Assessment of Plasma Tylosin Concentrations: A Comparative Study of Immunoassay, Microbiological Assay, and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
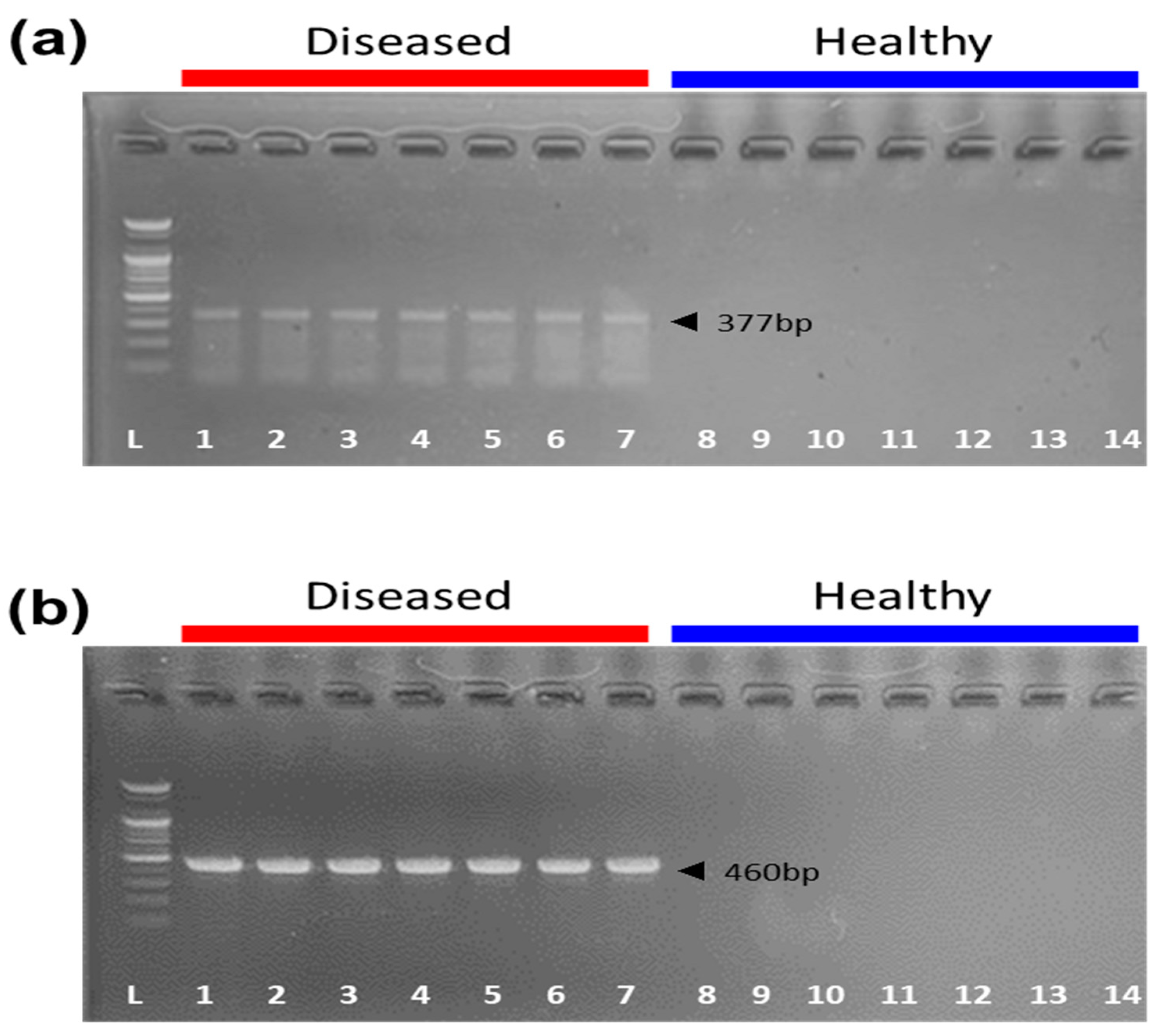
2.1. Clinical Signs and Target Gene Detection in Pigs
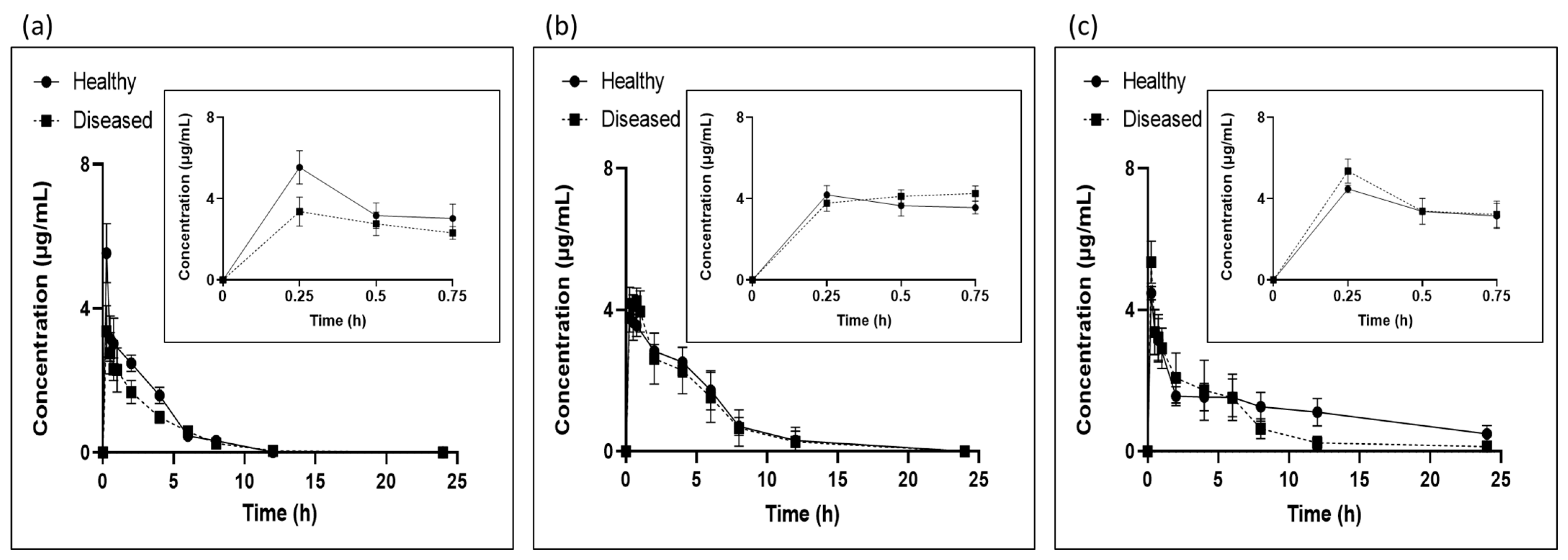
2.2. Determination of Plasma Tylosin Concentrations
2.2.1. LC/MS
2.2.2. Microbiological Assay
2.2.3. ELISA
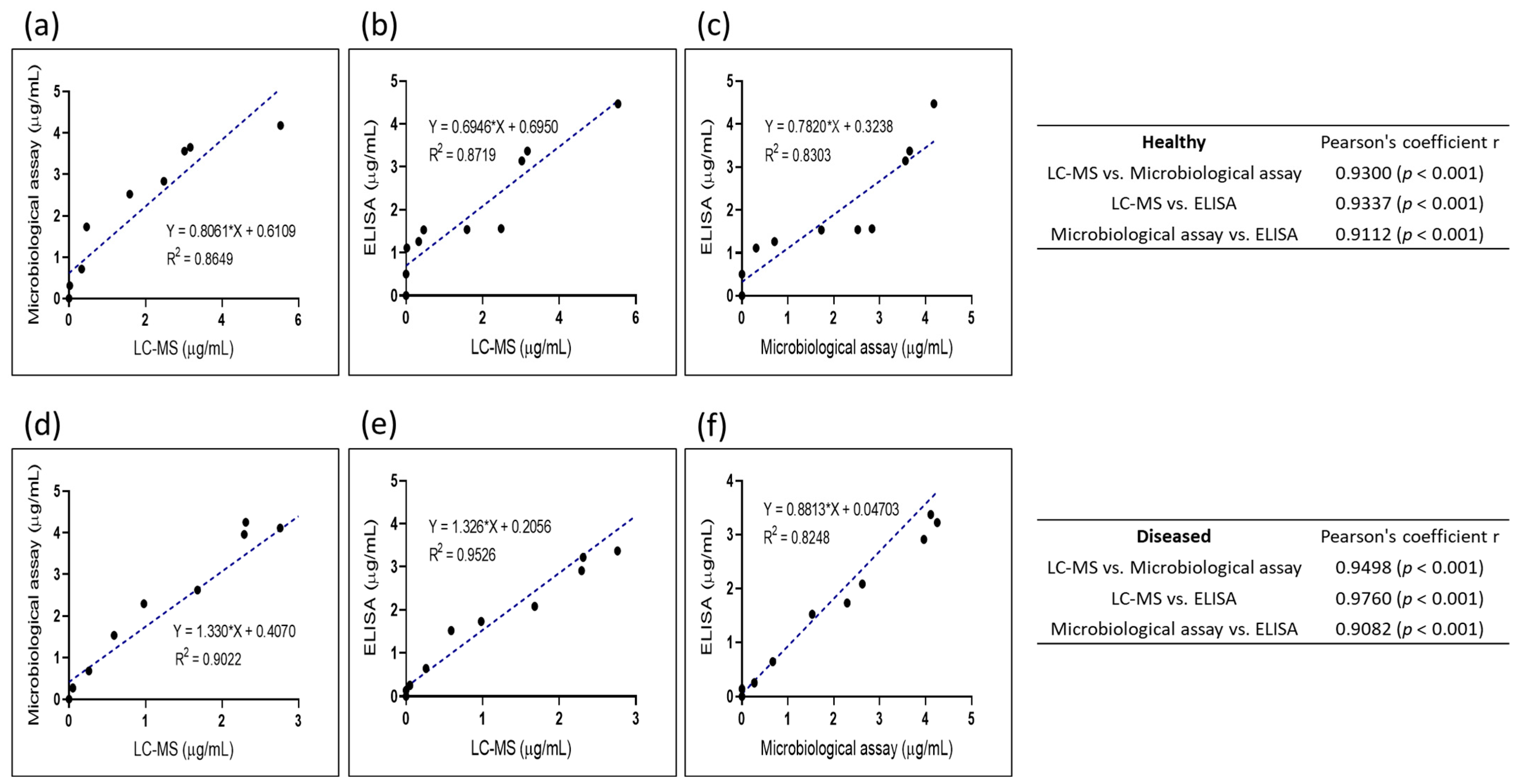
2.3. Comparison of Methods
2.3.1. Correlation of LC/MS and Microbiological Assay
2.3.2. Correlation of LC/MS and ELISA
2.3.3. Correlation of Microbiological Assay and ELISA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Bacterial Strains
4.3. Animal Experiment
4.3.1. Experimental Design
4.3.2. Blood Collection
4.3.3. Plasma Sample Processing for LC/MS Analysis
4.4. Analysis of Plasma Tylosin Concentrations
4.4.1. Microbiological Assay
4.4.2. ELISA
4.4.3. LC/MS Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urbanová, Z.; Zahradníkova, M.; Schovánek, V.; Polák, L.; Rabas, P.; Sechser, T.; Svandová, E.; Raskova, H.; Raska, K.; Janovská, D.; et al. Effect of tylosin in pigs. Vet. Med. 1975, 20, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Arsic, B.; Barber, J.; Čikoš, A.; Mladenovic, M.; Stankovic, N.; Novak, P. 16-Membered Macrolide Antibiotics: A Review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entorf, M.; Feßler, A.T.; Kadlec, K.; Kaspar, H.; Mankertz, J.; Peters, T.; Schwarz, S. Tylosin Susceptibility of Staphylococci from Bovine Mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazer, C.L.; Eldermire, E.R.B.; Lhermie, G.; Murray, S.A.; Scott, H.M.; Gröhn, Y.T. The Effect of Tylosin on Antimicrobial Resistance in Beef Cattle Enteric Bacteria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 176, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Carstensen, B. Effect of Tylosin Used as a Growth Promoter on the Occurrence of Macrolide-Resistant Enterococci and Staphylococci in Pigs. Microb. Drug Resist. 1998, 4, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Krochmal, B.; Dudek-Wicher, R. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaner, J.; Hill, A.; Acosta, E. Practical Implications for the Interpretation of Minimum Plasma Concentration/Inhibitory Concentration Ratios. Lancet 2001, 357, 1438–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, M.M.; Nejem, R.M.; El-Abadla, N.S.; El-Naby, M.K.; Roshdy, A.A.; Kheiralla, Z.A. Effects of Paracetamol on the Pharmacokinetics of Ciprofloxacin in Plasma Using a Microbiological Assay. Clin. Drug Investig. 