Cyclic Peptide MV6, an Aminoglycoside Efficacy Enhancer Against Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
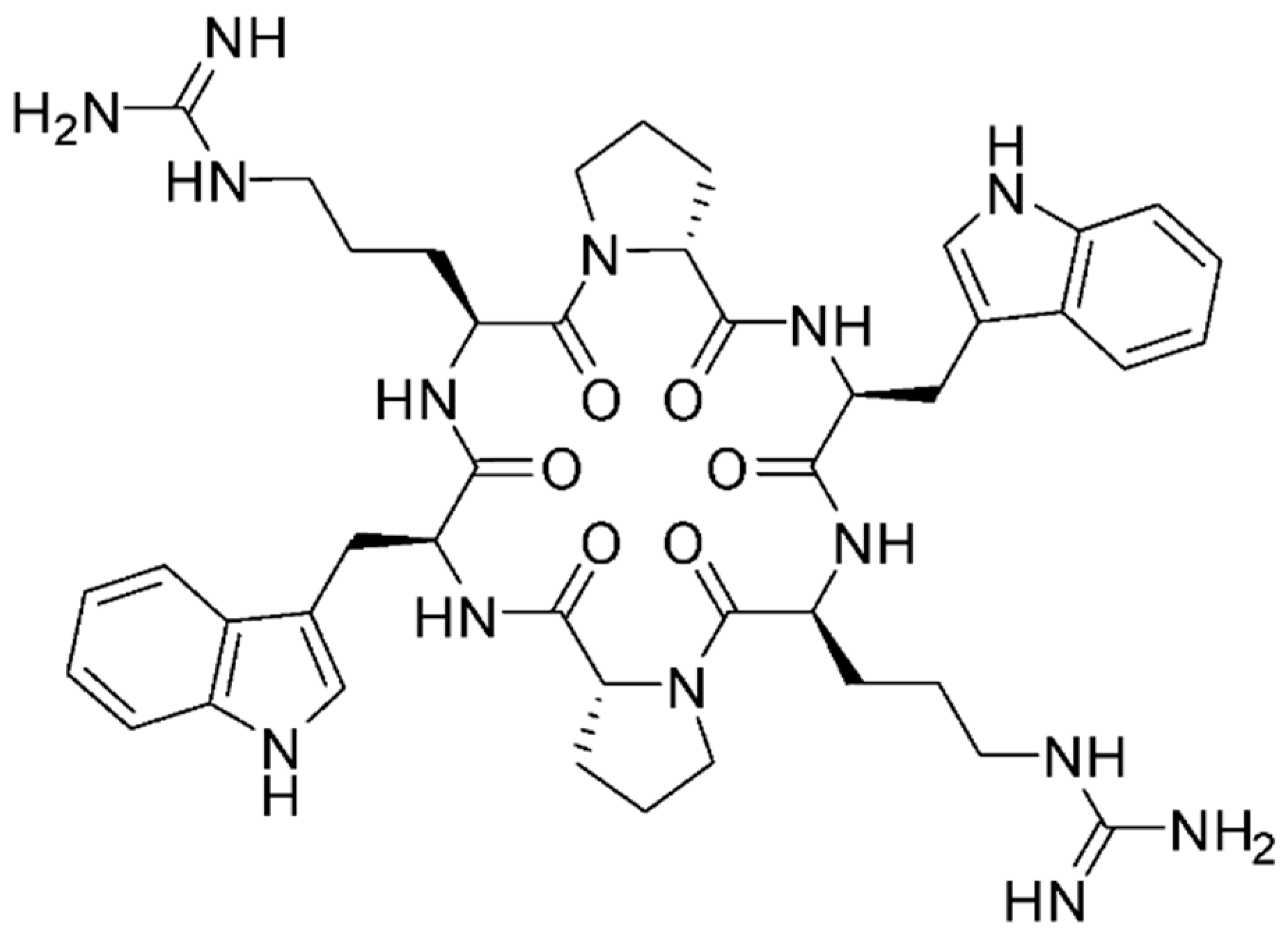
2.1. MV6 Structure
2.2. Strains’ Resistance Mechanisms
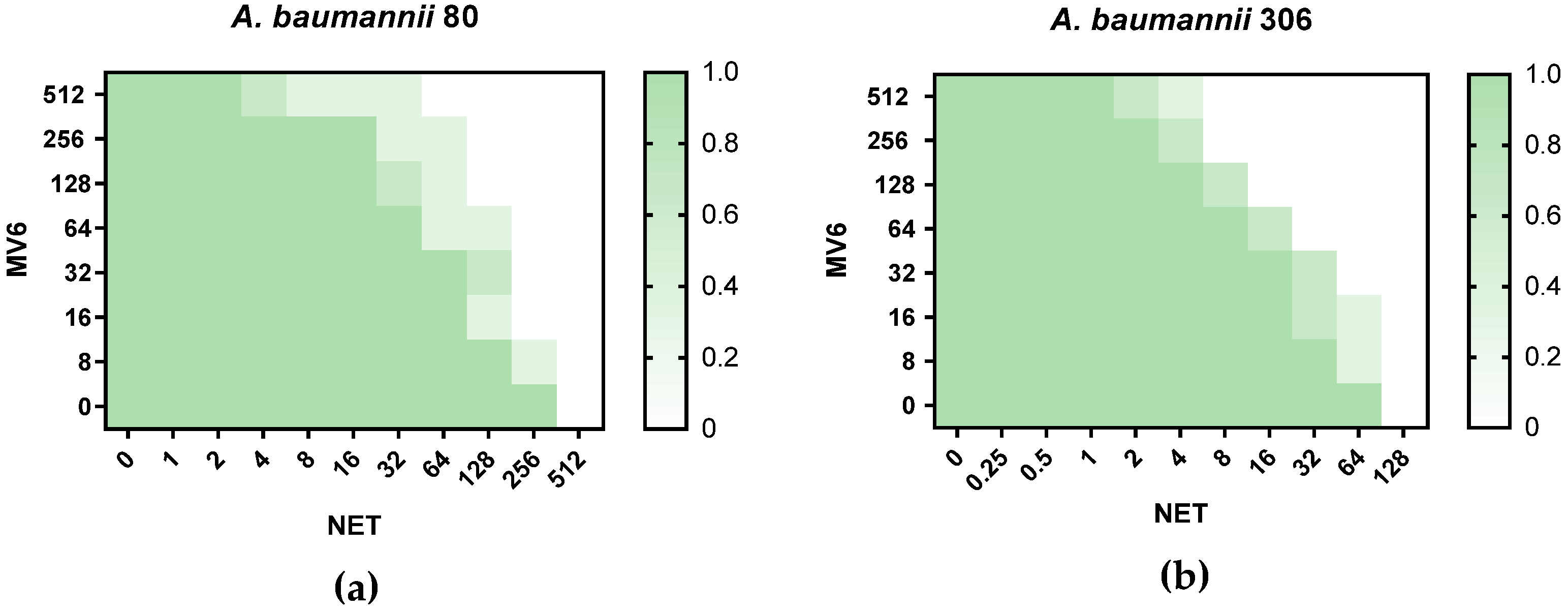
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Checkerboard Assays
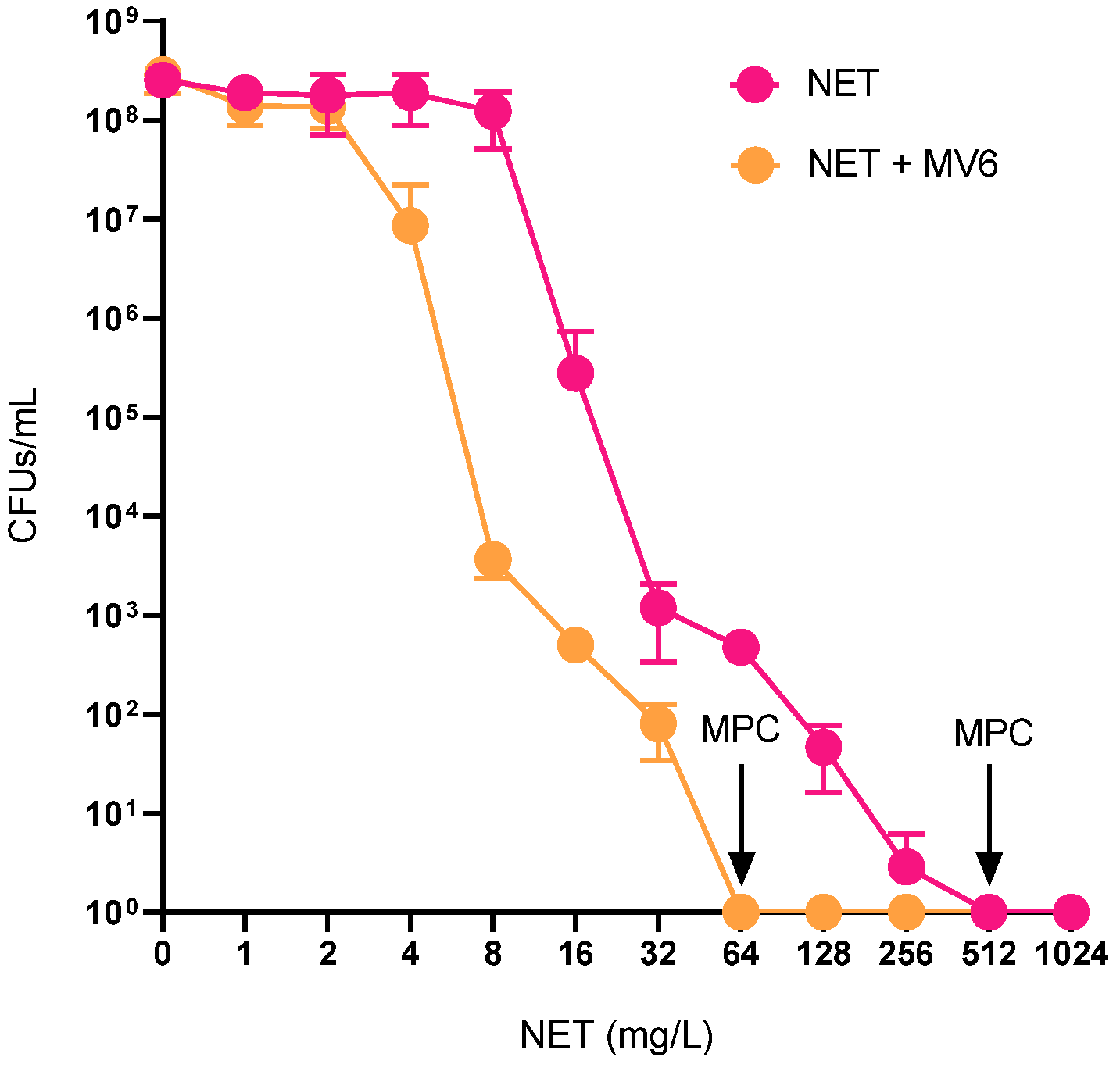
