Diagnostics in Late Periprosthetic Infections—Challenges and Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
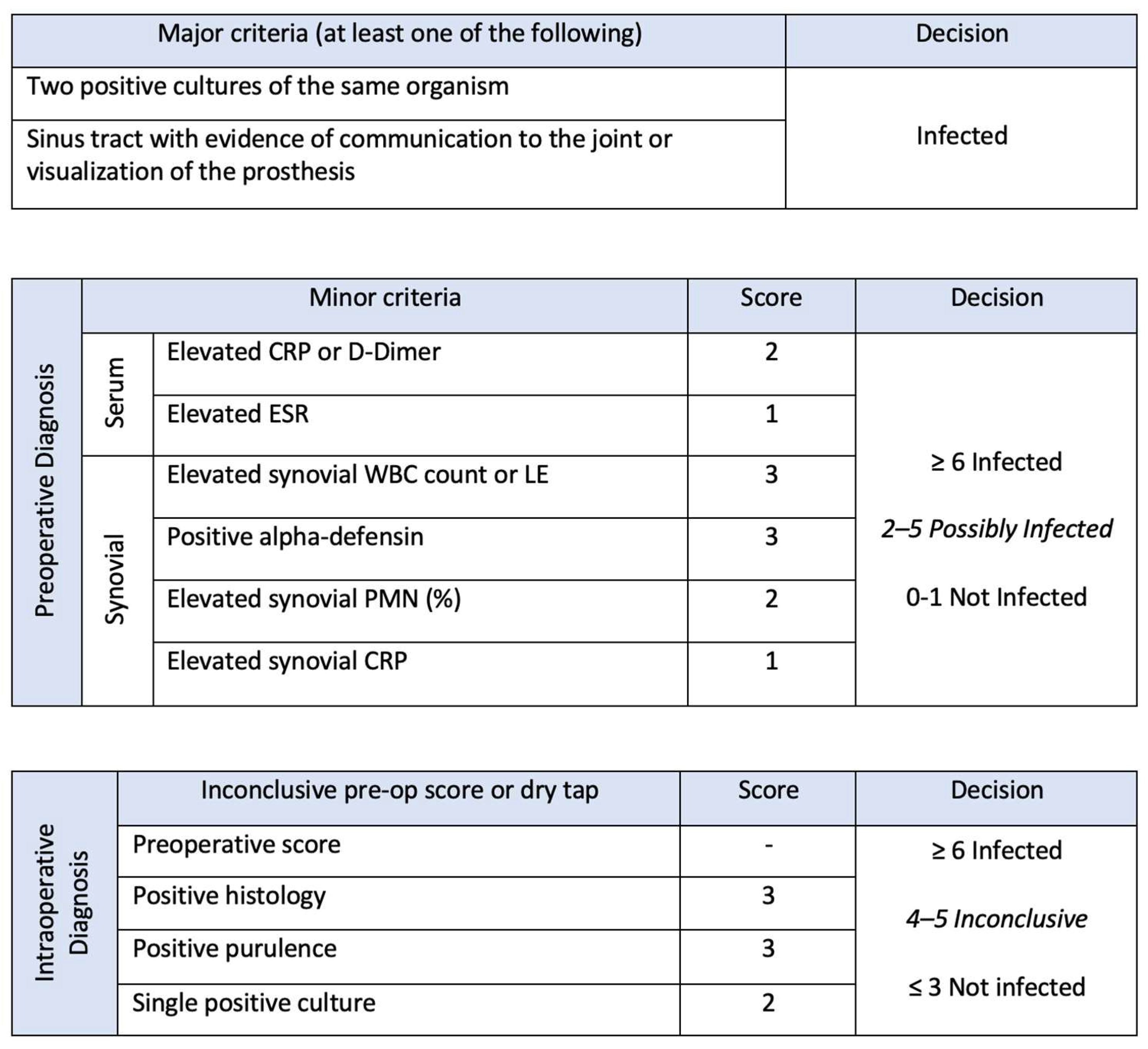
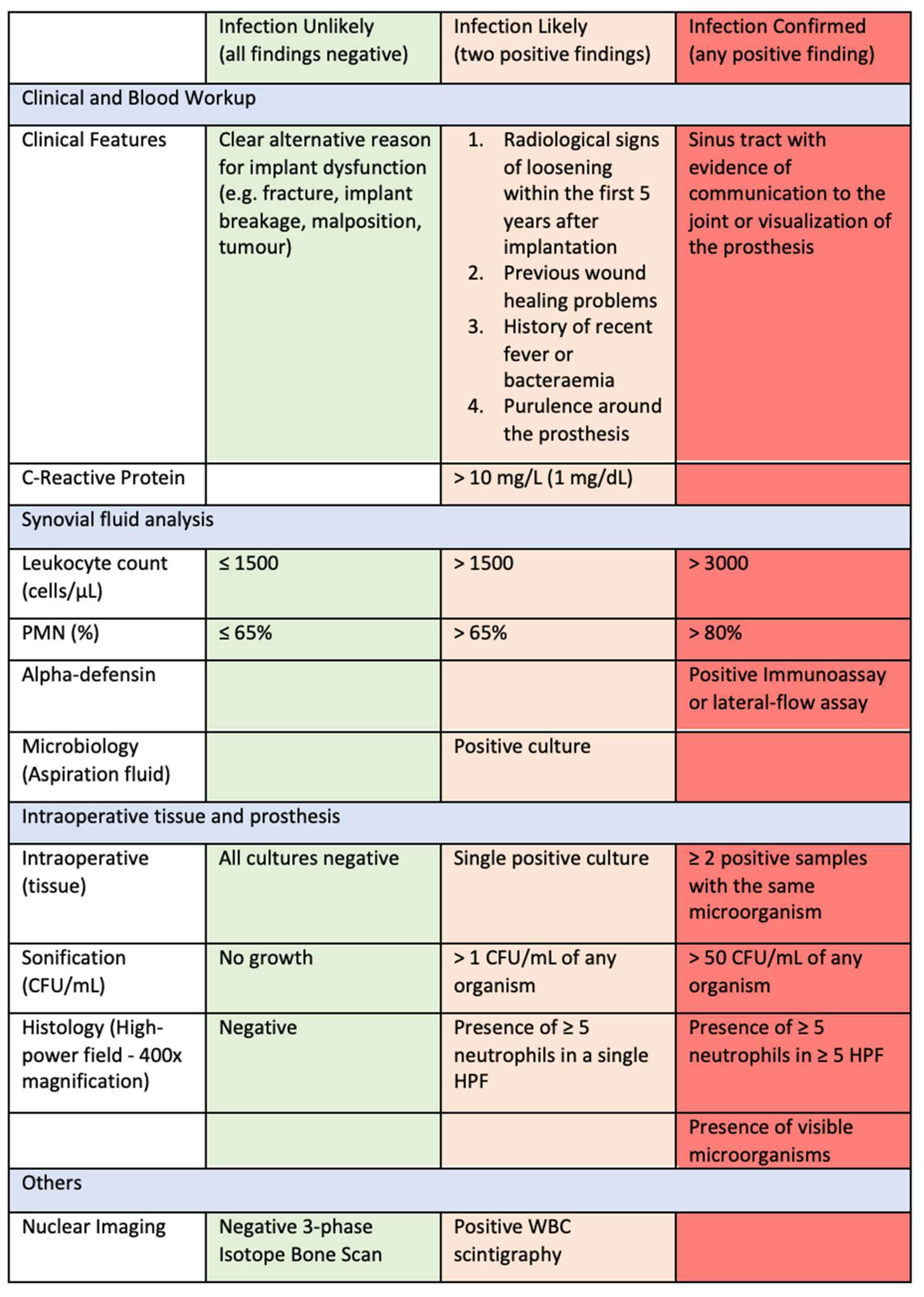
2. Diagnostic Categories
2.1. Clinical Examination
2.2. Imaging Procedures
2.3. Nuclear Imaging Techniques
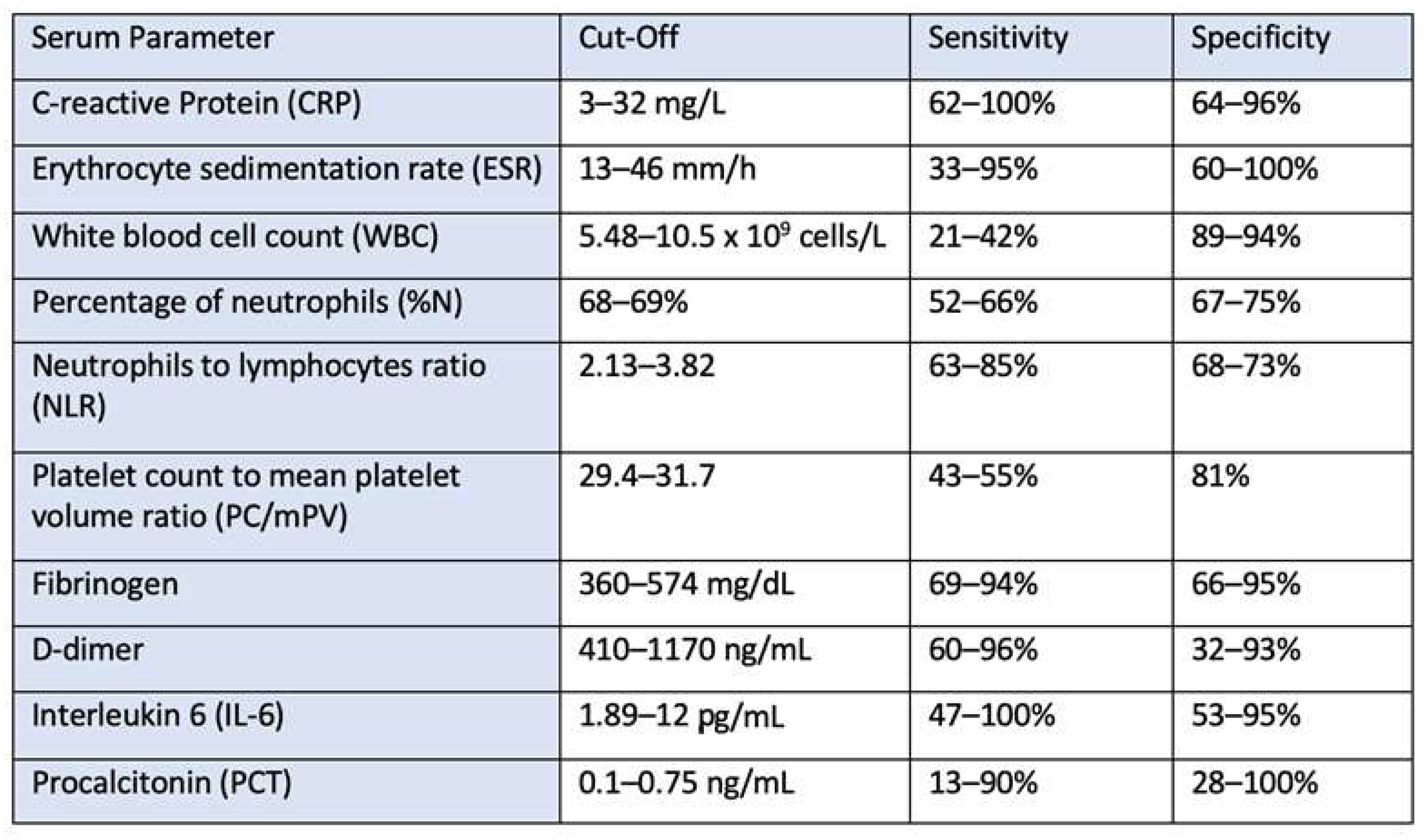
2.4. Serum Biomarkers
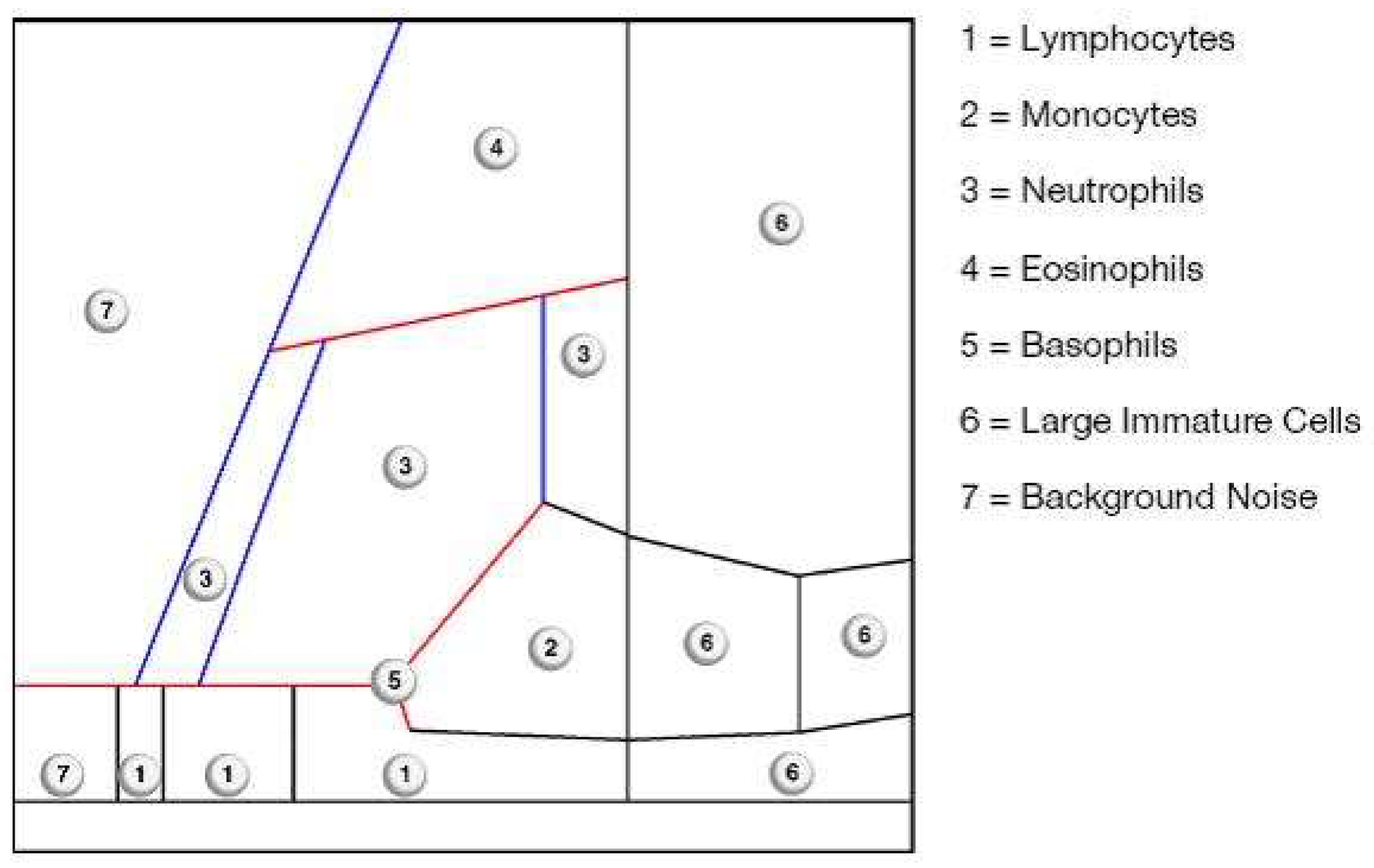
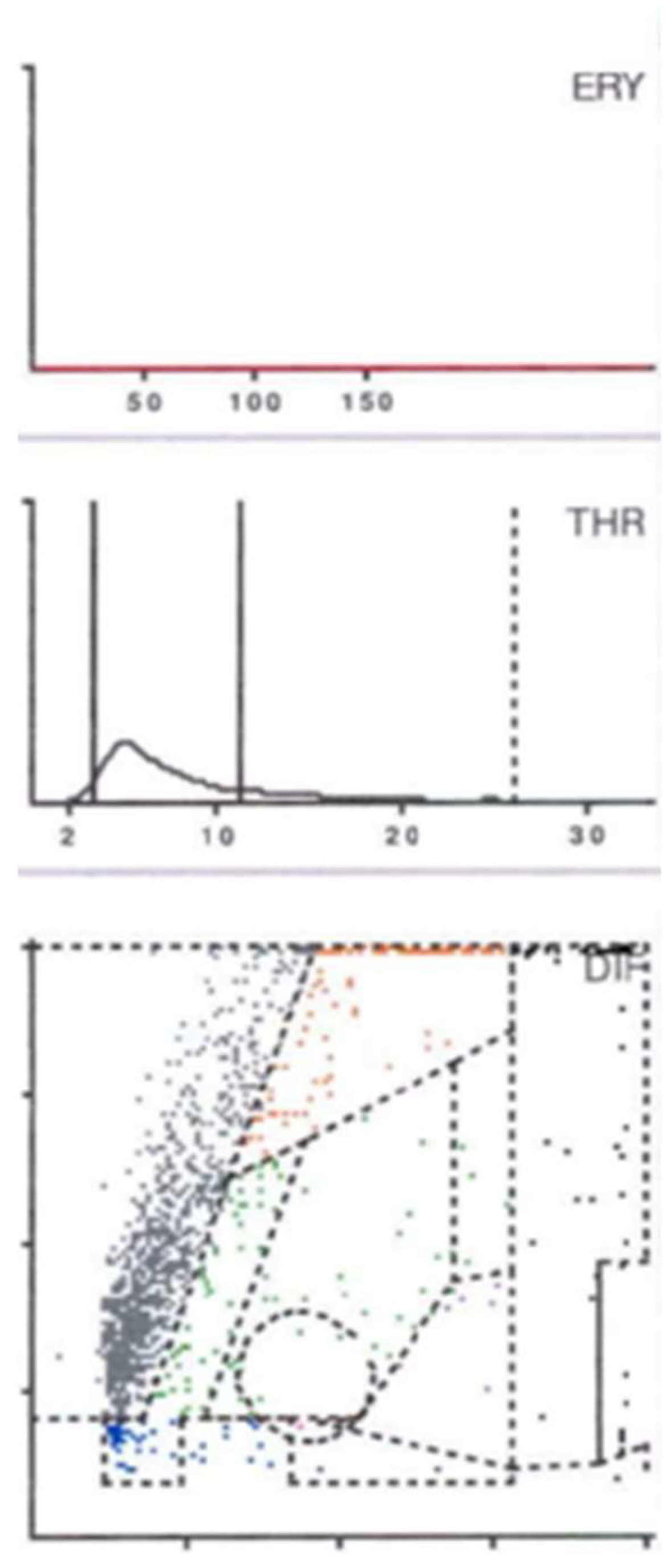
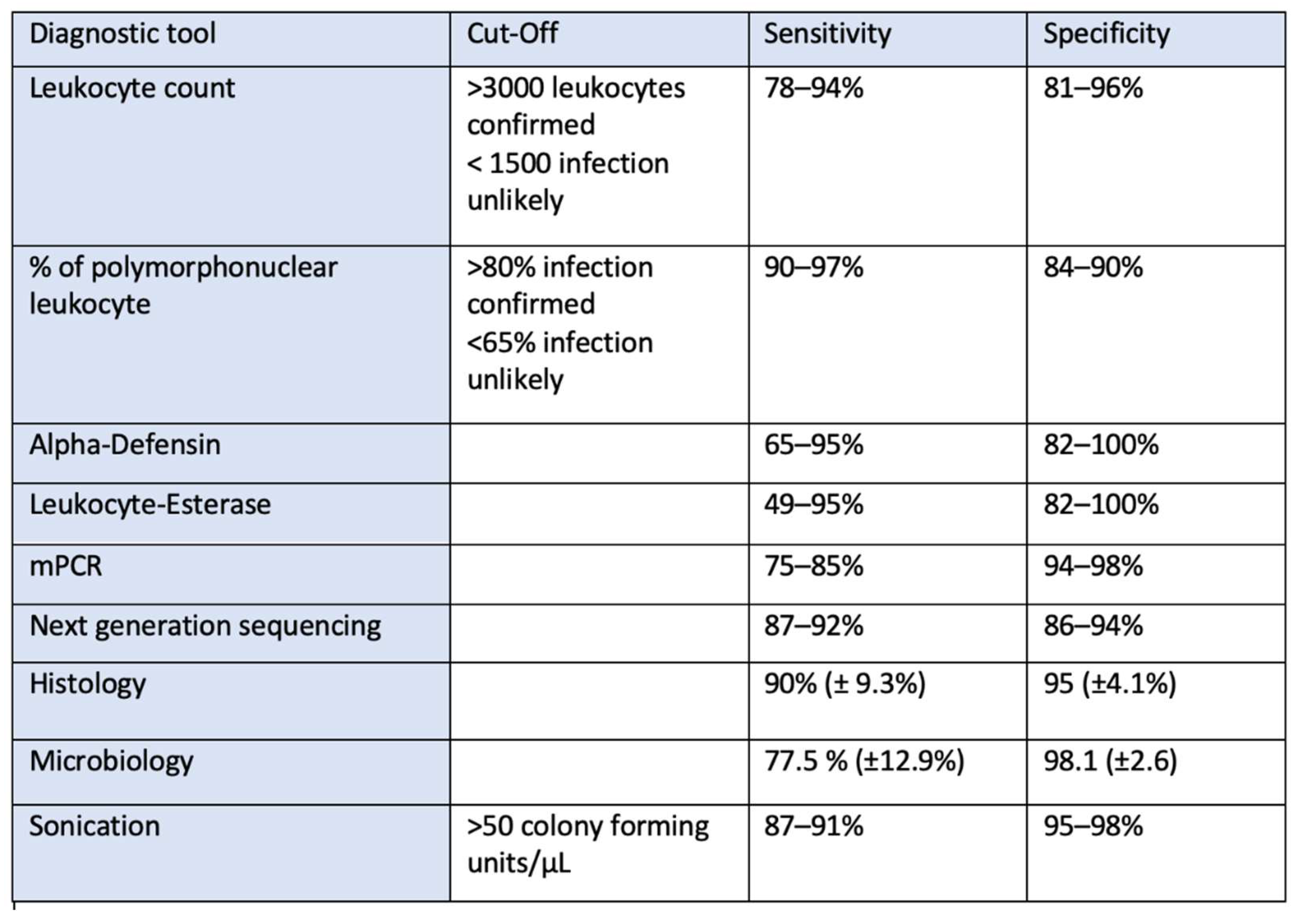
2.5. Synovial Testing
2.6. Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (mPCR)
2.7. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.8. Microbiology
2.9. Histology
3. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rupp, M.; Lau, E.; Kurtz, S.M.; Alt, V. Projections of Primary TKA and THA in Germany from 2016 through 2040. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slifka, K.J.; Yi, S.H.; Reddy, S.C.; Baggs, J.; Jernigan, J.A. 287. The Attributable Mortality of Prosthetic Joint Infection After Primary Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Among Medicare Beneficiaries, 2005–2012. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coventry, M.B. Treatment of Infections Occurring in Total Hip Surgery. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1975, 6, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukayama, D.T.; Estrada, R.; Gustilo, R.B. Infection after Total Hip Arthroplasty. A Study of the Treatment of One Hundred and Six Infections. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1996, 78, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornero, E.; Soriano, A. Importance of Selection and Duration of Antibiotic Regimen in Prosthetic Joint Infections Treated with Debridement and Implant Retention—Authors’ Response. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckey, D.G.; Christopher, Z.K.; Bingham, J.S.; Spangehl, M.J. Principles of Mechanical and Chemical Debridement with Implant Retention. Arthroplasty 2023, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Ende, B.; van Oldenrijk, J.; Reijman, M.; Croughs, P.D.; van Steenbergen, L.N.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Bos, P.K. Timing of Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention (DAIR) for Early Post-Surgical Hip and Knee Prosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) Does Not Affect 1-Year Re-Revision Rates: Data from the Dutch Arthroplasty Register. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2021, 6, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ojeda-Thies, C.; Renz, N.; Margaryan, D.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. The Global State of Clinical Research and Trends in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS Definition of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B.; Schlumberger, M.; Beyersdorff, J.; Schuster, P. C-Reactive Protein Is Not a Screening Tool for Late Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2020, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Cho, Y.J. Current Guideline for Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Review Article. Hip Pelvis 2021, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, M.; Sigmund, I.; Hotchen, A.; Sousa, R. Making the Diagnosis in Prosthetic Joint Infection: A European View. EFORT Open Rev. 2023, 8, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Berendt, A.R.; Lew, D.; Zimmerli, W.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Rao, N.; Hanssen, A.; Wilson, W.R. Infectious Diseases Society of America Diagnosis and Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, e1–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T. International Consensus Group on Periprosthetic Joint Infection Definition of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Current Concepts and Outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohat, N.; Goswami, K.; Tan, T.L.; Henstenburg, B.; Makar, G.; Rondon, A.J.; Parvizi, J. Fever and Erythema Are Specific Findings in Detecting Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2019, 4, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahar, A.; Sarungi, M. Diagnosis and Management of the Infected Total Knee Replacement: A Practical Surgical Guide. J. Exp. Orthop. 