Bioactive Naphtho-α-Pyranones from Two Endophytic Fungi of the Genus Polyphilus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Compounds (1 and 2)
2.2. Biological Assays
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
3.2.1. Solid State Fermentation
3.2.2. Liquid Fermentation
3.2.3. Analytical HPLC
3.2.4. Isolation of Compounds
3.3. Antimicrobial Assay
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayer:, W.A.; Craw, P.A.; Nozawa, K. Two 1H-naphtho [2,3-c]pyran-1-one metabolites from the fungus Paecilomyces variotii. Can. J. Chem. 1991, 69, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, F.; Kim, E.L.; Hong, J.; Jung, H.J. Viriditoxin, from a jellyfish-derived fungus, is antibiotic to fish pathogens. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2013, 19, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Elix, J.A.; Wardlaw, J.H. Pigmentosin A, a new naphthopyrone from the lichen Hyptotrachyna immaculata. Aust. J. Chem. 2004, 57, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.D.; Zhou, L.M.; Ma, Q.Y.; Huang, S.Z.; Wang, P.; Dai, H.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Metabolites with Gram-negative bacteria quorum sensing inhibitory activtiy from the marine animal endogenic fungus Penicillium sp. SCS-KFDo8. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-W.; Gao, C.-H.; Han, F.-H.; Chen, X.-Q.; Lin, X.-P.; Zhou, X.-F.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, Y.-H. A new naphthopyranone from the sponge-associated fungus Penicillium sp. XWSo2F62. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nozawa, K.; Nakajima, S.; Kawai, K. Structure revision of mycotoxin, viriditoxin, and its derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 3180–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnone, A.; Assante, G.; Montorsi, M.; Nasini, G. Asteromine, a bioactive secondary metabolite from a strain of Mycosphaerella asteroma. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nozawa, K.; Nakajima, S.; Udagawa, S.; Kawai, K. Isolation and structures of antibacterial binaphtho-α-pyrones, talaroderxines A and B, from Talaromyces derxii. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tan, N.P.H.; Donner, C.D. Total synthesis and confirmationn of the absolute stereochemistry of semiviriditoxin, a naphthopyranone metabolite from the fungus Paecilomyces variotii. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 4007–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helaly, S.E.; Kuephadungphan, W.; Phainuphong, P.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Tasanathai, K.; Mongkolsamrit, S.; Luangsa-ard, J.J.; Phongpaichit, S.