2007, 27, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, K.; Abusoglu, S.; Unlu, A. Comparison of Immunoassay and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Methods in the Measurement of Serum Androstenedione Levels. Clin. Lab. 2018, 64, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, F.; Eijkemans, M.J.C.; Goverde, A.J.; Lentjes, E.G.W.M.; Hoek, A.; Lambalk, C.B.; Hickey, T.E.; Fauser, B.C.J.M.; Norman, R.J. Assessment of Androgen Concentration in Women: Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Extraction RIA Show Comparable Results. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaucher, L.C.; Breier, A.R.; Schapoval, E.E.S. Microbiological Assay for the Determination of Telithromycin in Tablets. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.J.; Kulmann, R.R.; Silva, L.M.; Nogueira, D.R.; Zimmermann, E.S.; Schmidt, C.A. Development and In-House Validation of a Microbiological Assay for Determination of Cefepime in Injectable Preparations. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabay, A. Rapid Quantitative Microbiological Assay of Antibiotics and Chemical Preservatives of a Nonantibiotic Nature. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 22, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahler, G. European Pharmacopoeia (Eur Ph) BT—Dictionary of Pharmaceutical Medicine; Nahler, G., Ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2009; p. 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Rocha-Santos, T. Chapter 1—An Introduction to the Concept of One Health; Prata, J.C., Ribeiro, A.I., Rocha-Santos, T.B.T.-O.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.J. Principles and Applications of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Biochemistry. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2009, 30, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.N.; French, D.; Jannetto, P.J.; Rappold, B.A.; Clarke, W.A. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Clinical Diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2022, 2, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.L.; Jones, T.; Whittle, K.; Watkins, J.; Barnes, R.A. Comparison of Galactomannan Enzyme Immunoassay Performance Levels When Testing Serum and Plasma Samples. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, V.; Paul Theobald, J.; Algeciras-Schimnich, A. Evaluation of Plasma ACTH Stability Using the Roche Elecsys Immunoassay. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 81, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridlund, J.; Woksepp, H.; Schön, T. A Microbiological Method for Determining Serum Levels of Broad Spectrum β-Lactam Antibiotics in Critically Ill Patients. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 129, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfipour, F.; Valizadeh, H.; Hallaj-Nezhadi, S.; Milani, M.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Comparison of Microbiological and High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Methods for Determination of Clarithromycin Levels in Plasma. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2010, 9, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, M.; Small, B.; Oldfield, L.; Evans, A.; Greenhalf, W.; Halloran, C.; Costello, E. The Holding Temperature of Blood during a Delay to Processing Can Affect Serum and Plasma Protein Measurements. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezzi, J.-P.; Bulla, A.; Bellora, C.; Rose, M.; Lescuyer, P.; Kiehntopf, M.; Hiller, K.; Betsou, F. LacaScore: A Novel Plasma Sample Quality Control Tool Based on Ascorbic Acid and Lactic Acid Levels. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğan, N.Ö. Bland-Altman Analysis: A Paradigm to Understand Correlation and Agreement. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighe, P.J.; Ryder, R.R.; Todd, I.; Fairclough, L.C. ELISA in the Multiplex Era: Potentials and Pitfalls. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terato, K.; Do, C.T.; Cutler, D.; Waritani, T.; Shionoya, H. Preventing Intense False Positive and Negative Reactions Attributed to the Principle of ELISA to Re-Investigate Antibody Studies in Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 407, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Lowenstine, L.; Marx, P.; Higgins, J.; Baulu, J.; McGuire, M.; Gardner, M.B. The Causes of False-Positives Encountered during the Screening of Old-World Primates for Antibodies to Human and Simian Retroviruses by ELISA. J. Virol. Methods 