2021, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajonz, D.; Wuthe, L.; Tiepolt, S.; Brandmeier, P.; Prietzel, T.; von Salis-Soglio, G.F.; Roth, A.; Josten, C.; Heyde, C.-E.; Ghanem, M. Diagnostic Work-up Strategy for Periprosthetic Joint Infections after Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A 12-Year Experience on 320 Consecutive Cases. Patient Saf. Surg. 2015, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Porrino, J.; Wang, A.; Moats, A.; Mulcahy, H.; Kani, K. Prosthetic Joint Infections: Diagnosis, Management, and Complications of the Two-Stage Replacement Arthroplasty. Skeletal Radiol. 2020, 49, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, K. Diagnostics in Prosthetic Joint Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69 (Suppl. S1), i11–i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto-Lambertz, C.; Yagdiran, A.; Wallscheid, F.; Eysel, P.; Jung, N. Periprosthetic Infection in Joint Replacement. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, A.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Borens, O.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Cassar-Pullicino, V.; Trampuz, A.; Winkler, H.; Gheysens, O.; Vanhoenacker, F.M.H.M.; Petrosillo, N.; et al. Consensus Document for the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Joint Paper by the EANM, EBJIS, and ESR (with ESCMID Endorsement). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, B.S.; Weinberg, E.P. MR Imaging with Metal-Suppression Sequences for Evaluation of Total Joint Arthroplasty. Radiographics 2016, 36, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shufen, C.; Jinmin, L.; Xiaohui, Z.; Bin, G. Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sconfienza, L.M.; Signore, A.; Cassar-Pullicino, V.; Cataldo, M.A.; Gheysens, O.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A.; Wörtler, K.; Petrosillo, N.; Winkler, H.; et al. Diagnosis of Peripheral Bone and Prosthetic Joint Infections: Overview on the Consensus Documents by the EANM, EBJIS, and ESR (with ESCMID Endorsement). Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6425–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; de Vries, E.F.J.; Vermeulen, L.E.M.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Signore, A. A Large Retrospective Single-Centre Study to Define the Best Image Acquisition Protocols and Interpretation Criteria for White Blood Cell Scintigraphy with 99mTc-HMPAO-Labelled Leucocytes in Musculoskeletal Infections. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottink, K.D.; Gelderman, S.J.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Ploegmakers, J.J.W.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Jutte, P.C. Nuclear Imaging Does Not Have Clear Added Value in Patients with Low a Priori Chance of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. A Retrospective Single-Center Experience. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2022, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberne, S.J.; Raijmakers, P.G.; Temmerman, O.P.P. The Accuracy of Imaging Techniques in the Assessment of Periprosthetic Hip Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2016, 98, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Geng, L.; Li, Q.; Qi, E.