Mechanisms of Piperacillin/Tazobactam Nephrotoxicity: Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Induced Direct Tubular Damage in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
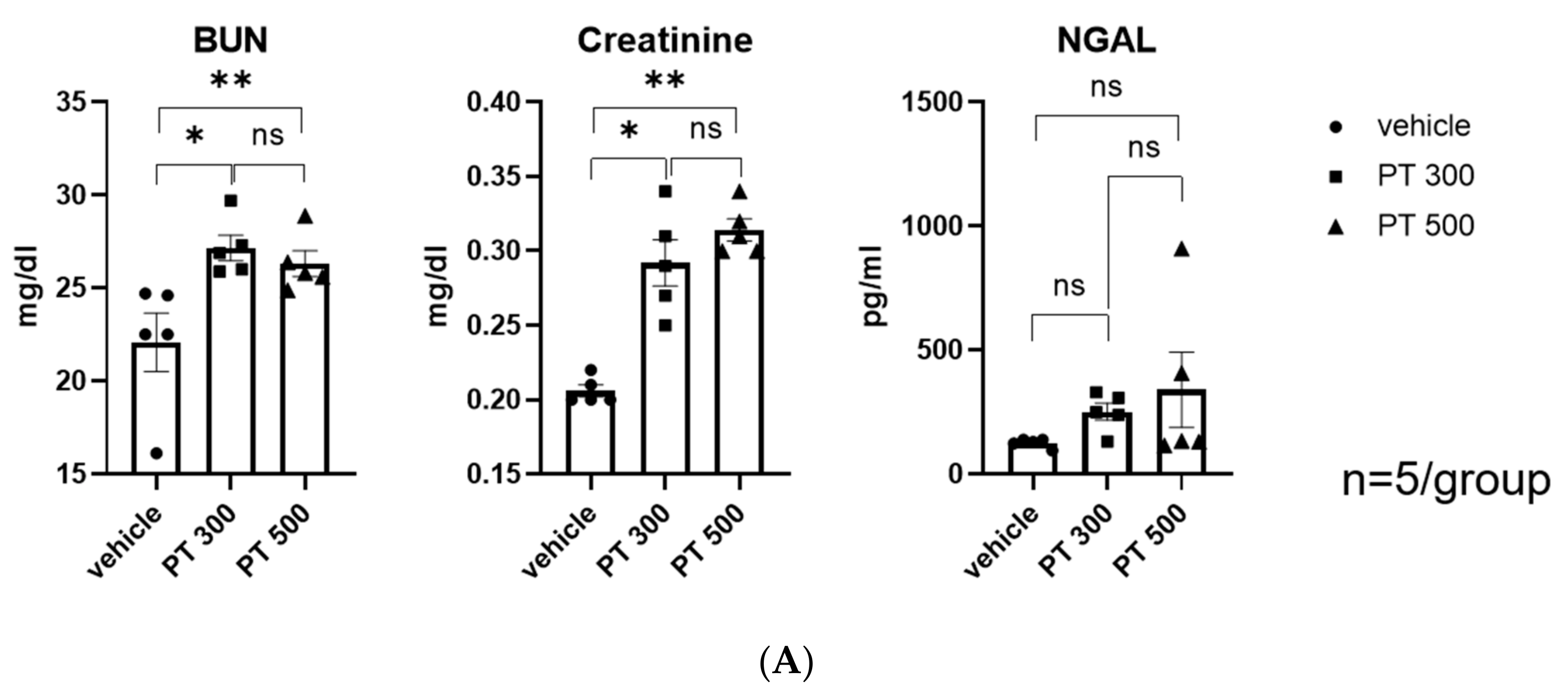
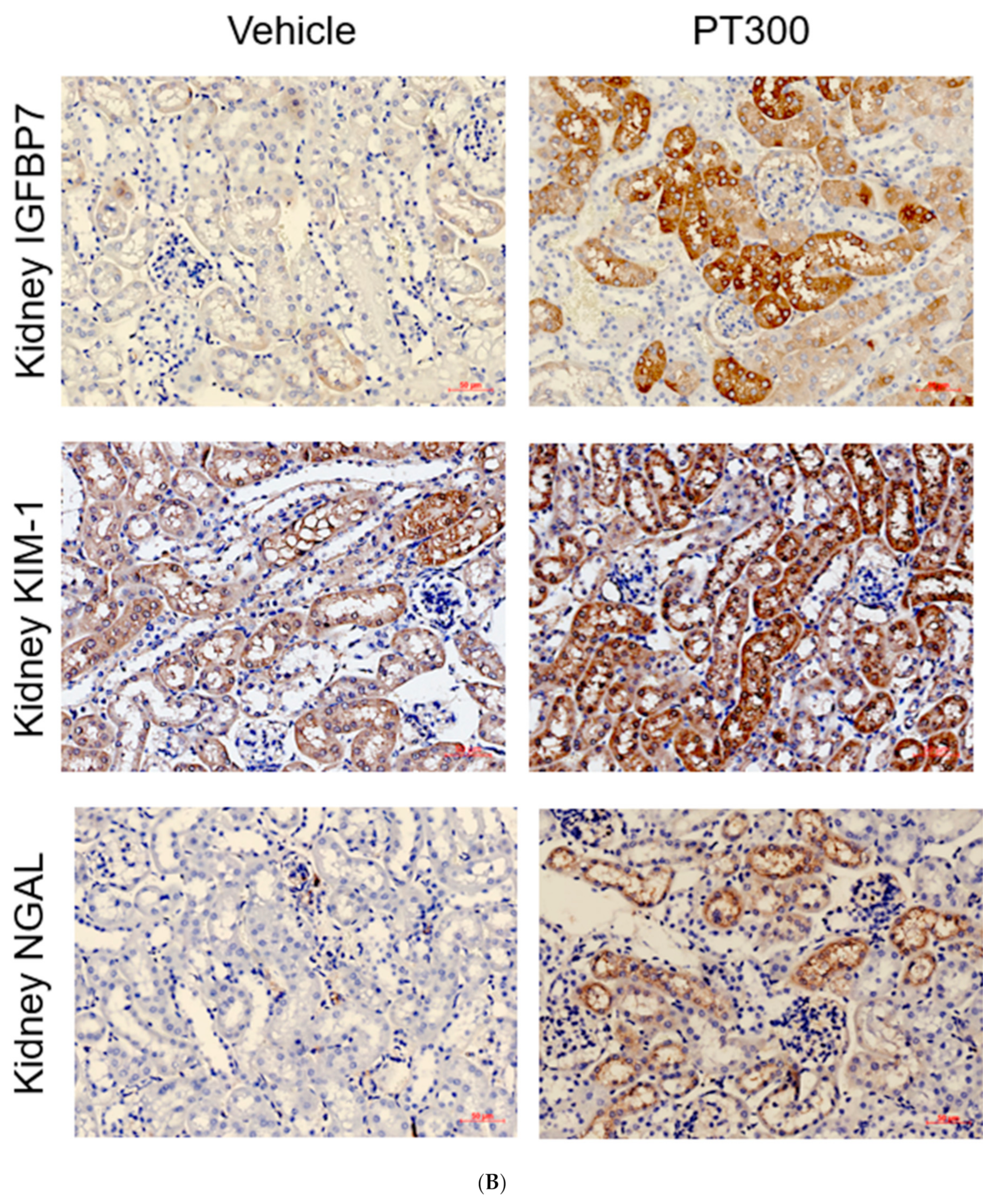
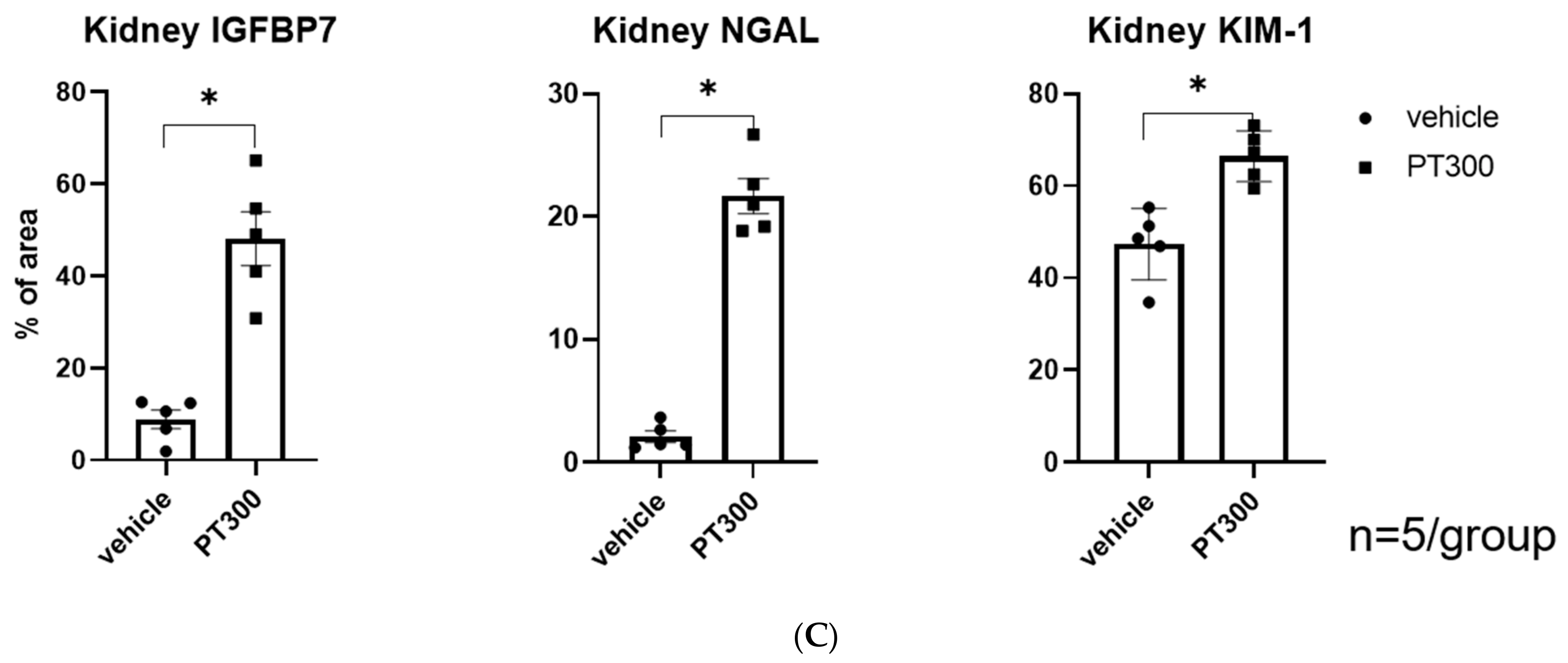
2.1. PT-Provoked AKI
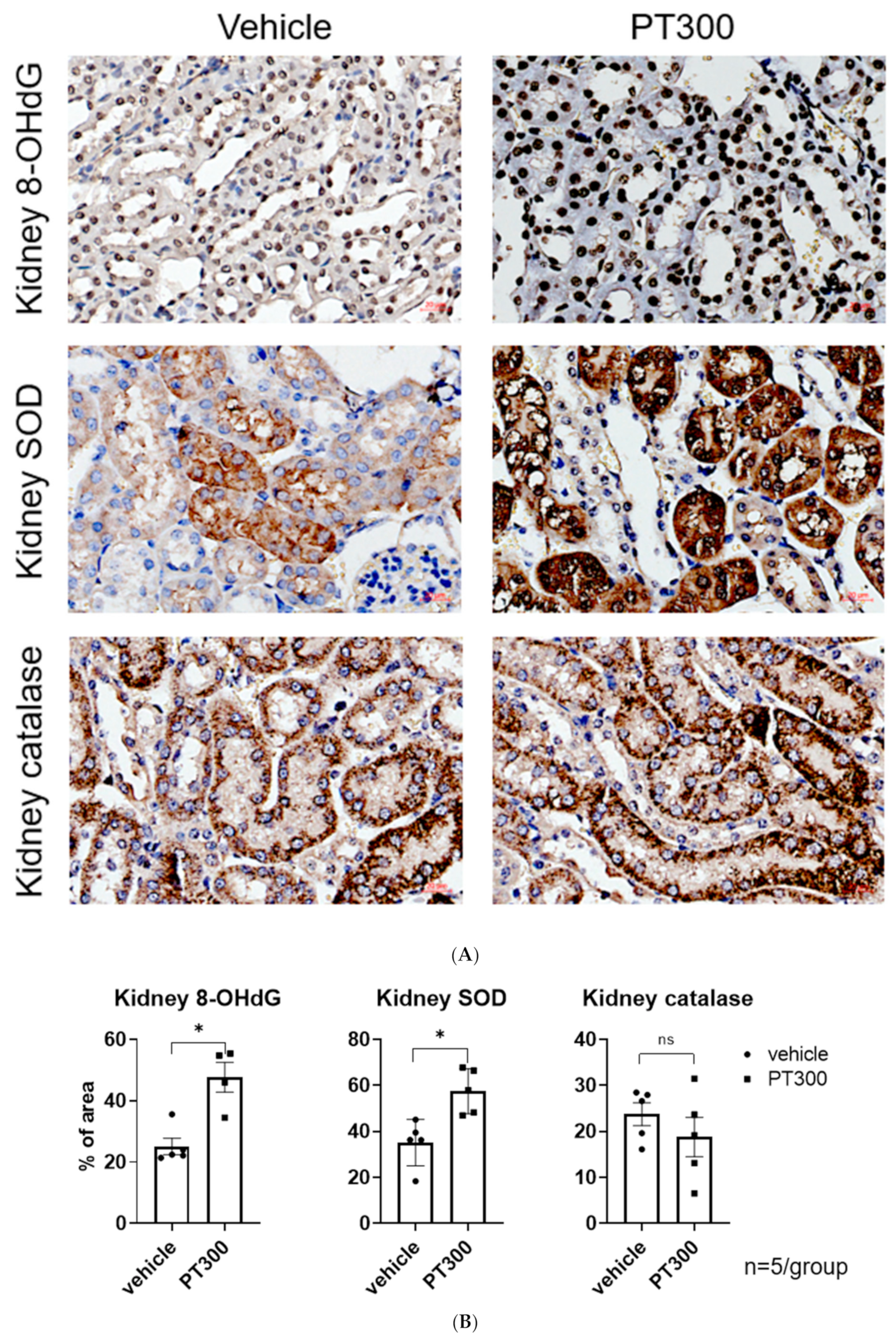
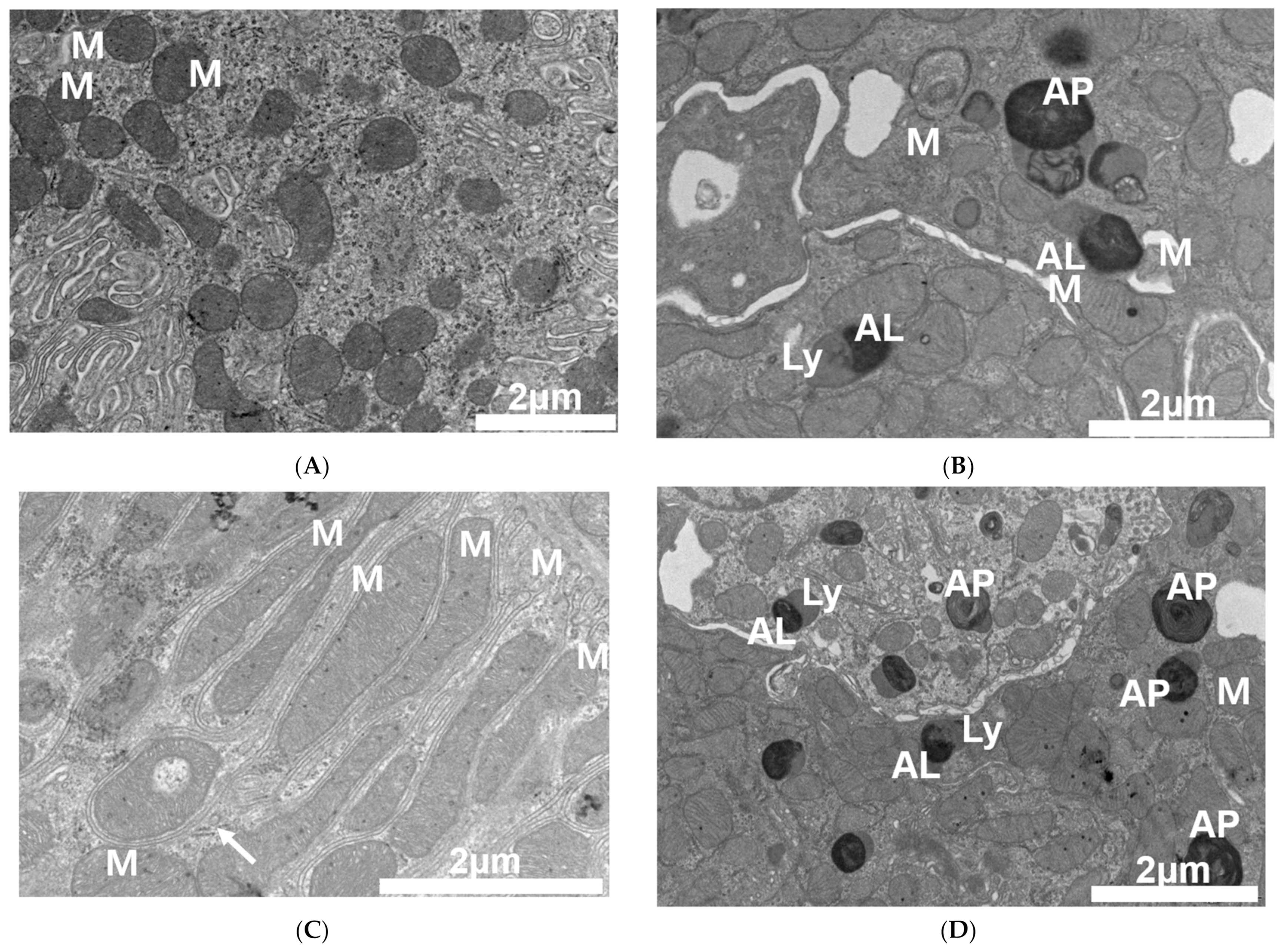
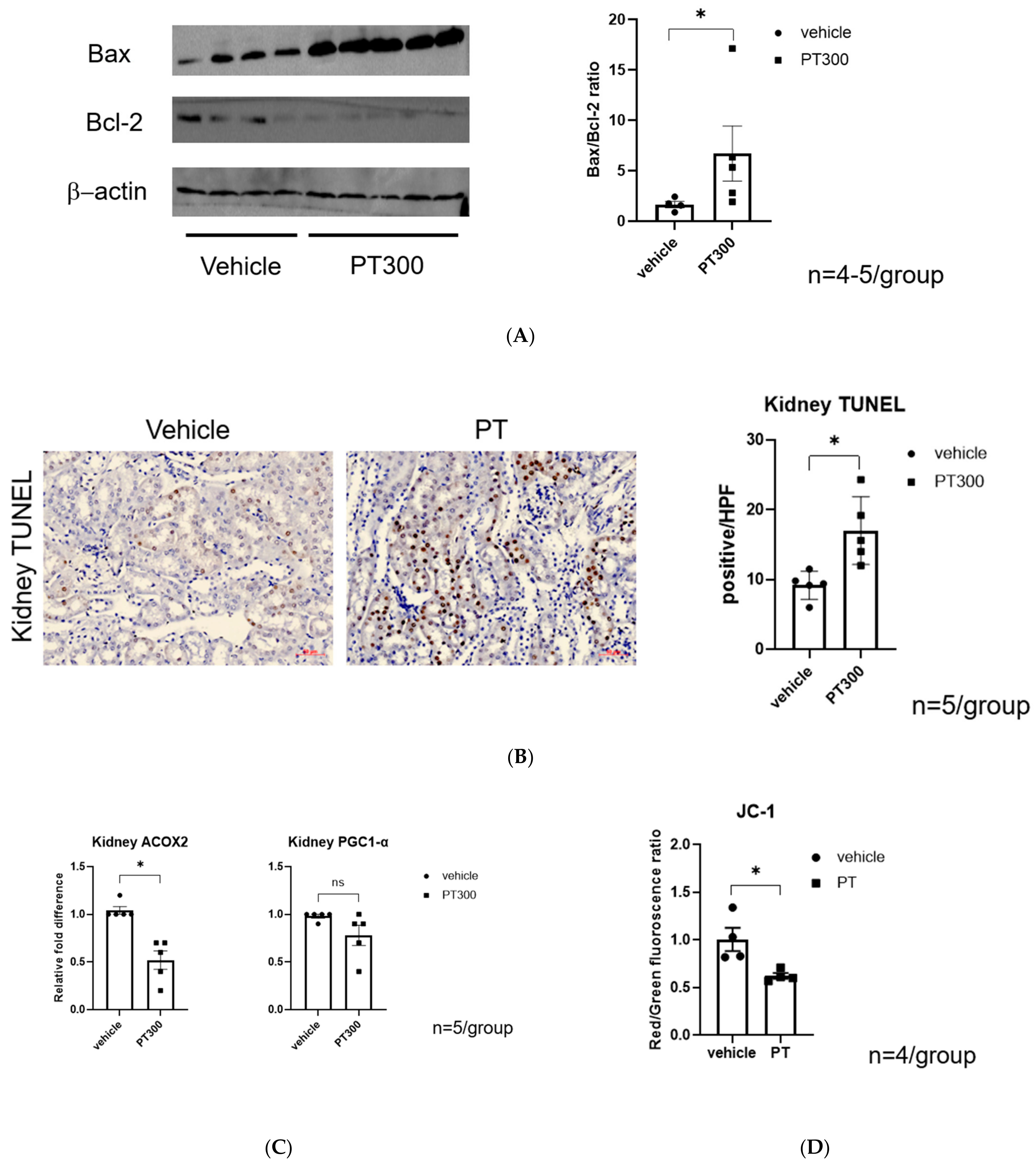
2.2. PT-Provoked Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage Leading to Apoptosis in Tubular Cells
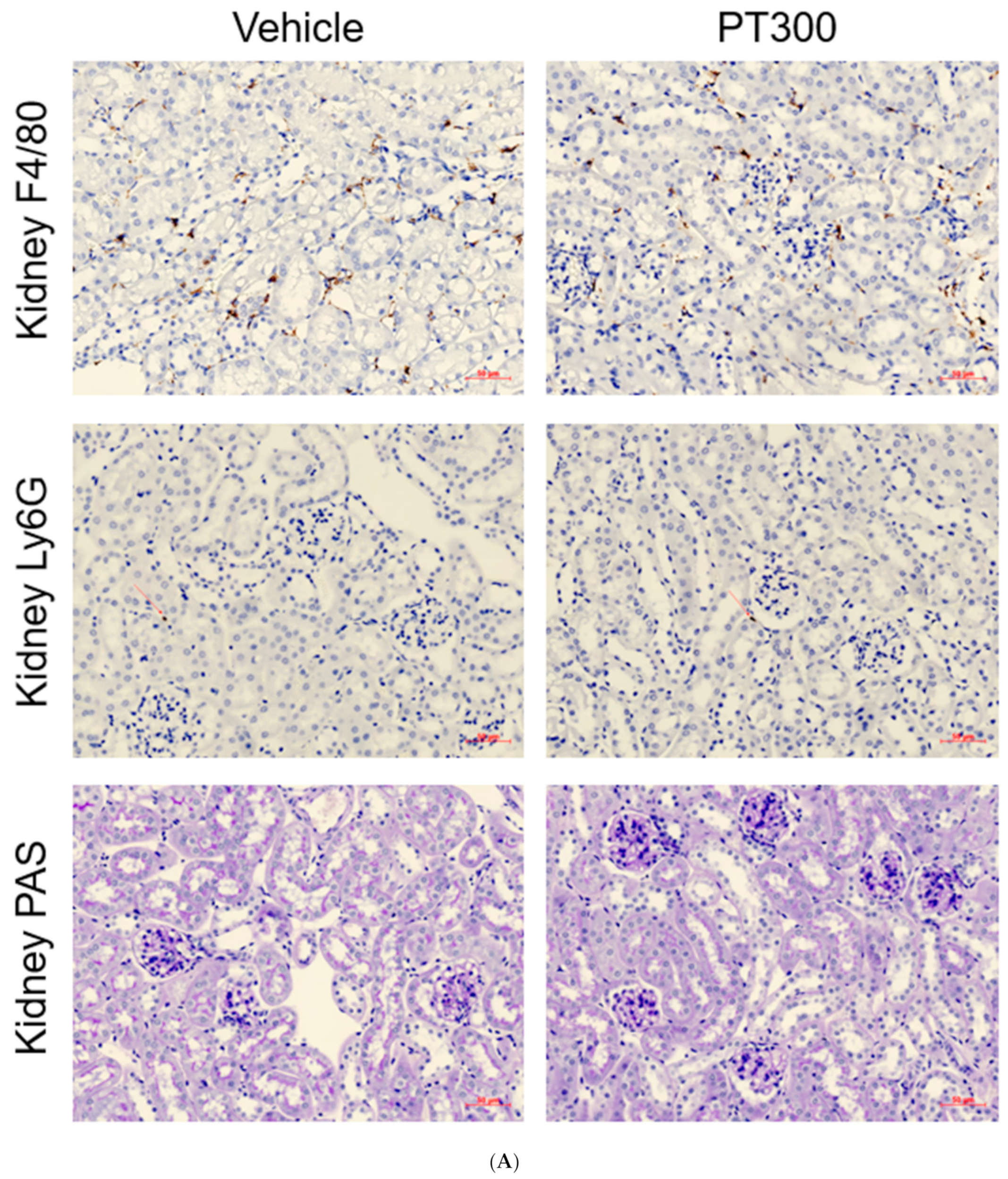
2.3. PT Does Not Provoke Inflammation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Study
4.2. Histological Analysis
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Electron Microscopy
4.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.6. In Vitro Study
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| PT | piperacillin/tazobactam |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| NGAL | neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
| VPT | vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam |
| OR | odds ratio |
| IGFBP7 | insulin-like growth factor-binding protein |
| KIM-1 | kidney injury molecule-1 |
| 8-OHdG | 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| ACOX2 | Acyl-CoA Oxidase 2 |
