Protective Effect of Willow (Salix babylonica L.) on Fish Resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Plant Materials
2.1.2. Bacterial Strains
2.1.3. Experimental Fish
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Plant Extracts
2.2.2. Chemical Composition Analysis
General Procedures
Isolation and Determination
2.2.3. Minimal Inhibition Concentration (MIC) and Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Determination
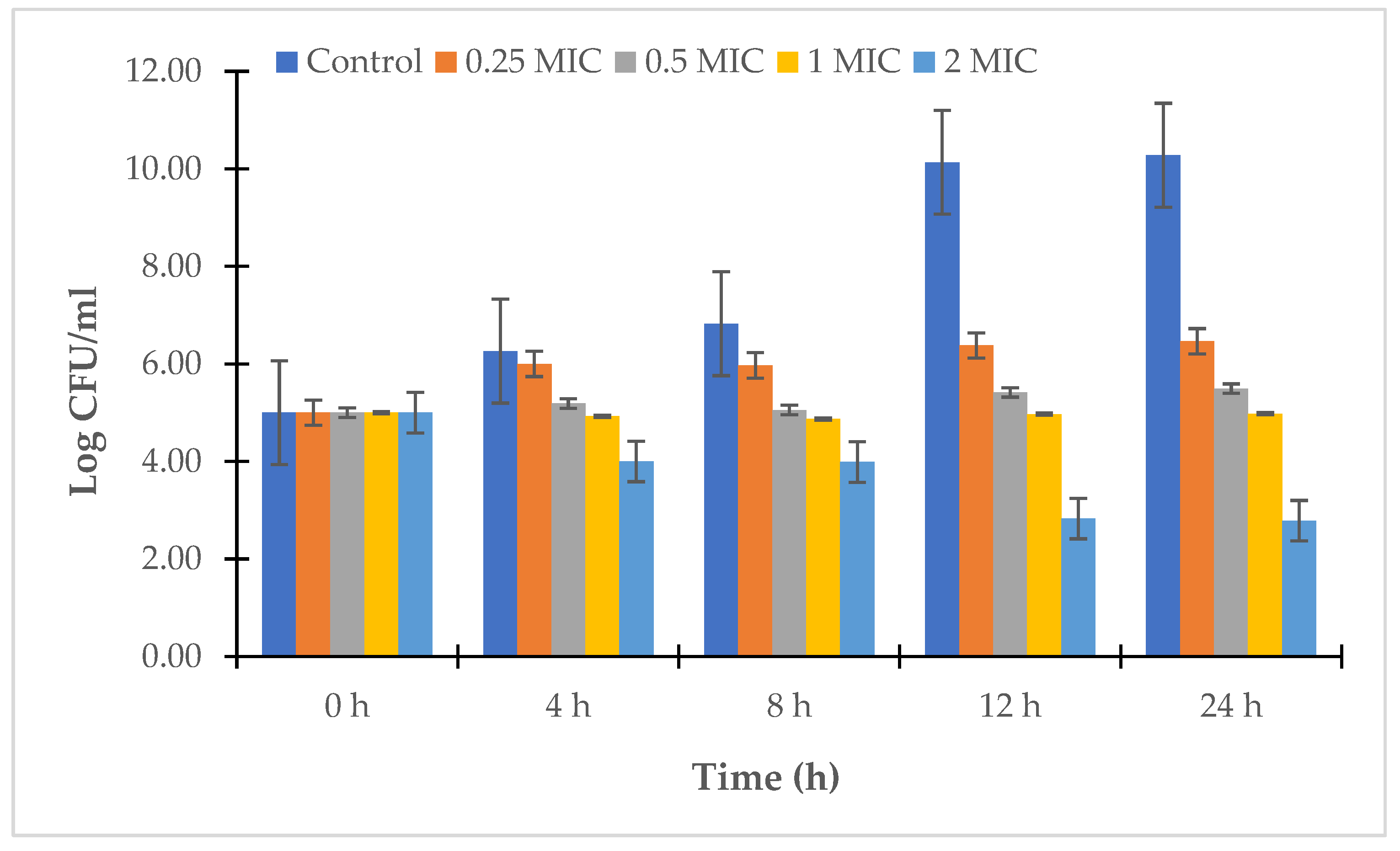
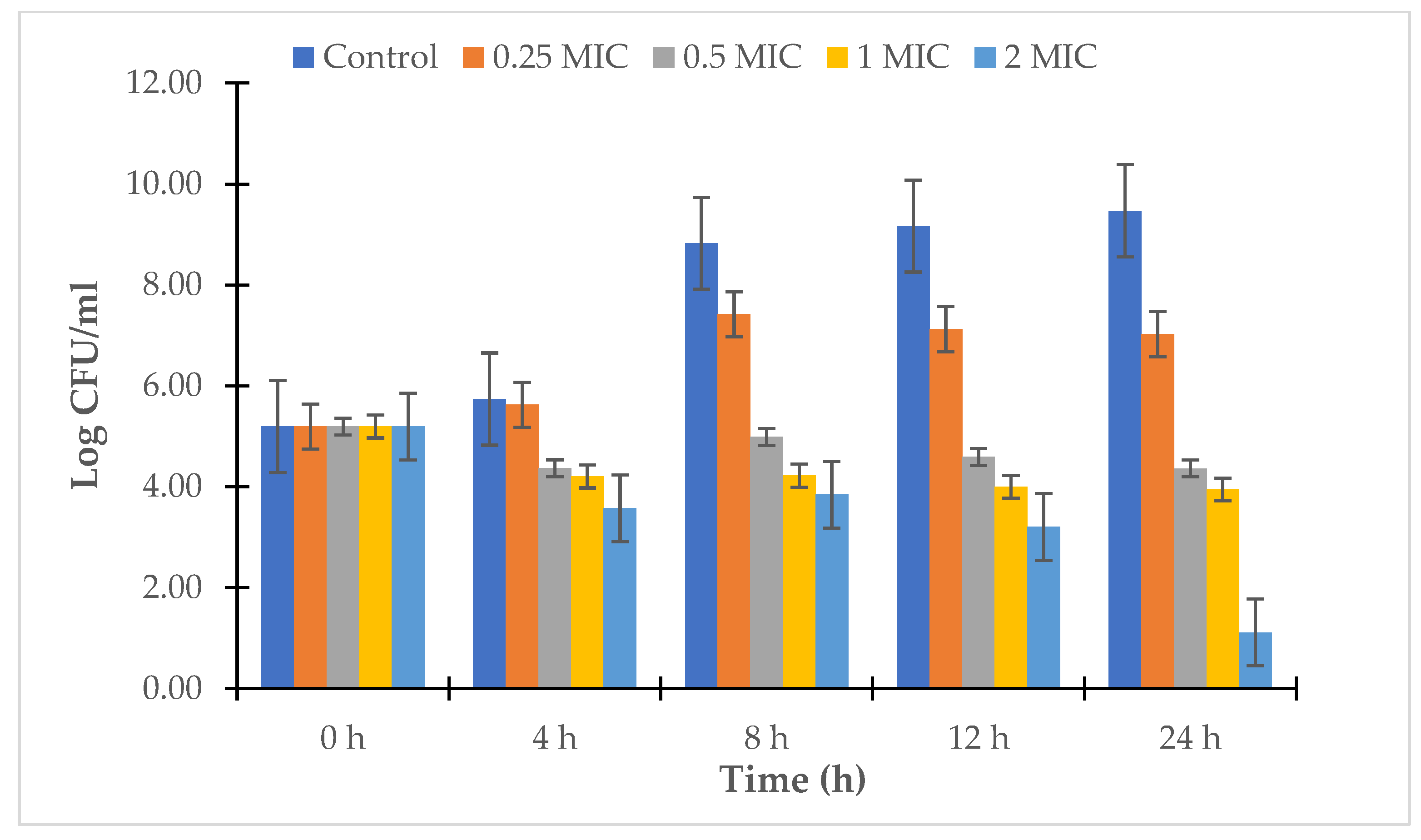
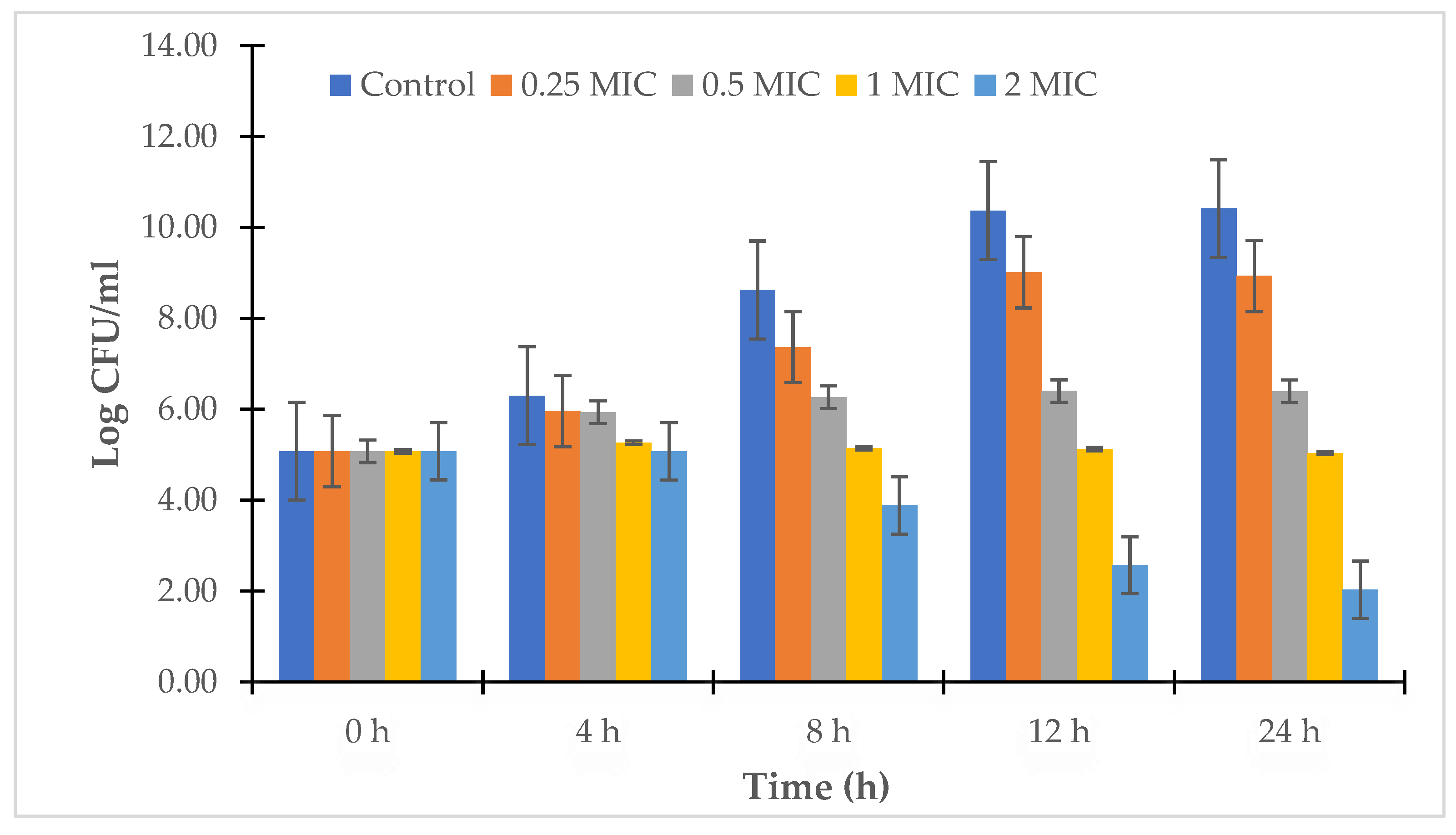
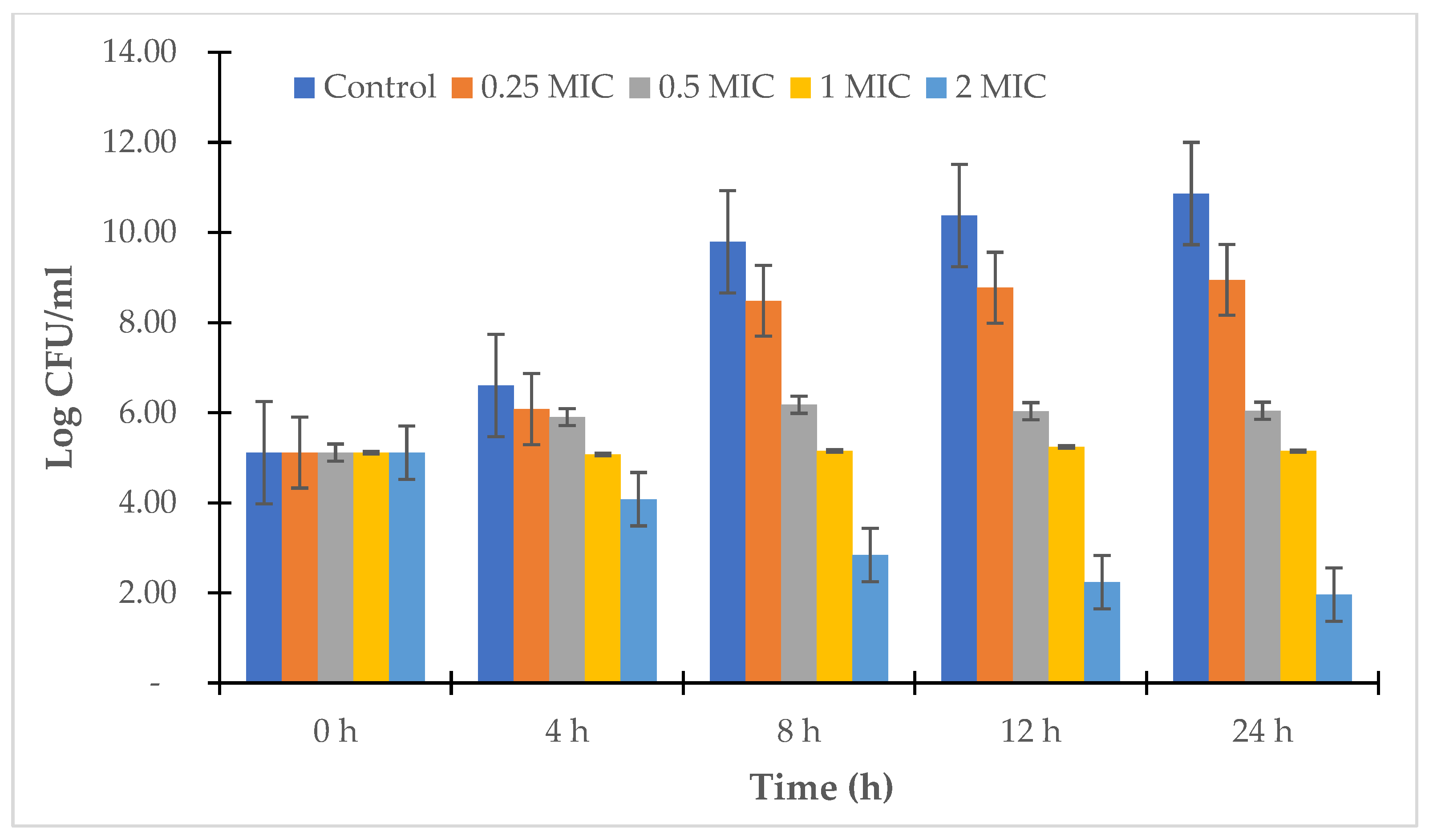
2.2.4. Time-Kill Study
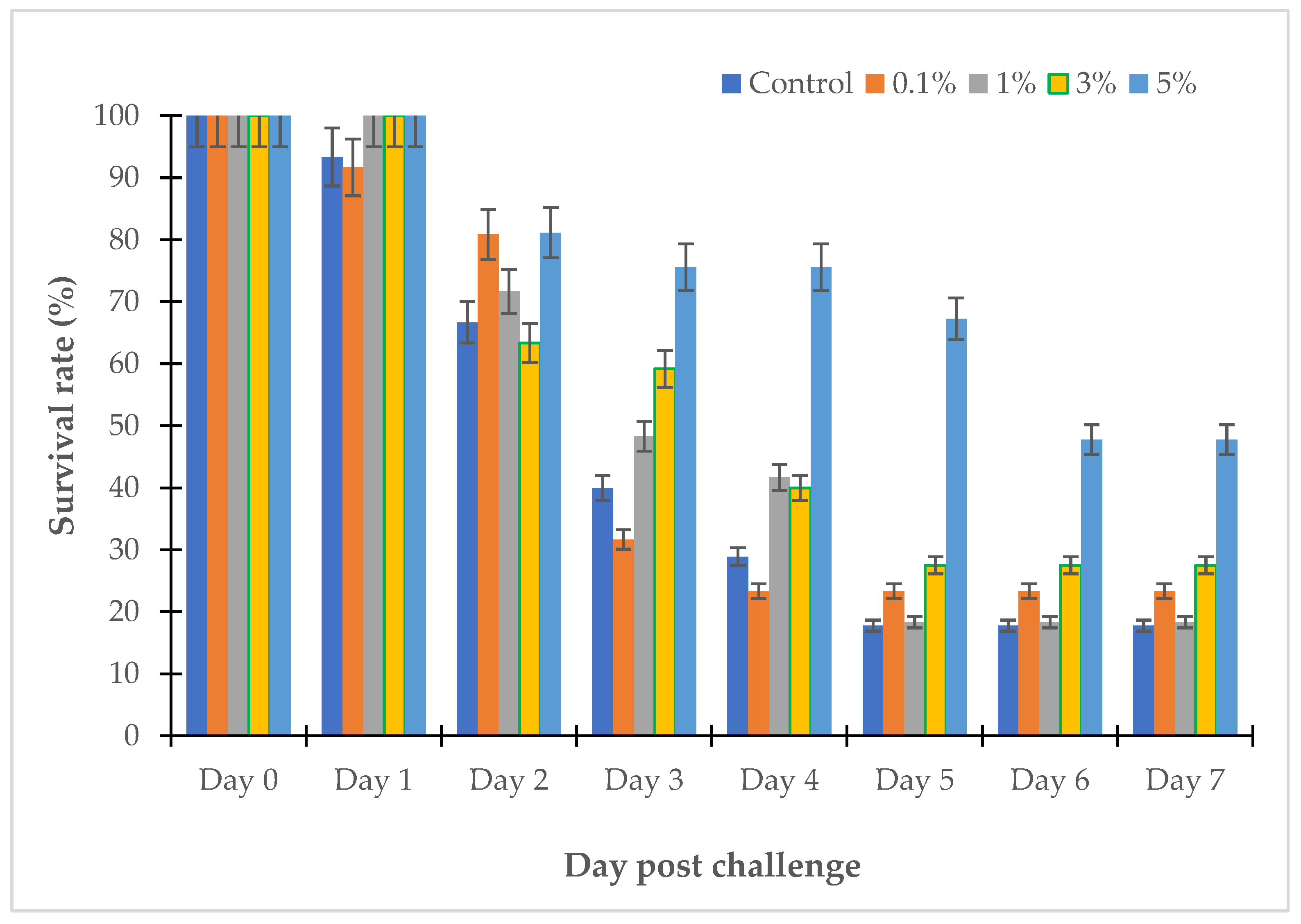
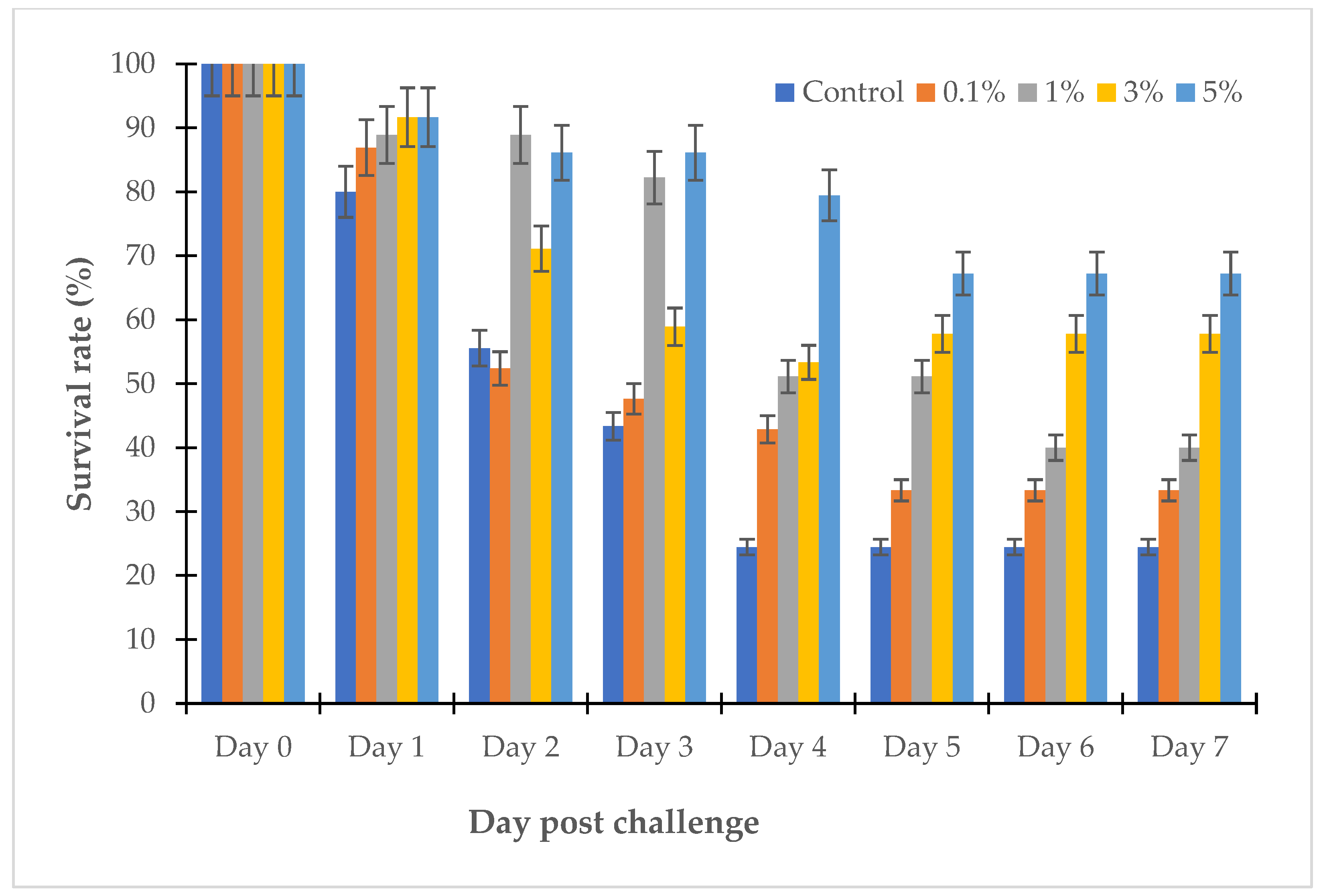
2.2.5. Trial of Willow Extract on Fish Challenged with Vibrio sp.
3. Results
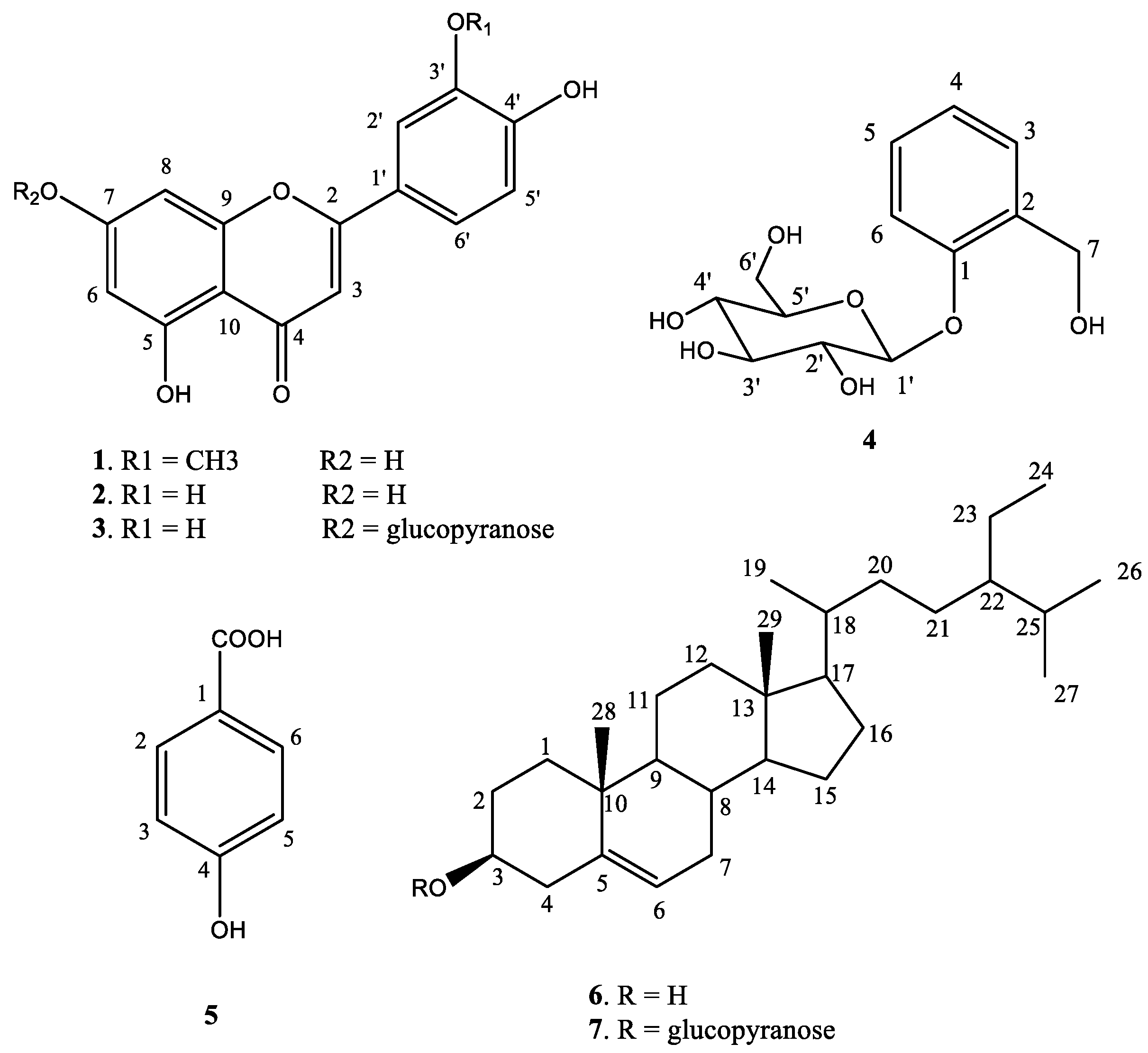
3.1. Isolation of Major Chemical Components of Extracts
3.2. Antibacterial Assay
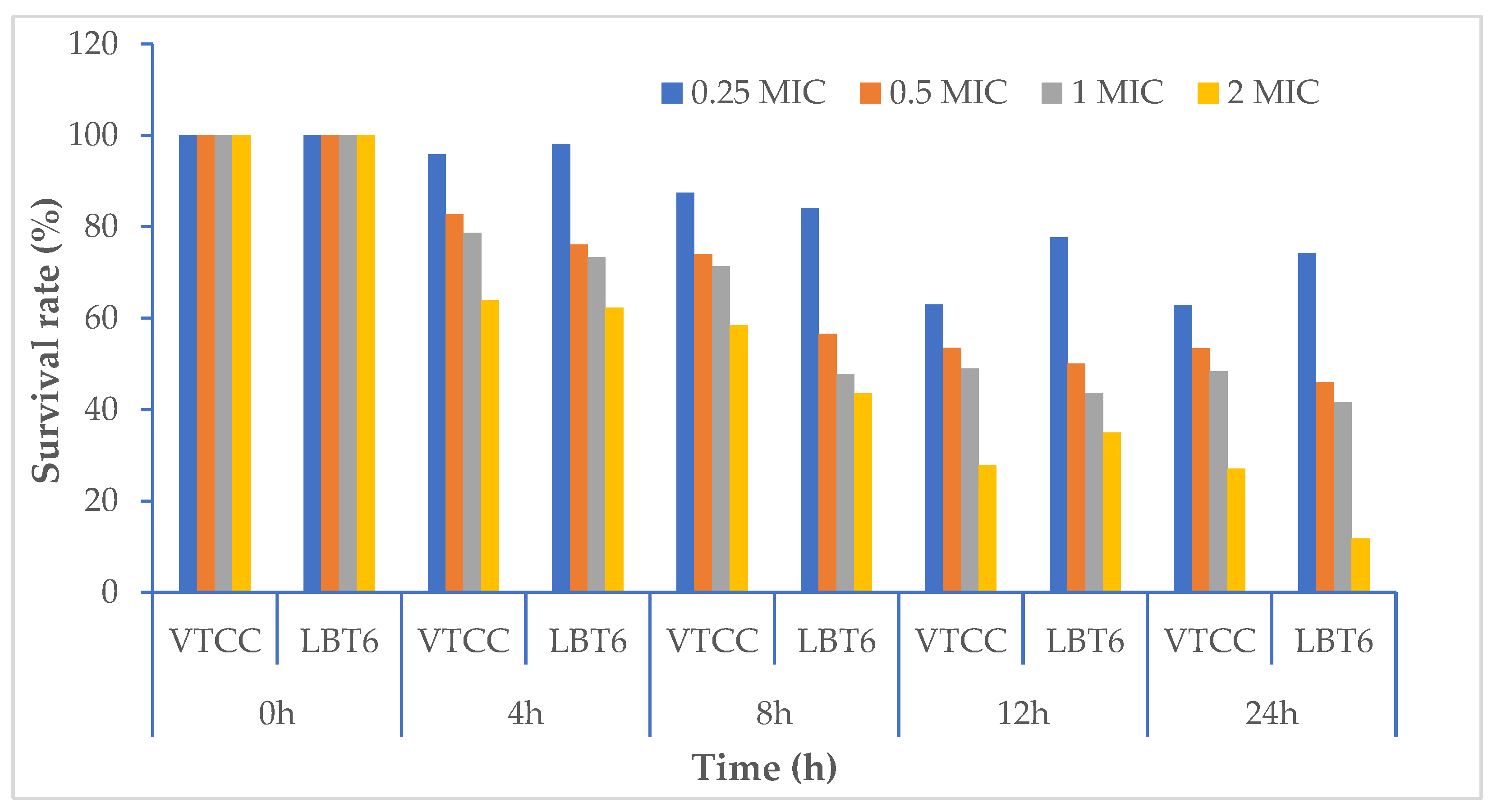
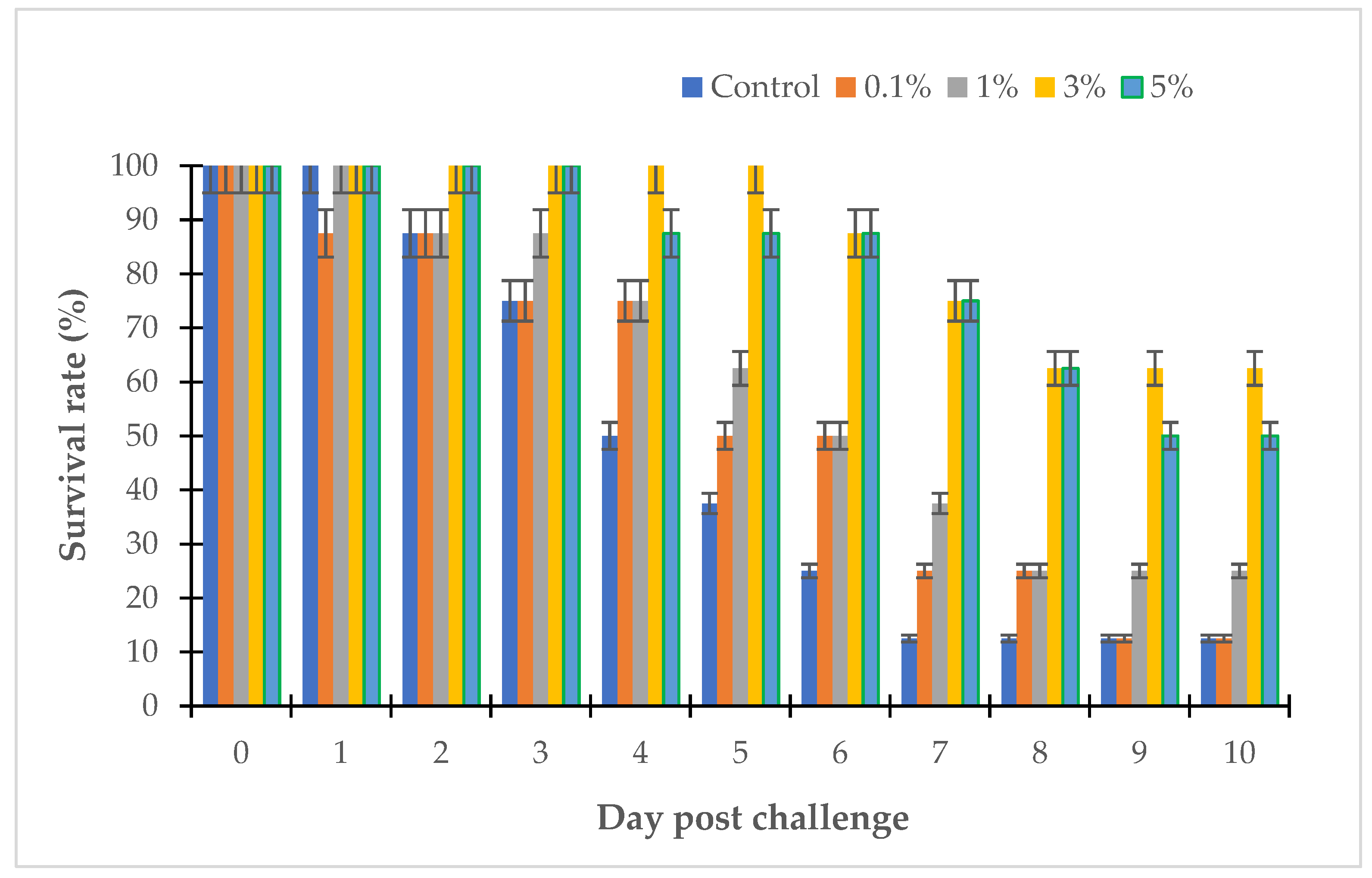
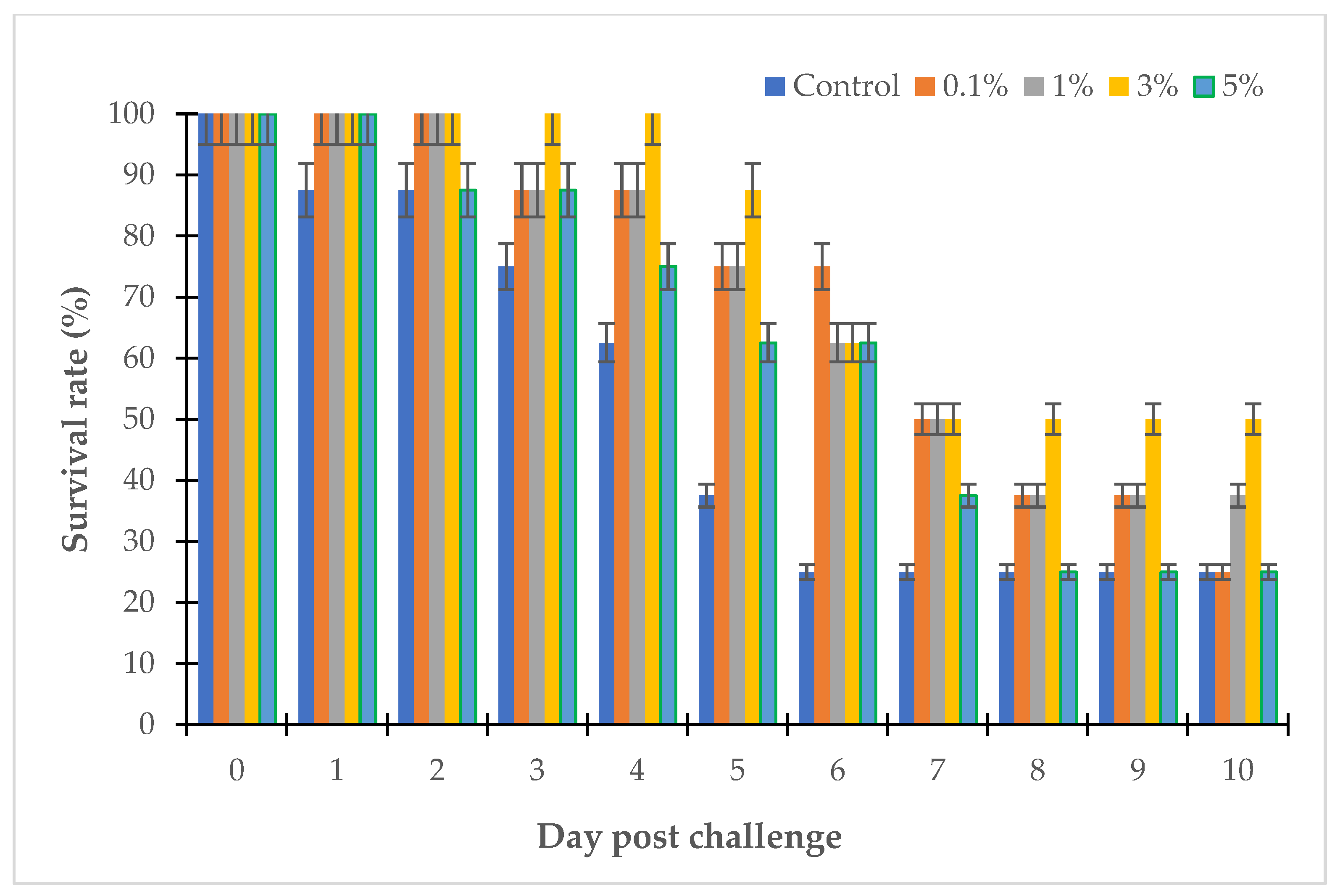
3.3. The Effects of Willow Extracts on Fish Challenged with Vibrio sp.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vietnam Directorate of Fisheries Report of the National Conference on Marine Aquaculture of Vietnam. 2022. Available online: https://tongcucthuysan.gov.vn/vi-vn/tin-t%E1%BB%A9c/-ngh%E1%BB%81-c%C3%A1-trong-n%C6%B0%E1%BB%9Bc/doc-tin/018148/2022-11-07/hoi-thao-quoc-gia-nuoi-bien-viet-nam-nam-2022 (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics—Global Production by Production Source 1950–2015. 