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; et al. Different Uptake Patterns of 68Ga-FAPI in Aseptic Loosening and Periprosthetic Joint Infection of Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Series and Literature Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1014463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechler, M.B.; Fu, W.; Turley, S.J. Fibroblast-Macrophage Reciprocal Interactions in Health, Fibrosis, and Cancer. Immunity 2021, 54, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qi, E.; Hao, L.; et al. Diagnostic Efficiency of [68 Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 in Differentiating Periprosthetic Hip Joint Infection and Aseptic Failure. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welling, M.M.; Warbroek, K.; Khurshid, C.; van Oosterom, M.N.; Rietbergen, D.D.D.; de Boer, M.G.J.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Pijls, B.G.; Buckle, T. A Radio- and Fluorescently Labelled Tracer for Imaging and Quantification of Bacterial Infection on Orthopaedic Prostheses. Bone Jt. Res. 2023, 12, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Dudareva, M.; Watts, D.; Morgenstern, M.; Athanasou, N.A.; McNally, M.A. Limited Diagnostic Value of Serum Inflammatory Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Fracture-Related Infections. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102-B, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Puchner, S.E.; Windhager, R. Serum Inflammatory Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbari, E.; Mabry, T.; Tsaras, G.; Spangehl, M.; Erwin, P.J.; Murad, M.H.; Steckelberg, J.; Osmon, D. Inflammatory Blood Laboratory Levels as Markers of Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Li, F.; Gong, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Hu, N. Combined Measurement of D-Dimer and C-Reactive Protein Levels: Highly Accurate for Diagnosing Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Holinka, J.; Staats, K.; Sevelda, F.; Lass, R.; Kubista, B.; Giurea, A.; Windhager, R. Inferior Performance of Established and Novel Serum Inflammatory Markers in Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akgün, D.; Müller, M.; Perka, C.; Winkler, T. The Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein Alone Cannot Be Used for the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infections, Especially in Those Caused by Organisms of Low Virulence. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100-B, 1482–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.A.; Passino, M.; Sachs, B.D.; Nuriel, T.; Akassoglou, K. Fibrin Mechanisms and Functions in Nervous System Pathology. Mol. Interv. 2004, 4, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klim, S.M.; Amerstorfer, F.; Gruber, G.; Bernhardt, G.A.; Radl, R.; Leitner, L.; Leithner, A.; Glehr, M. Fibrinogen—A Practical and Cost Efficient Biomarker for Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturfan, A.A.; Eralp, L.; Emekli, N. Investigation of Inflammatory and Hemostatic Parameters in Female Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty Surgery. Inflammation 2008, 31, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levent, A.; Neufeld, M.E.; Piakong, P.; Lausmann, C.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. Which International Consensus Meeting Preoperative Minor Criteria Is the Most Accurate Marker for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty? J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 3728–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, M.I.; Sharma, K.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Tande, A.J.; Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Mandrekar, J.; Beauchamp, C.P.; Hanssen, A.D.; Abdel, M.P.; et al. Synovial Fluid α Defensin Has Comparable Accuracy to Synovial Fluid White Blood Cell Count and Polymorphonuclear Percentage for Periprosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Xu, J.