Biomarker-Based Analysis of Pain in Patients with Tick-Borne Infections before and after Antibiotic Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
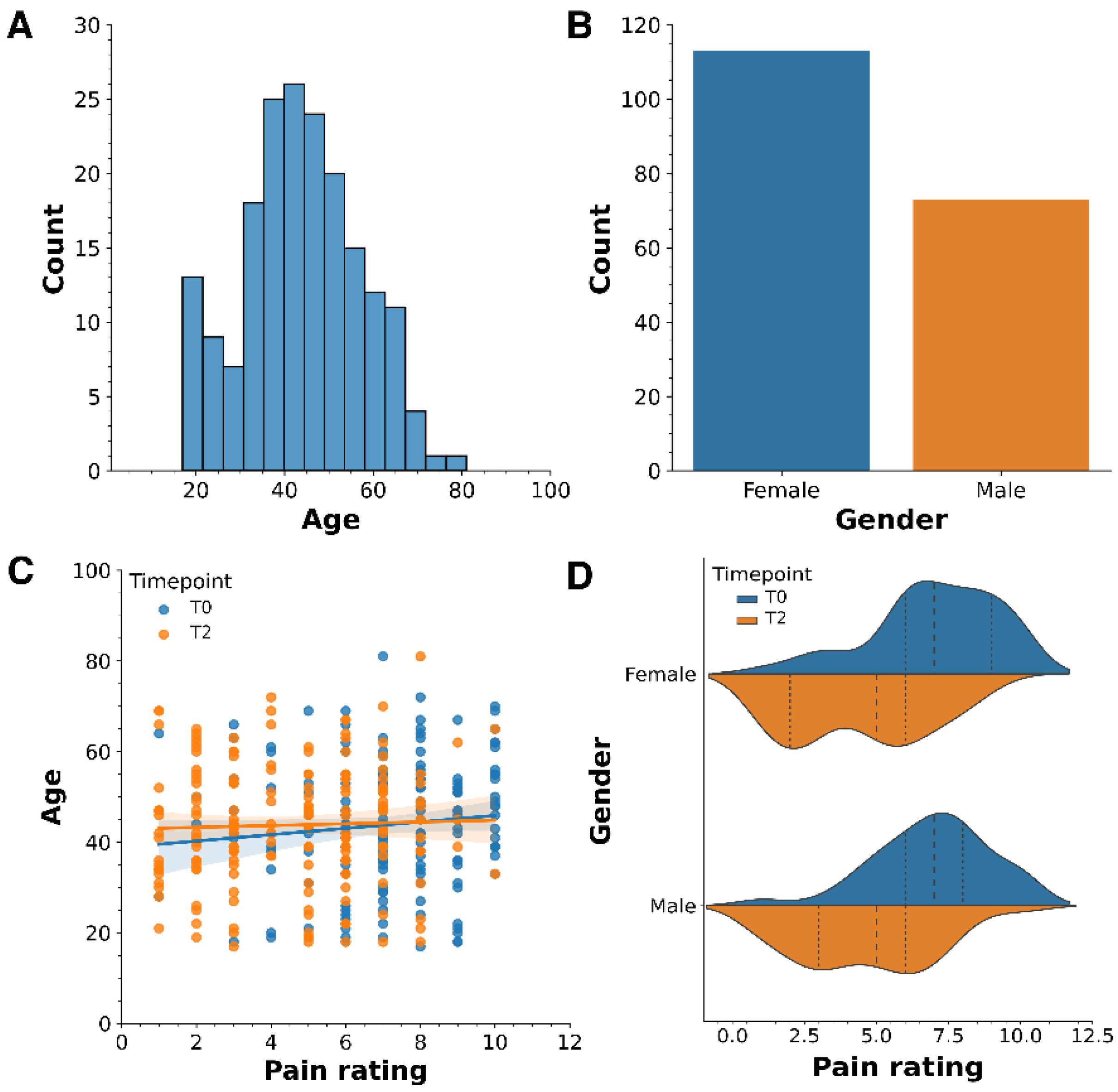
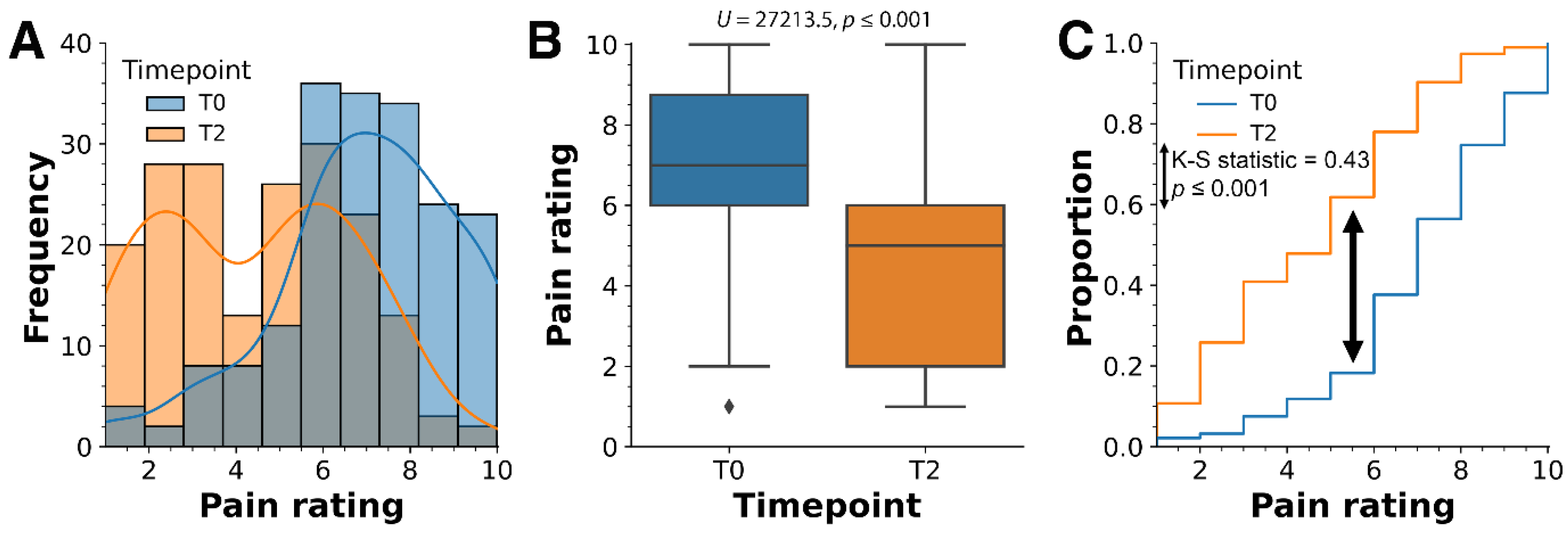
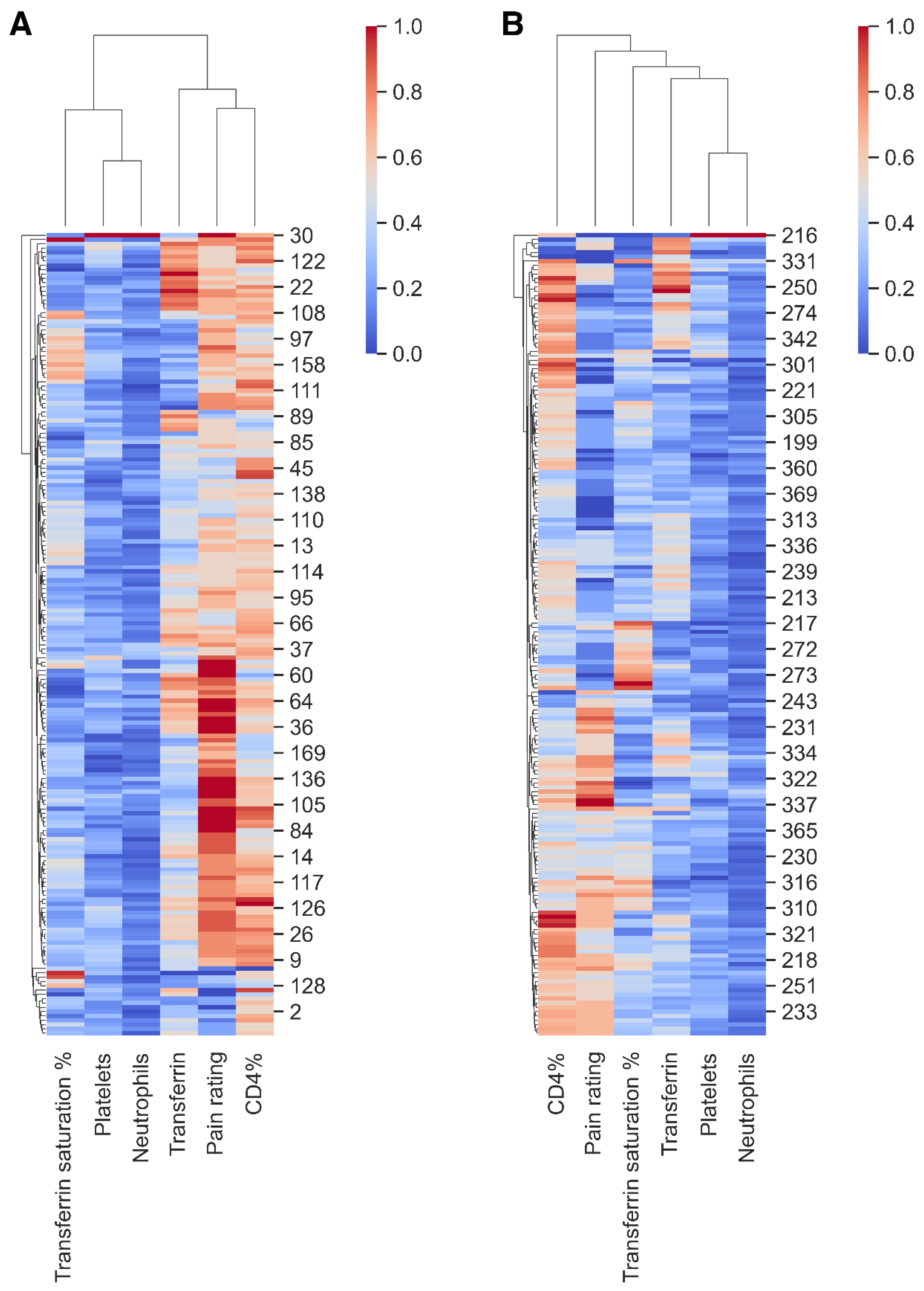
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Key Findings
3.2. Age and Gender
3.3. Pain and Biomarkers
3.4. Implications for Practice & Policy
3.5. Study Limitations and Future Research Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Approval
4.2. Patient Cohort and Sample Size Estimation
4.3. Analyses of Immune Markers and Biomarkers
4.4. Tools for Processing Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eisen, L. Stemming the Rising Tide of Human-Biting Ticks and Tickborne Diseases, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubert, U. Clinical aspects of Borrelia burgdorferi infections. Z. Hautkrankh. 1989, 64, 649–652, 655–656. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzová, K. Lyme borreliosis: Review of present knowledge. Ceskoslovenska Epidemiol. Mikrobiol. Imunol. 1993, 42, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lantos, P.M.; Rumbaugh, J.; Bockenstedt, L.K.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Auwaerter, P.G.; Baldwin, K.; Bannuru, R.R.; Belani, K.K.; Bowie, W.R.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and American College of Rheumatology (ACR): 2020 Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Lyme Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, e1–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgermans, L.; Goderis, G.; Vandevoorde, J.; Devroey, D. Relevance of Chronic Lyme Disease to Family Medicine as a Complex Multidimensional Chronic Disease Construct: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Fam. Med. 2014, 2014, 138016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ścieszka, J.; Dąbek, J.; Cieślik, P. Post-Lyme disease syndrome. Rheumatology 2015, 53, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.K.; Caboni, M.; Strandwitz, P.; D’Onofrio, A.; Lewis, K.; Patel, C.J. Systematic comparisons between Lyme disease and post- treatment Lyme disease syndrome in the U.S. with administrative claims data. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachner, A.R.; Steere, A.C. CNS manifestations of third stage lyme disease. Zentralblatt Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. Ser. A Méd. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Virol. Parasitol. 1987, 263, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A. Chronic Lyme Disease: A Review. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 22, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucott, J.N.; Rebman, A.W.; Crowder, L.A.; Kortte, K.B. Post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome symptomatology and the impact on life functioning: Is there something here? Qual. Life Res. 2013, 22, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursinus, J.; Vrijmoeth, H.D.; Harms, M.G.; Tulen, A.D.; Knoop, H.; Gauw, S.A.; Zomer, T.P.; Wong, A.; Friesema, I.H.; Vermeeren, Y.M.; et al. Prevalence of persistent symptoms after treatment for lyme borreliosis: A prospective observational cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 6, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, D.; Thoma, A.; Rajput-Ray, M.; Madigan, A.; Avramovic, G.; Garg, K.; Gilbert, L.; Lambert, J.S. A Longitudinal Study of a Large Clinical Cohort of Patients with Lyme Disease and Tick-Borne Co-Infections Treated with Combination Antibiotics. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, M.; Norman, S.; Gierdalski, M.; Marques, A.; Bost, J.E.; DeBiasi, R.L. Pediatric Lyme disease: Systematic assessment of post-treatment symptoms and quality of life. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 95, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, E.D. Lyme Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghoff, W. Chronic Lyme Disease and Co-infections: Differential Diagnosis. Open Neurol. J. 2012, 6, 158–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.C. Is Gulf War Syndrome actually chronic Lyme disease? Med. Hypotheses 2005, 64, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choutka, J.; Jansari, V.; Hornig, M.; Iwasaki, A. Unexplained post-acute infection syndromes. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.J.; Johnson, L.B.; Maloney, E.L. Evidence assessments and guideline recommendations in Lyme disease: The clinical management of known tick bites, erythema migrans rashes and persistent disease. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2014, 12, 1103–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebman, A.W.; Aucott, J.N. Post-treatment Lyme Disease as a Model for Persistent Symptoms in Lyme Disease. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Xing, L.; Liu, A.; Bao, F. Efficacy and safety of antibiotic therapy for post-Lyme disease? A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucott, J.N.; Crowder, L.A.; Kortte, K.B. Development of a foundation for a case definition of post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e443–e449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebman, A.W.; Bechtold, K.T.; Yang, T.; Mihm, E.A.; Soloski, M.J.; Novak, C.B.; Aucott, J.N. The Clinical, Symptom, and Quality-of-Life Characterization of a Well-Defined Group of Patients with Posttreatment Lyme Disease Syndrome. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steere, A.C. Musculoskeletal manifestations of Lyme disease. Am. J. Med. 1995, 98, 44S–51S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steere, A.C. Lyme Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP). Definitions of Chronic Pain Syndromes. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/advocacy/definitions-of-chronic-pain-syndromes/ (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- Zimering, J.H.; Williams, M.R.; Eiras, M.E.; Fallon, B.A.; Logigian, E.L.; Dworkin, R.H. Acute and chronic pain associated with Lyme borreliosis: Clinical characteristics and pathophysiologic mechanisms. Pain 2014, 155, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartley, E.J.; Fillingim, R.B. Sex differences in pain: A brief review of clinical and experimental findings. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenichiello, A.F.; Ramsden, C.E. The silent epidemic of chronic pain in older adults. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 93, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wettstein, M.; Eich, W.; Bieber, C.; Tesarz, J. Pain Intensity, Disability, and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: Does Age Matter? Pain Med. 2019, 20, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.L.; Wade, J.B.; Robinson, M.E.; Price, D.D. The stages of pain processing across the adult lifespan. J. Pain 2000, 1, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustøen, T.; Wahl, A.K.; Hanestad, B.R.; Lerdal, A.; Paul, S.; Miaskowski, C. Age and the Experience of Chronic Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2005, 21, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhde, M.; Ajamian, M.; Li, X.; Wormser, G.P.; Marques, A.; Alaedini, A. Expression