Combinatory Effect of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin in the Control of Uropathogenic Enterococci Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Susceptibility Profile of E. faecalis Strains for GEN and NTX
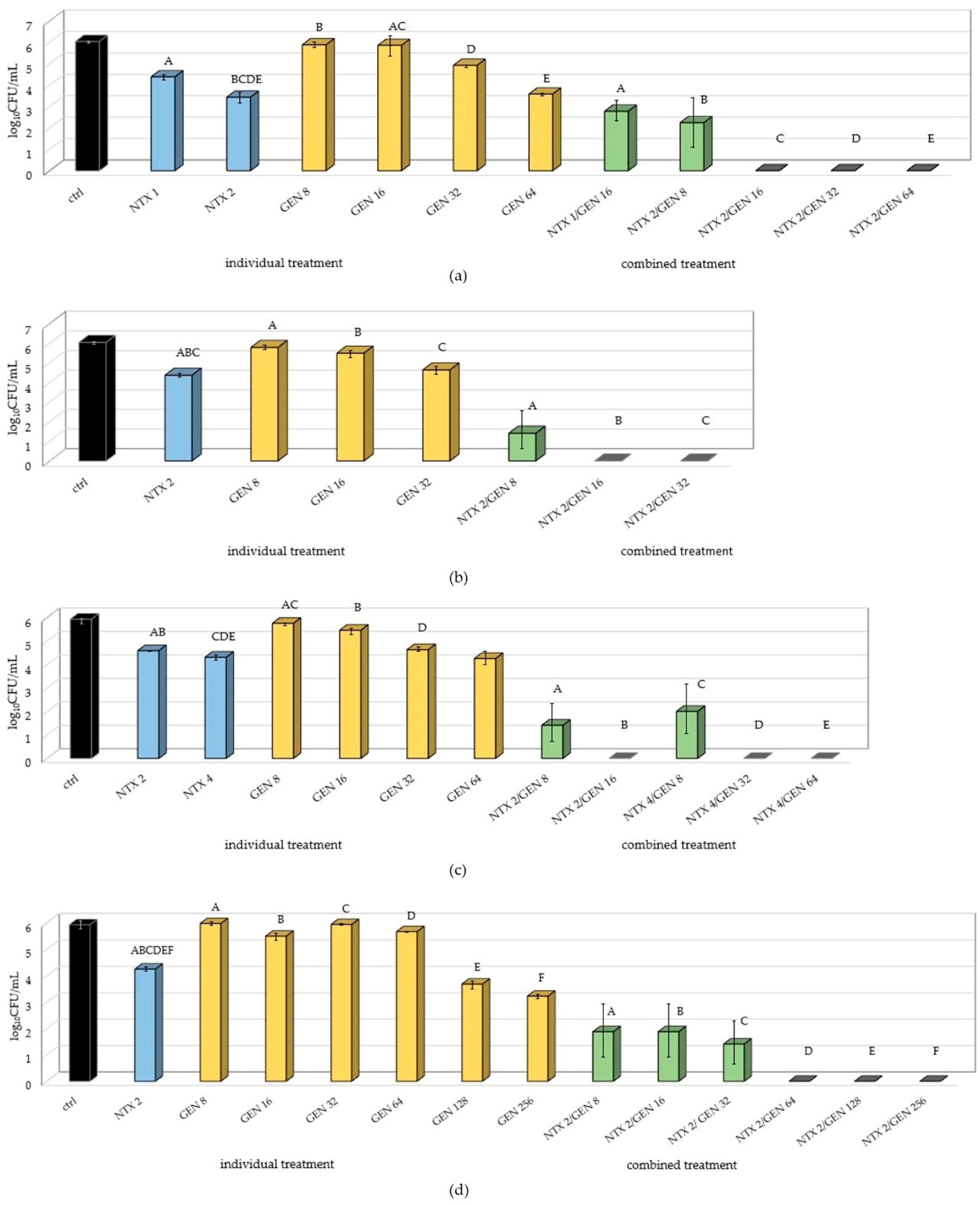
2.2. Synergism Testing of Selected Concentrations of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin on Uropathogenic E. faecalis Strains Using the Checkerboard Assay
- Synergistic (FICi ≤ 0.5);
- Additive (0.5 > FICi ≤ 1.0);
- Indifferent (1.0 > FICi ≤ 4);
- Antagonistic (FICi > 4).
