A New Guanidine-Core Small-Molecule Compound as a Potential Antimicrobial Agent against Resistant Bacterial Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Procedure
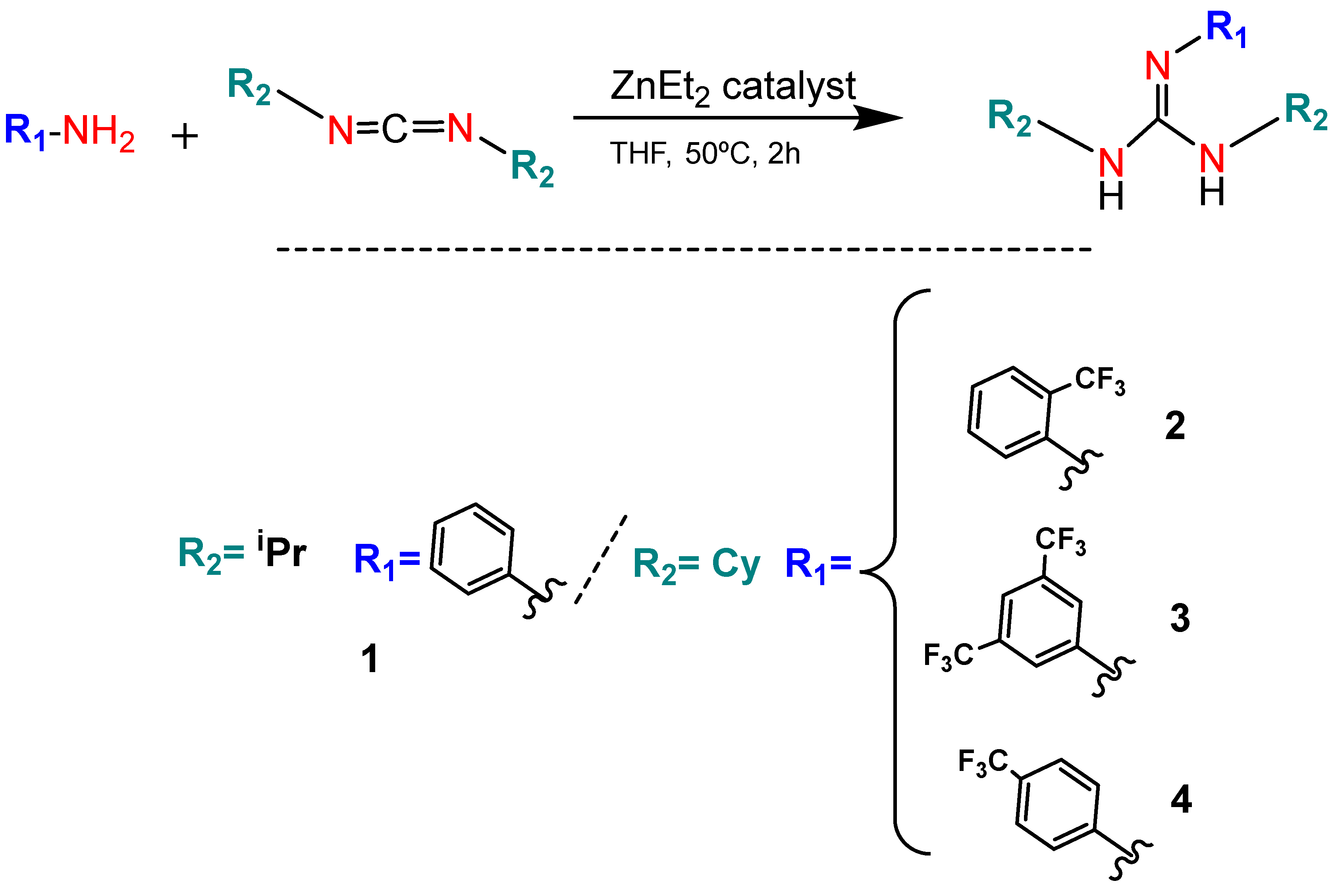
2.2. Synthesis of Guanidine Derivatives 1–5
2.3. Microbiological Studies
2.3.1. Bacterial Strains
2.3.2. MICs and MBCs
2.3.3. Drop Plate Assays (DP)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Guanidine-Core-Bearing Small Molecules
3.2. Microbiological Studies
3.2.1. MIC and MBC Studies
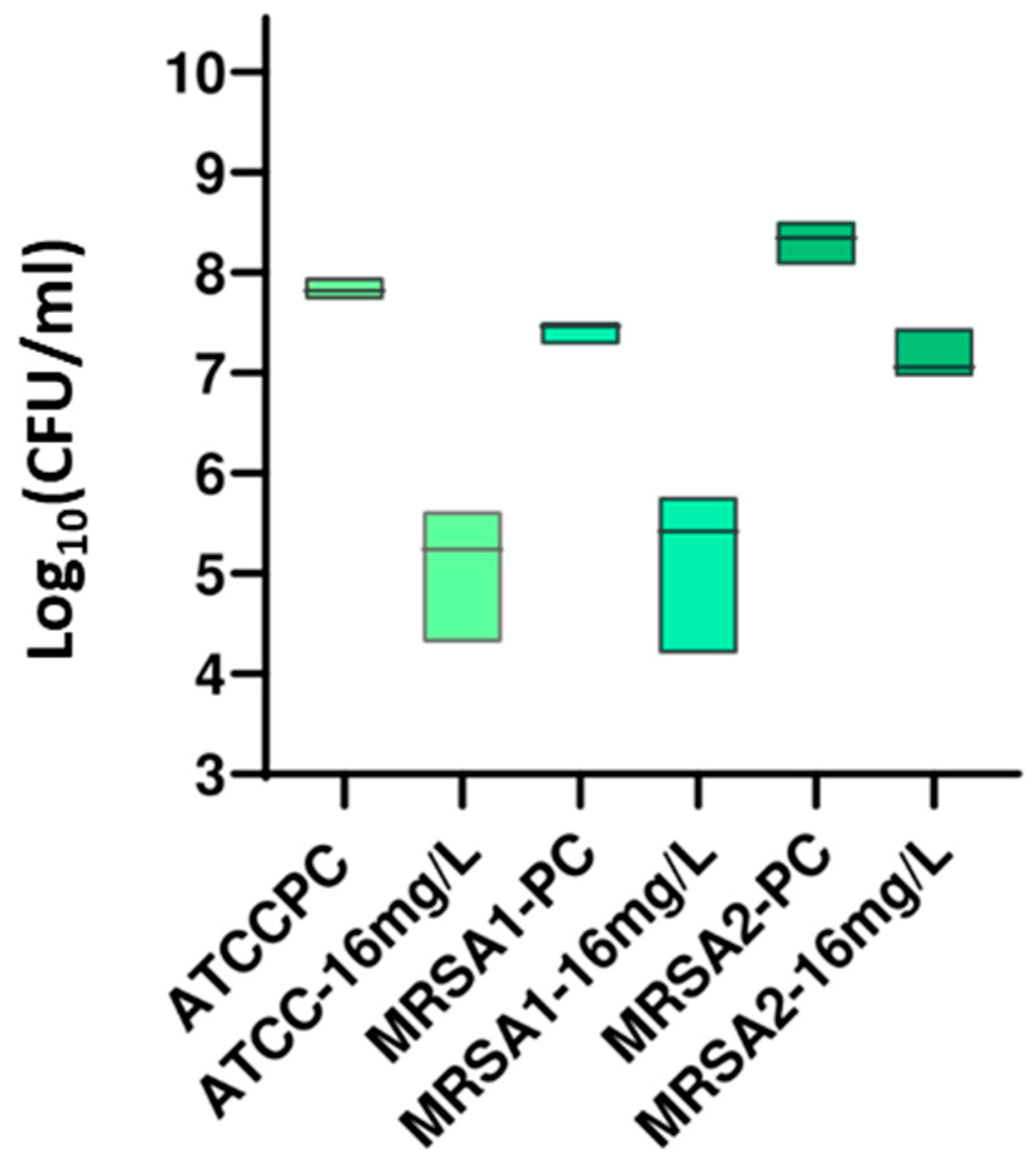
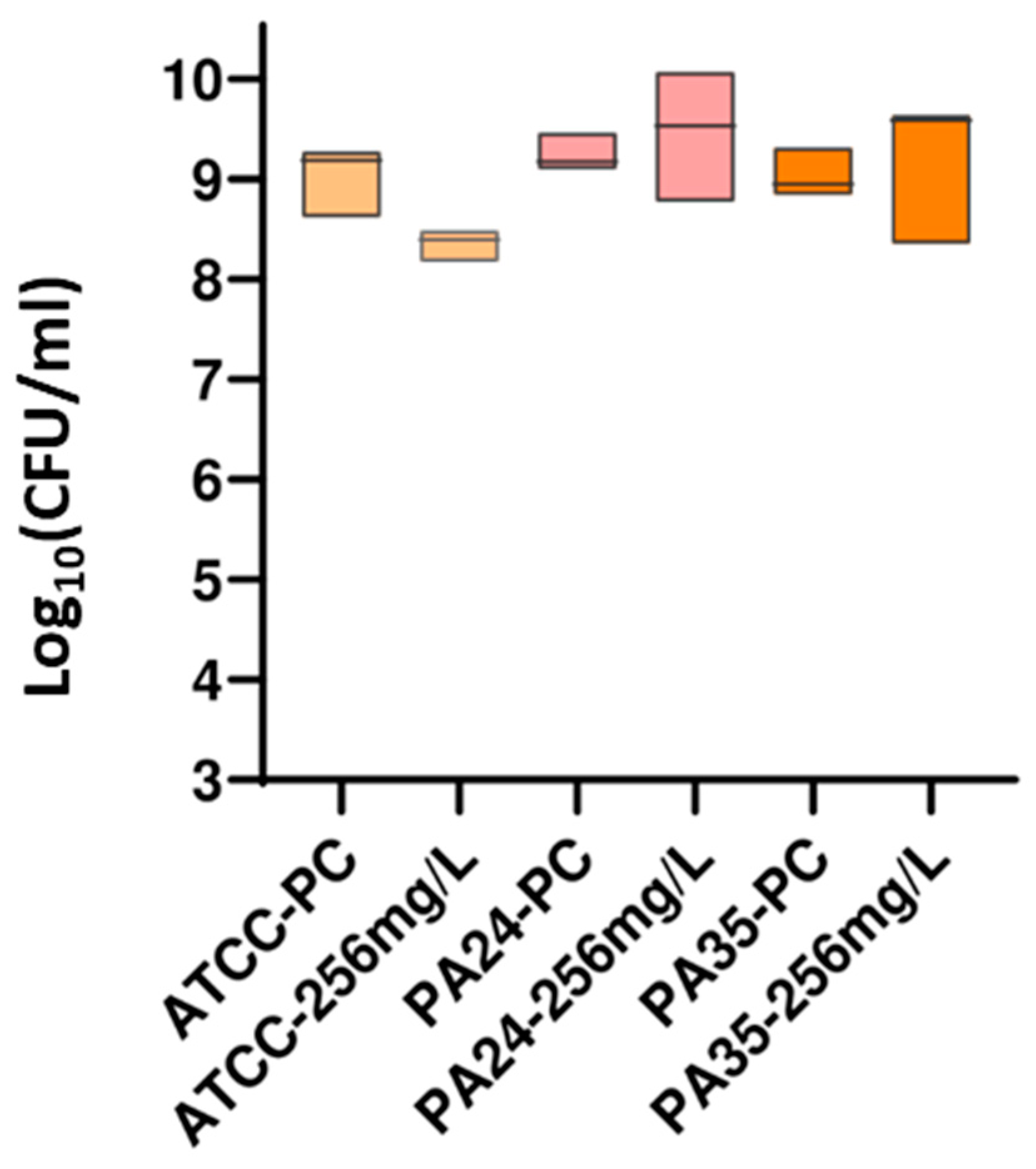
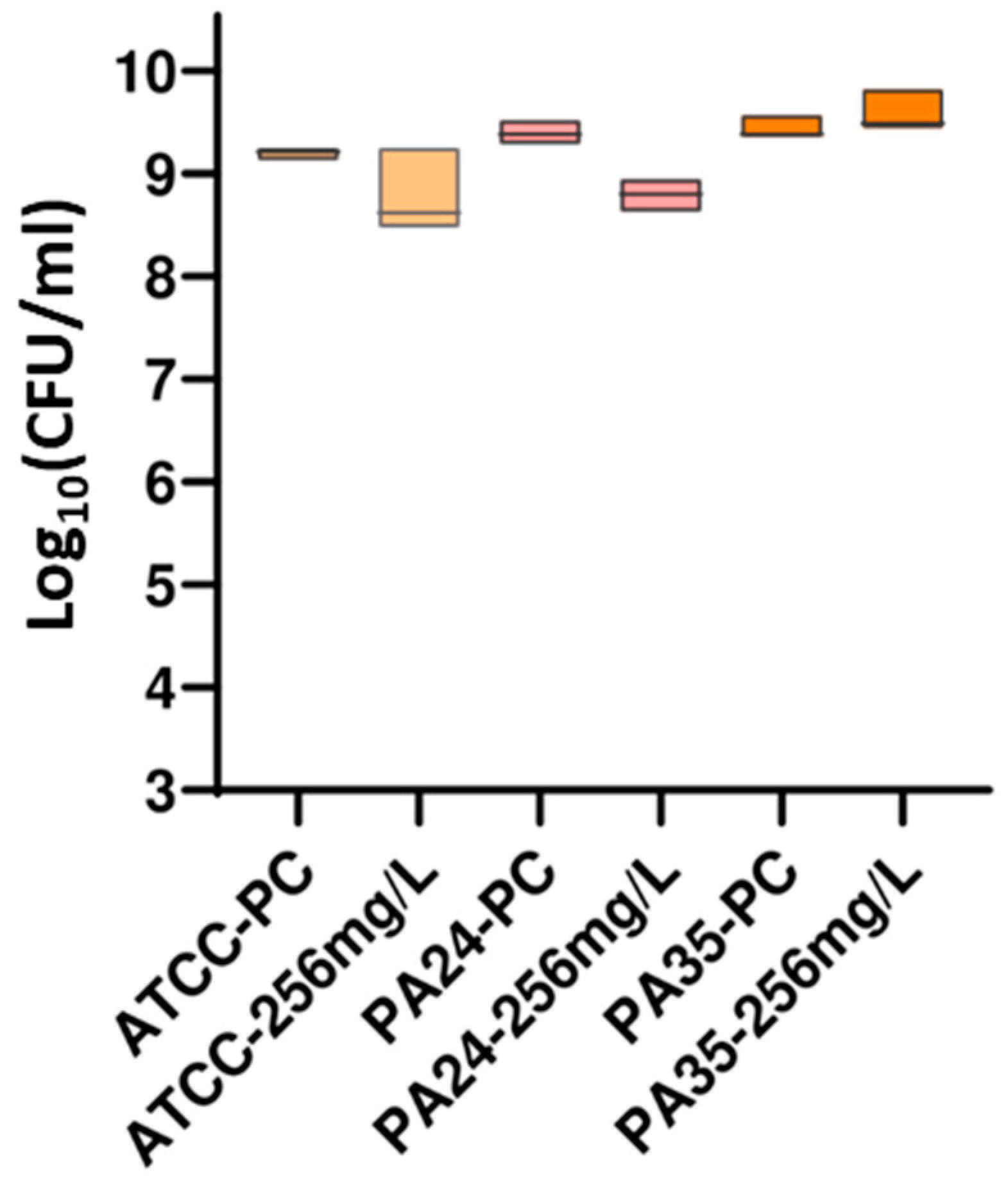
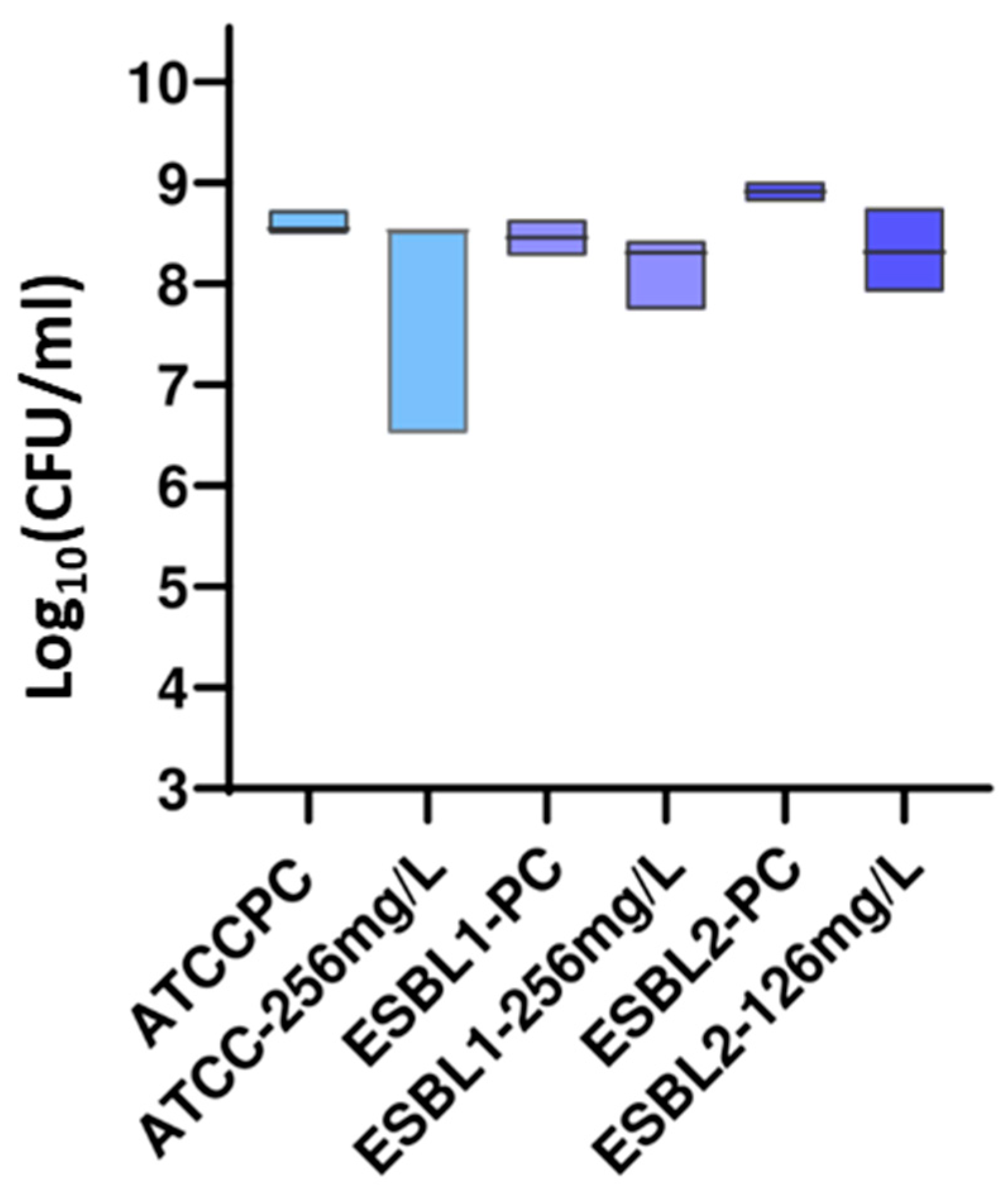
3.2.2. DP Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christaki, E.; Marcou, M.; Tofarides, A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria: Mechanisms, Evolution, and Persistence. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.-S.; Chai, Y.-Y.; Ser, W.-X.; Van Haeren, A.; Lim, Y.-H.; Raja, T.; Foo, J.-B.; Hamzah, S.; Sellappans, R.; Yow, H.Y. Novel drug candidates against antibiotic-resistant microorganisms: A review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwecińska, L. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health. Water 2020, 12, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bello, C. Antibiotic adjuvants—A strategy to unlock bacterial resistance to antibiotics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4221–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekshun, M.N.; Levy, S.B. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell 2007, 128, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chen, R.; Willcox, M.D.; Black, D.S.; Walsh, W.R.; Kumar, N. A New Era of Antibiotics: The Clinical Potential of Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, F.; Gesualdo, M.; Cortese, A.; Carbonara, S.; Devito, F.; Zito, A.; Ricci, G.; Scicchitano, P.; Ciccone, M.M. Rosuvastatin: Beyond the cholesterol-lowering effect. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMoia, T.E.; Shulman, G.I. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Metformin Action. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Gull, A.; Khuroo, T.; Aqil, M.; Sultana, Y. Glial Cell: A Potential Target for Cellular and Drug Based Therapy in Various CNS Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 2389–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, B.; Cronstein, B. Methotrexate mechanism in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Semenya, D.; Castagnolo, D. Antimicrobial drugs bearing guanidine moieties: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 216, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Moreno, C.; Antiñolo, A.; Carrillo-Hermosilla, F.; Otero, A. Guanidines: From classical approaches to efficient catalytic syntheses. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3406–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Campo-Balguerías, A.; Parra-Cadenas, B.; Nieto-Jimenez, C.; Bravo, I.; Ripoll, C.; Poyatos-Racionero, E.; Gancarski, P.; Carrillo-Hermosilla, F.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Ocaña, A. Guanylation Reactions for the Rational Design of Cancer Therapeutic Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Moreno, C.; Carrillo-Hermosilla, F.; Garcés, A.; Otero, A.; López-Solera, I.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Antiñolo, A. Simple, Versatile, and Efficient Catalysts for Guanylation of Amines. Organometallics 2010, 29, 2789–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam-Cha, S.H.; Domínguez-Jurado, E.; Tinoco-Valencia, S.L.