of C-Reactive Protein and Serum Amyloid A in Early to Late Manifestations of Lyme Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhe, M.; Grusell, M.; Ekerfelt, C.; Vrethem, M.; Forsberg, P.; Ernerudh, J. Cytokines in Lyme borreliosis: Lack of early tumour necrosis factor-α and transforming growth factor-β1 responses are associated with chronic neuroborreliosis. Immunology 2002, 107, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumet, G.; Ma, J.; Robison, A.J.; Kumari, S.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. T Cells as an Emerging Target for Chronic Pain Therapy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, R.B.; Winger, E.E. Decreased CD57 lymphocyte subset in patients with chronic Lyme disease. Immunol. Lett. 2001, 76, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stricker, R.B.; Burrascano, J.; Winger, E. Longterm decrease in the CD57 lymphocyte subset in a patient with chronic Lyme disease. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2002, 9, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stricker, R.B.; Winger, E.E. Natural Killer Cells in Chronic Lyme Disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 1704–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeidi, A.; Zandi, K.; Cheok, Y.Y.; Saeidi, H.; Wong, W.F.; Lee, C.Y.Q.; Cheong, H.C.; Yong, Y.K.; Larsson, M.; Shankar, E.M. T-Cell Exhaustion in Chronic Infections: Reversing the State of Exhaustion and Reinvigorating Optimal Protective Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batheja, S.; Nields, J.A.; Landa, A.; Fallon, B.A. Post-Treatment Lyme Syndrome and Central Sensitization. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 25, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, D.; Garg, K.; Lambert, J.S.; Rajput-Ray, M.; Madigan, A.; Avramovic, G.; Gilbert, L. Scrutinizing Clinical Biomarkers in a Large Cohort of Patients with Lyme Disease and Other Tick-Borne Infections. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.; Mysterud, A.; Jore, S.; Viljugrein, H.; Bakka, H.; Vindenes, Y. Demographic patterns in Lyme borreliosis seasonality over 25 years. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.E.; Anisimowicz, Y.; Miedema, B.; Hogg, W.; Wodchis, W.P.; Aubrey-Bassler, K. The influence of gender and other patient characteristics on health care-seeking behaviour: A QUALICOPC study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2016, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.; Shapiro, M.; Janicki, S.; Mankoff, J.; Stricker, R.B. Does Biological Sex Matter in Lyme Disease? The Need for Sex-Disaggregated Data in Persistent Illness. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2023, 16, 2557–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudenberg, T.; Böhm, S.; Böhmer, M.; Katz, K.; Willrich, N.; Stark, K.; Kuhnert, R.; Fingerle, V.; Wilking, H. Dynamics of Borrelia burgdorferi-Specific Antibodies: Seroconversion and Seroreversion between Two Population-Based, Cross-Sectional Surveys among Adults in Germany. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S. The Search for Pain Biomarkers. IEEE Pulse 2022, 13, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, M.M.; Caylor, J.; Strigo, I.; Lerman, I.; Henry, B.; Lopez, E.; Wallace, M.S.; Ellis, R.J.; Simmons, A.N.; Keltner, J.R. Toward Composite Pain Biomarkers of Neuropathic Pain—Focus on Peripheral Neuropathic Pain. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 869215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, E.M.; Neves, J.R.; Laranjeira, M.; Reis, J. The importance of inflammatory biomarkers in non-specific acute and chronic low back pain: A systematic review. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 3230–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calapai, F.; Mondello, E.; Mannucci, C.; Sorbara, E.E.; Gangemi, S.; Quattrone, D.; Calapai, G.; Cardia, L. Pain Biomarkers in Cancer: An Overview. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 27, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilello, J.A.; Tennant, F.S. Patterns of chronic inflammation in extensively treated patients with arachnoiditis and chronic intractable pain. Postgrad. Med. 2017, 129, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.P.; Wang, E.J.; Doshi, T.L.; Vase, L.; Cawcutt, K.A.; Tontisirin, N. Chronic pain and infection: Mechanisms, causes, conditions, treatments, and controversies. BMJ Med. 2022, 1, e000108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudick, C.N.; Billips, B.K.; Pavlov, V.I.; Yaggie, R.E.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Klumpp, D.J. Host-Pathogen Interactions Mediating Pain of Urinary Tract Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, I.