Abstract
Background/Objectives: Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a common commensal bacterium that has emerged as an important nosocomial pathogen. Its multi-antibiotics resistance presents substantial therapeutic challenges in healthcare settings worldwide. Despite its growing clinical relevance, most investigations into antimicrobial resistance determinants have been focused on Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis, leaving S. haemolyticus comparatively understudied. This study aimed to elucidate the genetic basis of multi-drug resistance by characterizing mobile genetic elements associated with predominant S. haemolyticus clones circulating in Taiwan. Methods: From 2010 to 2017, 140 clinical targeted isolates of S. haemolyticus were obtained from individual patients. Two representative strains, SH53 (ST3) and SH51 (ST42), were sequenced using the PacBioTM platform. The structural organization of SCCmec cassettes and phage-associated resistance islands in the remaining 138 isolates was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using specifically designed primers. Results: Of the 140 isolates, 92 (65.7%) were ST42 and 48 (34.3%) were ST3. PCR analysis showed that over two-thirds harbored heavy metal resistance genes. cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, and arsR occurred in 90.2% of ST42 isolates, with copA in 71.7%. In ST3, these five genes were present in 89.6%, and copA in 64.6%. Fusidic acid (FA) resistance was more frequent in ST42 (46.7%) than ST3 (22.9%) (p = 0.015). Only one ST42 isolate carried fusC. The remaining 52 FA-resistant isolates contained a type I aj1–leader peptide (LP)–fusB structure downstream of smpB, except for a single ST42 isolate with the type IV structure. Conclusions: MDR ST42 S. haemolyticus carrying SCCmec cassettes with heavy metal resistance genes and phage-related islands carrying type I aj1–leader peptide (LP)–fusB structures may represent emerging opportunistic pathogens in Taiwan. Continued longitudinal surveillance is warranted to track the evolution of resistance-associated mobile elements under selective antimicrobial pressure.
Keywords:
S. haemolyticus; fusB; fusC; ΨSCCmec57395; heavy metal resistance; mobile genetic elements 1. Introduction
Staphylococcus haemolyticus, first identified in 1975, is a non-motile, non-spore-forming, catalase-positive, coagulase-negative, and Gram-positive coccus [1,2]. Similarly to S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus is one of the most commensal normal floras in both humans and animals. Like other coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS), it is typically regarded as less virulent in healthy individuals due to its lack of coagulase, an enzyme that facilitates fibrin clot formation from fibrinogen and hinders host defense mechanisms [2,3]. This zoonotic microorganism can also be found in food and environmental sources [3]. Although often considered as harmless commensals, accumulating evidence indicates that S. haemolyticus contributes substantially to foreign-body or medical device–related infections, including bloodstream infections, arthritis, and valvular endocarditis in hospitalized and immunocompromised patients, including neutropenic patients, preterm neonates, and burn center patients with compromised skin or mucosal barriers [2,3,4].
In our previous reports, ST42 and ST3 were identified as the predominant multilocus sequence typing (MLST) lineages among clinically isolated S. haemolyticus and were associated with an outbreak of bacteremia in 36 patients at a burn center in Taiwan [4,5,6]. Of particular concern is their multidrug-resistant (MDR) profile, characterized by resistance to oxacillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracycline, and fusidic acid (FA), which poses substantial therapeutic challenges, particularly for ST42 isolates [5,6].
The genetic determinants underlying MDR are frequently located on mobile genetic elements (MGEs), which facilitate horizontal transfer between bacteria via transduction, transformation, and conjugation/mobilization, including S. haemolyticus [7,8]. The MGEs include plasmids, staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) cassettes, and phage-related resistance islands [2,3]. The intracellular and intercellular mobility of MGEs harboring resistance genes contributes to the widespread dissemination of multidrug-resistant bacteria, particularly under sustained antibiotic selective pressure [7]. Intracellular movement is mediated by insertion sequences, transposons, and integrons, whereas intercellular transfer involves mechanisms such as transformation, transduction, and conjugation/mobilization [7]. Among these MGEs, SCCmec is notable for conferring methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Two new SCCmec types, XIV and XV, were described recently [9,10,11].
