Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Pathogens Among Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Persistent Threat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Population
4.2. Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UTI | Urinary tract infection |
| TMP-SMX | trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole |
| ESBL | Extended spectrum beta lactamase |
| KPC | Carbapenemase |
References
- Adamska, Z.; Karczewski, M.; Cichanska, L.; Wieckowska, B.; Malkiewicz, T.; Mahadea, D.; Stronka, M. Bacterial infections in renal transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, O.; Yildirim, M.; Kucuk, H.F.; Gencer, S.; Demir, T. Infections in renal transplant patients: Risk factors and infectious agents. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchera, B.; Trucillo, E.; D’Agostino, A.; Gentile, I. Urinary Tract Infections in Kidney Transplant Patients: An Open Challenge-Update on Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Management. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chacón-Mora, N.; Pachón Díaz, J.; Cordero Matía, E. Urinary tract infection in kidney transplant recipients. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, P.; Braß, P.; Jäger, J.; Jacquet, L.; Jansen, S.; Gäckler, A.; Jürgens, C.; Reinold, J.; Eisenberger, U.; Rath, P.M.; et al. Antibiotic resistance of urinary pathogens after kidney transplantation: A 10-year single-center survey in Germany. Infection 2025, 53, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- So, M.; Walti, L. Challenges of Antimicrobial Resistance and Stewardship in Solid Organ Transplant Patients. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 24, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rostkowska, O.M.; Kuthan, R.; Burban, A.; Salińska, J.; Ciebiera, M.; Młynarczyk, G.; Durlik, M. Analysis of Susceptibility to Selected Antibiotics in Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium Causing Urinary Tract Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients over 8 Years: Single-Center Study. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shapouri Moghaddam, A.; Arfaatabar, M.; Tavakol Afshari, J.; Shakerimoghaddam, A.; Mohammadzamani, Z.; Khaledi, A. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacterial Uropathogens Isolated from Iranian Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran. J. Public Health 2019, 48, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Korth, J.; Kukalla, J.; Rath, P.M.; Dolff, S.; Krull, M.; Guberina, H.; Bienholz, A.; Wilde, B.; Becker, S.; Ross, B.; et al. Increased resistance of gram-negative urinary pathogens after kidney transplantation. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memikoğlu, K.O.; Keven, K.; Sengül, S.; Soypaçaci, Z.; Ertürk, S.; Erbay, B. Urinary tract infections following renal transplantation: A single-center experience. Transplant. Proc. 2007, 39, 3131–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veroux, M.; Giuffrida, G.; Corona, D.; Gagliano, M.; Scriffignano, V.; Vizcarra, D.; Tallarita, T.; Zerbo, D.; Virgilio, C.; Sciacca, A.; et al. Infective complications in renal allograft recipients: Epidemiology and outcome. Transplant. Proc. 2008, 40, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, P.; Parikh, C.R.; Langone, A. Urinary tract infections after renal transplantation: A retrospective review at two US transplant centers. Clin. Transplant. 2005, 19, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, A.D.; Abasi Montazeri, E.; Ghorbani, A.; Parhizgari, N. Bacterial urinary tract infection in renal transplant recipients and their antibiotic resistance pattern: A four-year study. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hooton, T.M. Uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 235–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azap, Ö.; Togan, T.; Yesilkaya, A.; Arslan, H.; Haberal, M. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of uropathogen Escherichia coli in renal transplant recipients: Dramatic increase in ciprofloxacin resistance. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 956–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanipour, A.; Dashti-Khavidaki, S.; Abbasi, M.R.; Abdollahi, A. Antibiotic resistance patterns of microorganisms isolated from nephrology and kidney transplant wards of a referral academic hospital. J. Res. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, S.S.; Arslan, H.; Azap, O.K.; Timurkaynak, F.; Cağir, U.; Haberal, M. Urinary tract infections in renal transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2007, 39, 1016–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadban, S.J.; Ahn, C.; Axelrod, D.A.; Foster, B.J.; Kasiske, B.L.; Kher, V.; Kumar, D.; Oberbauer, R.; Pascual, J.; Pilmore, H.L.; et al. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Candidates for Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2020, 104 (Suppl. S1), S11–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.D.; Julian, K. Urinary tract infections in solid organ transplant recipients: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promsuwan, O.; Malathum, K.; Ingsathit, A. Epidemiology of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales infection in kidney transplant recipients. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2023, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ben-Ami, R.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Arslan, H.; Pitout, J.D.; Quentin, C.; Calbo, E.S.; Azap, O.K.; Arpin, C.; Pascual, A.; Livermore, D.M.; et al. A multinational survey of risk factors for infection with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing enterobacteriaceae in nonhospitalized patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, S.F.; Eidgahi, E.S.; Lotfi, Z.; Khaledi, A.; Shakeri, S.; Sheikhi, M.; Bahrami, A. Urinary tract infections in kidney transplant recipients 1st year after transplantation. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bodro, M.; Sanclemente, G.; Lipperheide, I.; Allali, M.; Marco, F.; Bosch, J.; Cofan, F.; Ricart, M.J.; Esforzado, N.; Oppenheimer, F.; et al. Impact of antibiotic resistance on the development of recurrent and relapsing symptomatic urinary tract infection in kidney recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas-Frenette, C.; Dorais, M.; Tavares-Brum, A.; Frenette, C.; Yang, B.; Medani, S.; Duclos, A.; Rouleau, D.; Mawad, H.; Barama, A.; et al. Epidemiology and outcome of antimicrobial resistance to gram-negative pathogens in bacteriuric kidney transplant recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, e12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antibiogram Interpretation Criteria and Restricted Reporting Rules. National Microbiology Standards. Ministry of Health of the Republic of Turkey; KLIMUD: Ankara, Turkey, May 2019 (printed and online version). Çağhan Offset Printing Co. Ltd. Available online: https://www.klimud.org/uploads/content/Antibiyotik%20Duyarl%C4%B1l%C4%B1k%20Verilerinin%20Analizi%20ve%20Sunumu%20RRehberi.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. EUCAST, Version 10.0; Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters; The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
| Uropathogens | Number of Strains | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | 176 | 49 |
| Klebsiella spp. | 88 | 24 |
| Enterococcus spp. | 23 | 6 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 9 | 2 |
| Staphylococcus spp. 1 | 7 | 2 |
| Enterobacter spp. | 7 | 2 |
| Proteus spp. | 6 | 2 |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 6 | 2 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 4 | 1 |
| Candida spp. | 12 | 3 |
| Others 2 | 25 | 7 |
| Total | 363 | 100 |
| Uropathogens | CIP (%) | ERT (%) | GEN (%) | TMP-SMX (%) | ESBL (%) | KPC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||||
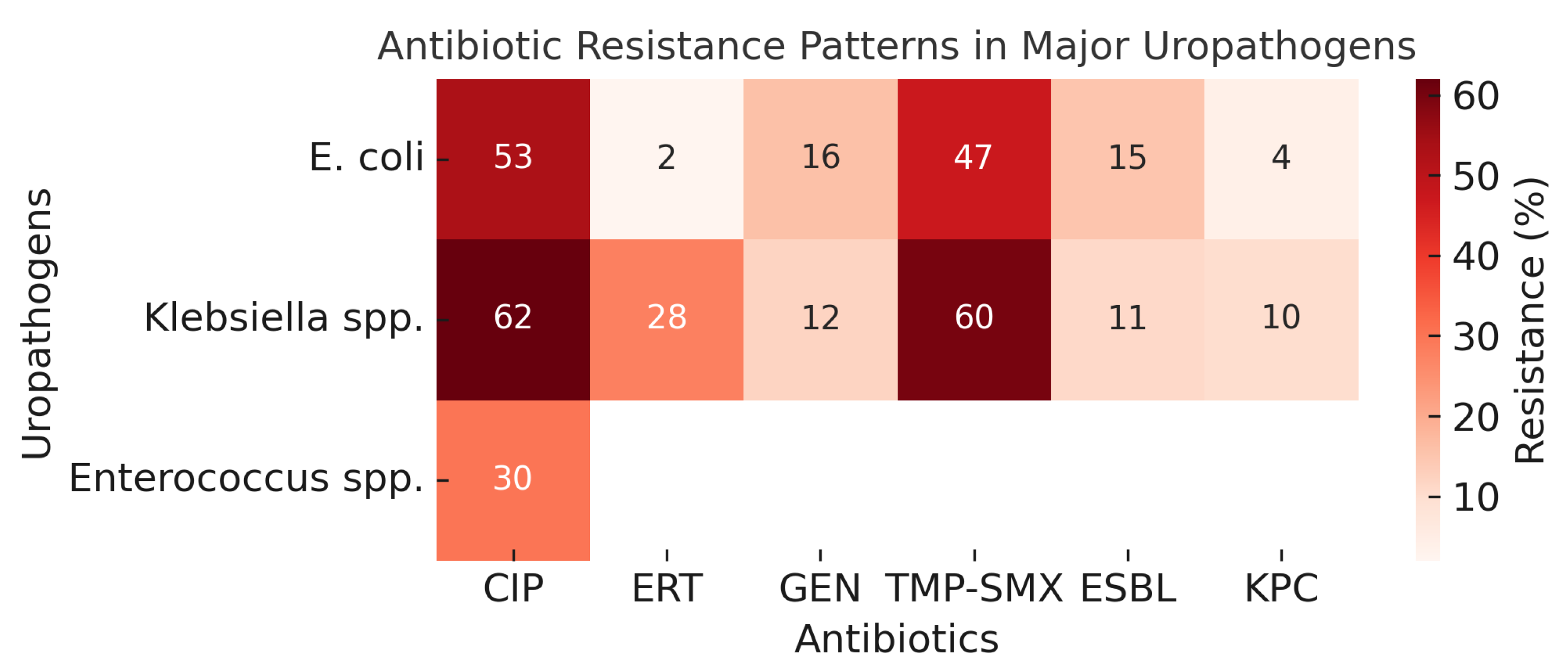
| E. coli (n = 176) | 53 | 2 | 16 | 47 | 15 | 4 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 88) | 62 | 28 | 12 | 60 | 11 | 10 |
| Enterobacter spp. (n = 7) | 29 | 14 | 0 | 29 | - | - |
| Proteus spp. (n = 6) | 67 | 0 | 50 | 83 | - | - |
| Acinetobacter spp. (n = 6) | 100 | 100 | 67 | 67 | - | - |
| P. aeruginosa (n = 4) | 75 | 100 | - | - | - | - |
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||||
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 23) | 30 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Staphylococcus spp. (n = 9) | 71 | - | 14 | 29 | - | - |
