Environmental Amoxicillin Exposure Induces Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryos: A Comprehensive Assessment of Heart Function and Molecular Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
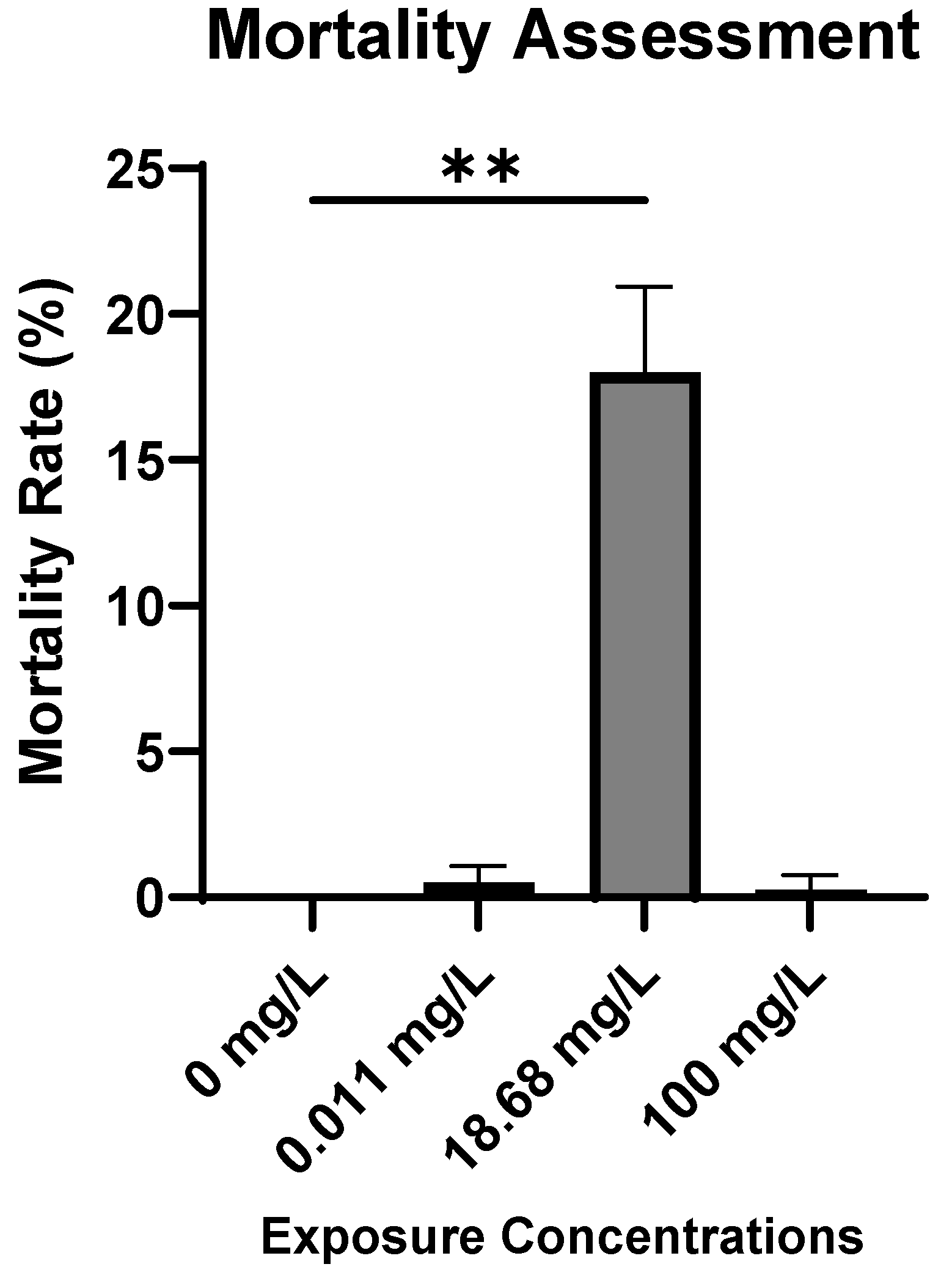
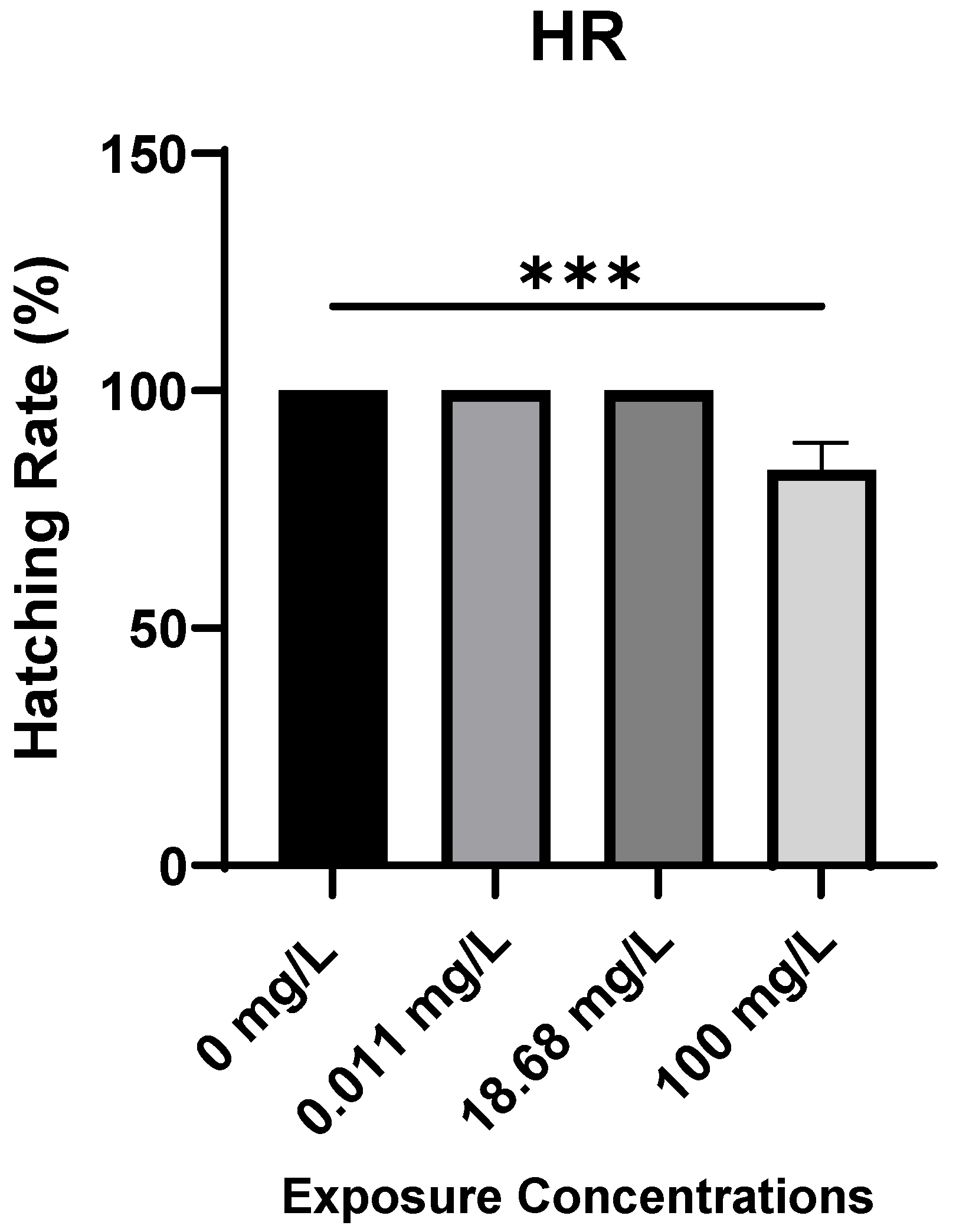
2.1. Embryotoxicity Assessment
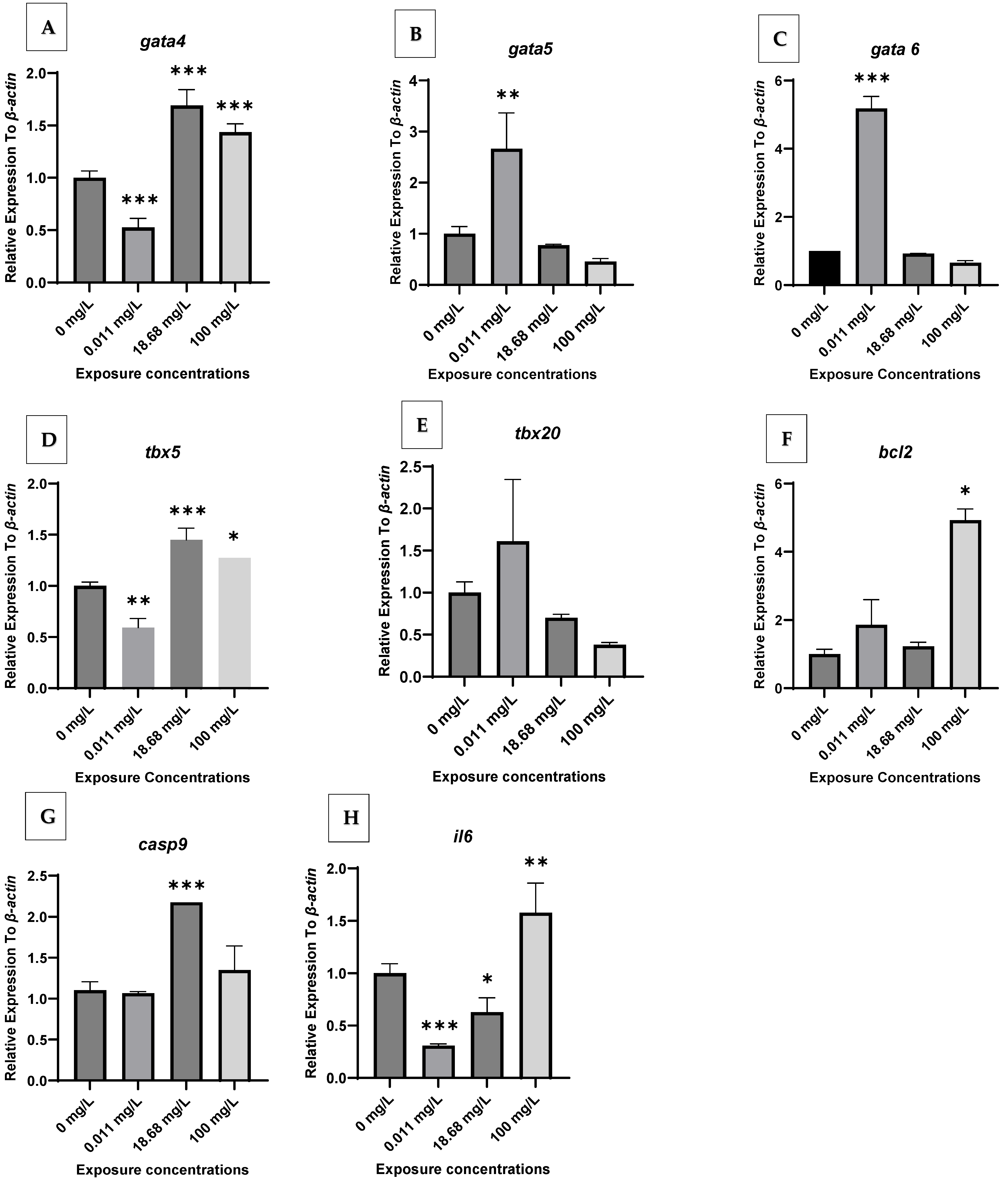
2.2. Gene Expression
2.3. Heart Function Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Zebrafish Maintenance and Exposure
4.3. Embryotoxicity Assessment
4.4. RNA Isolation and qPCR Analysis
4.5. Heart Function Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
| AMX | Amoxicillin |
| hpf | Hours Post-Fertilization |
| PCV | Posterior Cardinal Vein |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| LC50 | Lethal Concentration 50% |
| LC18 | Lethal Concentration 18% |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| EOCs | Emerging Organic Contaminants |
| EF1α | Elongation Factor 1-Alpha (housekeeping gene) |
References
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthee, C.; Brown, A.R.; Lange, A.; Tyler, C.R. Factors Determining the Susceptibility of Fish to Effects of Human Pharmaceuticals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8845–8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-S.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.-G.; Li, Y.-T.; Li, J.-Y.; Gao, Y. Agricultural land-use change exacerbates the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes via surface runoffs in Lake Tai Basin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Wilson, S.; Sanjay Preeth, R.S.; Prakash, P.; Sathiyasree, M.; Saigeetha, S.; Shobana, N.; Pachiyappan, S.; Rajesh, V.V. Sources of Antibiotic Contamination in Wastewater and Approaches to Their Removal—An Overview. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, M.; Pérez, S.; Kantiani, L.; Barceló, D. Fate and toxicity of emerging pollutants, their metabolites and transformation products in the aquatic environment: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- González-González, E.D.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Islas-Flores, H.; Galar-Martínez, M. Developmental Effects of Amoxicillin at Environmentally Relevant Concentration Using Zebrafish Embryotoxicity Test (ZET). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielen, A.; Šimatović, A.; Kosić-Vukšić, J.; Senta, I.; Ahel, M.; Babić, S.; Jurina, T.; Plaza, J.J.G.; Milaković, M.; Udiković-Kolić, N. Negative environmental impacts of antibiotic-contaminated effluents from pharmaceutical industries. Water Res. 2017, 126, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galla, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Cheng, X.; Yeo, J.Y.; Mell, B.; Chiu, N.; Wenceslau, C.F.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Joe, B. Exposure to Amoxicillin in Early Life Is Associated With Changes in Gut Microbiota and Reduction in Blood Pressure: Findings From a Study on Rat Dams and Offspring. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, P.; Khanna, S.; Vijhani, P. Amoxicillin; StatPearls: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Modarresi Chahardehi, A.; Arsad, H.; Lim, V. Zebrafish as a Successful Animal Model for Screening Toxicity of Medicinal Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jijie, R.; Mihalache, G.; Balmus, I.-M.; Strungaru, S.-A.; Baltag, E.S.; Ciobica, A.; Nicoara, M.; Faggio, C. Zebrafish as a Screening Model to Study the Single and Joint Effects of Antibiotics. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Chung, K.W.; Choi, B.O.; Lee, J.E. Therapeutic Potential of CKD-504, a Novel Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor, in a Zebrafish Model of Neuromuscular Junction Disorders. Mol. Cells 2022, 45, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Yuan, X.; Racioppi, C.; Leslie, M.; Stutt, N.; Aleksandrova, A.; Christiaen, L.; Wilson, M.D.; Scott, I.C. GATA4/5/6 family transcription factors are conserved determinants of cardiac versus pharyngeal mesoderm fate. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabg0834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrie, L.E.; Renfrew, E.M.; Wal, A.V.; Mueller, R.L.; Garrity, D.M. Zebrafish tbx5 paralogs demonstrate independent essential requirements in cardiac and pectoral fin development. Dev. Dyn. 2013, 242, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, J.G.S.; Lima, C.; Lopes-Ferreira, M. Zebrafish Larvae Behavior Models as a Tool for Drug Screenings and Pre-Clinical Trials: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; McDonough, S.; Ladewig, J.C.; Soares, A.M.; Nogueira, A.J.; Domingues, I. Effects of oxytetracycline and amoxicillin on development and biomarkers activities of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, J.; Mandal, T.K.; Mondal, S. Genotoxic impact of emerging contaminant amoxicillin residue on zebra fish (Danio rerio) embryos. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Dodd, A.; Lai, D.; McNabb, W.C.; Love, D.R. Validation of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-time RT-PCR Normalization. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurley, A.T.; Callard, G.V. Characterization of housekeeping genes in zebrafish: Male-female differences and effects of tissue type, developmental stage and chemical treatment. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, G.; You, J.; Park, H.; Hong, T.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Dimethenamid promotes oxidative stress and apoptosis leading to cardiovascular, hepatic, and pancreatic toxicities in zebrafish embryo. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 273, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Chang, C.; Liang, J.; Du, F.; Zhang, R. Embryonic Amoxicillin Exposure Has Limited Impact on Liver Development but Increases Susceptibility to NAFLD in Zebrafish Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’aguanno, S.; Del Bufalo, D. Inhibition of Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins in Preclinical and Clinical Studies: Current Overview in Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwain, D.R.; Berger, T.; Mak, T.W. Caspase Functions in Cell Death and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benslimane, F.M.; Zakaria, Z.Z.; Shurbaji, S.; Khatib Ali Abdelrasool, M.; Al-Badr, M.A.H.I.; Said Khalil Al-Absi, E.; Yalcin, H.C. Cardiac function and blood flow hemodynamics assessment of zebrafish (Danio rerio) using high-speed video microscopy. Micron 2020, 136, 102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Genes | Primers | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| gata4 | Forward Reverse | 5′-CCAGTCTGCAACGCATGTG-3′ 5′-GATCGCCGACTGACCTTCAG-3′ |
| gata5 | Forward Reverse | 5′-GGGACGCCAGGGAACTCTA-3′ 5′-CACGCGTTGCACAGGTAGTG-3′ |
| gata6 | Forward Reverse | 5′-AGTCGCGACCAGTACCTTTCAA-3′ 5′-CCTTCGGGATTGCAGTGAGT-3′ |
