Repurposing MK-8245 as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor to Suppress Virulence and Potentiate Antibiotic Activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Screening of Candidate Compounds for Inhibition of the Rhl Quorum Sensing Pathway
2.2. MK-8245 Interacts with RhlR and Reduces QS Signal Molecule Production Without Affecting Growth
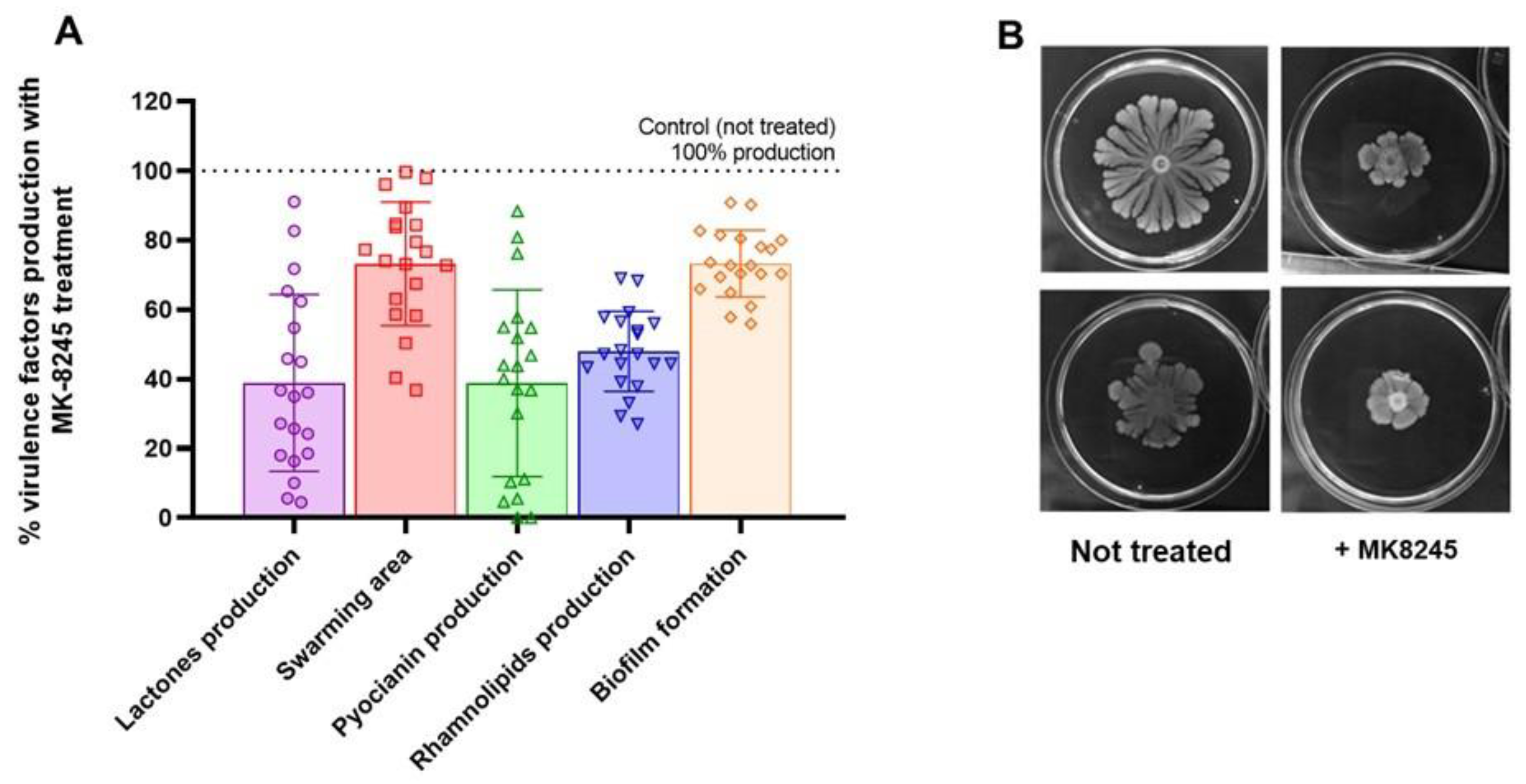
2.3. MK-8245 Reduces Virulence-Associated Factor in P. aeruginosa PAO1
2.4. MK-8245 Inhibits Biofilm Formation and Enhances Antibiotic Activity Against Pre-Formed Biofilms
2.5. MK-8245 Improves Survival in the Galleria mellonella Infection Model
2.6. MK-8245 Reduces Virulence Factor Production in Clinical P. aeruginosa Isolates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Clinical Isolates
4.3. Compound Selection
4.4. RNA Isolation and Gene Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
4.5. Growth Inhibition Assay
4.6. Quorum Sensing Biosensor Assays
4.7. Effect of MK-8245 on Biofilm Development and Established Biofilms
- (i)
- At inoculation, to evaluate effects on biofilm development;
- (ii)
- After 24 h of incubation, to evaluate effects on pre-formed biofilms.
