Abstract
This study aimed to conduct a bioequivalence study of applying three pour-on ivermectin formulations at a dose of 1 mg/kg on the back of Korean native beef cattle (Hanwoo). To conduct bioequivalence testing, the pharmacokinetics of three groups (control Innovator, test Generic A, and test Generic B) of five clinically healthy Korean Hanwoo cattle (average weight 500 kg) were studied. After topical application to the skin, blood samples were drawn at the indicated times. These blood samples were analyzed using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The time required to reach the maximum concentration (Tmax), the maximum concentration (Cmax), and the area under the curve (AUClast) of each pharmacokinetic parameter were compared for bioequivalence. The results showed that the control had a Tmax of 41 ± 1.24 h, a Cmax of 0.11 ± 0.01 μg/mL, and an AUClast of 9.33 ± 0 h*μg/mL). The comparator Generic A had a Tmax of 40 ± 1.14 h, a Cmax of 0.10 ± 0.01 (μg/mL, and an AUClast of 9.41 ± 0.57 h*μg/mL, while Generic B had a Tmax of 40 ± 2.21 h, a Cmax of 0.10 ± 0.01 μg/mL, and an AUClast of 9 h*μg/mL. The values of the bioequivalence indicators Cmax, Tmax, and AUC were all within the range of 80% to 120%, confirming that all three tested formulations were bioequivalent. In conclusion, the study showed that the two generic products were bioequivalent to the original product in Hanwoo cattle.
1. Introduction
Ivermectin is a well-known drug that has received approval from both the US Food and Drug Administration and the World Health Organization for its use as an antiparasitic medication [1]. Ivermectin is a macrocyclic lactone with high endectocide efficacy against both internal and external parasites. It also exhibits long-lasting antiparasitic activity [2]. It is commonly employed in low- and middle-income nations to treat worm infections [3]. Over its more than 25 years of use, researchers have discovered that it possesses antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, thereby expanding its potential applications in medicine [4]. Ivermectin is readily available and cost-effective in many regions worldwide [5]. Among various anti-ectoparasitic drugs, it has been shown to be a beneficial medicine for managing cattle on pastures and acts as an effective tick repellent [6].
The pharmacokinetics of ivermectin have been reported in various animal species, including cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, horses, and dogs. Ali & Hennessy (1996) investigated the pharmacokinetic disposition and efficacy of ivermectin in sheep after administration of a feed mixture that contained it [7]. Echeverria et al. (1997) reported the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin after intravenous and subcutaneous administration in cattle [8]. Gonzalez et al. (2006) conducted a study on the pharmacokinetics of a new formulation of ivermectin in goats [9]. Craven et al. (2001) reported the pharmacokinetics of moxidectin and ivermectin after intravenous injection in pigs with different body compositions [10]. Gokbulut et al. (2001) investigated the plasma pharmacokinetics and fecal excretion of ivermectin, doramectin, and moxidectin after oral administration in horses [11]. Based on these reports, pharmacokinetic models can be used to indicate one or two compartments, depending on the route of administration and the formulation used. In addition, Lifschitz et al. (2004) performed a pharmacokinetic evaluation of four generic formulations in calves and found various pharmacokinetic parameters, including Cmax, Tmax, and AUC, in the aforementioned animal species [12]. These results suggest that the pharmacokinetic profile of ivermectin may be influenced by factors such as the body fat composition of the animal and the composition of the ivermectin formulation.
Hanwoo cattle, which are small-bodied, gradually maturing, and adaptable animals known for generating superbly flavored and marbled meat [13], are currently raised as beef cattle in South Korea and are an economic mainstay in the livestock industry [14]. Several ivermectin formulations have been used in veterinary drugs without any reports on its pharmacokinetics in Korean cattle [6]. For this reason, the availability of generic products is necessary, and establishing a bioequivalence assessment in Hanwoo cattle is important. Bioequivalence studies play a pivotal role in determining the therapeutic interchangeability of different medicinal products and have been conducted in various animal species [15,16].
Hanwoo cattle are primarily raised in South Korea, where their meat is highly prized. Therefore, drugs applied to these cattle are based on beef cattle. However, the unique physiological and metabolic characteristics of Hanwoo cattle have not been well studied. Unlike Holstein cattle, Hanwoo is a breed of small cattle that is native to Korea. Previously, they were used as raw livestock, although this has all but disappeared, and they are now primarily raised as a meat source. They have brown fur, while both males and females have horns. Their maternal qualities are good, yet they produce relatively little milk—less than 400 L over a 170-day lactation period [17]. Considering this knowledge gap, the present study aimed to explore bioequivalence based on the pharmacokinetic results for commercially available topical ivermectin formulations in Korean Hanwoo cattle. Potential differences in drug absorption, metabolism, distribution, and elimination of these products may play a key role in the decision-making process of veterinarians and livestock producers regarding drug application, dosage, and treatment [18].
For this purpose, this study was performed to obtain pharmacokinetic data for the original patented ivermectin product and two generic products (three top-selling ivermectin-containing pour-on medications) that are currently available in the Korean market for Hanwoo cattle. Each product was applied at the same dose using the same method of administration. Subsequently, using the obtained pharmacokinetic parameters, the bioequivalence of these existing three ivermectin products was determined in Korean Hanwoo cattle.
