Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Plasma, Urine, and Feces of Donkey (Equus asinus) after a Single Intragastric Administration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HPLC Method Validation
2.2. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in the Plasma of Donkeys
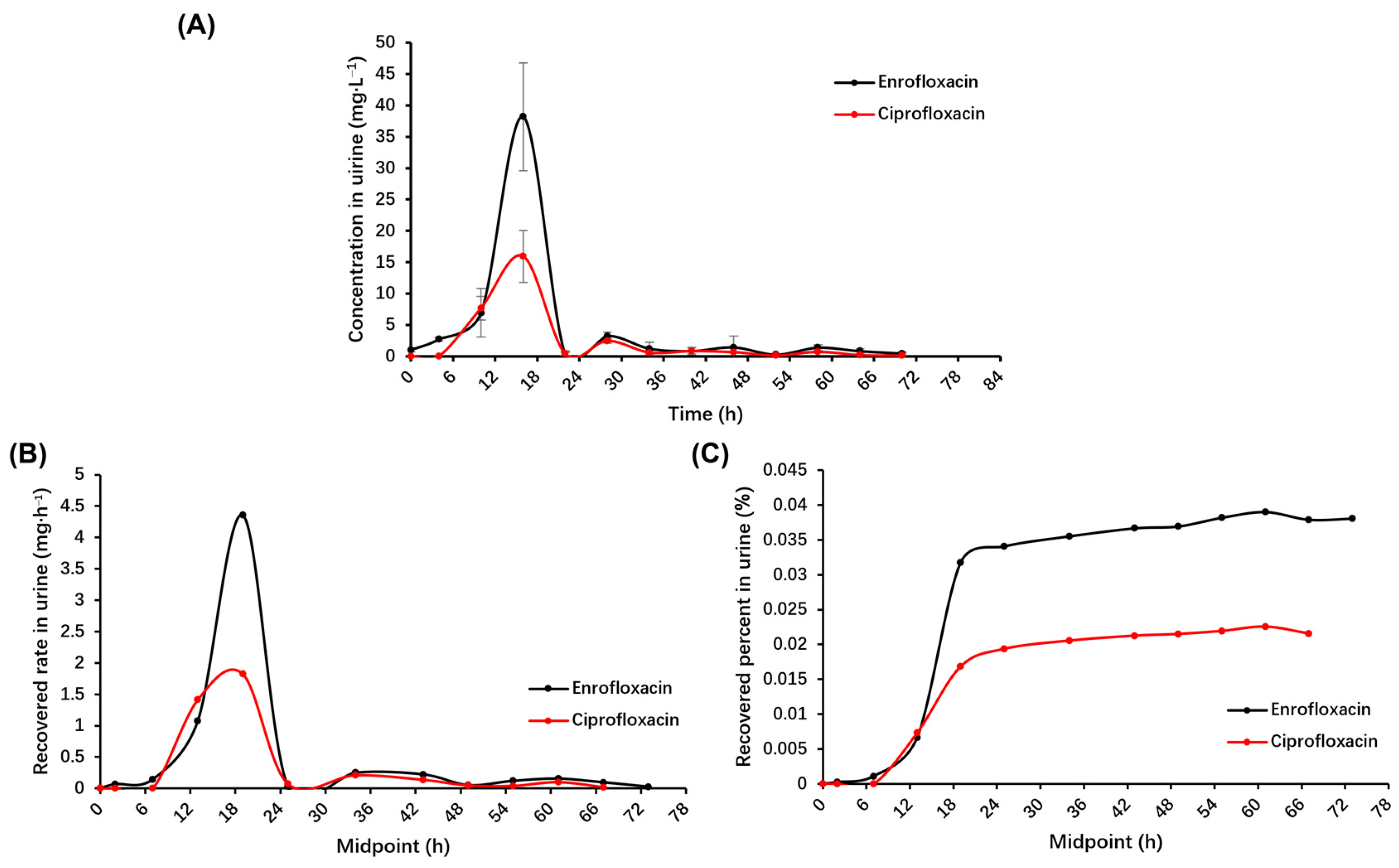
2.3. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in the Urine of Donkeys
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Feces of Donkeys
2.5. PK/PD Parameters for Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin in Donkeys
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Animals
3.3. Experimental Design
3.4. Determination of Enrofloxacin
3.5. HPLC Method Validation
3.6. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adam, S.Y.; Ahmed, A.A.; Musa, H.H.; Fedail, J.S.; Musa, T.H. A Comparison between Working and Nonworking Donkeys Welfare Issues in Nyala City, South Darfur, Sudan. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 118, 104110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galardi, M.; Contalbrigo, L.; Toson, M.; Bortolotti, L.; Lorenzetto, M.; Riccioli, F.; Moruzzo, R. Donkey Assisted Interventions: A Pilot Survey on Service Providers in North-Eastern Italy. Explore 2022, 18, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, Y.F.; Tatemoto, P.; Reeves, E.; Burden, F.A.; Santurtun, E. Donkey Skin Trade and Its Non-Compliance with Legislative Framework. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 849193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickards, K.J.; Thiemann, A.K. Respiratory Disorders of the Donkey. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2019, 35, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickards, K.; Toribio, R.E. Clinical Insights: Recent Advances in Donkey Medicine and Welfare. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekkin, S.; Gokbulut, C.; Kum, C.; Karademir, U. Plasma Disposition of Enrofloxacin Following Intravenous and Intramuscular Administration in Donkeys. Vet. Rec. 2012, 171, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, K.; Mealey, K.L.; Matthews, N.S.; Taylor, T.S. Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Caffeine and Three Metabolites in Clinically Normal Horses and Donkeys. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mealey, K.L.; Matthews, N.S.; Peck, K.E.; Ray, A.C.; Taylor, T.S. Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Phenylbutazone and Its Metabolite Oxyphenbutazone in Clinically Normal Horses and Donkeys. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga, I.; Sumano, H.; Brumbaugh, G.W. Pharmacological and Pharmacokinetic Differences between Donkeys and Horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2004, 16, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Vu, H.P.; Nguyen, L.N.; Wang, Q.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Donner, E.; Yin, H.; Nghiem, L.D. Monitoring Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Treatment: Current Strategies and Future Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, Ł.; Gaffke, L.; Pierzynowska, K.; Cyske, Z.; Choszcz, M.; Węgrzyn, G.; Węgrzyn, A. Enrofloxacin-the Ruthless Killer of Eukaryotic Cells or the Last Hope in the Fight against Bacterial Infections? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Marawan, M.A.; Ares, I.; Martinez, M.A.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Wang, X.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M. Toxicity Induced by Ciprofloxacin and Enrofloxacin: Oxidative Stress and Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2021, 51, 754–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.; Chatterjee, S. Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics: Occurrence, Mode of Action, Resistance, Environmental Detection, and Remediation—A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellerbrock, R.E.; Curcio, B.R.; Zhong, L.; Honoroto, J.; Wilkins, P.; Lima, F.S.; Giguere, S.; Canisso, I.F. Pharmacokinetics of Intravenous and Oral Administration of Enrofloxacin to the Late-Term Pregnant and Non-Pregnant Mares. Equine Vet. J. 2020, 52, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.L.; Foster, D.M.; Papich, M.G. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Enrofloxacin and Its Active Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Calves. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 30, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; Yue, L.; Sun, Y.; Ding, H.; Liu, Y. Excretion of Enrofloxacin in Pigs and Its Effect on Ecological Environment. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKellar, Q.; Gibson, I.; Monteiro, A.; Bregante, M. Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin and Danofloxacin in Plasma, Inflammatory Exudate, and Bronchial Secretions of Calves Following Subcutaneous Administration. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1988–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Otero, J.L.; Mestorino, N.; Errecalde, J.O. Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin after Single Intravenous Administration in Sheep. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2009, 28, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Mair, T.; Williams, N.; McGowan, C.; Pinchbeck, G. Antimicrobial Prescribing and Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Equine Practice. Equine Vet. J. 2023, 55, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensink, J.M.; van Klingeren, B.; Houwers, D.J.; Klein, W.R.; Vulto, A.G. In-Vitro Susceptibility to Antimicrobial Drugs of Bacterial Isolates from Horses in the Netherlands. Equine Vet. J. 1993, 25, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguère, S.; Sweeney, R.W.; Bélanger, M. Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Adult Horses and Concentration of the Drug in Serum, Body Fluids, and Endometrial Tissues after Repeated Intragastrically Administered Doses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 57, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Q.; Huang, H.; Zheng, G.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ma, L.; Zhou, H.; Xie, W.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Residue Profiles of Enrofloxacin in Crucian Carp (Carassius Auratus Gibelio) Following Single and Multiple Oral Administration. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 872828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluemlein, K.; Nowak, N.; Ellinghusen, B.; Gerling, S.; Badorrek, P.; Hansen, T.; Hohlfeld, J.M.; Paul, R.; Schuchardt, S. Occupational Exposure to Veterinary Antibiotics: Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Humans after Dermal, Inhalation and Oral Uptake—A Clinical Study. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 100, 104139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.; Song, J.S.; Ahn, S. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of (13)C-Labeled Succinic Acid in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.V.; Fanget, M.C.; MacLauchlin, C.; Clausen, V.A.; Li, J.; Cloutier, D.; Shen, L.; Robbie, G.J.; Mogalian, E. Clinical and Preclinical Single-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Vir-2218, an Rnai Therapeutic Targeting Hbv Infection. Drugs R&D 2021, 21, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Su, M.; Cheng, W.; Xia, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, R.; Sun, S.; Feng, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Urinary Excretion, and Pharmaco-Metabolomic Study of Tebipenem Pivoxil Granules after Single Escalating Oral Dose in Healthy Chinese Volunteers. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 696165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, J.A.; Gelone, S.P. The Newer Fluoroquinolones. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 18, 691–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blokhina, S.V.; Sharapova, A.V.; Ol’khovich, M.V.; Volkova, T.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Solubility, Lipophilicity and Membrane Permeability of Some Fluoroquinolone Antimicrobials. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Arshadi, M.; Khosrojerdi, M.A.; Abedinzadeh, M.; Ganjalishahi, M.; Maleki, A.; Heidary, M.; Khoshnood, S. The Resistance Mechanisms of Bacteria against Ciprofloxacin and New Approaches for Enhancing the Efficacy of This Antibiotic. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1025633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, V.C.; Sedrish, S.; Boothe, D.M. Disposition of Single-Dose Oral Enrofloxacin in the Horse. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 19, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, E.C.; Papich, M.G.; Vivrette, S.L. Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin Administered Intravenously and Orally to Foals. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, F.J.; Perez-Ecija, A.; Toribio, R.E. Clinical Pharmacology in Donkeys and Mules. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2019, 35, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, A.; Britzi, M.; Levi, O.; Lavy, E.; Lichter, A.; Soback, S. Lack of Effect of Diet on the Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Horses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 29, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrou, M.; Bousquet-Melou, A.; Laroute, V.; Vrins, A.; Doucet, M.Y. Enrofloxacin and Marbofloxacin in Horses: Comparison of Pharmacokinetic Parameters, Use of Urinary and Metabolite Data to Estimate First-Pass Effect and Absorbed Fraction. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 29, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Jimenez, L.E.; Aranda-Aguirre, E.; Castelan-Ortega, O.A.; Shettino-Bermudez, B.S.; Ortiz-Salinas, R.; Miranda, M.; Li, X.; Angeles-Hernandez, J.C.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Gonzalez-Ronquillo, M. Worldwide Traceability of Antibiotic Residues from Livestock in Wastewater and Soil: A Systematic Review. Animals 2021, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.A. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Parameters: Rationale for Antibacterial Dosing of Mice and Men. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, A.; Fuhst, C.; Wiedemann, B. Pharmacological Indices in Antibiotic Therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.H.; Brown, G.H.; Peterson, M.L.; Rotschafer, J.C. Application of Fluoroquinolone Pharmacodynamics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidgood, T.L.; Papich, M.G. Plasma and Interstitial Fluid Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin, Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin, and Marbofloxacin after Oral Administration and a Constant Rate Intravenous Infusion in Dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 28, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, O.R.; Peggins, J.O.; Cullison, R.; Bredow, J. Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin in Lactating Dairy Cows and Beef Steers Following Intravenous Administration of Enrofloxacin. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaje, R.M.; Sidhu, P.K.; Kaur, G.; Rampal, S. Mutant Prevention Concentration and Pk-Pd Relationships of Enrofloxacin for Pasteurella Multocida in Buffalo Calves. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messenger, K.M.; Papich, M.G.; Blikslager, A.T. Distribution of Enrofloxacin and Its Active Metabolite, Using an in Vivo Ultrafiltration Sampling Technique after the Injection of Enrofloxacin to Pigs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Marra, M.; Zummo, S.; Biondo, C. Urinary Tract Infections: The Current Scenario and Future Prospects. Pathogens 2023, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drekonja, D.M.; Trautner, B.; Amundson, C.; Kuskowski, M.; Johnson, J.R. Effect of 7 Vs 14 Days of Antibiotic Therapy on Resolution of Symptoms among Afebrile Men with Urinary Tract Infection: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Items | Enrofloxacin | Ciprofloxacin |
|---|---|---|
| T1/2 (h) | 11.40 ± 6.40 | 7.25 ± 4.93 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.55 ± 0.12 | 0.52 ± 0.08 |