4.8. In Vivo Assays Using Galleria mellonella
4.9. Virulence Factor Assays
4.9.1. Pyocyanin Production
4.9.2. Swarming Motility
4.9.3. Rhamnolipid Production
4.9.4. Lactone Production (AHLs)
4.10. Data Management and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, N.-H.; Jang, K.-M.; Jin, H.; Shin, K.; Jeong, B.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, S.H. Prioritization of Critical Factors for Surveillance of the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, S.; Le Gouellec, A.; Bleves, S. What Is New in the Anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Development Pipeline Since the 2017 WHO Alert? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 909731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breidenstein, E.B.M.; de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Hancock, R.E.W. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: All roads lead to resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024-Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461 (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- ECDC. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe; ECDC: Solna, Schweden, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacchini, S.; Boros, S.; Pezzotti, P.; Caramia, A.; Errico, G.; Del Grosso, M.; Camilli, R.; Giufrè, M.; Pantosti, A.; Maraglino, F.; et al. AR-ISS: Sorveglianza nazionale dell’Antibiotico-Resistenza. Dati 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.iss.it (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Qin, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, C.; Pu, Q.; Deng, X.; Lan, L.; Liang, H.; Song, X.; Wu, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, L. The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, M.C.; de Oliveira Pereira, T.; Groleau, M.C.; Hoffman, L.R.; Dandekar, A.A.; Déziel, E. “The end of the reign of a master regulator’’? A defect in function of the LasR quorum sensing regulator is a common