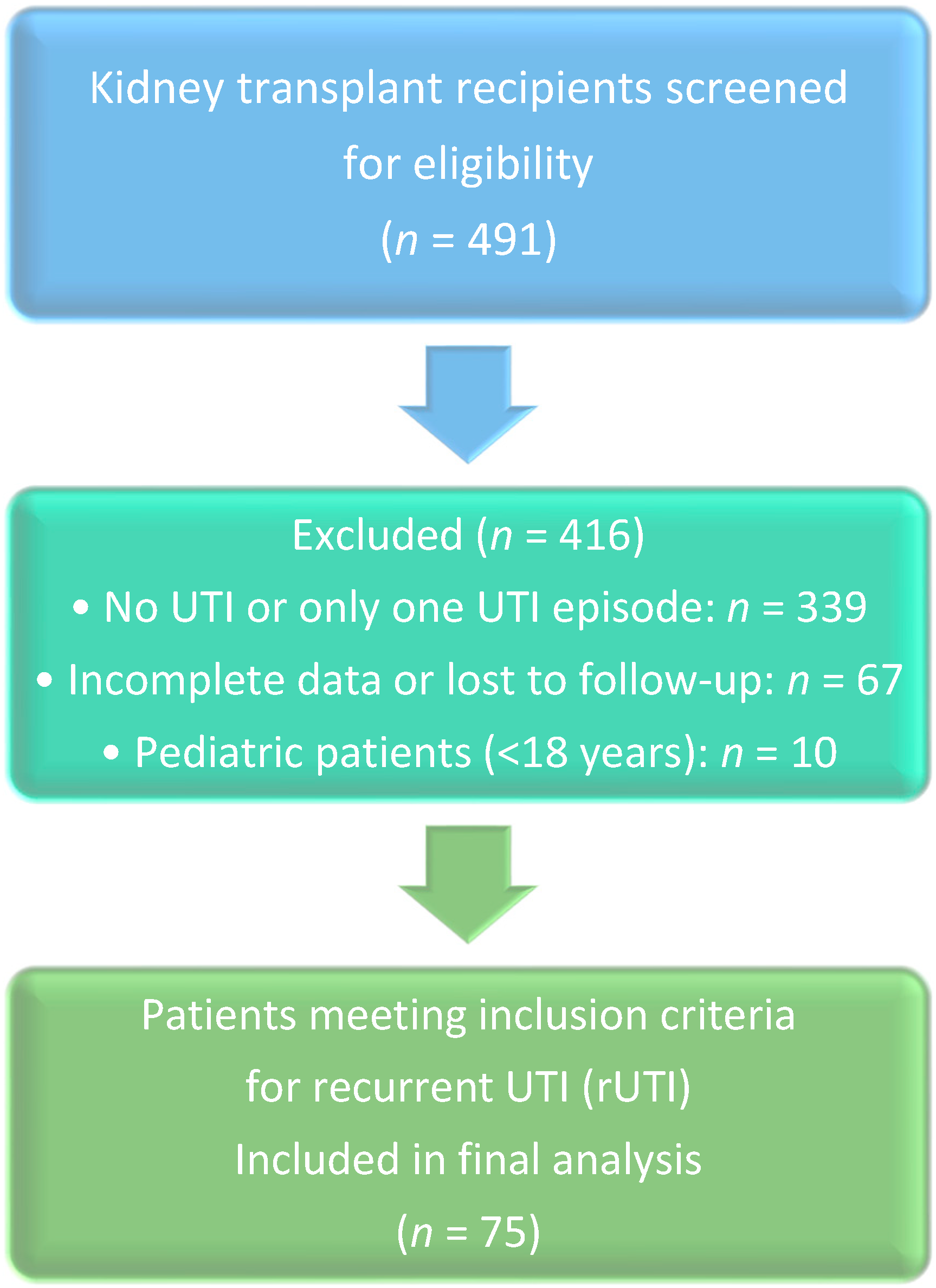
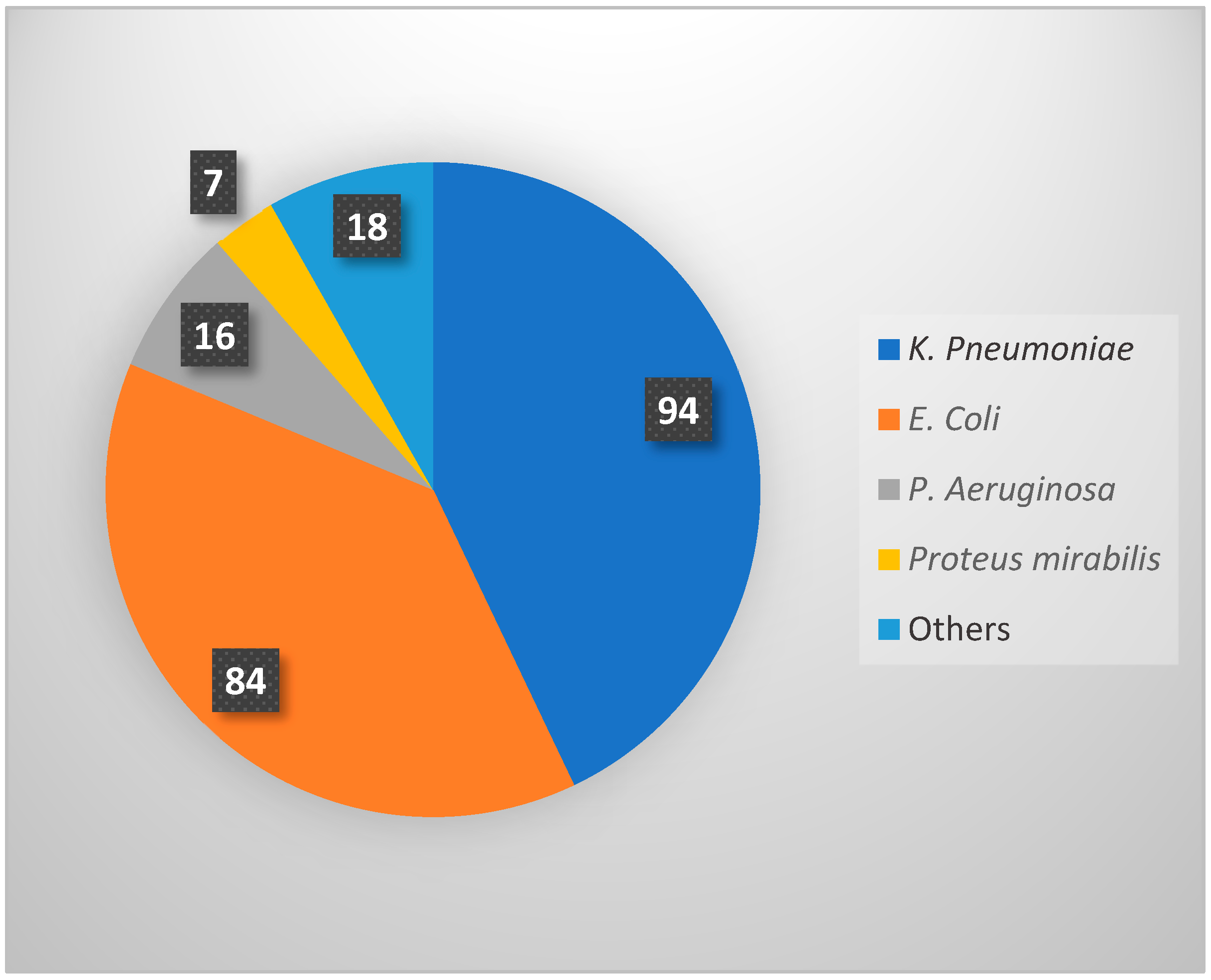
| Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Screened Patients | 491 | 100.0% |
| Included | 75 | 15.3% |
| Excluded | 416 | 84.7% |
| Reason for Exclusion | ||
| -Single/No UTI episode | 339 | 69.0% |
| -Missing data/Lost to follow-up | 67 | 13.6% |
| -Pediatric age (<18 years) | 10 | 2.0% |
| Included Patients (n = 75) | ||
| Gender | ||
| -Male | 32 | 42.7% |
| -Female | 43 | 57.3% |
| Donor Type | ||
| -Living Donor | 64 | 85.3% |
| -Deceased Donor | 11 | 14.7% |
| Age (years), Mean ± SD | 48.2 ± 15.8 | |
| BMI (kg/m2), Mean ± SD | 24.9 ± 5.9 |
| Factor | p-Value | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI for OR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (per year increase) | 0.151 | 1.022 | 0.992–1.054 |
| Gender (Female vs. Male) | 0.048 | 0.382 | 0.148–0.990 |
| Diabetes Mellitus (Yes vs. No) | 0.039 | 1.833 | 0.685–4.909 |
| MDRO Infection (Yes vs. No) | 0.021 | 3.143 | 1.185–8.334 |
| Ureteric Stent (Yes vs. No) | 0.042 | 4.065 | 1.054–15.670 |
| Complicated UTI (Yes vs. No) | 0.005 | 4.600 | 1.567–13.502 |
| Urinary Catheter (Yes vs. No) | 0.002 | 0.189 | 0.066–0.540 |
| Descriptives | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | Std. Error | ||||||
| SCr | Mean | 106.23 | 8.228 | ||||
| Median | 85.00 | ||||||
| Minimum | 16 | ||||||
| Maximum | 544 | ||||||
| Range | 529 | ||||||
| Interquartile Range | 48 | ||||||
| WBC_level | Mean | 9.16 | 0.553 | ||||
| Median | 8.65 | ||||||
| Minimum | 2 | ||||||
| Maximum | 29 | ||||||
| Range | 26 | ||||||
| Interquartile Range | 6 | ||||||
