Abstract
Bacterial histidine kinase (BHK) is a constituent of the two-component signaling (TCS) pathway, which is responsible for the regulation of a number of processes connected to bacterial pathogenicity, virulence, biofilm development, antibiotic resistance, and bacterial persistence. As BHK regulation is diverse, inhibitors can be developed, such as antibiotic synergists, bacteriostatic/bactericidal agents, virulence inhibitors, and biofilm inhibitors. Inhibition of essential BHK has always been an amenable strategy due to the conserved binding sites of the domains across bacterial species and growth dependence. Hence, an inhibitor of BHK might block multiple TCS regulatory networks. This review describes the TCS system and the role of BHK in bacterial virulence and discusses the available inhibitors of BHK, which is a specific response regulator with essential structural features.
1. Introduction
Bacterial infections have a substantial effect on global health. However, the discovery of wonder medications known as “antibiotics” offered consistent health advantages, reduced infections and decreased patient mortality during the last decade [1]. Moreover, the extensive use and misuse of antibiotics exacerbates selective pressure on microbes, leading to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). The global scope of the problem, as well as the impact of AMR on human health, health-care expenses, and society, remains largely unclear [2]. AMR is a complicated worldwide public health concern, and no single or simple solution will suffice to fully control the emergence and spread of pathogenic organisms resistant to existing antibacterial medications [3]. AMR is caused by a number of different mechanisms, such as drug or target inactivation (penicillinases, cephalosporinases, carbapenemases, and β-lactamases), binding site modifications (PBP2a in Staphylococcus aureus, which changes the cross-linking target of the peptidoglycan layer in Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis), and the development of resistance to AMR (the reduced level of OprD porin protein in Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits resistance against imipenem) [4,5,6,7]. In 2010, Neisseria, Staphylococcus, and Enterobacteriaceae developed resistance to the antibiotic ceftaroline (2010); Staphylococcus developed resistance to both linezolid (2000) and daptomycin (2003) in 2001; and Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas developed resistance to these antibiotics in 2004 and 2005, respectively. According to statistics from the WHO, 1.27 million patients died due to infections caused by resistant bacteria in 2019 [8,9,10]. Furthermore, the mortality rate might increase to 10 million patients each year by 2050, as reported by O’Neill. Therefore, immediate action is needed to counteract the emergence and rampant dissemination of AMR [11].
Many targets have been investigated for the development of antibacterial drugs [1]. The cell wall biosynthesis process has been widely investigated and validated as an antibacterial target of the β-lactam and glycopeptide classes of antibiotics [12]. The fatty acid production pathway has also been validated by the widespread use of well-known medications such as isoniazid, an antitubercular treatment, and triclosan, an antiseptic [13]. Bacterial folate biosynthesis is a well-known and appealing target that involves many types of enzymes. However, the well-known targets are DHFR (dihydrofolate reductase) and DHPS (dihydropteroate synthase). DHFR has been verified by the use of drugs such as trimethoprim (an antifolate antibiotic) and pyrimethamine (an antiprotozoal agent). DHPS is another target that has been proven to be crucial for folate synthesis and was validated as a sulfonamide [14].
Another potent antibacterial target is the dual inactivation of DNA GyrB and ParE. By inhibiting these topoisomerases, DNA replication, repair, and catenation are prevented [15]. Furthermore, protein synthesis, primarily carried out by the molecular machinery known as ribosomes and translational machinery, is regarded as a vulnerable target for antibiotics [16]. Tetracyclines are widely used antibacterial medications that target protein synthesis (blocking the A site of the 30S subunit of the ribosome, thereby preventing the binding of aminoacyl t-RNA) [17]. Aminoglycosides interfere with the formation of initiation complexes of the 30S subunit [18]. During the transpeptidation cycle, macrolides interfere with the elongation of peptides [19]. Despite the fact that these antibiotics and their targets have been shown to be clinically significant, the increase in resistance necessitates the development of novel strategies. Several strategies already reported in the literature include structural modification, bacteriophage therapy, and targeting of the explored pathways with novel molecules.
None of these strategies were found to be effective in preventing AMR. Therefore, research is more focused on the discovery of novel untapped or unexplored pathways. One such attractive target is bacterial histidine kinases (BHKs). BHKs are constituents of bacterial two-component systems (TCSs), which are involved in primary signal transduction pathways. BHK is highly conserved among all bacterial species and has broad-spectrum activity. In addition, no human homologs or proteins with similar structures (with the exception that mammalian kinases possess comparable protein folds in the ATP domain) exhibit selectivity toward bacterial species [20]. Furthermore, BHK is important for bacterial survival, the inhibition or inactivation of which results in bacterial death. All these characteristics make BHK a potential antibacterial target. In this review, we discussed the biological significance of TCS-BHKs in the identification of new antibacterial agents as well as existing TCS-BHK inhibitors, which can be used further to develop new and diverse antibacterial agents.
2. TCS Signaling Pathway and BHK
TCSs are considered appealing antibacterial targets because they are conserved in almost all bacterial species. In addition, the TCS is and involved in the regulation of a number of processes connected to bacterial pathogenicity, virulence, biofilm development, antibiotic resistance, and bacterial persistence. Although crucial for bacterial adaptability and fitness, only a few of these TCSs are considered essential for bacterial cell survival. However, some TCSs are not essential for bacterial survival in laboratory environments, but they enhance bacterial fitness by enabling adaptation to environmental changes. Certain responses are expressed by pathogenic bacteria in response to their host environment, and these responses typically rely on the TCS system. Another important consideration is the difference between targeting essential and nonessential TCSs in pathogens. Essential TCSs are essential for the survival and growth of bacteria. While inhibiting TCSs can efficiently kill or suppress bacteria, it can also lead to the swift development of resistance, as bacteria are under strong selective pressure to survive. On the other hand, nonessential TCSs often regulate virulence factors rather than basic survival. By targeting these systems, we can reduce the pathogen’s ability to cause disease without necessarily killing it, which may result in slower resistance development. For example, studies have shown that targeting the Agr system in Staphylococcus aureus, which is not essential for survival but crucial for virulence, can significantly diminish its ability to cause infections without inducing rapid resistance [21,22]. This approach could offer a more sustainable way to manage bacterial infections. TCS signaling involves autophosphorylation of a membrane-bound BHK, phosphotransfer of the phosphoryl group to a cognate response regulator (RR), and ultimately modulation of the expression of target genes (Figure 1) [23]. BHKs are present in both essential and nonessential TCSs. Appropriate phosphorylation levels of RR are tightly regulated by the phosphatase activity of BHK, RR, or a partner protein [23,24]. BHK autophosphorylation is mediated via the catalytic and ATP-binding (CA) domain, which binds ATP and phosphorylates BHK at a conserved histidine residue in the dimerization and histidine phosphotransfer (DHp) domain. The CA and DHp domains are conserved and present in all HKs, whereas the remaining sensor domains (periplasmic, PAS, GAF, HAMP) are variable and not present in all HKs [23].
