Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Two High-Risk Klebsiella pneumoniae Clones (ST258-blaKPC-2 and ST11-blaNDM-1) from a Greek Tertiary Hospital
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
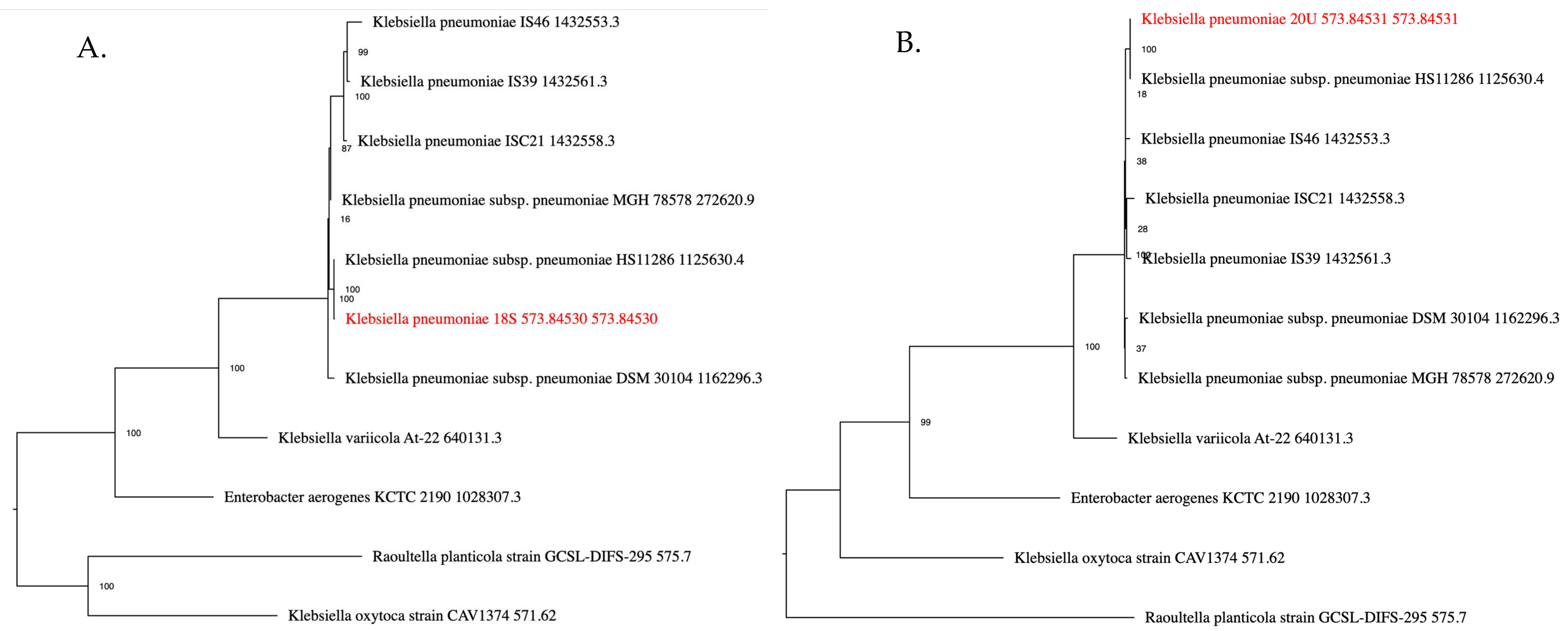
2.1. Isolate Identification
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes (ARGs)
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.4. Plasmid Detection and Additional Genomic Features
2.5. Yersiniabactin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection and Identification of Bacterial Strains
4.2. DNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR Gene Detection
4.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing
4.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbas, R.; Chakkour, M.; Zein El Dine, H.; Obaseki, E.F.; Obeid, S.T.; Jezzini, A.; Ghssein, G.; Ezzeddine, Z. General overview of Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology and the role of siderophores in its pathogenicity. Biology 2024, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela Fuente, J.; Diaz-Colunga, J.; Sanchez, A.; San Millan, A. Global epistasis in plasmid-mediated antimicrobial resistance. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2024, 20, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ying, L.; Xiong, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Wang, Y.; Shen, P.; Xiao, Y. Understanding carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Key virulence factors and evolutionary convergence. hLife 2024, 2, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, D.; Memar, M.H.; Leylabadlo, H.E.; Ghotaslou, A.; Ghotaslou, R. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A comprehensive review of phenotypic and genotypic methods for detection. Microbe 2025, 6, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletis, G. Carbapenem resistance: Overview of the problem and future perspectives. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, F.; Xiao, Y.; Qu, J. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 index from a single strain enhances rapid parallel evolution during persistent infection. hLife 2025, 3, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Zhao, J.; Lu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhuo, X.; Cao, B. Within-host resistance evolution of a fatal ST11 hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 61, 106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Fleres, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, G.; Hao, B.; Newbrough, A.; Driscoll, E.; Shields, R.K.; Squires, K.M.; Chu, T.-Y.; et al. Within-host genotypic and phenotypic diversity of contemporaneous carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from blood cultures of patients with bacteremia. mBio 2022, 13, e0290622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, M.; Aihara, M.; Gotoh, Y.; Akimoto, M.; Tatsuhara, W.; Kiyosuke, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Uchiumi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Kang, D. Stepwise evolution of a Klebsiella pneumoniae clone within a host leading to increased multidrug resistance. mSphere 2021, 6, e0073421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafiz, T.A.; Alanazi, S.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Mubaraki, M.A.; Aljabr, W.; Madkhali, N.; Alharbi, S.R.; Binkhamis, K.; Alotaibi, F. Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteraemia epidemiology, resistance profiles and clinical outcome of King Fahad Medical City isolates, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzon, G.; Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Functional characterization of Tn4401, a Tn3-based transposon involved in blaKPC gene mobilization. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5370–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budia-Silva, M.; Kostyanev, T.; Ayala-Montaño, S.; Acosta, J.B.