2. Results
2.1. Validation of Ivermectin Quantification Methods
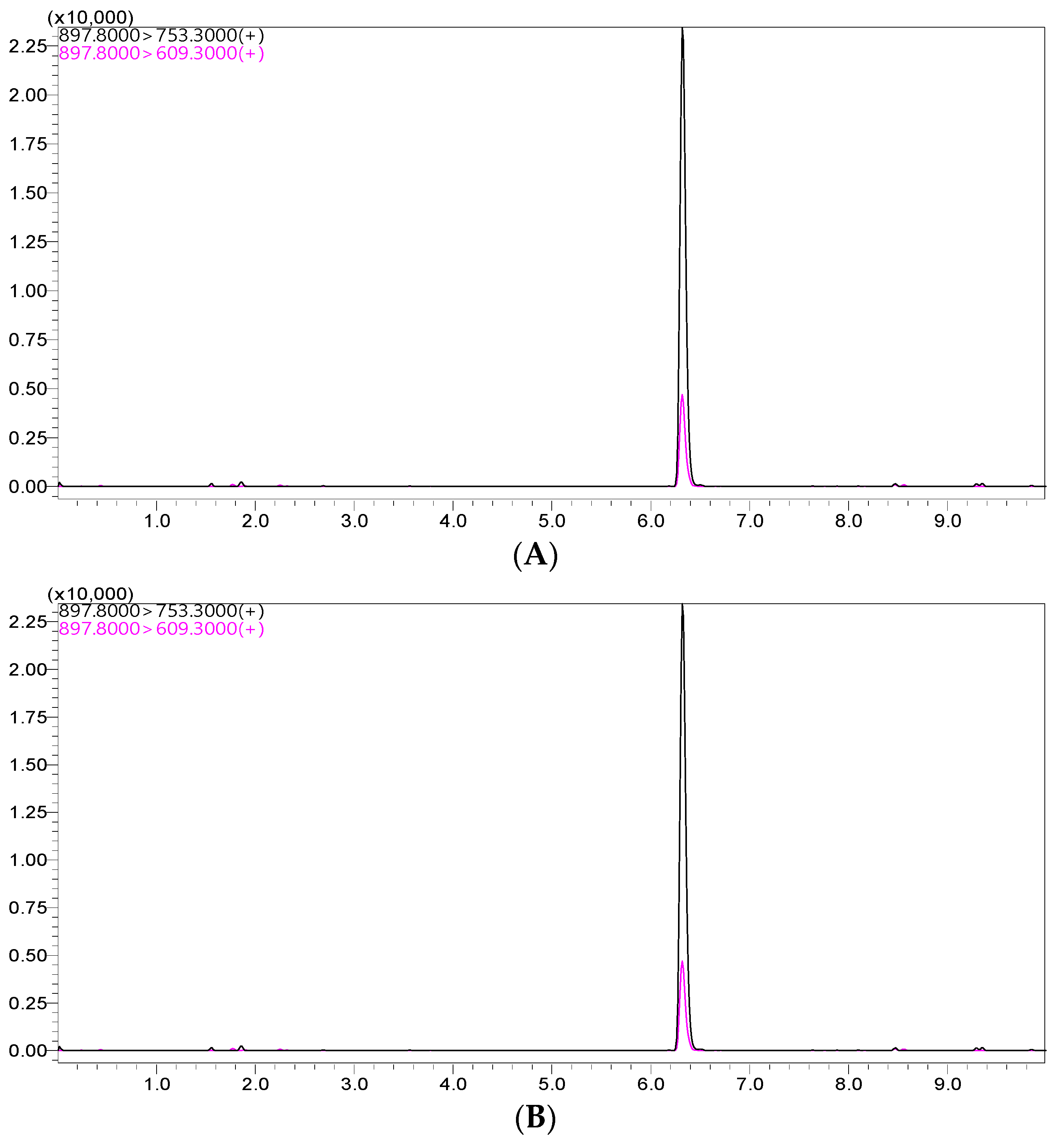
The peak for the ivermectin extracted from the standard solution was observed in the chromatogram at approximately 6.3 min, as shown in Figure 1. Using the optimized settings, the LC–MS/MS system showed an improved symmetric peak for ivermectin in both the standard solution and plasma matrix.
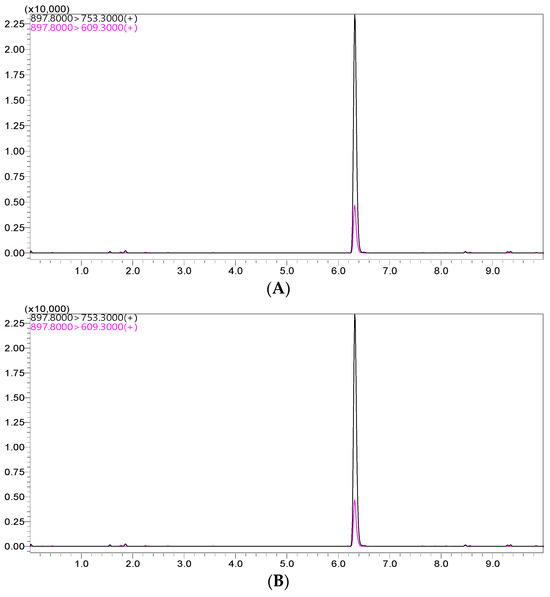
Figure 1.
Representative LC–MS/MS chromatograms for ivermectin from the spiked sample (A) and standard solutions (B).
Ivermectin was extracted quickly, efficiently, and simply using the optimized analytical technique. The LC–MS/MS analysis did not require derivatization, which is applied to reduce the analysis time. To assess the validity of the ivermectin concentration assay in plasma, its linearity, selectivity, accuracy, and precision were evaluated. These results are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Validation of an LC–MS/MS method for quantifying ivermectin in the plasma of cattle.
Linearity was assessed using a calibration curve derived from three different concentrations (25, 50, and 100 ng/mL) of a standard solution. As shown in Table 1, the analytical method demonstrated excellent linearity with the calibration curve, showing an r2 value greater than 0.99. The recovery and precision of ivermectin were evaluated at concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 ng/mL, with three replicates analyzed at each concentration level. The mean recovery of ivermectin was calculated at 98%, and the coefficient of variation percentage (CV) was less than 10%. The sensitivity of the method was determined by assessing the limits of detection (LOD) and limits of quantification (LOQ) values using the signal-to-noise ratio measurements. The analyte concentrations that corresponded to signal-to-noise ratio values of 3 and 10 were defined as the LOD and LOQ, respectively. Thus, the LOD and LOQ values for ivermectin were 3 and 10 ng/mL, respectively.
