Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections in Critically Ill Patients: A Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pharmacokinetic Parameters, PK/PD Targets, and Susceptibility Data
4.2. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Analysis and Monte Carlo Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Y.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsueh, P.R. Update on infections caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia with particular attention to resistance mechanisms and therapeutic options. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, M.F.; Humphries, R.; Lipuma, J.J.; Mathers, A.J.; Rao, G.G.; Shelburne, S.A.; Fouts, D.E.; Van Duin, D.; Bonomo, R.A. Clinical challenges treating Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections: An update. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 4, dlac040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlizzi, V.; Tomaselli, M.; Giacomini, G.; Dalpiaz, I.; Chiappini, E. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in people with Cystic Fibrosis: A systematic review of prevalence, risk factors and management. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Aitken, S.L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Mathers, A.J.; van Duin, D.; Clancy, C.J. Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2023, ciad428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Aitken, S.L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Mathers, A.J.; van Duin, D.; Clancy, C.J. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidance on the Treatment of AmpC β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales, Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 2089–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gales, A.C.; Seifert, H.; Gur, D.; Castanheira, M.; Jones, R.N.; Sader, H.S. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii Complex and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Clinical Isolates: Results From the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1997–2016). Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6 (Suppl. S1), S34–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Shortridge, D.; Carvalhaes, C.G.; Castanheira, M. Trends in the susceptibility of U.S. Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus species complex and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates to minocycline, 2014–2021. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0198123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, M.F.; Bonomo, R.A.; van Duin, D. Treatment approaches for severe Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 36, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Perfomance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 14.0. 2024. Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. MIC and Zone Diameter Distributions and ECOFFs. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/mic_and_zone_distributions_and_ecoffs (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Huang, C.; Lin, L.; Kuo, S. Risk factors for mortality in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia—A meta-analysis. Infect. Dis. 2024, 56, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Aguirre-Quiñonero, A.; Aspiazu, M.A.S.; Canut-Blasco, A. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Tedizolid Phosphate Compared to Linezolid for the Treatment of Infections Caused by Gram-Positive Bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Isla, A.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Calvo, B.; Canut, A.; Solinís, M.Á. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis as a tool for surveillance of the activity of antimicrobials against Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated in critically ill patients. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Isla, A. The Role of PK/PD Analysis in the Development and Evaluation of Antimicrobials. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, J.W.; Brown, D.F.; Apfalter, P.; Cantón, R.; Giske, C.G.; Ivanova, M.; MacGowan, A.P.; Rodloff, A.; Soussy, C.J.; Steinbakk, M.; et al. The role of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics in setting clinical MIC breakpoints: The EUCAST approach. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, E37–E45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asín-Prieto, E.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Isla, A. Applications of the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) analysis of antimicrobial agents. J. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasko, M.J.; Tabor-Rennie, J.L.; Nicolau, D.P.; Kuti, J.L. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole pharmacodynamics against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the in vitro chemostat model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 3187–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasko, M.J.; Gethers, M.L.; Tabor-Rennie, J.L.; Nicolau, D.P.; Kuti, J.L. In Vitro Time-Kill Studies of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia versus Escherichia coli Using Cation-Adjusted Mueller-Hinton Broth and ISO-Sensitest Broth. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0216721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullar, R.; Wenzler, E.; Alexander, J.; Goldstein, E.J.C. Overcoming Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Resistance for a More Rational Therapeutic Approach. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, J.; Wong, D.W. Antimicrobial Treatment Strategies for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A Focus on Novel Therapies. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asín, E.; Isla, A.; Canut, A.; Rodríguez Gascón, A. Comparison of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic breakpoints with EUCAST and CLSI clinical breakpoints for Gram-positive bacteria. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakris, A.; Koumaki, V.; Dokoumetzidis, A. Minocycline susceptibility breakpoints for Acinetobacter baumannii: Do we need to re-evaluate them? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banar, M.; Sattari-Maraji, A.; Bayatinejad, G.; Ebrahimi, E.; Jabalameli, L.; Beigverdi, R.; Emaneini, M.; Jabalameli, F. Global prevalence and antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1163439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agwuh, K.N.; MacGowan, A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Ni, W.; Cai, X.; Zhao, J.; Cui, J. Evaluation of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole (SXT), Minocycline, Tigecycline, Moxifloxacin, and Ceftazidime Alone and in Combinations for SXT-Susceptible and SXT-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia by In Vitro Time-Kill Experiments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, D.J.; Sader, H.S.; Jones, R.N. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of a worldwide collection of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates tested against tigecycline and agents commonly used for S. maltophilia infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2735–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Avdic, E.; Li, D.X.; Dzintars, K.; Cosgrove, S.E. Association of Adverse Events With Antibiotic Use in Hospitalized Patients. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.H.; Kang, C.I.; Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Yeh, K.M.; Wang, C.