Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Genetic Determinants in Gram-Negative Fecal-Microbiota of Wild Birds and Chicken Originated at Trimmu Barrage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Prevalence of ESBL-Producing Bacteria and Genetic Determinants in Bird Species
2.2. Diversity of ESBL-Producing Bacteria
2.3. Genetic Determinants Detected in Different ESBL-Producing Bacteria
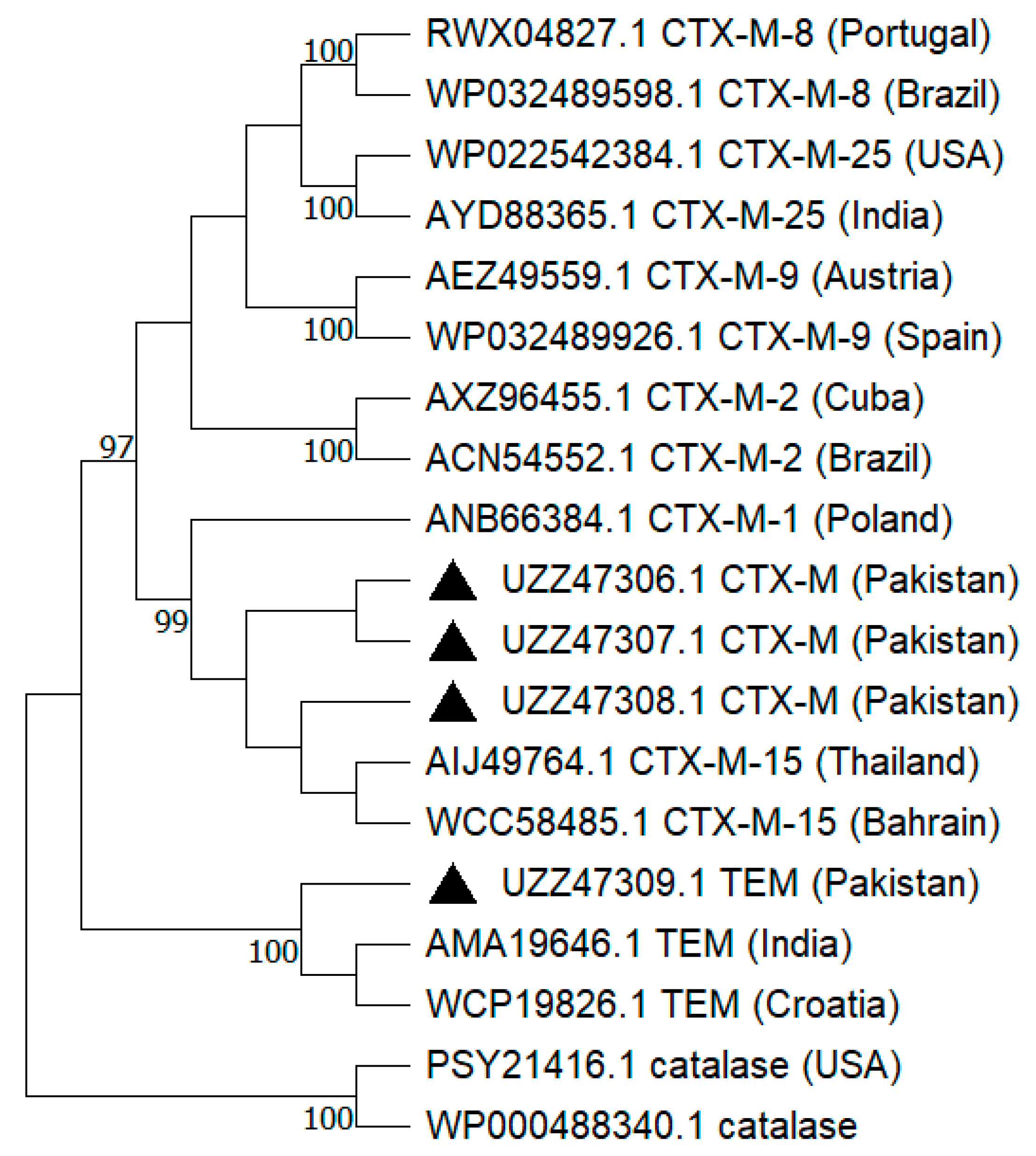
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Pooled Fecal Material
4.2. Isolation and Confirmation of ESBL-Producing Bacteria
4.3. Molecular Identification of ESBL-Producing Bacteria and Detection of Genetic Determinants of β-Lactamase Associated Genes
4.4. Sequencing of PCR Amplicons and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perestrelo, S.; Amaro, A.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Clemente, L.; Duarte, A.S.R.; Kaesbohrer, A.; Karpiskova, R.; Lopez-Chavarrias, V.; Morris, D.; Prendergast, D.; et al. Building an international One Health strain level database to characterise the epidemiology of AMR threats: ESBL-AmpC producing E. coli as an example-challenges and perspectives. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Ochomogo, M.; Lohans, C.T. beta-Lactam antibiotic targets and resistance mechanisms: From covalent inhibitors to substrates. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, M.; Simner, P.J.; Bradford, P.A. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases: An update on their characteristics, epidemiology and detection. JAC-Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, R.; Husin, S.A.; Ahmad, N.; Bahari, N.; Abu, N.; Ali, R.M.; Hashim, N.H.F.; Ramasamy, P.; Saberi, M.R.H.; Laine, L.Y.; et al. Tricycle Project—One Health approach: Whole genome sequencing(WGS) of Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Eschericia (E.) coli derived from human, food chain and environment. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 116, S105–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Shimoda, S.; Shimono, N. Current epidemiology, genetic evolution and clinical impact of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 61, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame-Korevaar, A.; Fischer, E.A.J.; van der Goot, J.; Stegeman, A.; Mevius, D. Transmission routes of ESBL/pAmpC producing bacteria in the broiler production pyramid, a literature review. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 162, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castronovo, C.; Agozzino, V.; Schirò, G.; Mira, F.; Di Bella, S.; Lastra, A.; Antoci, F.; Pennisi, M.; Giudice, E.; Guercio, A. Evaluation of the antimicrobial resistance of different serotypes of Salmonella enterica from livestock farms in Southern Italy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Martinez, J.L. Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from One Health and Global Health perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala, L.; Alonso, C.A.; Simon, C.; Gonzalez-Esteban, C.; Oros, J.; Rezusta, A.; Ortega, C.; Torres, C. Wild birds, Frequent carriers of extended-spectrum beta-Lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli of CTX-M and SHV-12 types. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.; Gremillet, D.; Afan, I.; Miranda, F.; Bouten, W.; Forero, M.G.; Figuerola, J. Pathogen transmission risk by opportunistic gulls moving across human landscapes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, M.; Guamparito, C.; Diaz, S.; Olave, A.; Guerrero, K.; Canton, R.; Baquero, F.; Gahona, J.; Valenzuela, N.; et al. Molecular characterization and genetic diversity of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli colonizing the migratory Franklin’s gulls (Leucophaeus pipixcan) in Antofagasta, North of Chile. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeballos-Gross, D.; Rojas-Sereno, Z.; Salgado-Caxito, M.; Poeta, P.; Torres, C.; Benavides, J.A. The role of Gulls as reservoirs of antibiotic resistance in aquatic environments: A scoping review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 703886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Rao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K. Evidence for environmental dissemination of antibiotic resistance mediated by wild birds. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.; Rahman, S.; Jan, A.T.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Mondal, A.H.; Haq, Q.M.R. Antibiotics, resistome and resistance mechanisms: A bacterial perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, S.; Zaib-un-Nisa. Diversity of Avifauna of Trimmu Barrage, District Jhang, Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2009, 41, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.P.; Minichino, A.; Gargiulo, A.; Varriale, L.; Borrelli, L.; Pace, A.; Santaniello, A.; Pompameo, M.; Fioretti, A.; Dipineto, L. Prevalence and phenotypic antimicrobial resistance among ESKAPE bacteria and Enterobacterales strains in wild birds. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.F.; Schmitt, H.; Borjesson, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Stehling, E.G.; Boerlin, P.; Topp, E.; Jardine, C.; Li, X.W.; Li, B.; et al. The potential of using E. coli as an indicator for the surveillance of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, M.; Tahir, M.F.; Ullah, R.W.; Ali, J.; Siddique, N.; Rasheed, A.; Akram, M.; Zaheer, M.U.; Mohsin, M. Quantification and trends of antimicrobial use in commercial broiler chicken production in Pakistan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Saleemi, M.K.; Umair, M.; Naseem, M.N.; He, C.; Khan, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Excessive use of medically important antimicrobials in food animals in Pakistan: A five-year surveillance survey. Glob. Health Action 2019, 12, 1697541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do V. Barroso, M.; da Silva, J.S.; Moreira, S.M.; Sabino, Y.N.; Rocha, G.C.; Moreira, M.A.; Bazzolli, D.M.; Mantovani, H.C. Selection of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteria in weaned pigs and its association with in-feed subtherapeutic combination of colistin and tylosin. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechesso, A.F.; Park, S. Tylosin exposure reduces the susceptibility of Salmonella Typhimurium to florfenicol and tetracycline. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, S.; Hussain, S.; Khan, R.A.; Ul Ain, N.; Haider, H.; Riaz, S. Prevalence of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: First systematic meta-analysis report from Pakistan. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Rehman, T.A.U.; Irshad, H.; Shahzad, M.A.; Siddique, A.; Jamil, A.; Ali, A. Antibiotic resistance pattern and molecular detection of ESBL-associated genes in E. coli from surface and wastewater of Islamabad capital territory, Pakistan. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, L.; Ibrar, K.; Sadiq, A.; Hamid, A.K.; Ullah, M.; Noor, R. Extended spectrum beta lactamases-producing Escherichia coli in retail chicken meat from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Arshed, M.J.; Qamar, M.U.; Aslam, B.; Almatroudi, A.; Khurshid, M. The Escherichia coli sequence type 131 harboring extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and carbapenemases genes from poultry birds. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, Z.; Khan, I.; Azam, S.; Anwar, Y.; Althubaiti, E.H.; Maroof, L. Isolation and molecular characterization of extended spectrum beta lactamase producing Escherichia coli from chicken meat in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, T.; Oueslati, S.; Bonnin, R.A.; Dabos, M.L.; Zavala, A.; Dortet, L.; Retailleau, P.; Iorga, B.I. Beta-lactamase database (BLDB)—structure and function. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagar, S.; Qambrani, N.A. Bacteriological quality assessment of poultry chicken meat and meat contact surfaces for the presence of targeted bacteria and determination of antibiotic resistance of Salmonella spp. in Pakistan. Food Control 2023, 151, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Sobur, M.A.; Rahman, S.; Ballah, F.M.; Ievy, S.; Siddique, M.P.; Rahman, M.; Kafi, M.A.; Rahman, M.T. Detection of bla(TEM), bla(CTX-M), bla(CMY), and bla(SHV) genes among extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolated from migratory birds travelling to Bangladesh. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fashae, K.; Engelmann, I.; Monecke, S.; Braun, S.D.; Ehricht, R. Molecular characterisation of extended-spectrum ss-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in wild birds and cattle, Ibadan, Nigeria. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Yahia, H.; Chairat, S.; Gharsa, H.; Alonso, C.A.; Ben Sallem, R.; Porres-Osante, N.; Hamdi, N.; Torres, C.; Ben Slama, K. First report of KPC-2 and KPC-3-producing Enterobacteriaceae in wild birds in Africa. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 79, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasakopoulou, Z.; Diezel, C.; Braun, S.D.; Sofia, M.; Giannakopoulos, A.; Monecke, S.; Gary, D.; Krahmer, D.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Touloudi, A.; et al. Occurrence and characteristics of ESBL- and carbapenemase- producing Escherichia coli from wild and feral birds in Greece. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.H.; Lv, X.; Han, B.; Gu, X.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; He, Z. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates in surface water of Taihu Lake Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 11412–11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, R.; Maqsood, A.; Baig, A.; Pande, C.B.; Zahra, S.M.; Saad, A.; Anwar, M.; Singh, S.K. A comprehensive review on water pollution, South Asia Region: Pakistan. Urban. Clim. 2023, 48, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N.; Shahbaz, M. Heavy metals in eggshells of cattle egret (Bubulcus ibis) and little egret (Egretta garzetta) from the Punjab province, Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 89, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tausova, D.; Dolejska, M.; Cizek, A.; Hanusova, L.; Hrusakova, J.; Svoboda, O.; Camlik, G.; Literak, I. Escherichia coli with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in great cormorants and mallards in Central Europe. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osińska, M.; Nowakiewicz, A.; Zięba, P.; Gnat, S.; Łagowski, D.; Trościańczyk, A. A rich mosaic of resistance in extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolated from red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Poland as a potential effect of increasing synanthropization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Alam, S.; Kabir, M.; Fazal, S.; Khurshid, A.; Iqbal, A.; Khan, M.M.; Khan, W.; Qayyum, A.; Hussain, M. Migratory birds as the vehicle of transmission of multi drug resistant extended spectrum β lactamase producing Escherichia fergusonii, an emerging zoonotic pathogen. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessman, J.; Atterby, C.; Olsen, B.; Jarhult, J.D. High prevalence and temporal variation of extended spectrum beta-lactamase-producing bacteria in urban Swedish Mallards. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.; Mohsin, M.; Madni, W.A.; Sarwar, F.; Saqib, M.; Aslam, B. First Report of bla (CTX-M-15)-Type ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in wild migratory birds in Pakistan. Ecohealth 2017, 14, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picão, R.C.; Poirel, L.; Gales, A.C.; Nordmann, P. Further identification of CTX-M-2 extended-spectrum β-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.M.; Stegger, M.; Aziz, M.; Johnson, T.J.; Waits, K.; Nordstrom, L.; Gauld, L.; Weaver, B.; Rolland, D.; Statham, S. Escherichia coli ST131-H 22 as a Foodborne Uropathogen. MBio 2018, 9, e00470-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, M.; Raza, S.; Schaufler, K.; Roschanski, N.; Sarwar, F.; Semmler, T.; Schierack, P.; Guenther, S. High prevalence of CTX-M-15-type ESBL-producing E. coli from migratory avian species in Pakistan. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwich, L.; Vidal, A.; Seminati, C.; Albamonte, A.; Casado, A.; Lopez, F.; Molina-Lopez, R.A.; Migura-Garcia, L. High prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and emergence of OXA-48 producing Enterobacterales in wildlife in Catalonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Tang, M.; Yang, Y. The avian gut microbiota: Diversity, influencing factors, and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 934272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimbach, A.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt, U. E. coli as an All-Rounder: The thin line between commensalism and pathogenicity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 358, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.D.; Zhao, S.Y.; Wu, H.; Hu, G.Z.; Zhao, J.F.; Zong, Z.Y.; Pan, Y.S. Antimicrobial resistance-encoding plasmid clusters with heterogeneous MDR regions driven by IS 26 in a single Escherichia coli isolate. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; CLSI Supplement M100-S25; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Monstein, H.J.; Ostholm-Balkhed, A.; Nilsson, M.V.; Nilsson, M.; Dornbusch, K.; Nilsson, L.E. Multiplex PCR amplification assay for the detection of blaSHV, blaTEM and blaCTX-M genes in Enterobacteriaceae. APMIS 2007, 115, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coculescu, B.; Palade, A.; Delcaru, C.; Coculescu, E.C. Genetic analysis of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains producing extended-spectrum B-lactamases (ESBL) associated with diarrhea in romanian pediatric patients. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 21, 11393–11403. [Google Scholar]
- Uysal, A.; Gunes, E.; Arslan, E.; Durak, Y. Characterization of uropathogenic Escherichia coli stains: Antibiotic resistance patterns, detection of Esbl genes and interactions by lytic phages. Fresenius Environ. Bullet. 2018, 27, 402–414. [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, K.R.; Atchley, W.R. Separation of phylogenetic and functional associations in biological sequences by using the parametric bootstrap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3288–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bird Species | Total ESBL n (%) | ESBL Gene/Gene Combinations Identified | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaCTX-M n (%) | blaTEM n (%) | blaSHV n (%) | blaOXA n (%) | blaCTX-M + blaTEM n (%) | blaCTX-M + blaSHV n (%) | blaTEM + blaOXA n (%) | ||
| Cattle egret (Bubulcus ibis) | 17 (24.3) | 11 (64.7) | 3 (17.7) | 1 (5.9) | - | 2 (11.8) | - | - |
| Little egret (Egretta garzetta) | 29 (41.4) | 18 (62.1) | 5 (17.2) | 1 (3.5) | 4 (13.8) | - | 1 (3.5) | - |
| Common teal (Anas crecca) | 20 (28.6) | 5 (25) | 8 (4) | - | - | 5 (25) | - | 2 (10) |
| Chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) | 31 (44.3) | 16 (51.6) | 4 (12.9) | - | 2 (6.5) | 9 (29) | - | - |
| Total number | 97 (34.6) | 50 (51.6) | 20 (20.6) | 2 (2.1) | 6 (6.2) | 16 (16.5) | 1 (1) | 2 (2.1) |
| Bird Species | No. of Samples | ESBL Bacterian (%) | E. coli n (%) | E. cloacae n (%) | K. pneumoniae n (%) | S. enterica n (%) | P. aeruginosa n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle egret (Bubulcus ibis) | 70 | 17 (24.3%) | 12 (12.37%) | 4 (4.12%) | 0 | 1 (1.03%) | 0 |