-F.; Garcia-Castillo, M.; Cantón, R.; Goossens, H.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Grundmann, H.; Reuter, S. International and regional spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Su, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, M. The pivotal role of IncFIB(Mar) plasmid in the emergence and spread of hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci Adv. 2025, 11, eado9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Chan, E.W.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Functional characterization of plasmid-borne rmpADC homologues in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0308122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryfinopoulou, K.; Linkevicius, M.; Pappa, O.; Alm, E.; Karadimas, K.; Svartström, O.; Polemis, M.; Mellou, K.; Maragkos, A.; Brolund, A.; et al. Emergence and persistent spread of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae high-risk clones in Greek hospitals, 2013 to 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2300571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souli, M.; Galani, I.; Antoniadou, A.; Papadomichelakis, E.; Poulakou, G.; Panagea, T.; Vourli, S.; Zerva, L.; Armaganidis, A.; Kanellakopoulou, K.; et al. An outbreak of infection due to beta-Lactamase Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase 2-producing K. pneumoniae in a Greek University Hospital: Molecular characterization, epidemiology, and outcomes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatopoulos, A. High rates of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Greece: A review of the current evidence. Eurosurveillance 2008, 13, 8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakkoupi, P.; Maltezou, H.; Polemis, M.; Pappa, O.; Saroglou, G.; Vatopoulos, A.; The Greek System for the Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance Collective. KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in Greek hospitals are mainly due to a hyperepidemic clone. Eurosurveillance 2009, 14, 19218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakidou, P.; Kyriazidi, M.A.; Varlamis, S.; Chatzopoulou, F.; Frydas, I.; Kyriazidis, K.A.; Kalinderi, K.; Mitka, S.; Skepastianos, P.; Chatzidimitriou, M. NDM-1 and VIM-1 dual metallo-β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15 high-risk clone from a blood culture of a patient at intensive care unit in a Greek tertiary care hospital. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2025, 72, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidimitriou, M.; Tsolakidou, P.; Panagiota, C.; Mylona, E.; Mitka, S. KPC-2 and VIM-1 producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST39 high-risk clone isolated from a clinical sample in Volos, Greece. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2024, 71, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidimitriou, M.; Tsolakidou, P.; Kyriazidi, M.A.; Chatzopoulou, F.; Varlamis, S.; Mavridou, M.; Kalinderi, K.; Kyriazidis, K.A.; Mitka, S. Identification of NDM-1 producing and colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11: A highly drug-resistant strain detected in intensive care unit of a Greek tertiary care hospital. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2025, 72, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Carbapenem- and/or Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Greece: Molecular Follow-Up Survey 2022; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Protonotariou, E.; Meletis, G.; Pilalas, D.; Mantzana, P.; Tychala, A.; Kotzamanidis, C.; Papadopoulou, D.; Papadopoulos, T.; Polemis, M.; Metallidis, S.; et al. Polyclonal endemicity of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in ICUs of a Greek tertiary care hospital. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, M.; Di Pilato, V.; Riccobono, E.; Giachi, F.; Pupillo, F.; Lanzafame, M.; Meini, S.; Antonelli, A.; Rossolini, G.M. Intra-hospital acquisition of colonization and infection by Klebsiella pneumoniae strains producing carbapenemases and carriage evolution: A longitudinal analysis in an Italian teaching hospital from January 2017 to August 2019. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Ye, Y.; Sai, F.; Huang, H. Intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: Risk factors and prediction model of mortality. Medicine 2023, 102, e33269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, C.; Xu, S.; et al. Expanding of ST11 Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Subclones in a Chinese Hospital, Shenzhen, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, L.; Chavda, K.D.; Melano, R.G.; Jacobs, M.R.; Levi, M.H.; Bonomo, R.A.; Kreiswirth, B.N. Complete sequence of a blaKPC-2-harboring IncFII(K1) plasmid from a Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 strain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1542–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirano, G.; Bradford, P.A.; Kazmierczak, K.M.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Pitout, J.D. Importance of clonal complex 258 and IncFK2-like plasmids among a global collection of Klebsiella pneumoniae with blaKPC. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02610-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.W.; Mustapha, M.M.; Griffith, M.P.; Evans, D.R.; Ezeonwuka, C.; Pasculle, A.W.; Shutt, K.A.; Sundermann, A.; Ayres, A.M.; Shields, R.K.; et al. Evolution of outbreak-causing carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 at a tertiary care hospital over 8 years. mBio 2019, 10, e01945-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Li, P.; Yu, W.; Chu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Kang, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; et al. Clinical imipenem non-susceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from China: Epidemiology, molecular characterization and in vitro activity of imipenem/relebactam. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2025, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galani, I.; Karaiskos, I.; Karantani, I.; Papoutsaki, V.; Maraki, S.; Papaioannou, V.; Kazila, P.; Tsorlini, H.; Charalampaki, N.; Toutouza, M.; et al. Epidemiology and resistance phenotypes of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Greece, 2014 to 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1700775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, S.; Lu, Y.J.; Tohya, M.; Watanabe, S.; Misawa, S.; Tabe, Y.; Miida, T.; Mya, S.; Tin, H.H.; Tada, T.; et al. Spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates producing NDM-type metallo-β-lactamase in Myanmar. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0067322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.; Wyres, K.L.; Duchêne, S.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gan, Y.-H.; Hoh, C.-H.; Archuleta, S.; Molton, J.S.; Kalimuddin, S.; et al. Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaiskos, I.; Daikos, G.L.; Gkoufa, A.; Adamis, G.; Stefos, A.; Symbardi, S.; Chrysos, G.; Filiou, E.; Basoulis, D.; Mouloudi, E.; et al. Ceftazidime/avibactam in the era of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Experience from a national registry study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Chen, R.; Li, C.; Liu, R.; Shen, Y.; Guo, X.; Sun, J. The association between the genetic structures of commonly incompatible plasmids in Gram-negative bacteria, their distribution and the resistance genes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1472876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, D.; Hou, Q.; Li, G.; Han, H. Genomic epidemiology and anti-biofilm mechanisms of Lactobacillus in ST11 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1619621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Slotta, D.J.; Tolstoy, I.; Tyson, G.H.; Zhao, S.; Hsu, C.H.; McDermott, P.F.; et al. Validating the AMR Finder tool and resistance gene database by using antimicrobial resistance genotype-phenotype correlations in a collection of isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00483-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, T.H.; Ayuni, N.N.; Yin, M.; Liew, J.