| Ranks | |||||||
| N | Mean Rank | Sum of Ranks | |||||
| SCr at Baseline-SCr at UTI#1 | Negative Ranks | 14 | 35.93 | 503.00 | |||
| Positive Ranks | 58 | 36.64 | 2125.00 | ||||
| Ties | 3 | ||||||
| Total | 75 | ||||||
| Test Statistics a | |||||||
| SCr at Baseline-SCr at UTI#1 | |||||||
| Z | −4.552 b | ||||||
| Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | ||||||
| Antibiotic Class | Used Alone (n) | Used in Combination (n) | Total Courses, n (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbapenem | 84 | 11 | 95 (40.8%) | ||||
| Cephalosporin | 50 | 17 | 67 (28.8%) | ||||
| Penicillins | 22 | 6 | 28 (12.0%) | ||||
| Fluoroquinolone | 20 | 7 | 27 (11.6%) | ||||
| Treatment Duration | n | % | |||||
| <7 days | 10 | 13.3% | |||||
| 7–10 days | 39 | 52.0% | |||||
| 11–14 days | 13 | 17.3% | |||||
| >14 days | 5 | 6.7% | |||||
| Descriptives | |||||||
| Statistic | SE | ||||||
| Duration of treatment | Mean | 9.7793 | 0.53613 | ||||
| 95% Confidence Interval for Mean | Lower Bound | 8.7111 | |||||
| Upper Bound | 10.8476 | ||||||
| 5% Trimmed Mean | 9.2378 | ||||||
| Median | 9.0000 | ||||||
| Variance | 21.558 | ||||||
| Std. Deviation | 4.64304 | ||||||
| Minimum | 3.00 | ||||||
| Maximum | 37.50 | ||||||
| Range | 34.50 | ||||||
| Interquartile Range | 3.50 | ||||||
| Skewness | 3.349 | 0.277 | |||||
| Kurtosis | 17.162 | 0.548 | |||||
| Chi-Square Tests | Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-Sided) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Chi-Square | 43.462 | 10 | <0.001 |
| Likelihood Ratio | 52.697 | 10 | <0.001 |