| HK-2 cell | human kidney-2 cell |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| Bcl2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| PGC-1-alpha | proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 alpha |
| TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling |
| PAS | periodic acid–Schiff-stained kidney tissue sections |
| OAT | the organic anion transporter |
References
- Young, M.; Plosker, G.L. Piperacillin/tazobactam: A pharmacoeconomic review of its use in moderate to severe bacterial infections. Pharmacoeconomics 2001, 19, 1135–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelesidis, T.; Braykov, N.; Uslan, D.Z.; Morgan, D.J.; Gandra, S.; Johannsson, B.; Schweizer, M.L.; Weisenberg, S.A.; Young, H.; Cantey, J.; et al. Indications and Types of Antibiotic Agents Used in 6 Acute Care Hospitals, 2009–2010: A Pragmatic Retrospective Observational Study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, Y.; Louis, K.; Jouanneau, C.; Placier, S.; Esteve, E.; Bazin, D.; Rondeau, E.; Letavernier, E.; Wolfromm, A.; Gosset, C.; et al. Vancomycin-Associated Cast Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Xu, R.X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.Y.; Xie, X.F. Acute kidney injury associated with concomitant vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam administration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D.A.; Smith, M.N.; Li, C.; Hayes, S.M.; Lusardi, K.; Bookstaver, P.B. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Acute Kidney Injury Associated with Concomitant Vancomycin and Piperacillin/tazobactam. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, C.A.; Patel, C.R.; Kale-Pradhan, P.B. Is the Combination of Piperacillin-Tazobactam and Vancomycin Associated with Development of Acute Kidney Injury? A Meta-analysis. Pharmacotherapy 2016, 36, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, M.K.; Timbrook, T.T.; Caffrey, A.R.; Dosa, D.; Lodise, T.P.; LaPlante, K.L. Vancomycin Plus Piperacillin-Tazobactam and Acute Kidney Injury in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.M.; Smotherman, C.; Birch, A.; Dupree, L.; Della Vecchia, B.J.; Kraemer, D.F.; Jankowski, C.A. Comparison of acute kidney injury during treatment with vancomycin in combination with piperacillin-tazobactam or cefepime. Pharmacotherapy 2014, 34, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyko, V.; Smalley, S.; Cohen, H. Prospective Comparison of Acute Kidney Injury During Treatment With the Combination of Piperacillin-Tazobactam and Vancomycin Versus the Combination of Cefepime or Meropenem and Vancomycin. J. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 30, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCleir, L.K.; Pettit, R.S. Piperacillin-tazobactam versus cefepime incidence of acute kidney injury in combination with vancomycin and tobramycin in pediatric cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalkele, B.; Pogue, J.M.; Karino, S.; Nishan, B.; Salim, M.; Solanki, S.; Pervaiz, A.; Tashtoush, N.; Shaikh, H.; Koppula, S.; et al. Risk of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients on Concomitant Vancomycin and Piperacillin-Tazobactam Compared to Those on Vancomycin and Cefepime. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, W.C.; Cox, J.N.; Martin, C.A.; Burgess, D.R.; Burgess, D.S. Nephrotoxicity during Vancomycin Therapy in Combination with Piperacillin-Tazobactam or Cefepime. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02089-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.R.; Deresinski, S. Increasing Evidence of the Nephrotoxicity of Piperacillin/Tazobactam and Vancomycin Combination Therapy-What Is the Clinician to Do? Clin. Infect Dis. 2017, 65, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, G.M.; Liu, J.; Avedissian, S.N.; Hiner, D.; Xanthos, T.; Chalkias, A.; d’Aloja, E.; Locci, E.; Gilchrist, A.; Prozialeck, W.C.; et al. Lack of synergistic nephrotoxicity between vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam in a rat model and a confirmatory cellular model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, E.L.; Kane-Gill, S.L.; Priyanka, P.; Fuhrman, D.Y.; Kellum, J.A. Piperacillin/Tazobactam and Antibiotic-Associated Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, A.; Kawanishi, K.; Morikawa, S.; Nakano, T.; Kodama, M.; Mitobe, M.; Taneda, S.; Koike, J.; Ohara, M.; Nagashima, Y.; et al. Biopsy-proven vancomycin-induced acute kidney injury: A case report and literature review. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pill, M.W.; O’Neill, C.V.; Chapman, M.M.; Singh, A.K. Suspected acute interstitial nephritis induced by piperacillin-tazobactam. Pharmacotherapy 1997, 17, 166–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kraleti, S.; Khatri, N.; Jarrett, D. Piperacillin-Tazobactam Induced Interstitial Nephritis, Hepatitis and Serum Sckness-Like Illness. J. Ark. Med. Soc. 2016, 112, 278–280. [Google Scholar]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Saba, A.I.; Panchal, H.; Shanmugan, S.; Alsaleh, N.A.; Ahmadein, M. Artificial Intelligence for Forecasting the Prevalence of COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hm, B.; Rn, B. Piperacillin/Tazobactam. A Review of Its Antibacterial Activity, Pharmacokinetic Properties and Therapeutic Potential. Drugs 1994, 47, 506–535. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, C.M.; Markham, A. Piperacillin/Tazobactam: An Updated Review of Its Use in the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Drugs 1999, 57, 805–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.; Kim, H.-I.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.-H. Population Pharmacokinetics of Piperacillin/Tazobactam in Critically Ill Korean Patients and the Effects of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shotwell, M.S.; Nesbitt, R.; Madonia, P.N.; Gould, E.R.; Connor, M.J.; Salem, C.; Aduroja, O.A.; Amde, M.; Groszek, J.J.; Wei, P.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Extended Infusion Versus Short Infusion Piperacillin-Tazobactam in Critically Ill Patients Undergoing CRRT. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, J.; Min, K.L.; Kang, S.; Yang, S.; Park, M.S.; Wi, J.; Chang, M.J. Population Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Optimization of Piperacillin-Tazobactam in Critically Ill Patients on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and the Influence of Concomitant Renal Replacement Therapy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0063321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.U.; Hein, L.; Lundgren, B.; Bestle, M.H.; Mohr, T.; Andersen, M.H.; Thornberg, K.J.; Løken, J.; Steensen, M.; Fox, Z.; et al. Kidney failure related to broad-spectrum antibiotics in critically ill patients: Secondary end point results from a 1200 patient randomised trial. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e000635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; McCullough, P.A.; Forni, L.G.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Joannidis, M.; Shi, J.; Kashani, K.; Honore, P.M.; Chawla, L.S.; Kellum, J.A.; et al. Kinetics of Urinary Cell Cycle Arrest Markers for Acute Kidney Injury Following Exposure to Potential Renal Insults. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Ostermann, M.; Shi, J.; Joyce, E.L.; Kellum, J.A. Evaluating Renal Stress Using Pharmacokinetic Urinary Biomarker Data in Critically Ill Patients Receiving Vancomycin and/or Piperacillin-Tazobactam: A Secondary Analysis of the Multicenter Sapphire Study. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Capili, A.; Choi, M.E. Mitochondrial dysfunction in kidney injury, inflammation, and disease: Potential therapeutic approaches. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 39, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Deray, G. Antiviral drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlitz, L.C.; Mohan, S.; Stokes, M.B.; Radhakrishnan, J.; D’Agati, V.D.; Markowitz, G.S. Tenofovir nephrotoxicity: Acute tubular necrosis with distinctive clinical, pathological, and mitochondrial abnormalities. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyesubula, R.; Perazella, M.A. Nephrotoxicity of HAART. AIDS Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 562790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Drug-induced nephropathy: An update. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2005, 4, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Ahmed, Z. Drug-associated renal dysfunction and injury. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2006, 2, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.E.; Evans, T.A. Modification of the Bicinchoninic Acid Protein Assay to Eliminate Lipid Interference in Determining Lipoprotein Protein Content. Anal Biochem. 1992, 204, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Fang, Y.; Oh, S.W.; Kim, M.-G.; Cho, W.Y.; Jo, S.-K. Mechanisms of Piperacillin/Tazobactam Nephrotoxicity: Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Induced Direct Tubular Damage in Mice. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071121
Yang J, Ko YS, Lee HY, Fang Y, Oh SW, Kim M-G, Cho WY, Jo S-K. Mechanisms of Piperacillin/Tazobactam Nephrotoxicity: Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Induced Direct Tubular Damage in Mice. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071121
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jihyun, Yoon Sook Ko, Hee Young Lee, Yina Fang, Se Won Oh, Myung-Gyu Kim, Won Yong Cho, and Sang-Kyung Jo. 2023. "Mechanisms of Piperacillin/Tazobactam Nephrotoxicity: Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Induced Direct Tubular Damage in Mice" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071121
APA StyleYang, J., Ko, Y. S., Lee, H. Y., Fang, Y., Oh, S. W., Kim, M.-G., Cho, W. Y., & Jo, S.-K. (2023). Mechanisms of Piperacillin/Tazobactam Nephrotoxicity: Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Induced Direct Tubular Damage in Mice. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071121