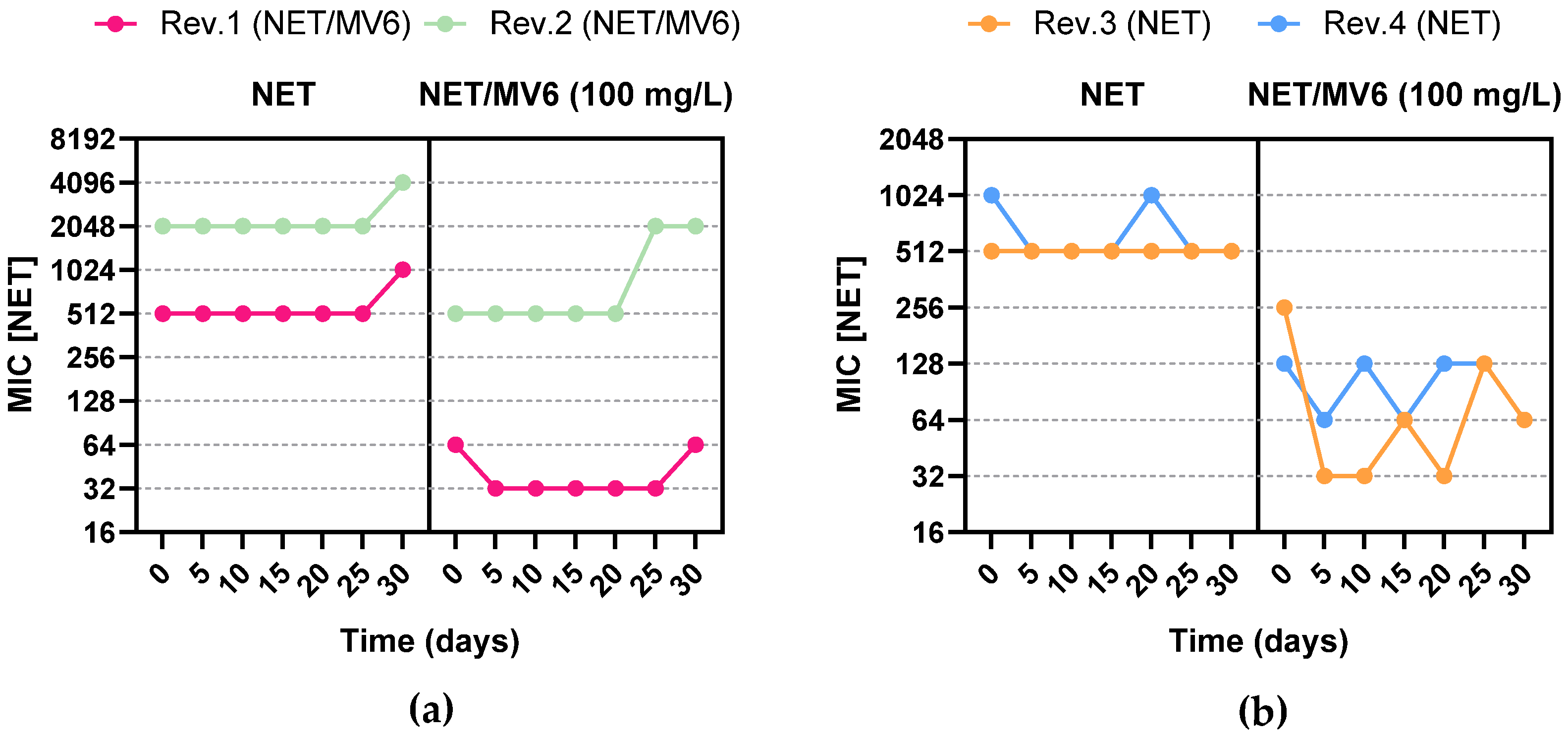
2.4. Resistance Profile Characterization of Spontaneous Mutants
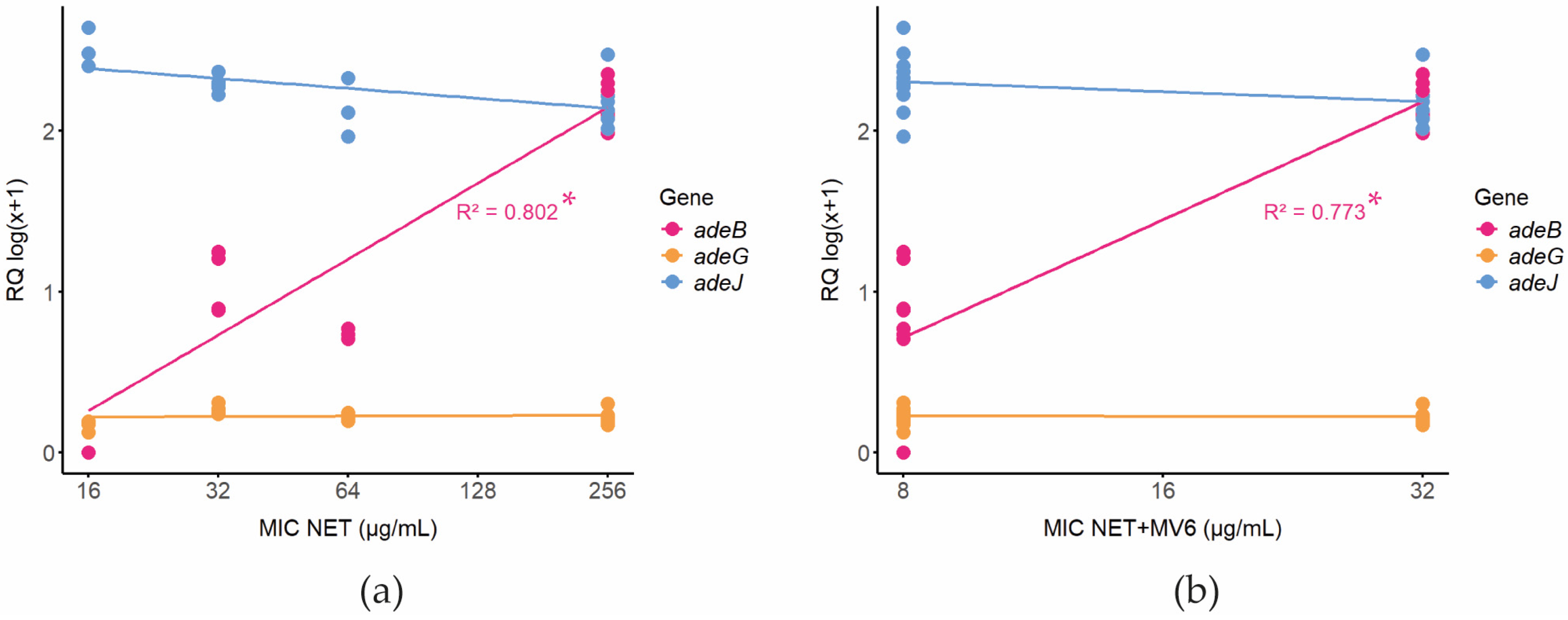
2.5. Prediction of Resistance Mechanisms
3. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecules Used in This Study
4.2. Strain Selection and Characterization of Aminoglycoside Modifying Enzymes (AMEs) and Relevant Efflux Pumps
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Checkerboard Assays
- FICMV6 = (MIC of MV6 in combination)/(MIC of MV6 alone);
- FICNET = (MIC of NET in combination)/(MIC of NET alone);
- FICI = FICMV6 + FICNET;
- Synergistic effect if FICI ≤ 0.5; additive effect if 0.5 < FICI ≤ 1.0; indifferent effect if 1.0 < FICI ≤ 2.0; and finally, antagonistic effect if FICI > 2.0.