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Gözel, M.G.; Kim, S.H.; Hsueh, P.R.; Sekiya, N.; et al. Fluoroquinolones versus trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the treatment of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Ni, W.; Cai, X.; Cui, J. A Monte Carlo pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic simulation to evaluate the efficacy of minocycline, tigecycline, moxifloxacin, and levofloxacin in the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Infect. Dis. 2015, 47, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratoni, A.J.; Nicolau, D.P.; Kuti, J.L. Levofloxacin pharmacodynamics against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in a neutropenic murine thigh infection model: Implications for susceptibility breakpoint revision. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 77, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, R.; Oota, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sato, T.; Yamano, Y. In Vitro Activity and In Vivo Efficacy of Cefiderocol against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e01436-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanghadiri, N.; Sholeh, M.; Navidifar, T.; Dadgar-Zankbar, L.; Elahi, Z.; van Belkum, A.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. Global mapping of antibiotic resistance rates among clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2024, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratoni, A.J.; Kuti, J.L.; Nicolau, D.P. Optimised cefiderocol exposures in a successfully treated critically ill patient with polymicrobial Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteraemia and pneumonia receiving continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, A.J.; Simner, P.J.; Bergman, Y.; Mathers, A.J.; Tamma, P.D. Successful Treatment of Persistent Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Bacteremia With Cefiderocol in an Infant. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sader, H.S.; Duncan, L.R.; Arends, S.J.R.; Carvalhaes, C.G.; Castanheira, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Aztreonam-Avibactam and Comparator Agents When Tested against a Large Collection of Contemporary Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates from Medical Centers Worldwide. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01433-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida Torres, N.; Morales Junior, R.; Bueno Lopes, L.F.; Zeigler, R.; Everson Uip, D. Synergistic combination of aztreonam and ceftazidime/avibactam against resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia on pancreatitis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2023, 17, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, A.; Pascal, L.; Carpentier, B.; Baclet, N.; Cabaret, P.; Georgel, A.F.; Dubreuil, L.; Weyrich, P. Successful use of avibactam and aztreonam combination for a multiresistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bloodstream infection in a patient with idiopathic medullary aplasia. Infect. Dis. Now 2021, 51, 637–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowart, M.C.; Ferguson, C.L. Optimization of Aztreonam in Combination With Ceftazidime/Avibactam in a Cystic Fibrosis Patient With Chronic Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Pneumonia Using Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: A Case Study. Ther. Drug Monit. 2021, 43, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]; Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of ATM-AVI in the Treatment of Serious Infection Due to MBL-Producing Gram-Negative Bacteria. Identifier NCT03580044; 2018. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03580044?term=NCT03580044&rank=1 (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]; Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). A Study to Determine the Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of Aztreonam-Avibactam (ATM-AVI) ± Metronidazole (MTZ) Versus Meropenem (MER) ± Colistin (COL) for the Treatment of Serious Infections Due to Gram Negative Bacteria. (REVISIT). Identifier NCT03329092; 2017. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03329092?term=NCT03329092&rank=1 (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Mauri, C.; Maraolo, A.E.; Di Bella, S.; Luzzaro, F.; Principe, L. The Revival of Aztreonam in Combination with Avibactam against Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Gram-Negatives: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies and Clinical Cases. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prawang, A.; Chanjamlong, N.; Rungwara, W.; Santimaleeworagun, W.; Paiboonvong, T.; Manapattanasatein, T.; Pitirattanaworranat, P.; Kitseree, P.; Kanchanasurakit, S. Combination Therapy versus Monotherapy in the Treatment of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.C.; McBryde, E.S.