Exploring the Impact of Antibiotics on Fever Recovery Time and Hospital Stays in Children with Viral Infections: Insights from Advanced Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Co-Variates
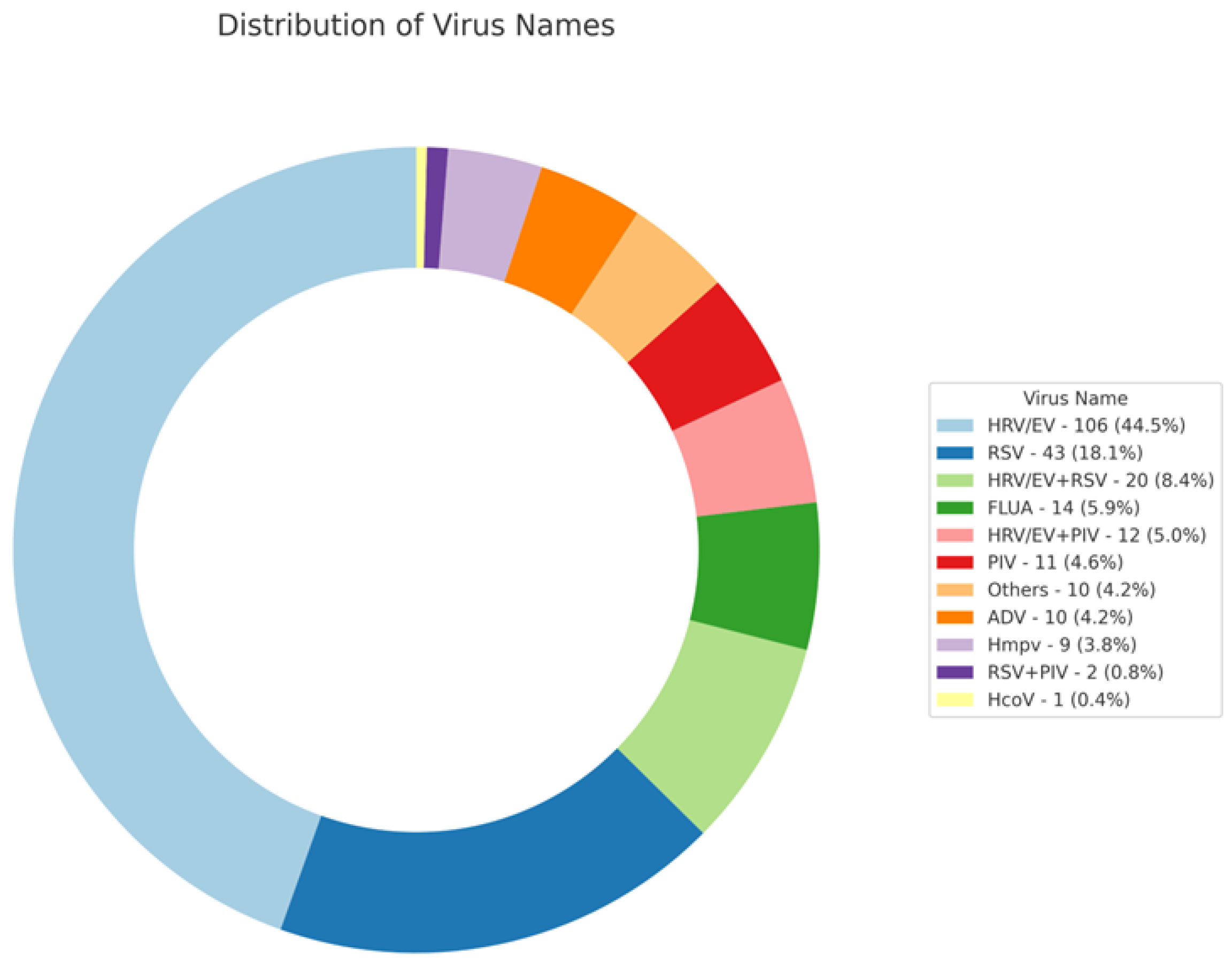
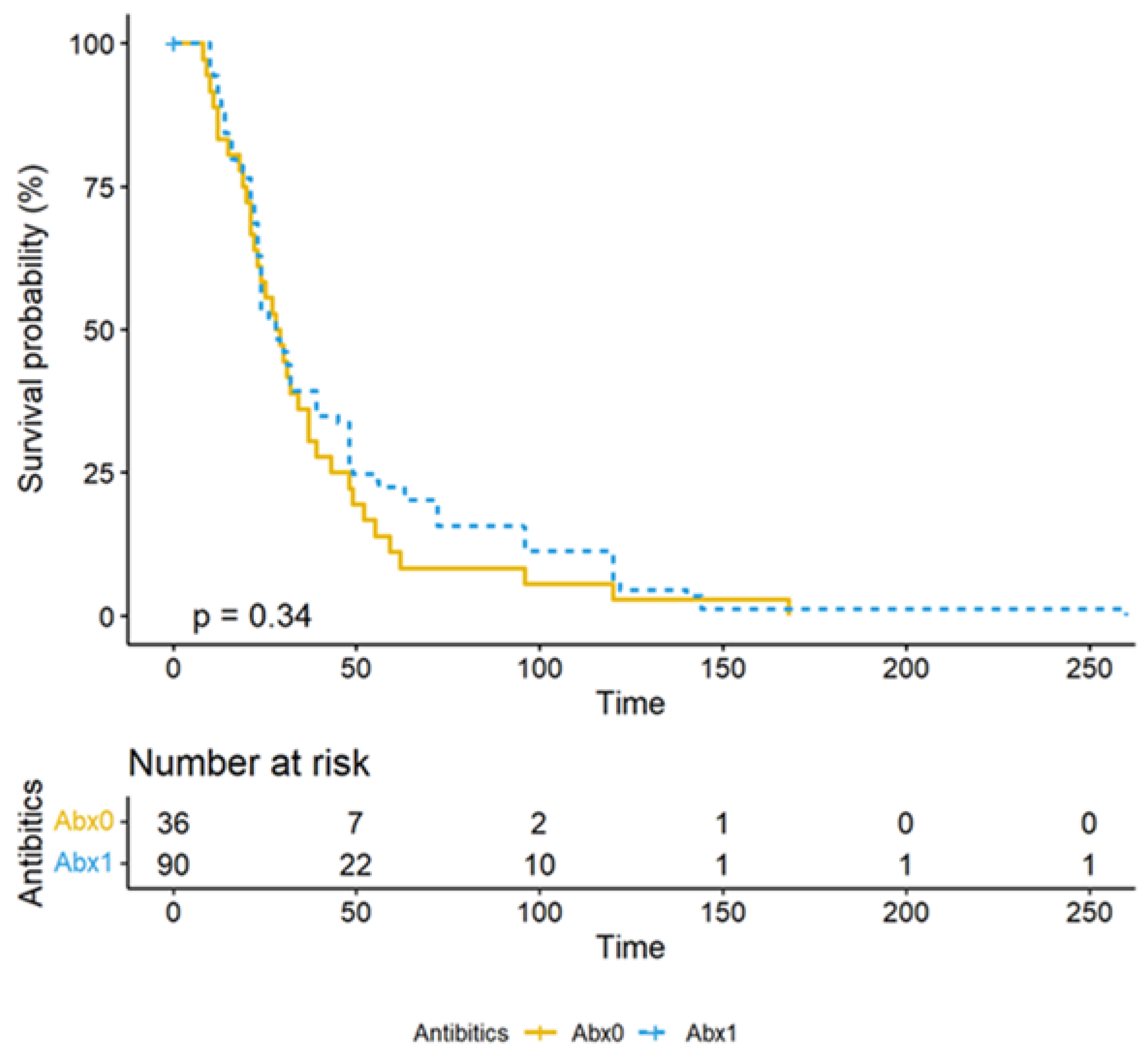
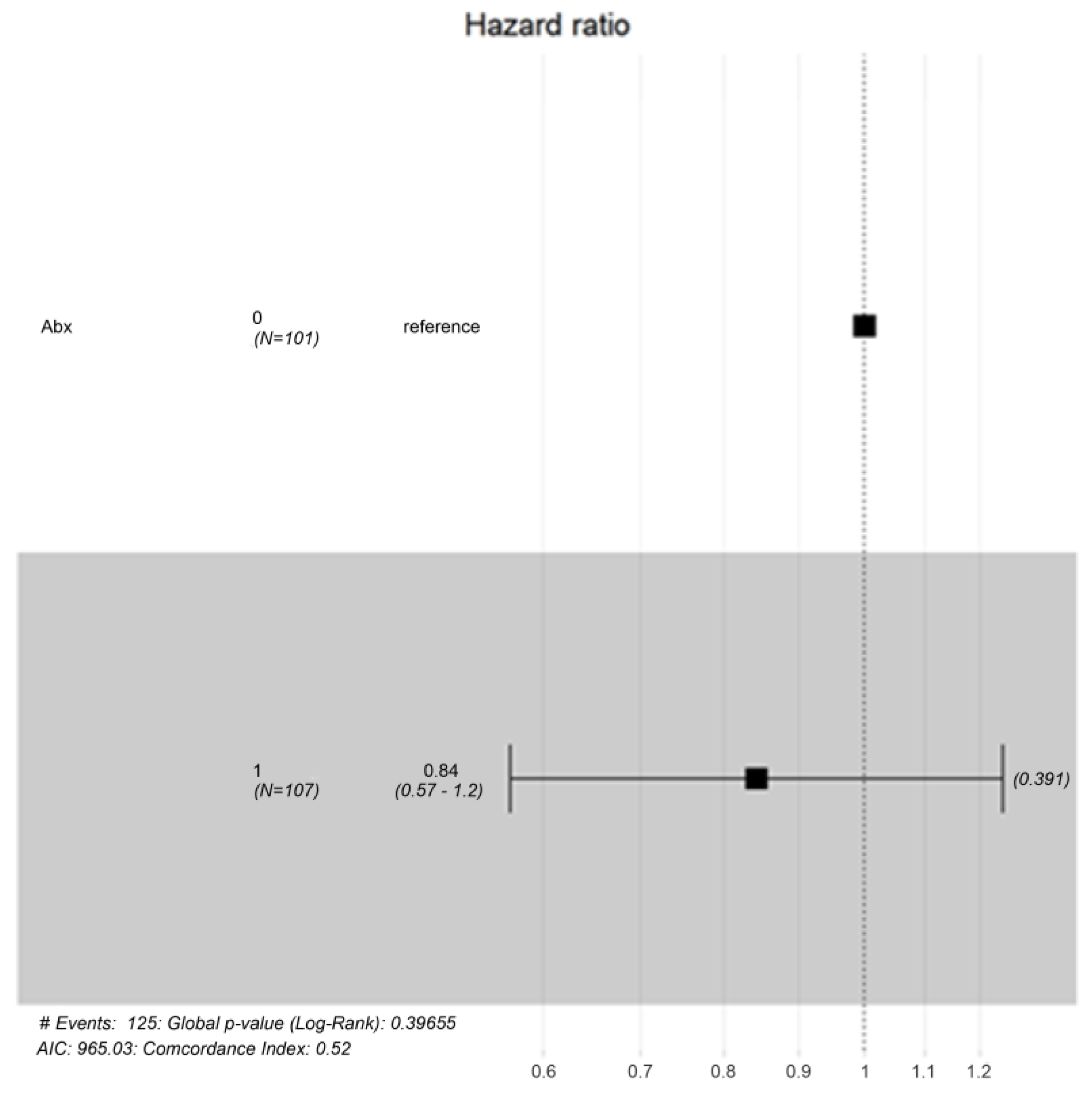
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martens, E.; Demain, A.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis, with a focus on the United States. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance—The need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyka, L.F.; Robinson, D.S.; Lachant, N.; Monaco, J. The Misuse of Antibiotics for Treatment of Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Children. Pediatrics 1975, 55, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.P.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byington, C.L.; Castillo, H.; Gerber, K.; Daly, J.A.; Brimley, L.A.; Adams, S.; Pavia, A.T. The effect of rapid respiratory viral diagnostic testing on antibiotic use in a children’s hospital. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2002, 156, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Matsoso, P.; Pant, S.; Brower, C.; Røttingen, J.-A.; Klugman, K.; Davies, S. Access to effective antimicrobials: A worldwide challenge. Lancet 2015, 387, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroll, B. Antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections: An overview of Cochrane reviews. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaig, L.F.; Besser, R.E.; Hughes, J.M. Trends in antimicrobial prescribing rates for children and adolescents. JAMA 2002, 287, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piltcher, O.B.; Kosugi, E.M.; Sakano, E.; Mion, O.; Testa, J.R.G.; Romano, F.R.; Santos, M.C.J.; Di Francesco, R.C.; Mitre, E.I.; Bezerra, T.F.P.; et al. How to avoid the inappropriate use of antibiotics in upper respiratory tract infections? A position statement from an expert panel. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 84, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawker, J.I.; Smith, S.; Smith, G.E.; Morbey, R.; Johnson, A.P.; Fleming, D.M.; Shallcross, L.; Hayward, A.C. Trends in antibiotic prescribing in primary care for clinical syndromes subject to national recommendations to reduce antibiotic resistance, UK 1995-2011: Analysis of a large database of primary care consultations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- on behalf of the ESAC Project Group; Adriaenssens, N.; Coenen, S.; Versporten, A.; Muller, A.; Minalu, G.; Faes, C.; Vankerckhoven, V.; Aerts, M.; Hens, N.; et al. European Surveillance of Antimicrobial Consumption (ESAC): Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe (1997–2009). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66 (Suppl. S6), vi3–vi12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korppi, M.; Heikkilä, P.; Palmu, S.; Huhtala, H.; Csonka, P. Antibiotic prescribing for children with upper respiratory tract infection: A Finnish nationwide 7-year observational study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Houten, C.B.; Cohen, A.; Engelhard, D.; Hays, J.P.; Karlsson, R.; Moore, E.; Bont, L.J. Antibiotic misuse in respiratory tract infections in children and adults—A prospective, multicentre study (TAILORED Treatment). Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredericks, I.; Hollingworth, S.; Pudmenzky, A.; Rossato, L.; Syed, S.; Kairuz, T. Consumer knowledge and perceptions about antibiotics and upper respiratory tract infections in a community pharmacy. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2015, 37, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher-Lartey, S.; Yee, M.; Gaarslev, C.; Khan, R. Why do general practitioners prescribe antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections to meet patient expectations: A mixed methods study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, L.; Stewart, K.; Marino, R.; McCullough, M. Antibiotic resistance and relevance to general dental practice in Australia. Aust. Dent. J. 2018, 63, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotwani, A.; Holloway, K. Trends in antibiotic use among outpatients in New Delhi, India. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, D.; Pathak, A.; Marrone, G.; Diwan, V.; Lundborg, C.S. Adherence to treatment guidelines for acute diarrhoea in children up to 12 years in Ujjain, India—A cross-sectional prescription analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zowawi, H.M.; Harris, P.N.; Roberts, M.J.; Tambyah, P.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Pezzani, M.D.; Williamson, D.A.; Paterson, D.L. The emerging threat of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in urology. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2015, 12, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrafiaah, A.S.; Alqarny, M.H.; Alkubedan, H.Y.; AlQueflie, S.; Omair, A. Are the Saudi parents aware of antibiotic role in upper respiratory tract infections in children? J. Infect. Public Health 2017, 10, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alumran, A.; Hurst, C.; Hou, X.-Y. Antibiotics Overuse in Children with Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Saudi Arabia: Risk Factors and Potential Interventions. Clin. Med. Diagn. 2012, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitrez, P.M.; Pitrez, J.L. Acute upper respiratory tract infections—Outpatient diagnosis and treatment. J. De Pediatr. 2003, 79, S77–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.M.; A Blumberg, D.; Lowe, L.G. Guidelines for the use of antibiotics in acute upper respiratory tract infections. Am. Fam. Physician. 2006, 74, 956–966. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Z.; Ehle, E.A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, M. Systematic review of evidence-based guidelines on medication therapy for upper respiratory tract infection in children with AGREE instrument. PloS ONE 2014, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J. Antibiotic use and its consequences for the normal microbiome. Science 2016, 352, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, P.D.; Avdic, E.; Li, D.X.; Dzintars, K.; Cosgrove, S.E. Association of adverse events with antibiotic use in hospitalized patients. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellberg, B.; Gilbert, D.N. The future of antibiotics and resistance: A tribute to a career of leadership by john bartlett. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59 (Suppl. S2), S71–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.C.; Hood, K.; Verheij, T.; Little, P.; Melbye, H.; Nuttall, J.; Kelly, M.J.; Molstad, S.; Godycki-Cwirko, M.; Almirall, J.; et al. Variation in antibiotic prescribing and its impact on recovery in patients with acute cough in primary care: Prospective study in 13 countries. BMJ 2009, 338, b2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.R.; Hassan, F.; Jackson, M.A.; Selvarangan, R. Impact of multiplex molecular assay turn-around-time on antibiotic utilization and clinical management of hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 110, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatt, S.P.; Yultyev, A.; Huang, M.; Friedstrom, S.; Steinbrunner, J. Impact of respiratory virus molecular testing on antibiotic utilization in community-acquired pneumonia. Am. J. Infect. Control 2017, 45, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-Y.; Wu, W.-T.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wong, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Chan, Y.-J.; Wu, K.-G.; Hung, M.-C. Viral etiologies of acute respiratory tract infections among hospitalized children—A comparison between single and multiple viral infections. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, T.; Stocks, N.; Thomas, T. Systematic review of the treatment of upper respiratory tract infection. Arch. Dis. Child. 1998, 79, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, I.; Johnson, A.M.; Islam, A.; Duckworth, G.; Livermore, D.M.; Hayward, A.C. Protective effect of antibiotics against serious complications of common respiratory tract infections: Retrospective cohort study with the UK General Practice Research Database. BMJ 2007, 335, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, Z.U.; Salman, M.; Rao, A.Z.; Asif, N.; Butt, S.A.; Shehzadi, N.; Hussain, K. Assessment of antibiotics use for children upper respiratory tract infections: A retrospective, cross-sectional study from Pakistan. Infect. Dis. 2020, 52, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, P.; Rumsby, K.; Kelly, J.; Watson, L.; Moore, M.; Warner, G.; Williamson, I. Information leaflet and antibiotic prescribing strategies for acute lower respiratory tract infection: A randomized controlled trial. Jama 2005, 293, 3029–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichichero, M.E.; Green, J.L.; Francis, A.B.; Marsocci, S.M.; Murphy, M.L. Outcomes after judicious antibiotic use for respiratory tract infections seen in a private pediatric practice. Pediatrics 2000, 105, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Lodha, R.; Kabra, S.K. Upper respiratory tract infections. Indian J. Pediatr. 