2.3. Testing Inhibition of Biofilm Formation at Selected Concentrations of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin
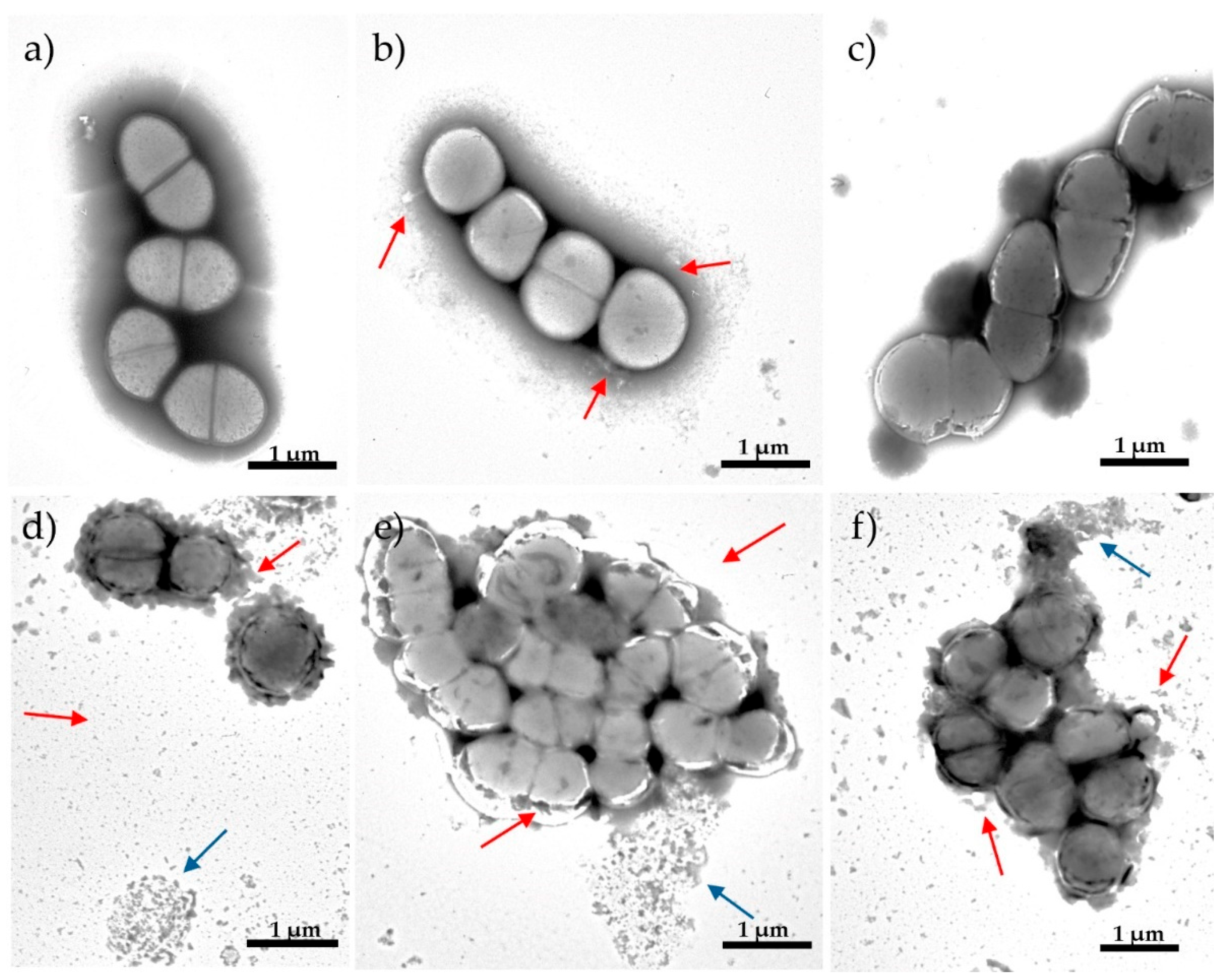
2.4. The Effect of the NTX/GEN Combined Treatment on the Morphology of ATCC29212 Strain Cells
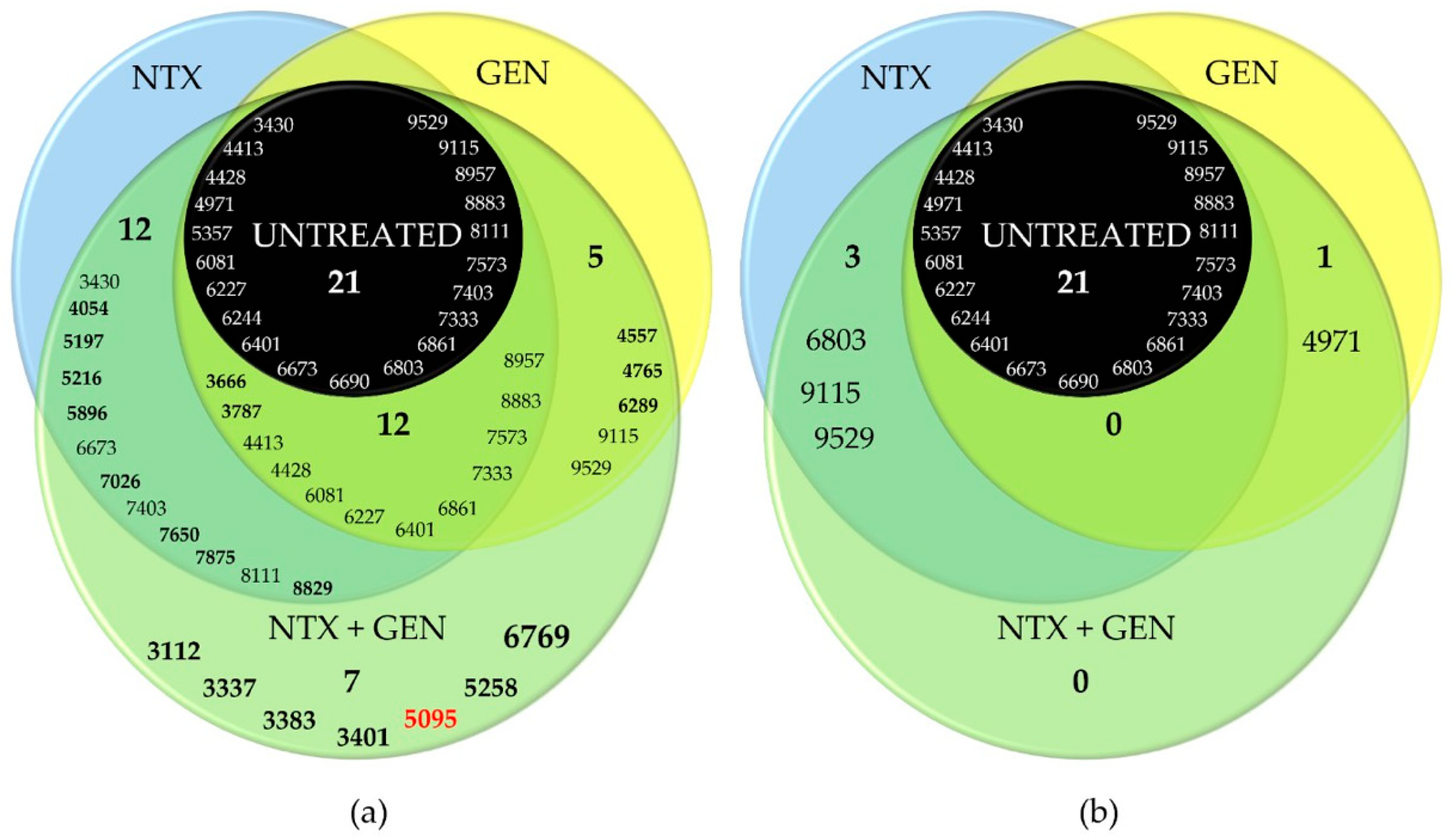
2.5. MALDI-TOF MS Analysis of ATCC29212 Wild and Mutant Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Culture Conditions, and Chemicals
4.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Selected Uropathogenic Enterococci
4.3. Biofilm Formation Assay
4.4. Examination of the Interaction of Selected Concentrations of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin on E. faecalis Strains Using the Checkerboard Assay
4.5. Examination of the Bacterial Cell Morphology Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.6. Examination of the Protein Profile of Selected Uropathogenic Enterococci Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bereket, W.; Hemalatha, K.; Getenet, B.; Wondwossen, T.; Solomon, A.; Zeynudin, A.; Kannan, S. Update on Bacterial Nosocomial Infections. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Xia, Y.; Yang, M.; Zou, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ma, L. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Membrane Proteins in Enterococcus faecalis with Low-Level Linezolid-Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Arana, A.; Valle, J.; Solano, C.; Arrizubieta, M.J.; Cucarella, C.; Lamata, M.; Amorena, B.; Leiva, J.; Penadés, J.R.; Lasa, I. The Enterococcal Surface Protein, Esp, is Involved in Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm Formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4538–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.; Capelo, J.L.; Santos, H.M.; Oliveira, I.; Marinho, C.; Gonçalves, A.; Araújo, J.E.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G. Use of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Fingerprinting to Characterize Enterococcus spp. and Escherichia coli isolates. J. Proteomics 2015, 127, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.E.; Draghi, D.C.; Thornsberry, C.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Sahm, D.F.; Wenzel, R.P. Emerging Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens in the Intensive Care Unit-a European and North American Surveillance Study (2000–2002). Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2004, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, R. Enterococci Acquire New Kinds of Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, S80–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moellering, R.C.; Weinberg, A.N. Studies on Antibiotic Synergism against Enterococci. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 2580–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, A.; Arthur, M.; Garry, L.; Carbon, C.; Courvalin, P.; Fantin, B. Bactericidal Activity of Gentamicin against Enterococcus faecalis In Vitro and In Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gaston, J.R.; Andersen, M.J.; Johnson, A.O.; Bair, K.L.; Sullivan, C.M.; Guterman, L.B.; White, A.N.; Brauer, A.L.; Learman, B.S.; Flores-Mireles, A.L.; et al. Enterococcus faecalis Polymicrobial Interactions Facilitate Biofilm Formation, Antibiotic Recalcitrance, and Persistent Colonization of the Catheterized Urinary Tract. Pathogens 2020, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, J.A.; Huang, D.B. Biofilm Formation by Enterococci. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, Y.A.; Amin, H.M.; Essam, T.M.; Yassin, A.S.; Aziz, R.K. Biofilm Formation in Enterococci: Genotype-Phenotype Correlations and Inhibition by Vancomycin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Enterococci. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2014, 12, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tyne, D.; Gilmore, M.S. Friend Turned Foe: Evolution of Enterococcal Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, J. The Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Intravenous Injections of Chinosol with Formaldehyde. Lancet 1910, 176, 1408–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wijma, R.A.; Huttner, A.; Koch, B.C.P.; Mouton, J.W.; Muller, A.E. Review of the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Nitrofurantoin and Nitroxoline. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2916–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, H.; Juretschke, C. Nitroxoline: An Option for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection with Multi-Resistant Uropathogenic Bacteria. Infection 2019, 47, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrhar, A.; Kopitar, Z.; Kozjek, F.; Presl, V.; Karba, R. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Nitroxoline. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Biopharm. 1980, 17, 476–481. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, F.; Hof, H.; Hofmann, S.; Kurzai, O.; Meis, J.F.; Hamprecht, A. Antifungal Activity of Nitroxoline against Candida auris Isolates. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1697.e7–1697.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurie, M.T.; White, C.V.; Retallack, H.; Wu, W.; Moser, M.S.; Sakanari, J.A.; Ang, K.; Wilson, C.; Arkin, M.R.; DeRisi, J.L. Functional Assessment of 2,177 U.S. and International Drugs Identifies the Quinoline Nitroxoline as a Potent Amoebicidal Agent against the Pathogen Balamuthia mandrillaris. mBio 2018, 9, e02051-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-R.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Li, X.-D.; Deng, C.-L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.-Q.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhang, B.; et al. Generation and Characterization of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Expressing GFP Reporter Gene for High Throughput Drug Screening. Antiviral Res. 2020, 182, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.; Wille, J.; Hamprecht, A.; Parcina, M.; Lehmann, C.; Schwarze-Zander, C.; Seifert, H.; Higgins, P.G. IN vitro Activity of Mecillinam and Nitroxoline against Neisseria gonorrhoeae—Re-Purposing Old Antibiotics in the Multi-Drug Resistance Era. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschner, F.; Risch, T.; Baier, C.; Schlüter, D.; Herrmann, J.; Müller, R. Nitroxoline Resistance is Associated with Significant Fitness Loss and Diminishes In Vivo Virulence of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03079-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.S.; Matsui, Y.; Bhat, S.; Nacev, B.A.; Xu, J.; Bhang, H.C.; Dhara, S.; Han, K.C.; Chong, C.R.; Pomper, M.G.; et al. Effect of Nitroxoline on Angiogenesis and Growth of Human Bladder Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1855–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresken, M.; Körber-Irrgang, B. In Vitro Activity of Nitroxoline against Escherichia coli Urine Isolates from Outpatient Departments in Germany. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 7019–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Taggart, J.E.; Zhang, X.; Benbrook, D.M.; Lind, S.E.; Ding, W.-Q. Nitroxoline (8-Hydroxy-5-Nitroquinoline) is More a Potent Anti-Cancer Agent than Clioquinol (5-Chloro-7-Iodo-8-Quinoline). Cancer Lett. 2011, 312, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureshkumar, B.; Mary, Y.S.; Mary, Y.S.; Suma, S. Spectroscopic and DFT Investigations of 8-Hydroxy Quinoline-5-Sulfonic Acid-5-Chloro-8-Hydroxyquinoline Cocrystal. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Wakiel, N.; El-Ghamry, H. Nitroxoline Azo Dye Complexes as Effective Heterogeneous Catalysts for Color Removal and Degradation of Some Organic Textile Dyes. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2017, 49, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S. 8-Hydroxyquinolines: A Review of Their Metal Chelating Properties and Medicinal Applications. DDDT 2013, 7, 1157–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.B. Privileged Structures: Efficient Chemical “Navigators” toward Unexplored Biologically Relevant Chemical Spaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14629–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repac Antić, D.; Parčina, M.; Gobin, I.; Petković Didović, M. Chelation in Antibacterial Drugs: From Nitroxoline to Cefiderocol and Beyond. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, A.R.; Gionbelli, M.P.; Gosmann, G.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Lopes, M.S.; Fernandes de Andrade, S. Novel Antimicrobial 8-Hydroxyquinoline-Based Agents: Current Development, Structure–Activity Relationships, and Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 16349–16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, J.; Mitrović, A. Nitroxoline: Repurposing Its Antimicrobial to Antitumor Application. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobke, A.; Klinger, M.; Hermann, B.; Sachse, S.; Nietzsche, S.; Makarewicz, O.; Keller, P.M.; Pfister, W.; Straube, E. The Urinary Antibiotic 5-Nitro-8-Hydroxyquinoline (Nitroxoline) Reduces the Formation and Induces the Dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Chelation of Iron and Zinc. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6021–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelhassan, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yousaf, H.; Nguyen, M.T.; Rolfe, M.; Schultz, G.S.; Huigens, R.W. Nitroxoline: A Broad-Spectrum Biofilm-Eradicating Agent against Pathogenic Bacteria. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlioux, P.; Karam, D.; Amgar, A.; Perdiz, M. Relation of the chelating property of nitroxoline, the surface hydrophobicity and the inhibition of bacterial adherence. Pathol. Biol. 1989, 37, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bourlioux, P.; Botto, H.; Karam, D.; Amgar, A.; Camey, M. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by nitroxoline on cellular adhesion and on urinary catheter surfaces. Pathol. Biol. 1989, 37, 451–454. [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero, L.; Perdiz, M.; Bourlioux, P. Direct effect of nitroxoline in the inhibition of bacterial adherence to urinary catheters. Pathol. Biol. 1990, 38, 455–458. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Home Page. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 14.0. 2024. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/eucast_news/news_singleview?tx_ttnews%5Btt_news%5D=566&cHash=db55f3a8829726044512a1ff74cce44b (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Wantia, N.; Gatermann, S.G.; Rothe, K.; Laufenberg, R. New EUCAST Definitions of S, I and R from 2019—German Physicians are Largely Not Aware of the Changes. Infection 2020, 48, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdtrakulkiat, R.; Boonpangrak, S.; Sinthupoom, N.