Abstract
Helicobacter pylori is a Gram-negative bacterium that is able to colonize the human stomach, whose high prevalence has a major impact on human health, due to its association with several gastric and extra-gastric disorders, including gastric cancer. The gastric microenvironment is deeply affected by H. pylori colonization, with consequent effects on the gastrointestinal microbiota, exerted via the regulation of various factors, including gastric acidity, host immune responses, antimicrobial peptides, and virulence factors. The eradication therapy required to treat H. pylori infection can also have detrimental consequences for the gut microbiota, leading to a decreased alpha diversity. Notably, therapy regimens integrated with probiotics have been shown to reduce the negative effects of antibiotic therapy on the gut microbiota. These eradication therapies combined with probiotics have also higher rates of eradication, when compared to standard treatments, and are associated with reduced side effects, improving the patient’s compliance. In light of the deep impact of gut microbiota alterations on human health, the present article aims to provide an overview of the complex interaction between H. pylori and the gastrointestinal microbiota, focusing also on the consequences of eradication therapies and the effects of probiotic supplementation.
1. Introduction
1.1. Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral bacterium with a diameter of approximately 3 μm, which is able to colonize the human stomach. More than half of the world’s population is estimated to be infected, with approximately 4.4 billion H. pylori-positive individuals worldwide in 2015. The global prevalence is higher in adult males and in subjects living in developing countries, with a wide range of variability, from 24% in Oceania to 70% in Africa [1,2,3].
The high prevalence of H. pylori has a huge impact on human health, as it has been associated with several gastric and extra-gastric disorders [4,5]. H. pylori infection is one of the most common causes of gastritis and peptic ulcer [6], as well as gastric cancer [7]. Nearly 2–3% of patients with H. pylori can develop gastric adenocarcinoma, and 0.1% will experience mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma [8]. However, H. pylori has also been negatively associated with several extra-gastric digestive disorders, including, coeliac disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Barrett’s esophagus, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) [5]. Notably, the pathogenesis of the gastrointestinal disorders associated with H. Pylori could also be influenced by the gastric microbiota. Interestingly, it has been shown that the presence of non-H. pylori bacteria in the gastric microbiota can influence the development of gastric cancer, even after H. pylori eradication, but their role is still not well defined [9].
H. pylori has developed several strategies to increase its survival within the human stomach, through a complex interplay with the gastric ecosystem and the immune system.
One of the main mechanisms that mediate its survival and persistence within the gastric environment is the production of urease [10,11]. Through the action of Urel, a pH-gated urea channel that allows urea entry in an acid environment, intrabacterial urease activity is activated. Urea is thus hydrolyzed, with the production of ammonia (NH3) and CO2, consequently alkalizing the gastric pH [12,13]. NH3, which can disrupt tight cell junctions and the gastric epithelium, and CO2, which can interfere with host bactericidal strategies, are involved in the pathogenesis of complications by H. pylori infection [14]. Moreover, H. pylori produces specific virulence factors, including the vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA), the cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) product, sialic acid-binding adhesin A (SabA), and the high-temperature requirement A (HtrA) protease [15]. VacA leads to the vacuolation and apoptosis of the host cell, disrupting membrane transport proteins, mitochondrial activities, endocytic trafficking, and uncontrolled activation of MAP kinases [16]. VacA toxin also inhibits the degradation of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and increases the activity of T regulatory cells, reducing the host immune response to H. pylori and easing its persistence in the gastric environment [17]. CagA toxin is an oncoprotein with cytotoxic and immunosuppressant activities [18], associated also with increased bacterial motility [19], impairing specifically cytoskeleton activities and the MAP kinase pathway [15]. In a recent meta-analysis, CagA was the most common risk factor for non-cardial gastric cancer (OR = 3.22; 95%CI: 2.10–4.94), while patients infected with VacA-positive strains were associated with a doubled neoplastic risk (OR = 2.05; 95%CI: 1.67–2.52) [20].
HtrA, an E-cadherin protease of the extracellular compartment, damages the adherent junctions and the epithelial barrier, favoring H. pylori invasion through the gastric epithelium [21]. Therefore, specific HtrA polymorphisms have been directly linked to an increased risk of gastric cancer [22].
Other pathogenic pathways are the production and expression of nearly 64 specific outer membrane proteins (OMPs) [10], including blood group antigen-binding adhesin A (BabA), sialic acid-binding adhesin A (SabA) [23], HopQ [24], Helicobacter outer membrane B (HomB), and outer inflammatory protein A (OipA) [25]. In particular, BabA and SabA are fundamental in the adhesion process, while HopQ plays an essential role as membrane porin to transport toxins into the host cell, and HomB and OipA act as inhibitors of the apoptotic cascade and as pro-inflammatory factors. Therefore, OMPs such as HomB or blood group antigen-binding adhesion 2 (BabA2) are more expressed by the strains found in the presence of peptic ulcer (OR = 1.36; 95%CI: 1.07–1.72) and gastric cancer (respectively, OR = 2.16; 95%CI: 1.37–3.40; and OR = 2.05, 95%CI: 1.30–3.24; p = 0.002) [26,27].
Other relevant strategies employed by H. pylori to improve its survival within the stomach include the release of outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), which contain various molecules such as LPS, peptidoglycan, outer membrane proteins, and virulence factors. These vesicles mediate the communication between the host environment and the bacteria and can be employed to introduce H. pylori products into host cells, where they can promote infection, regulate immune responses and impair cellular functions [28]. OMVs could also be involved in bacterial mechanisms of antibiotic resistance [29].
Moreover, H. pylori is able to switch from a spiral, vegetative form to a coccoid one in case of adverse conditions, e.g., the poor availability of nutrients, increasing the chance of long-lasting colonization [30]. This is due to not only its higher resistance to antibiotics but also because the coccoid form can be hardly cultured and often results in false-negative diagnoses [31].