feature of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. mBio 2024, 15, e0237623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.L.; Asfahl, K.L.; Van den Bossche, S.; Coenye, T.; Crabbé, A.; Dandekar, A.A. RhlR-Regulated Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Quorum Sensing in a Cystic Fibrosis Isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2020, 11, e00532-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanek, K.A.; Schumacher, M.L.; Mallery, C.P.; Shen, S.; Li, L.; Paczkowski, J.E. Quorum-sensing synthase mutations re-calibrate autoinducer concentrations in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to enhance pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbanipour, R.; Ghalavand, Z. Anti-virulence therapeutic strategies against bacterial infections: Recent advances. Germs 2022, 12, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Yue, Y.; Wei, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, J. Research Progress on the Combination of Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors and Antibiotics against Bacterial Resistance. Molecules 2024, 29, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ANgelo, F.; Baldelli, V.; Halliday, N.; Pantalone, P.; Polticelli, F.; Fiscarelli, E.; Williams, P.; Visca, P.; Leoni, L.; Rampioni, G. Identification of FDA-Approved Drugs as Antivirulence Agents Targeting the pqs Quorum-Sensing System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01296-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Chadha, J.; Khullar, L.; Rashpa, S.; Harjai, K. FDA-approved drugs for targeting virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A drug repurposing approach to combat multidrug resistance. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 206, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabè, G.; Marzaro, G.; Di Pietra, G.; Otero, A.; Bellato, M.; Pauletto, A.; Scarpa, M.; Sut, S.; Chilin, A.; Dall’aCqua, S.; et al. A novel phenolic derivative inhibits AHL-dependent quorum sensing signaling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 996871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró-Canturri, A.; Ayerbe-Algaba, R.; Smani, Y. Drug Repurposing for the Treatment of Bacterial and Fungal Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburn, T.T.; Thor, K.B. Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Nassar, M.S.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bendary, M.M. Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, M.T.; Abbas, H.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Yehia, F.A.-Z.A. Synergistic Benefits: Exploring the Anti-Virulence Effects of Metformin/Vildagliptin Antidiabetic Combination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Controlling Quorum Sensing Systems. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Darwish, K.M.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ali, M.A.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. Hiring of the Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Hypoglycemic Agent Linagliptin to Alleviate the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pathogenesis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Ham, S.-Y.; Nam, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, H.-D.; Byun, Y. Recent Advance in Small Molecules Targeting RhlR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Contreras, R.; Maeda, T.; Wood, T.K. Resistance to quorum-quenching compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6840–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.F. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 276–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lifestyle: A Paradigm for Adaptation, Survival, and Persistence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackman, G.; Coenye, T. Quorum sensing inhibitors as anti-biofilm agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldelli, V.; D’aNgelo, F.; Pavoncello, V.