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Kurepina, N.; Chen, L.; Bifani, P. Differential mucosal tropism and dissemination of classical and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. iScience 2024, 27, 108875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Kapoor, A.; Sinha, A.; Manoharan, S. Virulence factors of Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into canonical and emerging mechanisms driving pathogenicity and drug resistance. Microbe 2025, 7, 100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Huang, W.; Lalsiamthara, J.; Ullah, S.; Xu, Y.; Lu, A. Exploring current hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae infections: Insights into pathogenesis, drug resistance, and vaccine prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1604763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, M.J.; Findlay, J.; Hopkins, K.L.; Meunier, D.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Horner, C.; McEwan, A.; Guiver, M.; McCrae, L.X.; Woodford, N.; et al. Multicentre evaluation of a real-time PCR assay to detect genes encoding clinically relevant carbapenemases in cultured bacteria. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Isolate | MLST | AMR Genes | Center for Genomic Epidemiology—DTU-Predicted Resistance Phenotypes |
|---|---|---|---|
| INT18S | ST258 | aac(6′)-Ib, aac(6′)-Ibcr, fosA6, OqxA, OqxB, aadA2, aph(3′)-Ia, blaKPC-2, blaSHV-12, catA1, dfrA12, qacE, sul1, mph(A) | Amikacin, Tobramycin, Netilmicin, Fluoroquinolones, Amoxicillin, Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid, Ampicillin, Ampicillin/Clavulanic Acid, Aztreonam, Cefepime, Cefotaxime, Cefoxitin, Ceftazidime, Ertapenem, Imipenem, Meropenem, Piperacillin, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Ticarcillin, Ceftriaxone, Chloramphenicol, Trimethoprim, Fosfomycin, Nalidixic Acid, Streptomycin, Neomycin, Kanamycin, Ticarcillin/Clavulanic Acid, Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Sulfamethoxazole |
| INT20U | ST11 | aac(6′)-Ib, aac(6′)-Ibcr, fosA6, OqxA, OqxB, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, blaCTXM-15, blaNDM-1, blaOXA-1, blaSHV-182, catB3, dfrA14 | Amikacin, Tobramycin, Netilmicin, Fluoroquinolones, Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Aztreonam, Cefepime, Cefotaxime, Ceftazidime, Ceftriaxone, Piperacillin, Ticarcillin, Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid, Ampicillin/Clavulanic Acid, Cefoxitin, Ertapenem, Imipenem, Meropenem, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Chloramphenicol, Trimethoprim, Fosfomycin, Nalidixic Acid, Cefixime, Temocillin |
| INT18S | INT20U | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic | MIC (mg/L) | Interpretation | MIC (mg/L) | Interpretation |
| Amikacin | >16 | R | >16 | R |
| Amoxicillin/Clavulanate | >8/4 | R | >8/4 | R |
| Ampicillin | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Aztreonam | >4 | R | >4 | R |
| Cefepime | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Cefotaxime | >16 | R | >16 | R |
| Cefoxitin | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Ceftazidime | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Cefuroxime | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Chloramphenicol | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Ciprofloxacin | >1 | R | >1 | R |
| Colistin | ≤2 | S | ≤2 | S |
| Ertapenem | >1 | R | >1 | R |
| Gentamicin | ≤2 | S | >4 | R |