In the era of extensive antimicrobial usage, MGEs carrying resistance genes are pivotal in driving the evolution and dissemination of MDR pathogens [7]. Under antibiotic selective pressure, MDR S. haemolyticus has emerged globally in hospital settings, especially ST42 strains in recent years [4,6,12,13,14]. However, the MGEs present in these MDR S. haemolyticus strains remain under-investigated. In this study, we aimed to characterize the MGEs carried by MDR S. haemolyticus isolates in Taiwan.
2. Results
2.1. MLST and Antimicrobial Resistance
Among the 140 S. haemolyticus isolates analyzed, MLST revealed that 92 strains belonged to ST42 and 48 strains to ST3. All isolates were resistant to penicillin, oxacillin, and erythromycin, and all remained susceptible to vancomycin (Table 1). Chloramphenicol resistance was more frequent in ST3 than in ST42 (14.6% vs. 4.3%, p = 0.048), whereas ST42 exhibited significantly higher resistance to tetracycline (70.7% vs. 4.3%, p < 0.0001) and fusidic acid (46.7% vs. 22.9%, p = 0.015).

Table 1.
Comparison of antimicrobial resistance and heavy metal resistance gene segments between ST3 and ST42 among 140 S. haemolyticus isolates.
2.2. The SCCmec Cassette Structures
Whole-genome sequencing showed that the ST42 isolate SH51 harbored a SCCmec cassette approximately 12,000 bp in size, comprising orfX, heavy-metal resistance genes (cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, arsR), IS431, mecA, paaZ, ugpQ, IS431, copA, and ydhK (Figure 1b). In contrast, the ST3 isolate SH53 possessed a larger SCCmec cassette (~32,000 bp), including orfX, Mod, PRK15483, helicase, ADP-ribosylglycohydrolase, ydjH, SMP2 superfamily, YafY superfamily, heavy-metal resistance genes (cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, arsR), IS431, mecA, paaZ, ugpQ, PksG superfamily, IS431, copA, and ydhK (Figure 1a). In GenBank, the SCCmec cassette of S. haemolyticus strain WCH1 (GenBank: JQ764731.1) and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strain 57395 (GenBank: HE984157.2) encode all of the aforementioned heavy-metal resistance genes (cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, arsR, and copA) (Figure 1c and Figure 1d, respectively), whereas S. haemolyticus strain SH621 (GenBank: AB478934.1) contains only cadD, arsC, arsB, and arsR, lacking cadX and copA (Figure 1e). Notably, S. haemolyticus strain ATCC29970 (RefSeq: NZ_CP035291.1) carries mecA only and lacks other SCCmec-associated components (Figure 1f).
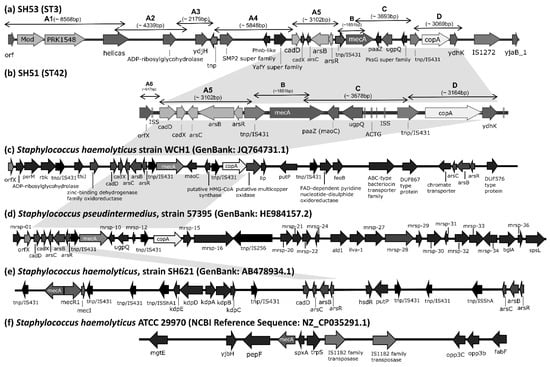
Figure 1.