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Morata-Moreno, N.; Alfaro-Ruiza, R.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Esteban, J.; Luján, R.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activities of a heteroscorpionate derivative platinum complex against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Gozalo, M.; Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Rescalvo-Casas, C.; Seijas-Pereda, L.; García-Bertolín, C.; de la Mata, F.J.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; Cuadros, J.; Pérez-Tanoira, R. Study of the antimicrobial activity of cationic carbosilane dendrimers against clinical strains of multidrug-resistant bacteria and their biofilms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1203991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Ambler, J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Castanheira, M.; Dingle, T.; Hindler, J.A.; Koeth, L.; Sei, K.; on behalf of the CLSI Methods Development and Standardization Working Group of the Subcommittee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. CLSI Methods Development and Standardization Working Group Best Practices for Evaluation of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01934-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí, P.; Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Domínguez-Jurado, E.; Sánchez-López, C.M.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Ocaña, A.V.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Esteban, J.; Marcilla, A.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; et al. A novel bis(pyrazolyl)methane compound as a potential agent against Gram-positive bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herigstad, B.; Hamilton, M.; Heersink, J. How to optimize the drop plate method for enumerating bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitt, A.; Sofrata, A.; Slizen, V.; Sugars, R.V.; Gustafsson, A.; Gudkova, E.I.; Kazeko, L.A.; Ramberg, P.; Buhlin, K. Antimicrobial activity of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate in comparison to chlorhexidine using the quantitative suspension method. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2015, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klancnik, A.; Piskernik, S.; Jersek, B.; Mozina, S.S. Evaluation of diffusion and dilution methods to determine the antibacterial activity of plant extracts. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 81, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.R.; Varela, C.L.; Pires, A.S.; Tavares-da-Silva, E.J.; Roleira, F.M.F. Synthetic and natural guanidine derivatives as antitumor and antimicrobial agents: A review. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 138, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, N.; de Aquino, T.M.; de Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; da Silva-Júnior, E.; Gomes, E.A.; Gomes, A.A.S.; Siqueira-Júnior, J.P.; Junior, F.J.B.M. Aminoguanidine hydrazones (AGH’s) as modulators of norfloxacin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus that overexpress NorA efflux pump. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 280, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Song, M. Synthesis, antibacterial and anticancer activity, and docking study of aminoguanidines containing an alkynyl moiety. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, M.; Mark, L.; Zhang, Y.; Parhi, A.K.; Lavoie, E.J.; Pilch, D.S. An FtsZ-targeting prodrug with oral antistaphylococcal efficacy in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5860–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Sumii, Y.; Shibata, N. Contribution of Organofluorine Compounds to Pharmaceuticals. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10633–10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamperini, C.; Maccari, G.; Deodato, D.; Pasero, C.; D’agostino, I.; Orofino, F.; De Luca, F.; Dreassi, E.; Docquier, J.D.; Botta, M. Identification, synthesis and biological activity of alkyl-guanidine oligomers as potent antibacterial agents. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, G.; Ameta, G.; Ameta, C.; Ameta, R.; Punjabi, P.B. Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline-drug conjugates as effective antituberculosis agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Strain | Compound | MIC a (mg/L) | MBC b (mg/L) | %Inhibition at MIC Wells c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 29213 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 19.24 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 12.58 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 19.45 | |
| 4 | 16 | 128 | 99.53 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 17.33 | |
| MRSA 1 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 18.26 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 11.40 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 18.12 | |
| 4 | 16 | 32 | 100.00 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 26.24 | |
| MRSA 2 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 15.70 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 23.25 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 24.13 | |
| 4 | 16 | 128 | 100.00 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 15.84 |
| Strain | Compound | MIC a (mg/L) | MBC b (mg/L) | %Inhibition at MIC Wells c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 27853 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 14.24 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 13.08 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 21.09 | |
| 4 | >256 | >256 | 19.04 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 15.82 | |
| PA 24 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 28.10 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 4.11 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 33.75 | |
| 4 | >256 | >256 | 22.20 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 14.88 | |
| PA 35 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 38.52 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 3.36 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 41.83 | |
| 4 | >256 | >256 | 21.54 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 3.72 |
| Strain | Compound | MIC a (mg/L) | MBC b (mg/L) | %Inhibition at MIC Wells c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 35218 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 0 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 0 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 0 | |
| 4 | >256 | >256 | 0 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 0 | |
| ESBL 1 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 0 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 5.49 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 12.36 | |
| 4 | >256 | >256 | 28.54 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 0 | |
| ESBL 2 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 0 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | 0 | |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | 5.33 | |
| 4 | >256 | >256 | 40.61 | |
