Engineering and Purification of Microcin C7 Variants Resistant to Trypsin and Analysis of Their Biological Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
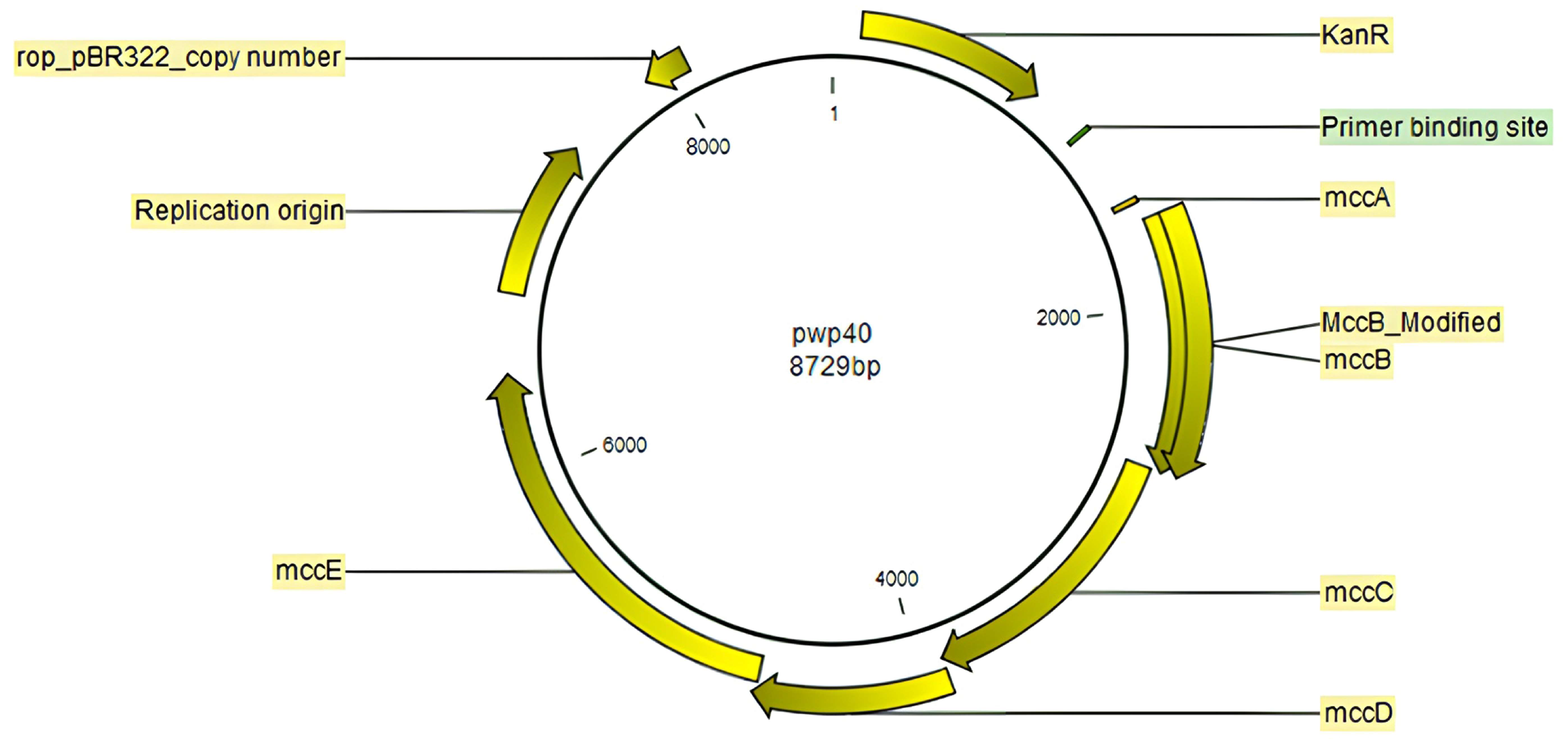
2.1. Production of the Mutated Peptides
2.2. Production of the Mutated Peptide Activity and Protease Resistance of the McC Variants
2.3. Optimization of HPLC Purification Conditions
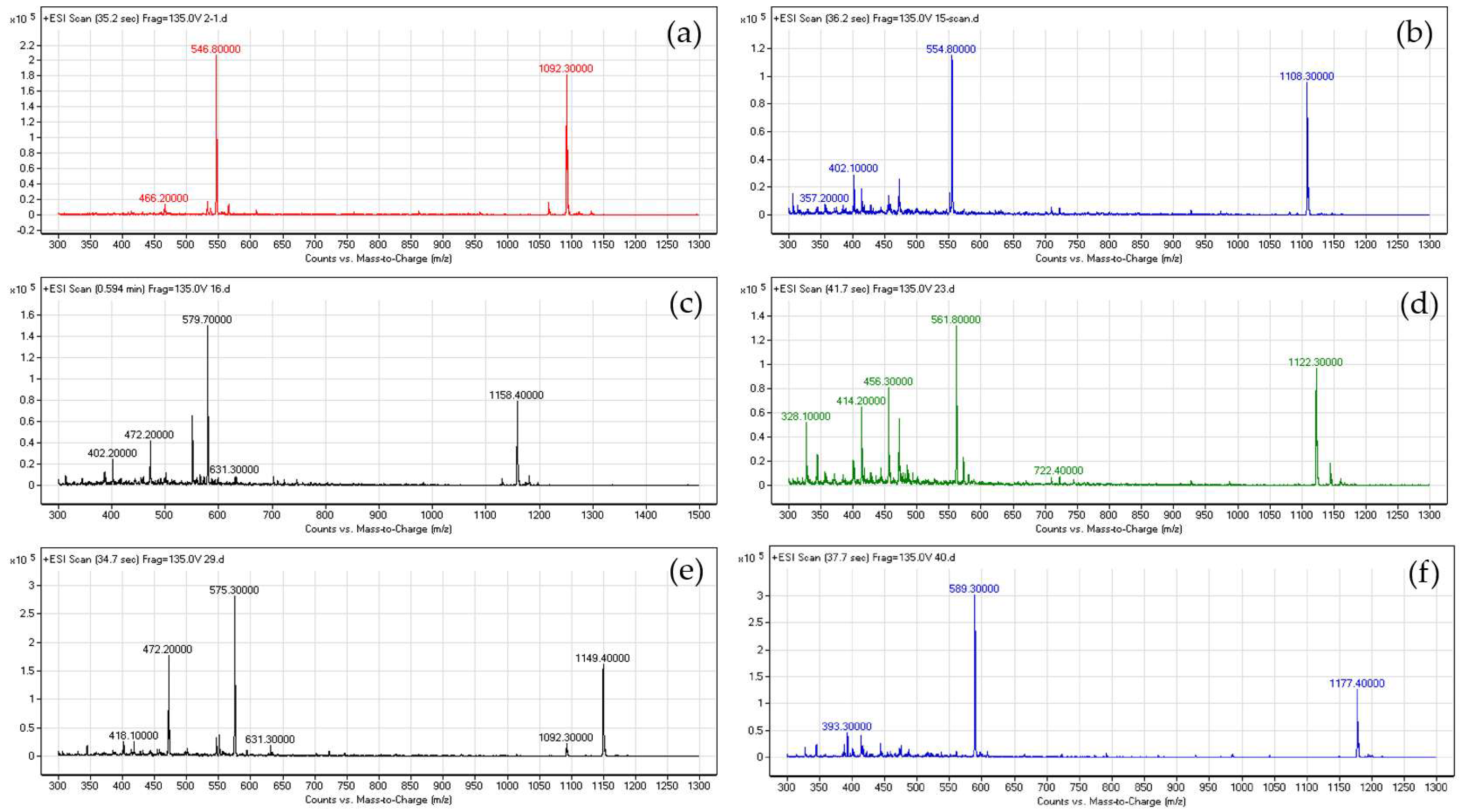
2.4. Characterization of the McC Variants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Culture Conditions
4.2. DNA Preparation and Transformation
4.3. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of the mccA Gene Encoding the McC Precursor Peptide
4.4. Fermentation
4.5. Trypsin Treatment of the McC Variants
4.6. Analysis of the McC Variants
4.7. Determination of Antimicrobial Activity and Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Glennon, E.E.; Chen, D.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Reducing antimicrobial use in food animals. Science 2017, 357, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabant, P.; Borrero, J. PARAGEN 1.0: A Standardized Synthetic Gene Library for Fast Cell-Free Bacteriocin Synthesis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurdle, J.G.; O’Neill, A.J.; Chopra, I. Prospects for aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors as new antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4821–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metlitskaya, A.; Kazakov, T.; Kommer, A.; Pavlova, O.; Praetorius-Ibba, M.; Ibba, M.; Krasheninnikov, I.; Kolb, V.; Khmel, I.; Severinov, K. Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase is the target of peptide nucleotide antibiotic Microcin C. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18033–18042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijarro, J.I.; González-Pastor, J.E.; Baleux, F.; San Millán, J.L.; Castilla, M.A.; Rico, M.; Moreno, F.; Delepierre, M. Chemical structure and translation inhibition studies of the antibiotic microcin C7. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 23520–23532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuffat, S. Microcins in action: Amazing defence strategies of Enterobacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikova, M.; Metlitskaya, A.; Datsenko, K.; Kazakov, T.; Kazakov, A.; Wanner, B.; Severinov, K. The Escherichia coli Yej transporter is required for the uptake of translation inhibitor microcin C. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8361–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakov, T.; Vondenhoff, G.H.; Datsenko, K.A.; Novikova, M.; Metlitskaya, A.; Wanner, B.L.; Severinov, K. Escherichia coli peptidase A, B, or N can process translation inhibitor microcin C. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2607–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vondenhoff, G.H.M.; Dubiley, S.; Severinov, K.; Lescrinier, E.; Rozenski, J.; van Aerschot, A. Extended targeting potential and improved synthesis of Microcin C analogs as antibacterials. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5462–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pastor, J.E.; San Millán, J.L.; Moreno, F. The smallest known gene. Nature 1994, 369, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Bacteriocins—A viable alternative to antibiotics? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakov, T.; Metlitskaya, A.; Severinov, K. Amino acid residues required for maturation, cell uptake, and processing of translation inhibitor microcin C. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Vijver, P.; Vondenhoff, G.H.; Kazakov, T.S.; Semenova, E.; Kuznedelov, K.; Metlitskaya, A.; Van Aerschot, A.; Severinov, K. Synthetic microcin C analogs targeting different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6273–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vondenhoff, G.H.; Blanchaert, B.; Geboers, S.; Kazakov, T.; Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L.; Rozenski, J.; Severinov, K.; Van Aerschot, A. Characterization of peptide chain length and constituency requirements for YejABEF-mediated uptake of microcin C analogues. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3618–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantysh, O.; Serebryakova, M.; Zukher, I.; Kulikovsky, A.; Tsibulskaya, D.; Dubiley, S.; Severinov, K. Enzymatic Synthesis and Functional Characterization of Bioactive Microcin C-Like Compounds with Altered Peptide Sequence and Length. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 3133–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakov, T.; Kuznedelov, K.; Semenova, E.; Mukhamedyarov, D.; Datsenko, K.A.; Metlitskaya, A.; Vondenhoff, G.H.; Tikhonov, A.; Agarwal, V.; Nair, S.; et al. The RimL transacetylase provides resistance to translation inhibitor microcin C. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 3377–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; He, S.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Dou, X.; Shan, A. Antimicrobial Peptides with High Proteolytic Resistance for Combating Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2286–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, J.; Montville, T.J.; Nes, I.F.; Chikindas, M.L. Bacteriocins: Safe, natural antimicrobials for food preservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 71, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Leroy, F. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Production, purification, and food applications. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 13, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, B.; Le Lay, C.; Jean, J.; Fliss, I. Growth, acid production and bacteriocin production by probiotic candidates under simulated colonic conditions. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shang, L.; Yang, G.; Dai, Z.; Zeng, X.; Qiao, S. Biosynthetic Microcin J25 Exerts Strong Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory Activities, Low Cytotoxicity Without Increasing Drug-Resistance to Bacteria Target. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 811378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierbaum, G.; Szekat, C.; Josten, M.; Heidrich, C.; Kempter, C.; Jung, G.; Sahl, H.G. Engineering of a novel thioether bridge and role of modified residues in the lantibiotic Pep5. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neis, S.; Bierbaum, G.; Josten, M.; Pag, U.; Kempter, C.; Jung, G.; Sahl, H.G. Effect of leader peptide mutations on biosynthesis of the lantibiotic Pep5. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 149, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, J.R.; Rollema, H.S.; Siezen, R.J.; Beerthuyzen, M.M.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Vos, W.M. Influence of amino acid substitutions in the nisin leader peptide on biosynthesis and secretion of nisin by Lactococcus lactis. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 3555–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variant Plasmids | Mutagenic Oligonucleotides | Amino Acid Sequence | Primers |
|---|---|---|---|
| pLL14 | R2A | MATGNAN | Z14f/Z14r |
| pLL15 | R2S | MSTGNAN | Z15f/Z15r |
| pLL16 | R2H | MHTGNAN | Z16f/Z16r |
| pLL17 | R2W | MWTGNAN | Z17f/Z17r |