Due to its association with various disorders, including gastric cancer, H. pylori infection requires adequate intervention upon diagnosis [32], and a series of antibiotic regimens have been trialed to eradicate it. Multiple classes of drugs are used in combination, as triple or quadruple therapies [33]. The principal components of these therapies are microbial agents, such as imidazole (metronidazole or tinidazole), macrolides (clarithromycin or azithromycin), tetracycline, amoxicillin, rifabutin, and furazolidone [34,35]. Regardless of the potential antibiotic resistance that may be present, the use of bismuth components in quadruple therapy increases the rates of eradication [36]. In combination with antimicrobial agents, proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) contribute to the treatment process by decreasing the acid secretion in the stomach, allowing previously formed ulcerations to heal [37]. This blocking effect on the secretory mechanism is accomplished through the inhibition of the H+/K+ adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) enzyme on the parietal cell canalicular membrane [38]. Other than attenuating the acidity of the gastric environment, PPIs also help by enhancing the stability of acid-labile antibiotics, increasing the gastric pH [37].
First-line therapies should be chosen depending on the local prevalence of clarithromycin resistance, and a triple regimen is recommended in regions with a low prevalence of clarithromycin resistance. This combination includes a standard dose of PPI, amoxicillin (1 g), and clarithromycin (500 mg) twice daily for 7–14 days. A quadruple therapy containing bismuth can be implemented as a first-line therapy in regions with high (>15%) or unknown prevalence of clarithromycin resistance [33]. The rising trend of resistance to first-line therapies has put forward the concept of susceptibility testing pre-treatment, favoring a culture-guided approach [39]. Although susceptibility can be examined using both invasive and non-invasive approaches, upper endoscopy with specimen cultures and minimum inhibitory concentration calculation is considered the most common one [39]. However, given the challenge of standardizing the quality of the method and the scarce availability of expertise, this approach still has to be prioritized in the future [39].
1.2. The Human Microbiota
The gastrointestinal tract hosts trillions of microorganisms over its entire length, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa [40,41,42], and the collection of their genetic material is called microbiota. The gut microbiota is a highly dynamic ecosystem and is influenced by multiple factors, such as diet, lifestyle, antibiotic therapies, long-term proton PPI consumption, and H. pylori infection [43,44]. The interaction between the host and microbiota plays a pivotal role when it comes to balancing health and disease states [45], as microbiota is involved in the regulation of several immune and metabolic pathways [46,47]. Indeed, a large body of evidence shows that microbiota alterations are associated with a wide spectrum of disorders, including gastrointestinal and liver diseases, allergies, cardiometabolic and autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders, and malignancies [48,49,50].
Bacterial-derived metabolites are important mediators in this interaction between the host and microbiota, and specific metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), play a key role in maintaining the host’s health [43]. The decreased abundance of SCFA-producing bacteria, such as Faecalibacterium and Roseburia, has been linked to a higher risk of type-1 and type-2 diabetes, liver cirrhosis, IBD, and atherosclerosis [51,52,53,54,55,56].
A crucial role in the maintenance of gut health is played by the mucus layer, which is present throughout the whole length of the gastrointestinal tract. The mucus layer activity is also regulated by the microbiota [57], and the expression of Muc2, the main glycoprotein of the mucus layer of the colon, has been positively associated with a higher abundance of pathogens and worse intestinal damage in mouse models [58]. Muc2 glycosylation is involved in safeguarding the protein structure against host and bacterial proteases, also facilitating the retention of water for the creation of a mucus gel. Microbial colonization has been shown to influence the glycosylation process of Muc2 [59].
The abovementioned aspects of the interaction between the host and the gut microbiota have also an important role during the H. pylori infection because this bacterium is not only located in the epithelium but also in the gastric surface mucous gel layer [60], and bacterial-derived metabolites such as SCFAs could inhibit its growth [61]. Thus, considering the profound effects of the gut microbiota on human health and the relevant role of H. pylori in influencing the host’s microbiota, the present review aims to offer a summary of the intricate interplay between H. pylori and the gastrointestinal microbiota, with a particular emphasis on the effects of eradication therapies and the impact of probiotic supplementation.
2. The Effect of H. pylori on Gastric Microbiota
Although the human stomach was previously considered unfit for bacterial growth, it has now been demonstrated that it is colonized by a complex microbial community [62]. The gastric microbiota is characterized by a reduced richness and diversity compared with the ileal and colonic microbiota, and it hosts fewer aero-intolerant species [63]. The most relevant phyla observed are Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Fusobacteria, while the most important genera reported are Helicobacter, Streptococcus, Prevotella, Neisseria, Veillonella, Fusobacterium, and Haemophilus [9,64,65]. Furthermore, the gastric microbiota found in gastric biopsies is different from that observed in gastric juice, showing the presence of a distinct mucosal microbiota in the stomach [66].
The relationship between H. pylori and gastric microbiota could be mediated through multiple mechanisms, such as virulence factors, the modification of gastric acidity, host immune responses, and competition [67,68,69].
One of the main virulence factors of H. pylori, the cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA), is capable of impairing cellular proliferation, apoptosis, cell motility, inflammatory response, and the arrangement of the cytoskeleton in host cells [15] and may also lead to gastric dysbiosis. In a transgenic Drosophila model of CagA expression, without the presence of H. pylori, Jones et al. observed that the virulence protein altered the host microbiota. Moreover, they found the increased activation of innate immunity to be a consequence of CagA-induced dysbiosis [70]. Furthermore, Wang et al. showed that in the gastric biopsies of patients affected by chronic gastritis or gastric cancer, the presence of different CagA and VacA virulence genotypes influenced the gastric microbiome’s composition [71].
The colonization of human gastric mucosa by H. pylori affects gastric luminal acidity, altering the expression of proton pumps and allowing the colonization of the gastric microenvironment to other microorganisms that are otherwise incapable of surviving in the stomach [72]. The acute phase of the infection results in an initial reduction in gastric pH, stimulating gastrin release, and the consequent abundance of H. pylori that predominates the microenvironment. On the other hand, chronic infection, leading to the development of atrophic gastritis, is associated with a decreased luminal acidity that favors the colonization of other bacteria, leading to microbial growth that can outnumber H. pylori [73].
The chronic H. pylori infection can progress over time through different stages according to the Correa cascade: chronic gastritis, atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and eventually gastric adenocarcinoma. However, carcinogenesis could also progress independently from H. pylori or even after its eradication, suggesting the presence of other relevant factors in the gastric microenvironment participating in the process [9,74]. Moreover, even though multiple studies have shown that the gastric microbiota is altered in various gastric diseases, they have revealed heterogeneous results, without identifying the specific microbial signatures associated with different gastric pathologies [9].