| Cmax (mg·L−1) | 2.46 ± 0.14 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| AUC0–∞ (mg·L−1·h) | 10.30 ± 3.37 | 0.24 ± 0.16 |
| MRT (h) | 7.88 ± 1.26 | 12.70 ± 12.63 |
| Cl/F (L·kg−1·h−1) | 0.81 ± 0.28 | - |
| Vz/F (L·kg−1) | 12.88 ± 6.70 | - |
| Items | Enrofloxacin | Ciprofloxacin |
|---|---|---|
| T1/2 (h) | 40.58 ± 14.59 | 15.71 ± 4.06 |
| Cmax (mg·L−1) | 38.18 ± 8.56 | 15.94 ± 4.15 |
| Time of maximum rate (h) | 19.75 ± 1.30 | 16.00 ± 3.00 |
| Maximum excretion rate (mg·h−1) | 4.36 ± 1.10 | 1.82 ± 0.98 |
| AURC0–∞ (mg) | 47.00 ± 9.20 | 28.09 ± 10.23 |
| Items | MIC Values (mg·L−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 2.00 | ||
| Plasma | AUC24 (mg·L−1·h) | AUC24/MIC | ||||||
| Enrofloxacin | 9.54 | 318.00 | 159.00 | 79.50 | 38.16 | 19.08 | 9.54 | 4.77 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.12 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.06 |
| Enro + Cipro | 9.66 | 322.00 | 161.00 | 80.50 | 38.64 | 19.32 | 9.66 | 4.83 |
| Pathogen | Enrofloxacin | Ciprofloxacin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC50 † | MIC90 (Range) ‡ | MIC50 | MIC90 (Range) | |
| Salmonella spp. | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
| E. coli | 0.015 | 0.03 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
| Strept. zooepidemicus | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Staphylococcus spp. | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| T. equigenitalis | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| Klebsiella spp. | 0.015 | 0.03 | 0.015 | (0.004–0.015) |
| Proteus spp. | 0.12 | (0.06–0.12) | 0.015 | (0.008–0.03) |
| P. aeruginosa | 0.5 | (0.25–0.05) | 0.12 | (0.06–0.12) |
| A. equuli | 0.008 | (0.008–0.12) | 0.004 | (0.004–0.03) |
| R. equui | 2 | - | 1 | - |
| Strept. equi | 2 | - | 1 | - |
| Strept. equisimilis | 1 | (0.5–2) | 0.5 | (0.25–1) |
| Items | Donkey | ± sd | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Body weight (kg) | 171.00 | 185.00 | 158.00 | 105.00 | 119.00 | 147.60 ± 34.20 |
| Single oral dose (mg·kg−1) | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | 7.50 | - |
| Administered dose (mg) | 1282.50 | 1387.5 | 1185.00 | 787.50 | 892.50 | 1107.00 ± 229.63 |
| Concentrated feed intake (kg·d−1) | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | - |
| Coarse fodder intake (kg·d−1) | 2.15 | 1.96 | 1.87 | 1.73 | 1.69 | 1.88 ± 0.17 |
| Total feces volume (kg) | 31.65 | 31.65 | 39.73 | 31.80 | 29.80 | 32.93 ± 3.48 |
| Water intake (L·d−1) | 7.62 | 6.51 | 9.29 | 8.87 | 6.25 | 7.71 ± 1.22 |
| Total urine volume (L) | 11.84 | 10.16 | 14.21 | 12.86 | 11.20 | 12.05 ± 1.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qu, H.; Guo, Y.; Ji, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Plasma, Urine, and Feces of Donkey (Equus asinus) after a Single Intragastric Administration. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040355
Yang B, Liu S, Cheng J, Qu H, Guo Y, Ji C, Wang Y, Zhao S, Huang S, Zhao L, et al. Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Plasma, Urine, and Feces of Donkey (Equus asinus) after a Single Intragastric Administration. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(4):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040355
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Bowen, Shijie Liu, Jie Cheng, Honglei Qu, Yanxin Guo, Chuanliang Ji, Yantao Wang, Shancang Zhao, Shimeng Huang, Lihong Zhao, and et al. 2024. "Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Plasma, Urine, and Feces of Donkey (Equus asinus) after a Single Intragastric Administration" Antibiotics 13, no. 4: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040355
APA StyleYang, B., Liu, S., Cheng, J., Qu, H., Guo, Y., Ji, C., Wang, Y., Zhao, S., Huang, S., Zhao, L., & Ma, Q. (2024). Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Plasma, Urine, and Feces of Donkey (Equus asinus) after a Single Intragastric Administration. Antibiotics, 13(4), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040355