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y.; Yue, B.; Qu, X. Reliable Diagnostic Tests and Thresholds for Preoperative Diagnosis of Non-Inflammatory Arthritis Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 2822–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B.; Hoyka, M.; Weissbarth, E.; Schuster, P.; Berger, I. The Graphical Representation of Cell Count Representation: A New Procedure for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenn, V.; Morawietz, L.; Jakobs, M.; Kienapfel, H.; Ascherl, R.; Bause, L.; Kuhn, H.; Matziolis, G.; Skutek, M.; Gehrke, T. Joint endoprosthesis pathology. Histopathological diagnostics and classification. Pathologe 2011, 32, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, D.G.; Gordon, A.; Townsend, R. False-Positive Synovial Fluid Alpha-Defensin Test in a Patient with Acute Gout Affecting a Prosthetic Knee. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2017, 27, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deirmengian, C.A.; Kazarian, G.S.; Feeley, S.P.; Sizer, S.C. False-Positive Automated Synovial Fluid White Blood Cell Counting Is a Concern for Both Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Aspirates. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S304–S307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, B.; Hoyka, M.; Weissbarth, E.; Schuster, P.; Berger, I. A New Graphic Type Differentiation of Cell Account Determination for Distinguishing Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection from Hemarthrosis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalirezaie, A.; Bauer, T.W.; Fayaz, H.; Griffin, W.; Higuera, C.A.; Krenn, V.; Krenn, V.; Molano, M.; Moojen, D.-J.; Restrepo, C.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, Diagnosis, Reimplantation: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S369–S379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausmann, C.; Kolle, K.N.; Citak, M.; Abdelaziz, H.; Schulmeyer, J.; Delgado, G.D.; Gehrke, T.; Gebauer, M.; Zahar, A. How Reliable Is the next Generation of Multiplex-PCR for Diagnosing Prosthetic Joint Infection Compared to the MSIS Criteria? Still Missing the Ideal Test. Hip Int. 2020, 30, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, J.W.P.; Verberne, S.J.; Vos, S.J.; van Egmond, P.W. Does the Alpha Defensin ELISA Test Perform Better than the Alpha Defensin Lateral Flow Test for PJI Diagnosis? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeman-Forsthuber, L.T.; Dennis, D.A.; Brady, A.C.; Pollet, A.K.; Johnson, R.M.; Jennings, J.M. Alpha-Defensin Is Not Superior to Traditional Diagnostic Methods for Detection of Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Total Hip Arthroplasty and Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 2144–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.M.; Dennis, D.A.; Abila, P.M.; Johnson, R.M.; Jennings, J.M. Alpha-Defensin Offers Limited Utility in Work-Up Prior to Reimplantation in Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Patients. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, A.; Parvizi, J.; Kazarian, G.S.; Higuera, C.; Frangiamore, S.; Bingham, J.; Beauchamp, C.; Valle, C.D.; Deirmengian, C. The Alpha-Defensin Test for Periprosthetic Joint Infections Is Not Affected by Prior Antibiotic Administration. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okroj, K.T.; Calkins, T.E.; Kayupov, E.; Kheir, M.M.; Bingham, J.S.; Beauchamp, C.P.; Parvizi, J.; Della Valle, C.J. The Alpha-Defensin Test for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection in the Setting of an Adverse Local Tissue Reaction Secondary to a Failed Metal-on-Metal Bearing or Corrosion at the Head-Neck Junction. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1896–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, D.C.; Dennis, D.A.; Kim, R.H.; Miner, T.M.; Yang, C.C.; Jennings, J.M. Determining False Positive Rates of Leukocyte Esterase Reagent Strip When Used as a Detection Tool for Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, M.C.; Beswick, A.D.; Kunutsor, S.K.; Wilson, M.J.; Whitehouse, M.R.; Blom, A.W. The Alpha-Defensin Immunoassay and Leukocyte Esterase Colorimetric Strip Test for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2016, 98, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.