Structural organization of SCCmec cassettes in S. haemolyticus strains SH51, SH53, and other reference genomes, except S. haemolyticus strain ATCC 29970, which lacks a SCCmec cassette and genomic region surrounding the mecA locus is presented. Genome diagrams are not scaled proportionally to their actual sizes. Gray shading highlights structurally similar regions of heavy metal resistance genes shared across different strains. The pairwise sequence similarities among SCCmec cassettes from SH51, SH53, and reference genomes are provided in the Supplementary Material Table S1-1. mrsp-01: metallo-beta-lactamase superfamily proteins; mrsp-16: putative type I DNA modification methylase; mrsp-27: amino acid permease; mrsp-28: lead, cadmium, zinc and mercury transporting ATPase; mrsp-29: transcriptional regulator; mrsp-30: putative type II restriction endonuclease, DpnII superfamily; mrsp-32: putative restriction modification DNA methylase; mrsp-33: putative DNA methylase; mrsp-34: GntR family transcriptional regulator; mrsp-10, 12, 15, 31, 36: hypothetical protein; cadD: cadmium binding protein; cadX: cadmium resistant accessory protein; arsC: arsenate reductase; arsB: arsenical pump membrane protein; arsR: arsenical resistance operon repressor; copA: copper-translocating P-type ATPase.
Based on PCR product sizes obtained using five primer pairs (A5, A6, B, C, and D), 53 ST42 strains (53/92, 57.6%) exhibited SCCmec cassette structures similar to that of strain SH51. With the exception of mecA, the remaining ST42 isolates carried heterogeneous gene fragments of varying lengths (38/92, 41.3%; see Figure 2b). Notably, over two-thirds of these isolates contained full-length heavy metal resistance genes comparable to those in SH51: cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, and arsR were detected in 83/92 strains (90.2%), while 66/92 strains (71.7%) carried copA. Among the 47 ST3 strains analyzed, five (5/48, 10.4%) possessed SCCmec structures resembling that of strain SH53 (Figure 2a). Aside from mecA and two strains containing larger gene structures spanning regions A1 to A4, the remaining 40 strains exhibited truncated or reduced variants of the SCCmec cassette components. As observed in ST42, the majority of ST3 strains also carried full-length heavy metal resistance genes: 43/48 (89.6%) harbored cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, and arsR, whereas 31/48 (64.6%) possessed copA. Overall, there were no significant differences between ST3 and ST42 isolates in the carriage of heavy metal resistance gene segments, despite their high prevalence (Table 1). Detailed SCCmec cassette comparisons among S. haemolyticus strains SH51, SH53, and selected reference genomes are provided in the Supplementary Material Table S1-1.
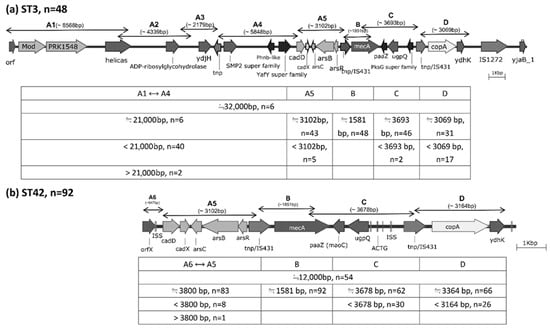
Figure 2.
Distribution of gene fragments amplified by nine primer pairs, designed based on the SCCmec cassettes of S. haemolyticus strains SH53 (ST3) and SH51 (ST42), as determined by whole-genome sequencing.
2.3. Phage-Related FA Resistance Islands
FA resistance was also more prevalent in ST42 isolates (43/92, 46.7%) than in ST3 isolates (11/48, 22.9%). Among these, only one ST42 isolate carried fusC, and one ST3 strain harbored a type IV fusB structure. The remaining 52 FA-resistant isolates all carried a type I aj1–leader peptide (LP)–fusB structure inserted downstream of smpB, rather than groEL or rpsR (Figure 3a). Detailed comparative analyses of phage-related fusidic acid resistance islands between SH51 and other reference genomes are provided in the Supplementary Material Figure S1.