1986, 14, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, S.D.; Keren, D.F.; Torretti, B.; Dieterle, R.C.; Grauds, S. Factors Affecting Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Insulin Antibodies in Serum. Clin. Chem. 1981, 27, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhuang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Cao, J. Comparison of Pharmacokinetics of Tilmicosin in Healthy Pigs and Pigs Experimentally Infected with Actinobacillus Pleuropneumoniae. N. Z. Vet. J. 2019, 67, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccone, C.D. Basic Pharmacokinetics and the Potential Effect of Physical Therapy Interventions on Pharmacokinetic Variables. Phys. Ther. 1995, 75, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsa, H.; Zamir, A.; Rasool, M.F.; Imran, I.; Saeed, H.; Ahmad, T.; Alsanea, S.; Alshamrani, A.A.; Alruwaili, A.H.; Alqahtani, F. Development and Evaluation of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model of Labetalol in Healthy and Diseased Populations. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahle, J.L.; Haynes, J.S.; Andrews, J.J. Experimental Reproduction of Haemophilus Parasuis Infection in Swine: Clinical, Bacteriological, and Morphologic Findings. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1995, 7, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, C.; Kokkonen, T.; Heinonen, M.; Sankari, S.; Peltoniemi, O. Feeding Sows with High Fibre Diet around Farrowing and Early Lactation: Impact on Intestinal Activity, Energy Balance Related Parameters and Litter Performance. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 86, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbur, P.G.; Paul, P.S.; Frey, M.L.; Landgraf, J.; Eernisse, K.; Meng, X.J.; Lum, M.A.; Andrews, J.J.; Rathje, J.A. Comparison of the Pathogenicity of Two US Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Isolates with That of the Lelystad Virus. Vet. Pathol. 1995, 32, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, A.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Eamens, G.J.; Forbes, W.A.; Kuhn, R.; Kuhnert, P.; Gottschalk, M.; Nicolet, J.; Frey, J. Identification and Detection of Actinobacillus Pleuropneumoniae by PCR Based on the Gene ApxIVA. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 79, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, A.; Bakry, N.; El-Demerdash, A. Virulence Attitude Estimation of Pasteurella Multocida Isolates in Embryonated Chicken Eggs. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 6153–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couper, A.; Cromie, L.; Neeve, S.; Pommier, P.; Keïta, A.; Pagot, E. Treatment of Pneumonia in Pigs with Long-Acting Injectable Tylosin. Vet. Rec. 2006, 159, 805–807. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.V.; Brodie, J.L.; Benner, E.J.; Kirby, W.M. Simplified, Accurate Method for Antibiotic Assay of Clinical Specimens. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachunskii, L.S.; Gagaeva, E.V.; Kuleshova, E.É.; Dombrovskii, V.S.; Suina, Z.M.; Kuleshov, S.E.; Firsov, A.A. Evaluation of the Bioavailability of Preparations Subjected to Hepato-Intestinal Circulation: Lincomycin. Pharm. Chem. J. 1993, 27, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazedey, E.C.L.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and Validation of a Microbiological Agar Assay for Determination of Orbifloxacin in Pharmaceutical Preparations. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyra, E.; Nebot, C.; Gavilán, R.; Cepeda, A.; Kwiatek, K. Development and Validation of an LC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of Tiamulin, Trimethoprim, Tylosin, Sulfadiazine and Sulfamethazine in Medicated Feed. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Graubard, B.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Use and Reporting of Bland–Altman Analyses in Studies of Self-Reported versus Measured Weight and Height. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Assays | Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.025 | ||
| Intra-assay | Mean concentration (n = 5) | 4.06 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Precision (RSD, %) | 0.95 | 2.13 | 13.63 | 8.34 | 16.90 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 101.39 | 104.21 | 113.62 | 101.34 | 101.56 | |
| Inter-assay | Mean concentration (n = 5) | 4.08 | 0.97 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Precision (RSD, %) | 1.94 | 11.84 | 14.91 | 16.15 | 20.05 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 102.03 | 97.38 | 108.36 | 101.85 | 105.77 | |
| Assays | Nominal Concentration (μg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Intra-assay | Mean concentration (n = 5) | 14.41 | 8.38 | 3.44 | 2.32 | 0.90 |