2.2. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Bioequivalence
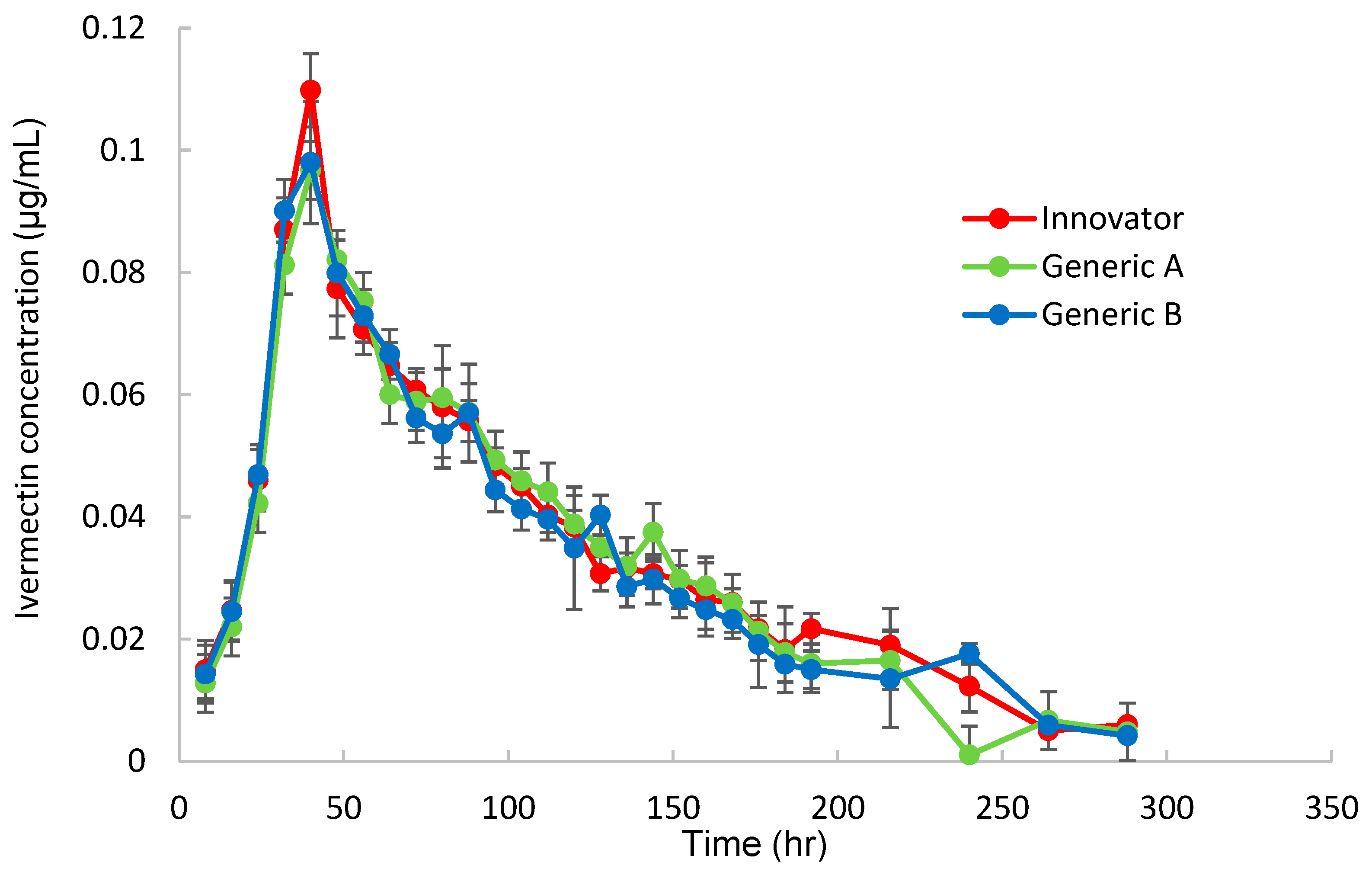
To obtain the pharmacokinetic parameters for Korean Hanwoo cattle, the plasma ivermectin concentration was measured over time after topical administration of three products (Innovator, Generic A, and Generic B) at a dose of 1 mg/kg, and the results are shown in Figure 2.
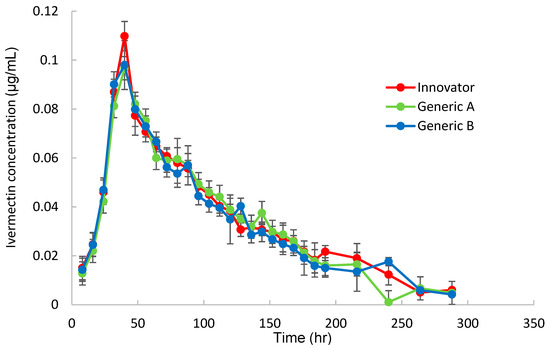
Figure 2.
Concentration(μg/mL)–time profiles for ivermectin in plasma following pour-on applying the control Innovator or test Generic A and Generic B ivermectin formulations to cattle.
As shown in Figure 3, all three products showed the same time–concentration changes, and the pharmacokinetics were calculated by non-compartmental analysis (NCA), as shown in Table 2.