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Derivatives (Halogen, Nitro and Amino) of 8-Hydroxyquinoline with Highly Potent Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 6, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobke, A.; Makarewicz, O.; Baier, M.; Bär, C.; Pfister, W.; Gatermann, S.G.; Pletz, M.W.; Forstner, C. Empirical Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Infections in the Face of Spreading Multidrug Resistance: In vitro Study on the Effectiveness of Nitroxoline. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Vidya, K.; Mallya, P. Inhibition of Bacterial Adhesion by Subinhibitory Concentrations of Antibiotics. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 23, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallapareddy, S.R.; Singh, K.V.; Okhuysen, P.C.; Murray, B.E. A Functional Collagen Adhesin Gene, acm, in Clinical Isolates of Enterococcus faecium Correlates with the Recent Success of This Emerging Nosocomial Pathogen. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4110–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallapareddy, S.R.; Singh, K.V.; Sillanpaa, J.; Garsin, D.A.; Hook, M.; Erlandsen, S.L.; Murray, B.E. Endocarditis and Biofilm-Associated Pili of Enterococcus faecalis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2799–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccella, M.; Santella, B.; Pagliano, P.; De Filippis, A.; Casolaro, V.; Galdiero, M.; Borrelli, A.; Capunzo, M.; Boccia, G.; Franci, G. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterococcus Species: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Italy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emaneini, M.; Khoramian, B.; Jabalameli, F.; Beigverdi, R.; Asadollahi, K.; Taherikalani, M.; Lari, A.R. Prevalence of High-Level Gentamicin-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium in an Iranian hospital. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2016, 57, E197–E200. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Di Luca, M.; Tkhilaishvili, T.; Trampuz, A.; Gonzalez Moreno, M. Synergistic Activity of Fosfomycin, Ciprofloxacin, and Gentamicin against Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, G.F.; Tsang, S.-T.J.; Gwynne, P.J.; MacKenzie, S.P.; Simpson, A.H.R.W.; Breusch, S.J.; Gallagher, M.P. Unexpected Synergistic and Antagonistic Antibiotic Activity against Staphylococcus Biofilms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, L.; Hartung, A.; Makarewicz, O.; Pletz, M.W. In Vivo Synergism of Ampicillin, Gentamicin, Ceftaroline and Ceftriaxone against Enterococcus faecalis Assessed in the Galleria mellonella Infection Model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, dkaa129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.R.; Robinson, R.G.; Koornhof, H.J. Antibacterial Activity of Nitroxoline and Sulphamethizole Alone and in Combination in Urinary Tract Infections. S. Afr. Med. J. Suid-Afr. Tydskr. Vir Geneeskd. 1978, 54, 959–962. [Google Scholar]
- Emerson, D.; Agulto, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, L. Identifying and Characterizing Bacteria in an Era of Genomics and Proteomics. BioScience 2008, 58, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Z.-M.; Halachev, M.R.; Loman, N.J.; Constantinidou, C.; Pallen, M.J. Defining Bacterial Species in the Genomic Era: Insights from the Genus Acinetobacter. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.; Phillips, C. The Ecology, Epidemiology and Virulence of Enterococcus. Microbiology 2009, 155, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenbeck, B.L.; Rice, L.B. Intrinsic and Acquired Resistance Mechanisms in Enterococcus. Virulence 2012, 3, 421–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril, A.G.; Quintela-Baluja, M.; Villa, T.G.; Calo-Mata, P.