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Chierakul, W.; Amornchai, P.; Day, N.P.; White, N.J.; Peacock, S.J. Dosing regimens of cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) for melioidosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4193–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, T.W.; Vandenbroucke, A.; Fong, I.W. Pharmacokinetics of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in critically ill and non-critically ill AIDS patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Cotta, M.O.; Cojutti, P.; Lugano, M.; Della Rocca, G.; Pea, F. Does Critical Illness Change Levofloxacin Pharmacokinetics? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, D.N.; Chow, A.T. The clinical pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1997, 32, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodise, T.P.; Van Wart, S.; Sund, Z.M.; Bressler, A.M.; Khan, A.; Makley, A.T.; Hamad, Y.; Salata, R.A.; Silveira, F.P.; Sims, M.D.; et al. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profiling of Minocycline for Injection following a Single Infusion in Critically Ill Adults in a Phase IV Open-Label Multicenter Study (ACUMIN). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e01809-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuk-De Moor, A.; Rypulak, E.; Potręć, B.; Piwowarczyk, P.; Borys, M.; Sysiak, J.; Onichimowski, D.; Raszewski, G.; Czuczwar, M.; Wiczling, P. Population Pharmacokinetics of High-Dose Tigecycline in Patients with Sepsis or Septic Shock. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02273-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, N.; Katsube, T.; Echols, R.; Wajima, T. Population Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Analyses of Cefiderocol, a Parenteral Siderophore Cephalosporin, in Patients with Pneumonia, Bloodstream Infection/Sepsis, or Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e01437-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; El Tabei, L.; Büsker, S.; Krauss, C.; Fuhr, U.; Taubert, M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Cefiderocol. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Isla, A.; Barrasa, H.; Del Barrio-Tofiño, E.; Oliver, A.; Canut, A.; Solinís, M.Á. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Susceptibility in Spain: Antimicrobial Activity and Resistance Suppression Evaluation by PK/PD Analysis. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principe, L.; Lupia, T.; Andriani, L.; Campanile, F.; Carcione, D.; Corcione, S.; De Rosa, F.G.; Luzzati, R.; Stroffolini, G.; Steyde, M.; et al. Microbiological, Clinical, and PK/PD Features of the New Anti-Gram-Negative Antibiotics: β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Inhibitors in Combination and Cefiderocol-An All-Inclusive Guide for Clinicians. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, W.W.; Newell, P.; Critchley, I.A.; Riccobene, T.; Das, S. Avibactam Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Targets. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02446-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, R.C., Jr.; Bhavnani, S.M.; Ambrose, P.G. Assessment of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic target attainment of gemifloxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 51, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J.W.; Dudley, M.N.; Cars, O.; Derendorf, H.; Drusano, G.L. Standardization of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) terminology for anti-infective drugs: An update. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, G.E.; Smith, C.L.; Scharmen, A.; Kidd, J.M.; Cooper, C.; Kuti, J.; Mitra, S.; Nicolau, D.P.; Havlichek, D.H. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Ceftazidime/Avibactam in Critically Ill Patients. Surg. Infect. 2019, 20, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

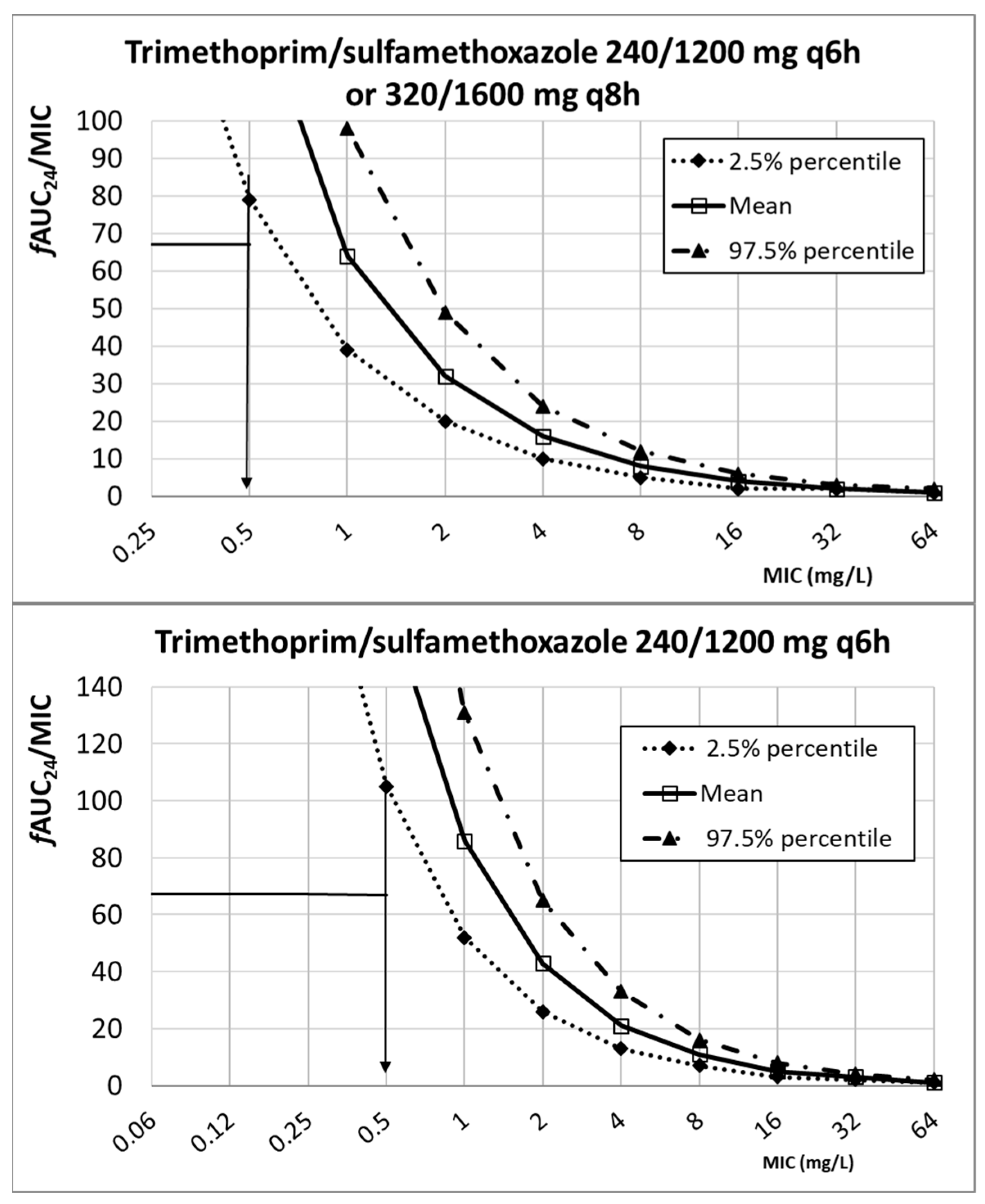
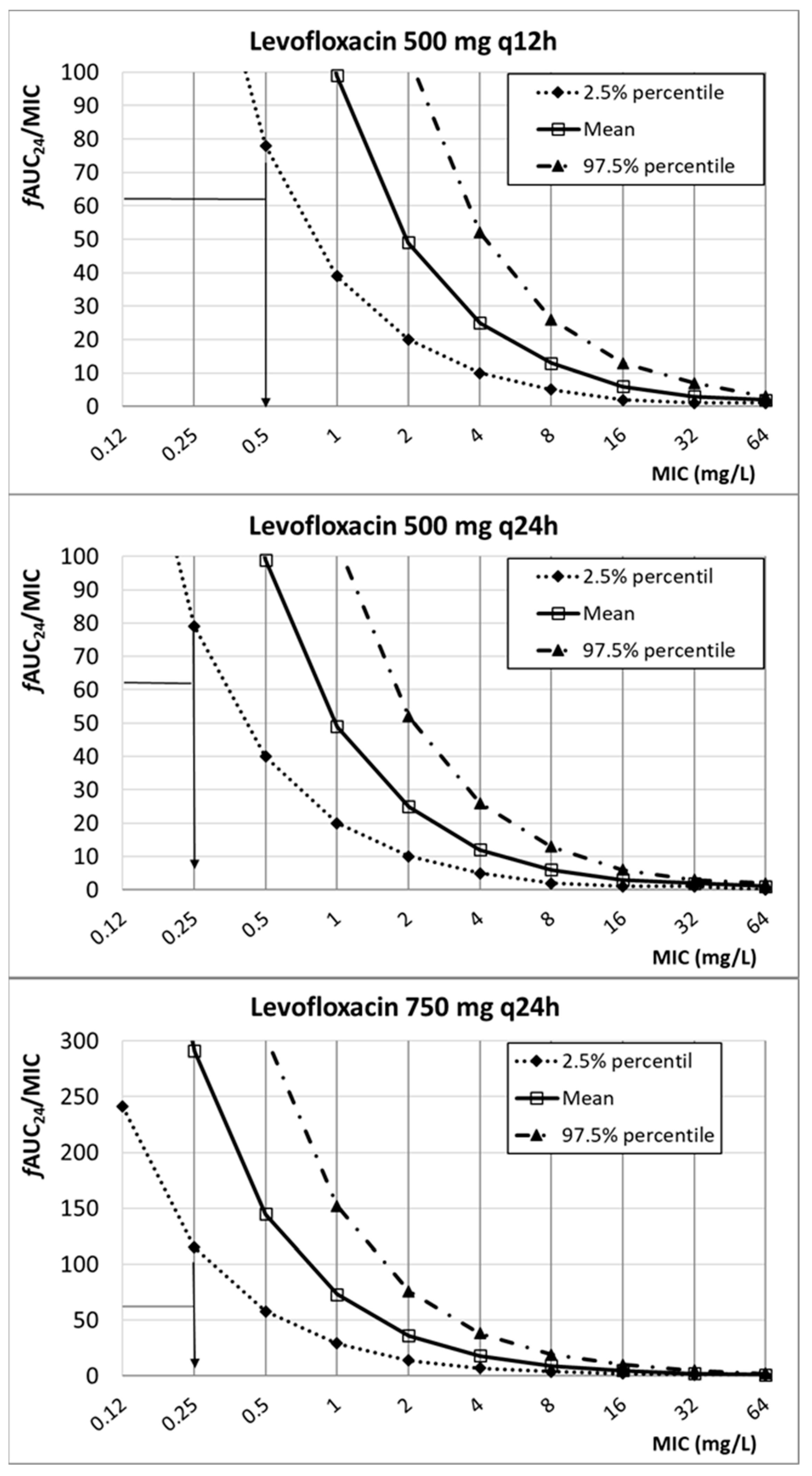
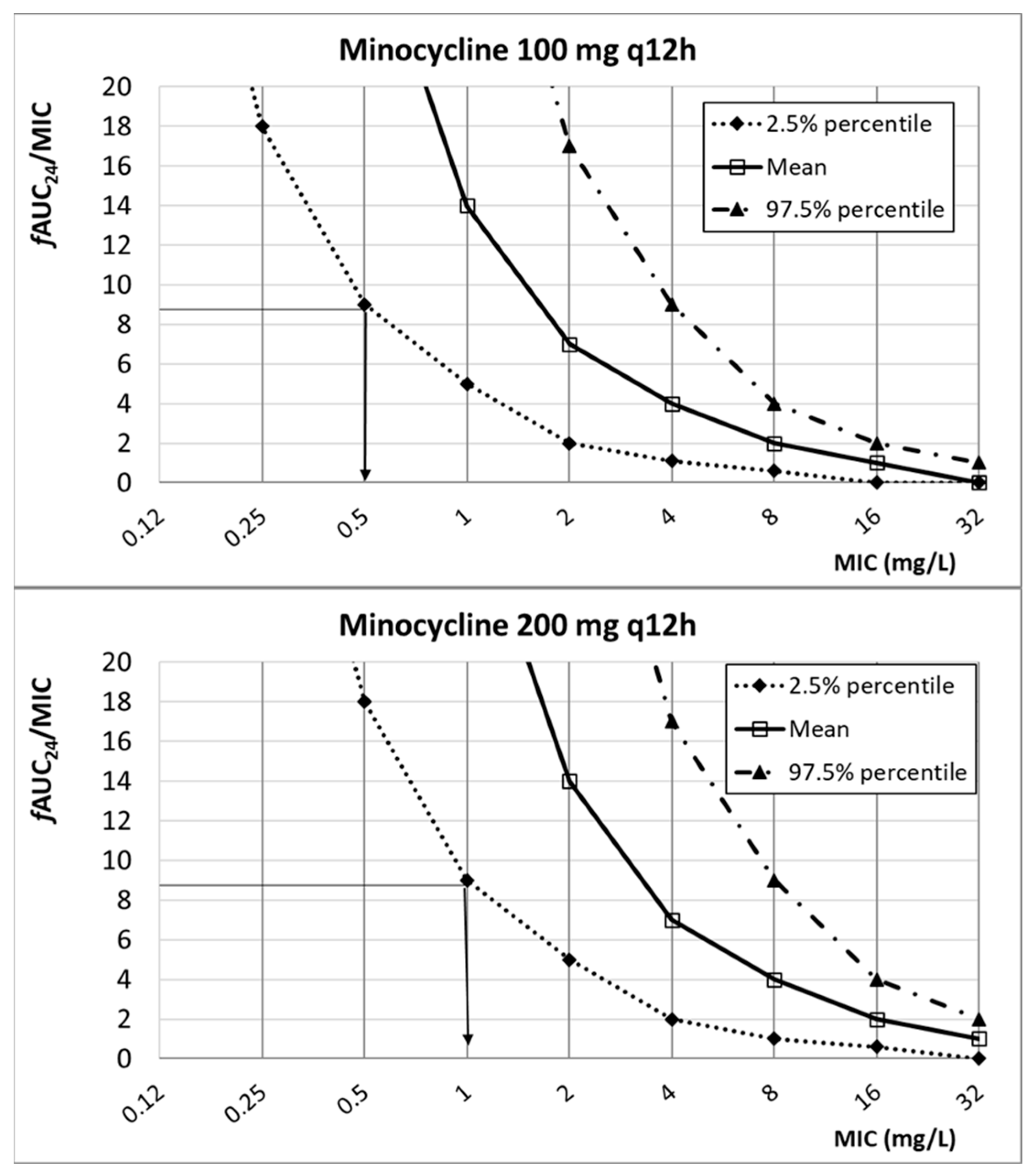


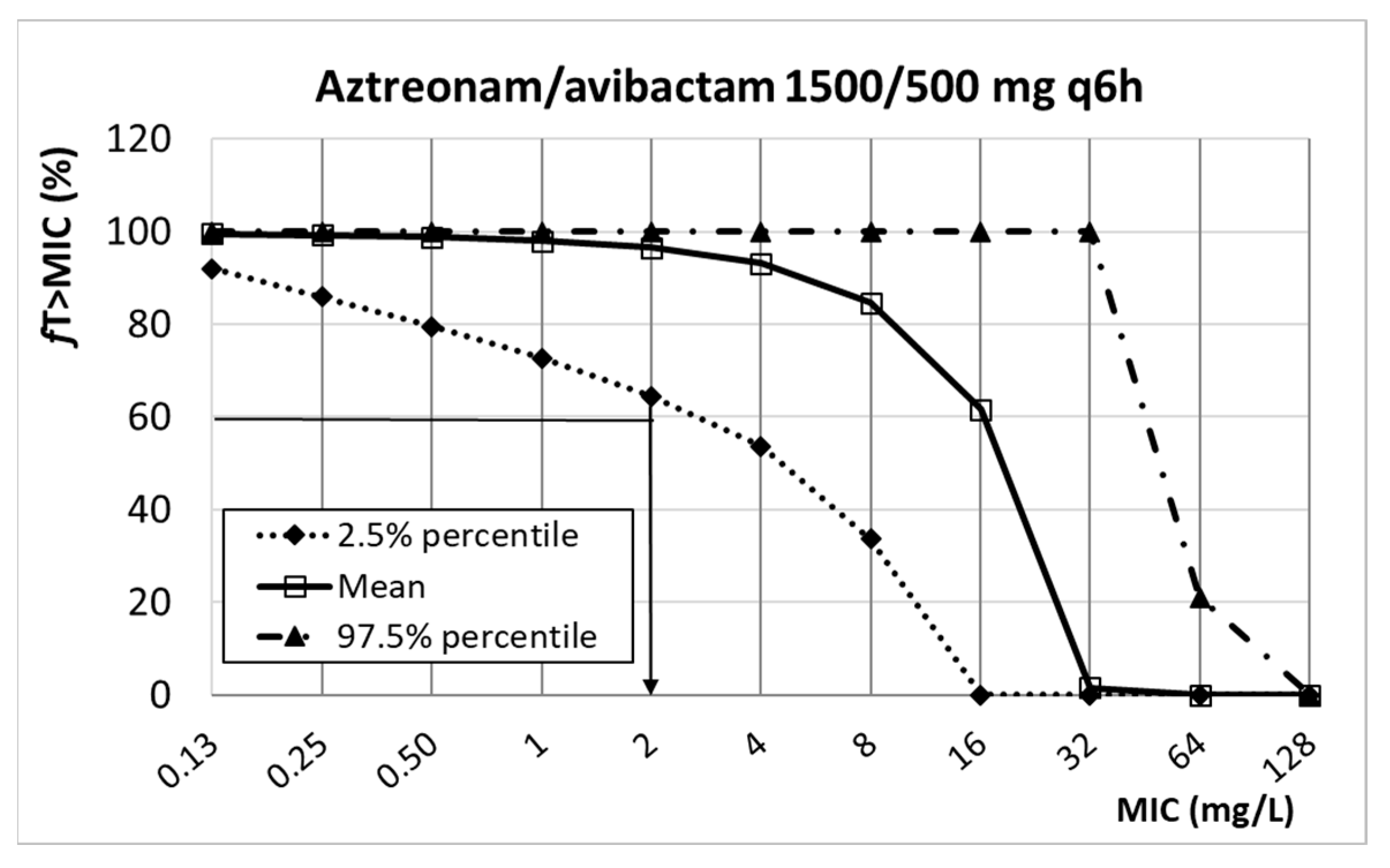
| Antibiotic | PK/PD Breakpoint | Clinical Breakpoint | ECOFFs a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLSI | EUCAST | |||
| Cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) | ≤2 b | ≤4 b,c | 2 | |
| 240/1200 mg q6h | 0.5 | |||
| 320/1600 mg q8h | 0.5 | |||
| 320/1600 mg q6h | 0.5 | |||
| Levofloxacin | ≤2 | n.d. | 4 | |
| 500 mg q24h | 0.25 | |||
| 500 mg q12h | 0.5 | |||
| 750 mg q24h | 0.25 | |||
| Minocycline | ≤4 | n.d. | 1 | |
| 100 mg q12h | 0.5 | |||
| 200 mg q12h | 1 | |||
| Tigecycline | n.d. | n.d. | 4 | |
| 50 mg q12h | 0.5 | |||
| 100 mg q12h | 1 | |||
| Cefiderocol | ≤1 | n.d. | 0.125 | |
| 2 g q8h | 4 | |||
| Aztreonam/avibactam | n.d. | n.d. | 8 d | |
| 1500/500 mg q6h | 2 | |||
| Antibiotic | CFR (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| EUCAST Isolates | U.S.Isolates | |
| Cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) | ||
| 240/1200 mg q6h | 66 | 90 |
| 320/1600 mg q8h | 66 | 90 |
| 320/1600 mg q6h | 73 | 91 |
| Levofloxacin | ||
| 500 mg q24h | 30 | 28 |
| 500 mg q12h | 55 | 57 |
| 750 mg q24h | 44 | 44 |
| Minocycline | ||
| 100 mg q12h | 74 | 84 |
| 200 mg q12h | 92 | 94 |
| Tigecycline | ||
| 50 mg q12h | 76 | * |
| 100 mg q12h | 91 | * |
| Cefiderocol | ||
| 2 g q8h | 99 | * |