-Z.; Li, R.; Fu, J.; Chai, W.; Hao, L.-B.; Chen, J.-Y. Leukocyte Esterase Test and Alpha-Defensin Test Have Similar Accuracy for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, A.; Alvand, A.; Ghanem, E.; Restrepo, C.; Parvizi, J. The Leukocyte Esterase Test for Periprosthetic Joint Infection Is Not Affected by Prior Antibiotic Administration. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2019, 101, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünwald, L.; Schmidutz, F.; Döttger, P.; Erne, F.; Schreiner, A.J.; Hemmann, P. Leukocyte Esterase and Alpha-Defensin in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Predictive Quality and Correlation in a Prospective Study. Int. Orthop. 2023, 47, 2663–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, M.; Ettinger, M.; Reichling, M.; Petri, M.; Guenther, D.; Gehrke, T.; Krettek, C.; Mommsen, P. Synovial C-Reactive Protein as a Marker for Chronic Periprosthetic Infection in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97-B, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Jacovides, C.; Adeli, B.; Jung, K.A.; Hozack, W.J.; Mark, B. Coventry Award: Synovial C-Reactive Protein: A Prospective Evaluation of a Molecular Marker for Periprosthetic Knee Joint Infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, M.W.; Wetters, N.G.; Moric, M.; Gross, C.E.; Della Valle, C.J. Is Synovial C-Reactive Protein a Useful Marker for Periprosthetic Joint Infection? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirmengian, C.; Kardos, K.; Kilmartin, P.; Cameron, A.; Schiller, K.; Parvizi, J. Combined Measurement of Synovial Fluid α-Defensin and C-Reactive Protein Levels: Highly Accurate for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.M.; Goh, G.S.; Tarabichi, S.; Shohat, N.; Parvizi, J. Synovial C-Reactive Protein Is a Useful Adjunct for Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 2437–2443.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qin, L.; Wang, J.; Hu, N.; Huang, W. Combined Serum and Synovial C-Reactive Protein Tests: A Valuable Adjunct to the Diagnosis of Chronic Prosthetic Joint Infection. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.-Z.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Chai, W.; Zhou, Y.-G.; Chen, J.-Y. The Relationship of C-Reactive Protein/Interleukin-6 Concentrations between Serum and Synovial Fluid in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, J.; Svoboda, M.; Zapletalova, J.; Proskova, J.; Juranova, J. Serum IL-6 in Combination with Synovial IL-6/CRP Shows Excellent Diagnostic Power to Detect Hip and Knee Prosthetic Joint Infection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randau, T.M.; Friedrich, M.J.; Wimmer, M.D.; Reichert, B.; Kuberra, D.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Limmer, A.; Wirtz, D.C.; Gravius, S. Interleukin-6 in Serum and in Synovial Fluid Enhances the Differentiation between Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Aseptic Loosening. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W. Synovial Fluid Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Can Be Used to Accurately Diagnose Prosthetic Joint Infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 123, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkman, C.; Thomas, A.R.; Koenraadt, K.L.M.; Ermens, A.a.M.; van Geenen, R.C.I. Synovial Neutrophilic Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2020, 140, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Qin, J.; Song, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. LTF, PRTN3, and MNDA in Synovial Fluid as Promising Biomarkers for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Identification by Quadrupole Orbital-Trap Mass Spectrometry. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2019, 101, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirmengian, C.; Kardos, K.; Kilmartin, P.; Cameron, A.; Schiller, K.; Parvizi, J. Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Has the Era of the Biomarker Arrived? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 3254–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirmengian, C.; Feeley, S.; Kazarian, G.S.; Kardos, K. Synovial Fluid Aspirates Diluted with Saline or Blood Reduce the Sensitivity of Traditional and Contemporary Synovial Fluid Biomarkers. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Windhager, R.; Sevelda, F.; Staats, K.; Puchner, S.E.; Stenicka, S.; Thalhammer, F.; Holinka, J. Multiplex PCR Unyvero I60 ITI Application Improves Detection of Low-Virulent Microorganisms in Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meta-Analysis of Sonication Prosthetic Fluid PCR for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection—PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5922553/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Suren, C.; Feihl, S.; Cabric, S.; Banke, I.J.; Haller, B.; Trampuz, A.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Prodinger, P.M. Improved Pre-Operative Diagnostic Accuracy for Low-Grade Prosthetic Joint Infections Using Second-Generation Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction on Joint Fluid Aspirate. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Renz, N.; Feihl, S.; Morgenstern, C.; Cabric, S.; Trampuz, A. Value of Multiplex PCR for Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance in Samples Retrieved from Patients with Orthopaedic Infections. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Hu, H.; Zhu, S.; Ding, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Fang, X. Diagnostic Role of mNGS in Polymicrobial Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W. Can Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing Identify the Pathogens Responsible for Culture-Negative Prosthetic Joint Infection? BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivy, M.I.; Thoendel, M.J.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Hanssen, A.D.; Abdel, M.P.; Chia, N.; Yao, J.Z.; Tande, A.J.; Mandrekar, J.N.; et al. Direct Detection and Identification of Prosthetic Joint Infection Pathogens in Synovial Fluid by Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00402–e00418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, T.L.; Sanderson, N.D.; Atkins, B.L.; Brent, A.J.; Cole, K.; Foster, D.; McNally, M.A.; Oakley, S.; Peto, L.; Taylor, A.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of Orthopedic-Device-Related Infection Directly from Sonication Fluid by Metagenomic Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2334–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kildow, B.J.; Ryan, S.P.; Danilkowicz, R.; Lazarides, A.L.; Penrose, C.; Bolognesi, M.P.; Jiranek, W.; Seyler, T.M. Next-Generation Sequencing Not Superior to Culture in Periprosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, K.; Clarkson, S.; Phillips, C.D.; Dennis, D.A.; Klatt, B.A.; O’Malley, M.J.; Smith, E.L.; Gililland, J.M.; Pelt, C.E.; Peters, C.L.; et al. An Enhanced Understanding of Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection with Next-Generation Sequencing: A Multicenter Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2022, 104, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchia, M.T.; Austin, D.C.; Kunkel, S.T.; Dwyer, K.W.; Moschetti, W.E. Next-Generation Sequencing vs Culture-Based Methods for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, B.; Lass, R. Diagnostic Algorithm for Failure Analysis of Painful Total Hip Arthroplasties. Z. Orthop. Unf. 2016, 154, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zhai, Z.; Wu, C.; Jin, F.