| Uropathogens | Rate (%) | CIP (%) | ERT (%) | GEN (%) | TMP-SMX (%) | ESBL (%) | KPC (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n = 58) | E. coli (n = 20) | 35 | 75 | 0 | 20 | 75 | 5 | 0 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 18) | 31 | 94 | 61 | 50 | 94 | 17 | 17 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 8) | 25 | 29 | ||||||
| Female (n = 305) | E. coli (n = 160) | 52 | 51 | 3 | 18 | 44 | 16 | 4 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 69) | 23 | 54 | 20 | 3 | 52 | 10 | 9 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 16) | 5 | 31 |
| Uropathogens | Rate (%) | CIP (%) | ERT (%) | GEN (%) | TMP-SMX (%) | ESBL (%) | KPC (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deceased Donor (n = 154) | E. coli (n = 64) | 42 | 56 | 3 | 19 | 52 | 17 | 2 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 54) | 35 | 70 | 28 | 17 | 67 | 9 | 9 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 10) | 7 | 60 | ||||||
| Living Donor (n = 209) | E. coli (n = 115) | 55 | 53 | 2 | 17 | 46 | 13 | 5 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 34) | 16 | 50 | 29 | 6 | 50 | 15 | 12 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 13) | 6 | 15 |
| Uropathogens | Rate (%) | CIP (%) | ERT (%) | GEN (%) | TMP-SMX (%) | ESBL (%) | KPC (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤50 age (n = 196) | E. coli (n = 100) | 51 | 56 | 3 | 13 | 38 | 14 | 5 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 49) | 25 | 65 | 33 | 6 | 63 | 14 | 14 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 13) | 7 | 31 | ||||||
| >50 age (n = 166) | E. coli (n = 80) | 48 | 53 | 1 | 24 | 60 | 15 | 3 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 39) | 24 | 59 | 23 | 21 | 56 | 8 | 5 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 10) | 6 | 40 |
| Uropathogens | Rate (%) | CIP (%) | ERT (%) | GEN (%) | TMP-SMX (%) | ESBL (%) | KPC (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First year (n = 58) | E. coli (n = 24) | 41 | 63 | 8 | 42 | 92 | 13 | 8 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 16) | 28 | 94 | 44 | 63 | 100 | 13 | 6 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 7) | 12 | 43 | ||||||
| 2–28 years (n = 301) | E. coli (n = 155) | 52 | 54 | 1 | 14 | 42 | 8 | 2 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 72) | 24 | 56 | 25 | 1 | 51 | 11 | 11 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 16) | 5 | 27 |
| Uropathogens | Rate (%) | CIP (%) | ERT (%) | GEN (%) | TMP-SMX (%) | ESBL (%) | KPC (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Single
infections (n = 35) | E. coli (n = 20) | 57 | 35 | 5 | 0 | 30 | 25 | 10 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 5) | 14 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 20 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 3) | 9 | 0 | ||||||
| Recurrent infections (n = 327) | E. coli (n = 160) | 49 | 57 | 2 | 20 | 50 | 13 | 3 |
| Klebsiella spp. (n = 83) | 25 | 64 | 28 | 13 | 63 | 11 | 10 | |
| Enterococcus spp. (n = 20) | 6 | 37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çalışır, B.; Çalışır, A.İ.; Rodoplu, O.; Yıldız, A.; Ersoy, A.; Özakın, C. Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Pathogens Among Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Persistent Threat. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111135
Çalışır B, Çalışır Aİ, Rodoplu O, Yıldız A, Ersoy A, Özakın C. Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Pathogens Among Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Persistent Threat. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111135
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇalışır, Büşra, Abdullah İbrahim Çalışır, Oktay Rodoplu, Abdulmecit Yıldız, Alparslan Ersoy, and Cüneyt Özakın. 2025. "Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Pathogens Among Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Persistent Threat" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111135
APA StyleÇalışır, B., Çalışır, A. İ., Rodoplu, O., Yıldız, A., Ersoy, A., & Özakın, C. (2025). Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Pathogens Among Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Persistent Threat. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111135