| Imipenem | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Levofloxacin | >1 | R | >1 | R |
| Meropenem | >8 | R | >8 | R |
| Nalidixic Acid | >16 | R | >16 | R |
| Nitrofurantoin | >64 | R | >64 | R |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | >16 | R | >16 | R |
| Tigecycline | 2 | S | 2 | S |
| Tobramycin | >4 | R | >4 | R |
| Trimethoprim/ Sulfamethoxazole | >4/76 | R | >4/76 | R |
| Aztreonam/Avibactam | 0.19 | S | 0.25 | S |
| Ceftazidime/Avibactam | 0.75 | S | 32 | R |
| Imipenem/Relebactam | 0.75 | S | 16 | R |
| Meropenem/Vaborbactam | 0.50 | S | 32 | R |
| Plasmid Type | Relaxase Type | MPF Type | Predicted Mobility | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INT18S | ColRNAI, ColRNAI, ColRNAI, IncFIB(K), IncFIB(pQil), IncX3 | MOBC, MOBF, MOBP | MPF_T | Conjugative |
| INT20U | IncFIA(HI1), IncFIB(K), IncFII(K), IncR | MOBF | MPF_F | Conjugative |
| INT18S | INT20U | |
|---|---|---|
| YbST | 299-1LV | 230-2LV |
| Yersiniabactin Lineage | Ybt13; ICEKp2 | Ybt15; ICEKp11 |
| Alleles | ||
| ybtS | 6 | 6 |
| ybtX | 4 | 15 |
| ybtQ | 20 | 22 |
| ybtP | 14 | 4 |
| ybtA | 1 | 1 |
| irp2 | 220 | 37 |
| irp1 | 131 | 34 |
| ybtU | 2 | 14 |
| ybtT | 4 | 1 |
| ybtE | 52 | 4 |
| fyuA | 2 | 17 |
| TargetGene | Type | Name | Sequence (5′ → 3′) | 5′ Label | 3′ Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KPC | Primer (forward) | KPC_fwd | GCAGCGGCAGCAGTTTGTTGATT | – | – |
| Primer (reverse) | KPC_rev | GTAGACGGCCAACACAATAGGTGC | – | – | |
| Probe | KPC_probe | CAGTCGGAGACAAAACCGGAACCTGC | ROX | BHQ-2 | |
| NDM | Primer (forward) | NDM_fwd | CCAGCAAATGGAAACTGGCGAC | – | – |
| Primer (reverse) | NDM_rev | ATCCAGTTGAGGATCTGGGCG | – | – | |
| Probe (ABI7500) | NDM_probe_ABI7500 | ACCGAATGTCTGGCAGCACACTTC | TAM | BHQ-2 | |
| OXA-48 | Primer (forward) | OXA48_fwd | GATTATGGTAATGAGGACATTTCGGGC | – | – |
| Primer (reverse) | OXA48_rev | CATATCCATATTCATCGCAAAAAACCACAC | – | – | |
| Probe (ABI7500) | OXA48_probe_ABI7500 | CCATTGGCTTCGGTCAGCATGGCTTGTTT | JOE | BHQ-1 | |
| VIM | Primer (forward) | VIM_fwd | TTGCTTTTGATTGATACAGCGTGGGG | – | – |
| Primer (reverse) | VIM_rev | GTACGTTGCCACCCCAGCC | – | – | |
| Probe | VIM_probe | TCTCGCGGAGATTGAAAAGCAAATTGGACTTCC | CY5 | BHQ-3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frydas, I.S.; Kouklakis, E.; Meletis, G.; Malousi, A.; Kyriazidi, M.A.; Chatzopoulou, F.; Amargianitaki, I.; Kalinderi, K.; Mavridou, M.; Mitka, S.; et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Two High-Risk Klebsiella pneumoniae Clones (ST258-blaKPC-2 and ST11-blaNDM-1) from a Greek Tertiary Hospital. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111146
Frydas IS, Kouklakis E, Meletis G, Malousi A, Kyriazidi MA, Chatzopoulou F, Amargianitaki I, Kalinderi K, Mavridou M, Mitka S, et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Two High-Risk Klebsiella pneumoniae Clones (ST258-blaKPC-2 and ST11-blaNDM-1) from a Greek Tertiary Hospital. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111146
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrydas, Ilias S., Emmanouil Kouklakis, Georgios Meletis, Andigoni Malousi, Maria Anna Kyriazidi, Fani Chatzopoulou, Irini Amargianitaki, Kallirhoe Kalinderi, Maria Mavridou, Stella Mitka, and et al. 2025. "Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Two High-Risk Klebsiella pneumoniae Clones (ST258-blaKPC-2 and ST11-blaNDM-1) from a Greek Tertiary Hospital" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111146
APA StyleFrydas, I. S., Kouklakis, E., Meletis, G., Malousi, A., Kyriazidi, M. A., Chatzopoulou, F., Amargianitaki, I., Kalinderi, K., Mavridou, M., Mitka, S., Panagiotaki, E., & Chatzidimitriou, M. (2025). Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Two High-Risk Klebsiella pneumoniae Clones (ST258-blaKPC-2 and ST11-blaNDM-1) from a Greek Tertiary Hospital. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111146