2001, 68, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, J.Y.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Jang, K.M.; Hau, Y.S.; Lee, J.M. Rapid molecular tests for detecting respiratory pathogens reduced the use of antibiotics in children. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papan, C.; Willersinn, M.; Weiß, C.; Karremann, M.; Schroten, H.; Tenenbaum, T. Antibiotic utilization in hospitalized children under 2 years of age with influenza or respiratory syncytial virus infection–a comparative, retrospective analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Hicks, L.A. Principles of judicious antibiotic prescribing for upper respiratory tract infections in pediatrics. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, C.C.; Hood, K.; Kinnersley, P.; Robling, M.; Prout, H.; Houston, H. Predicting the clinical course of suspected acute viral upper respiratory tract infection in children. Fam. Pract. 2005, 22, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spurling, G.K.; Del Mar, C.B.; Dooley, L.; Foxlee, R.; Farley, R. Delayed antibiotics for respiratory infections. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 4, CD004417. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson-Caswell, M.; Muncie Jr, H.L. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in children. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 83, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaarslev, C.; Yee, M.; Chan, G.; Fletcher-Lartey, S.; Khan, R. A mixed methods study to understand patient expectations for antibiotics for an upper respiratory tract infection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2016, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.R.; To, T.; McIsaac, W.J.; Wang, E.E. Antibiotic prescribing for upper respiratory tract infection: The importance of diagnostic uncertainty. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyoud, S.H.; Abu Taha, A.; Araj, K.F.; Abahri, I.A.; Sawalha, A.F.; Sweileh, W.M.; Awang, R.; Al-Jabi, S.W. Parental knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding antibiotic use for acute upper respiratory tract infections in children: A cross-sectional study in Palestine. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsky, B.A.; Hayden, R.T. Cost-Effective Respiratory Virus Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00373-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgeway, G.; McCaffrey, D.F.; Morral, A.R.; Cefalu, M.; Burgette, L.F.; Pane, J.D.; Griffin, B.A. Toolkit for Weighting and Analysis of Nonequivalent Groups: A Tutorial for the R TWANG Package; Rand: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgeway, G. Generalized Boosted Models: A guide to the gbm package. Update 2007, 1, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Launes, C.; Armero, G.; Anton, A.; Hernandez, L.; Gimferrer, L.; Cisneros, C.; Jordan, I.; Muñoz-Almagro, C. Molecular epidemiology of severe respiratory disease by human rhinoviruses and enteroviruses at a tertiary paediatric hospital in Barcelona, Spain. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 799.e5–799.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, S.E.; Lamson, D.M.; St. George, K.; Walsh, T.J. Human rhinoviruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comte, A.; Bour, J.-B.; Darniot, M.; Pitoiset, C.; Aho-Glélé, L.S.; Manoha, C. Epidemiological characteristics and clinical outcomes of human rhinovirus infections in a hospitalized population. Severity is independently linked to RSV coinfection and comorbidities. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 125, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, R.P.; Hilty, M.; Xu, B.; Usemann, J.; Korten, I.; Mika, M.; Müller, L.; Latzin, P.; Frey, U. Nasal microbiota and symptom persistence in acute respiratory tract infections in infants. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4, 00066–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, D.; Gaudy-Graffin, C.; Garot, D.; Sunder, S.; De Gialluly, C.; Goudeau, A. Diagnosis of community-acquired acute respiratory illness: From conventional microbiological methods to molecular detection (multiplex). Pathol. Biol. 2015, 63, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclos, M.; Hommel, B.; Allantaz, F.; Powell, M.; Posteraro, B.; Sanguinetti, M. Multiplex PCR detection of respiratory tract infections in SARS-CoV-2-negative patients admitted to the emergency department: An international multicenter study during the COVID-19 pandemic. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02368-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, E.A. Environmental and demographic risk factors for respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract disease. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.M.; van Wijhe, M.; Tong, S.; Lehtonen, T.; Stona, L.; Teirlinck, A.C.; Fernandez, L.V.; Li, Y.; Giaquinto, C.; Fischer, T.K.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus-associated hospital admissions in children younger than 5 years in 7 european countries using routinely collected datasets. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 222 (Suppl. S7), S599–S605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacımustafaoğlu, M.; Celebi, S.; Bozdemir, S.E.; Ozgür, T.; Ozcan, I.; Güray, A.; Cakır, D. RSV frequency in children below 2 years hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infections. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2013, 55, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kenmoe, S.; Bigna, J.J.; Well, E.A.; Simo, F.B.N.; Penlap, V.B.; Vabret, A.; Njouom, R. Prevalence of human respiratory syncytial virus infection in people with acute respiratory tract infections in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2018, 12, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskill, S.D.; O’bryant, S.C. Respiratory Virus Co-infection in Acute Respiratory Infections in Children. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebey-Lopez, M.; Herberg, J.; Pardo-Seco, J.; Gomez-Carballa, A.; Martinon-Torres, N.; Salas, A.; Martinón-Sánchez, J.M.; Justicia, A.; Rivero-Calle, I.; Sumner, E.; et al. Does viral co-infection influence the severity of acute respiratory infection in children? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Woensel, J.B.M.; Bos, A.P.; Lutter, R.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Schuurman, R. Absence of human metapneumovirus co-infection in cases of severe respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2006, 41, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, S.A.; Michelle, E.; Science, M.E.; Tran, D.; Smieja, M.; Merglen, A.; Mertz, D. Clinical Disease Severity of Respiratory Viral Co-Infection versus Single Viral Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Yan, H.; Ren, P.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Deubel, V. Correlation Between Bocavirus Infection and Humoral Response, and Co-Infection with Other Respiratory Viruses in Children with Acute Respiratory Infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esper, F.P.; Spahlinger, T.; Zhou, L. Rate and influence of respiratory virus co-infection on pandemic (H1N1) influenza disease. J. Infect. 2011, 63, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Mencacci, A.; Cenci, E.; Camilloni, B.; Silvestri, E.; Principi, N. Multiplex platforms for the identification of respiratory pathogens: Are they useful in pediatric clinical practice? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, D.; Chetty, Y.; Cooper, B.S.; Virk, M.; Glass, S.K.; Letters, A.; Jeyaratnam, D. Multiplex PCR point of care testing versus routine, laboratory-based testing in the treatment of adults with respiratory tract infections: A quasi-randomised study assessing impact on length of stay and antimicrobial use. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnden, A.; Perera, R.; Brueggemann, A.B.; Mayon-White, R.; Crook, D.W.; Thomson, A.; Mant, D. Respiratory infections for which general practitioners consider prescribing an antibiotic: A prospective study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total Number (N) | N = 238 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (median [IQR]) | 15.00 [7.00, 37.00] | |
| Gender, n (%) | Male | 112 (47.1) |
| Wt (median [IQR]) | 10.00 [6.91, 14.07] | |
| DOI (median [IQR]) | 3.00 [2.00, 4.00] | |
| Fever, n (%) | Yes | 125 (52.5) |
| MaxTem (median [IQR]) | 37.95 [37.23, 38.90] | |
| Cough, n (%) | Yes | 175 (74.2) |
| SOB, n (%) | Yes | 163 (68.5) |
| Wheeze, n (%) | Yes | 122 (51.7) |
| Vomiting, n(%) | Yes | 90 (37.8) |
| Diarrhea, n(%) | Yes | 28 (11.8) |
| Convulsion, n(%) | Yes | 15 (6.3) |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | Yes | 80 (34.3) |
| Co-infection, n (%) | Yes | 63 (26.9) |
| WBC (median [IQR]) | 11.30 [8.70, 15.80] | |
| Hb (median [IQR]) | 12.00 [10.50, 12.80] | |
| Neutrophil (median [IQR]) | 5.58 [3.10, 9.32] | |
| Lymphocyte (median [IQR]) | 3.90 [2.18, 6.08] | |
| Platelets (median [IQR]) | 330.5 [271, 430] | |
