Analysis of Staphylococcal Diversity in the Skin Microbiota of Healthy Riding Horses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Staphylococci Residing on the Skin and Constituting the Normal Equine Microbiota
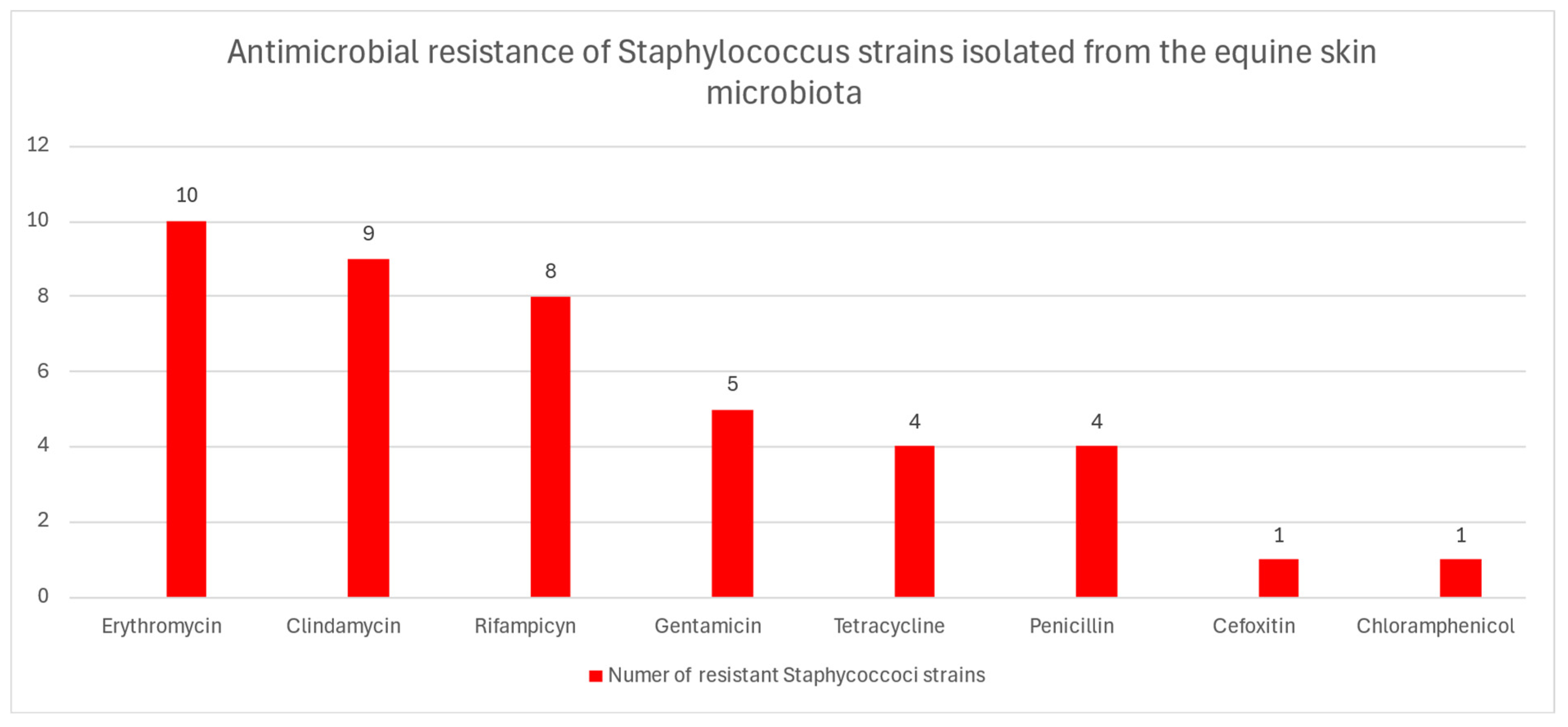
2.2. Antibiotic Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Sampling and Bacterial Identification
4.2. Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Preparation of Total DNA for PCR and Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lönker, N.S.; Fechner, K.; Wahed, A.A.E. Horses as a crucial part of One Health. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairullah, A.R.; Sudjarwo, S.A.; Effendi, M.H.; Ramandinianto, S.C.; Widodo, A.; Riwu, K.H.P. A review of horses as a source of spreading livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to human health. Vet. World 2022, 15, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosseau, C.; Romano-Bertrand, S.; Duplan, H.; Lucas, O.; Ingrassia, I.; Pigasse, C.; Roques, C.; Jumas-Bilakb, E. Proteobacteria from the human skin microbiota: Species-level diversity and hypotheses. One Health 2016, 2, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, K.; Marsella, R. Evolution of the prevalence of antibiotic resistance to Staphylococcus spp. isolated from horses in Florida over a 10-year period. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, F. Staphylococcal cutaneous infection in horses: From the early 2000s to the present. Can. Vet. J. 2021, 62, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaiser-Thom, S.; Gerber, V.; Collaud, A.; Hurni, J.; Perreten, V. Prevalence and WGS-based characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus in the nasal mucosa and pastern of horses with equine pastern dermatitis. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, U.; Lützau, K.; Schlattmann, A.; Rösler, U.; Köck, R.; Becker, K. Zoonotic multidrug-resistant microorganisms among non-hospitalized horses from Germany. One Health 2019, 7, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.D. Equine bacterial and fungal diseases: A diagnostic and therapeutic update. Clin. Tech. Equine Pract. 2005, 4, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beims, H.; Overmann, A.; Fulde, M.; Steinert, M.; Bergmann, S. Isolation of Staphylococcus sciuri from horse skin infection. Open Vet. J. 2016, 6, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Westgate, S.J.; Percival, S.L.; Knottenbelt, D.C.; Clegg, P.D.; Cochrane, C.A. Microbiology of equine wounds and evidence of bacterial biofilms. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamus, L.J.; Theoret, C.; Costa, M.C. Use of next generation sequencing to investigate the microbiota of experimentally induced wounds and the effect of bandaging in horses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Feßler, A.T.; Loncaric, I.; Wu, C.; Kadlec, K.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Antimicrobial resistance among staphylococci of animal origin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, ARBA-0010-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isgren, C.M. Improving clinical outcomes via responsible antimicrobial use in horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2022, 34, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among animals: Current overview. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhaiyan, M.; Wirth, J.S.; Saravanan, V.S. Phylogenomic analyses of the Staphylococcaceae family suggest the reclassification of five species within the genus Staphylococcus as heterotypic synonyms, the promotion of five subspecies to novel species, the taxonomic reassignment of five Staphylococcus species to Mammaliicoccus gen. nov., and the formal assignment of Nosocomiicoccus to the family Staphylococcaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5926–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, E.; Kawano, J.; Yasuda, R.; Takagi, M.; Shimizu, A.; Anzai, T.; Hashikura, S. Species distribution of Staphylococci in the nares and skin of horses. J. Equine Sci. 2001, 12, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnellmann, C.; Gerber, V.; Rossano, A.; Jaquier, V.; Panchaud, Y.; Doherr, M.G.; Thomann, A.; Straub, R.; Perreten, V. Presence of new mecA and mph(C) variants conferring antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from the skin of horses before and after clinic admission. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4444–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida-Fujii, E.; Niwa, H.; Kanai, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kuroda, T.; Toshio Nukada, T.; Takanori Ueno, T. Outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 1, spa type t1784, in an equine hospital in Japan. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2022, 17, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Loubet, P.; Pouget, C.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P.; Molle, V. Staphylococcus aureus toxins: An update on their pathogenic properties and potential treatments. Toxins 2021, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaney, M.H.; Kalan, L.R. Living in your skin: Microbes, molecules, and mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00695-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shittu, A.; Lin, J.; Morrison, D.; Kolawole, D. Isolation and molecular characterization of multiresistant Staphylococcus sciuri and Staphylococcus haemolyticus associated with skin and soft-tissue infections. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanovic, S.; Dakic, I.; Morrison, D.; Hauschild, T.; Jezek, P.; Petrás, P.; Martel, A.; Vukovic, D.; Shittu, A.; Devriese, L.A. Identification and characterization of clinical isolates of members of the Staphylococcus sciuri group. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanovic, S.; Jezek, P.; Vukovic, D.; Dakic, I.; Petras, P. Isolation of members of the Staphylococcus sciuri group from urine and their relationship to urinary tract infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5262–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazal, C.; Sieger, B. Staphylococcus lentus: The troublemaker. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.; Dominguez, M.D.; Mendiola, N.R.; Roso, G.R.; Quereda, C. Staphylococcus lentus peritonitis: A case report. Perit. Dial. Int. 2014, 34, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, C.Y.; Sherris, D.A. Staphylococcus lentus sinusitis: A new sinonasal pathogen. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020, 99, NP62–NP63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, N.; Corallo, C.; Miracco, C.; Papakostas, P.; Montella, A.; Figura, N.; Nuti, R. Erythema nodosum associated with Staphylococcus xylosus septicemia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, Y.E.; Rufer, B. Late prosthetic knee joint infection with Staphylococcus xylosus. ID Cases 2021, 24, e01160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novaková, D.; Sedláček, I.; Pantuček, R.; Štètina, V.; Švec, P.; Petráš, P. Staphylococcus equorum and Staphylococcus succinus isolated from human clinical specimens. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusro, A.; Aarti, C.; Barbabosa-Pilego, A.; Hernández, S.H. Anti-pathogenic, antibiofilm, and technological properties of fermented food associated Staphylococcus succinus strain AAS2. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, B.E.; Tschetter, A.J.; Wanat, K.A. Staphylococcus simulans: An emerging cutaneous pathogen. JAAD Case Rep. 2016, 2, 428–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Makri, P.; Zacharias, G.; Stefanitsi, P.; Karachalios, A. Vertebral osteomyelitis and native valve endocarditis due to Staphylococcus simulans: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2008, 2, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, S.; Qi, H.; Tan, X. Etiology and clinical characteristics of neonatal sepsis in different medical setting models: A retrospective multi-center study. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 5, 1004750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razonable, R.R.; Lewallen, D.G.; Patel, R.; Osmon, D.R. Vertebral osteomyelitis and prosthetic joint infection due to Staphylococcus simulans. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, S.; Kutsuna, S.; Shiojiri, D.; Tamura, S.; Isaka, E.; Wakimoto, Y. Leuconostoc lactis and Staphylococcus nepalensis bacteremia, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakulska, J.; Fijałkowski, K.; Nawrotek, P.; Pobucewicz, A.; Poszumski, F.; Czernomysy-Furowicz, D. Identification and methicillin resistance of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from nasal cavity of healthy horses. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.; Reid-Smith, R.; McClure, J.T.; Weese, J.S. Staphylococcus aureus colonization in healthy horses in Atlantic Canada. Can. Vet. J. 2008, 49, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mota, S.L.; dos Santos, L.O.; Vidaletti, M.R.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Coppola, M.M.; Mayer, F.Q. Antimicrobial resistance of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus isolated from healthy Crioulo horses and associated risk factors. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 107, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isgren, C.M.; Williams, N.J.; Fletcher, O.D.; Timofte, D.; Newton, R.J.; Maddox, T.W. Antimicrobial resistance in clinical bacterial isolates from horses in the UK. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 54, 390–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, S.; Jordan, D.; Worthing, K.A.; Norris, J.M.; Wong, H.S.; Abraham, R. Antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-positive staphylococci isolated from companion animals in Australia: A one year study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Leyssene, D.; Chacornac, J.P.; Kostrzewa, M.; Schmit, P.O.; Talon, R.; Bonnet, R.; Delmas, J. Identification of a variety of Staphylococcus species by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI M100-ED32:2022; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 34th Ed. Available online: https://clsi.org/shop/standards/m100/ (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Version 15.0. 2025. Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Sawant, A.A.; Gillespie, B.E.; Oliver, S.P. Antimicrobial susceptibility of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species isolated from bovine milk. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Khambaty, F.M.; Cerniglia, C.E. Comparative molecular analysis of erythromycin-resistance determinants in staphylococcal isolates of poultry and human origin. Mol. Cell. Probes 2000, 14, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Zadernowska, A.; Nalepa, B.; Sierpińska, M.; Łaniewska-Trokenheim, L. Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) isolated from ready-to-eat food of animal origin--phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Torres, C.; Lozano, C.; Fernández-Pérez, R.; Aspiroz, C.; Ruiz-Larrea, F.; Zarazaga, M. Detection, molecular characterization, and clonal diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 and CC97 in Spanish slaughter pigs of different age groups. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardic, N.; Sareyyupoglu, B.; Ozyurt, M.; Haznedaroglu, T.; Ilga, U. Investigation of aminoglycoside modifying enzyme genes in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Microbiol. Res. 2006, 161, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bouter, A.; Leclercq, R.; Cattoir, V. Molecular basis of resistance to macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins in Staphylococcus saprophyticus clinical isolates. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 37, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Identified Stapylococcus Species | Number of Strains | % |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | 1 | 1.64 |
| S. chromogenes | 1 | 1.64 |
| S. equorum | 10 | 16.39 |
| S. fleurettii | 1 | 1.64 |
| S. lentus | 1 | 1.64 |
| S. nepalensis | 1 | 1.64 |
| S. sciuri | 13 | 21.31 |
| S. simulans | 1 | 1.64 |
| S. succinus | 7 | 11.48 |
| S. vitulinus | 12 | 19.67 |
| S. xylosus | 13 | 21.31 |
| Overall | 61 | 100.00 |
| Strain | Isolate ID | Antimicrobial Resistance Profile | mecA | blaZ | tetK | tetM | tetL | tetO | aac(6′)/ aph(2″) | aph(30)-IIIa | ant(40)-Ia | ermA | ermB | ermC | msr(A) | lnu(A/B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. vitulinus | H11 | RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. xylosus | H18 | RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sciuri | H28 | Tet | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sciuri | H.29 | CC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. sciuri | H.30 | GN, E, RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sciuri | H.31 | GN, E. CC, RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sciuri | H.32 | GN, E. CC, RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sciuri | H.34 | E, CC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sciuri | H36 | CC, Tet, P | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sciuri | H37 | E, CC, P | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. equorum | H39 | E | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. equorum | H40 | E, CC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. equorum | H42 | GN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. equorum | H44 | E, RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. equorum | H45 | E, RA, C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. succinus | H52 | P | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. succinus | H53 | P | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. succinus | H54 | P | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. nepalensis | H56 | Tet | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. lentus | H57 | CC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. aureus | H59 | FOX E, CC, Tet, GN, P | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| S. chromogenes | H60 | RA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wesołowska, M.; Szczuka, E. Analysis of Staphylococcal Diversity in the Skin Microbiota of Healthy Riding Horses. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101037
Wesołowska M, Szczuka E. Analysis of Staphylococcal Diversity in the Skin Microbiota of Healthy Riding Horses. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101037
Chicago/Turabian StyleWesołowska, Maria, and Ewa Szczuka. 2025. "Analysis of Staphylococcal Diversity in the Skin Microbiota of Healthy Riding Horses" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101037
APA StyleWesołowska, M., & Szczuka, E. (2025). Analysis of Staphylococcal Diversity in the Skin Microbiota of Healthy Riding Horses. Antibiotics, 14(10), 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101037