| pLL18 | R2Y | MYTGNAN | Z18f/Z18r |
| pLL19 | R2L | MLTGNAN | Z19f/Z19r |
| pLL20 | R2I | MITGNAN | Z20f/Z20r |
| pLL21 | R2V | MVTGNAN | Z21f/Z21r |
| pLL22 | R2M | MMTGNAN | Z22f/Z22r |
| pLL23 | R2T | MTTGNAN | L-23F/L-23R, L-24F/L-24R |
| pLL24 | R2G | MGTGNAN | Z24f/Z24r |
| pLL25 | R2C | MCTGNAN | Z25f/Z25r |
| pLL26 | R2P | MPTGNAN | Z26f/Z26r |
| pLL27 | R2F | MFTGNAN | L-23F/L-27R, L-27F/L-24R |
| WpLL28 | R2N | MNTGNAN | Z28f/Z28r |
| pLL29 | R2Q | MQTGNAN | Z29f/Z29r |
| pLL30 | R2K | MKTGNAN | Z30f/Z30r |
| pLL31 | R2D | MDTGNAN | Z31f/Z31r |
| pLL32 | R2E | METGNAN | Z32f/Z32r |
| pLL34 | RPT | MRPTGNAN | L-23R/L-34F, L-34R/L-24R |
| pLL35 | T3P | MRPGNAN | L-23F/L-35F, L-35R/L-24R |
| Variants | Trypsin-Untreated Group | Trypsin-Treated Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yej+rimL− | K88 | Yej+rimL− | K88 | |
| R2A | 21.82 | 16.53 | 19.07 | 11.96 |
| R2S | 17.35 | 13.46 | 16.34 | 9.44 |
| R2H | 18.39 | 15.55 | 15.92 | 11.99 |
| R2W | - | - | - | - |
| R2Y | 18.87 | - | 14.93 | - |
| R2L | 14.41 | - | 0 | - |
| R2I | 18.36 | 10.18 | 15.67 | - |
| R2V | 21.34 | - | 14.62 | - |
| R2M | 21.57 | 12.37 | 14.31 | - |
| R2T | 21.74 | 15.27 | 17.23 | 11.68 |
| R2G | 18.86 | - | 14.15 | - |
| R2C | - | - | - | - |
| R2P | - | - | - | - |
| R2F | 13.05 | 14.34 | 10.95 | - |
| R2N | - | - | - | - |
| R2Q | 19.45 | 21.67 | 19.38 | 14.56 |
| R2K | 20.91 | 16.95 | 0 | - |
| R2D | 17.71 | - | 14.11 | - |
| R2E | - | - | - | - |
| RPT | - | - | - | - |
| T3P | - | - | - | - |
| McC | 29.12 | 20.25 | - | - |
| Chloramphenicol | 23.44 | 23.63 | 20.96 | 22.79 |
| Variants | Retention Time/min | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| R2A | 17.167 | 93.05 |
| R2S | 17.004 | 94.86 |
| R2H | 16.872 | 95.47 |
| R2Y | 18.591 | 92.30 |
| R2L | 19.425 | 81.38 |
| R2I | 18.166 | 92.51 |
| R2V | 18.151 | 81.74 |
| R2M | 19.622 | 88.21 |
| R2T | 17.418 | 93.19 |
| R2G | 17.253 | 98.06 |
| R2Q | 16.910 | 91.37 |
| R2D | 17.625 | 94.95 |
| McC | 17.198 | 84.38 |
| Variants | Molecular Mass |
|---|---|
| R2A | 1091.339 |
| R2S | 1107.339 |
| R2H | 1157.409 |
| R2Y | 1183.439 |
| R2L | 1133.419 |
| R2I | 1133.419 |
| R2V | 1119.399 |
| R2M | 1151.459 |
| R2T | 1121.369 |
| R2G | 1077.319 |
| R2Q | 1148.399 |
| R2D | 1135.349 |
| McC | 1176.449 |
| Variants | R2A | R2S | R2H | R2Y | R2L | R2I | R2V | R2M | R2T | R2G | R2Q | R2D | McC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (μg/mL) | 12.5 | 100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 25 | >100 | 25 | >100 | 1.56 |