4.6. Mutant Generation Analysis
4.7. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Variant Calling
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peleg, A.Y.; Harald, S.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a Successful Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneechoutte, M.; Young, D.M.; Ornston, L.N.; De Baere, T.; Nemec, A.; Van Der Reijden, T.; Carr, E.; Tjernberg, I.; Dijkshoorn, L. Naturally Transformable Acinetobacter Sp. Strain ADP1 Belongs to the Newly Described Species Acinetobacter Baylyi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.-E.; Vallenet, D.; Barbe, V.; Audic, S.; Ogata, H.; Poirel, L.; Richet, H.; Robert, C.; Mangenot, S.; Abergel, C.; et al. Comparative Genomics of Multidrug Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 9789240093461. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; McClean, S. Mapping Global Prevalence of Acinetobacter baumannii and Recent Vaccine Development to Tackle It. Vaccines 2021, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, M.J.; Actis, L.; Pachón, J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Human Infections, Factors Contributing to Pathogenesis and Animal Models. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 130–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.S.; Visca, P.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Evolution of a Global Pathogen. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 71, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, I.; Espinal, P.; Vila-farrés, X.; Vila, J. The Acinetobacter baumannii Oxymoron: Commensal Hospital Dweller Turned Pan-Drug-Resistant Menace. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, P.; Sacha, P.; Hauschild, T.; Zórawski, M.; Krawczyk, M.; Tryniszewska, E. Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii—The Role of AdeABC (RND Family) Efflux Pump in Resistance to Antibiotics. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2008, 46, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.F.; Bilya, S.R.; Xu, W. AdeABC Efflux Gene in Acinetobacter baumannii. New Microbes New Infect. 2019, 30, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damier-Piolle, L.; Magnet, S.; Brémont, S.; Lambert, T.; Courvalin, P. AdeIJK, a Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Pump Effluxing Multiple Antibiotics in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leus, I.V.; Weeks, J.W.; Bonifay, V.; Smith, L.; Richardson, S.; Zgurskaya, H.I. Substrate Specificities and Efflux Efficiencies of RND Efflux Pumps of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00049-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, I.; Marti, S.; Espinal, P.; Martínez, P.; Gibert, I.; Vila, J. CraA, a Major Facilitator Superfamily Efflux Pump Associated with Chloramphenicol Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4013–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí, S.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Pascual, Á.; Ribera, A.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Bou, G.; Miguel Cisneros, J.; Pachón, J.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Vila, J. Prevalencia de Los Genes TetA y TetB Como Mecanismo de Resistencia a Tetraciclina y Minociclina En Aislamientos Clínicos de Acinetobacter baumannii. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2006, 24, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian-Zhong, S.; Jing, C.; Tohru, M.; Teruo, K.; Tomofusa, T. AbeM, an H+-Coupled Acinetobacter baumannii Multidrug Efflux Pump Belonging to the MATE Family of Transporters. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4362–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvé-Deacon, E.; Jové, T.; Afouda, P.; Barraud, O.; Tilloy, V.; Scaon, E.; Hervé, B.; Burucoa, C.; Kempf, M.; Marcos, J.Y.; et al. Class 1 Integrons in Acinetobacter baumannii: A Weak Expression of Gene Cassettes to Counterbalance the Lack of LexA-Driven Integrase Repression. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.S.; Gigante, V.; Sati, H.; Paulin, S.; Al-Sulaiman, L.; Rex, J.H.; Fernandes, P.; Arias, C.A.; Paul, M.; Thwaites, G.E.; et al. Analysis of the Clinical Pipeline of Treatments for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections: Despite Progress, More Action Is Needed. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0199121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterkamp, T. Antibiotics Clinical Development and Pipeline BT—How to Overcome the Antibiotic Crisis: Facts, Challenges, Technologies and Future Perspectives; Stadler, M., Dersch, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 447–474. ISBN 978-3-319-49284-1. [Google Scholar]
- Provenzani, A.; Hospodar, A.R.; Meyer, A.L.; Leonardi Vinci, D.; Hwang, E.Y.; Butrus, C.M.; Polidori, P. Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Organisms: A Review of Recently Approved Antibiotics and Novel Pipeline Agents. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2020, 42, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, M.; Cosentino, F.; Giannella, M.; Viale, P.; Pea, F. Clinical Efficacy of Cefiderocol-Based Regimens in Patients with Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.J.; Zhu, E.; Jayakumar, R.A.; Shan, G.; Viswesh, V. Efficacy of Eravacycline Versus Best Previously Available Therapy for Adults With Pneumonia Due to Difficult-to-Treat Resistant (DTR) Acinetobacter baumannii. Ann. Pharmacother. 2022, 56, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimy, S.; Morrisette, T.; Lagnf, A.M.; Rojas, L.M.; King, M.A.; Pullinger, B.M.; Hobbs, A.L.V.; Perkins, N.B., 3rd; Veve, M.P.; Bouchard, J.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Eravacycline in Patients Treated Predominately for Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00479-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landman, D.; Kelly, P.; Bäcker, M.; Babu, E.; Shah, N.; Bratu, S.; Quale, J. Antimicrobial Activity of a Novel Aminoglycoside, ACHN-490, against Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa from New York City. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keam, S.J. Sulbactam/Durlobactam: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.P.; Pinto, N.A.; Vu, T.N.; Lee, H.; Cho, Y.L.; Byun, J.-H.; D’Souza, R.; Yong, D. In Vitro Activity of a Novel Siderophore-Cephalosporin, GT-1 and Serine-Type β-Lactamase Inhibitor, GT-055, against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter spp. Panel Strains. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Yoshikuni, O.; Megumi, C.; Kazuki, H.; Naomasa, G. Potent In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of DS-8587, a Novel Broad-Spectrum Quinolone, against Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1978–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, B.; Doi, Y.; Bonomo, R.A.; Paterson, D.L. New Treatment Options against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, R.E.; Zainab, S.; Yousuf, F.J.; Mughal, S. AI-Driven Drug Discovery: Exploring Abaucin as a Promising Treatment against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Luo, T.; Yang, Y.; Dong, D.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Guo, X.; Hu, F.; He, P. Phage Therapy as a Promising New Treatment for Lung Infection Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lood, R.; Winer, B.Y.; Pelzek, A.J.; Diez-Martinez, R.; Thandar, M.; Euler, C.W.; Schuch, R.; Fischetti, V.A. Novel Phage Lysin Capable of Killing the Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii in a Mouse Bacteremia Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, T.B.; Pantapalangkoor, P.; Luna, B.M.; Bruhn, K.W.; Yan, J.; Dekitani, K.; Hsieh, S.; Yeshoua, B.; Pascual, B.; Vinogradov, E.; et al. Monoclonal Antibody Protects Against Acinetobacter baumannii Infection by Enhancing Bacterial Clearance and Evading Sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, M.J.; Rumbo, C.; Bou, G.; Pachón, J. Outer Membrane Vesicles as an Acellular Vaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii. Vaccine 2011, 29, 5705–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Tiwari, M.; Tiwari, V. Efflux Pumps in Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Current Status and Challenges in the Discovery of Efflux Pumps Inhibitors. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Barnie, P.A.; Su, Z.; Xu, H. Development of Efflux Pumps and Inhibitors (EPIs) in A. baumanii. Clin. Microb. 2014, 3, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.; Hall, R.M. AbaR5, a Large Multiple-Antibiotic Resistance Region Found in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2667–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbo, C.; Gato, E.; López, M.; Ruiz de Alegría, C.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Vila, J.; Pachón, J.; Cisneros, J.M.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; et al. Contribution of Efflux Pumps, Porins, and β-Lactamases to Multidrug Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5247–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.F.; Jiang, J.P.; Ml, Z.H. Relationship between Antimicrobial Resistance and Aminoglycoside-Modifying Enzyme Gene Expressions in Acinetobacter baumannii. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 118, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onohuean, H.; Nwodo, U.U. Polymorphism and Mutational Diversity of Virulence (VcgCPI/VcgCPE) and Resistance Determinants (Aac(3)-IIa, (AacC2, StrA, Sul 1, and 11) among Human Pathogenic Vibrio Species Recovered from Surface Waters in South-Western Districts of Uganda. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2023, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacha, P.; Jaworowska, J.; Ojdana, D.; Wieczorek, P.; Czaban, S.; Tryniszewska, E. Occurrence of the AacA4 Gene among Multidrug Resistant Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Bronchial Secretions Obtained from the Intensive Therapy Unit at University Hospital in Bialystok, Poland. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2012, 50, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cabrera, R.; Fernández-Barat, L.; Vázquez, N.; Alcaraz-Serrano, V.; Bueno-Freire, L.; Amaro, R.; López-Aladid, R.; Oscanoa, P.; Muñoz, L.; Vila, J.; et al. Resistance Mechanisms and Molecular Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains from Patients with Bronchiectasis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C.; Klaus, S.; Herz, S.; Zou, Z.; Koop, H.U.; Golds, T. Efficient Plastid Transformation in Tobacco Using the AphA-6 Gene and Kanamycin Selection. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2002, 268, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neshani, A.; Sedighian, H.; Mirhosseini, S.A.; Ghazvini, K.; Zare, H.; Jahangiri, A. Antimicrobial Peptides as a Promising Treatment Option against Acinetobacter baumannii Infections. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 146, 104238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, K.; Lechuga, G.C.; Provance, D.W.; Morel, C.M.; De Simone, S.G. An Update on the Therapeutic Potential of Antimicrobial Peptides against Acinetobacter baumannii Infections. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjla, A.; Kaul, G.; Chopra, S.; Titz, A.; Verma, S. Short Peptides and Their Mimetics as Potent Antibacterial Agents and Antibiotic Adjuvants. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 2731–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, D.; Kong, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Antimicrobial Peptides as Promising Antibiotic Adjuvants to Combat Drug-Resistant Pathogens. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 50, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnet, S.; Courvalin, P.; Lambert, T. Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division-Type Efflux Pump Involved in Aminoglycoside Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Strain BM4454. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3375–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.B.; Venkataramaiah, M.; Mondal, A.; Rajamohan, G. Functional Characterization of AbeD, an RND-Type Membrane Transporter in Antimicrobial Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipton, K.A.; Farokhyfar, M.; Rather, P.N. Multiple Roles for a Novel RND Type Efflux System in Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, V.; Kumar, A. Update on Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pumps in Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0051421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, L.; Nodwell, J.R. The TetR Family of Regulators. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 440–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, J.L.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Molina-Henares, A.J.; Terán, W.; Watanabe, K.; Zhang, X.; Gallegos, M.T.; Brennan, R.; Tobes, R. The TetR Family of Transcriptional Repressors. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 326–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Bueno, M.; Molina-Henares, A.J.; Pareja, E.; Ramos, J.L.; Tobes, R. BacTregulators: A Database of Transcriptional Regulators in Bacteria and Archaea. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2787–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, L.G.; Weiss, A.; Pérez-Rueda, E.; Antonio Ibarra, J.; Shaw, L.N. Towards the Complete Proteinaceous Regulome of Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, mgen000107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.F.; Mutzel, R.; Barbé, J.; Müller, W. A Multifunctional Gene (TetR) Controls Tn10-Encoded Tetracycline Resistance. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 150, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, N.; Bouchier, C.; Courvalin, P.; Périchon, B. Expression of the Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Pump AdeIJK in Acinetobacter baumannii Is Regulated by AdeN, a TetR-Type Regulator. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2504–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, S.N.; Ghotaslou, R.; Ganbarov, K.; Mobed, A.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Kafil, H.S. Acinetobacter baumannii Efflux Pumps and Antibiotic Resistance. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaetano, G.V.; Lentini, G.; Famà, A.; Coppolino, F.; Beninati, C. Antimicrobial Resistance: Two-Component Regulatory Systems and Multidrug Efflux Pumps. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, U.; Yamashita, E.; Neuberger, A.; Morimoto, M.; van Veen, H.W.; Murakami, S. Crystal Structure of Tripartite-Type ABC Transporter MacB from Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirshikova, T.V.; Sierra-Bakhshi, C.G.; Kamaletdinova, L.K.; Matrosova, L.E.; Khabipova, N.N.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Khilyas, I.V.; Danilova, I.V.; Mardanova, A.M.; Sharipova, M.R.; et al. The ABC-Type Efflux Pump MacAB Is Involved in Protection of Serratia Marcescens against Aminoglycoside Antibiotics, Polymyxins, and Oxidative Stress. mSphere 2021, 6, e00033-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukun, L.; Shumpei, A.; Takumi, I.; Hiroyasu, O. Regulation of Multidrug Efflux Pumps by TetR Family Transcriptional Repressor Negatively Affects Secondary Metabolism in Streptomyces Coelicolor A3(2). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e01822-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, M. Foldseek Gives AlphaFold Protein Database a Rapid Search Tool. Nature, 2023; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rojas, R.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Lepe, J.A.; Pachón, J. Acinetobacter baumannii Resistant to Colistin Alters Its Antibiotic Resistance Profile: A Case Report From Spain. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 1147–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Tomás-carmona, M.; Caballero-moyano, F.; Bou, G.; Martínez-martínez, L.; Vila, J.; Pachón, J.; Miguel, J. Actividad de 18 Agentes Antimicrobianos Frente a Aislados Clínicos de Acinetobacter baumannii: Segundo Estudio Nacional Multicéntrico (Proyecto GEIH-REIPI-Ab 2010). Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2013, 31, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishk, R.; Soliman, N.; Nemr, N.; Eldesouki, R.; Mahrous, N.; Gobouri, A.; Azab, E.; Anani, M. Prevalence of Aminoglycoside Resistance and Aminoglycoside Modifying Enzymes in Acinetobacter baumannii Among Intensive Care Unit Patients, Ismailia, Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegeni, F.B.; Cheraghipour, K.; Shakib, P. Detection of Aacc1 and Aacc2 Genes in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Int. J. Med. Investig. 2020, 9, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rastegar Lari, A.; Valadan Tahbaz, S. Characterization of aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from burn wound colonization mécanismes de résistance aux aminosides d’Acinetobacter baumannii isolé de zones brûlées. Ann. Fires Burn Disaster 2019, 32, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgaya, C.; Ratia, C.; Marí-Almirall, M.; Rubio, L.; Higgins, P.G.; Seifert, H.; Roca, I.; Vila, J. In Vitro and in Vivo Virulence Potential of the Emergent Species of the Acinetobacter baumannii (Ab) Group. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; Volume 40, ISBN 9781684400669. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Data Transformation BT—Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Wickham, H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 203–220. ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Billal, D.S.; Fedorko, D.P.; Yan, S.S.; Hotomi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Nelson, N.; Yamanaka, N. In Vitro Induction and Selection of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Mutants of Streptococcus Pyogenes Strains with Multiple Emm Types. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Drlica, K. The Mutant Selection Window and Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwengers, O.; Jelonek, L.; Dieckmann, M.A.; Beyvers, S.; Blom, J.; Goesmann, A. Bakta: Rapid and Standardized Annotation of Bacterial Genomes via Alignment-Free Sequence Identification. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A Program for Annotating and Predicting the Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the Genome of Drosophila Melanogaster Strain W1118; Iso-2; Iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