2019. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/static/Yearbook/YB2019_USBcard/booklet/web_cb7874t.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Abert, V.; Ransangan, J. Effect of water temperature on susceptibility of culture marine fish species to Vibriosis. Int. J. Res. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ge, M.; Zheng, X.; Tao, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, G. Investigation of V. alginolyticus, V. harveyi, and V. parahaemolyticus in large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea (Richardson) reared in Xiangshan Bay, China. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 3, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, B.Q. Research on Some Common Diseases in Marine Fish Cultured in Ba Ria—Vung Tau Province and Propose Solutions for Prevention and Treatment. Report on the Results of a Research Project in Ba Ria—Vung Tau Province. 2012. Available online: http://csdlqg.vista.gov.vn/kq_chitiet_du.asp?id=KQT019/10/2018%2014:13:05 (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Ngo, T.H.; Vu, X.N.; Le, D.L.O.; Dang, L.Q.; Le, T.T.M.; Pham, T.T.; Dong, V.Q.; Vu, T.B.H. The Antibiotics resistance of Vibrio spp. isolated from aquaculture water in some areas of Northern Vietnam. Hue Univ. J. Sci. Nat. Sci. 2022, 131, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, P.T.A.; Trang, N.C. The status of antibiotics resistance of Vibrio spp. that isolated from white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) farming pond in Ben Tre province. J. Aquat. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cam, V.H.; Hang, P.T.T.; Thinh, D.V.; Tho, N.T.A.; Cuong, L.T. Biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from seacage lobster Panulirus spp. Vietnam. Natl. Conf. Biotechnol. 2020, 1, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Etinosa, O.I.; Omoruyi, G.I. Anti-vibrio potentials of acetone and aqueous leaf extracts of Ocimum gratissimum (Linn). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 743–750. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; Zhao, P.; He, Y.; Kang, S.; Shen, C.; Wang, S.; Guo, M.; Wang, L.; Shi, C. Antibacterial effect of oregano essential oil against Vibrio vulnificus and its mechanism. Foods 2022, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ut, T.M.; Uyen, D.T.T.; Dung, T.T. Antimicrobial activity of herbal extracts against Vibrio spp. bacteria isolated from white feces syndrome on white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in some provinces in the Mekong delta. Cantho Univ. J. Sci. 2021, 13, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel-López, L.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A.; Valladares-Carranza, B.; Peláez-Acero, A.; Sosa-Gutiérrez, C.G.; Hetta, H.F.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Alqahtani, A.; Rivero-Perez, N. In vitro antibacterial potential of Salix babylonica extract against bacteria that affect Oncorhynchus mykiss and Oreochromis spp. Animals 2020, 10, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, D.; Farr, D.A.; Walton, M.G.; Withey, J.H. Zebrafish models for pathogenic Vibrios. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, e00165-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na-Phatthalung, P.; Chusri, S.; Suanyuk, N.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. In vitro and in vivo assessments of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf extract as an alternative anti-streptococcal agent in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.H.; Arias, C.R. Protective efficacy of Nigella sativa seeds and oil against columnaris disease in fishes. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, B.H.; Cuong, N.M.; Huong, T.T.; Choi, E.-M.; Kim, J.-A.; Kim, Y.H. Chrysoeriol isolated from the leaves of Eurya ciliata stimulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-C.; Pai, Y.-F.; Tsai, T.-H. Isolation of Luteolin and Luteolin-7-O-glucoside from Dendranthema morifolium Ramat Tzvel and Their Pharmacokinetics in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7700–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, R.; Chao, Z. Isomeric phenolic glycosides from from Populus tomentosa. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2018, 13, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Conte, M.M.; Huang, X.-C.; Khalil, Z.; Capon, R.J. A search for BACE inhibitors reveals new biosynthetically related pyrrolidones, furanones and pyrroles from a southern Australian marine sponge, Ianthella sp. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedula, V.S.P.; Prakash, I. Isolation of Stigmasterol and β-Sitosterol from the dichloromethane extract of Rubus suavissimus. Int. Curr. Pharm. J. 2012, 1, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van NT, H.; Ha, L.M.; Phuong, N.T.; Anh, L.T.; Bach, P.C.; Binh, N.Q.; Vien, T.A.; Long, P.Q. Some naphthalene lactone relatives from Eleutherine bulbosa in Vietnam. Vietnam J. Chem. 2012, 51, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Canillac, N.; Mourey, A. Antibacterial activity of the essential oil of Picea excelsa on Listeria, Staphylococcus aureus and coliform bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2001, 18, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, I.; Abbas, H.A.; Ashour, M.L.; Yasri, A.; El-Shazly, A.M.; Wink, M.; Sobeh, M. Polyphenols from Salix tetrasperma impair virulence and inhibit quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2020, 25, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, Y.; Rustaiyan, A.; Monajjemi, M.; Khavarinejad, R.A. Study of anti-retroviral effects of Salix aegyptiaca L. Herbal extract on HIV-1 in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 398–405. [Google Scholar]
- Gligorić, E.; Igić, R.; Suvajdžić, L.; Grujić-Letić, N. Species of the genus Salix L.: Biochemical screening and molecular docking approach to potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobeh, M.; Mahmoud, M.F.; Rezq, S.; Alsemeh, A.E.; Sabry, O.M.; Mostafa, I.; Abdelfattah, M.A.O.; El-Allem, K.A.; El-Shazly, A.M.; Yasri, A.; et al. Salix tetrasperma Roxb. extract alleviates neuropathic pain in rats via modulation of the NF-κB/TNF-α/NOX/iNOS pathway. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostanska, K.; Jürgenliemk, G.; Abel, G.; Nahrstedt, A.; Saller, R. Willow bark extract (BNO1455) and its fractions suppress growth and induce apoptosis in human colon and lung cancer cells. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2007, 31, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, J.G. Medicinal potential of willow: A chemical perspective of aspirin discovery. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2010, 14, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Seong, K.Y.; Park, K.H. Antimicrobial activity of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid isolated and identified from rice hull. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 2273–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.H.; Park, J.R.; Kim, K.M. Antimicrobial activity of Chrysoeriol 7 and Chochlioquinone 9, white-backed planthopper-resistant compounds, against rice pathogenic strains. Biology 2020, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiruvella, K.K.; Mohammed, A.; Dampuri, G.; Ghanta, R.G.; Raghavan, S.C. Phytochemical and antimicrobial studies of methyl angolensate and Luteolin-7-O-glucoside isolated from callus cultures of Soymida febrifuga. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. IJBS 2007, 3, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierre Luhata, L.; Usuki, T. Antibacterial activity of β-sitosterol isolated from the leaves of Odontonema strictum (Acanthaceae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 48, 128248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njinga, N.S.; Sule, M.I.; Pateh, U.U.; Hassan, H.S.; Abdullahi, S.T.; Ache, R.N. Isolation and antimicrobial activity of β-Sitosterol-3-O-Glucoside from Lannea Kerstingii Engl. & K. Krause (Anacardiacea). J. Health Allied Sci. NU 2016, 6, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, G.A.; Sallam, A.; Elgaml, A.; Lahloub, M.F.; Afifi, M.S. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salix babylonica extracts. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- González-Alamilla, E.; Jacobo, M.R.; Sosa-Gutiérrez, C.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, L.; Valladares-Carranza, B.; Rosenfeld-Miranda, C.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A.; Rivero-Pérez, A. Antibacterial effect of the methanol extract of Salix babylonica against important bacteria in public health. Abanico Vet. 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bacteria | LL2 (μg/mL) | LL3 (μg/mL) | Cefotaxim (μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | |
| V. alginolyticus ATCC 17749 | 3.75 | 17.5 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| V. alginolyticus NG20 | 3.5 | 17.5 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| V. parahaemolyticus VTCC 12233 | 2.0 | 9.5 | 2.0 | 3.75 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| V. parahaemolyticus LBT6 | 3.5 | 12.0 | 2.0 | 3.75 | 0.56 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mai, T.M.N.; Vu, T.B.H.; Le, M.H.