| Strains and Plasmids | Relevant Properity | Source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli Top 10 | Cloning strain | TianGen |
| E. coli MC4100 | Expression strain | Our laboratory |
| Yej+rimL− | Knr and Ampr | Our laboratory |
| K88 | / | Our laboratory |
| pWP40 | Carrying the mcc genes, Knr | Our laboratory |
| pLL14 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL15 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL16 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL17 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL18 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL19 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL20 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL21 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL22 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL23 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL24 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL25 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL26 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL27 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL28 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL29 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL30 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL31 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL32 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL34 | Knr | This paper |
| pLL35 | Knr | This paper |
| Primers 1 | DNA Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| z14f | GGAGGCGTAAAATGgctACTGGTAATGCAAAC |
| z14r | GTTTGCATTACCAGTagcCATTTTACGCCTCC |
| z15f | GGAGGCGTAAAATGagtACTGGTAATGCAAAC |
| z15r | GTTTGCATTACCAGTactCATTTTACGCCTCC |
| z16F | GGAGGCGTAAAATGcatACTGGTAATGCAAAC |
| z17f | GGCGTAAAATGtggACTGGTAATGC |
| z17r | GCATTACCAGTccaCATTTTACGCC |
| z18f | GGCGTAAAATGtatACTGGTAATGC |
| z18r | GCATTACCAGTataCATTTTACGCC |
| z19f | GGCGTAAAATGcttACTGGTAATGC |
| z19r | GCATTACCAGTaagCATTTTACGCC |
| z20f | GGCGTAAAATGattACTGGTAATGC |
| z20r | GCATTACCAGTaatCATTTTACGCC |
| z21f | GGCGTAAAATGgttACTGGTAATGC |
| z21r | GCATTACCAGTaacCATTTTACGCC |
| z22f | GGCGTAAAATGatgACTGGTAATGC |
| z22r | GCATTACCAGTcatCATTTTACGCC |
| z23f | GGCGTAAAATGaccACTGGTAATGC |
| z23r | GCATTACCAGTggtCATTTTACGCC |
| z24f | GGCGTAAAATGggtACTGGTAATGC |
| z24r | GCATTACCAGTaccCATTTTACGCC |