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Woolf, C.J. Pain and infection. Pain 2016, 157, 1192–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.M.; Klumpp, D.J. Mechanisms of pain from urinary tract infection. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.J.; Karri, J.; Tontisirin, N.; Cohen, S.P. Antimicrobial therapies for chronic pain (part 1): Analgesic mechanisms. Korean J. Pain 2023, 36, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.J.; Dolomisiewicz, E.; Karri, J.; Tontisirin, N.; Cohen, S.P. Antimicrobial therapies for chronic pain (part 2): The prevention and treatment of chronic pain. Korean J. Pain 2023, 36, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, J.; Lucente, M.; Sonino, N.; Fava, G.A. Allostatic Load and Its Impact on Health: A Systematic Review. Psychother. Psychosom. 2020, 90, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibille, K.T.; McBeth, J.; Smith, D.; Wilkie, R. Allostatic load and pain severity in older adults: Results from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 88, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeboye, A.; Hart, R.; Senapathi, S.H.; Ali, N.; Holman, L.; Thomas, H.W. Assessment of Functional Pain Score by Comparing to Traditional Pain Scores. Cureus 2021, 13, e16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Fiorini, T.; Panni, B.; Turiel, M.; Cazzola, M.; Atzeni, F. Correlation of the score for subjective pain with physical disability, clinical and radiographic scores in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2002, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagen, J.L.; Shelton, J.A.; Luché-Thayer, J. Medical Gaslighting and Lyme Disease: The Patient Experience. Healthcare 2023, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, B.A.; Keilp, J.G.; Corbera, K.M.; Petkova, E.; Britton, C.B.; Dwyer, E.; Slavov, I.; Cheng, J.; Dobkin, J.; Nelson, D.R.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of repeated IV antibiotic therapy for Lyme encephalopathy. Neurology 2008, 70, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupp, L.B.; Hyman, L.G.; Grimson, R.; Coyle, P.K.; Melville, P.; Ahnn, S.; Dattwyler, R.; Chandler, B. Study and Treatment of Post Lyme Disease (STOP-LD): A Randomized Double Masked Clinical Trial. Neurology 2003, 60, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempner, M.S. Controlled Trials of Antibiotic Treatment in Patients with Post-Treatment Chronic Lyme Disease. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2002, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, A.K.; Blossom, B.; Maloney, E.L.; Phillips, S.E. Antibiotic retreatment of Lyme disease in patients with persistent symptoms: A biostatistical review of randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trials. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2012, 33, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.J. Observational research methods. Research design II: Cohort, cross sectional, and case-control studies. Emerg. Med. J. 2003, 20, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Chung, K.C.M. Observational Studies: Cohort and Case-Control Studies. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-0-203-77158-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pandas Development Team. Pandas-Dev/Pandas: Pandas; Zenodo: Geneve, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M.L. seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, E. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS. Second Edition. J. Adv. Nurs. 2007, 58, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-387-84858-7. [Google Scholar]
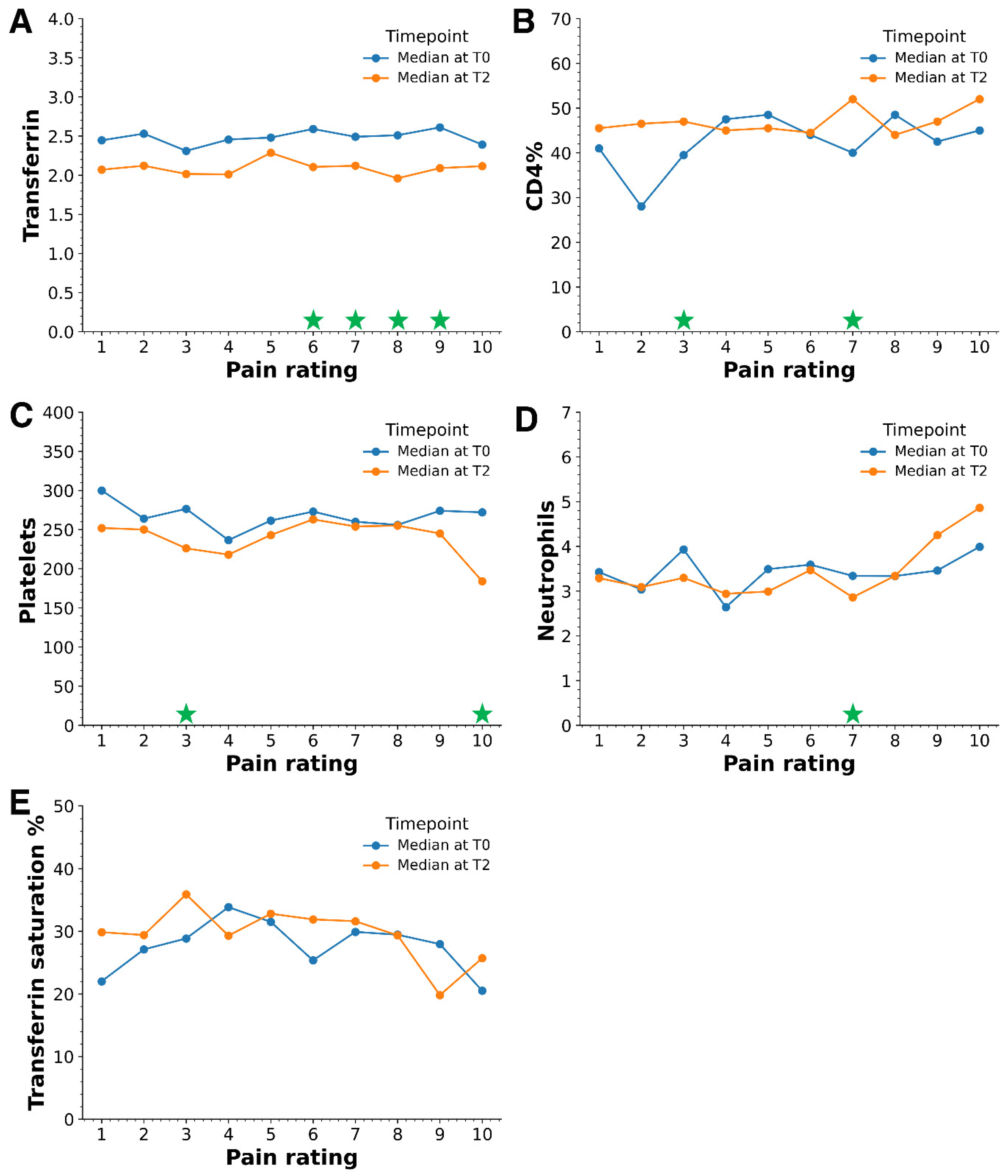
| Biomarker (Reference Range) | Median | Mann–Whitney U Test Statistic | Kolmogorov–Smirnov (K-S) Test Statistic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T2 | |||
| Transferrin (1.88–3.02 g/dL) | 2.50 | 2.09 | 25,815 *** | 0.40 *** |
| Transferrin saturation (%) (19–55%) | 27.8 | 31.6 | 13,646 *** | 0.20 *** |
| Platelets (150–400 × 109/L) | 269 | 245 | 20,555 ** | 0.19 ** |
| CD4% (32–60%) | 44 | 47 | 14,399 ** | 0.15 * |
| Neutrophils (2–8 × 109/L) | 3.4 | 3.1 | 19,944 * | 0.15 * |
| CD4+ Helper T-cell count (540–1600 cells/μL) | 822 | 914 | 15,593 | 0.13 |
| Hemoglobin (11.5–16.5 g/dL) | 14.1 | 13.9 | 18,633 | 0.11 |
| Helper/suppressor (H/S) ratio (0.9–4.5) | 2.07 | 2.08 | 15,883 | 0.09 |
| CD3% (61–84%) | 70 | 71 | 15,927 | 0.09 |
| White cell count (3.5–11 × 109/L) | 6.1 | 5.8 | 19,070 | 0.08 |
| CD3 Total (960–2600 cells/μL) | 1304 | 1420 | 16,421 | 0.08 |
| Lymphocytes (1–4 × 109/L) | 1.8 | 1.8 | 16,558 | 0.06 |
| Ferritin (22–275 μg/mL) | 76 | 75 | 18,076 | 0.06 |
| Creatine kinase (33–208 I.U./L) | 81 | 81 | 16,861 | 0.06 |
| Iron (6–33 μmol/L) | 17.8 | 17.6 | 17,623 | 0.05 |
| CD8% (13–40%) | 22 | 22 | 17,350 | 0.05 |