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 1.413 | 1 | 0.235 |
| N of Valid Cases | 72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, K.A.; Mirdad, R.Y.; Khogeer, A.T.; Alammash, B.B.; Alhazmi, A.Y.; Alotaibi, N.E.; Alshammari, A.S.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Alnuhait, M.A. Recurrent and Multidrug-Resistant UTI Treatments in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Retrospective Study from Saudi Arabia. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111147
Alzahrani KA, Mirdad RY, Khogeer AT, Alammash BB, Alhazmi AY, Alotaibi NE, Alshammari AS, Alotaibi AS, Alnuhait MA. Recurrent and Multidrug-Resistant UTI Treatments in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Retrospective Study from Saudi Arabia. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111147
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Khalid A., Redwan Y. Mirdad, Anas T. Khogeer, Buthainah B. Alammash, Abdulfattah Y. Alhazmi, Nouf E. Alotaibi, Abdullah S. Alshammari, Abdulmalik S. Alotaibi, and Mohammed A. Alnuhait. 2025. "Recurrent and Multidrug-Resistant UTI Treatments in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Retrospective Study from Saudi Arabia" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111147
APA StyleAlzahrani, K. A., Mirdad, R. Y., Khogeer, A. T., Alammash, B. B., Alhazmi, A. Y., Alotaibi, N. E., Alshammari, A. S., Alotaibi, A. S., & Alnuhait, M. A. (2025). Recurrent and Multidrug-Resistant UTI Treatments in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Retrospective Study from Saudi Arabia. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111147