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Carrera, M. Proteomic Characterization of Virulence Factors and Related Proteins in Enterococcus Strains from Dairy and Fermented Food Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryaletha, K.; Narendrakumar, L.; John, J.; Radhakrishnan, M.P.; George, S.; Thomas, S. Decoding the Proteomic Changes Involved in the Biofilm Formation of Enterococcus faecalis SK460 to Elucidate Potential Biofilm Determinants. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazvinian, M.; Asgharzadeh Marghmalek, S.; Gholami, M.; Amir Gholami, S.; Amiri, E.; Goli, H.R. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns, Virulence Genes, and Biofilm Formation in Enterococci Strains Collected from Different Sources. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaze, M.T.M.; Aydin, B.; Carlson, R.P.; Hanley, L. Identification and Imaging of Peptides and Proteins on Enterococcus faecalis Biofilms by Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Analyst 2012, 137, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woitschach, F.; Kloss, M.; Schlodder, K.; Borck, A.; Grabow, N.; Reisinger, E.C.; Sombetzki, M. Bacterial Adhesion and Biofilm Formation of Enterococcus faecalis on Zwitterionic Methylmethacrylat and Polysulfones. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 868338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parga, A.; Manoil, D.; Brundin, M.; Otero, A.; Belibasakis, G.N. Gram-Negative Quorum Sensing Signalling Enhances Biofilm Formation and Virulence Traits in Gram-Positive Pathogen Enterococcus faecalis. J. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2208901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo-Moreno, A.M.; González-Martín, M.L.; Pérez-Giraldo, C.; Bruque, J.M.; Gómez-García, A.C. Serum as a Factor Influencing Adhesion of Enterococcus faecalis to Glass and Silicone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5784–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela-Baluja, M.; Böhme, K.; Fernández-No, I.C.; Morandi, S.; Alnakip, M.E.; Caamaño-Antelo, S.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Calo-Mata, P. Characterization of Different Food-isolated Enterococcus strains by MALDI—TOF Mass Fingerprinting. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2240–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Hauschild, T.; Ró Żański, P.; Marek, A. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry as a Useful Tool for Identification of Enterococcus spp. from Wild Birds and Differentiation of Closely Related Species. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, P.M.; Price, G.R.; Schooneveldt, J.M.; Schlebusch, S.; Tilse, M.H.; Urbanski, T.; Hamilton, B.; Venter, D. Use of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry To Identify Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci and Investigate the Epidemiology of an Outbreak. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2918–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, S.; Courvalin, P. Regulation of VanB-Type Vancomycin Resistance Gene Expression by the VanS(B)-VanR (B) Two-Component Regulatory System in Enterococcus faecalis V583. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, N.; Kumar, M.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Virdi, J.S. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: An Emerging Technology for Microbial Identification and Diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, L. MALDI-TOF Characterization of Protein Expression Mutation during Morphological Changes of Bacteria under the Impact of Antibiotics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2352–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenlehner, F.M.E.; Münch, F.; Pilatz, A.; Bärmann, B.; Weidner, W.; Wagenlehner, C.M.; Straubinger, M.; Blenk, H.; Pfister, W.; Kresken, M.; et al. Urinary Concentrations and Antibacterial Activities of Nitroxoline at 250 Milligrams versus Trimethoprim at 200 Milligrams against Uropathogens in Healthy Volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Bai, B.; Lin, Z.; Pu, Z.; Yao, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Deng, X.; Deng, Q.; Yu, Z. Characterization of Biofilm Formation by Enterococcus faecalis Isolates Derived from Urinary Tract Infections in China. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tendolkar, P.M.; Baghdayan, A.S.; Gilmore, M.S.; Shankar, N. Enterococcal Surface Protein, Esp, Enhances Biofilm Formation by Enterococcus faecalis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6032–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banin, E.; Brady, K.M.; Greenberg, E.P. Chelator-Induced Dispersal and Killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cells in a Biofilm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2064–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avidan, O.; Satanower, S.; Banin, E. Iron and Bacterial Biofilm Development. In Microbial Mats; Seckbach, J., Oren, A., Eds.; Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 14, pp. 359–383. ISBN 978-90-481-3798-5. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R.; Santhakumari, S.; Poonguzhali, P.; Geetha, M.; Dyavaiah, M.; Xiangmin, L. Bacterial Biofilm Inhibition: A Focused Review on Recent Therapeutic Strategies for Combating the Biofilm Mediated Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 676458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, L.; Goraya, M.; Arafat, Y.; Ajmal, M.; Chen, J.-L.; Yu, D. Molecular Mechanism of Quorum-Sensing in Enterococcus faecalis: Its Role in Virulence and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellon-Fontaine, M.-N.; Rault, J.; van Oss, C.J. Microbial Adhesion to Solvents: A Novel Method to Determine the Electron-donor/Electron-Acceptor or Lewis Acid-Base Properties of Microbial cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1996, 7, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkić, I.; Gobin, I.; Begić, G.; Antić, D.R.; Ristivojević, P.; Jurica, K.; Berić, T.; Lozo, J.; Abram, M.; Stanković, S. Antibacterial Activity of Herbal Extracts towards Uropathogenic Enterococcus Isolates as a Natural Approach in Control of Urinary Tract Infections. J. Herb. Med. 2021, 28, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatoom, A.A.; Cunningham, S.A.; Ihde, S.M.; Mandrekar, J.; Patel, R. Comparison of Direct Colony Method versus Extraction Method for Identification of Gram-Positive Cocci by Use of Bruker Biotyper Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2868–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topić Popović, N.; Kazazić, S.P.; Bojanić, K.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Čož-Rakovac, R. Sample Preparation and Culture Condition Effects on MALDI-TOF MS Identification of Bacteria: A Review. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 42, mas.21739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
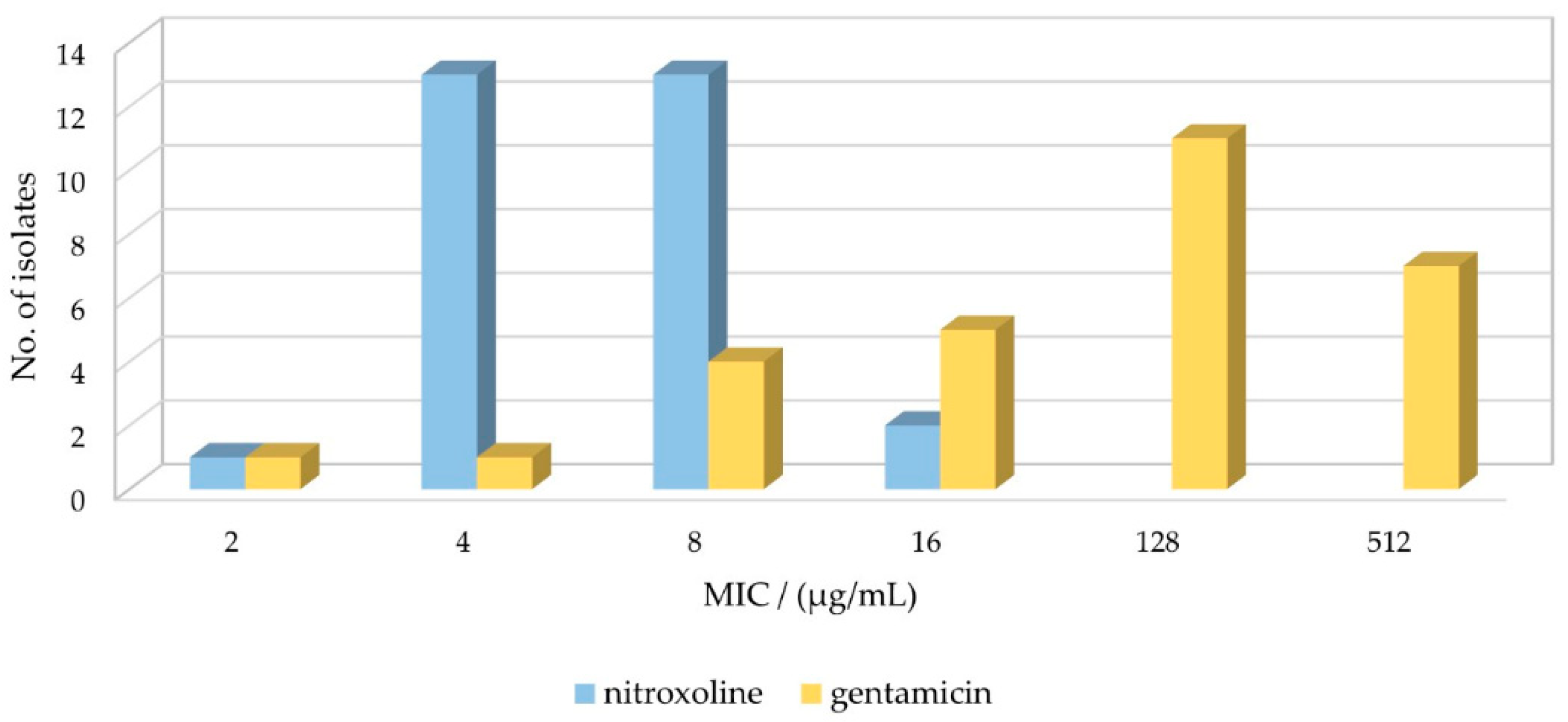

| E. faecalis Strain | Gentamicin | Nitroxoline | GROUP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (µg/mL) | MIC (µg/mL) | MBC (µg/mL) | MAC (µg/mL) | ||
| E46 | 2 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 1 |
| E61 | 4 | 16 | >64 | 8 | 2 |
| E34 | 8 | 2 | 32 | 2 | 3 |
| E36 | 8 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| ATCC29212 | 8 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 4 |
| E69 | 8 | 8 | >64 | 4 | |