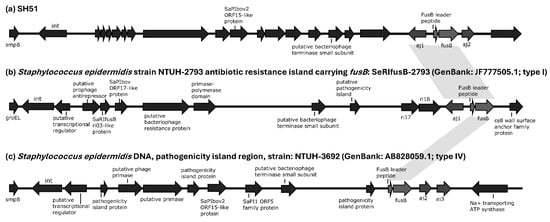
Figure 3.
Structural organization of phage-related fusidic acid resistance islands in S. haemolyticus strain SH51 and selected reference genomes. Genome diagrams are not proportionally scaled to actual sequence lengths. Gray shading denotes type 1 and type 4 aj1–leader peptide (LP)–fusB configurations shared across SH51 and reference strains. The sequence similarity of phage-related fusidic acid resistance islands among SH51, and other reference strains is detailed in the Supplementary Material Table S1-2.
3. Discussion
In our previous reports, ST42 (59.8%) and ST3 (20.6%) were the predominant MLST lineages among clinical S. haemolyticus isolates, particularly those from burn center patients [5]. The two sequence types differ at the SH1431 locus among the seven housekeeping genes used in MLST, and phylogenetic analysis of MLST allelic profiles indicated a close relationship between ST42 and ST3 [5]. In the present study, an even greater proportion of ST42 isolates (65.7%) was observed, and the ST42 lineage has recently been reported as an emerging nosocomial pathogen in China [14]. Moreover, the antimicrobial resistance rates among these 140 S. haemolyticus isolates, against penicillin, oxacillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, exceeded those reported previously [12,13]. The ST42 lineage, in particular, exhibited significantly higher resistance to tetracycline, fusidic acid, and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole. This MDR phenotype may facilitate dissemination in the era of widespread antibiotic use, although vancomycin remains a clinically useful therapeutic option.
Among these 140 isolates, more than 60% harbored heavy metal resistance genes, including cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, arsR, and copA. The determinants for copper (copA), arse-nic (arsC, arsB, arsR), and cadmium (cadD, cadX) were associated with elevated minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for the respective metals [15]. CopA, encoding a copper-translocating P-type ATPase, is suspected to mediate efflux and maintain intracellular copper homeostasis in staphylococci [15]. The functions of the arsenic resistance determinants are as follows: arsC encodes an arsenate reductase that reduces intracellular As5+ to As3+; arsB encodes an arsenical pump membrane protein responsible for exporting As3+ from the cytosol to the periplasmic or extracellular space; and arsR encodes an operon repressor that regulates transcription of the ars operon [16,17]. Regarding cadmium resistance, cadD encodes an energy-dependent efflux pump (cadmium-binding protein) that contributes to increased Cd2+ MICs, while cadX, a cadmium-resistance accessory protein, regulates cadD expression by binding to its promoter region [17,18]. Several staphylococcal species, including S. aureus, S. haemolyticus, S. saprophyticus, S. epidermidis, S. warneri, and S. pseudintermedius, were reported to carry these heavy metal resistance genes [10,15,17,19,20,21]. Notably, the SCCmec structures of S. haemolyticus strains SH51 and SH53 closely resemble the pseudo-Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec element (ΨSCCmec57395) from S. pseudintermedius strain 57395 in Thailand (GenBank: HE984157.2, Figure 1c) and S. haemolyticus strain WCH1 in China (GenBank: JQ764731.1) [17,21]. This study is the first report of ΨSCCmec57395 in clinically significant S. haemolyticus isolates from Taiwan. These findings suggest that this MGE has disseminated across diverse Staphylococcus species and geographic regions, underscoring its potential role in the global transmission of methicillin resistance. Heavy metal resistance genes frequently coexist with antibiotic resistance determinants on the same mobile genetic elements (e.g., SCCmec), which may promote the evolution and dissemination of DMR bacterial strains [15,22].