The complex immune response to H. pylori is changeable during life. During infancy, this is mainly a regulatory inflammatory pattern, with higher concentrations of IL-10 and TGF-β1 with an increased number of mucosal FOXP3 + Treg cells. The predominantly regulatory pattern allows the gastric environment to be more vulnerable to H. pylori, but there is a mild degree of inflammation and mucosal damage. On the other hand, in adults, there is a predominant Th1 response, with higher mucosal levels of IFN-γ and IL12p70 [75]. Adults also have an increased Th17 response, with higher levels of IL-17A and IL-23 and lower concentrations of TGF-β1, with a cytokine profile more associated with epithelial damage [76]. Another mechanism involved in this crosstalk involves antimicrobial peptides such as defensins, molecules known to be active against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, which are increased in H. pylori-induced gastritis [77]. Furthermore, H. pylori can produce cecropin-like antibacterial peptides that have an important bactericidal effect and proinflammatory activity [78].
Beyond these pathways, H. pylori is able to predominate over other gastric bacteria. When H. pylori colonizes the gastric mucosa, it succeeds in becoming the most abundant organism, accounting for 40–90% of the gastric microbiota composition [45,64,79]. Consequently, the presence of H. pylori leads to a significant decrease in gastric alpha diversity [79,80]. In general, in H. pylori-positive subjects, there is an increased abundance of Proteobacteria, likely due to the contribution of H. pylori itself, while the abundance of Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria, and Firmicutes is reduced [79,81]. In a study by Wang et al., some species, such as Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Chryseobacterium unclassified, Pedobacter unclassified, Stenotrophomonas unclassified, Variovorax unclassified, and Pseudomonas stutzeri, have been associated with the presence of H. pylori infection, through the shotgun sequencing of stomach swab samples of 96 patients [82]. On the other hand, in a rhesus macaque model, Martin et al. observed the impact of H. pylori on the antecedent gastric microbiota and found no significant variations in the relative abundance of non-Helicobacter taxa, indicating that in the rhesus macaque model, the gastric microbiome is stable despite the presence of the H. pylori infection [83].
There is also initial evidence of the influence of H. pylori on the gastric microbiota of pediatric patients. In a cohort of 122 children with gastrointestinal symptoms, 57 of whom were diagnosed with H. pylori infection, Zheng et al. analyzed the gastric microbiome from mucosal biopsies [84]. The authors observed that the group of patients diagnosed with H. pylori infection (H. pylori-positive group) had a lower gastric bacterial diversity than those without H. pylori infection and that the two groups had a significantly different compositions based on beta diversity. In the H. pylori-positive group, the relative abundance of Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, and Verrucomicrobia was significantly decreased compared with the H. pylori-negative group. Moreover, at the genus level, Achromobacter, Devosia, Halomonas, Mycobacterium, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Sphingopyxis, and Stenotrophomonas were more abundant in the H. pylori-negative group, while only Helicobacter was more abundant in the H. pylori-positive group. The relative abundance of the Helicobacter genus was significantly different among the H. pylori-positive patients, with levels ranging from 2.19% to 80.98% [84]. Figure 1 illustrates the main mechanisms mediating the relationship between H. pylori and the gastric microbiota.
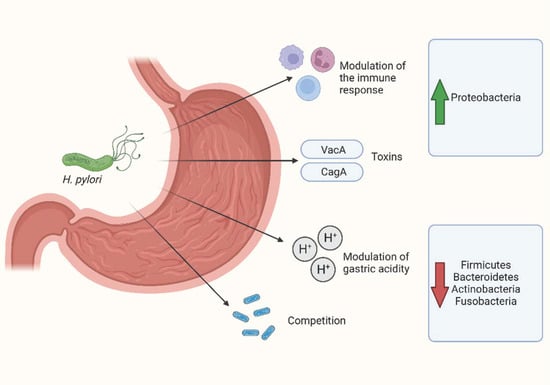
Figure 1.
Main mechanisms mediating the relationship between H. pylori and gastric microbiota. Created with BioRender.com.
3. The Influence of H. pylori on Gut Microbiota
The presence of H. pylori in the human organism can influence the composition of the gut microbiota through several pathways, including a direct effect of the infection or as a consequence of H. pylori eradication regimens.
Although H. pylori infection can have systemic effects and consequently influence not only the gastric microbiota but also the microbial communities of the whole gastrointestinal tract [45,85], relatively few studies have investigated the influence of the infection itself on the human gut microbiota.
In some studies, patients infected by H. pylori presented with increased diversity of gut microbiota compared with uninfected controls [86,87]. However, this association was not confirmed in other studies [64,88]. In an animal model of Mongolian gerbils, the H. pylori infection caused a distinct and prolonged shift in gut microbiota composition [89]. Moreover, in a large study of 212 patients with H. pylori and 212 matched controls [87], H. pylori infection was significantly associated with increased microbial diversity and fecal microbiota alterations, including a decreased abundance of Parasutterella and increased levels of Haemophilus and Pseudoflavonifractor in the infected cohort. Moreover, the H. pylori antigen load was correlated with larger alterations in the gut microbiota than sex or age, while it was negatively correlated with the abundance of Bacteroides, Fusicatenibacter, Alistipes, and Barnesiella [87].
Beyond its direct influence, the major impact of H. pylori on the intestinal microbiota is mediated by drug-based eradication regimens, including antibiotics and PPIs, which can lead to significant changes in the composition of the human gut microbiome.
As is widely known, the use of antibiotics has various harmful effects on the gut microbiota, such as a reduction in microbial diversity, alterations in its metabolic activity, and the selection of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms [90]. The impact of antibiotic therapies on the gut microbiota is influenced by their class, administration route, duration, dosage, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics, as well as host-related factors, such as baseline microbiota composition, age, and lifestyle [91].
Antibiotic use seems to play a role in the development of several disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, metabolic disorders, and liver disease. A clear example of antibiotic-driven dysbiosis is C. difficile infection, which frequently follows antibiotic therapies [91].
The use of PPIs has been investigated in the context of several gastrointestinal disorders. Regardless of the therapy regimen they are included in, PPIs have been shown to induce changes in the gut microbiome, favoring the development of enteric infections, including C. difficile infection [92]. In a study including more than 200 participants, the chronic use of PPIs demonstrated a decrease in gut microbiome diversity [93]. On the level of different bacterial populations, changes such as an increase in Actinomycetales in families Streptococcoceae and Micrococcoceae and species Lactobacillus salivarius were observed [93].