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Visca, P.; Rampioni, G.; Leoni, L. Identification of FDA-approved antivirulence drugs targeting the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing effector protein PqsE. Virulence 2020, 11, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellini, M.; Letizia, M.; Caruso, L.; Guiducci, A.; Meneghini, C.; Heeb, S.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M.; Visca, P.; Imperi, F.; et al. RsaL-driven negative regulation promotes heterogeneity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. mBio 2023, 14, e02039-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KAsfahl, L.; Smalley, N.E.; Chang, A.P.; Dandekar, A.A. Genetic and Transcriptomic Characteristics of RhlR-Dependent Quorum Sensing in Cystic Fibrosis Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mSystems 2022, 7, e0011322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltner, J.B.; Wolter, D.J.; E Pope, C.; Groleau, M.-C.; E Smalley, N.; Greenberg, E.P.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Burns, J.; Déziel, E.; Hoffman, L.R.; et al. LasR Variant Cystic Fibrosis Isolates Reveal an Adaptable Quorum-Sensing Hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2016, 7, e01513-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Mar Cendra, M.; Torrents, E. Differential adaptability between reference strains and clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa into the lung epithelium intracellular lifestyle. Virulence 2020, 11, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, O.K.; Islam, I.; Saha, O.; Rahaman, M.; Sultana, M.; Bockmühl, D.P.; Hossain, M.A. Genomic variability correlates with biofilm phenotypes in multidrug resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplantier, M.; Lohou, E.; Sonnet, P. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors to Quench P. aeruginosa Pathogenicity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touati, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Tighilt, L.; Idres, T. Anti-QS Strategies Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanek, K.A.; Paczkowski, J.E.; Hardouin, J.; Simanek, K.A.; Paczkowski, J.E. Resistance Is Not Futile: The Role of Quorum Sensing Plasticity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections and Its Link to Intrinsic Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Cheng, J. Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Relationship to Biofilm Development. ACS Symp. Ser. 2019, 1323, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Terabayashi, Y.; Shiroma, A.; Shimoji, M.; Tamotsu, H.; Ashimine, N.; Ohki, S.; Shinzato, M.; Teruya, K.; Satou, K.; et al. First complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Schroeter 1872) Migula 1900 (DSM 50071T), determined using PacBio single-molecule real-time technology. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00932-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, J.M.; Bassler, B.L. Three Parallel Quorum-Sensing Systems Regulate Gene Expression in Vibrio harveyi. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 6902–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.A.; Bassler, B.L. A genetic analysis of the function of LuxO, a two-component response regulator involved in quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, R.; Lemme, A.; Thiel, V.; Schulz, S.; Sztajer, H.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Analysing traces of autoinducer-2 requires standardization of the Vibrio harveyi bioassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellini, M.; Letizia, M.; Leoni, L.; Rampioni, G. Chapter 5 Whole-Cell Biosensors for Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Quorum Sensing Signal Molecules and the Investigation of Quorum Quenching Agents. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 64, 137–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.Y.; Loh, J.M.S.