Currently, determinants associated with fusidic acid resistance include fusA, fusB, fusC, fusD, fusE, and fusF [23,24]. Mutations in fusA, which encodes the drug target elongation factor G (EF-G), can lead to high-level resistance (e.g., MIC > 64 μg/mL). In contrast, the small protein products encoded by fusB, fusC, fusD, and fusF bind to EF-G and interfere with fusidic acid binding, resulting in low-level resistance [23,24]. Additionally, mutation of rplF, encoding ribosomal protein L6, a contact site for EF-G, leads to fusE, which is associated with small-colony variants of S. aureus exhibiting low-level fusidic acid resistance [25]. In this study, fusB accounted for the majority of fusidic acid resistance among S. haemolyticus isolates (53/54, 98.1%), with the remaining one isolate carrying fusC. Horizontal gene transfer of fusB among Staphylococcus species can occur via plasmids, transposon-like elements, or pathogenicity islands, contributing to clonal dissemination [26]. Previous reports showed that resistance islands carrying fusB frequently integrate at smpB, groEL, or rpsR loci in S. epidermidis isolates. Four structural types of the aj1–leader peptide (LP)–fusB region were described (Figure 3 and Figure S1): full-length aj1 (type I), partial aj1 fragments (type II), truncated aj1 (type III), and structures lacking aj1 (type IV) [27,28,29]. Among the 53 fusB-positive S. haemolyticus isolates in this study, all carried type I aj1–LP–fusB structures inserted downstream of smpB; the exception was a single ST3 strain that possessed a type IV variant. The predominance of type I aj1–LP–fusB structures within resistance islands harboring fusB in clinical S. haemolyticus isolates has not been previously reported.
This study has several limitations. The isolates were collected from only two hospitals, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Whole-genome sequencing was performed for only two representative strains (SH51 and SH53), which would reduce the reliability of genomic comparisons. The uneven enrollment of ST42 (n = 92) and ST3 (n = 48) strains may introduce bias in results interpretation. Detailed clinical information, such as underlying diseases, antimicrobial therapies, and patient outcomes, was not available, limiting the study’s clinical applicability. Future work should include multi-hospital sampling, comprehensive clinical characteristics and outcomes surveillance, and broader investigation of mobile genetic elements in both clinically significant and commensal S. haemolyticus and other coagulase-negative staphylococci. Despite these constraints, the data indicate that the predominant S. haemolyticus clones circulating in nosocomial environments in Taiwan are ST3 and ST42. Most strains carried ΨSCCmec57395, which harbors heavy metal resistance genes, including cadD, cadX, arsC, arsB, arsR, and copA, similar to those described in S. pseudintermedius strain 57395 and S. haemolyticus strain WCH1. The coexistence of heavy metal resistance genes and antibiotic resistance genes within the same mobile genetic elements may contribute to enhanced adaptability of these strains in hospital environments with antimicrobial and heavy metal exposure [15,22]. Among these dominant lineages, resistance islands integrated downstream of smpB, carrying a type I aj1–LP–fusB structure, accounted for fusidic acid resistance in most isolates.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Enrolled Isolates, Antimicrobial Testing and MLST
Between 2010 and 2017, a total of 140 clinical isolates of S. haemolyticus were recovered from clinically indicated cultures of individual patients and identified using the Bruker MALDI Biotyper® system (Bruker Daltonik GmbH, Bremen, Germany). Antimicrobial susceptibility testing were performed by the disc diffusion method on Mueller–Hinton agar (Nippon Becton Dickinson Company, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines [30], except vancomycin which susceptibility was determined using the ETEST® (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France). Staphylococcus aureus ATCC® 25923 was used as the quality control strain, and the results interpretation followed CLSI recommendations [31], whereas the FA results were interpreted according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) criteria [32]. BD BBL™ Sensi-Disc™ antimicrobial susceptibility test discs (Becton Dickinson, Sparks, MD, USA) were used for the disc diffusion assays except vancomycin. These strains were collected from two hospitals in Taiwan, with 92 isolates from a northern hospital and 48 from a southern hospital. This study was approved by the Biosafety Committee of Chang Gung Medical Foundation (Approval No. 00417-2020092285432). MLST of each S. haemolyticus isolate was determined based on the sequences of seven housekeeping genes: arc, SH1200, hemH, leuB, SH1431, cfxE, and RiboseABC, as previously described [33]. The sequence types (STs) were assigned via the PubMLST database (https://pubmlst.org/shaemolyticus/) (accessed on 1 July 2022) [34].
