Sublethal Sodium Hypochlorite Exposure: Impact on Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Efflux Pump Overexpression and Cross-Resistance to Imipenem
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Exposure to Disinfectants on Gram-Negative Bacteria
2.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility Was Reduced According to NaOCl Exposure
2.3. Cross-Resistance between NaOCl Disinfectant and β-Lactams in Klebsiella pneumoniae
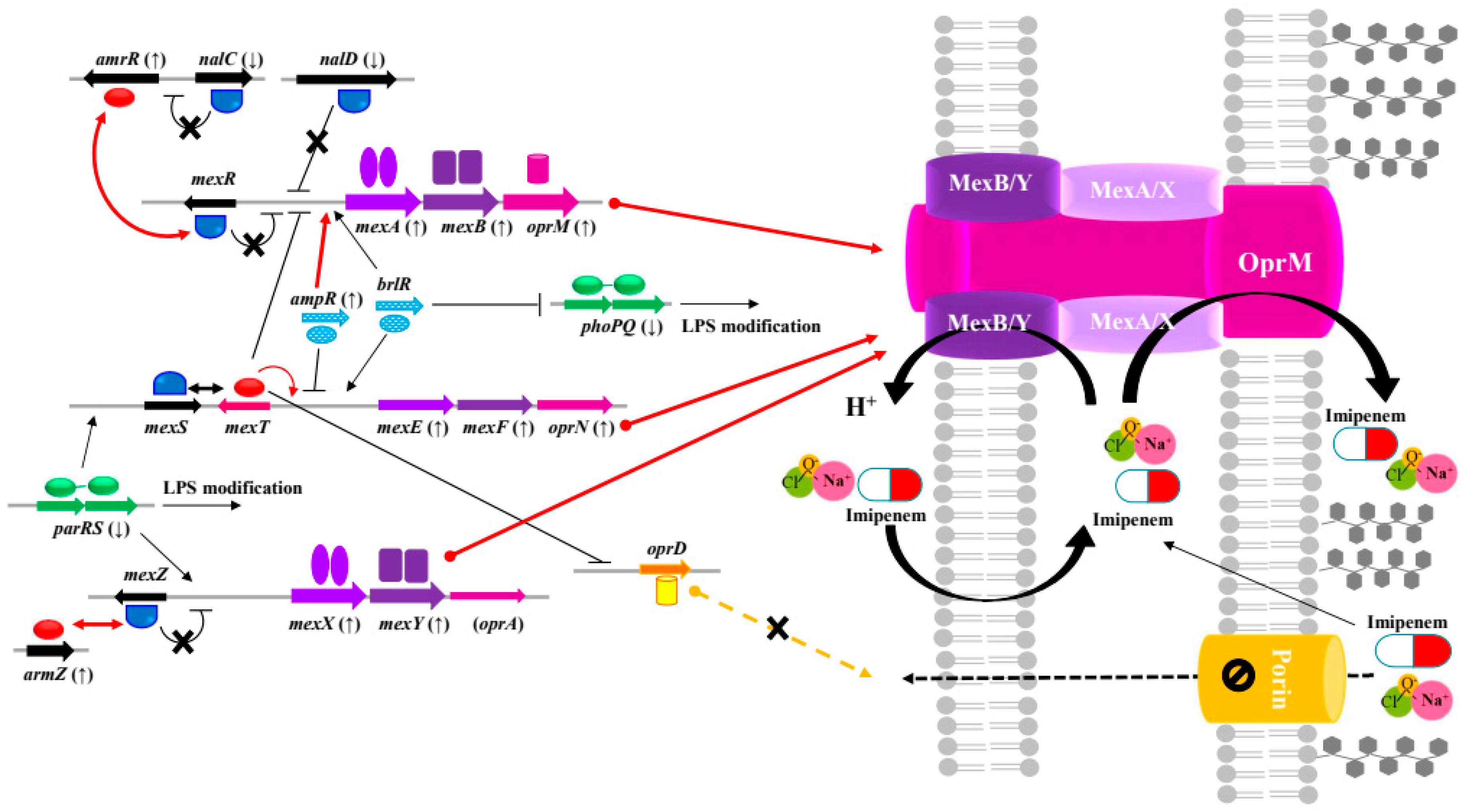
2.4. Cross-Resistance between NaOCl Disinfectant and β-Lactams in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Discussion

4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Identification of Bacterial Strains
4.2. Determination of Antibiotic and Disinfectant Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
4.3. NaOCl Disinfectant Exposure and Bacterial Subculturing
4.4. RNA Extraction, Transcriptome Sequencing, and Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPA, 2022. List N Advanced Search Page: Disinfectant for Coronavirus (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/coronavirus-and-disinfectants/list-n-advanced-search-page-disinfectants-coronavirus-covid-19 (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Chen, B.; Han, J.; Dai, H.; Jia, P. Biocide-tolerance and antibiotic-resistance in community environments and risk of direct transfers to humans: Unintended consequences of community-wide surface disinfecting during COVID-19? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobie, T.A.; Roba, A.A.; Booth, J.A.; Kristiansen, K.I.; Aseffa, A.; Skarstad, K.; Bjørås, M. Antimicrobial resistance: A challenge awaiting the post-COVID-19 era. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 111, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.R.; Safaee, M.M.; Wuest, W.M.; Furst, A.L. The silent pandemic: Emergent antibiotic resistances following the global response to SARS-CoV-2. IScience 2021, 24, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elekhnawy, E.; Sonbol, F.; Abdelaziz, A.; Elbanna, T. Potential impact of biocide adaptation on selection of antibiotic resistance in bacterial isolates. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Yutao, L.; Goh, S.G.; Ng, C.; Luhua, Y.; Tran, N.H.; Gin, K.Y.H. Quaternary ammonium compounds of emerging concern: Classification, occurrence, fate, toxicity and antimicrobial resistance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, Z.; Song, H.; Bond, P.L.; Guo, J. Chlorine disinfection facilitates natural transformation through ROS-mediated oxidative stress. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2969–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion (DHQP). 2016. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection/disinfection-methods/chemical.html (accessed on 18 September 2016).
- Nasr, A.M.; Mostafa, M.S.; Arnaout, H.H.; Elshimy, A.A.A. The effect of exposure to subinhibitory concentrations of hypochlorite and quaternary ammonium compounds on antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2018, 46, e57–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauf, G.A.; Cunningham, A.L.; Kazi, M.I.; Riddington, I.M.; Crofts, A.A.; Cattoir, V.; Trent, M.S.; Davies, B.W. Exploring the antimicrobial action of quaternary amines against Acinetobacter baumannii. mBio 2018, 9, e02394-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz Nizer, W.S.; Inkovskiy, V.; Overhage, J. Surviving reactive chlorine stress: Responses of gram-negative bacteria to hypochlorous acid. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks. Assessment of the Antibiotic Resistance Effects of Biocides. 2009. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/04_scenihr/docs/scenihr_o_021.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Jones, I.A.; Joshi, L.T. Biocide use in the antimicrobial era: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Beattie, T.K.; Knapp, C.W. Relationship between antibiotic-and disinfectant-resistance profiles in bacteria harvested from tap water. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Guo, J. Disinfection spreads antimicrobial resistance. Science 2021, 371, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, M.E.; Sutton, J.M. Efflux-mediated tolerance to cationic biocides, a cause for concern? Microbiology 2022, 168, 001263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitiku, M.; Ali, S.; Kibru, G. Antimicrobial drug resistance and disinfectants susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from clinical and environmental samples in Jimma University specialized hospital, Southwest Ethiopia. Am. J. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 2, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Xie, X.; Huang, S. Disinfection Strategies for Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Healthcare Facility. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamori, H.; Rutala, W.A.; Gergen, M.F.; Sickbert-Bennett, E.E.; Weber, D.J. Germicidal activity against carbapenem/colistin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae using a quantitative carrier test method. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, R.; Waite-Cusic, J.; Weisberg, A.J.; Riutta, E.R.; Chang, J.H.; Kovacevic, J. Adaptation to a commercial quaternary ammonium compound sanitizer leads to cross-resistance to select antibiotics in Listeria monocytogenes isolated from fresh produce environments. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Bai, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Qu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. Chlorine tolerance and cross-resistance to antibiotics in poultry-associated Salmonella isolates in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzari, M.; Chetia, P. RND efflux pump mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A major issue worldwide. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Elkins, C.A.; Zgurskaya, H.I. Efflux-Mediated Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria: Mechanisms, Regulation and Clinical Implications; Li, X.Z., Elkins, C.A., Zgurskaya, H.I., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhu, L. Molecular mechanism of antibiotic resistance induced by mono-and twin-chained quaternary ammonium compounds. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.P.; Woodward, M.J. The multiple antibiotic resistance (mar) locus and its significance. Res. Vet. Sci. 2002, 72, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetri, S.; Das, B.J.; Bhowmik, D.; Chanda, D.D.; Chakravarty, A.; Bhattacharjee, A. Transcriptional response of mar, sox and rob regulon against concentration gradient carbapenem stress within Escherichia coli isolated from hospital acquired infection. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbood, H.M.; Hijazi, K.; Gould, I.M. Chlorhexidine resistance or Cross-resistance, that is the question. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wand, M.E.; Darby, E.M.; Blair, J.M.; Sutton, J.M. Contribution of the efflux pump AcrAB-TolC to the tolerance of chlorhexidine and other biocides in Klebsiella spp. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 001496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Plésiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdial, C.; Serrano, I.; Tavares, L.; Gil, S.; Oliveira, M. Mechanisms of Antibiotic and Biocide Resistance That Contribute to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Persistence in the Hospital Environment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubonja-Sonje, M.; Matovina, M.; Skrobonja, I.; Bedenic, B.; Abram, M. Mechanisms of carbapenem resistance in multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a Croatian hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulyayangkul, P.; Satapoomin, N.; Avison, M.B.; Charoenlap, N.; Vattanaviboon, P.; Mongkolsuk, S. Over-expression of hypochlorite inducible Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) pumps reduces antimicrobial drug susceptibility by increasing the production of MexXY Mediated by ArmZ in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 592153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradali, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lifestyle: A paradigm for adaptation, survival, and persistence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Strains | MICs (mg/L) | Antibiotic Susceptibility (Exposure to 1250 µg/mL NaOCl) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before 1 | After | Increased | Reduced | |||
| K. pneumoniae | CRKP * | Z0317KP0159 | 500 | 2500 | FOX, IMI, CHL † | ND 2 |
| Z0317KP0181 | 500 | 2500 | IMI | GEN ‡ | ||
| Z0318KP0099 | 500 | 2500 | IMI | STR | ||
| Z0318KP0107 | 500 | 2500 | IMI, CHL, AZI | ND | ||
| Z0318KP0236 | 500 | 2500 | IMI, CHL | GEN, AZI | ||
| P. aeruginosa | CSPA | ATCC 27853 | 500 | 2500 | AXO, IMI, STR, COL | TAZ, CIP, NAL, TET, GEN, AMI, SXT |
| Z0219PA0007 | 500 | 1250 | AXO, IMI, COL | CIP, NAL, STR, SXT | ||
| CRPA | I0020PA0021 (HL-IMI) | 500 | 2500 | X 3 | X | |
| I0020PA0028 | 500 | 1250 | IMI, CIP, NAL, TET, AMI, STR | FOT, TAZ, AXO, GEN | ||
| Z0217PA0020 (HL-IMI) | 500 | 2500 | FOT, TAZ, CIP, CHL, GEN, STR, SXT | NAL, AMI | ||
| Group | Function | Gene Locus Tag (Gene Name) | Gene Expression Fold Change * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z0317 KP0159 | Z0318 KP0107 | |||
| Enzymatic degradation | Class A carbapenemase Kpc-2 | KPHS_p200360 (blaKPC-2) | −2.26 | 3.40 |
| β-lactamase | KPHS_25220 (blaSHV) | 2.43 | −1.44 | |
| KPHS_13880 | - | 2.71 | ||
| RND efflux pump | Repression of porin OmpF (mar-sox-rob regulon activator) | KPHS_25470 (marA) | −1.44 | 67.73 |
| Multidrug efflux membrane fusion protein | KPHS_11890 (acrA) | 1.46 | 5.18 | |
| Multidrug efflux transporter | KPHS_11880 (acrB) | 2.19 | 2.30 | |
| Multidrug efflux transporter (permease EefB) | KPHS_52090 (acrB) | 2.07 | 2.65 | |
| Outer membrane channel protein | KPHS_45760 (tolC) | 2.83 | 1.30 | |