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Stadler, M. Pigmentosins from Gibellula sp. as antibiofilm agents and a new glycosylated asperfuran from Cordyceps javanica. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2968–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Yangchum, A.; Rachtawee, P.; Komwijit, S.; Lutthisungneon, A. Hopane-type triterpenes and binaphthopyrones from the scale insect pathogenic fungus Aschersonia paraphysata BCC 11964. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, S.E.; Drochner, D.; Müller, M. Synthesis, biosynthesis and absolute configuration of vioxanthin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5916–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, F.; Ng, A.S.; Just, G. Metabolites of pathogenic fungi. V. Isolation and tentative structures of vioxanthin and viopurpurin, two coloured metabolites from Trichophyton violaceum. Can. J. Chem. 1966, 44, 2873–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Chávez, J.; Caesar, L.K.; Garcia-Salazar, J.J.; Raja, M.A.; Cech, N.B.; Pearce, C.J.; Oberlies, N.H. Mycopyranone: A 8,8′-binaphthopyranone with potent anti-MRSA activity from the fungus Phialemoniopsis sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Bigelis, R.; Yang, H.Y.; Chang, L.-P.; Singh, M.P. Lichenicolins A and B, new bisnaphthopyrones from an unidentified lichenicolous fungus, strain LL-RB0668. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, M.; Rainsford, P.; Juskewitz, E.; Andersen, J.H.; Hansen, E.H.; Isaksson, J.; Rämä, T.; Hansen, K.Ø. Lulworthinone, a new dimeric naphthopyrone from a marine fungus in the family Lulworthiaceae with antibacterial activity against clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Galgoci, A.; Kodali, S.; Herath, K.B.; Jayasuriya, H.; Dorso, K.; Vicente, F.; González, A.; Cully, D.; Bramhill, D.; et al. Discovery of a small molecule that inhibits cell division by blocking FtsZ, a novel therapeutic target of antibiotics. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44424–44428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, S.; Knapp, D.G.; Blaudez, D.; Chalot, M.; Maciá-Vicente, J.G.; Zagyva, I.; Dababat, A.A.; Maier, W.; Kovács, G.M. Inhabiting plant roots, nematodes and truffles-Polyphilus, a new helotialean genus two globally distributed species. Mycologia 2018, 110, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajula, M.; Ward, J.M.; Turpenien, A.; Tejesvi, M.V.; Hokkanen, J.; Tolonen, A.; Häkkänen, H.; Picart, P.; Ihalainen, J.; Sahl, H.-G.; et al. Bridged epipolythiodiketopiperazines from Penicillium raciborskii, an endophytic fungus of Rhododendron tomentosum Harmaja. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhou, D.; Kimishima, A.; Setiawan, A.; Arai, M. Selective cytotoxicity of marine-derived fungal metabolite (3S,6S)-3,6-dibenzylpiperazine-2,5-dione against cancer cells adapted to nutrient starvation. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, C.I.; Di Maso, M.J.; Jaipuri, F.A.; Kim, M.B.; Shaw, J.T. Synthesis of 6,6′-binaphthopyran-2-one natural products: Pigmentosin A, talaroderxines A and B. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4338–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Narita, R.; Takahashi, R.; Namikoshi, M. Induced production of halogenated epidithiodiketopiperazines by a marine-derived Trichoderma cf. brevicompactum with sodium halides. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2319–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipanovic, R.D.; Howell, C.R. The structure of gliovirin, a new antibiotic from Gliocladium virens. J. Antibiot. 1982, 35, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, M.; Otoguro, K.; Ishiyama, A.; Namatame, M.; Nishihara-Tukashima, A.; Hashida, J.; Nakashima, T.; Masuma, R.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamada, H.; et al. In vitro antitrypanosomal activity of 12-low-molecular-weight antibiotics and observations of structure/activity relationships. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Seephonkai, P.; Kongsaeree, S.; Prabpai, S.; Isaka, M.; Thebtaranonth, Y. Transformation of an irregularly bridged epidithiodiketopiperazine to trichodermamide A. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 3073–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepkirui, C.; Cheng, T.; Matasyoh, J.; Decock, C.; Stadler, M. An unprecedented spiro[furan-2,1’-indene]-3-one derivative and other nematicidal and antimicrobial metabolites from Sanghuangporus sp. (Hymenochaetaceae, Basidiomycota) collected in Kenya. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 25, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charria-Girón, E.; Stchigel, A.M.; Čmoková, A.; Kolařík, M.; Surup, F.; Marin-Felix, Y. Amesia hispanica sp. nov., producer of the antifungal class of antibiotics dactylfungins. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niego, A.G.T.; Lambert, C.; Mortimer, P.; Thongklang, N.; Rapior, S.; Grosse, M.; Schrey, H.; Charria-Girón, E.; Walker, A.; Stadler, M. The contribution of fungi to the global economy. Fungal Divers. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
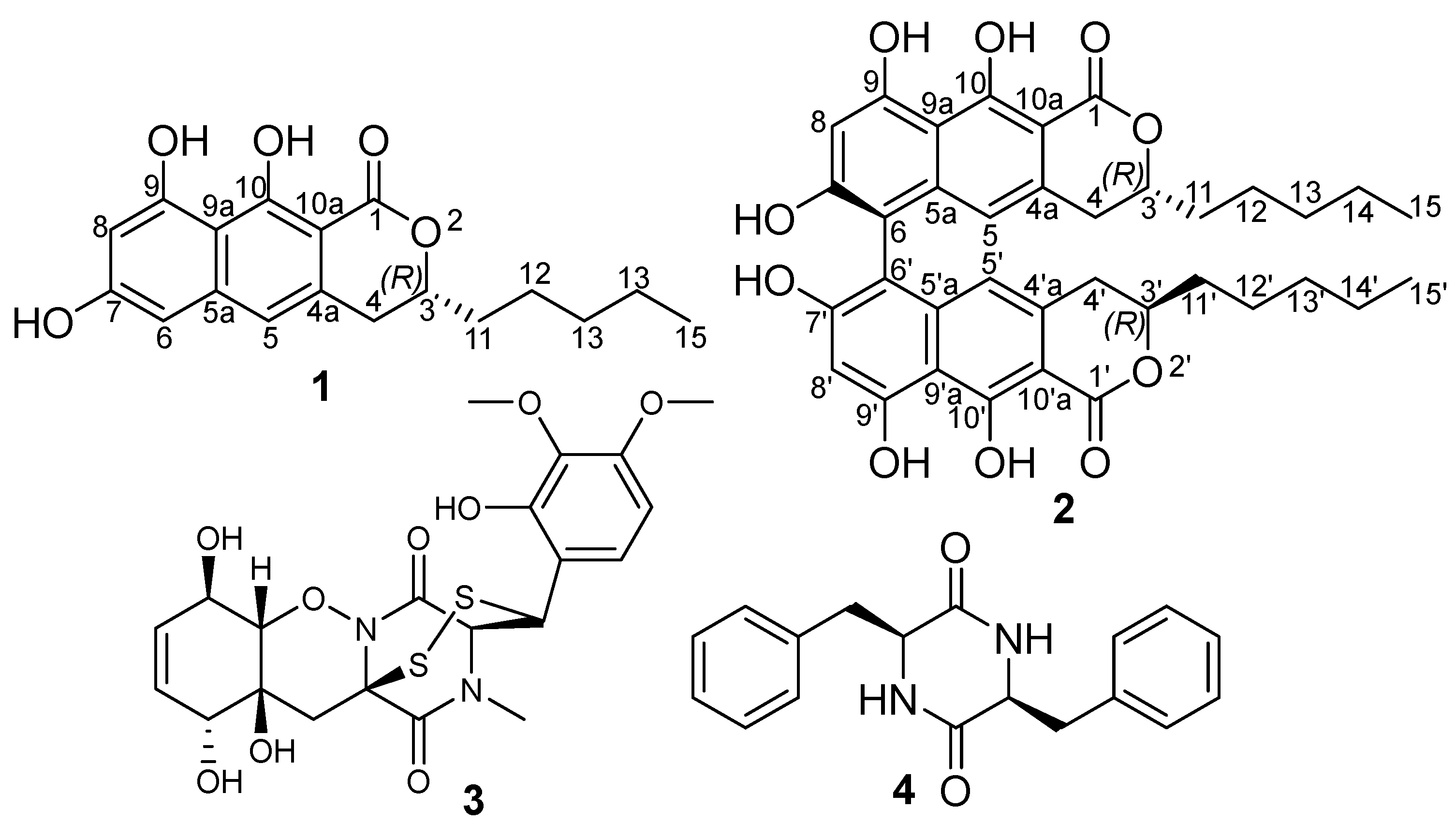
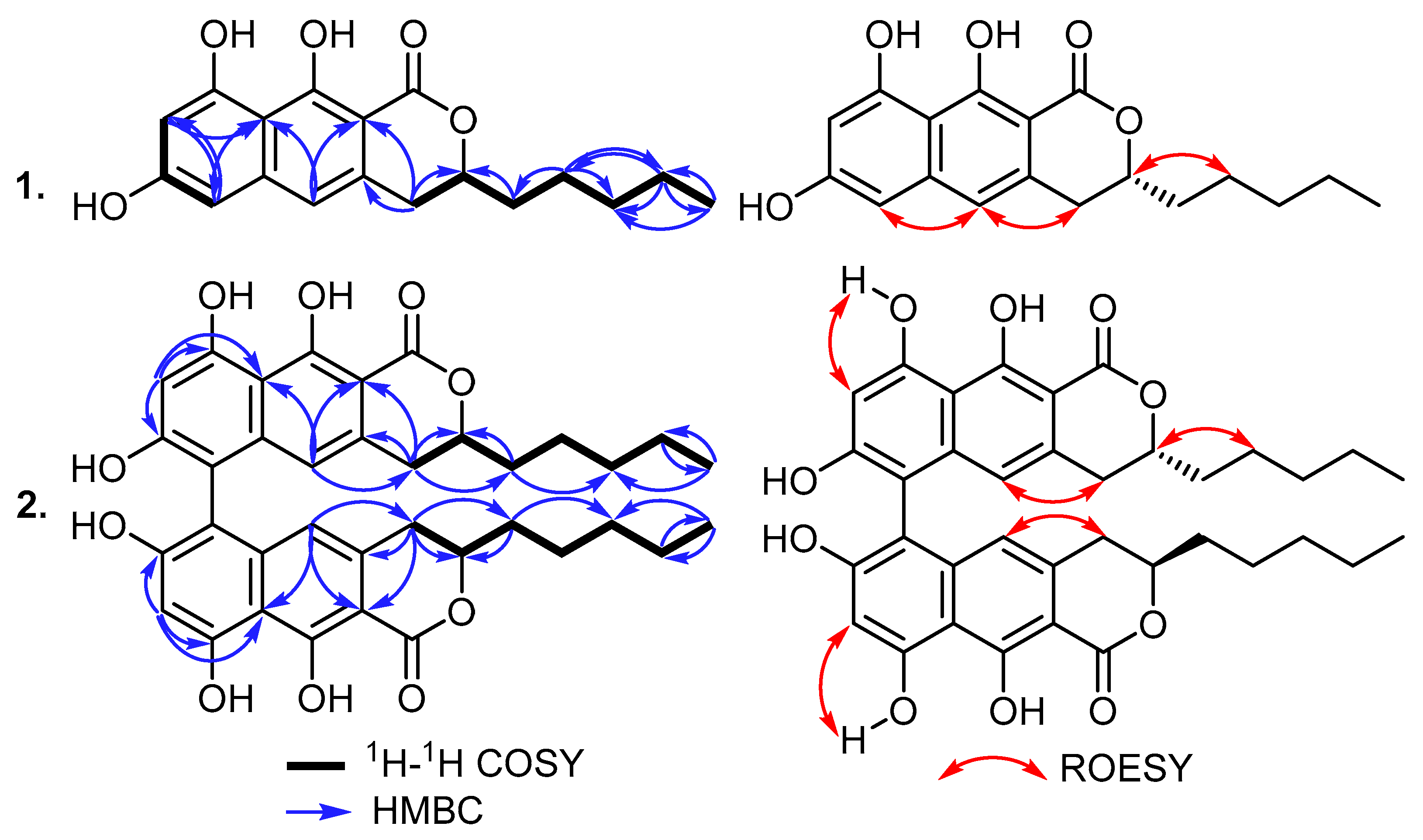
| 1 | 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos. | δH (Multi, J(Hz)) a | δC, Type b,c | Pos. | δH (Multi, J(Hz)) a | δC, Type b,c |
| 1 | 170.7, CO | 1/1′ | 170.6, CO | ||