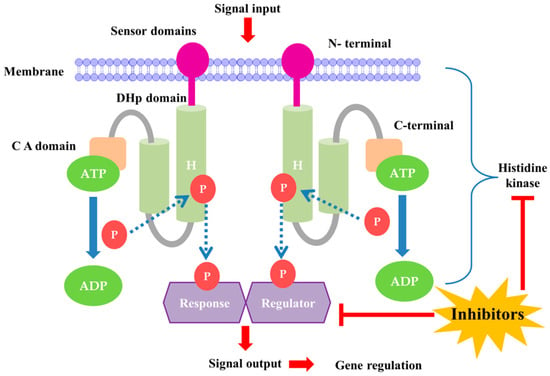
Figure 1.
The TCS signaling pathway and role of bacterial histidine kinase in gene regulation. DHp domain-Dimerization and histidine phosphotransfer domain; C A domain-Catalytic and ATP binding domain; H-box-Highly conserved histidine residue; P-Phosphoryl group.
The BHK CA domain is a desirable target for structure-based virtual screening and phenotypic screening of pharmacological inhibitors due to its conserved properties and crucial function in TCS signal transduction. The high level of sequence conservation in the CA catalytic site further suggests that inhibitors directed against this region will have broad-spectrum antibacterial effects. The CA domain is thus a promising BHK target location for the discovery and development of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Drug polypharmacology, which involves simultaneous inhibition of many targets, has been suggested as a method to prevent the emergence of drug resistance to novel antibiotics [25,26,27,28]. Because bacteria have several TCSs, inhibitors of the highly conserved CA domain are likely to shut down a number of signaling pathways, impairing the bacteria’s capacity to quickly adapt to environmental changes, including those that occur during an infection of the host. TCS inhibition may not be bactericidal for some bacteria, but it is likely to limit efficient growth, lowering survival capacity [23] (Figure 1). The ATP-binding Bergerat fold found in the CA domain of many human protein families, which is also present in essential proteins such as Hsp90, is one potential drawback of BHKs. The Bergerat fold may cause BHK autophosphorylation inhibitors (HKAIs) to have off-target effects on human ATP-binding domains and may also cause toxicity to mammalian cells. This fold is present in both microbial and human ATP-binding protein domains [29].
TCS-BHK Inhibitors
For almost 20 years, TCSs have been identified as viable antibacterial therapeutic targets. Some TCSs are essential or required for bacterial growth. Furthermore, given the high degree of conservation among TCS active sites and the occurrence of several TCSs in every bacterium, an inhibitor with broad-spectrum activity that targets various TCS regulatory networks should be identified. Overall, targeting TCSs is likely to effectively disable bacteria’s ability to adapt to environmental and physiological changes. The availability of crystal structures of BHK has made the design of BHK inhibitors possible. In the current review, we discussed novel BHK inhibitors with different response regulators identified in the literature (Table 1).

Table 1.
BHK and its inhibitors.
In 2022, Radwan et al. synthesized a series of novel isatin derivatives with either β-hydroxyketone or chalcone moieties and examined their antibacterial activity. These compounds (1a–1j) (Figure 2) exhibited potent activity against S. aureus in the range of 0.044–0.057 mmol/L (MIC). Among these compounds, 1a showed the most potent antibacterial activity, with an MIC of 0.026 mmol/L. The activity of 1a against S. aureus was explained by its significant docking score values (glide score −36.231 kcal mol−1, electrostatic energy −0.697 kcal mol−1, and van der Waals energy −35.534 kcal mol−1) within the binding site of BHK (S. aureus) (PDB: 5C93). Compound 1a could be further optimized for the development and synthesis of more potent antibacterial agents [48].
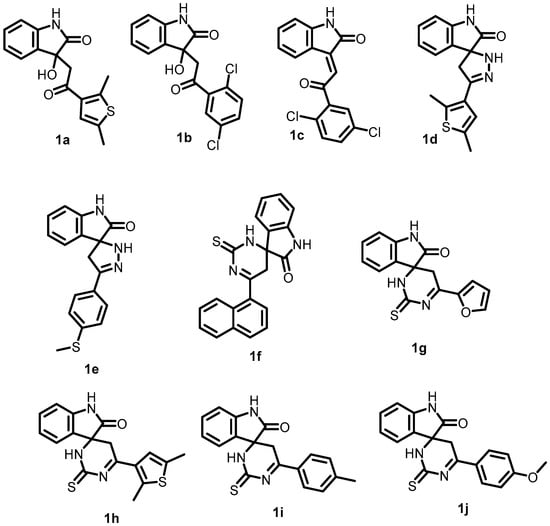
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of isatin derivatives (1a–1j).
Focusing on the discovery of novel antibacterial agents in 2020, Carabajal et al. screened 686 compounds from the published kinase inhibitor set (PKIS), a compound library published by GlaxoSmithKline, to identify inhibitors of PhoP/PhoQ in S. typhimurium. The results demonstrated that a series of compounds with quinazoline scaffolds exhibited potent and selective downregulation of PhoP/PhoQ-activated genes. Among these quinazoline derivatives, 2a and 2b (Figure 3) showed more potent antibacterial activity, with IC50 values of 6.9 and 3.2 µM, respectively. Furthermore, these compounds can emerge as appealing lead molecules for the development of antibacterial agents [49].