| Multidrug efflux transport outer membrane protein EefC | KPHS_52100 (adeK) | 2.13 | −1.16 | |
| Porin | Outer membrane protein 1A/OmpK35 porin | KPHS_18370 (ompF) | −2.45 | 1.52 |
| Outer membrane pore protein C/OmpK36 porin | KPHS_37010 (ompC) | - | 2.22 | |
| Group | Function | Gene Locus Tag (Gene Name) | Gene Expression Fold Change * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 27853 | Z0219 PA0007 | Z0217 PA0020 | ||||
| β- lactamase | AmpC beta-lactamase | PA4110 (ampC) | - | −2.32 | −1.07 | |
| Beta-hexosaminidase | PA3005 (nagZ) | 4.30 | - | - | ||
| Transport of degraded muropeptides (GlcNAc-anhMurNAc) | PA4218 (ampG) | −6.95 | 13.74 | 1.92 | ||
| RND efflux pump | MexAB-OprM | MexR anti-repressor ArmR | PA3719 (armR) | - | 2.29 | 3.87 |
| Transcriptional regulator AmpR | PA4109 (ampR) | - | 2.31 | 2.62 | ||
| Transcriptional regulator | PA3721 (nalC) | −2.65 | - | - | ||
| Transcriptional regulator | PA3574 (nalD) | −2.39 | −2.33 | −1.75 | ||
| Multidrug resistance protein MexA | PA0425 (mexA) | - | 2.50 | 2.03 | ||
| Multidrug resistance protein MexB | PA0426, PA4375 (mexB) | - | 2.75 | 3.09 | ||
| Outer membrane protein OprM | PA0427 (oprM) | - | 2.09 | 3.06 | ||
| MexEF-OprN | Multidrug efflux membrane fusion protein MexE | PA2493 (mexE) | 11.88 | - | - | |
| Multidrug efflux transporter MexF | PA2494 (mexF) | 4.11 | - | - | ||
| Transcriptional regulator AmpR | PA2495 (oprN) | 9.75 | - | - | ||
| MexXY-(OprM) | Transcriptional regulator | PA2020 (mexZ) | - | 2.84 | −2.21 | |
| Two-component response regulator ParR | PA1799 (parR) | −7.73 | −2.53 | −2.06 | ||
| Multidrug efflux membrane fusion protein | PA2019 (mexX) | 4.04 | 20.45 | 8.88 | ||
| Multidrug efflux transporter | PA2018 (mexY) | 2.32 | 21.02 | 8.00 | ||
| Outer membrane protein | PA4144 (oprM) | 2.64 | 1.11 | −2.13 | ||
| MexZ anti-repressor | PA5471 (armZ) | 9.59 | 4.59 | 10.34 | ||
| MexVW-OprM | Multidrug efflux membrane fusion protein MexV | PA4374 (mexV) | - | - | - | |
| Multidrug efflux membrane protein | PA4375 (mexW) | - | 1.31 | 2.62 | ||
| Outer membrane protein OprM | PA4974 (oprM) | - | −2.63 | 5.65 | ||
| Porin | Porin D (imipenem) | PA0958 (oprD) | - | - | 2.91 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, J.-H.; Yoo, J.S. Sublethal Sodium Hypochlorite Exposure: Impact on Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Efflux Pump Overexpression and Cross-Resistance to Imipenem. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090828
Nam J-H, Yoo JS. Sublethal Sodium Hypochlorite Exposure: Impact on Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Efflux Pump Overexpression and Cross-Resistance to Imipenem. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(9):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090828
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Ji-Hyun, and Jung Sik Yoo. 2024. "Sublethal Sodium Hypochlorite Exposure: Impact on Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Efflux Pump Overexpression and Cross-Resistance to Imipenem" Antibiotics 13, no. 9: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090828
APA StyleNam, J.-H., & Yoo, J. S. (2024). Sublethal Sodium Hypochlorite Exposure: Impact on Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Efflux Pump Overexpression and Cross-Resistance to Imipenem. Antibiotics, 13(9), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090828






