Controlled Size Oils Based Green Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
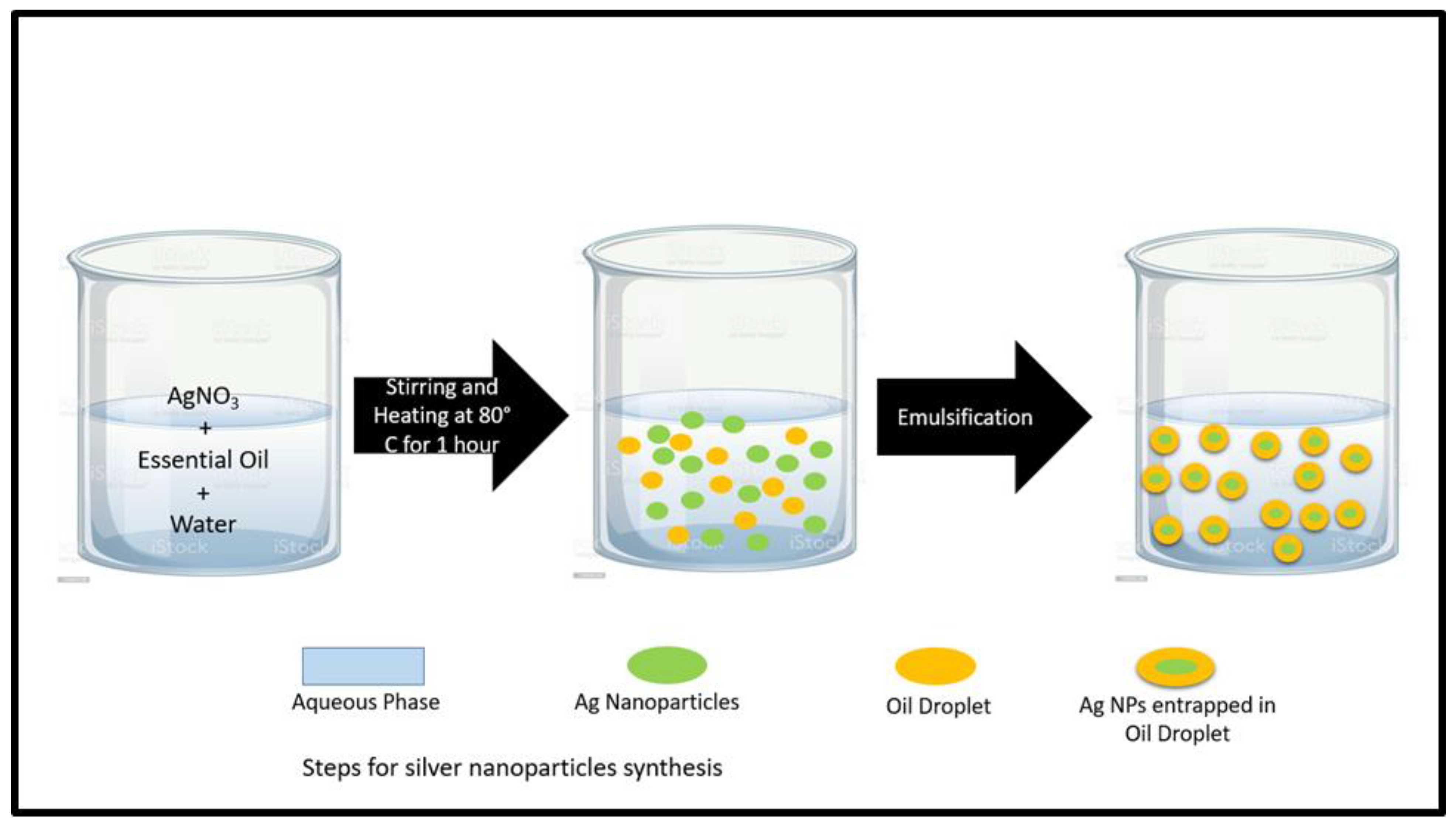
2.1. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
2.4. Catalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
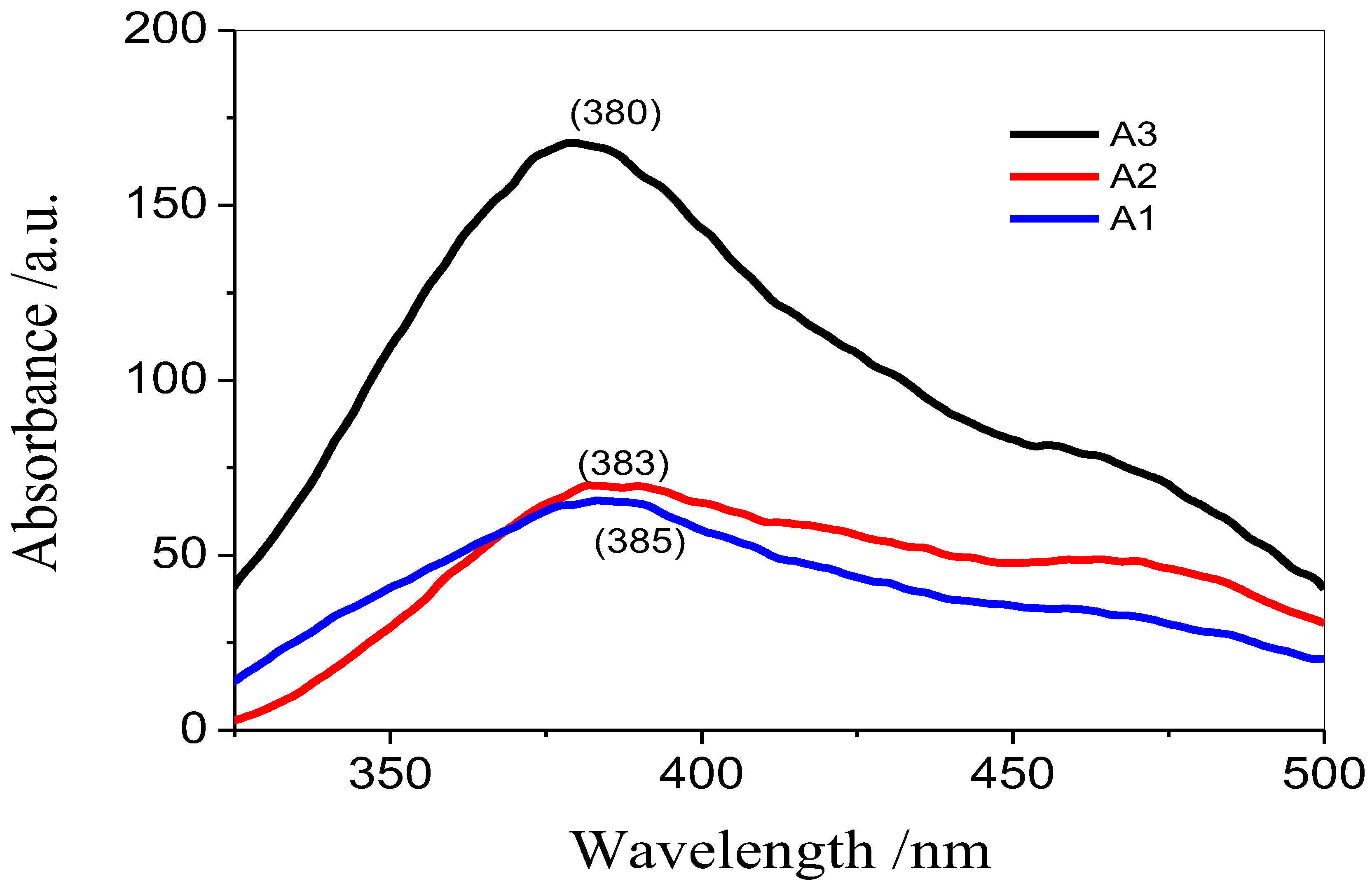
3.1. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
3.2. Dynamic Laser Light Scattering
3.3. X-ray Diffraction
3.4. FT-IR Spectroscopy
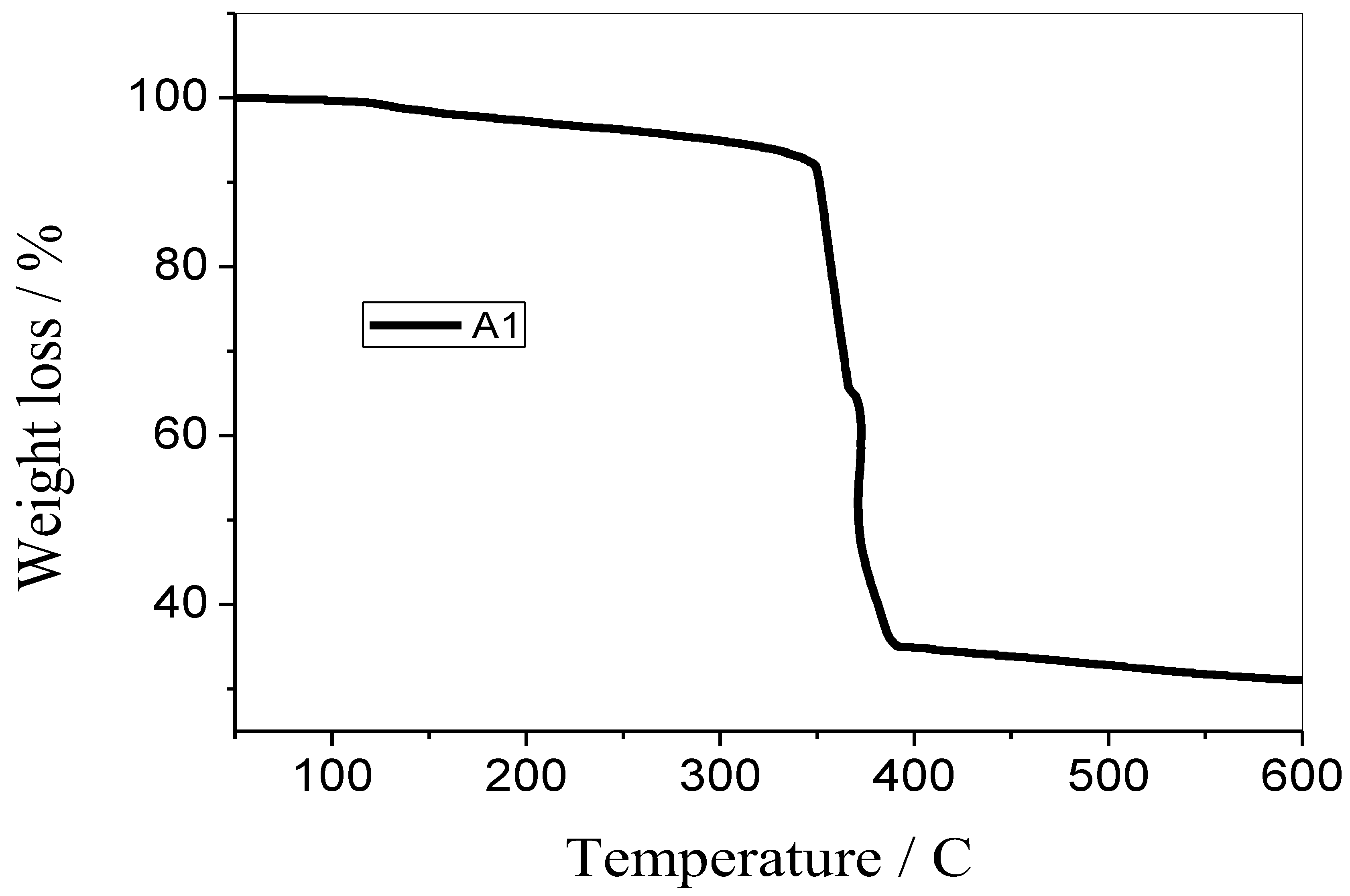
3.5. TGA Analysis
3.6. EDX Analysis
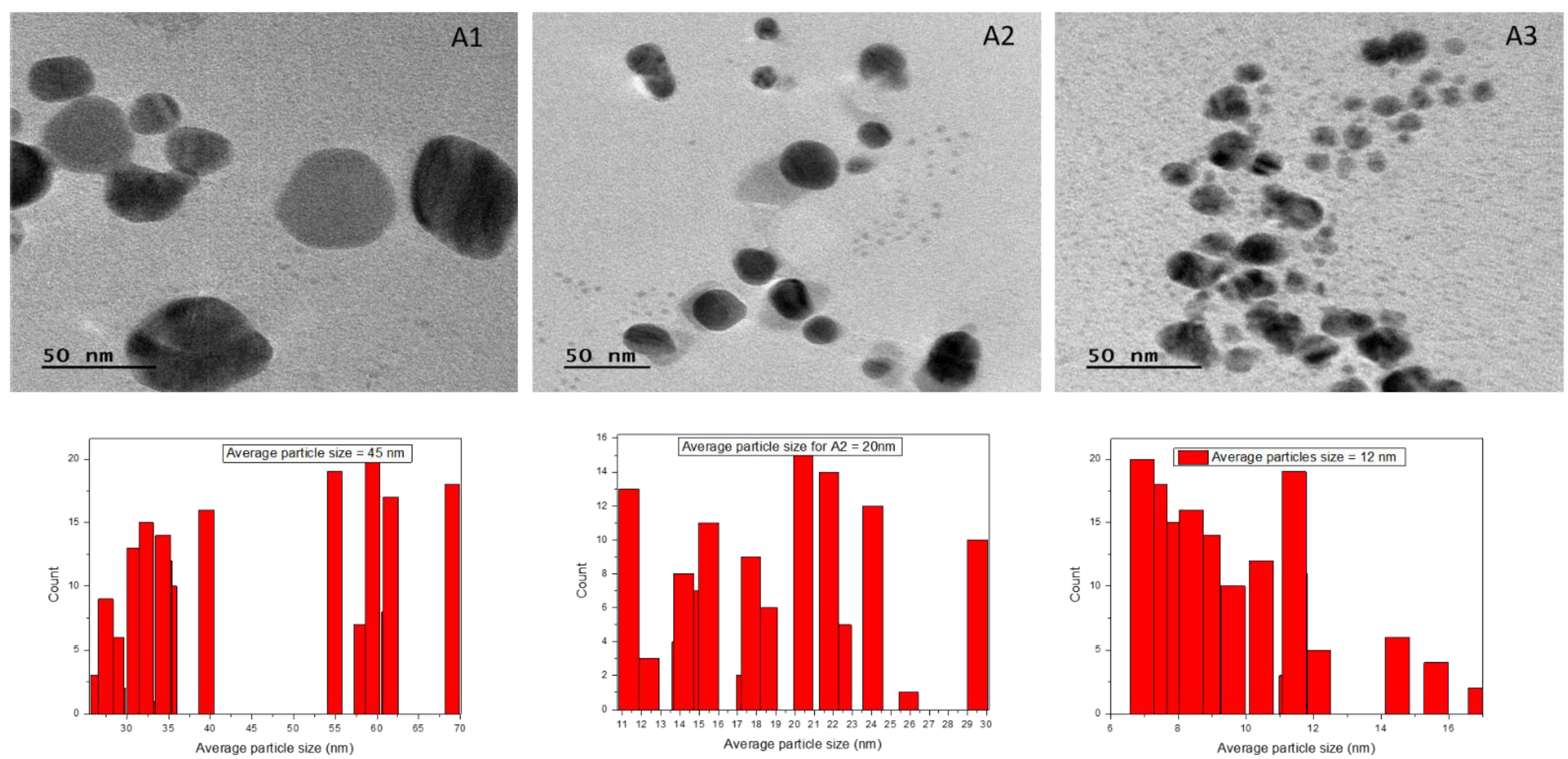
3.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity
3.9. Photocatalytic Activity
3.10. Comparison with Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veisi, H.; Dadres, N.; Mohammadi, P.; Hemmati, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles based on oil-water interface method with essential oil of orange peel and its application as nanocatalyst for A3 coupling. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou El-Nour, K.J.J.C.; Eftaiha, A.; Al-Warthan, A.; Ammar, R.A. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröfel, A.; Kratošová, G.; Šafařík, I.; Šafaříková, M.; Raška, I.; Shor, L.M.J.A.b. Applications of biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles—A review. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4023–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaiz, S.; Bibi, I.; Shah, S.W.H.; Wahab, Z.U.; Ilyas, H.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.; Zada, A.J. Oil mediated green synthesis of nano silver in the presence of surfactants for catalytic and food preservation application. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 2022, 236, 1493–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Chelliah, R.; MubarakAli, D.; Oh, D.-H.; Kathiresan, K.; Wang, M.-H.J.S.R. Unveiling the potentials of biocompatible silver nanoparticles on human lung carcinoma A549 cells and Helicobacter pylori. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Bharath, L.J.C.-B.I. Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles–a review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Rhee, Y.H.; Kwon, O.H.; Park, W. Shape-dependent antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 22, 2773–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, A.D.; Dayanand, A.; Sreedhar, B.; Dastager, S. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from novel Streptomyces species. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2010, 5, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Eastoe, M.; Hudson, L. Recent advances in nanoparticle synthesis with reversed micelles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, J.N.; Murthy, Z.V.P.J.I. Controlled size silver nanoparticles synthesis with water-in-oil microemulsion method: A topical review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 12311–12323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenashen, M.A.; El-Safty, S.A.; Elshehy, E.A.J.P. Synthesis, morphological control, and properties of silver nanoparticles in potential applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, V.; Sharma, B.; Shukla, G.; Srivastava, A.; Bhatnagar, A.J.C. Study of antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using green and chemical approach. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 554, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevika, A.; Shankaran, D.R. Seed-free synthesis of 1D silver nanowires ink using clove oil (Syzygium aromaticum) at room temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, M.V.d.O.B.; da Rosa Almeida, A.; Machado, M.H.; de Melo, A.P.Z.; da Rosa, C.G.; de Freitas, D.Z.; Noronha, C.M.; Teixeira, G.L.; de Armas, R.D.; Barreto, P.L.M. Syzygium aromaticum L. (clove) essential oil as a reducing agent for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Open J. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jirovetz, L.; Buchbauer, G.; Stoilova, I.; Stoyanova, A.; Krastanov, A.; Schmidt, E.J.J. Chemical composition and antioxidant properties of clove leaf essential oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6303–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Cai, Y.Z.; Sun, M.; Corke, H.J.J. Antioxidant capacity of 26 spice extracts and characterization of their phenolic constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7749–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, P.; Sanchez, C.; Batlle, R.; Nerin, C.J.J. Solid-and vapor-phase antimicrobial activities of six essential oils: Susceptibility of selected foodborne bacterial and fungal strains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6939–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisserand, R.; Young, R. Essential Oil Safety: A Guide for Health Care Professionals; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goudarzvand Chegini, S.; Abbasipour, H.J.T. Chemical composition and insecticidal effects of the essential oil of cardamom, Elettaria cardamomum on the tomato leaf miner, Tuta absoluta. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Farooq, A.; Ahmed, A.; Iqbal, M.; Demirci, B.; Başer, K. Antifungal activities and essential oil constituents of some spices from Pakistan. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2000, 22, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Hickey, J.W.; Santos, J.L.; Williford, J.-M.; Mao, H.-Q.J.J. Control of polymeric nanoparticle size to improve therapeutic delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N.J. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; De Jesus, M.B.; Seabra, A.B.; Fávaro, W.J.; Nakazato, G.J.N. Silver nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajitha, B.; Reddy, Y.A.K.; Reddy, P.S.J.P.T. Enhanced antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size by pH variation. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zada, A.; Muhammad, P.; Ahmad, W.; Hussain, Z.; Ali, S.; Khan, M.; Khan, Q.; Maqbool, M.J.A.F.M. Surface plasmonic-assisted photocatalysis and optoelectronic devices with noble metal nanocrystals: Design, synthesis, and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, H.; Zada, A.; Ali, S.; Khan, I.; Ali, W.; Khan, W.; Khan, M.; Anwar, N.; Ali, A.; Huerta-Flores, A.M.J.J. Visible light-excited surface plasmon resonance charge transfer significantly improves the photocatalytic activities of ZnO semiconductor for pollutants degradation. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravets, V.; Almemar, Z.; Jiang, K.; Culhane, K.; Machado, R.; Hagen, G.; Kotko, A.; Dmytruk, I.; Spendier, K.; Pinchuk, A.J.N. Imaging of biological cells using luminescent silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Nalini, S.K.; Prakash, N.U.; Madhankumar, D.J.M.L. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles by aqueous extract of Syzygium aromaticum. Mater. Lett. 2012, 75, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Malheiro, J.; Grenho, L.; Fernandes, M.H.; Simões, M.J.P. Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial action of selected phytochemicals against planktonic and sessile Streptococcus mutans. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, L.S.; Li, Y.; Kam, S.-L.; Wang, H.; Wong, E.Y.; Ooi, V.E. Antimicrobial activities of cinnamon oil and cinnamaldehyde from the Chinese medicinal herb Cinnamomum cassia Blume. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2006, 34, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keivani Nahr, F.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Samadi Kafil, H.; Hamishehkar, H.; Hoseini, M.J. The colloidal and release properties of cardamom oil encapsulated nanostructured lipid carrier. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amma, K.P.; Sasidharan, I.; Sreekumar, M.; Sumathykutty, M.; Arumughan, C.J. Total antioxidant capacity and change in phytochemicals of four major varieties of cardamom oils during decortication. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.J. Controllable preparation and mechanism of nano-silver mediated by the microemulsion system of the clove oil. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhu, V.; Aromal, S.A.; Philip, D.J. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Macrotyloma uniflorum. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 83, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieckmann, Y.; Cölfen, H.; Hofmann, H.; Petri-Fink, A.J. Particle size distribution measurements of manganese-doped ZnS nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3889–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindu, P.; Thomas, S.J. Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2014, 8, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, H.; Taddesse, A.; Kaushal, J.; Yadav, O.J. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. J. Surf. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanova, I.; Hasanova, U.; Gasimov, E.; Rzayev, F.; Hajiyev, E.; Eyvazova, G.; Shaliyev, M.; Mehdiyeva, A.; Aliyeva, N.; Yusifov, Y.J.M.C.; et al. PEG-assisted controlled precipitation of calcium hydroxide and calcium carbonate nanostructures for cement reinforcement. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 271, 124865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshiba, J.; Poonkothai, M.; Karthika, P.; Mythili, R. Green Route to a Novel and Ecofriendly Phytosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Platycladus Orientalis L. Leaf Extract. Mater. Lett. 2022, 309, 131347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Talat, M.; Singh, D.; Srivastava, O.J. Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles by natural precursor clove and their functionalization with amine group. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2010, 12, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.; Rangasamy, S.; Purushothaman, B.; Song, J.M.J.N. The application of bactericidal silver nanoparticles in wound treatment. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, F.; Hammad, E.-S.M.; Farag, M.; Ahemad, O.H.; Mohammed, M.; Salah, H.J. Detection of artificial colors added to cooked faba beans (Ful medames) and microbial examination for samples obtained from street vendors in Egypt. J. Med. Sci. Res. 2022, 5, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koe, W.S.; Lee, J.W.; Chong, W.C.; Pang, Y.L.; Sim, L.C. An overview of photocatalytic degradation: Photocatalysts, mechanisms, and development of photocatalytic membrane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2522–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, V.S.; Roy, A.; Rajeshkumar, S.J. Turmeric Oil Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antioxidant Activity. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2018, 10, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Rangel, R.D.; González-Muñoz, M.P.; Avila-Rodriguez, M.; Razo-Lazcano, T.A.; Solans, C.J.C.; Physicochemical, S. A Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles in oil-in-water microemulsion and nano-emulsion using geranium leaf aqueous extract as a reducing agent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 536, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfuraydi, A.A.; Devanesan, S.; Al-Ansari, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Ranjitsingh, A.J. Eco-friendly green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the sesame oil cake and its potential anticancer and antimicrobial activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 192, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.W.; Anwar, H.; Siddiqui, A.; Shah, M.R.; Ahmed, A.; Ali, S.A. Synthesis and chemosensing of nitrofurazone using olive oil based silver nanoparticles (O-AgNPs). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas, V.; Philip, D.; Mathew, J.J. Catalytically and biologically active silver nanoparticles synthesized using essential oil. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 132, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, B.S.; Birca, A.C.; Musat, M.C.; Holban, A.M.J.M. Wound dressings coated with silver nanoparticles and essential oils for the management of wound infections. Materials 2020, 13, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rivera, J.; Duce, C.; Ierardi, V.; Longo, I.; Spepi, A.; Tine, M.R.; Ferrari, C.J.C. Fast and Eco–friendly Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles using Rosemary Essential Oil as Renewable Reducing Agent. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, M.V.; da Rosa Almeida, A.; Machado, M.H.; Elias, W.C.; da Rosa, C.G.; Teixeira, G.L.; Noronha, C.M.; Bertoldi, F.C.; Nunes, M.R.; de Armas, R.D.J.B.; et al. Green synthesis, characteristics and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles mediated by essential oils as reducing agents. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 101746. [Google Scholar]
- Motelica, L.; Ficai, D.; Oprea, O.-C.; Ficai, A.; Ene, V.-L.; Vasile, B.-S.; Andronescu, E.; Holban, A.-M.J.N. Antibacterial biodegradable films based on alginate with silver nanoparticles and lemongrass essential oil–innovative packaging for cheese. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sr. No. | Sample Name | Diameter (nm) | Polydispersity Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | A1 | 92 | 0.0057 |
| 2. | A2 | 87.3 | 0.005 |
| 3. | A3 | 80.1 | 0.005 |
| Name of Sample | Average Crystallite Size (nm) | Dislocation Density (δ) |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 23.2 | 1.8 × 10−3 |
| A2 | 19.68 | 2.58 × 10−3 |
| A3 | 16.18 | 3.8 × 10−3 |
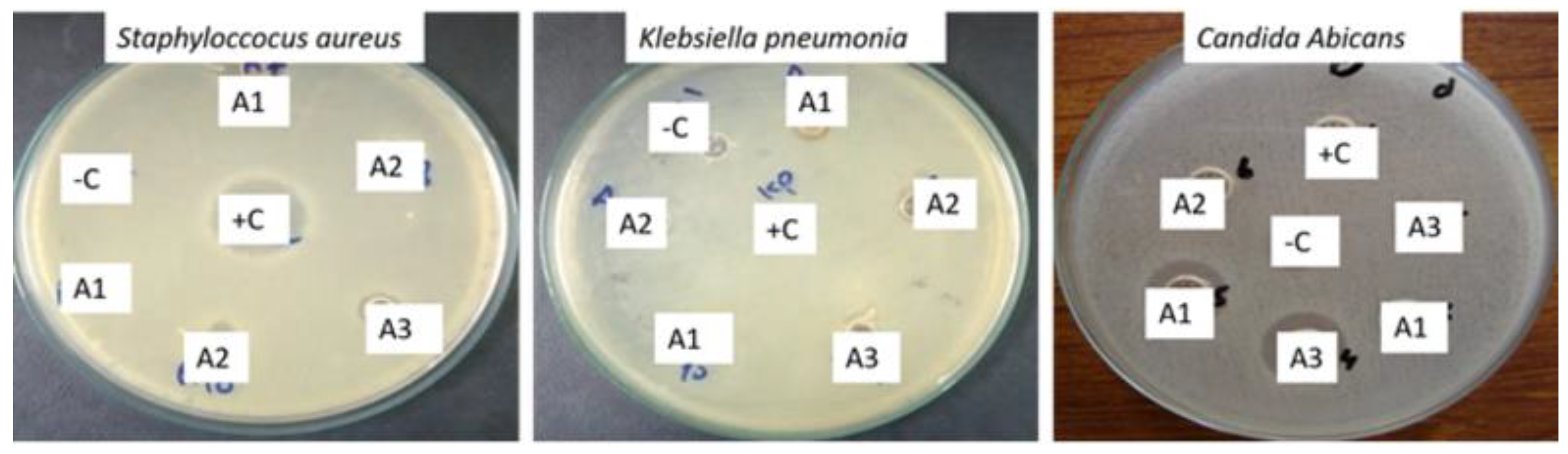
| Name of Species | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | |
| Staphyloccocus aureus | 15 | 12 | 18 |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | 23 | 21 | 24 |
| Candida albicans | 16 | 6 | 10 |
| S. NO. | Synthesis Method | Composition | Average Particle Size (NM) | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Green synthesis | AgN03 + Turmeric oil | ------- | Biomedical and antioxidant activities | [44] |
| 2 | Green synthesis | Silver Stearate + Castor oil + Birj surfactant | 25–150 | ------- | [45] |
| 3 | Green synthesis | AgNO3 + Sesame oil | 6.6–14.8 | Anticancer and antimicrobial | [46] |
| 4 | Green synthesis | AgNO3 + Orange peel oil extract | 2.76 | Nano catalysis | [1] |
| 5 | Green synthesis | AgNO3 + Clove oil + NaOH | 27–94 | Antibacterial activity | [14] |
| 6 | Green synthesis | AgNO3 + Olive oil | ------ | Antimicrobial and antibiofilm | [47] |
| 7 | Green synthesis | AgNO3 + leaves of M. fragrans + NaBH4 | ------- | Antioxidant and antimicrobial | [48] |