| Aztreonam/avibactam | ||
| 1500/500 mg q6h | 95 | * |
| Antibiotic | Dosing Regimen | CL (L/h) | Fu | V (L) | PK/PD Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) a | 240/1200 mg q6h 320/1600 mg q6h 320/1600 mg q8h | 1.88 ± 0.44 b | 0.5 ± 0.017 | fAUC24/MIC ≥ 67.4 | [18,44,45] | |
| Levofloxacin | 500 mg q12h 500 mgq24h 750 mgq24h | 8.66 ± 3.85 | 0.71 | fAUC24/MIC ≥ 62 | [30,46,47] | |
| Minocycline | 100 mg q12h 200 mgq12h | 4.70 ± 2.14 | 0.28 | fAUC24/MIC ≥ 8.75 | [30,48] | |
| Tigecycline | 50 mg q12h 100 mg q12h | 22.10 ± 3.82 | 0.2 | fAUC24/MIC ≥ 0.9 | [30,49] | |
| Cefiderocol | 2 g q8h, 3 h infusion | 4.04 ± 1.52 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | V1: 7.78 ± 4.43 V2: 5.77 ± 1.94 V3: 0.798 | %fT>MIC > 75% | [50,51] |
| Aztreonam/ avibactam | 1500/500 mg q6h 3 h infusion | 9.60 ± 5.00 11.09 ± 6.78 | 0.72 0.92 | 27.20 ± 20.80 50.81 ± 14.32 | %fT>MIC > 60% %ƒT>2.5 mg/L > 50% | [52,53,54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrasa, H.; Morán, M.A.; Fernández-Ciriza, L.; Isla, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Canut-Blasco, A.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A. Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections in Critically Ill Patients: A Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Approach. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060553
Barrasa H, Morán MA, Fernández-Ciriza L, Isla A, Solinís MÁ, Canut-Blasco A, Rodríguez-Gascón A. Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections in Critically Ill Patients: A Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Approach. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(6):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060553
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrasa, Helena, Miguel Angel Morán, Leire Fernández-Ciriza, Arantxa Isla, María Ángeles Solinís, Andrés Canut-Blasco, and Alicia Rodríguez-Gascón. 2024. "Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections in Critically Ill Patients: A Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Approach" Antibiotics 13, no. 6: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060553
APA StyleBarrasa, H., Morán, M. A., Fernández-Ciriza, L., Isla, A., Solinís, M. Á., Canut-Blasco, A., & Rodríguez-Gascón, A. (2024). Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections in Critically Ill Patients: A Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Approach. Antibiotics, 13(6), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060553