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella infection models for the study of bacterial diseases and for antimicrobial drug testing. Virulence 2016, 7, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, J.; Khullar, L.; Gulati, P.; Chhibber, S.; Harjai, K. Anti-virulence prospects of Metformin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A new dimension to a multifaceted drug. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 183, 106281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Shaldam, M.A. Repurposing metformin as a quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugurlu, A.; Yagci, A.K.; Ulusoy, S.; Aksu, B.; Bosgelmez-Tinaz, G. Phenolic compounds affect production of pyocyanin, swarming motility and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasamiravaka, T.; Vandeputte, O.; Jaziri, M. Procedure for Rhamnolipids Quantification Using Methylene-blue. Bio-Protocol 2016, 6, e1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
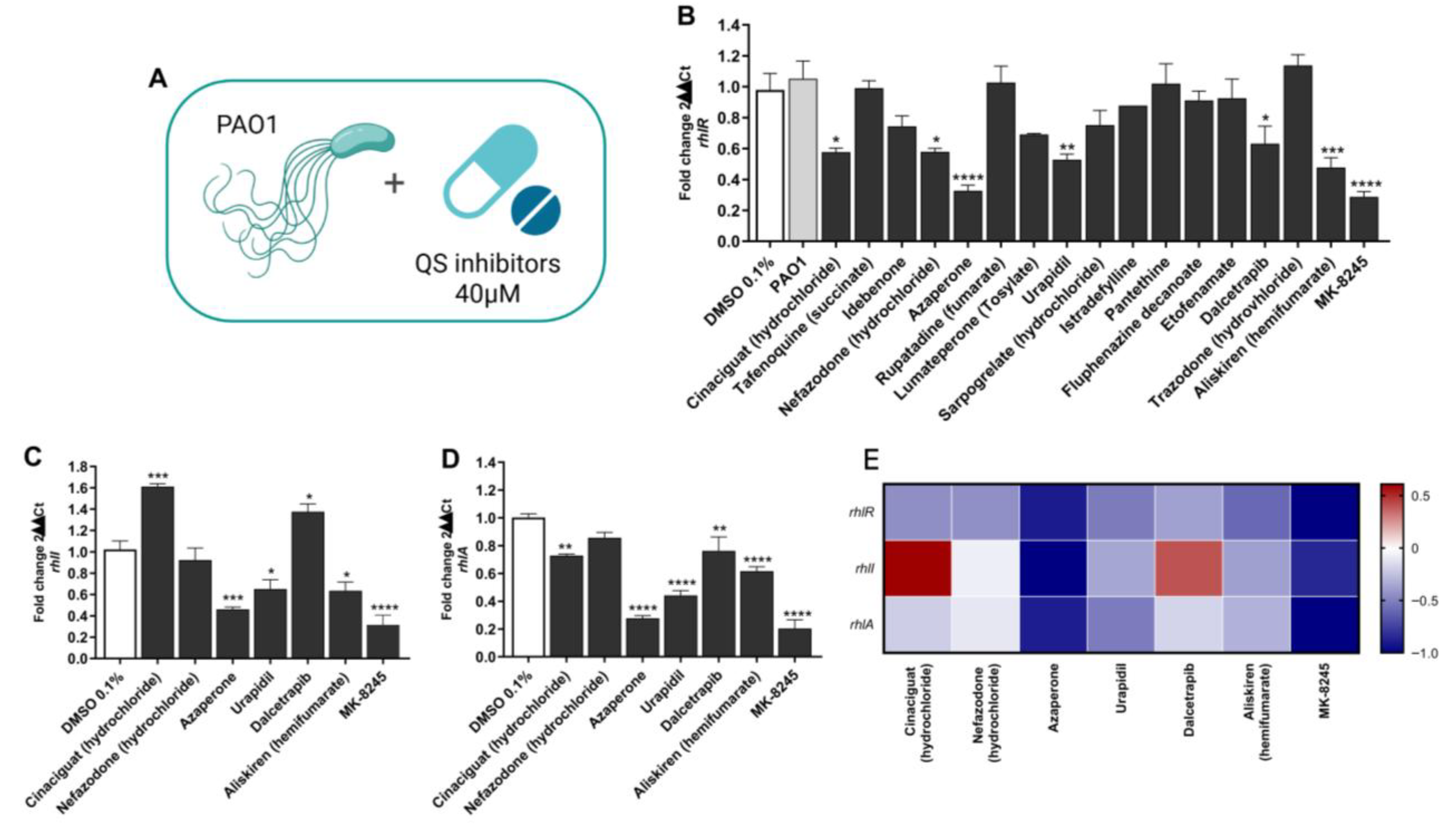
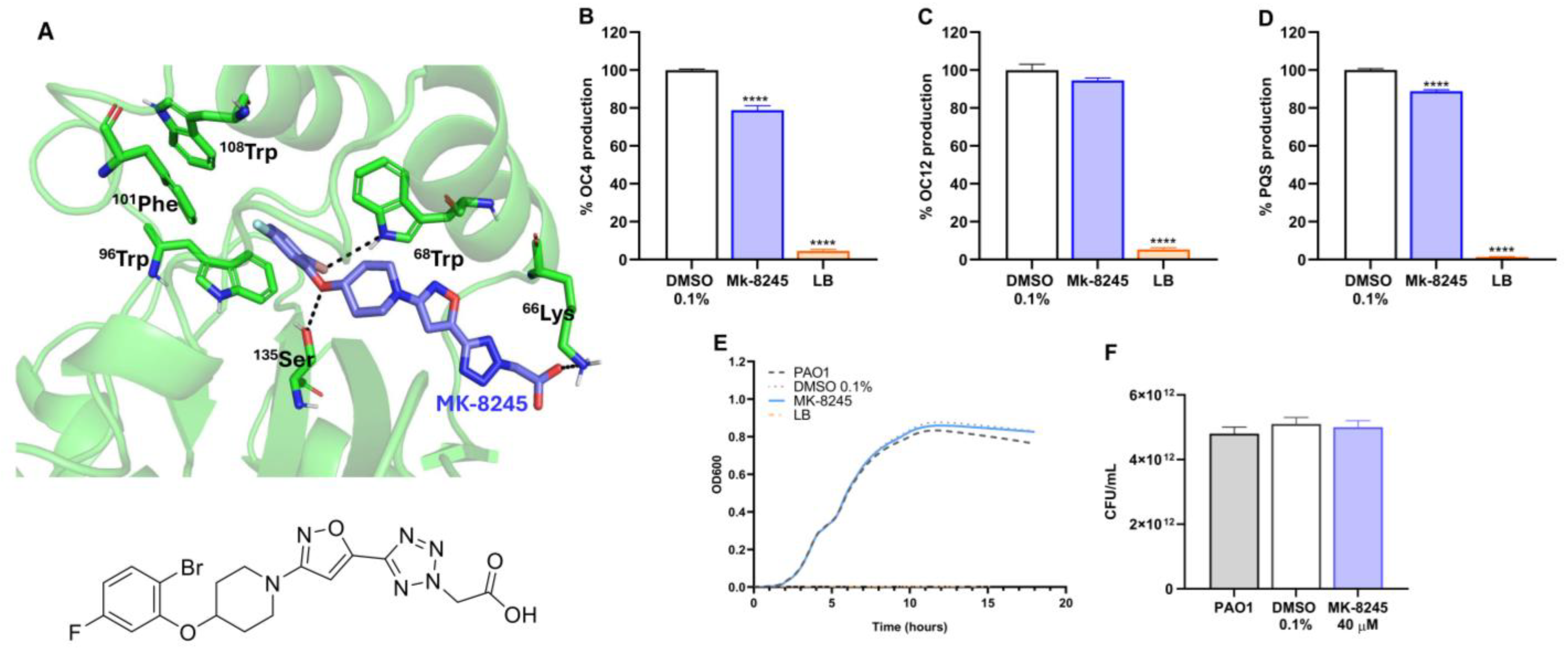

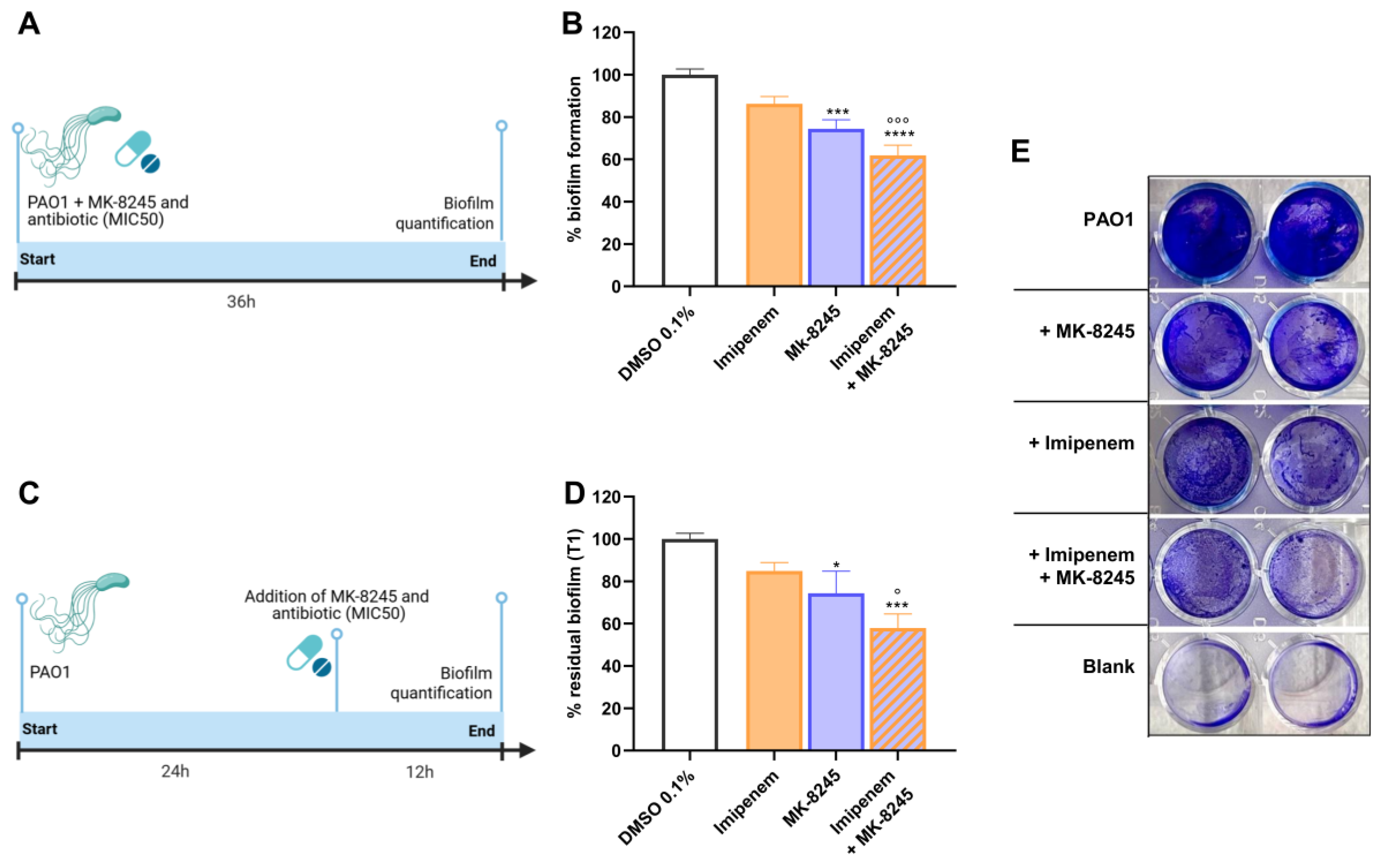
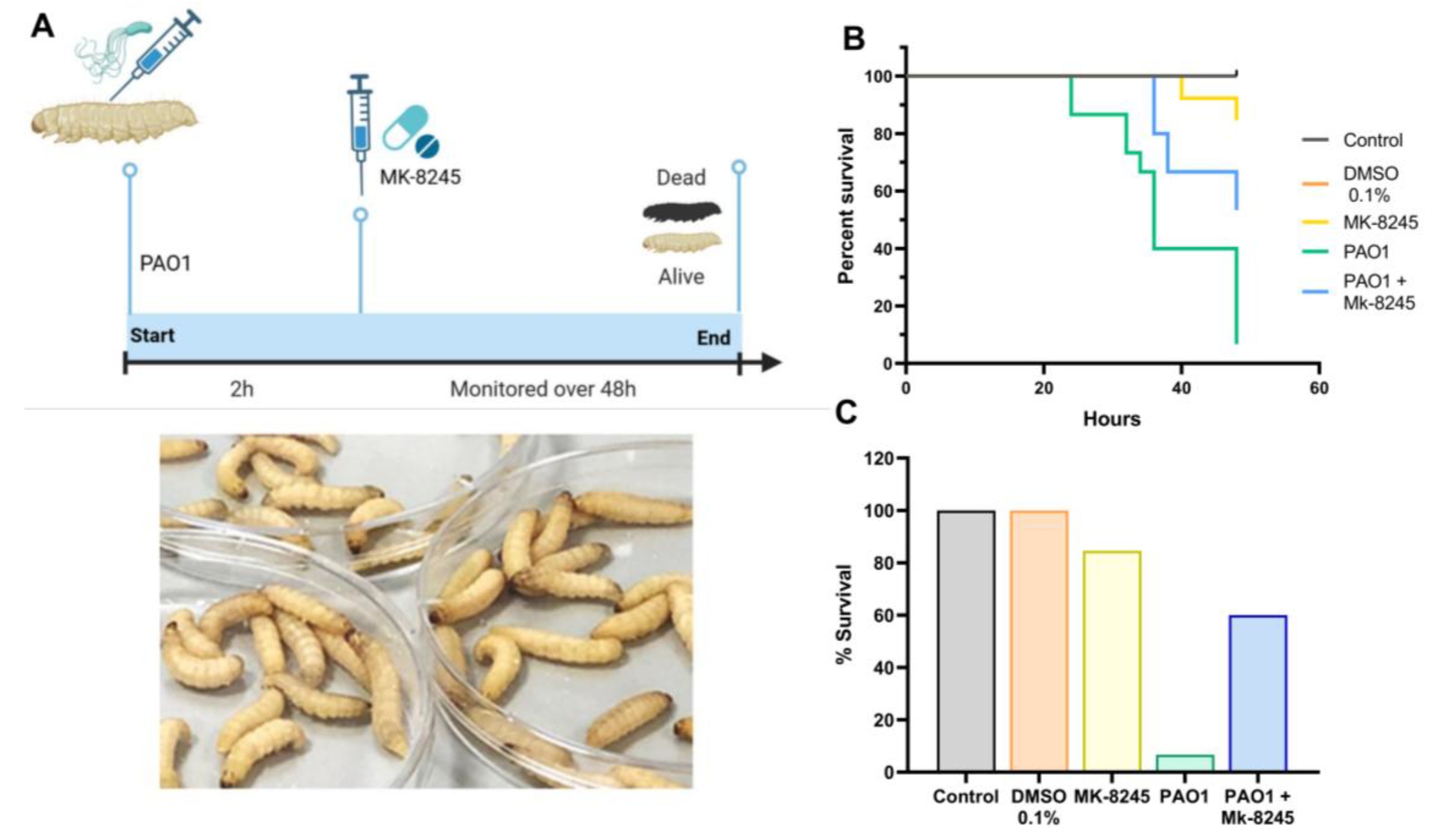
| Product Name | CAS Number | Purity | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cinaciguat | 329773-35-5 | 99.12% | HY14181A |
| Tafenoquine (Succinate) | 106635-81-8 | 98.97% | HY-111529A |
| Idebenone | 58186-27-9 | 99.45% | HY-N0303 |
| Nefazodone (hydrochloride) | 82752-99-6 | 99.03% | HY-B1396 |
| Azaperone | 1649-18-9 | 98.88% | HY-B1470 |
| Rupatadine (Fumarate) | 182349-12-8 | 99.27% | HY-13511A |
| Lumateperone (Tosylate) | 1187020-80-9 | 99.51% | HY-19733 |
| Urapidil | 34661-75-1 | 99.08% | HY-B0716 |
| Sarpogrelate (hydrochloride) | 135159-51-2 | 99.39% | HY-10564 |
| Istradefylline | 155270-99-8 | 98.94% | HY-10888 |
| Pantethine | 16816-67-4 | 99.22% | HY-B1028 |
| Fluphenazine decanoate | 5002-47-1 | 99.36% | HY-B1904 |
| Etofenamate | 30544-47-9 | 99.10% | HY-17361 |
| Dalcetrapib | 211513-37-0 | 98.99% | HY-14950 |
