Chronic Suppressive Antibiotic Treatment for Staphylococcal Bone and Joint Implant–Related Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
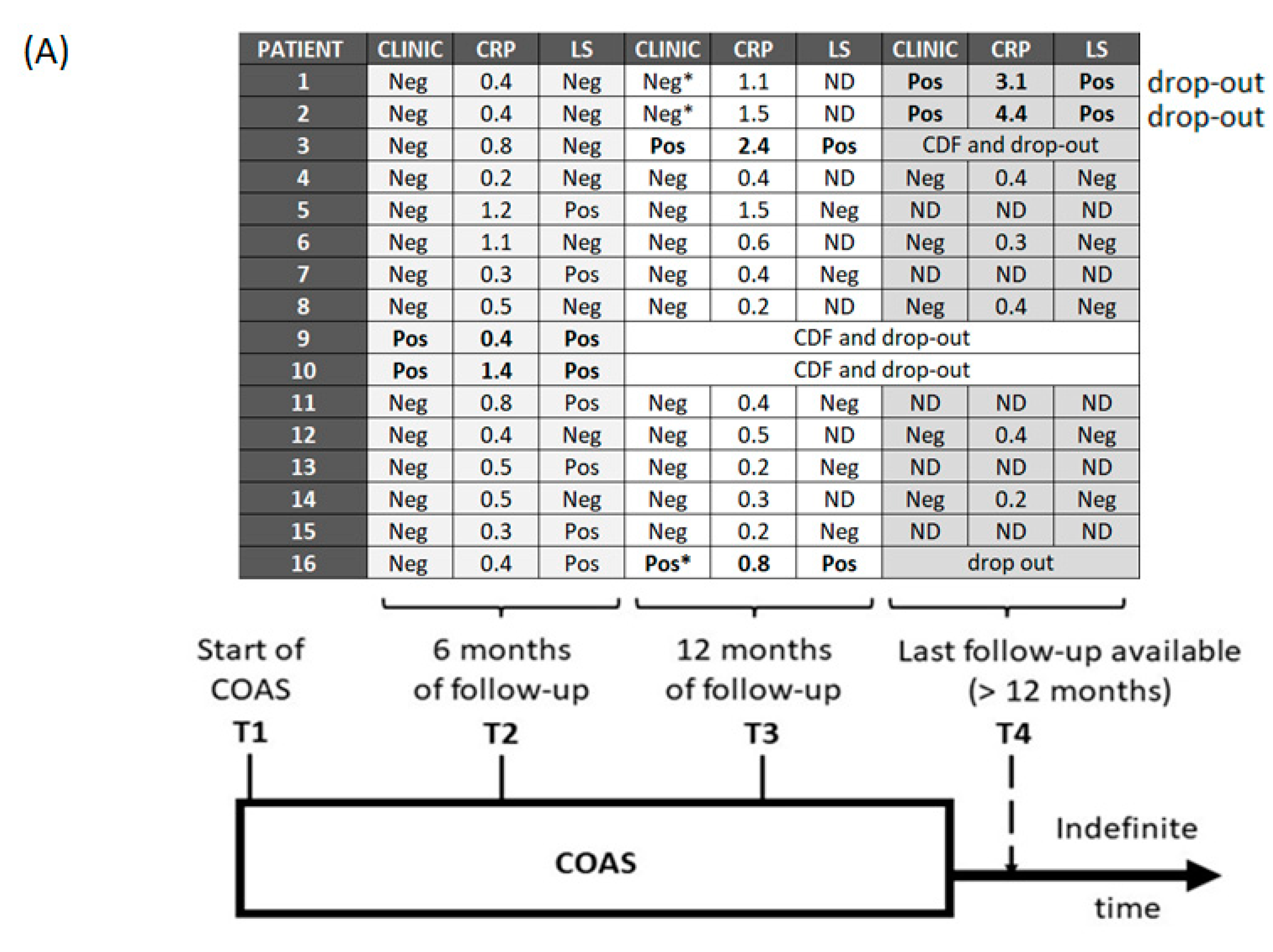
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prada, C.; Bengoa, F.; Bhandari, M. The management of fracture related infections: What practices can be supported by high-level evidence? J. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 30, 10225536221119580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R. Periprosthetic Joint Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic joint infection: Current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasso, M.; Capasso, L.; Corona, K.; Pola, E.; Toro, G.; Panni, A.S. Periprosthetic knee infection: Treatment options. Orthop. Rev. 2022, 14, 37537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Nijman, J.M.; Kampinga, G.A.; van Assen, S.; Jutte, P.C. Efficacy of Antibiotic Suppressive Therapy in Patients with a Prosthetic Joint Infection. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2017, 2, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, J.T.; Watts, C.D.; Mabry, T.M.; Hanssen, A.D.; Berry, D.J.; Abdel, M.P. Irrigation and debridement with chronic antibiotic suppression for the management of infected total knee arthroplasty: A Contemporary Analysis. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100-B, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, M.B.; Saleh, A.; Klika, A.K.; O’Rourke, C.; Schmitt, S.; Higuera, C.A.; Barsoum, W.K. Chronic Suppression of Periprosthetic Joint Infections with Oral Antibiotics Increases Infection-Free Survivorship. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2015, 97, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, A.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Borens, O.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Cassar-Pullicino, V.; Trampuz, A.; Winkler, H.; Gheysens, O.; Vanhoenacker, F.M.H.M.; Petrosillo, N.; et al. Consensus document for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections: A joint paper by the EANM, EBJIS, and ESR (with ESCMID endorsement). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 46, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS definition of periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberatore, M.; Gentile, G.; Follacchio, G.A.; Frantellizzi, V.; De Vincentis, G.; Monteleone, F.; Anagnostou, C.; Drudi, F.M.; Calvisi, V. 99mTc-labeled White Blood Cell Scan as a Guide to Open Biopsy in the Management of Hip and Knee Prosthesis Infection: Preliminary Results. Curr. Radiopharm. 2017, 10, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberatore, M.; Calandri, E.; Pavoni, G.L.; Baiocchi, P.; Iurilli, A.P.; Venditti, M.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Rubello, D. Reliability of white blood cell scan in the follow-up of osteomyelitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2007, 61, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanlı, Y.; Özkan, Z.G.; Ünal, S.N.; Türkmen, C.; Kılıçoğlu, Ö. The Additional Value of Tc 99m HMPAO White Blood Cell SPECT in the Evaluation of Bone and Soft Tissue Infections. Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther. 2011, 20, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsemakers, W.; Morgenstern, M.; McNally, M.; Moriarty, T.; McFadyen, I.; Scarborough, M.; Athanasou, N.; Ochsner, P.; Kuehl, R.; Raschke, M.; et al. Fracture-related infection: A consensus on definition from an international expert group. Injury 2017, 49, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, J.; Escudero-Sanchez, R. Suppressive Antibiotic Treatment in Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Perspective. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, E.F.; Roca, M.; Jamar, F.; Israel, O.; Signore, A. Guidelines for the labelling of leucocytes with 99mTc-HMPAO. Inflammation/Infection Taskgroup of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ometti, M.; Delmastro, E.; Salini, V. Management of prosthetic joint infections: A guidelines comparison. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2022, 106, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, J.; Miguel, L.G.S.; Euba, G.; Rodríguez, D.; García-Lechuz, J.; Riera, M.; Falgueras, L.; Palomino, J.; Benito, N.; del Toro, M.; et al. Early prosthetic joint infection: Outcomes with debridement and implant retention followed by antibiotic therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byren, I.; Bejon, P.; Atkins, B.L.; Angus, B.; Masters, S.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Gundle, R.; Berendt, A. One hundred and twelve infected arthroplasties treated with ‘DAIR’ (debridement, antibiotics and implant retention): Antibiotic duration and outcome. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, G.L.; Giannella, M.; Falcone, M.; Scorzolini, L.; Liberatore, M.; Carlesimo, B.; Serra, P.; Venditti, M. Conservative medical therapy of prosthetic joint infections: Retrospective analysis of an 8-year experience. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, F.; Coen, M.; Franceschini, M.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Hewlett, A.; Segreti, J.; Senneville, E. Hip and Knee Section, Treatment, Antimicrobial Suppression: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 34, S483–S485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominic, M.R. Adverse Reactions Induced by Minocycline: A Review of Literature. Curr. Drug Saf. 2021, 16, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendki, V.; Sergent, P.; Barrelet, A.; Oziol, E.; Beretti, E.; Berlioz-Thibal, M.; Bouchand, F.; Dauchy, F.; Forestier, E.; Gavazzi, G.; et al. Efficacy of indefinite chronic oral antimicrobial suppression for prosthetic joint infection in the elderly: A comparative study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 60, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradier, M.; Robineau, O.; Boucher, A.; Titecat, M.; Blondiaux, N.; Valette, M.; Loïez, C.; Beltrand, E.; Nguyen, S.; Dézeque, H.; et al. Suppressive antibiotic therapy with oral tetracyclines for prosthetic joint infections: A retrospective study of 78 patients. Infection 2017, 46, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, M.A.; Winner, J.S.; Beilke, M.A. Prolonged oral antibiotic suppression in osteomyelitis and associated outcomes in a Veterans population. Am. J. Health Pharm. 2015, 72, S150–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halouska, M.A.; Van Roy, Z.A.; Lang, A.N.; Hilbers, J.; Hewlett, A.L.; Cortes-Penfield, N.W. Excellent Outcomes With the Selective Use of Oral Antibiotic Therapy for Bone and Joint Infections: A Single-Center Experience. Cureus 2022, 14, 26982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyoola, A.L.; Adegbehingbe, O.O.; Aboderin, A.O. Therapeutic decision in chronic osteomyelitis: Sinus track culture versus intraoperative bone culture. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2008, 129, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, G.; Falcone, M.; Baiocchi, P.; Tarasi, A.; Cassone, M.; Serra, P.; Venditti, M. Conservative Medical Therapy of Infections Following Osteosynthesis: A Retrospective Analysis of a Six-Year Experience. J. Chemother. 2002, 14, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, A.J.; Hathaway-Schrader, J.D.; Lubker, R.; Davies, C.; Novince, C.M. Tetracyclines and bone: Unclear actions with potentially lasting effects. Bone 2022, 159, 116377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doub, J.B.; Nandi, S.; Putnam, N. Retention of Minocycline Susceptibility When Gram-Positive Periprosthetic Joint Infection Isolates Are Non-Susceptible to Doxycycline. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPlante, K.L.; Dhand, A.; Wright, K.; Lauterio, M. Re-establishing the utility of tetracycline-class antibiotics for current challenges with antibiotic resistance. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1686–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.B.; Hersh, B.L.; Kreger, A.; Sayeed, A.; Bullock, A.G.; Rothenberger, S.D.; Klatt, B.; Hamlin, B.; Urish, K.L. Benefits and Adverse Events Associated with Extended Antibiotic Use in Total Knee Arthroplasty Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 70, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.; Kelsberg, G.; Louden, D. Potential harms of long-term acne treatment with oral antibiotics. Can. Fam. Physician 2020, 66, 669–670. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, D.; Kalra, S. Minocycline and Doxycycline: More Than Antibiotics. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 1046–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, E.A.; Trombetta, R.P.; de Mesy Bentley, K.L.; Boyce, B.F.; Gill, A.L.; Gill, S.R.; Nishitani, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Morita, Y.; Ito, H.; et al. Evolving concepts in bone infection: Redefining “biofilm”, “acute vs. chronic osteomyelitis”, “the immune proteome” and “local antibiotic therapy”. Bone Res. 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfeld, J. Dynamic interactions of neutrophils and biofilms. J. Oral Microbiol. 2014, 6, 26102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teiler, J.; Åkerlund, B.; Brismar, H.; Savitcheva, I.; Ahl, M.; Bjäreback, A.; Hedlund, H.; Holstensson, M.; Axelsson, R. Dual-tracer approach vs. dual time-point approach in leukocyte scintigraphy in treatment evaluation of persistent chronic prosthetic joint infection. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2021, 42, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Stefani, S.; Venditti, M.; Di Domenico, E.G. Biofilm-Related Infections in Gram-Positive Bacteria and the Potential Role of the Long-Acting Agent Dalbavancin. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 749685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Rimoldi, S.G.; Cavallo, I.; D’agosto, G.; Trento, E.; Cagnoni, G.; Palazzin, A.; Pagani, C.; Romeri, F.; De Vecchi, E.; et al. Microbial biofilm correlates with an increased antibiotic tolerance and poor therapeutic outcome in infective endocarditis. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.A.G.d.; Afonina, I.; Kline, K.A. Eradicating biofilm infections: An update on current and prospective approaches. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 63, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeaux, D.; Ghigo, J.