A large study previously conducted has demonstrated that the 7-day antibiotic treatment for eradication profoundly disturbs the oral and colonic microbiota, and alterations can be observed even a week after treatment, persisting for up to 4 years [94]. Chen et al. compared the composition of fecal microbiota after 14 days of quadruple eradication therapy with healthy individuals’ samples, and the alpha diversity was remarkably lower after treatment. This poor diversity lasted for 6 weeks post-treatment [95].
Considering changes at the phylum level, there were some transient alterations demonstrated 14 days after treatment initiation; specifically, there was a decrease in the relative abundance of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, and Lentisphareae, while an increase in Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria was observed when compared to the baseline. A decrease in the relative abundance of Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae was also observed; however, it was only transient and disappeared after 2–3 months [95]. Another study conducted on a pediatric patient population who underwent bismuth quadruple therapy for 10 days, showed a statistically significant decrease in alpha diversity in the short term, up until 6 weeks post-treatment. In the same population, no long-term changes were noted, nor at the phylum level [96]. Contrastingly, He et al. reported a higher alpha diversity after eradication therapy in asymptomatic young adults [97]. Another meta-analysis focusing on changes in the taxon level illustrated a decrease in Actinobacteria in patients who have undergone eradication therapy when compared to baseline healthy individuals. Proteobacteria showed only a transient increase in the short term [98].
The eradication treatment also has an outcome regarding ghrelin levels, which is known as the “hunger hormone” and is predominantly secreted by the endocrine cells of the stomach and from the duodenum to a smaller extent. It is well known as one of the key regulators of appetite [99]. Regarding the ghrelin levels after triple or quadruple therapy for eradication, Martín-Núñez et al. observed a statistically significant decrease in fasting plasma ghrelin levels compared to the pre-treatment levels. This trend was also reflected in the gut microbiota profiles, where the abundance of Bacteroides Bifidobacterium longum and Parabacteroides distasonis predicted positive fasting ghrelin levels, while an increased abundance of Prevotellaceae, primarily its genus Prevotella, was linked to a lower amount of fasting ghrelin secretion in the stomach [100]. Nonetheless, the direct correlation and effects of H. pylori infection and its eradication treatment is still a topic of interest for further investigation.
There is well-established evidence that the integration of certain probiotics into H. pylori eradication regimens increases their success rates [101]. For this reason, the use of specific probiotic strains, including Saccharomyces boulardii, different strains of Lactobacillus spp., and Bifidobacterium spp., has been recommended by the latest Maastricht guidelines for the management of H. pylori infection [33,102].
Probiotics are defined as live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host [103]. The addition of probiotics to the H. pylori eradication therapy can be beneficial in improving both the eradication rates and decreasing the incidence of side effects often associated with the treatment, allowing better adherence to the therapy regimen [104,105]. The incidence of these adverse events, such as nausea, vomiting, or antibiotic-associated diarrhea, can occur in 5% to 30% of cases during the eradication therapy and could lead to the discontinuation of the treatment [106,107].
The mechanisms that mediate the effect of probiotics against H. pylori are still not clear and could involve the production of antimicrobial substances, competition, the reinforcement of mucosal barrier, and the modulation of the immune response [108,109,110,111]. Probiotics are known to increase the availability of lactic acid, SCFAs, hydrogen peroxide, and bacteriocin [112]. While SCFAs show an intense antibacterial activity, lactic acid also shares this effect, also inhibiting urease activity [112,113]. A study that focused on the bacteriocin secreted by multiple L. bulgaricus strains observed that it was able to inhibit H. pylori growth [114]. Recently, an acid-resistant strain, L. johnsonii, which was extracted from the gastric juice of healthy individuals, was able to antagonize H. pylori in both in vitro and mice models, indicating its potential therapeutical role [115].
In a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, involving 13 RCTs and 2306 patients, LÜ and colleagues [108] showed that probiotic supplementation improved the eradication rates by 11% and reduced the incidence of antibiotic-related side effects by 8% compared with the control group. Similar results have been confirmed in other meta-analyses [116,117].
Some studies have evaluated the benefits of specific strains, such as Saccharomyces boulardii; in a meta-analysis by Zhou et al., given in combination with the standard eradication treatment, it resulted in an improvement in H. pylori eradication rates and a significant reduction in the incidence of adverse events, compared with the control group [118]. Another meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials focused on Lactobacillus supplementation, finding that the H. pylori eradication rate was superior to that of the control group. In a subgroup analysis, the authors observed that in the L. casei and L. reuteri groups, the eradication rate was increased, but in the group of patients who received Lactobacillus GG, there was no improvement. Regarding the impact on the rates of side effects, no differences were observed between the supplementation group and the control group [119].
The application of advanced technologies for the sequencing of the microbial genome has allowed building initial evidence on the effect of probiotics on the gut microbiota during H. pylori eradication therapies. A study by Chen et al. [95] reported the effect of the eradication therapy with or without the supplementation of probiotics on the gut microbiota profile and alpha diversity. Patients were randomized into two groups: the first group received a bismuth-containing quadruple therapy without any addition of probiotics, while the second group received the same therapy with the supplementation of Clostridium butyricum, a butyrate-producing probiotic.
In both groups, alpha diversity decreased after treatment, and this reduction persisted for up to 6 weeks. The changes in alpha diversity were similar between both groups.
Regarding microbiota changes, at the phyla level, the short-term outcome (up to 14 days after therapy) revealed some alterations. Compared with baseline profiles, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Verrucomicrobia showed a decrease in abundance, while Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria increased. The authors also observed some specific changes only among patients who underwent therapy with probiotic supplementation: compared with the baseline, Fusobacteria and Tenericutes decreased, and Actinobacteria increased.
Another study instead demonstrated an alleviation in gastrointestinal symptoms, as well as an increase in alpha diversity, after receiving a specific probiotic containing S. boulardii [120]. The same patients showed a higher abundance of Enterobacteriaceae, while a decrease in the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Clostridia was observed upon treatment completion [120]. The amelioration of symptoms resulting from the use of probiotics in patients undergoing H. pylori eradication could be potentially attributed to their beneficial effect on the gut microbiota, but further studies are needed to clarify this issue. Therefore, these emerging data suggest that the use of therapy regimens integrated with probiotics should be more widely adopted.