| 8 | γ-radiation method | AgNO3 + NaOH + Glucose | 69 | Wound healing | [49] |
| 9 | Green synthesis | Silver Acetate + Rosemary essential oil + Microwave | 7–18 | Compounds synthesis | [50] |
| 10 | Green synthesis | AgNO3 + essential oils + methanol | ------ | Antimicrobial and food preservation | [51] |
| 11 | Green Synthesis | AgNO3 + sodium citrate + Lemon grass essential oil | ------- | Antimicrobial films for Cheese preservation | [52] |
| 12. | Green synthesis | Ag NO3 + Clove oil + Cinnamon oil + Cardamom oil | 8–100 | Photocatalytic and antimicrobial application | This work |
| Sr. No. | Sample Code | Average Effective Diameter from DLS Analysis | Average Value of Crystallite Size from XRD Analysis (nm) | Average Value of Particles Size from TEM Analysis (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | A1 | 92 | 23.2 | 45 |
| 2. | A2 | 87.3 | 19.68 | 20 |
| 3. | A3 | 80.1 | 16.18 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pervaiz, S.; Bibi, I.; Rehman, W.; Alotaibi, H.F.; Obaidullah, A.J.; Rasheed, L.; M. Alanazi, M. Controlled Size Oils Based Green Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Application. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071090
Pervaiz S, Bibi I, Rehman W, Alotaibi HF, Obaidullah AJ, Rasheed L, M. Alanazi M. Controlled Size Oils Based Green Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Application. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071090
Chicago/Turabian StylePervaiz, Seemab, Iram Bibi, Wajid Rehman, Hadil Faris Alotaibi, Ahmad J. Obaidullah, Liaqat Rasheed, and Mohammed M. Alanazi. 2023. "Controlled Size Oils Based Green Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Application" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071090
APA StylePervaiz, S., Bibi, I., Rehman, W., Alotaibi, H. F., Obaidullah, A. J., Rasheed, L., & M. Alanazi, M. (2023). Controlled Size Oils Based Green Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Application. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071090