-M.; Beloin, C. Biofilm-Related Infections: Bridging the Gap between Clinical Management and Fundamental Aspects of Recalcitrance toward Antibiotics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 510–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.L.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Su, B.-A.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Hsu, H.-J.; Ko, W.-C.; Tang, H.-J. Efficacy of combination oral antimicrobial agents against biofilm-embedded methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beganovic, M.; Luther, M.K.; Daffinee, K.; LaPlante, K.L. Biofilm prevention concentrations (BPC) of minocycline compared to polymyxin B, meropenem, and amikacin against Acinetobacter baumannii. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 94, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lensen, K.-J.D.F.; Escudero-Sanchez, R.; Cobo, J.; Trebše, R.; Gubavu, C.; Tedeschi, S.; Lomas, J.M.; Arvieux, C.; Rodriguez-Pardo, D.; Fantoni, M.; et al. The efficacy of suppressive antibiotic treatment in patients managed non-operatively for periprosthetic joint infection and a draining sinus. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2021, 6, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberatore, M.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Rubello, D. White blood cell scan in the follow-up of infectious diseases: Is the withdrawal of antibiotic therapy necessary? Nucl. Med. Commun. 2007, 28, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Demographic | Age (±SD) | 75 (±14) |
| Sex F/M | 9 (56%)/7 (44%) | |
| Clinical and laboratory | Overall PJI | 11 (69%) |
| Hip | 6 (54.55%) | |
| Knee | 5 (45.45%) | |
| Overall FRI | 5 (31%) | |
| Femur | 3 (60%) | |
| Sternum | 1 (20%) | |
| Humerus | 1 (20%) | |
| CRP at presentation | 4.5 (±5.70) | |
| Microbiology | CONS | 13 (82%) |
| CONS + E. coli | 1 (6%) | |
| MRSA | 2 (12%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceccarelli, G.; Perciballi, B.; Russo, A.; Martini, P.; Marchetti, F.; Capparuccia, M.R.; Iaiani, G.; Fabris, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; Villani, C.; et al. Chronic Suppressive Antibiotic Treatment for Staphylococcal Bone and Joint Implant–Related Infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050937
Ceccarelli G, Perciballi B, Russo A, Martini P, Marchetti F, Capparuccia MR, Iaiani G, Fabris S, Ciccozzi M, Villani C, et al. Chronic Suppressive Antibiotic Treatment for Staphylococcal Bone and Joint Implant–Related Infections. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(5):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050937
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeccarelli, Giancarlo, Beatrice Perciballi, Alessandro Russo, Paolo Martini, Francesco Marchetti, Marco Rivano Capparuccia, Giancarlo Iaiani, Silvia Fabris, Massimo Ciccozzi, Ciro Villani, and et al. 2023. "Chronic Suppressive Antibiotic Treatment for Staphylococcal Bone and Joint Implant–Related Infections" Antibiotics 12, no. 5: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050937
APA StyleCeccarelli, G., Perciballi, B., Russo, A., Martini, P., Marchetti, F., Capparuccia, M. R., Iaiani, G., Fabris, S., Ciccozzi, M., Villani, C., Venditti, M., D’Ettorre, G., & De Meo, D. (2023). Chronic Suppressive Antibiotic Treatment for Staphylococcal Bone and Joint Implant–Related Infections. Antibiotics, 12(5), 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050937