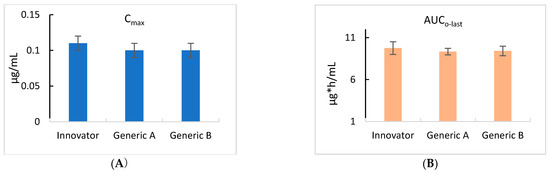
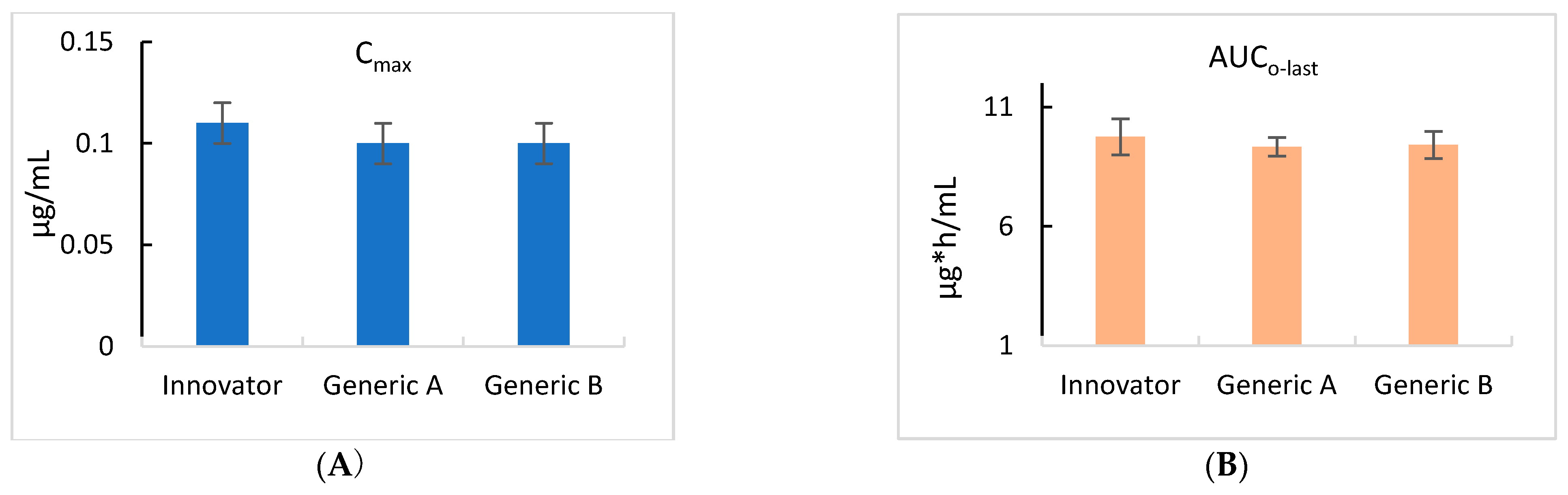
Figure 3.
Comparison of the maximum concentration (Cmax) (A) and the area under the curve to the last measurable concentration (AUClast) (B) in cattle for the control Innovator, Generic A, and Generic B ivermectin formulations. The values for Cmax and AUClast for each of the three products were identical and showed no statistically significant variations.

Table 2.
Main pharmacokinetic properties of patented and generic ivermectin formulations in cattle after pour-on administration at 1 mg/kg.bw.
Table 2 provides the pharmacokinetic parameters related to the pour-on applications of ivermectin. The Innovator, Generic A, and Generic B products showed ivermectin maximum concentrations (Cmax) of 0.11, 0.10, and 0.10 μg/mL, respectively. The area under the last observable plasma concentration-time curve (AUClast) following pour-on administration was 9.75 h*μg/mL, 9.33 h*μg/mL, and 9.41 h*μg/mL for the Innovator, Generic A, and Generic B products, respectively. The time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) was 40 h for each of the Innovator, Generic A, and Generic B products. To determine the differences in bioequivalence for the three formulations, the Cmax and AUC values are shown in Figure 3.
Pharmacokinetic analyses of the three formulations in this study showed that the Innovator, Generic A, and Generic B Cmax and AUC values were within the range of 80–120%, in the standard outlined in Article 17 (Evaluation) of the Regulations on Drug Equivalence Test Standards, previously established by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [19]. Thus, it was confirmed that all three products are bioequivalent.
3. Discussion
Ivermectin, a broad-spectrum parasiticide, is well-suited for sheep, and its pour-on formulation can efficiently and conveniently treat ectoparasitic infection [20]. Ivermectin has particularly antiparasitic effects against Ostertagia ostertagi and Cooperia oncophora. Moreover, ivermectin has antibacterial activity against Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycobacteria spp., as well as antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties [21]. For this reason, the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ivermectin have been studied in several animals [22]. Recently, Choi et al. (2019) studied the efficacy of ivermectin against Theieria orientalis infection in grazing cattle (Holstein cattle) [6]. From their study, ivermectin offered protection against Theieria orientalis and RBC hemolysis in cattle grazing in Korea, although no pharmacokinetic information was presented. Currently, ivermectin preparations are being used in Korean cattle, yet no information on the efficacy is available. Three ivermectin formulations are widely used in Korea as a topical pour-on method for ectoparasite control in native cattle, although there is no information on its pharmacokinetics.
An important procedure required to perform pharmacokinetic studies on ivermectin is to determine the low-level concentrations remaining in the blood after its administration to cattle. Analysis of ivermectin concentrations in the blood was performed by HPLC. When performing HPLC, fluorescence analysis was used after the derivatization of ivermectin to measure the low concentrations of the drug in the blood. Kitzman et al. (2006) used HPLC to analyze ivermectin levels in human plasma after administration, following the fluorescence induction of ivermectin by trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFAA) and N-methylimidazole (NMI) [23]. The results showed that the limit of quantitation (LOQ) for ivermectin in human plasma was 0.2 ng/mL, which was more than five times the baseline noise observed for the retention time of ivermectin. The coefficient of variation (n = 6) of the measured concentration at LOQ was 6.1%, and the deviation of the measured concentration from the mean and nominal value was 4.3%. However, this method is subject to losses occurring during the fluorescence induction process, so the use of liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), which extracts and analyzes the drug directly from plasma, may improve the accuracy of analyzing ivermectin in plasma. The analytical method is deemed linear when the correlation coefficient (r2) is greater than 0.9900 [24]. As per the criteria for developing and validating analytical methods, the precision (expressed as the coefficient of variation % CV) of the optimized LC–MS/MS method was within the accepted limits [25]. The meticulous methodology adhering to the standards set by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety serves as a guide for any subsequent investigations in this field [26].