| 5 | >256 | >256 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morata-Moreno, N.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; del Campo-Balguerias, A.; Carrillo-Hermosilla, F.; Hernando-Gozalo, M.; Rescalvo-Casas, C.; Ocana, A.V.; Segui, P.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Pérez-Martínez, F.C.; et al. A New Guanidine-Core Small-Molecule Compound as a Potential Antimicrobial Agent against Resistant Bacterial Strains. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070609
Morata-Moreno N, Pérez-Tanoira R, del Campo-Balguerias A, Carrillo-Hermosilla F, Hernando-Gozalo M, Rescalvo-Casas C, Ocana AV, Segui P, Alonso-Moreno C, Pérez-Martínez FC, et al. A New Guanidine-Core Small-Molecule Compound as a Potential Antimicrobial Agent against Resistant Bacterial Strains. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(7):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070609
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorata-Moreno, Noelia, Ramón Pérez-Tanoira, Almudena del Campo-Balguerias, Fernando Carrillo-Hermosilla, Marcos Hernando-Gozalo, Carlos Rescalvo-Casas, Ana V. Ocana, Pedro Segui, Carlos Alonso-Moreno, Francisco C. Pérez-Martínez, and et al. 2024. "A New Guanidine-Core Small-Molecule Compound as a Potential Antimicrobial Agent against Resistant Bacterial Strains" Antibiotics 13, no. 7: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070609
APA StyleMorata-Moreno, N., Pérez-Tanoira, R., del Campo-Balguerias, A., Carrillo-Hermosilla, F., Hernando-Gozalo, M., Rescalvo-Casas, C., Ocana, A. V., Segui, P., Alonso-Moreno, C., Pérez-Martínez, F. C., & Molina-Alarcón, M. (2024). A New Guanidine-Core Small-Molecule Compound as a Potential Antimicrobial Agent against Resistant Bacterial Strains. Antibiotics, 13(7), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070609