| CRP (median [IQR]) | 14.8 [5.53, 39.8] | |
| Albumin (median [IQR]) | 36 [32, 39] | |
| X-Ray result, n (%) | Abnormal | 130 (54.6) |
| Creatinine (median [IQR]) | 40 [36, 46] | |
| ALT (median [IQR]) | 26 [18, 35.5] | |
| Abx, n(%) | Yes | 137 (57.6) |
| Res support, n (%) | Yes | 67 (28.2) |
| LOS (median [IQR]) | 4.00 [3.00, 7.00] |
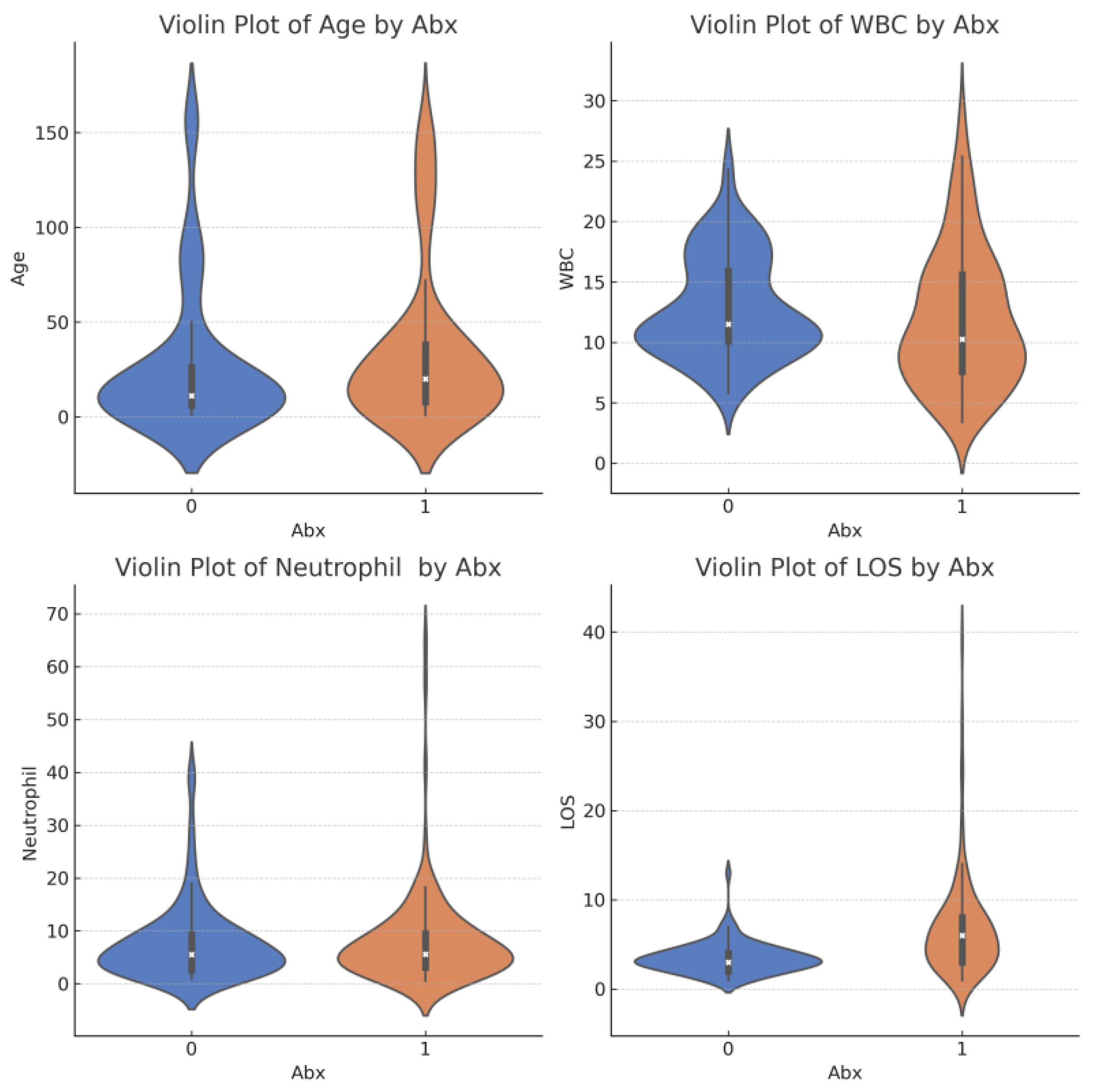
| Variable | Abx0 | Abx1 | SMD |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 101 | 137 | |
| Age (median [IQR]) | 11 [6, 26] | 20 [7.75, 38.00] | 0.183 |
| Gender (%), Male | 35 (34.7) | 77 (56.2) | 0.443 |
| Wt (median [IQR]) | 9.45 [6.34, 13.25] | 10.95 [7.73, 15.62] | 0.174 |
| Duration of illness (DOI) (median [IQR]) | 3.0 [1.0, 3.0] | 3.0 [2.00, 5.0] | 0.135 |
| Fever (5), Yes | 36 (35.6) | 89 (65.0) | 0.613 |
| Maximum temp (MaxTem) (median [IQR]) | 37.5 [37.1, 38.3] | 38.4 [37.6, 39.1] | 0.634 |
| Cough (5), Yes | 70 (70.0) | 105 (77.2) | 0.164 |
| Shortness of breath (SOB) (%), Yes | 71 (70.3) | 92 (67.2) | 0.068 |
| Wheeze (%), Yes | 57 (57.0) | 65 (47.8) | 0.185 |
| Vomiting (%), Yes | 39 (38.6) | 51 (37.2) | 0.029 |
| Diarrhea (%), Yes | 4 (4.0) | 24 (17.5) | 0.449 |
| Convulsion (%), No | 101 (100.0) | 137 (100.0) | <0.001 |
| Co-morbidity (%), Yes | 40 (40) | 40 (30.1) | 0.209 |
| Co-infection (%), Yes | 39 (39.4) | 24 (17.8) | 0.493 |
| WBC (median [IQR]) | 11.50 [10.10, 15.90] | 10.25 [7.57, 15.60] | 0.189 |
| Hb (median [IQR]) | 12.43 [11.70, 12.80] | 11.30 [10.17, 12.53] | 0.552 |
| Neutrophil (median [IQR]) | 5.52 [2.61, 9.30] | 5.60 [3.11, 9.45] | 0.062 |
| Lymphocyte (median [IQR]) | 4.94 [3.22, 8.01] | 3.50 [2.07, 5.45] | 0.361 |
| Platelets (median [IQR]) | 332 [270, 490.25] | 330.5 [271, 388.5] | 0.140 |
| CRP (median [IQR]) | 8 [2.6, 25.8] | 27.7 [10.1, 68.1] | 0.836 |
| Albumin (median [IQR]) | 37 [33, 39] | 35 [30, 39] | 0.481 |
| X-Ray result (%) Yes | 40 (39.6) | 90 (65.7) | 0.541 |
| Creatinine (median [IQR]) | 39.5 [36, 46] | 40.5 [36, 45.3] | 0.015 |
| ALT (median [IQR]) | 25.00 [19.00, 34.00] | 26.00 [18.00, 37.00] | 0.024 |
| ResSupport (%) | 101 (100.0) | 137 (100.0) | <0.001 |
| Length of stay (LOS) (median [IQR]) | 3.00 [2.00, 4.00] | 6.00 [3.00, 8.00] | 0.793 |
| n.treat | n.control | ess. treat | ess. control | max.es | mean.es | max. ks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unw | 137 | 101 | 137 | 101 | 0.612 | 0.220 | 0.340 |
| es. mean.ATT | 137 | 101 | 137 | 41 | 0.461 | 0.122 | 0.240 |
| mean. ks | iteration | ||||||
| unw | 0.164 | NA | |||||
| es. mean.ATT | 0.110 | 4285 | |||||
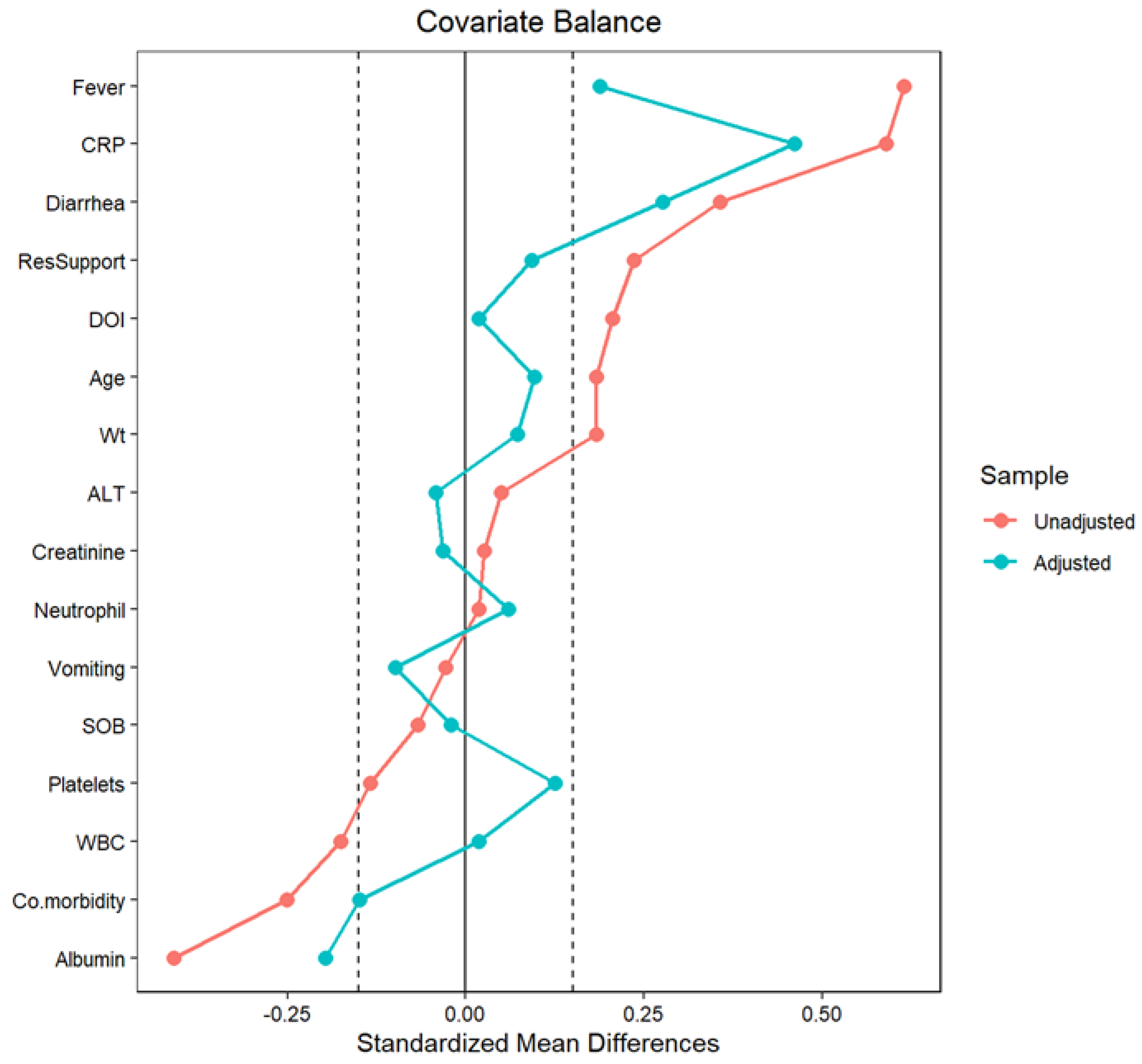
| Type | Diff.Adj | M.Threshold | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propensity score | Distance | 4.2665 | |
| Age | Continuous | 0.0964 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Weight | Continuous | 0.0731 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| DOI | Continuous | 0.0184 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Fever | Binary | 0.1885 | Not Balanced, >0.15 |