4. Future Insights
H. pylori infection affects the composition and structure of the gastrointestinal microbiota through the regulation of multiple factors such as gastric acidity, host immune responses, antimicrobial peptides, and virulence factors, playing a role in the development of gastric pathology and extra-gastrointestinal diseases. Some studies have also focused on the gastric microbiome beyond H. pylori, starting to clarify its impact on gastrointestinal health. However, most of the available studies have a retrospective and associative design, while future longitudinal and prospective studies may evaluate the dynamic process of the infection, hopefully also with a mechanistic approach, with the aim of clarifying the functional interaction between H. pylori, the gastric microbiome, and the host, and identifying novel biomarkers in order to prevent the development of gastric cancer.
Moreover, H. pylori eradication requires the administration of large doses of antibiotics and PPIs, but the impact of this treatment affects microbial communities through the entire gastrointestinal tract, with clinical effects that can last several weeks and have detrimental consequences for the gut microbiota, including a reduction in alpha diversity and beneficial taxa (e.g., Verrucomicrobia), and increased relative abundance of Proteobacteria [121,122]. Therapy regimens integrated with probiotics have shown higher rates of eradication than standard treatments, mainly because of a reduction in gastrointestinal symptoms and, consequently, higher compliance with therapies. Interestingly, probiotics may also reduce the impact of antibiotic treatment on the gastrointestinal microbiota, preserving its diversity. This issue, as well as the application of other therapeutic modulators of the gut microbiota to H. pylori eradication therapies, represent a valuable topic to expand upon in the upcoming years.
Author Contributions
M.F., E.T., L.E.D.V. and G.I. have written the initial draft of the manuscript. S.P., G.C. and A.G. have supervised the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Linea D-1 of the Catholic University of Rome and by the Ricerca Finalizzata Giovani Ricercatori 2018 of the Italian Ministry of Health (project GR-2018-12365734) to G.I. and by the BIOMIS grant of the Italian Ministry of Research to A.G., G.C., and G.I. A.G., G.C., and G.I. thank the Fondazione Roma for the invaluable support to their scientific research. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection analysis, the decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
A.G. reports personal fees for consultancy from Eisai Srl, 3PSolutions, Real Time Meeting, Fondazione Istituto Danone, Sinergie Srl, Board MRGE, and Sanofi SpA; personal fees for acting as a speaker for Takeda SpA, AbbVie, and Sandoz SpA; and personal fees for acting on advisory boards for VSL3 and Eisai. G.C. has received personal fees for acting as an advisor for Ferring Therapeutics. G.I. has received personal fees for acting as a speaker for Biocodex, Danone, Sofar, Malesci, Metagenics, and Tillotts Pharma, and for acting as consultant and/or advisor for Ferring Therapeutics, Giuliani, Malesci, and Tillotts Pharma. All other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
References
- Zamani, M.; Ebrahimtabar, F.; Zamani, V.; Miller, W.H.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Shokri-Shirvani, J.; Derakhshan, M.H. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Cai, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wei, L.; Yan, C.; Jin, G. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Korwin, J.-D.; Ianiro, G.; Gibiino, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Helicobacter pylori infection and extragastric diseases in 2017. Helicobacter 2017, 22 (Suppl. 1), e12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, L.E.; Fiorani, M.; Tohumcu, E.; Porcari, S.; Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G. Review: Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases. Microb. Health Dis. 2022, 4, e719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, G.L.; Grigg, S.E.; Yeomans, N.D. Helicobacter pylori and low-dose aspirin ulcer risk: A meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorolajal, J.; Moradi, L.; Mohammadi, Y.; Cheraghi, Z.; Gohari-Ensaf, F. Risk factors for stomach cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, M. Molecular Mechanism of Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 52, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Figueiredo, C.; Smet, A.; Hansen, R.; Kupcinskas, J.; Rokkas, T.; Andersen, L.; Machado, J.C.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Systematic review: Gastric microbiota in health and disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 582–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor Cytotoxin-Associated Gene A (CagA)-Mediated Gastric Pathogenicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, Y.Y.; Lee, C.Y.Q.; Cheong, H.C.; Vadivelu, J.; Looi, C.Y.; Abdullah, S.; Wong, W.F. An Overview of Helicobacter pylori Survival Tactics in the Hostile Human Stomach Environment. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.-L.; Cheng, D.-D.; Xu, W.-T.; Lu, N.-H. Adhesion and Invasion of Gastric Mucosa Epithelial Cells by Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.R.; Marcus, E.A.; Wen, Y.; Singh, S.; Feng, J.; Sachs, G. Cytoplasmic histidine kinase (HP0244)-regulated assembly of urease with UreI, a channel for urea and its metabolites, CO2, NH3, and NH4(+), is necessary for acid survival of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalstig, A.A.; Benoit, S.L.; Misra, S.K.; Sharp, J.S.; Maier, R.J. Noncatalytic Antioxidant Role for Helicobacter pylori Urease. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00124-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj, J.; Forma, A.; Sitarz, M.; Portincasa, P.; Garruti, G.; Krasowska, D.; Maciejewski, R. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors-Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenicity in the Gastric Microenvironment. Cells 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V. Relationship between VacA Toxin and Host Cell Autophagy in Helicobacter pylori Infection of the Human Stomach: A Few Answers, Many Questions. Toxins 2016, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharndama, H.C.; Mba, I.E. Helicobacter pylori: An up-to-date overview on the virulence and pathogenesis mechanisms. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghwan; Chowdhury, R. Host cell contact induces fur-dependent expression of virulence factors CagA and VacA in Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palrasu, M.; Zaika, E.; El-Rifai, W.; Garcia-Buitrago, M.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Wilson, K.T.; Peek, R.M.; Zaika, A.I. Bacterial CagA protein compromises tumor suppressor mechanisms in gastric epithelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hafa, F.; Wang, T.; Ndifor, V.M.; Jin, G. Association between Helicobacter pylori antibodies determined by multiplex serology and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.; Hilgenfeld, R. Architecture and regulation of HtrA-family proteins involved in protein quality control and stress response. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Kuo, H.-Y.; Chang, W.-L.; Yang, H.-B.; Lu, C.-C.; Cheng, H.-C.; Wu, M.-S.; Sheu, B.-S. H. pylori isolates with amino acid sequence polymorphisms as presence of both HtrA-L171 & CagL-Y58/E59 increase the risk of gastric cancer. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, D.M.; dos Santos Pereira, E.; Rabenhorst, S.H.B. What exists beyond cagA and vacA? Helicobacter pylori genes in gastric diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10563–10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegtmeyer, N.; Harrer, A.; Schmitt, V.; Singer, B.B.; Backert, S. Expression of CEACAM1 or CEACAM5 in AZ-521 cells restores the type IV secretion deficiency for translocation of CagA by Helicobacter pylori. Cell Microbiol. 2019, 21, e12965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Soyfoo, D.M.; Wu, Y.; Xu, S. Virulence of Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins: An updated review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keikha, M.; Karbalaei, M. Correlation between the geographical origin of Helicobacter pylori homB-positive strains and their clinical outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpoghomou, M.-A.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Jin, G. Association of Helicobacter pylori babA2 gene and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.F.; Díaz, P.; Sandoval-Bórquez, A.; Herrera, D.; Quest, A.F.G. Helicobacter pylori Outer Membrane Vesicles and Extracellular Vesicles from Helicobacter pylori-Infected Cells in Gastric Disease Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.O.; Dawson, R.A.; Alsharaf, L.M.; Anne Winter, J. Protective effects of Helicobacter pylori membrane vesicles against stress and antimicrobial agents. Microbiology 2020, 166, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P.; Grande, R. Transformation of Helicobacter pylori into Coccoid Forms as a Challenge for Research Determining Activity of Antimicrobial Substances. Pathogens 2020, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhariri, M.; Hamza, D.; Elhelw, R.; Hamza, E. Occurrence of cagA+ vacA s1a m1 i1 Helicobacter pylori in farm animals in Egypt and ability to survive in experimentally contaminated UHT milk. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito, B.B.; da Silva, F.A.F.; Soares, A.S.; Pereira, V.A.; Santos, M.L.C.; Sampaio, M.M.; Neves, P.H.M.; de Melo, F.F. Pathogenesis and clinical management of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5578–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.-M.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.H.; Leja, M.; O’Morain, C.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut 2022, 71, 1724–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-C.; Lu, C.-W.; Lin, C.-J. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Current status and future concepts. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, K.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.-W.; Wang, J.-S.; Xia, Y.-J.; Dai, W.-Q.; Wang, F.; Shen, M.; Cheng, P.; et al. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of probiotics in Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18013–18021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, M.V.; Ismail, S.; Heinemann, J.A.; Keenan, J.I. The action of bismuth against Helicobacter pylori mimics but is not caused by intracellular iron deprivation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, G.; Molnar, A.; Klausz, G.; Mandi, Y.; Kawase, M.; Motohashi, N.; Molnar, J. Inhibitory action of a new proton pump inhibitor, trifluoromethyl ketone derivative, against the motility of clarithromycin-susceptible and-resistant Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, G.; Shin, J.M.; Briving, C.; Wallmark, B.; Hersey, S. The pharmacology of the gastric acid pump: The H+, K+ ATPase. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 35, 277–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Bibbò, S.; Di Rienzo, T.A.; Masucci, L.; Sanguinetti, M.; Gasbarrini, A. Culture-guided treatment approach for Helicobacter pylori infection: Review of the literature. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5205–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, M.J.; Plummer, N.T. Part 1: The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. Integr. Med. 2014, 13, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ianiro, G.; Bruno, G.; Lopetuso, L.; Beghella, F.B.; Laterza, L.; D’Aversa, F.; Gigante, G.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Role of yeasts in healthy and impaired gut microbiota: The gut mycome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4565–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Iorio, A.; Porcari, S.; Masucci, L.; Sanguinetti, M.; Perno, C.F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Putignani, L.; Cammarota, G. How the gut parasitome affects human health. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221091524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.S.B.; Raes, J.; Bork, P. The human gut microbiome: From association to modulation. Cell 2018, 172, 1198–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-C.; Liou, J.-M.; Lee, Y.-C.; Hong, T.-C.; El-Omar, E.M.; Wu, M.-S. The interplay between Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sparks, J.B.; Karyala, S.V.; Settlage, R.; Luo, X.M. Host adaptive immunity alters gut microbiota. ISME J. 2015, 9, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N.; et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Severgnini, M.; Pecere, S.; Ponziani, F.R.; Boskoski, I.; Larghi, A.; Quaranta, G.; Masucci, L.; Ianiro, G.; Camboni, T.; et al. Esophageal microbiome signature in patients with Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benakis, C.; Brea, D.; Caballero, S.; Faraco, G.; Moore, J.; Murphy, M.; Sita, G.; Racchumi, G.; Ling, L.; Pamer, E.G.; et al. Commensal microbiota affects ischemic stroke outcome by regulating intestinal γδ T cells. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christovich, A.; Luo, X.M. Gut microbiota, leaky gut, and autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 946248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.-M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Fåk, F.; Nookaew, I.; Tremaroli, V.; Fagerberg, B.; Petranovic, D.; Bäckhed, F.; Nielsen, J. Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozuelo, M.; Panda, S.; Santiago, A.; Mendez, S.; Accarino, A.; Santos, J.; Guarner, F.; Azpiroz, F.; Manichanh, C. Reduction of butyrate- and methane-producing microorganisms in patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatanen, T.; Franzosa, E.A.; Schwager, R.; Tripathi, S.; Arthur, T.D.; Vehik, K.; Lernmark, Å.; Hagopian, W.A.; Rewers, M.J.; She, J.-X.; et al. The human gut microbiome in early-onset type 1 diabetes from the TEDDY study. Nature 2018, 562, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Jakobsson, H.E.; Holmén-Larsson, J.; Schütte, A.; Ermund, A.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.M.; Arike, L.; Wising, C.; Svensson, F.; Bäckhed, F.; et al. Normalization of Host Intestinal Mucus Layers Requires Long-Term Microbial Colonization. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, K.S.B.; Kissoon-Singh, V.; Gibson, D.L.; Ma, C.; Montero, M.; Sham, H.P.; Ryz, N.; Huang, T.; Velcich, A.; Finlay, B.B.; et al. Muc2 protects against lethal infectious colitis by disassociating pathogenic and commensal bacteria from the colonic mucosa. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arike, L.; Holmén-Larsson, J.; Hansson, G.C. Intestinal Muc2 mucin O-glycosylation is affected by microbiota and regulated by differential expression of glycosyltranferases. Glycobiology 2017, 27, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, E.; Ota, H.; Hidaka, H.; Hayama, M.; Matsuzawa, K.; Akamatsu, T.; Nakayama, J.; Katsuyama, T. Helicobacter pylori and two ultrastructurally distinct layers of gastric mucous cell mucins in the surface mucous gel layer. Gut 2001, 49, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, H.; Shen, C.