Most reported that animal pharmacokinetics are based on intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and oral administrations. As a result, pharmacokinetic parameters following pour-on administration are rarely reported. In this study, we used the LC–MS/MS system, which holds the potential to provide quicker and more precise outcomes. The drug concentration curve in plasma after administering ivermectin to cattle at a dose of 1 mg/kg·bw is shown in Figure 2. Interestingly, the time–concentration curves for ivermectin in the blood after administering the three products tested were almost identical. Although bioequivalence studies for ivermectin exist in several animals, including cattle [27], there are no reports of such studies in Korean Hanwoo cattle. In this study, pharmacokinetics analysis was performed for the first time, and a bioequivalence assessment of three commercially available formulations was performed, ultimately confirming bioequivalence. Ivermectin has been the subject of many pharmacokinetic studies since its introduction in 1981 [28]. Depending on the species, oral, intramuscular (IM), subcutaneous (SC), or topical administration has been used.. Blood was collected after topical administration at the specified time and analyzed by LC–MS/MS to determine the plasma concentration, as shown in Figure 2. In cattle, the behavior of the drug in the body after intravenous and intramuscular injections of ivermectin showed a two-compartment model and a one-compartment model, respectively [29,30]. However, Lanusse et al. (1997) analyzed the two-compartment model [31]. Gayrard et al. (1999) analyzed the one-compartment model behavior in cattle after pour-on administration, which was consistent with the one-compartment behavior shown in this study [32]. Ivermectin has a Cmax of 0.022 μg/mL after intramuscular injection [29]. Subcutaneous administration, the most commonly used route of administration, reported a 6-fold difference in Cmax from a low of 0.022 μg/mL to a high of 0.133.2 μg/mL for the same formulation and different formulations [18,29,30]. This was thought to be due to differences in the HPLC methods, differences in the formulations, and the method of administration. Gayrard et al. (1999) reported a Cmax of 0.012 μg/mL and a Tmax of 81.6 h after administering ivermectin using the same topical application [31]. Compared to the pharmacokinetic parameters obtained, the Cmax was 10 times higher, and the Tmax was 2 times faster in this study. These differences were thought to be due to differences in the HPLC and LC/MS analytical methods, in addition to the loss of the drug in cattle experiments due to the habit of licking. However, this study was conducted using individual cages to prevent this. Therefore, in this study, a dose of 1 mg/kg was applied, which is twice as high as the previously used dose, considering the route of administration and previous Cmax results.
Bioequivalence studies are commonly performed following the guidelines proposed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for human pharmacokinetics studies [32]. A notable aspect of creativity emerges through the comparison of pharmacokinetics between the original Innovator product and two generic versions. Table 2 provides the pharmacokinetic parameters related to the pour-on applications of ivermectin. Several formulations of ivermectin were made and tested for bioequivalence after subcutaneous injection [15,18,28,29]. The results showed significant differences between the formulations. Lo et al. (1985) prepared an aqueous vehicle: aqueous–glycerol-formal vehicle (50:50, v/v) and a propylene–glycol:glycerol-formed vehicle (60:40, v/v) and compared them [18]. The results showed that the aqueous vehicle formulation tended to be the most bioavailable, with a bioavailability of 55%; however, the propylene–glycol:glycerol-formed vehicle formulation showed a steadily higher Cmax of 0.046 μg/mL [12,15,29]. In this study, no statistical differences were seen when comparing the pharmacokinetic parameters of the three formulations; however, the Innovator and Generic B formulations tended to exhibit a longer T1/2 and higher Vz/F than those observed for the Generic A formulation. These differences were likely since the Innovator and Generic B formulations contained the same concentration of propylene glycol, while the Generic A formulation excluded this ingredient. From these results, it can be inferred that propylene glycol may affect the critical T1/2 and Vz/F when applied topically (pour-on). All three formulations used in the present study were formulated in various fat-soluble solvents with or without propylene glycol. After topical application of these formulations at 1 mg/kg, all of them showed Cmax of 0.1–0.11 μg/mL, Tmax of 40 h, and AUClast of 9.33–9.75 h*μg/mL, while also being found to be bioequivalent. However, the effect of propylene glycol is not statistically significant in the study. Despite the result, additional studies on the formulations would be an urgent and important topic for further research.
In summary, the pharmacokinetic characteristics of three commercially available ivermectin products were determined by administering a 1 mg/kg dose to Hanwoo cattle using a pour-on method. The study revealed that the maximum concentration (Cmax), time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax), and area under the curve (AUC) of these three products are bioequivalent, falling within the 80–120% range. The research also emphasizes the importance of comparing the original patented ivermectin with two generic versions. Verifying their bioequivalence suggests that these less expensive generic options can be used reliably, offering cost savings without sacrificing treatment efficacy.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Media
- Ivermectin standard was provided by Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Acetonirile was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Formic acid was supplied by Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA, USA). All solvents used in the analysis were LC–MS grade. Purified water was obtained using a Milli-Q system (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA).
- Innovator (Formulation A, Group A): SY Himecin (Samyang Anipharm): Ingredients and amounts (out of 1 L of the main preparation): Ivermectin (5 g), isopropanol (794.9 mL), propylene glycol (8 g), isopropyl myristate (160 g), oleyl alcohol (32 mL), butylated hydroxytoluene (0.1 g), food blue no. 1 (appropriate amount). Usage and capacity: Apply 0.1 mL of the main product (0.5 mg as ivermectin) per kg of body weight as a single dermal application along the midline of the back.
- Generic A (Formulation B, Group B): Gmectin-Pour On (GREEN CROSS Veterinary Products): Ingredients and amounts (out of 1 mL of the main preparation): Ivermectin (5 mg), triethanolamine (0.5 mg), food blue no. 1(0.01 mg), diethylene glycol monoethyl ether, isopropyl myristate, isopropanol (appropriate amount). Usage and capacity: Dermal application of 1 mL of the product per 10 kg of body weight.
- Generic B (Formulation C, Group C): IMEC-Pouron (SF company): Ingredients and amounts (out of 1 L of the main preparation): Ivermectin (5 g), propylene glycol (8 g), isopropanol, isopropyl myristate, food blue no. 1 (appropriate amount). Usage and capacity: Apply 0.1 mL of vehicle (0.5 mg as ivermectin) per kg of body weight as a single dermal application along the midline of the back.