4.2. MGEs Analysis
Genomic DNA from two representative S. haemolyticus strains—SH51 (ST42; accession numbers CP092478 and CP092479) and SH53 (ST3; accession numbers CP092476 and CP092477)—was extracted using the Puregene Yeast/Bact. Kit B (QIAGEN Sciences, Germantown, MD, USA). Whole-genome sequencing was performed on the PacBio™ sequencing platform (Pacific Biosciences, Menlo Park, CA, USA). Libraries were prepared using the standard SMRTbell protocol without PCR amplification (PCR-free); therefore, no technical PCR replicates were generated. Assemblies were polished and circularized, and the final Circlator builds were used for all analyses. Final assembly and quality control statistics were as follows: isolate SH51: 2 circular contigs; total length, 2,596,982 bp; largest contig, 2,563,044 bp; N50, 2,563,044 bp; GC content, 33%; isolate SH53: 2 circular contigs; total length, 2,586,626 bp; largest contig, 2,536,380 bp; N50, 2,536,380 bp; GC content, 33%. In both genomes, the N50 equaled the largest contig, consistent with a near-complete chromosome plus one smaller circular element. Antimicrobial resistance genes in these strains were identified from the sequencing data using basic local alignment search tool (BLAST)-based searches against the ResFinder database [35] and Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) [36]. Comparative analyses between these two strains and other reference genomes were performed using the blastn mode of the BLAST+ command-line suite (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/doc/blast-help/downloadblastdata.html#downloadblastdata, accessed on 1 July 2022).
4.2.1. SCCmec Cassettes Analysis
Based on the whole-genome sequencing results of the two selected strains, nine primer pairs (A1 to A6, B, C, and D) were designed to investigate the structural organization of the SCCmec cassettes in the remaining 138 S. haemolyticus isolates (Table S2). Each PCR assay was performed at least twice, with SH51 or SH52 included as controls depending on their MLST type.
4.2.2. Phage-Related Islands and FA Resistance Determinants Analysis
FA-resistant isolates were screened by PCR for the presence of fusB and fusC using previously described primers (Table 1) [26,29]. To investigate phage-associated resistance island structures among fusB-positive isolates, four primer pairs from earlier studies were employed to determine insertion sites (smpB, groEL, or rpsR) and to classify the aj1–leader peptide (LP)–fusB region into four structural types (Table 1) [27,28,29].
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Pearson’s chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test (when the expected frequency in any cell was <5) was employed to evaluate the statistical significance of differences between ST3 and ST42 isolates. All statistical analyses were conducted using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) for Windows, version 17.0 (Chicago, IL, USA). A p-value of ≤0.05 was considered indicative of statistical significance.