| tbx5 | Forward Reverse | 5′-CGGATGTTTCCCAGCTTCAA-3′ 5′-CATCGCAGGCTCAGCTTTC-3′ |
| tbx20 | Forward Reverse | 5′-GCACTCATGTCAAGTGGGAA -3′ 5′-CGAGGTTTGGATGGCATGA-3′ |
| bcl2 | Forward Reverse | 5′-TCACTCGTTCAGACCCTCAT-3′ 5′-ACGCTTTCCACGCACAT-3′ |
| casp9 | Forward Reverse | 5′-AAATACATAGCAAGGCAACC-3′ 5′-CACAGGGAATCAAGAAAGG-3′ |
| il6 | Forward Reverse | 5′-TCAACTTCTCCAGCGTGATG-3′ 5′-TCTTTCCCTCTTTTCCTCCTG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naïja, A.; Mohamed, D.; Abdulhakim, S.; Mohamed, A.; Yalcin, H.C. Environmental Amoxicillin Exposure Induces Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryos: A Comprehensive Assessment of Heart Function and Molecular Responses. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101029
Naïja A, Mohamed D, Abdulhakim S, Mohamed A, Yalcin HC. Environmental Amoxicillin Exposure Induces Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryos: A Comprehensive Assessment of Heart Function and Molecular Responses. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101029
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaïja, Azza, Dalal Mohamed, Somaiya Abdulhakim, Amera Mohamed, and Huseyin Cagatay Yalcin. 2025. "Environmental Amoxicillin Exposure Induces Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryos: A Comprehensive Assessment of Heart Function and Molecular Responses" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101029
APA StyleNaïja, A., Mohamed, D., Abdulhakim, S., Mohamed, A., & Yalcin, H. C. (2025). Environmental Amoxicillin Exposure Induces Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryos: A Comprehensive Assessment of Heart Function and Molecular Responses. Antibiotics, 14(10), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101029