| Precision (RSD, %) | 9.32 | 8.16 | 4.45 | 6.36 | 3.58 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 90.08 | 104.76 | 85.95 | 116.04 | 89.99 | |
| Inter-assay | Mean concentration (n = 5) | 14.25 | 8.16 | 3.37 | 2.32 | 0.90 |
| Precision (RSD, %) | 7.64 | 6.95 | 5.54 | 6.59 | 4.08 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 89.09 | 102.02 | 84.20 | 115.91 | 89.59 | |
| Assays | Nominal Concentration (μg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40.5 | 13.5 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | ||
| Intra-assay | Mean concentration (n = 5) | 42.35 | 12.88 | 4.48 | 1.47 | 0.56 |
| Precision (RSD, %) | 4.92 | 3.47 | 10.71 | 12.45 | 7.20 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 104.57 | 95.41 | 99.50 | 97.77 | 112.61 | |
| Inter-assay | Mean concentration (n = 5) | 42.17 | 13.14 | 4.62 | 1.52 | 0.54 |
| Precision (RSD, %) | 5.74 | 2.67 | 4.88 | 2.93 | 6.85 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 104.12 | 97.35 | 102.77 | 101.13 | 108.75 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, E.-B.; Sayem, S.A.J.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, T.-W.; Hossain, M.A.; Park, S.-C. Assessment of Plasma Tylosin Concentrations: A Comparative Study of Immunoassay, Microbiological Assay, and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061023
Lee E-B, Sayem SAJ, Lee G-Y, Kim T-W, Hossain MA, Park S-C. Assessment of Plasma Tylosin Concentrations: A Comparative Study of Immunoassay, Microbiological Assay, and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(6):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Eon-Bee, Syed Al Jawad Sayem, Ga-Yeong Lee, Tae-Won Kim, Md Akil Hossain, and Seung-Chun Park. 2023. "Assessment of Plasma Tylosin Concentrations: A Comparative Study of Immunoassay, Microbiological Assay, and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry" Antibiotics 12, no. 6: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061023
APA StyleLee, E.-B., Sayem, S. A. J., Lee, G.-Y., Kim, T.-W., Hossain, M. A., & Park, S.-C. (2023). Assessment of Plasma Tylosin Concentrations: A Comparative Study of Immunoassay, Microbiological Assay, and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Antibiotics, 12(6), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12061023