| Little egret (Egretta garzetta) | 70 | 29 (41.4%) | 24 (24.74%) | 1 (1.03%) | 2 (2.06%) | 1 (1.03%) | 1 (1.03%) |
| Common teal (Anas crecca) | 70 | 20 (28.6%) | 16 (16.49%) | 3 (3.09%) | 1 (1.03%) | 0 | 0 |
| Chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) | 70 | 31 (44.3%) | 20 (20.62%) | 3 (3.09%) | 5 (5.15%) | 2 (2.06%) | 1 (1.03%) |
| Total number | 280 | 97 (34.6%) | 72 (74.2%) | 11 (11.3%) | 8 (8.3%) | 4(4.1%) | 2 (2.1%) |
| Bacterial Species | Total ESBL n (%) | ESBL Gene/Gene Combinations Identified | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaCTX-M n (%) | blaTEM n (%) | blaSHV n (%) | blaOXA n (%) | blaCTX-M + blaTEM n (%) | blaCTX-M + blaSHV n (%) | blaTEM + blaOXA n (%) | ||
| Escherichia coli | 72 (74.2%) | 38 (52.8%) | 14 (19.5%) | 2 (2.8%) | 5 (6.9%) | 13 (18.1%) | 0 | 0 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 11 (11.3%) | 6 (54.5%) | 4 (36.4%) | 0 | 1 (9.1%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 8 (8.3%) | 3 (37.5%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (37.5%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1 (12.5%) |
| Salmonella enterica | 4 (4.1%) | 2 (50%) | 1 (25%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (25%) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 2 (2.1%) | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total number | 97 (34.6%) | 50 (51.55%) | 20 (20.6%) | 2 (2.06%) | 6 (6.2%) | 16 (16.5%) | 1 (1.03%) | 2 (2.1%) |
| Antibiotic | E. cloacae (n = 11) | K. pneumoniae (n = 8) | S. enterica (n = 4) | P. aeruginosa (n = 2) | E. coli (n = 72) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | S | I | R | S | I | R | S | I | R | S | I | R | S | I | |
| n (%) | |||||||||||||||
| Streptomycin | 1 (9) | 10 (90.9) | 0 | 2 (25) | 6 (75) | 0 | 2 (50) | 2 (50) | 0 | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 0 | 3 (4.16) | 69 (95.8) | 0 |
| Neomycin | 2 (18.2) | 8 (72.7) | 1 (9) | 1 (12.5) | 6 (75) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (25) | 3 (75) | 0 | 0 | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 21 (29.2) | 46 (63.9) | 5 (6.9) |
| Gentamicin | 0 | 11 (100) | 0 | 3 (37.5) | 3 (37.5) | 2 (25) | 1 (25) | 3 (75) | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 12 (16.7) | 55 (76.4) | 5 (6.9) |
| Florfenicol | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) | 0 | 2 (25) | 6 (75) | 0 | 0 | 4 (100) | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 7 (9.7) | 61 (84.7) | 4 (5.6) |
| Ceftiofur | 6 (54.5) | 5 (45.5) | 0 | 4 (50) | 3 (37.5) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (50) | 2 (50) | 0 | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 0 | 64 (88.9) | 8 (11.1) | 0 |
| Enrofloxacin | 3 (27.3) | 6 (54.5) | 2 (18.2) | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | 0 | 1 (25) | 3 (75) | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 6 (8.3) | 65 (90.3) | 1 (1.4) |
| Norfloxacin | 4 (36.4) | 7 (63.4) | 0 | 2 (25) | 6 (75) | 0 | 0 | 4 (100) | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 0 | 70 (97.2) | 2 (2.8) |
| Tylosin | 5 (45.5) | 5 (45.5) | 1 (9) | 4 (50) | 4 (50) | 0 | 2 (50) | 1 (25) | 1 (25) | 0 | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 11 (15.3) | 61 (84.7) | 0 |
| Ampicillin | 7 (63.6) | 4 (36.4) | 0 | 6 (75) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (12.5) | 3 (75) | 0 | 1 (25) | 2 (100) | 0 | 0 | 41 (56.9) | 27 (37.5) | 4 (5.5) |
| Doxycycline | 3 (27.3) | 6 (54.5) | 2 (18.2) | 1 (12.5) | 5 (62.5) | 2 (25) | 1 (25) | 2 (50) | 1 (25) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 0 | 14 (19.4) | 47 (65.3) | 11 (15.3) |
| Colistin | 4 (36.4) | 6 (54.5) | 1 (9) | 0 | 8 (100) | 0 | 2 (50) | 2 (50) | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 9 (12.5) | 60 (83.3) | 3 (4.2) |