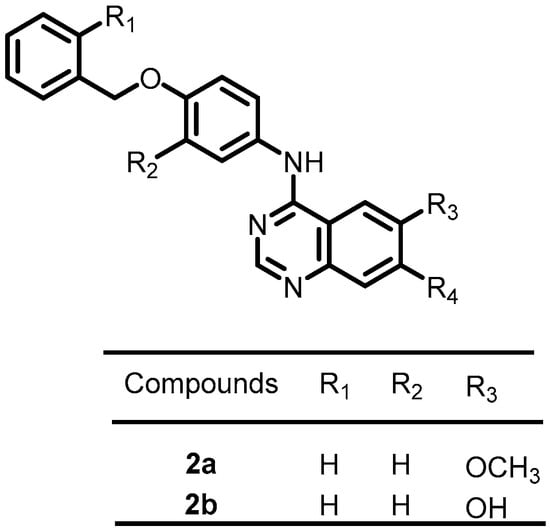
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of kinase inhibitors 2a–2b.
In an effort to discover novel antibacterial agents, waldiomycin (3a) and its methyl ester derivative (3b) (Figure 4) were identified as novel BHK inhibitors. Waldiomycin, a methyl ester derivative, exhibited significant inhibitory activity against the Walk-type H-box region, with IC50 values of 10.2 and 75.8 µM, respectively. The results demonstrated that the binding interactions of ligands with WalK-BHK could be studied further for the development of novel antibacterial agents [50].
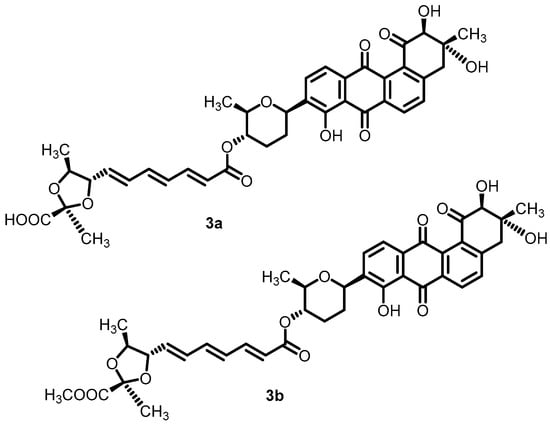
Figure 4.
Chemical structures of waldiomycin (3a) and its methylester derivative (3b).
In another study by Mizar et al. in 2018, xanthoangenol B 1 (4a) was identified using a GFP (green fluorescent protein) reporter system that was previously used to identify SaeRS TCS (response regulator in S. aureus) inhibitors obtained from plants. Approximately four derivatives (xanthoangenol (4b), xanthoangenol (4c) and PM-56 (4d)) (Figure 5) were identified and screened for their antibacterial activity. Among them, 4a and 4d demonstrated excellent inhibitory activity against SaeRS, with IC50 values of 2.1 and 4.3 µM, respectively [51].
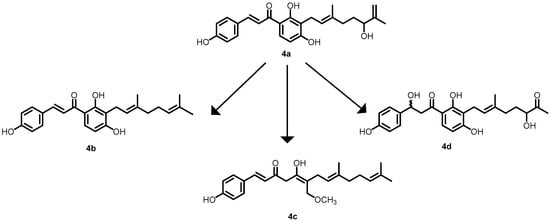
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of the xanthoangenol derivatives (4a–4d).
In 2019, Zhang et al. developed a system based on artificial proteoliposomes and used it for screening AgrC inhibitors. A library of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) monomers was selected and screened for ArgC inhibitory activity. The results showed that the two TCM monomers rhein (5a) and aloe emodin (5b) (Figure 6) inhibited AgrC autophosphorylation with IC50 values of 13.7 and 62.2 μM, respectively. Furthermore, these compounds inhibited the growth of S. aureus in a dose-dependent manner, with MIC values of 32 and 64 μg/mL, respectively [52].
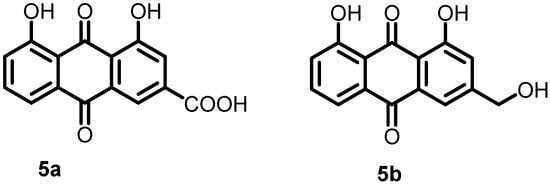
Figure 6.
Chemical structures of the traditional Chinese medicine monomers rhein (5a) and aloe emodin (5b).
In 2016, Velikova et al. reported the identification of putative BHK autophosphorylation inhibitors by combining in silico and in vitro fragment-based screening. Among the screened fragments, compound 6 (Figure 7) was the most potent compound, inhibiting the autophosphorylation of BHK in a concentration-dependent manner, with IC50s against S. aureus and E. coli BHK PhoR of 212 and 16 μM, respectively [31].
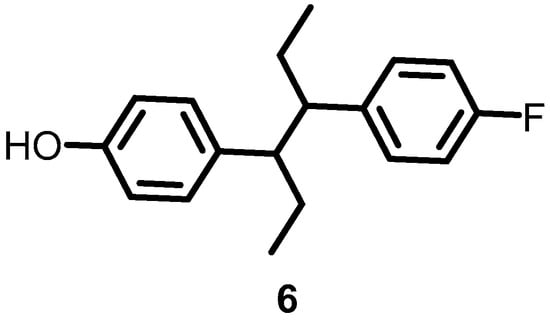
Figure 7.
Chemical structures of fragment 6.
Continued efforts to increase the potency of molecules against BHK led to the discovery of novel heterocycles. In 2017, Vo et al. demonstrated that repurposing diaryl pyrazole-based ATP-competitive (HSP90) inhibitors as effective antibacterial agents targeting BHKs is a promising strategy for the development of newer antibiotics. A total of nine CCT018159 (7a, Figure 8) derivatives were synthesized and evaluated against multiple BHKs (PhoQ, DivJ, and Cck). Compounds 7b, 7c, and 7d (Figure 8) showed favorable properties, both for the inhibition of CckA (C. crescentus) and PhoQ (Salmonella), which are essential for virulence. The results confirmed that the presence of a chlororesorcinol ring was essential for potent activity within the series. In summary, this study identified a pathway for the development of HSP90 inhibitors as novel antibacterial agents [30].
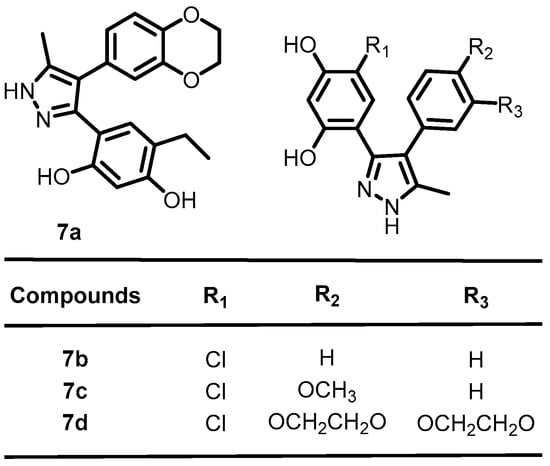
Figure 8.