| z25f | GGCGTAAAATGtgtACTGGTAATGC |
| z25r | GCATTACCAGTacaCATTTTACGCC |
| z26f | GGCGTAAAATGcctACTGGTAATGC |
| z26r | GCATTACCAGTaggCATTTTACGCC |
| z27f | GGCGTAAAATGtttACTGGTAATGC |
| z27r | GCATTACCAGTaaaCATTTTACGCC |
| z28f | GGCGTAAAATGaatACTGGTAATGC |
| z28r | GCATTACCAGTattCATTTTACGCC |
| z29f | GGCGTAAAATGcagACTGGTAATGC |
| z29r | GCATTACCAGTctgCATTTTACGCC |
| z30f | GGCGTAAAATGaagACTGGTAATGC |
| z30r | GCATTACCAGTcttCATTTTACGCC |
| z31f | GGCGTAAAATGgatACTGGTAATGC |
| z31r | GCATTACCAGTatcCATTTTACGCC |
| z32f | GGCGTAAAATGgaaACTGGTAATGC |
| z32r | GCATTACCAGTttcCATTTTACGCC |
| L-23F | ACTGTCTGCTTACATAAACAGTAATACAAGGGGTGTTATG |
| L-23R | CATTAGTTTGCATTACCAGTggtCATTTTACGCCTCCTAT |
| L-24F | ATAGGAGGCGTAAAATGaccACTGGTAATGCAAACTAATG |
| L-24R | CATAACACCCCTTGTATTACTGTTTATGTAAGCAGACAGT |
| L-27F | CATTAGTTTGCATTACCAGTaaaCATTTTACGCCTCCTAT |
| L-27R | ATAGGAGGCGTAAAATGtttACTGGTAATGCAAACTAATG |
| L-34F | TTTGCATTACCAGTcggACGCATTTTACGCCTCCTATTA |
| L-34R | TAATAGGAGGCGTAAAATGCGTccgACTGGTAATGCAAA |
| L-35F | CATTAGTTTGCATTACCcggACGCATTTTACGCCTCCTAT |
| L-35R | ATAGGAGGCGTAAAATGCGTccgGGTAATGCAAACTAATG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, G.; Shang, L.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Zeng, X.; Ding, X.; Huang, J.; Qiao, S.; Yu, H. Engineering and Purification of Microcin C7 Variants Resistant to Trypsin and Analysis of Their Biological Activity. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091346
Yang G, Shang L, Liu L, Li Z, Zeng X, Ding X, Huang J, Qiao S, Yu H. Engineering and Purification of Microcin C7 Variants Resistant to Trypsin and Analysis of Their Biological Activity. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(9):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091346
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Guangxin, Lijun Shang, Lu Liu, Zeqiang Li, Xiangfang Zeng, Xiuliang Ding, Jinxiu Huang, Shiyan Qiao, and Haitao Yu. 2023. "Engineering and Purification of Microcin C7 Variants Resistant to Trypsin and Analysis of Their Biological Activity" Antibiotics 12, no. 9: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091346
APA StyleYang, G., Shang, L., Liu, L., Li, Z., Zeng, X., Ding, X., Huang, J., Qiao, S., & Yu, H. (2023). Engineering and Purification of Microcin C7 Variants Resistant to Trypsin and Analysis of Their Biological Activity. Antibiotics, 12(9), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091346