| Imipenem | 0 | 11 (100) | 0 | 1 (12.5) | 7 (87.5) | 0 | 0 | 4 (100) | 0 | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 3 (4.2) | 69 (95.8) | 0 |
| Antimicrobials | E. cloacae | K. pneumoniae | S. enterica | P. aeruginosa | E. coli |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomycin | 90.9 | 75 | 50 | 50 | 95.8 |
| Neomycin | 72.7 | 75 | 75 | 50 | 63.9 |
| Gentamicin | 100 | 37.5 | 75 | 100 | 76.4 |
| Florfenicol | 72.7 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 84.7 |
| Ceftiofur | 45.5 | 37.5 | 50 | 50 | 11.1 |
| Enrofloxacin | 54.5 | 62.5 | 75 | 100 | 90.3 |
| Norfloxacin | 63.6 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 97.2 |
| Tylosin | 45.5 | 50 | 25 | 50 | 84.7 |
| Ampicillin | 36.4 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 37.5 |
| Doxycycline | 54.5 | 62.5 | 50 | 50 | 65.3 |
| Colistin | 54.5 | 100 | 50 | 100 | 83.3 |
| Imipenem | 100 | 87.5 | 100 | 100 | 95.8 |
| Mean | 65.90416667 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 70.83333 | 73.83833 |
| Standard Deviation | 21.62692533 | 24.42521052 | 31.07907803 | 33.4279 | 26.19029 |
| Standard Error | 6.243155581 | 7.050950935 | 8.971757032 | 9.649802 | 7.560486 |
| Minimum | 36.36 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 11.11 |
| Maximum | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 97.22 |
| Count | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Target Gene | Primers | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Amplicon Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaCTX-M | F | ATGTGCAGYACCAGTAARGTKATGGC | 58 | 593 bp | [51] |
| R | TGGGTRAARTARGTSACCAGAAYCAGCGG | ||||
| blaTEM | F | TCGCCGCATACACTATTCTCAGAATGA | 50 | 445 bp | |
| R | ACGCTCACCGGCTCCAGATTTAT | ||||
| blaSHV | F | CGCCGGGTTATTCTTATTTGTCGC | 68 | 1016 bp | [52] |
| R | TCTTTCCGATGCCGCCGCCAGTCA | ||||
| blaOXA | F | ATTATCTACAGCAGCGCCAGTG | 56 | 296 bp | [53] |
| R | TGCATCCACGTCTTTGGTG | ||||
| 16S rRNA | fD1 | AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG | 52 | 1500 bp | [54] |
| rP2 | ACGGCTACCTTGTTACGACTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeed, M.A.; Khan, A.U.; Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S.; Waheed, U.; Qamar, M.F.; Rehman, A.u.; Nasir, A.; Zaman, M.A.; Kashif, M.; Gonzalez, J.-P.; et al. Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Genetic Determinants in Gram-Negative Fecal-Microbiota of Wild Birds and Chicken Originated at Trimmu Barrage. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091376
Saeed MA, Khan AU, Ehtisham-ul-Haque S, Waheed U, Qamar MF, Rehman Au, Nasir A, Zaman MA, Kashif M, Gonzalez J-P, et al. Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Genetic Determinants in Gram-Negative Fecal-Microbiota of Wild Birds and Chicken Originated at Trimmu Barrage. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(9):1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091376
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeed, Muhammad Adnan, Aman Ullah Khan, Syed Ehtisham-ul-Haque, Usman Waheed, Muhammad Fiaz Qamar, Aziz ur Rehman, Amar Nasir, Muhammad Arfan Zaman, Muhammad Kashif, Jean-Paul Gonzalez, and et al. 2023. "Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Genetic Determinants in Gram-Negative Fecal-Microbiota of Wild Birds and Chicken Originated at Trimmu Barrage" Antibiotics 12, no. 9: 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091376
APA StyleSaeed, M. A., Khan, A. U., Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S., Waheed, U., Qamar, M. F., Rehman, A. u., Nasir, A., Zaman, M. A., Kashif, M., Gonzalez, J.-P., & El-Adawy, H. (2023). Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Genetic Determinants in Gram-Negative Fecal-Microbiota of Wild Birds and Chicken Originated at Trimmu Barrage. Antibiotics, 12(9), 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091376