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Trinh, T.T.H.; Le, M.H.; Tran, N.N.; Nguyen, Q.L.; Pham, T.H.Y.; Pham, H.N.; et al. Protective Effect of Willow (Salix babylonica L.) on Fish Resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060989
Mai TMN, Vu TBH, Le MH, Nguyen TTH, Trinh TTH, Le MH, Tran NN, Nguyen QL, Pham THY, Pham HN, et al. Protective Effect of Willow (Salix babylonica L.) on Fish Resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(6):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060989
Chicago/Turabian StyleMai, Thi Minh Ngoc, Thi Bich Huyen Vu, Minh Ha Le, Thi Thu Hien Nguyen, Thi Thu Hang Trinh, Minh Hai Le, Nguyen Ngoc Tran, Quang Linh Nguyen, Thi Hai Yen Pham, Hoang Nam Pham, and et al. 2023. "Protective Effect of Willow (Salix babylonica L.) on Fish Resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus" Antibiotics 12, no. 6: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060989
APA StyleMai, T. M. N., Vu, T. B. H., Le, M. H., Nguyen, T. T. H., Trinh, T. T. H., Le, M. H., Tran, N. N., Nguyen, Q. L., Pham, T. H. Y., Pham, H. N., & Pham, T. T. (2023). Protective Effect of Willow (Salix babylonica L.) on Fish Resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus. Antibiotics, 12(6), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12060989