Chemical structures of diaryl pyrazole-based derivatives 7a–7d.
In 2017, Zheng et al. used whole-cell phenotypic high-throughput screening to screen a small-molecule library of approximately 540,000 compounds to identify new DosRST inhibitors. Compounds 8a and 8b (Figure 9) were identified as potential antibacterial agents. Compound 8a reduced the autophosphorylation of DosS with an IC50 of 1.9 µM, and 8b inhibited the autophosphorylation of both DosS and DosT with IC50s of 0.5 and 5 µM, respectively [53].
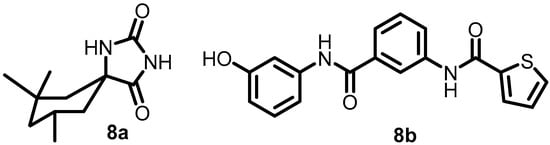
Figure 9.
Chemical structures of DosRST inhibitors 8a–8b.
In 2016, Boibessot et al. synthesized a series of thiophene derivatives and screened them for their antibacterial activity. Among them, eight compounds (9a–9h) (Figure 10) were found to inhibit the autophosphorylation activity of the BHKs WalK, PhoR, and ResE from B. subtilis, with IC50 values ranging from 52.81–196.9, 1.63–122.6, and 20.3–243.9 μM, respectively. These lead compounds can be used as a starting point for the development of novel antibacterial agents [36].
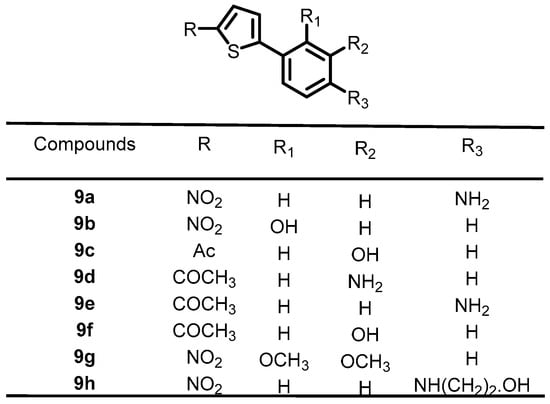
Figure 10.
Chemical structures of thiophene derivatives 9a–9h.
Prompted by TCM monomer activity against BHK, Zhang et al. in 2015 explored the other TCM monomers 10a–10e (Figure 11) using structure-based virtual screening of a natural TCM monomer library. These compounds specifically inhibited the autophosphorylation of VicK in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 3.8, 5.4, 15.4, 4.6, and 9.1 µM, respectively. In addition, the compounds exhibited potent antibacterial activity (10a: 37.1 µg/mL; 10b: 38.5 µg/mL; 10c: 17 µg/mL; 10d: 68.5 µg/mL; 10e: 21 µg/mL) against S. pneumoniae [54].
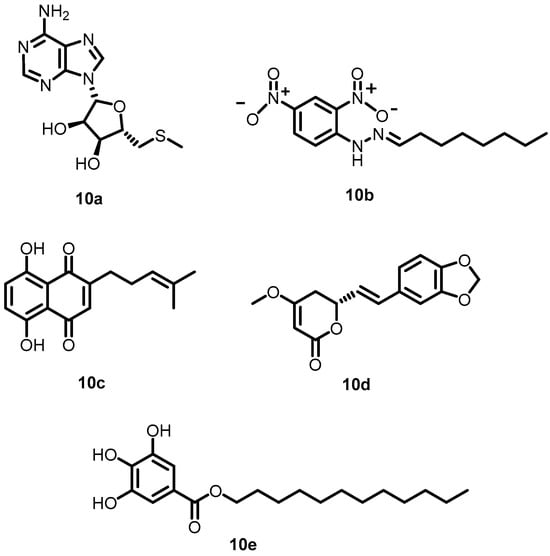
Figure 11.
Chemical structures of TCM derivatives 10a–10e.
In 2015, Wilke et al. elucidated the active site of BHK using an HTS-FP displacement assay. The results demonstrated that nine compounds exhibited potential inhibitory activity against different BHKs. Among them, four compounds (11a–11d) (Figure 12) containing adenine moieties possess significant targetable inhibitor space within the binding pocket. The other five compounds (11e–11i) (Figure 12) that possess unique chemical structures were found to be more potent, as evidenced by their IC50 values. These compounds could be utilized for the production of multitargeted, TCS-mediated antibiotics with innovative modes of action [46].
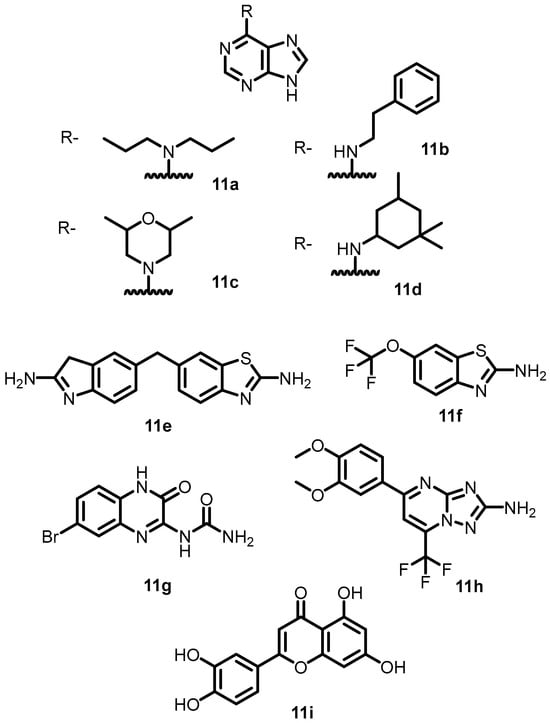
Figure 12.
Chemical structures of adenine derivatives 11a–11i.