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Effects of sodium butyrate supplementation on inflammation, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Marques, J.; Ferreira, R.M.; Machado, J.C.; Figueiredo, C. The influence of the gastric microbiota in gastric cancer development. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 50–51, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailhe, M.; Ricaboni, D.; Vitton, V.; Gonzalez, J.-M.; Bachar, D.; Dubourg, G.; Cadoret, F.; Robert, C.; Delerce, J.; Levasseur, A.; et al. Repertoire of the gut microbiota from stomach to colon using culturomics and next-generation sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapolli, R.; Schütte, K.; Schulz, C.; Vital, M.; Schomburg, D.; Pieper, D.H.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Malfertheiner, P. Analysis of transcriptionally active bacteria throughout the gastrointestinal tract of healthy individuals. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1081–1092.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuik, F.; Dicksved, J.; Lam, S.Y.; Fuhler, G.M.; van der Laan, L.; van de Winkel, A.; Konstantinov, S.R.; Spaander, M.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Engstrand, L.; et al. Composition of the mucosa-associated microbiota along the entire gastrointestinal tract of human individuals. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Schütte, K.; Koch, N.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Wos-Oxley, M.L.; Oxley, A.P.A.; Vital, M.; Malfertheiner, P.; Pieper, D.H. The active bacterial assemblages of the upper GI tract in individuals with and without Helicobacter infection. Gut 2018, 67, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iino, C.; Shimoyama, T. Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 6224–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.-H.; Han, J.-X.; Fang, J.-Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and eradication: Exploring their impacts on the gastrointestinal microbiota. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Molina-Infante, J.; Gasbarrini, A. Gastric Microbiota. Helicobacter 2015, 20 (Suppl. 1), 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.A.; Hernandez, D.Z.; Wong, Z.C.; Wandler, A.M.; Guillemin, K. The bacterial virulence factor CagA induces microbial dysbiosis that contributes to excessive epithelial cell proliferation in the Drosophila gut. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tian, Z.; Liu, C.; Yu, X.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, S.; Dong, Q. Gastric Mucosa-Associated Microbial Signatures of Early Gastric Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Smolka, A.J. Gastric Parietal Cell Physiology and Helicobacter pylori-Induced Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2158–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Pereira, V.; Saxena, S.; Ghosh, T.S.; Anbumani, D.; Bag, S.; Das, B.; Nair, G.B.; Abraham, P.; Mande, S.S. Gastric microbiome of Indian patients with Helicobacter pylori infection, and their interaction networks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.M.; Pereira-Marques, J.; Pinto-Ribeiro, I.; Costa, J.L.; Carneiro, F.; Machado, J.C.; Figueiredo, C. Gastric microbial community profiling reveals a dysbiotic cancer-associated microbiota. Gut 2018, 67, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi, A.; Bagheri, N.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Shirzad, M.; Rahimian, G.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Shirzad, H. Comparative Immune Response in Children and Adults with H. pylori Infection. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 315957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, G.R.L.; Marques, H.S.; Santos, M.L.C.; da Silva, F.A.F.; da Brito, B.B.; Correa Santos, G.L.; de Melo, F.F. Helicobacter pylori infection: How does age influence the inflammatory pattern? World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mărginean, C.O.; Meliț, L.E.; Săsăran, M.O. Gastric Microenvironment-A Partnership between Innate Immunity and Gastric Microbiota Tricks Helicobacter pylori. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylund, J.; Christophe, T.; Boulay, F.; Nyström, T.; Karlsson, A.; Dahlgren, C. Proinflammatory activity of a cecropin-like antibacterial peptide from Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymiuk, I.; Bilgilier, C.; Stadlmann, A.; Thannesberger, J.; Kastner, M.-T.; Högenauer, C.; Püspök, A.; Biowski-Frotz, S.; Schrutka-Kölbl, C.; Thallinger, G.G.; et al. The Human Gastric Microbiome Is Predicated upon Infection with Helicobacter pylori. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wan, C.; Wang, Z. The relationship of gastric microbiota and Helicobacter pylori infection in pediatrics population. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Contreras, A.; Goldfarb, K.C.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Karaoz, U.; Contreras, M.; Blaser, M.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G. Structure of the human gastric bacterial community in relation to Helicobacter pylori status. ISME J. 2011, 5, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Tao, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J. Helicobacter pylori infection affects the human gastric microbiome, as revealed by metagenomic sequencing. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.E.; Bhatnagar, S.; George, M.D.; Paster, B.J.; Canfield, D.R.; Eisen, J.A.; Solnick, J.V. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on the gastric microbiota of the rhesus macaque. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Miao, J.; Luo, L.; Long, G.; Chen, B.; Shu, X.; Gu, W.; Peng, K.; Li, F.; Zhao, H.; et al. The Effects of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Microbiota Associated With Gastric Mucosa and Immune Factors in Children. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 625586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.; Harris, P.R.; Smith, P.D.; Bimczok, D. Interactions between H. pylori and the Gastric Microbiome: Impact on Gastric Homeostasis and Disease. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2021, 21, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, N.R.; Khoder, G.; Nada, A.M.; Al Bataineh, M.T. Exploring the impact of Helicobacter pylori on gut microbiome composition. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, F.; Kacprowski, T.; Rühlemann, M.; Bang, C.; Franke, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Nauck, M.; Völker, U.; Völzke, H.; Biffar, R.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection associates with fecal microbiota composition and diversity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gerhard, M.; Gao, J.-J.; Mejias-Luque, R.; Zhang, L.; Vieth, M.; Ma, J.-L.; Bajbouj, M.; Suchanek, S.; et al. Effect of Helicobacterpylori on gastrointestinal microbiota: A population-based study in Linqu, a high-risk area of gastric cancer. Gut 2019, 69, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Fischer, A.; Plickert, R.; Wiedemann, T.; Loddenkemper, C.; Göbel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Rieder, G. Helicobacter pylori induced gastric immunopathology is associated with distinct microbiota changes in the large intestines of long-term infected Mongolian gerbils. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.; Guarner, F.; Bustos Fernandez, L.; Maruy, A.; Sdepanian, V.L.; Cohen, H. Antibiotics as major disruptors of gut microbiota. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Gasbarrini, A. Antibiotics as deep modulators of gut microbiota: Between good and evil. Gut 2016, 65, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weersma, R.K.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J. Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut 2020, 69, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhann, F.; Bonder, M.J.; Vich Vila, A.; Fu, J.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Cenit, M.C.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 2016, 65, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Jernberg, C.; Andersson, A.F.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Short-term antibiotic treatment has differing long-term impacts on the human throat and gut microbiome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Lee, A.; He, J.; Huang, B.; Zheng, W.; Su, T.; Lai, S.; Long, Y.; Chu, H.; et al. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection, eradication therapy and probiotic supplementation on gut microenvironment homeostasis: An open-label, randomized clinical trial. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Lu, J.; Miao, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. Long-term changes in the gut microbiota after 14-day bismuth quadruple therapy in penicillin-allergic children. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Peng, C.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N. The eradication of Helicobacter pylori restores rather than disturbs the gastrointestinal microbiota in asymptomatic young adults. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Shao, X.; Shen, R.; Chen, D.; Shen, J. Changes in the human gut microbiota composition caused by Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Abdalla, M.M. Ghrelin-Physiological Functions and Regulation. Eur. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Indias, I. Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy Affect the Gut Microbiota and Ghrelin Levels. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 712908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Reinhardt, J.D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, G. The effect of probiotics supplementation on Helicobacter pylori eradication rates and side effects during eradication therapy: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Wang, F.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, H.; Lv, N. Efficacy and safety of probiotics as adjuvant agents for Helicobacter pylori infection: A meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Yang, H. Using Probiotics as Supplementation for Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goderska, K.; Agudo Pena, S.; Alarcon, T. Helicobacter pylori treatment: Antibiotics or probiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyssen, O.P.; Perez-Aisa, A.; Tepes, B.; Castro-Fernandez, M.; Kupcinskas, J.; Jonaitis, L.; Bujanda, L.; Lucendo, A.; Jurecic, N.B.; Perez-Lasala, J.; et al. Hp-EuReg Investigators Adverse Event Profile During the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori: A Real-World Experience of 22,000 Patients From the European Registry on H. pylori Management (Hp-EuReg). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viazis, N.; Argyriou, K.; Kotzampassi, K.; Christodoulou, D.K.; Apostolopoulos, P.; Georgopoulos, S.D.; Liatsos, C.; Giouleme, O.; Koustenis, K.; Veretanos, C.; et al. A Four-Probiotics Regimen Combined with A Standard Helicobacter pylori-Eradication Treatment Reduces Side Effects and Increases Eradication Rates. Nutrients 2022, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, M.; Yu, S.; Deng, J.; Yan, Q.; Yang, C.; Xia, G.; Zhou, X. Efficacy of Probiotic Supplementation Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; González, A.; González, R.; Hernández, M.; Ferrús, M.A.; Sanz, Y. Antimicrobial peptides are among the antagonistic metabolites produced by Bifidobacterium against Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michetti, P.; Dorta, G.; Wiesel, P.H.; Brassart, D.; Verdu, E.; Herranz, M.; Felley, C.; Porta, N.; Rouvet, M.; Blum, A.L.; et al. Effect of whey-based culture supernatant of Lactobacillus acidophilus (johnsonii) La1 on Helicobacter pylori infection in humans. Digestion 1999, 60, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Paek, N.S.; Kwon, O.S.; Hahm, K.B. Anti-inflammatory actions of probiotics through activating suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) expression and signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection: A novel mechanism. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homan, M.; Orel, R. Are probiotics useful in Helicobacter pylori eradication? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10644–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesbros-Pantoflickova, D.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I.; Blum, A.L. Helicobacter pylori and Probiotics. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 812S–818S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyanova, L.; Gergova, G.; Markovska, R.; Yordanov, D.; Mitov, I. Bacteriocin-like inhibitory activities of seven Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strains against antibiotic susceptible and resistant Helicobacter pylori strains. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Koga, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Komatsu, Y. A highly acid-resistant novel strain of Lactobacillus johnsonii No. 1088 has antibacterial activity, including that against Helicobacter pylori, and inhibits gastrin-mediated acid production in mice. Microbiologyopen 2015, 4, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.L.; Ran, Z.H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, C.X.; Xiao, S.D. Meta-analysis: The effect of supplementation with probiotics on eradication rates and adverse events during Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Fang, J.-Y. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of Lactobacillus-containing and Bifidobacterium-containing probiotic compound preparation in Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-G.; Chen, L.-X.; Li, B.; Wan, L.-Y.; Ai, Y.-W. Saccharomyces boulardii as an adjuvant therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, R.; Ni, P.; Chen, S.; Duan, G. Efficacy of Lactobacillus-supplemented triple therapy for H. pylori eradication: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, P.A.; Garcés, D.; Prado-Vivar, B.; Flores, N.; Fornasini, M.; Cohen, H.; Salvador, I.; Cargua, O.; Baldeón, M.E. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 as complementary treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on gut microbiome. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-I.; Pan, C.-Y.; Kao, J.Y.; Tsay, F.-W.; Peng, N.-J.; Kao, S.-S.; Wang, H.-M.; Tsai, T.-J.; Wu, D.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; et al. Taiwan Acid-related Disease (TARD) Study Group Helicobacter pylori eradication with bismuth quadruple therapy leads to dysbiosis of gut microbiota with an increased relative abundance of Proteobacteria and decreased relative abundances of Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.-M.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, C.-M.; Fang, Y.-J.; Bair, M.-J.; Chen, P.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Chen, M.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; et al. Taiwan Gastrointestinal Disease and Helicobacter Consortium Long-term changes of gut microbiota, antibiotic resistance, and metabolic parameters after Helicobacter pylori eradication: A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).