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; et al. Preoperative Aspiration Culture for Preoperative Diagnosis of Infection in Total Hip or Knee Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3830–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Cooper, J.R.; Kerry, R.M.; Hamer, A.J.; Norman, P.; Stockley, I. Accuracy of Joint Aspiration for the Preoperative Diagnosis of Infection in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2006, 21, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbari, E.F.; Marculescu, C.; Sia, I.; Lahr, B.D.; Hanssen, A.D.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Gullerud, R.; Osmon, D.R. Culture-Negative Prosthetic Joint Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Piper, K.E.; Jacobson, M.J.; Hanssen, A.D.; Unni, K.K.; Osmon, D.R.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Cockerill, F.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Greenleaf, J.F.; et al. Sonication of Removed Hip and Knee Prostheses for Diagnosis of Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peel, T.N.; Spelman, T.; Dylla, B.L.; Hughes, J.G.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Cheng, A.C.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Optimal Periprosthetic Tissue Specimen Number for Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holinka, J.; Bauer, L.; Hirschl, A.M.; Graninger, W.; Windhager, R.; Presterl, E. Sonication Cultures of Explanted Components as an Add-on Test to Routinely Conducted Microbiological Diagnostics Improve Pathogen Detection. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, B.L.; Athanasou, N.; Deeks, J.J.; Crook, D.W.M.; Simpson, H.; Peto, T.E.A.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Berendt, A.R.; Group, T.O.C.S. Prospective Evaluation of Criteria for Microbiological Diagnosis of Prosthetic-Joint Infection at Revision Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, P.; Fink, B.; Sandow, D.; Margull, A.; Berger, I.; Frommelt, L. Prolonged Bacterial Culture to Identify Late Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Promising Strategy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bémer, P.; Léger, J.; Tandé, D.; Plouzeau, C.; Valentin, A.S.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Lemarié, C.; Kempf, M.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Bret, L.; et al. How Many Samples and How Many Culture Media To Diagnose a Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Clinical and Microbiological Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hischebeth, G.T.R.; Randau, T.M.; Molitor, E.; Wimmer, M.D.; Hoerauf, A.; Bekeredjian-Ding, I.; Gravius, S. Comparison of Bacterial Growth in Sonication Fluid Cultures with Periprosthetic Membranes and with Cultures of Biopsies for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 84, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; Xu, Y.; Bay, L.; Schønheyder, H.C.; Jakobsen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Thomsen, T.R. Sampling Challenges in Diagnosis of Chronic Bacterial Infections. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bori, G.; Muñoz-Mahamud, E.; Garcia, S.; Mallofre, C.; Gallart, X.; Bosch, J.; Garcia, E.; Riba, J.; Mensa, J.; Soriano, A. Interface Membrane Is the Best Sample for Histological Study to Diagnose Prosthetic Joint Infection. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, G.S.; Parvizi, J. Think Twice before Prescribing Antibiotics for that Swollen Knee: The Influence of Antibiotics on the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peel, T.N.; Dylla, B.L.; Hughes, J.G.; Lynch, D.T.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Cheng, A.C.