In 2014, Bellale et al. discovered a particular class of diarylthiazole compounds (Figure 13) that had potent inhibitory activity against PrrBA TCA, which is required for the viability of M. tuberculosis. Over 40 diarylthiazole derivatives, such as 12a and 12b, which demonstrated remarkable antibacterial activities with MICs of 0.4 and 0.25 µg/mL, respectively, were subsequently developed, and the majority of these derivatives exhibited favorable physicochemical characteristics and significant MICs against M. tuberculosis (MIC ≤1 µg/mL) [55].
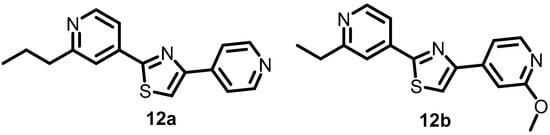
Figure 13.
Chemical structures of diarylthiazole derivatives 12a–12b.
In another study by Liu et al. in 2014, six analogs of thiazolidine (13a) (13b–13g) (Figure 14) were developed and created by altering functional groups to enhance the antibacterial activity and decrease the toxicity of 13a. The results indicated the inhibitory effects of these compounds on the autophosphorylation of WalK, with IC50 values ranging from 24.2 to 71.2 µM. With MICs ranging from 1.5 to 6.3 µM, these compounds exhibited strong antibacterial activity against S. epidermidis and S. aureus, including clinical methicillin-resistant S. epidermis (MRSE) and MRSA, which were dramatically improved compared to 13a [35].
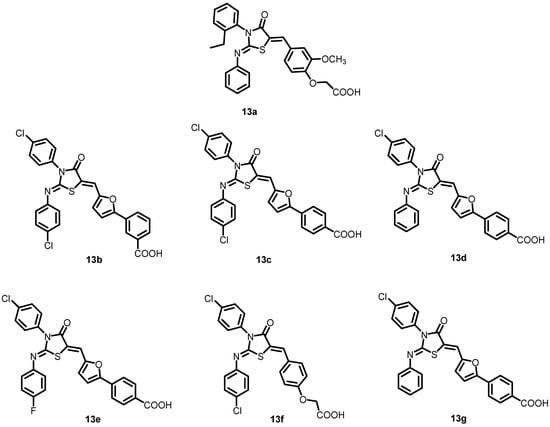
Figure 14.
Chemical structures of compounds 13a–13g.
In 2012, Watanabe et al. screened more than 10,000 Streptomyces extracts by using differential growth assays and identified signermycin B (14) (Figure 15) as a potent compound that interfered with the WalK dimerization domain. Furthermore, its inhibitory activity against WalK was evaluated for different bacterial species (S. aureus, E. faecalis, B. subtilis, and S. mutans), and IC50 values ranging from 37–62 µM were calculated. These results demonstrated that the WalK dimerization domain could serve as a potent binding site, and further optimization of singermycin B could lead to the development of novel antibacterial agents [40].
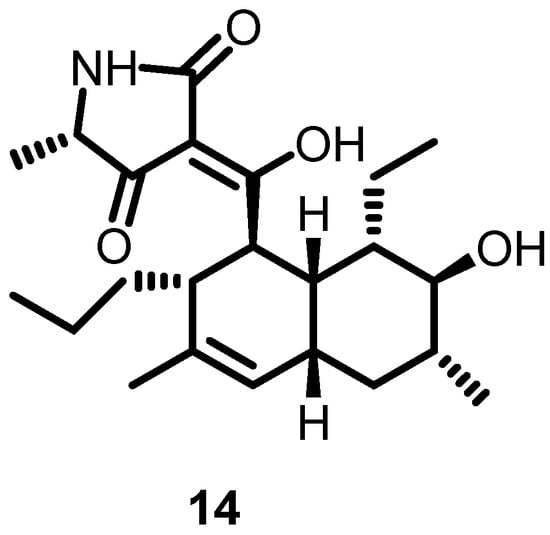
Figure 15.
Chemical structure of signermycin B (14).
In another study, Cai et al. in 2011, identified four compounds, 15a–15d (Figure 16), as possible PhoQ inhibitors using HTS and enzymatic activity-coupled assays. These four compounds had significant binding affinities to the S. flexneri PhoQc protein in the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) response and inhibited the autophosphorylation activity of S. flexneri PhoQc (KD = 4.50, 10.6, 7.56, and 9.40 µM, respectively). The IC50 values of these four compounds calculated during the luminescent kinase assay were 69.37 (15a), 48.9 (15b), 7.99 (15c), and 27.2 (15d) μM. The results showed that all four putative PhoQ inhibitors were able to reduce Shigella virulence [56].
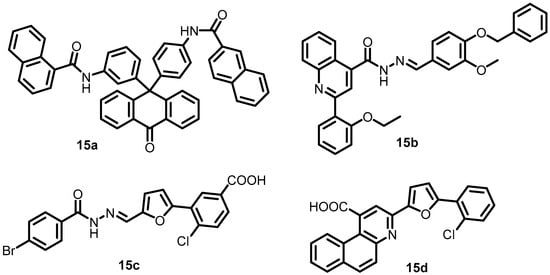
Figure 16.
Chemical structures of PhoQ inhibitors 15a–15d.
Another study by Eguchi et al. in 2011 investigated the effect of walkmycin C (16) (Figure 17) on WalK BHK in B. subtilis and S. aureus. Furthermore, walkmycin also exhibited significant activity against the cytoplasmic domains of VicK (IC50: 2.53 μg/mL), CiaH (IC50: 4.29 μg/mL), and LiaS (IC50: 4.96 μg/mL) of Streptococcus mutans. Moreover, it also inhibited the autophosphorylation activities of EnvZ and PhoQ from E. coli, both with IC50s of 1.25 μM. Studies of the inhibitory activity of walkmycin C on the virulence factors of S. mutans showed that exposure to walkmycin C at sub-MICs could inhibit biofilm formation, acid tolerance, and competence. Thus, walkmycin C can be used as a potential lead molecule for the development of BHK inhibitors [39].
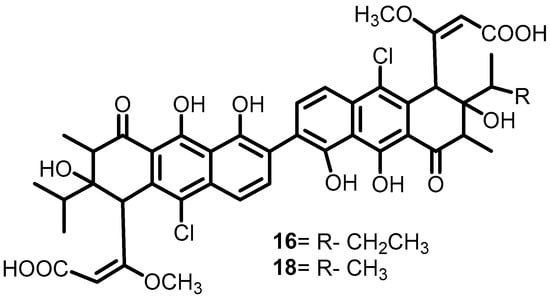
Figure 17.