| SOB | Binary | −0.0207 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Vomiting | Binary | −0.0985 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Diarrhea | Binary | 0.2761 | Not Balanced, >0.15 |
| Co-morbidity | Binary | −0.1490 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| WBC | Continuous | 0.0189 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Neutrophil | Continuous | 0.0601 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Platelets | Continuous | 0.1250 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| CRP | Continuous | 0.4608 | Not Balanced, >0.15 |
| Albumin | Continuous | −0.1972 | Not Balanced, >0.15 |
| ALT | Continuous | −0.0414 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Creatinine | Continuous | −0.0313 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| ResSupport | Binary | 0.0932 | Balanced, <0.15 |
| Balance tally for standardized mean differences | |||
| Balanced, <0.15 | 12 | ||
| Not Balanced, >0.15 | 4 | ||
| Model Information | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation 238 | ||||
| Dependent Variable: Length of Hospital Stay (LOHS) | ||||
| Type: Survey-weighted linear regression | ||||
| MODEL FIT: R2 = 0.37 | ||||
| Adj. R2 = 0.36 | ||||
| Standard errors: Robust | ||||
| Est | S. E | t val | p value | |
| (Intercept) | 1.86 | 3.01 | 6.19 | 0.00 |
| Abx | 2.19 | 0.53 | 4.11 | 0.00 |
| Fever | −0.37 | 0.63 | −0.59 | 0.56 |
| Diarrhea | −2.26 | 0.55 | −4.08 | 0.00 |
| CRP | −0.00 | 0.00 | −1.06 | 0.29 |
| Albumin | −0.40 | 0.08 | −4.90 | 0.00 |
| Estimated dispersion parameter = 15.58 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Qahtani, M.; AlFulayyih, S.F.; Al Baridi, S.S.; Alomar, S.A.; Alshammari, A.N.; Albuaijan, R.J.; Uddin, M.S. Exploring the Impact of Antibiotics on Fever Recovery Time and Hospital Stays in Children with Viral Infections: Insights from Advanced Data Analysis. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060518
Al Qahtani M, AlFulayyih SF, Al Baridi SS, Alomar SA, Alshammari AN, Albuaijan RJ, Uddin MS. Exploring the Impact of Antibiotics on Fever Recovery Time and Hospital Stays in Children with Viral Infections: Insights from Advanced Data Analysis. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(6):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060518
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Qahtani, Mohammed, Saleh Fahad AlFulayyih, Sarah Saleh Al Baridi, Sara Amer Alomar, Ahmed Nawfal Alshammari, Reem Jassim Albuaijan, and Mohammed Shahab Uddin. 2024. "Exploring the Impact of Antibiotics on Fever Recovery Time and Hospital Stays in Children with Viral Infections: Insights from Advanced Data Analysis" Antibiotics 13, no. 6: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060518
APA StyleAl Qahtani, M., AlFulayyih, S. F., Al Baridi, S. S., Alomar, S. A., Alshammari, A. N., Albuaijan, R. J., & Uddin, M. S. (2024). Exploring the Impact of Antibiotics on Fever Recovery Time and Hospital Stays in Children with Viral Infections: Insights from Advanced Data Analysis. Antibiotics, 13(6), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060518