| Trazodone (hydrochloride) | 25332-39-2 | 99.48% | HY-B0478 |
| Aliskiren | 173334-57-1 | 99.05% | HY-12177 |
| MK-8245 | 1030612-90-8 | 99.04% | HY-13070 |
| Gene | Primers Used for qRT-PCR | Annealing Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| proC (HK) | fw 5′-CAGGCCGGGCAGTTGCTGTC-3′ | 60 °C |
| rv 5′-GGTCAGGCGCGAGGCTGTCT-3′ | ||
| rhlI | fw 5′-AAGGACGTCTTCGCCTACCT-3′ | 60 °C |
| rv 5′-GCAGGCTGGACCAGAATATC-3′ | ||
| rhlR | fw 5′-CATCCGATGCTGATGTCCAACC-3′ | 60 °C |
| rv 5′-ATGATGGCGATTTCCCCGGAAC-3′ | ||
| rhlA | fw 5′-TGGCCGAACATTTCAACGT-3′ | 60 °C |
| rv 5′-GATTTCCACCTCGTCGTCCTT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernabè, G.; Marzaro, G.; Shalata, M.E.M.; Iosob, D.; Inglima, V.; Bellato, M.; Castagliuolo, I.; Brun, P. Repurposing MK-8245 as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor to Suppress Virulence and Potentiate Antibiotic Activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111116
Bernabè G, Marzaro G, Shalata MEM, Iosob D, Inglima V, Bellato M, Castagliuolo I, Brun P. Repurposing MK-8245 as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor to Suppress Virulence and Potentiate Antibiotic Activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111116
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernabè, Giulia, Giovanni Marzaro, Mahmoud Elsayed Mosaad Shalata, Daniela Iosob, Valentina Inglima, Massimo Bellato, Ignazio Castagliuolo, and Paola Brun. 2025. "Repurposing MK-8245 as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor to Suppress Virulence and Potentiate Antibiotic Activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111116
APA StyleBernabè, G., Marzaro, G., Shalata, M. E. M., Iosob, D., Inglima, V., Bellato, M., Castagliuolo, I., & Brun, P. (2025). Repurposing MK-8245 as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor to Suppress Virulence and Potentiate Antibiotic Activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111116