Chemical structure of walkmycin C (16).
In 2010, to identify potent inhibitors of BHK, Henriksen et al. performed virtual screening of a library containing approximately 106 compounds. Forty-nine compounds were found to exhibit potent inhibitory activity, and among them, eighteen compounds were directly evaluated against three different S. aureus strains and two E. coli strains via disk inhibition assays. Compounds 17a and 17b (Figure 18) were the most potent, with G-score values of −7.70 and −7.68 kcal/mol, respectively, and MM-GBSA values of −20.34 and −20.53 kcal/mol, respectively. These compounds can be further optimized for the development of future antibacterial agents [57].
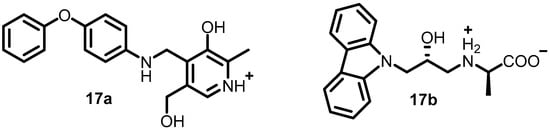
Figure 18.
Chemical structures of BHK inhibitors 17a–17b.
In 2010, Okada et al. screened approximately 1368 cultures of Streptomyces sp. by using differential growth assays and produced different walkmycin derivatives. Among these, walkmycin B (18) (Figure 17) had the greatest binding affinity for WalK in B. subtilis, with a KD value of 7.63 µM. Furthermore, they measured the autophosphorylation bands densitometrically and calculated the IC50 values of 18 against WalK of S. aureus (5.7 μM) and B. subtilis (1.6 µM) [38].
In another study, Pan et al. (2010) designed and created a series of new 2-arylimino-3-aryl-thiazolidine-4-one compounds based on the core structure of compound 13a (Figure 14) to develop more potent and less harmful BHK inhibitors. Six derivatives (19a–19f) (Figure 19) were created by altering the functional groups through cyclization, aldol condensation, substitution, and hydrolysis. The autophosphorylation activity of WalK was inhibited by all six derivatives in a concentration-dependent manner, with IC50 values that are comparable to those of 13a (IC50 = 47.9 µM) at 88.35, 61.15, 34.83, 66.68, 22.15, and 82.51 µM [58].
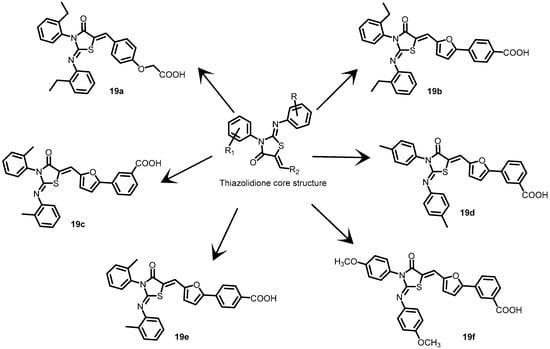
Figure 19.
Chemical structures of thiazolidine derivatives 19a–19f.
In 2006, Qin et al. initially employed a structure-based virtual screening (SBVS) method to identify potential inhibitors of S. epidermidis WalK from a small-molecule library of chemical compounds. Among the 76 candidates that target the WalK ATP binding domain, only seven exhibited significant growth-inhibitory effects on S. epidermidis. Compounds 13a and 20a–20b (Figure 20), which possess a thiazolidione scaffold, exhibited greater ATPase activity of the WalK protein, with IC50s ranging from 6.5 to 29 µM. Only the non-biofilm-forming S. epidermidis ATCC 12228 was susceptible to 20b, while 13a and 20a were effective against S. aureus, S. pyogenes, and S. mutans [33].
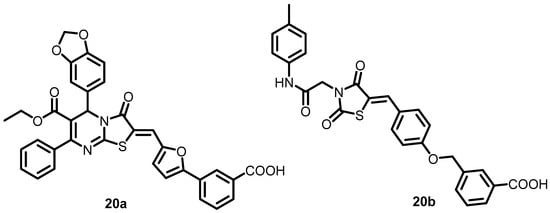
Figure 20.
Chemical structures of compounds 20a–20b.
Gilmour et al. (2005) identified thienopyridine (CAS 332175-01-6) (21) (Figure 21) as a novel class of competitive ATP inhibitors of BHKs and analyzed its antibacterial activity by using the HTVS of compound libraries. The results indicated that 21 has a core ring structure that is similar to that of purines, although the exact structural mechanism by which TEP inhibits BHKs is yet unknown. However, its hydrophobic portion may be responsible for cell wall permeation, thereby inhibiting bacterial growth. Competitive ATP inhibition was evaluated using Lineweaver–Burk analysis, and the average Ki value for 21 was found to be 0.62 ± 0.11 µM. Furthermore, 21 could serve as a starting material for novel inhibitors that specifically inhibit BHKs [37].
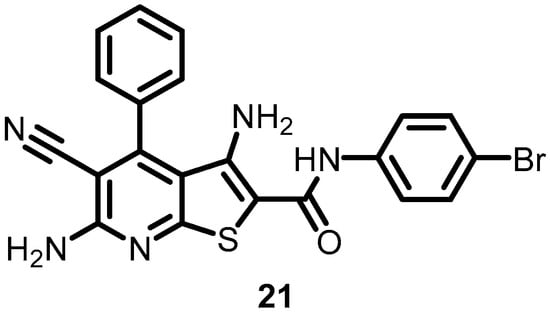
Figure 21.
Chemical structure of thienopyridine (21).
In 2001, Yamamoto et al. developed and examined a series of imidazole (22a–22e) and zerumbone (22f–22k) derivatives (Figure 22). Prompted by the inhibitory activity of imidazoles against BHK, the authors screened imidazole derivatives against the autophosphorylation of YycG. Astonishing results were observed for the derivatives, with IC50 values ranging from 6.6 to 120 µM. Almost 100 zerumbone derivatives were screened for their ability to inhibit YycG autophosphorylation. However, the results were not positive, and no inhibitor was detected during the study. Then, the authors tried to synthesize zerumbone derivatives by cleaving their cyclic structures. Upon structural modification, the obtained zerumbone derivatives were found to be active (IC50: 750–2300 µM). The derivative 29 h was found to be a more potent inhibitor of YycG, with an IC50 value of 750 µM [32].