| 3 | 4.58, m | 79.3, CH | 3/3′ | 4.50, m | 79.4, CH |
| 4 | α 2.88, dd, (15.6, 11.1) β 3.00, br d, (15.6) | 32.3, CH2 | 4/4′ | α 2.72, dd, (16.2, 11.0) β 2.81, dd, (16.5, 3.1) | 32.5, CH2 |
| 4a | 133.9, C | 4a/4′a | 133.6, C | ||
| 5 | 6.82, s | 114.5, CH | 5/5′ | 6.20, s | 112.7, CH |
| 5a | 140.6, C | 5a/5′a | 139.9, C | ||
| 6 | 6.31, s | 101.4, CH | 6/6′ | 107.7, C | |
| 7 | 161.0, C, C | 7/7′ | 157.8, C | ||
| 8 | 6.47, s | 101.5, CH | 8/8′ | 6.57, s | 101.6, CH |
| 9 | 160.7, C | 9/9′ | 158.9, C | ||
| 9a | 107.2, C | 9a/9′a | 107.7, C | ||
| 10 | 162.6, C | 10/10′ | 163.2, C | ||
| 10a | 98.8, C | 10a/10′a | 98.7, C | ||
| 11 | α 1.68, m β 1.74, m | 34.0, CH2 | 11/11′ | α 1.57, ddd, (14.2, 10.8, 5.6) β 1.66, m | 34.1, CH2 |
| 12 | α 1.41, m; β 1.46, m | 24.0, CH2 | 12/12′ | 1.36, m (2H) | 23.9, CH2 |
| 13 | 1.31, m, 2H | 31.0, CH2 | 13/13′ | 1.23, m (2H) | 31.0, CH2 |
| 14 | 1.31, m, 2H | 22.0, CH2 | 14/14′ | 1.25, m (2H) | 22.0, CH2 |
| 15 | 0.88, t, (7.0) | 13.9, CH3 | 15/15′ | 0.84, t (6.8, 3H) | 13.9, CH3 |
| 7-OH | 10.11, br s | 7-OH | 10.17, br s | ||
| 9-OH | 9.66, br s | 9-OH | 9.65, s | ||
| 10-OH | 13.35, br s | 10-OH | 13.43, br s | ||
| Compound | IC50 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L929 | KB3.1 | A431 | A549 | PC-3 | MCF-7 | |
| Talaroderxine C (2) in µM | 1.19 | 10.32 | 2.38 | 2.06 | 8.73 | 0.068 |
| Epothilone B in nM | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.065 | 0.053 | 0.091 | 0.075 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wennrich, J.-P.; Sepanian, E.; Ebada, S.S.; Llanos-Lopez, N.A.; Ashrafi, S.; Maier, W.; Kurtán, T.; Stadler, M. Bioactive Naphtho-α-Pyranones from Two Endophytic Fungi of the Genus Polyphilus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081273
Wennrich J-P, Sepanian E, Ebada SS, Llanos-Lopez NA, Ashrafi S, Maier W, Kurtán T, Stadler M. Bioactive Naphtho-α-Pyranones from Two Endophytic Fungi of the Genus Polyphilus. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(8):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081273
Chicago/Turabian StyleWennrich, Jan-Peer, Ellen Sepanian, Sherif S. Ebada, Natalia A. Llanos-Lopez, Samad Ashrafi, Wolfgang Maier, Tibor Kurtán, and Marc Stadler. 2023. "Bioactive Naphtho-α-Pyranones from Two Endophytic Fungi of the Genus Polyphilus" Antibiotics 12, no. 8: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081273
APA StyleWennrich, J.-P., Sepanian, E., Ebada, S. S., Llanos-Lopez, N. A., Ashrafi, S., Maier, W., Kurtán, T., & Stadler, M. (2023). Bioactive Naphtho-α-Pyranones from Two Endophytic Fungi of the Genus Polyphilus. Antibiotics, 12(8), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081273