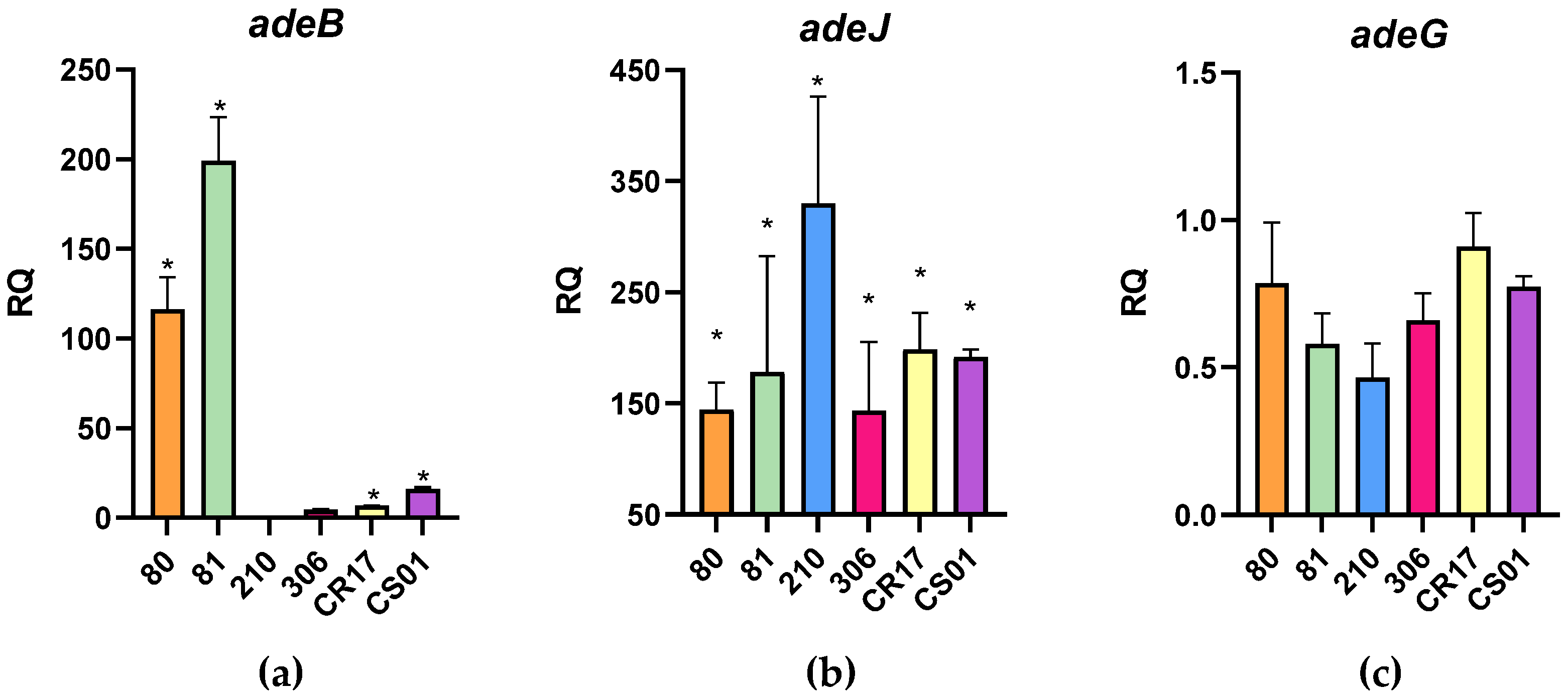
| Strain | Aminoglycoside Modifying Enzymes (AMEs) | Efflux Pumps | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aacC1 | aacC2 | aacA4 | aadA1 | aadB | aphA6 | aphA1 | adeB | adeJ | adeG | tetA | tetB | |
| 80 | ||||||||||||
| 81 | ||||||||||||
| 210 | ||||||||||||
| 306 | ||||||||||||
| CR17 | ||||||||||||
| CS01 | ||||||||||||
| Product | AAC(3)-I | AAC(3)-II | AAC(6′)-I | ANT(3″)-9 | ANT(2″)-I | APH(3′)-VI | APH(3′)-I | AdeABC 1 | AdeIJK 1 | AdeFGH 1 | TetA | TetB |
| Substrates | GM, TOB, NET | KN, NIT, GM | GM, AK, TOB | STR, SPT | GM, KN AK | AK, KN, NEO | NEO, KN | AMG, FQ, BL, CHL, TMP, TET, E, EtBr | BL, TET, FQ, CHL, TMP, FA, RIF, E, LIN, ACR, NOV, PYO, SDS | TET, TGC, NAL, FQ, SUL, EtBr, E, SDS | TET | TET, MIN |
| Source | [37,38,39] | [40] | [41] | [37] | [38,42] | [43] | [38] | [35] | [35] | [35] | [35] | [35] |
| Strains A. baumannii | NET | NET + MV6 | Fold-Change | NET + PAβN | Fold-Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 256 | 32 | 8-fold | 128 | 2-fold |
| 81 | 256 | 32 | 8-fold | 64 | 4-fold |
| 210 | 16 | 8 * | 2-fold | 8 * | 2-fold |
| 306 | 64 | 8 * | 8-fold | 16 | 4-fold |
| CR17 | 32 | 8 * | 4-fold | 8 * | 4-fold |
| CS01 | 32 | 8 * | 4-fold | 16 | 2-fold |
| MIC (mg/L) | Sensititre (DKNGM) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutant Strains | [NET] | [NET]/MV6 | MERO | GEN | CIP | AUGC | COL | TGC | TAZ | IMI | AZT | C/T | SXT | P/T4 | FOT | CZA | ETP | AMI | TOB | |
| AB1 | WT 306 | 64 | 8 | 16 | 8 | >2 | >64/2 | 1 | 2 | >16 | >16 | 32 | 16/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 8 | 2 |
| AB2 | Ab306_NET8_MV6 | 1024 | 32 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 1 | 1 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 16/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 16 | 2 |
| AB3 | Ab306_NET32_MV6 | 512 | 64 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 1 | 1 | >16 | >16 | 32 | >32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 2 |
| AB4 | Ab306_NET64_MV6 | 4096 | 512 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | >4 | >16 | 16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB5 | Ab306_NET64_MV6 | 4096 | 512 | 8 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB6 | Ab306_NET32_MV6 | 2048 | 512 | >16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | >4 | >16 | >16 | 16 | >32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 16 | 8 |
| AB7 | Ab306_NET16_MV6 | 1024 | 128 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | >4 | >16 | 16 | 16 | 16/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 16 | 8 |
| AB8 | Ab306_NET16_MV6 | 512 | 256 | 8 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 32 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 16 | 8 |
| AB9 | Ab306_NET16_MV6 | 512 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | 16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB10 | Ab306_NET16_MV6 | 512 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | 16 | 8 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB11 | Ab306_NET16_MV6 | 512 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | 16 | 8 | 16/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB12 | Ab306_NET128 | 512 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 1 | 2 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 8 | 2 |
| AB13 | Ab306_NET256 | 1024 | 128 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 1 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 16/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 8 | 4 |
| AB14 | Ab306_NET256 | 2048 | 512 | >16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 1 | >4 | >16 | >16 | 32 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB15 | Ab306_NET256 | 2048 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 16 | 8 |
| AB16 | Ab306_NET256 | 2048 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 8 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB17 | Ab306_NET256 | 4096 | 512 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 16 | 8 |
| AB18 | Ab306_NET128 | 2048 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 1 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | >8 |
| AB19 | Ab306_NET128 | 2048 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | >4 | >16 | >16 | 16 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 16 | 8 |
| AB20 | Ab306_NET128 | 4096 | 256 | >16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 32 | 32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| AB21 | Ab306_NET128 | 2048 | 256 | 16 | >8 | >2 | >64/2 | 0.5 | 4 | >16 | >16 | 32 | >32/4 | >8/152 | >32/4 | >8 | >16/4 | >2 | 32 | 8 |
| NET/MV6 | ||||||
| Mutant | Gene | Mutation | Annotation (NCBI) | Reference (NCBI) | Impact | Type |
| AB2 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| Intergenic TetR/AcrR family | SNP (T>C) | GBFHJJIP_02069_gene-CHR_END | GBFHJJIP_02069 | M/L | IR | |
| AB3 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| AB4 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| adeR | DEL 40274 (TCTCCACACTTA>T) | GBFHJJIP_02896_gene/GBFHJJIP_02897_gene | WP_000459542.1 | M/L | IR | |
| AB5 | TetR family | INS 363 (C>CAT) | GBFHJJIP_01215 | GBFHJJIP_01215 | HIGH | FV |
| ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV | |
| AB6 | TetR family | DEL 364 (182 nucleotides>C) | GBFHJJIP_01215 | GBFHJJIP_01215 | HIGH | FV |
| HP [domain cpo] | INS 155 (T>TGGACGTGGA) | GBFHJJIP_03384 | HMPREF0010_00495 | MOD | DII | |
| ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV | |
| AB7 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 1069 A>C/T357P SNP 1086 A>C/E362D | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| AB8 | HP [domain fadD] | SNP 192 T>G/H64Q | GBFHJJIP_03655 | D0CB89_ACIB2 | MOD | MV |
| AB9 | adeR | DEL (TCTCCACACTTA>T) | GBFHJJIP_02896_gene-GBFHJJIP_02897_gene | WP_000459542.1 | M/L | IR |
| TetR/AcrR family | SNP (T>C) | GBFHJJIP_02069_gene-CHR_END | GBFHJJIP_02069 | M/L | IR | |
| AB10 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 1069 A>C/T357P SNP 1086 A>C/E362D | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| AB11 | HP [domain fadD] | SNP 192 T>G/H64Q | GBFHJJIP_03655 | D0CB89_ACIB2 | MOD | MV |
| HP [domain GntR family] | SNP 197 T>C/I66T | GBFHJJIP_03660 | HMPREF0010_00945 | MOD | MV | |
| NET | ||||||
| Mutant | Gene | Mutation | Annotation (NCBI) | Reference (NCBI) | Impact | Type |
| AB12 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| AB13 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| AB14 | adeR–adeA | DEL (TCTCCACACTTA>T) | GBFHJJIP_02896_gene-GBFHJJIP_02897_gene | WP_000459542.1 | M/L | IR |
| TetR/AcrR family | SNP (A>G) | GBFHJJIP_02069_gene y CHR_END | GBFHJJIP_02069 | M/L | IR | |
| AB15 | TetR family | INS 512 (T>20 nucleotides) | GBFHJJIP_01215 | GBFHJJIP_01215 | HIGH | FV/S |
| HP [domain fadD] | SNP 192 T>G/H64Q | GBFHJJIP_03655 | D0CB89_ACIB2 | MOD | MV | |
| HP [domain GntR family] | SNP 197 T>C/I66T | GBFHJJIP_03660 | HMPREF0010_00945 | MOD | MV | |
| AB16 | TetR family | DEL 174 (18 nucleotides>A) | GBFHJJIP_01215 | GBFHJJIP_01215 | HIGH | FV |
| ATP-binding protein | SNP 865 G>A/A289T | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV | |
| AB17 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 1069 A>C/T357P | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| HP [domain GntR family] | SNP 197 T>C/I66T | GBFHJJIP_03660 | HMPREF0010_00945 | MOD | MV | |
| TetR family | INS 511 (T>TCTG) | GBFHJJIP_01215 | GBFHJJIP_01215 | HIGH | DII | |
| AB18 | adeR–adeA | DEL (TCTCCACACTTA>T) | GBFHJJIP_02896_gene-GBFHJJIP_02897_gene | WP_000459542.1 | M/L | IR |
| TetR/AcrR family | SNP (A>G) | GBFHJJIP_02069 | GBFHJJIP_02069 | M/L | IR | |
| AB19 | ATP-binding protein | SNP 1069 A>C/T357P | GBFHJJIP_03385 | WP_001207474.1 | MOD | MV |
| HP [domain fadD] | SNP 192 T>G/H64Q | GBFHJJIP_03655 | D0CB89_ACIB2 | MOD | MV | |
| AB20 | HP [domain fadD] | SNP 192 T>G/H64Q | GBFHJJIP_03655 | D0CB89_ACIB2 | MOD | MV |
| TetR/AcrR family | SNP (A>G) | GBFHJJIP_02069 | GBFHJJIP_02069 | M/L | IR | |
| adeR–adeA | DEL (TCTCCACACTTA>T) | GBFHJJIP_02896_gene-GBFHJJIP_02897_gene | WP_000459542.1 | M/L | IR | |
| HP [domain fadD] | SNP (A>G) | CHR_START/GBFHJJIP_03655 | GBFHJJIP_03655 | M/L | IR | |
| AB21 | TetR/AcrR family | SNP (T>C) | GBFHJJIP_02069 | GBFHJJIP_02069 | M/L | IR |
| HP [domain fadD] | SNP (A>C) | GBFHJJIP_03655 | D0CB89_ACIB2 | M/L | IR | |
| PA4642 family protein/tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase | INS (>CAATCAAATCA) | GBFHJJIP_01042_gene/GBFHJJIP_01043_gene | WP_001218560.1–WP_031969348.1 | M/L | IR | |
| adeR–adeA | DEL (TCTCCACACTTA>) | GBFHJJIP_02896_gene-GBFHJJIP_02897_gene | WP_000459542.1 | M/L | IR | |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aacC1 | 1: ATGGGCATCATTCGCACATGTAGG | 52 | 456 | [66] |
| 2: TTAGGTGGCGGTACTTGGGTC | ||||
| aacC2 | 1. ATTGATTCAGCAGGCCGAAC | 59 | 247 | [67] |
| 2: CTCTTGATGGTGCATGCCTC | ||||
| aacA4 | 1: TTGCGATGCTCTATGAGTGGCTA | 63 | 482 | [68] |
| 2: CTCGAATGCCTGGCGTGTTT | ||||
| aadA1 | 1: ATGAGGGAAGCGGTGATCG | 52 | 792 | [66] |
| 2: TTATTTGCCGACTACCTTGGTG | ||||
| aadB | 1: ATGGACACAACGCAGGTCGC | 55 | 534 | [66] |
| 2: TTAGGCCGCATATCGCGACC | ||||
| aphA6 | 1: ATGGAATTGCCCAATATTATTC | 55 | 797 | [66] |
| 2: TCAATTCAATTCATCAAGTTTTA | ||||
| aphA1 | 1: AAACGTCTTGCTCGAGGC | 56 | 461 | [68] |
| 2: CAAACCGTTATTCATTCGTGA | ||||
| adeB | 1: ATGTCACAATTTTTTATTCGTCGTC | 56 | 3104 | [69] |
| 2: TTAGGATGAGATTTTTTTCTTAGAGG | ||||
| adeJ | 1: CTGGCTTATGACACGACTC | 61 | 988 | [69] |
| 2: GGATCCCCATACCACGCTGG | ||||
| adeG | 1: GTTGCTCGTGTCGAACTTGC | 57 | 918 | [69] |
| 2: AGGAACGAAACCACCTGGAAC | ||||
| tetA | 1: GTAATTCTGAGGACTGTCGC | 55 | 950 | [16] |
| 2: CTGCCTGGACAACATTGCTT | ||||
| tetB | 1: TTGGTTAGGGGCAAGTTTTG | 56 | 659 | [16] |
| 2: GTAATGGGCCAATAACACCG | ||||
| adeB (RT-qPCR) | 1: CTGCTGTACCGGAGGTATCTGTT | 60 | ~60 | This study |
| 2: GCGCGAATTATCGGGTGTAA | ||||
| adeJ (RT-qPCR) | 1: AGGCGAATGGACGTATGGTT | 60 | ~60 | This study |
| 2: AACCGATGACACGCCGTTA | ||||
| adeG (RT-qPCR) | 1: CGCGACCGAAATTGTGAAT | 60 | ~60 | This study |
| 2: GATTGTACCCGCTGCAACCT | ||||
| gyrB (RT-qPCR) | 1: CTGCAGCAGAAACCCCTTCT | 60 | ~60 | This study |
| 2: ATAATGGCCGCGGTATTCC | ||||
| rpoB (RT-qPCR) | 1: TCCATTCCTTGAACACGATGAC | 60 | ~60 | This study |
| 2: CTGCCTGACGTTGCATGTTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roson-Calero, N.; Lucas, J.; Gomis-Font, M.A.; de Pedro-Jové, R.; Oliver, A.; Ballesté-Delpierre, C.; Vila, J. Cyclic Peptide MV6, an Aminoglycoside Efficacy Enhancer Against Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121147
Roson-Calero N, Lucas J, Gomis-Font MA, de Pedro-Jové R, Oliver A, Ballesté-Delpierre C, Vila J. Cyclic Peptide MV6, an Aminoglycoside Efficacy Enhancer Against Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(12):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121147
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoson-Calero, Natalia, Jimmy Lucas, María A. Gomis-Font, Roger de Pedro-Jové, Antonio Oliver, Clara Ballesté-Delpierre, and Jordi Vila. 2024. "Cyclic Peptide MV6, an Aminoglycoside Efficacy Enhancer Against Acinetobacter baumannii" Antibiotics 13, no. 12: 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121147
APA StyleRoson-Calero, N., Lucas, J., Gomis-Font, M. A., de Pedro-Jové, R., Oliver, A., Ballesté-Delpierre, C., & Vila, J. (2024). Cyclic Peptide MV6, an Aminoglycoside Efficacy Enhancer Against Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics, 13(12), 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121147