| E89 | 16 | 4 | 32 | 2 | 5 |
| E85 | 16 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E10 | 16 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E16 | 16 | 8 | >64 | 4 | 6 |
| E35 | 16 | 8 | >64 | 4 | |
| E47 | 128 | 4 | 32 | 2 | 7 |
| E15 | 128 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E32 | 128 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E84 | 128 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E95 | 128 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E79 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 8 |
| E38 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 4 | |
| E55 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 4 | |
| E45 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 4 | |
| E72 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 4 | |
| E41 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 4 | |
| E39 | 512 | 4 | 32 | 2 | 9 |
| E8 | 512 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E58 | 512 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E1 | 512 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| E7 | 512 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 10 |
| E48 | 512 | 8 | 32 | 4 | |
| E37 | 512 | 8 | >64 | 4 | |
| Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. faecalis Strains | Individual MICs NTX/GEN (μg/mL) | Combination MICs NTX+GEN (μg/mL) | ||
| GROUP 8 (E79, E38, E55, E45, E72, E41) | 8/128 | 2/8 | 2/16 | 2/32 |
| GROUP 4 (ATCC29212, E69) | 8/8 | 2/0.5 | 2/1 | 2/2 |
| Additive Antimicrobial Effect | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. faecalis Strains | Individual MICs NTX/GEN (μg/mL) | Combination MICs NTX + GEN (μg/mL) | |||||
| GROUP 8 (E79, E38, E55, E45, E72, E41) | 8/128 | 4/8 | 4/16 | 4/32 | 4/64 | 2/64 | 1/64 |
| GROUP 4 (ATCC29212, E69) | 8/8 | 4/0.5 | 4/1 | 4/2 | 4/4 | 2/4 | |
| GROUP 7 (E47, E15, E32, E84, E95) | 4/128 | 2/8 | 2/16 | 2/32 | 2/64 | 1/64 | |
| GROUP 3 (E34, E36) | 4/8 | 2/0.5 | 2/1 | 2/2 | 2/4 | 1/4 | |
| GROUP 5 (E89, E85, E10) | 4/16 | 2/2 | 2/4 | 2/8 | 1/8 | ||
| GROUP 2 (E61) | 8/4 | 4/0.5 | 4/1 | 4/2 | |||
| GROUP 6 (E16, E35) | 8/16 | 4/2 | 4/4 | 4/8 | |||
| GROUP 9 (E39, E8, E58, E1) | 4/512 | 2/8 | 2/16 | 2/32 | 2/64 | 2/128 | 2/256 |
| GROUP 10 (E7, E48, E37) | 8/512 | 4/8 | 4/16 | 4/32 | 4/64 | 4/128 | 4/256 |
| GROUP 1 (E46) | 8/2 | 4/0.5 | 4/1 | 2/1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Repac Antić, D.; Kovač, B.; Kolenc, M.; Brčić Karačonji, I.; Gobin, I.; Petković Didović, M. Combinatory Effect of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin in the Control of Uropathogenic Enterococci Infections. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090829
Repac Antić D, Kovač B, Kolenc M, Brčić Karačonji I, Gobin I, Petković Didović M. Combinatory Effect of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin in the Control of Uropathogenic Enterococci Infections. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(9):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090829
Chicago/Turabian StyleRepac Antić, Davorka, Bruno Kovač, Marko Kolenc, Irena Brčić Karačonji, Ivana Gobin, and Mirna Petković Didović. 2024. "Combinatory Effect of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin in the Control of Uropathogenic Enterococci Infections" Antibiotics 13, no. 9: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090829
APA StyleRepac Antić, D., Kovač, B., Kolenc, M., Brčić Karačonji, I., Gobin, I., & Petković Didović, M. (2024). Combinatory Effect of Nitroxoline and Gentamicin in the Control of Uropathogenic Enterococci Infections. Antibiotics, 13(9), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090829