4.2. Animal Experimental Procedure and Treatments
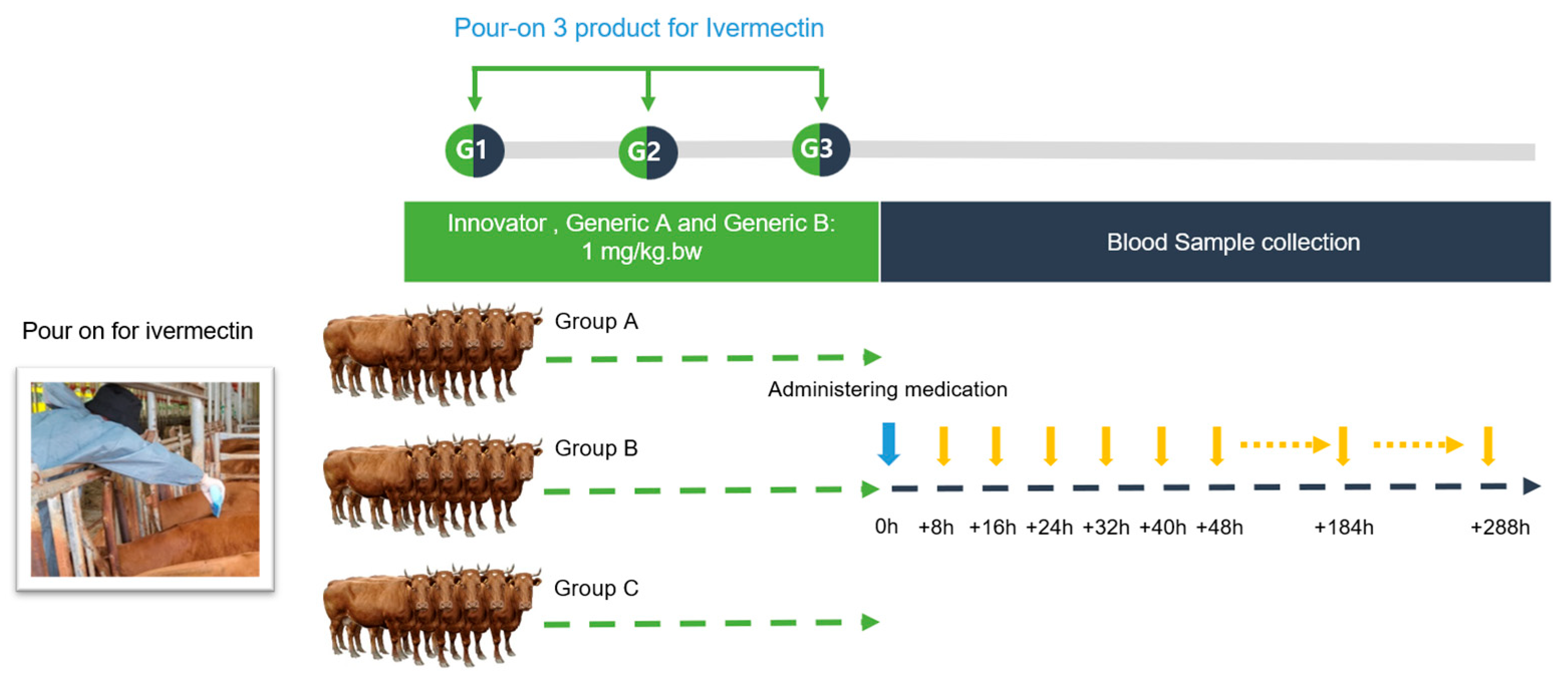
The Hanwoo experiment was conducted at the Korea Animal Testing Center (KULF), which specializes in preclinical and clinical trials. The animals were housed individually in an environment with a 12 h light/dark cycle. The ambient temperature was maintained at 25 to 28 °C. The animals had free access to food and water without restriction during the study. Fifteen male Hanwoo cattle weighing 500 ± 30 kg and aged between 18 and 20 months were randomly divided into 3 groups of 5 animals each and treated as described below.
Innovator (Formulation A, Group A): This group was treated with the ivermectin test formulation at a dose of 1 mg/kg per body weight. The pour-on solution was meticulously applied using a 1 L measuring cup. The application was along the topline of the cattle, forming a continuous slender strip stretching from the withers to the tail, as visually represented in Figure 4. This particular preparation was designated as the reference (Innovator) product for the study. Animals in the Generic A and B groups were administered the ivermectin test formulations using an identical methodology and dosage to those used in the Innovator group. For the purposes of this bioequivalence trial, the formulations given to the Generic A and B groups were categorized as the test products.
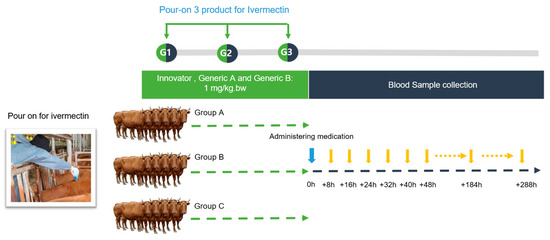
Figure 4.
Experimental design to determine how ivermectin formulations work on Korean Hanwoo cattle. Fifteen Korean beef cattle were randomly divided into three groups: Innovator (group A), Generic A (group B), and Generic B (group C). Ivermectin was applied in a continuous strip along the midline of the upper back to the tip of the tail. After application, the animals were individually housed to prevent the possibility of licking each other.
To mitigate any cross-contamination or interference, specifically the potential for animals to lick the formulations off of one another post-treatment, all cattle were securely housed in individual enclosures. The animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Korea (approval number: 2021-470) and was conducted in accordance with animal testing guidelines.
4.3. Collection and Processing of Blood Samples
Ivermectin was applied to each subject, and blood was collected and monitored for 12 days, followed by 7 days for abnormalities. Blood samples of 3 mL were taken from the jugular veins of each subject at intervals of 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96, 104, 112, 120, 128, 136, 144, 152, 160, 168, 176, 184, 192, 216, 240, 264, and 288 h using vacutainer heparin tubes (Becton Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). The blood samples were centrifuged at 2000× g for 10 min at 4 °C to obtain plasma samples. A total of 1.5 mL of 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile was added to 0.5 mL of plasma to collect plasma proteins. The mixtures were mixed for 20 min before being centrifuged at 5000× g for 30 min. Nitrogen was used to evaporate the supernatant fluid at 50 °C until the volume was reduced to 500 µL, after which the samples were kept in a 70 °C freezer.