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Improved Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection by Culturing Periprosthetic Tissue Specimens in Blood Culture Bottles. mBio 2016, 7, e01776-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Prieto, D.; Portillo, M.E.; Puig-Verdié, L.; Alier, A.; Gamba, C.; Guirro, P.; Martínez-Díaz, S.; Horcajada, J.P.; Trampuz, A.; Monllau, J.C. Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Prosthetic Joint Infections: Not a Concern for Intraoperative Cultures. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 86, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, R.S.J.; Aggarwal, A.; Givens, S.A.; McClure, J.T.; Morgan, P.M.; Barrack, R.L. Prophylactic Antibiotics Do Not Affect Cultures in the Treatment of an Infected TKA: A Prospective Trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Shohat, N.; Sebillotte, M.; Arvieux, C.; Parvizi, J.; Soriano, A. Is Gram Staining Still Useful in Prosthetic Joint Infections? J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2019, 4, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirra, J.M.; Amstutz, H.C.; Matos, M.; Gold, R. The Pathology of the Joint Tissues and Its Clinical Relevance in Prosthesis Failure. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1976, 117, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, C.; Zhao, G.-S.; Lin, T.; Shi, Z.-L.; Yan, S.-G. Ten versus Five Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes as Threshold in Frozen Section Tests for Periprosthetic Infection: A Meta-Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, I.K.; McNally, M.A.; Luger, M.; Böhler, C.; Windhager, R.; Sulzbacher, I. Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Counts in Histopathological Tissue Analysis in Periprosthetic Joint Infection Using the ICM, IDSA, and EBJIS Criteria. Bone Jt. Res. 2021, 10, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bori, G.; McNally, M.A.; Athanasou, N. Histopathology in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: When Will the Morphomolecular Diagnosis Be a Reality? Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1412701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B.; Makowiak, C.; Fuerst, M.; Berger, I.; Schäfer, P.; Frommelt, L. The Value of Synovial Biopsy, Joint Aspiration and C-Reactive Protein in the Diagnosis of Late Peri-Prosthetic Infection of Total Knee Replacements. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, B.; Hoyka, M.; Blersch, B.; Baum, H.; Sax, F.H. Graphic Type Differentiation of Cell Count Data for Diagnosis of Early and Late Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A New Method. Technol. Health Care 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlhofer, H.; Renz, N.; Zahar, A.; Lüdemann, M.; Rudert, M.; Hube, R.; Frommelt, L.; Ascherl, R.; Perka, C.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R. Diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: Development of an evidence-based algorithm by the work group of implant-associated infection of the AE-(German Society for Arthroplasty). Orthopade 2021, 50, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sax, F.H.; Hoyka, M.; Blersch, B.P.; Fink, B. Diagnostics in Late Periprosthetic Infections—Challenges and Solutions. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040351
Sax FH, Hoyka M, Blersch BP, Fink B. Diagnostics in Late Periprosthetic Infections—Challenges and Solutions. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(4):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040351
Chicago/Turabian StyleSax, Florian Hubert, Marius Hoyka, Benedikt Paul Blersch, and Bernd Fink. 2024. "Diagnostics in Late Periprosthetic Infections—Challenges and Solutions" Antibiotics 13, no. 4: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040351
APA StyleSax, F. H., Hoyka, M., Blersch, B. P., & Fink, B. (2024). Diagnostics in Late Periprosthetic Infections—Challenges and Solutions. Antibiotics, 13(4), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040351