5. Conclusions
With the growing number of elderly and debilitated patients in Taiwan, as reported in the Taiwan Health and Welfare Report 2023 and in our previous studies [4,6,37], MDR ST42 S. haemolyticus harboring ΨSCCmec57395-like SCCmec with heavy metal resistance genes and phage-related islands carrying type I aj1–leader peptide (LP)–fusB structures may represent emerging opportunistic pathogens in Taiwan. Continuous surveillance of mobile genetic elements carrying antibiotic resistance genes in clinical Staphylococcus isolates is essential to elucidate their evolutionary dynamics and multidrug resistance potential under the selective pressure of widespread antibiotic use.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics14101015/s1, Figure S1: Structural organization of phage-related fusidic acid resistance islands in S. haemolyticus reference genomes; Table S1-1: Comparative analyses of SCCmec cassettes between SH51, SH53 and other reference genomes using the blastn mode of the BLAST+ command-line suite; Table S1-2: Comparative analyses of phage-related fusidic acid resistance islands between SH51 and other reference genomes using the blastn mode of the BLAST+ command-line suite; Table S2: Primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-M.H., L.-C.L. and J.-J.L.; methodology, Y.-H.O. and K.-H.L.; software, Y.-H.O. and K.-H.L.; validation, C.-M.H., L.-C.L. and J.-J.L.; formal analysis, L.-C.L. and Y.-H.O.; investigation, L.-C.L. and Y.-H.O.; resources, J.-J.L.; data curation, L.-C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-M.H.; writing—review and editing, L.-C.L. and J.-J.L.; visualization, L.-C.L.; supervision, J.-J.L.; project administration, J.-J.L.; funding acquisition, J.-J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grant from Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan (CMRPG3M1041) to Y.-H. Ou, and by grants from the Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation [TCRD-TPE-NSTC-113-18 and TCRD-TPE-114-04(1/3)] and grant from the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan (NSTC 113-2320-B-303-006) to J.-J. Lu.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are contained within the article and its Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the bacterial isolates provided by the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital bacterial storage bank program (CLRPG3E0025) and for the technical support from the Core Laboratory of the Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SCCmec | Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec |
| MLST | multilocus sequence typing |
| MDR | multidrug-resistant |
| ST | sequence type |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| LP | leader peptide |
| CoNS | coagulase-negative staphylococci |
| MGEs | mobile genetic elements |
| BLAST | basic local alignment search tool |
| CARD | Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database |
| FA | fusidic acid |
References
- Schleifer, K.H.; Kloos, W.E. Isolation and characterization of Staphylococci from human skin I. Amended descriptions of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus and descriptions of three new species: Staphylococcus cohnii, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, and Staphylococcus xylosus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1975, 25, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.C.; Ahmad, F.; Giambiagi-deMarval, M. Staphylococcus haemolyticus: An updated review on nosocomial infections, antimicrobial resistance, virulence, genetic traits, and strategies for combating this emerging opportunistic pathogen. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 282, 127652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.H.; Liu, T.P.; Huang, P.Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Lin, J.F.; Yeh, C.F.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, T.S.; Lu, J.J. Clinical features, outcomes, and molecular characteristics of an outbreak of Staphylococcus haemolyticus infection, among a mass-burn casualty patient group, in a tertiary center in northern Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.C.; Liu, T.P.; Chang, S.C.; Lu, J.J. Characterization of New Staphylococcus haemolyticus ST42 Populations in Northern Taiwan. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.C.; Chang, S.C.; Ou, Y.H.; Liu, T.P.; Lu, J.J. Clonal Spreading of ST42 Staphylococcus haemolyticus Strains Occurs Possibly Due to fusB and tetK Resistant Genes and Capsule-Related Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pain, M.; Hjerde, E.; Klingenberg, C.; Cavanagh, J.P. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Staphylococcus haemolyticus Reveals Key to Hospital Adaptation and Pathogenicity. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushibara, N.; Aung, M.S.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Kobayashi, N. Novel staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) type XIV (5A) and a truncated SCCmec element in SCC composite islands carrying speG in ST5 MRSA in Japan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Baker, M.; Dottorini, T.; Li, H.; Dong, Y.; Bai, Y.; Fanning, S.; Li, F. Novel SCCmec type XV (7A) and two pseudo-SCCmec variants in foodborne MRSA in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska-Gebarzewska, M.; Miedzobrodzki, J.; Kosecka-Strojek, M. Current types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) in clinically relevant coagulase-negative staphylococcal (CoNS) species. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 50, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekaj, T.; Ciszewski, M.; Szewczyk, E.M. Staphylococcus haemolyticus—An emerging threat in the twilight of the antibiotics age. Microbiology 2015, 161, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, E.M.; Ceotto, H.; Bastos, M.C.; Dos Santos, K.R.; Giambiagi-Demarval, M. Staphylococcus haemolyticus as an important hospital pathogen and carrier of methicillin resistance genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.; Chen, P.; Deng, B.; He, R.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Deng, W.; Ding, X.; Yang, F.; Xie, C.; et al. The Emergence of a Multidrug-Resistant and Pathogenic ST42 Lineage of Staphylococcus haemolyticus from a Hospital in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0234221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.U.; Fraqueza, M.J.; Worning, P.; Bouchami, O.; Bartels, M.D.; Goncalves, L.; Paixao, P.; Goncalves, E.; Toscano, C.; Empel, J.; et al. Staphylococcus saprophyticus Causing Infections in Humans Is Associated with High Resistance to Heavy Metals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0268520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zong, G.; Chen, X.; Tan, M.; Gao, W.; Fu, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Cao, G. Bifunctional protein ArsR(M) contributes to arsenite methylation and resistance in Brevundimonas sp. M20. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z. Characterization of a complex context containing mecA but lacking genes encoding cassette chromosome recombinases in Staphylococcus haemolyticus. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, Z.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Yao, H.; Wu, Z. The cadDX operon contributes to cadmium resistance, oxidative stress resistance, and virulence in zoonotic streptococci. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.; Kumari, W.; Chandrasekharan, N.V.; Wijayarathna, C.D. Isolation of heavy metal-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain TWSL_22 and evaluation of heavy metal bioremediation potential of recombinant E. coli cloned with isolated cadD. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2023, 370, fnad092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.C.; Chandrasekharan, N.V.; Wijayarathna, C.D. Multi-metal-resistant Staphylococcus warneri strain TWSL_1: Revealing heavy metal-resistant genomic features by whole-genome sequencing and analysis. Access Microbiol. 2025, 7, 000954.v5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreten, V.; Chanchaithong, P.; Prapasarakul, N.; Rossano, A.; Blum, S.E.; Elad, D.; Schwendener, S. Novel pseudo-staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec element (psiSCCmec57395) in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius CC45. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5509–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirsoleimani, A.; Brion, G.; Francois, P. Co-Carriage of Metal and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Sewage Associated Staphylococci. Genes 2021, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P. Fusidic Acid: A Bacterial Elongation Factor Inhibitor for the Oral Treatment of Acute and Chronic Staphylococcal Infections. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Hung, W.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Tsai, J.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Hsueh, P.R.; Teng, L.J. A novel fusidic acid resistance determinant, fusF, in Staphylococcus cohnii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norstrom, T.; Lannergard, J.; Hughes, D. Genetic and phenotypic identification of fusidic acid-resistant mutants with the small-colony-variant phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4438–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Hung, W.C.; Tseng, S.P.; Tsai, J.C.; Hsueh, P.R.; Teng, L.J. Fusidic acid resistance determinants in Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4985–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Tsai, J.C.; Hung, W.C.; Tseng, S.P.; Hsueh, P.R.; Teng, L.J. Identification of fusB-mediated fusidic acid resistance islands in Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5842–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsai, J.C.; Hung, W.C.; Lin, Y.T.; You, S.J.; Tseng, S.P.; Teng, L.J. New structure of phage-related islands carrying fusB and a virulence gene in fusidic acid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5737–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hung, W.C.; Chen, H.J.; Lin, Y.T.; Tsai, J.C.; Chen, C.W.; Lu, H.H.; Tseng, S.P.; Jheng, Y.Y.; Leong, K.H.; Teng, L.J. Skin Commensal Staphylococci May Act as Reservoir for Fusidic Acid Resistance Genes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 13th ed.; CLSI Standard M02; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Version 12.0; 2022. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Panda, S.; Jena, S.; Sharma, S.; Dhawan, B.; Nath, G.; Singh, D.V. Identification of Novel Sequence Types among Staphylococcus haemolyticus Isolated from Variety of Infections in India. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; Sharma, A.N.; et al. CARD 2017: Expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan. Taiwan Health and Welfare Report 2023; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2023.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).