4.4. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) Analysis
The ivermectin serum concentration was assayed using a Shimadzu LC-MS 8045 triple–quadrupole mass spectrometer outfitted with a Nexera X2 ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography system (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and connected to an electrospray ionization (ESI) interface. Chromatographic separation was performed using an Xbride BEH C18 column measuring 2.1 × 100 mm with a particle size of 2.5 μm (Waters, Milford, KS, USA) at 40 °C and a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min, with an injection volume of 2 μL. A gradient program for the mobile phase was set as follows: mobile phase A of 0.1% formic acid in distilled water and mobile phase B of 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile. A gradient program was used with a total run time of 10.00 min: 0.00–1.00 min at 10% B; 1.01–5.00 min at 95% B; 5.01–7.00 min at 95% B; 7.01–10.00 min at 10% B. Ionization was performed using an electrospray ionization source in positive mode. The MS/MS condition parameters were optimized as follows: interface temperature of 150 °C, heating gas flow of 10 L/min, DL temperature of 250 °C, heating block temperature of 400 °C, drying gas flow of 10 L/min, and nebulizing gas flow of 3 L/min. To quantify ivermectin, multiple reaction monitoring was performed. Chromatographic separation was performed using an Xbride BEH C18 column measuring 2.1 × 100 mm with a particle size of 2.5 μm (Waters, Milford, KS, USA) at 40 °C and a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min, with an injection volume of 2 μL.
4.5. Standard Solution Preparation
Ivermectin was accurately weighed and transferred to a volumetric flask, where it was dissolved in methanol (MeOH) to yield a stock solution with a concentration of 1.0 mg/mL. This solution was stored in a polypropylene tube, kept at a temperature of 4 °C, and sealed in bottles until needed. A working solution was prepared by diluting the stock solution with more methanol to attain the desired concentration.
4.6. Validation of Ivermectin Quantification Methods
The specificity of the ivermectin quantification method was evaluated using a standard ivermectin solution, a known amount of ivermectin in bovine plasma, and untreated bovine plasma. This was to determine if any interference from the matrix occurred at the ivermectin retention time. Ivermectin was dissolved in 0.1% aqueous formic acid to produce a 1 mg/mL stock solution. This solution was further diluted to generate various standard ivermectin solutions. To create ivermectin-spiked plasma samples at concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 ng/mL, different volumes of the ivermectin solutions were added to the plasma of untreated cows. All samples were filtered using a 0.2 µm polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) syringe filter for LC–MS/MS analysis. Each sample was analyzed three times, and the ivermectin concentrations were measured by LC–MS/MS following sample injection.
4.7. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Bioequivalence
The concentration–time profiles acquired from the plasma of individual animals were subjected to analysis using the WinNonlin software (Version 6.1), developed by Statistical Consultants Inc. (Lexington, KY, USA). Non-compartmental analysis (NCA) was employed to assess the pharmacokinetic parameters of each animal. The use of NCA allowed the determination of key pharmacokinetic parameters. In addition, the analysis included the determination of each maximum plasmatic ivermectin concentration (Cmax) and the corresponding time required to reach the peak value (Tmax). The terminal-phase disposition rate constant (λ) was estimated through a least-squares linear regression of the natural log-transformed ivermectin concentrations over time. Subsequently, the half-life (T1/2) was calculated using the formula: t1/2 = 0.693/λ.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
The results are represented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) derived from three repeated examinations. Statistical analyses were conducted using the F-test and one-way ANOVA. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. In the assessment of bioequivalence between formulations, a 90% confidence interval approach using ANOVA on logarithmically transformed data was adopted. This analysis accounts for the sequence, subject variability, period, and formulation as fixed effects, while non-parametric methods are deemed unsuitable for this evaluation [25].
5. Conclusions
This study characterized the pharmacokinetics of a patented brand of pour-on ivermectin (Innovator), an antiparasitic, after application to Hanwoo cattle. In addition, two generic formulations (Generic A and Generic B) of ivermectin were prepared and tested for bioequivalence in order to expand its application in Hanwoo cattle. As a result, the AUC and Cmax values of all three formulations tested in beef cattle showed the same levels, confirming their bioequivalence according to the ‘Guideline for Bioequivalence Testing of Veterinary Drugs’. In conclusion, the pharmacokinetic parameters, Cmax, AUC, and Tmax of the three products were compared after applying the same dosages to the skin of Korean beef cattle, and they were all in the range of 80–120%, confirming that all three products are bioequivalent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K.; methodology, S.K., H.C., E.-B.L., G.L. and J.K.; formal analysis, S.K., H.C., E.-B.L. and G.L.; investigation, J.K., H.C. and S.K.; resources, J.K.; data curation, J.K., S.K., H.C., E.-B.L., G.L. and S.-C.P.; validation, S.K., G.L. and S.-C.P., writing—original draft preparation, S.K., H.C. and E.-B.L.; writing—review and editing, J.K. and S.-C.P.; project administration, J.K.; funding acquisition, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by veterinary science research project grants from the Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Republic of Korea (B-1543073-24-01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures performed in this study were approved by the ethics committee of the Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Republic of Korea (2021-470).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated for this study are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the laboratory personnel of the Veterinary Drugs and Biologics Division, Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- The Blue Book Marketing Authorization of Pharmaceutical Products with Special Reference to Multisource (Generic) Products; Manual for Natinal Medicines Regulatory Authorities (NMRAs); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–148.