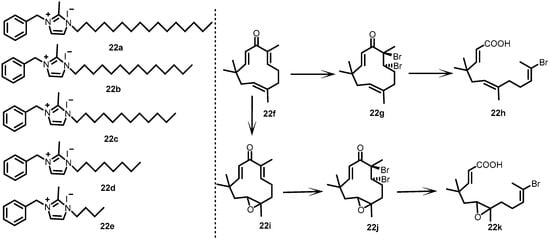
Figure 22.
Chemical structures of imidazole derivatives 22a–22e and zerumbone derivatives 22f–22k.
In 1993, Roychoudhury et al. identified compounds that prevent the phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of AlgR2 and the DNA-binding activity of AlgR1, which prevent the production of the alginate gene. In this study, 15 compounds were shown to be effective in screening approximately 25,000 compounds for the inhibition of algD promoter activation. Furthermore, four (23a–23d) (Figure 23) of fifteen compounds strongly inhibited AlgR1-AlgR2 phosphorylation, AlgR2 kinase activity, AlgR2 phosphatase activity, the DNA-binding activity of AlgR1, and the kinase activities of CheA, NRⅡ, and KinA [41].
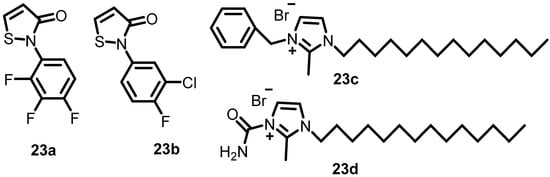
Figure 23.
Chemical structures of the thiazole and imidazole derivatives (23a–23d).
3. Conclusions
In the present review, we described the roles of the TCS pathway and BHK in bacterial survival and AMR. Furthermore, we also summarize the advancements in the discovery of novel BHK inhibitors in the 21st century. However, despite these massive efforts, none of the discovered inhibitors have entered clinical use or are, to the best of our knowledge, even undergoing clinical studies. To make progress and eventually find new effective antimicrobial medications, challenges must be recognized and overcome. We will use this conclusion section to predict and discuss these possible challenges and obstacles.
Although the chemical structures of the reported inhibitors are diverse, their exact structure–activity relationships cannot be elucidated. Furthermore, progress in the discovery of BHK inhibitors is still in its infancy. Although crystal structures are available, the lack of cocrystals makes it cumbersome to identify potential receptor–ligand interactions. Some studies based on fragment-based and structure-based virtual screening and drug repositioning were implemented to identify BHK inhibitors that exhibited significant inhibitory potential. In the near future, understanding the binding mode and conducting molecular modeling studies will significantly accelerate the discovery of novel BHK inhibitors with greater potency. In addition, researchers can perform more prospective analyses by inducing spontaneous mutants to BHK inhibitors that are under development to elucidate on-target effects and possible resistance mechanisms. Although challenging, designing and developing novel BHK inhibitors is a viable approach for combating AMR.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, R.A., S.K. (Sumaiya Kifayat), and K.K.P.; data curation, S.K. (Sunita Kularia) and B.S.A.; writing—review and editing, supervision, B.K.R.S.; writing—review and editing, supervision, conceptualization, V.S.; conceptualization, formal analysis, supervision, D.K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, B.; Webster, T.J. Bacteria antibiotic resistance: New challenges and opportunities for implant-associated orthopedic infections. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, H.C. The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 1992, 257, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlet, J.; Jarlier, V.; Harbarth, S.; Voss, A.; Goossens, H.; Pittet, D. Ready for a world without antibiotics? The pensières antibiotic resistance call to action. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2012, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, P.A. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Modified target sites. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1471–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K. Efflux pumps as antimicrobial resistance mechanisms. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiodras, S.; Gold, H.S.; Sakoulas, G.; Eliopoulos, G.M.; Wennersten, C.; Venkataraman, L.; Moellering, R.C., Jr.; Ferraro, M.J. Linezolid resistance in a clinical isolate of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 2001, 358, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravolatz, L.D.; Stein, G.E.; Johnson, L.B. Ceftaroline: A novel cephalosporin with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabol, K.; Patterson, J.E.; Lewis, J.S.; Owens, A.; Cadena, J.; Jorgensen, J.H. Emergence of daptomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium during daptomycin therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1664–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations 2014. 2014. Available online: http://amr-review.org/ (accessed on 15 January 2015).
- Green, D.W. The bacterial cell wall as a source of antibacterial targets. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2002, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.T.; Reynolds, K.A. Antibacterial targets in fatty acid biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, C.R. Utility of the biosynthetic folate pathway for targets in antimicrobial discovery. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, M.A.; Thathan, J.; Jubie, S. Dual targeting DNA gyrase B (GyrB) and topoisomerse IV (ParE) inhibitors: A review. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 62, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenz, S.; Wilson, D.N. Bacterial protein synthesis as a target for antibiotic inhibition. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline antibiotics: Mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotra, L.P.; Haddad, J.; Mobashery, S. Aminoglycosides: Perspectives on mechanisms of action and resistance and strategies to counter resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, T.; Mini, E.; Novelli, A.; Periti, P. Chemistry and mode of action of macrolides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1993, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomason, P.; Kay, R. Eukaryotic signal transduction via histidine-aspartate phosphorelay. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3141–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Virulence factors of the coagulase-negative staphylococci. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 841–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, R.P. Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1429–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casino, P.; Rubio, V.; Marina, A. The mechanism of signal transduction by two-component systems. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, L.J. How important is the phosphatase activity of sensor kinases? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, N.; Bem, A.E.; van Baarlen, P.; Wells, J.M.; Marina, A. WalK, the path towards new antibacterials with low potential for resistance development. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossage, L.; Eisen, T. Targeting Multiple Kinase Pathways: A Change in Paradigm. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network pharmacology: The next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovskaya, V.; Baasov, T. Dual-acting hybrid antibiotics: A promising strategy to combat bacterial resistance. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 883–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, M.T.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; Zhao, R. The Hsp90 inhibitor radicicol interacts with the ATP-binding pocket of bacterial sensor kinase PhoQ. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 379, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, C.D.; Shebert, H.L.; Zikovich, S.; Dryer, R.A.; Huang, T.P.; Moran, L.J.; Cho, J.; Wassarman, D.R.; Falahee, B.E.; Young, P.D. Repurposing Hsp90 inhibitors as antibiotics targeting histidine kinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 5235–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, N.; Fulle, S.; Manso, A.S.; Mechkarska, M.; Finn, P.; Conlon, J.M.; Oggioni, M.R.; Wells, J.M.; Marina, A. Putative histidine kinase inhibitors with antibacterial effect against multi-drug resistant clinical isolates identified by in vitro and in silico screens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kitayama, T.; Minagawa, S.; Watanabe, T.; Sawada, S.; OKAMoTo, T.; Utsumi, R. Antibacterial agents that inhibit histidine protein kinase YycG of Bacillus subtilis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 2306–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, X.; Molin, S.; Danchin, A.; Jiang, H. Structure-based discovery of inhibitors of the YycG histidine kinase: New chemical leads to combat Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zheng, L.K.; Liu, H.Y.; Pan, B.; Hu, J.; Zhu, T. Thiazolidione Derivatives Targeting the Histidine Kinase YycG Are Effective Against Both Planktonic and Biofilm-Associated Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, D.; Chang, J.; Yan, L.; Zhao, F.; Wu, Y.; Xu, T.; Gong, T.; Chen, L.; He, N. Efficacy of novel antibacterial compounds targeting histidine kinase YycG protein. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6003–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boibessot, T.; Zschiedrich, C.P.; Lebeau, A.; Bénimèlis, D.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Szurmant, H.; Benfodda, Z.; Meffre, P. The rational design, synthesis, and antimicrobial properties of thiophene derivatives that inhibit bacterial histidine kinases. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8830–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmour, R.; Foster, J.E.; Sheng, Q.; McClain, J.R.; Riley, A.; Sun, P.-M.; Ng, W.-L.; Yan, D.; Nicas, T.I.; Henry, K. New class of competitive inhibitor of bacterial histidine kinases. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 8196–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, A.; Igarashi, M.; Okajima, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Umekita, M.; Sawa, R.; Inoue, K.; Watanabe, T.; Martin, A.; Quinn, J. Walkmycin B targets WalK (YycG), a histidine kinase essential for bacterial cell growth. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Kubo, N.; Matsunaga, H.; Igarashi, M.; Utsumi, R. Development of an antivirulence drug against Streptococcus mutans: Repression of biofilm formation, acid tolerance, and competence by a histidine kinase inhibitor, walkmycin C. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Igarashi, M.; Okajima, T.; Ishii, E.; Kino, H.; Hatano, M.; Sawa, R.; Umekita, M.; Kimura, T.; Okamoto, S. Isolation and characterization of signermycin B, an antibiotic that targets the dimerization domain of histidine kinase WalK. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3657–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, S.; Zielinski, N.A.; Ninfa, A.J.; Allen, N.E.; Jungheim, L.N.; Nicas, T.I.; Chakrabarty, A. Inhibitors of two-component signal transduction systems: Inhibition of alginate gene activation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanojia, R.M.; Murray, W.; Bernstein, J.; Fernandez, J.; Barrett, J.F. 6-Oxa isosteres of anacardic acids as potent inhibitors of bacterial histidine protein kinase (HPK)-mediated two-component regulatory systems. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 18, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner-Wells, M.A.; Ohemeng, K.A.; Nguyen, V.N.; Hlasta, D.J. Amidino benzimidazole inhibitors of bacterial two-component systems. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.; Chinardet, N.; Mourey, L.; Birck, C.; Samama, J.P. Structure of the CheY-binding domain of histidine kinase CheA in complex with CheY. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1998, 5, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pioszak, A.A.; Ninfa, A.J. Genetic and biochemical analysis of phosphatase activity of Escherichia coli NRII (NtrB) and its regulation by the PII signal transduction protein. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wilke, K.E.; Francis, S.; Carlson, E.E. Inactivation of multiple bacterial histidine kinases by targeting the ATP-binding domain. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, M.; Espinasse, A.; Carlson, E.E. Disarming the Virulence Arsenal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Blocking Two-Component System Signaling. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7332–7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, A.A.; Aanazi, F.K.; Al-Agamy, M.; Mahrous, G.M. Design, synthesis and molecular modeling study of substituted indoline-2-ones and spiro [indole-heterocycles] with potential activity against Gram-positive bacteria. Acta Pharm. 2022, 72, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabajal, M.A.; Asquith, C.R.; Laitinen, T.; Tizzard, G.J.; Yim, L.; Rial, A.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Zuercher, W.J.; García Véscovi, E. Quinazoline-based antivirulence compounds selectively target Salmonella PhoP/PhoQ signal transduction system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 64, e01744-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, A.; Mahrous, G.M. Docking studies and molecular dynamics simulations of the binding characteristics of waldiomycin and its methyl ester analog to Staphylococcus aureus histidine kinase. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizar, P.; Arya, R.; Kim, T.; Cha, S.; Ryu, K.-S.; Yeo, W.-s.; Bae, T.; Kim, D.W.; Park, K.H.; Kim, K.K. Total synthesis of Xanthoangelol B and its various fragments: Toward inhibition of virulence factor production of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10473–10487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Quan, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Fan, S. Proteoliposome-based model for screening inhibitors targeting histidine kinase AgrC. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Colvin, C.J.; Johnson, B.K.; Kirchhoff, P.D.; Wilson, M.; Jorgensen-Muga, K.; Larsen, S.D.; Abramovitch, R.B. Inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DosRST signaling and persistence. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Antibacterial effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine monomers against Streptococcus pneumoniae via inhibiting pneumococcal histidine kinase (VicK). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellale, E.; Naik, M.; VB, V.; Ambady, A.; Narayan, A.; Ravishankar, S.; Ramachandran, V.; Kaur, P.; McLaughlin, R.; Whiteaker, J. Diarylthiazole: An antimycobacterial scaffold potentially targeting PrrB-PrrA two-component system. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6572–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, X.; Qu, D.; Jiang, H. The effect of the potential PhoQ histidine kinase inhibitors on Shigella flexneri virulence. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, S.T.; Liu, J.; Estiu, G.; Oltvai, Z.; Wiest, O. Identification of novel bacterial histidine biosynthesis inhibitors using docking, ensemble rescoring, and whole-cell assays. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5148–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Huang, R.-Z.; Han, S.-Q.; Qu, D.; Zhu, M.-L.; Wei, P.; Ying, H.-J. Design, synthesis, and antibiofilm activity of 2-arylimino-3-aryl-thiazolidine-4-ones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).