| CD8-suppressor count (270–930 cells/μL) | 419 | 426 | 17,203 | 0.04 |
| C-reactive protein (<7 mg/L) | 1 | 1 | 17,514 | 0.03 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Standard Error | Z-Statistic | p Value | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Transferrin | 3.29 | 0.54 | 6.05 | 0.000 | 2.22–4.36 |
| CD4% | −0.12 | 0.03 | −3.15 | 0.002 | −0.20–−0.04 |
| Platelets | 0.006 | 0.005 | 1.28 | 0.19 | −0.004–0.01 |
| Neutrophils | −0.07 | 0.16 | −0.47 | 0.63 | −0.40–0.24 |
| Transferrin saturation % | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.83 | −0.02–0.03 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Standard Error | Z-Statistic | p Value | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | −2.49 | 0.26 | −9.37 | 0.000 | −3.01–−1.97 |
| Transferrin | −0.09 | 0.58 | −0.16 | 0.86 | −1.24–1.04 |
| CD4% | −0.02 | 0.03 | −0.72 | 0.47 | −0.09–0.04 |
| Platelets | −0.004 | 0.005 | −0.99 | 0.31 | −0.01–0.005 |
| Neutrophils | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.88 | −0.26–0.30 |
| Transferrin saturation % | −0.01 | 0.01 | −0.99 | 0.31 | −0.04–0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garg, K.; Thoma, A.; Avramovic, G.; Gilbert, L.; Shawky, M.; Ray, M.R.; Lambert, J.S. Biomarker-Based Analysis of Pain in Patients with Tick-Borne Infections before and after Antibiotic Treatment. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080693
Garg K, Thoma A, Avramovic G, Gilbert L, Shawky M, Ray MR, Lambert JS. Biomarker-Based Analysis of Pain in Patients with Tick-Borne Infections before and after Antibiotic Treatment. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(8):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080693
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarg, Kunal, Abbie Thoma, Gordana Avramovic, Leona Gilbert, Marc Shawky, Minha Rajput Ray, and John Shearer Lambert. 2024. "Biomarker-Based Analysis of Pain in Patients with Tick-Borne Infections before and after Antibiotic Treatment" Antibiotics 13, no. 8: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080693
APA StyleGarg, K., Thoma, A., Avramovic, G., Gilbert, L., Shawky, M., Ray, M. R., & Lambert, J. S. (2024). Biomarker-Based Analysis of Pain in Patients with Tick-Borne Infections before and after Antibiotic Treatment. Antibiotics, 13(8), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080693