- Sarli, M.; Miró, M.V.; Rossner, M.V.; Nava, S.; Lifschitz, A. Successive Treatments with Ivermectin (3.15%) to Control the Tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) Microplus in Cattle: Pharmacokinetic and Efficacy Assessment. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrows, N.J.; Campos, R.K.; Powell, S.T.; Prasanth, K.R.; Schott-Lerner, G.; Soto-Acosta, R.; Galarza-Muñoz, G.; McGrath, E.L.; Urrabaz-Garza, R.; Gao, J. A Screen of FDA-Approved Drugs for Inhibitors of Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircik, L.H.; Del Rosso, J.Q.; Layton, A.M.; Schauber, J. Over 25 Years of Clinical Experience with Ivermectin: An Overview of Safety for an Increasing Number of Indications. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15, 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, K.; Nandy, M.; Dalai, C.K.; Ahmed, S.N.; Res, D.; West, T.; Bengal, W.; Kolkata, H.; Kolkata, H.; Bengal, W.; et al. The Battle against COVID 19 Pandemic: What We Need to Know Before We “Test Fir” Ivermectin. Drug Res. 2020, 70, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Chae, J.B.; Kim, S.; Yu, D.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, B.K.; Chae, J.S.; Choi, K.S. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Ivermectin against Theileria Orientalis Infection in Grazing Cattle. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.N.; Hennessy, D.R. The Effect of Level of Feed Intake on the Pharmacokinetic Disposition of Oxfendazole in Sheep. Int. J. Parasitol. 1995, 25, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverrı´a, J.; Mestorino, N.; Giorgieri, S.; Turic, E.; Alt, M.; Errecalde, J. Pharmacokinetics of Ivermectin after Its Intravenous and Subcutaneous Administration to Cattle. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 20, 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Sahagun, A.M.; Diez, M.J.; Fernandez, N.; Sierra, M.; Garcia, J.J. Pharmacokinetics of a Novel Formulation of Ivermectin after Administration to Goats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, J.; Bjørn, H.; Hennessy, D.; Friis, C.; Nansen, P. Pharmacokinetics of Moxidectin and Ivermectin Following Intravenous Injection in Pigs with Different Body Compositions. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 24, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokbulut, C.; Nolan, A.M.; Mckellar, Q.A. Plasma Pharmacokinetics and Faecal Excretion of Ivermectin, Doramectin and Moxidectin Following Oral Administration in Horses. Equine Vet. J. 2001, 33, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifschitz, A.; Sallovitz, J.; Imperiale, F.; Pis, A.; Jauregui Lorda, J.; Lanusse, C. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Four Ivermectin Generic Formulations in Calves. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 119, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.-W. The Korean Hanwoo Beef Cattle. Anim. Genet. Resour. Inf. 1994, 14, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, J.; Park, B.Y.; Seong, P.N.; Kang, G.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, S.G.; Im, S.K.; Kim, D. Assessment of Meat Quality Properties and Development of a Palatability Prediction Model for Korean Hanwoo Steer Beef. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lifschitz, A.; Pis, A.; Alvarez, L.; Virkel, G.; Sanchez, S.; Sallovitz, J.; Kujanek, R.; Lanusse, C. Bioequivalence of Ivermectin Formulations in Pigs and Cattle. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 22, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robaina, D.M.; Alvariza, S.; Suárez, G. Bioequivalence of Two Novel Formulations of Ivermectin 1% Combined with Fluazuron 12.5% for Subcutaneous Administration in Cattle. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2021, 9, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breed Data Sheet: Hanwoo/Republic of Korea; Domestic Animal Diversity Information System of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Anyang, Republic of Korea. Available online: https://www.fao.org/dad-is/browse-by-country-and-species/en/ (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Albert Lo, P.K.; Fink, D.W.; Williams, J.B.; Blodinger, J. Pharmacokinetic Studies of Ivermectin: Effects of Formulation. Vet. Res. Commun. 1985, 9, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard on Pharmaceutical Equivalence Study, The Ministry of Foodand Drug Safety Notice No.2021-91, 22 September 2020 Partially Amended on 11 November 2021 and Enforced on 12 November 2021. Available online: https://www.mfds.go.kr/eng/brd/m_18/view.do?seq=71525 (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Piras, C.; Gugliandolo, E.; Castagna, F.; Palma, E.; Britti, D. Ivermectin (IVM) Possible Side Activities and Implications in Antimicrobial Resistance and Animal Welfare: The Authors’ Perspective. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cao, X.; Liao, J.; Wei, Y. Pharmacokinetics of Tenvermectin in Swine, a Novel Antiparasitic Drug Candidate—Comparison with Ivermectin. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 1011, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzman, D.; Wei, S.Y.; Fleckenstein, L. Liquid Chromatographic Assay of Ivermectin in Human Plasma for Application to Clinical Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, P.; Procajło, Z.; Wolska, J.; Jaroszewski, J.J.; Ziółkowski, H. Development, Validation, and Application of the LC-MS/MS Method for Determination of 4-Acetamidobenzoic Acid in Pharmacokinetic Pilot Studies in Pigs. Molecules 2021, 26, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Chaudhry, U.; Raza, A.; Ghosh, D.; Zhao, X. In Vitro Activity of Ivermectin against Staphylococcus Aureus Clinical Isolates. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products Guidelines for the Conduct of Bioequivalence Studies for Veterinary Medicinal Products Approval by Efficacy Working Party; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021.
- González Canga, A.; Sahagún Prieto, A.M.; José Diez Liébana, M.; Martínez, N.F.; Vega, M.S.; Vieitez, J.J.G. The Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Ivermectin in Domestic Animal Species. Vet. J. 2009, 179, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez, M.; Schcolnik-Cabrera, A.; Dueñas-Gonzalez, A. The Multitargeted Drug Ivermectin: From an Antiparasitic Agent to a Repositioned Cancer Drug. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bousquet-Mélou, A.; Mercadier, S.; Alvinerie, M.; Toutain, P.-L. Endectocide Exchanges between Grazing Cattle after Pour-on Administration of Doramectin, Ivermectin and Moxidectin. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifschitz, A.; Virkel, G.; Pis, A.; Imperiale, F.; Sanchez, S.; Alvarez, L.; Kujanek, R.; Lanusse, C. Ivermectin Disposition Kinetics after Subcutaneous and Intramuscular Administration of an Oil-Based Formulation to Cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 86, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanusse, C.; Lifschitz, A.; Virkel, G.; Alvarez, L.; Sánchez, S.; Sutra, J.F.; Galtier, P.; Alvinerie, M. Comparative Plasma Disposition Kinetics of Ivermectin, Moxidectin and Doramectin in Cattle. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 20, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayrard, V.; Alvinerie, M.; Toutain, P.L. Comparison of Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Doramectin and Ivermectin Pour-on Formulations in Cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 81, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, X.Y.; Li, B.V. FDA Bioequivalence Standards; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 13, ISBN 978-1-4939-1251-3. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).