Fast and Sensitive Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Meropenem and Vaborbactam in Human Plasma Microsamples by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimization of LC-MS/MS Conditions
2.2. Method Validation
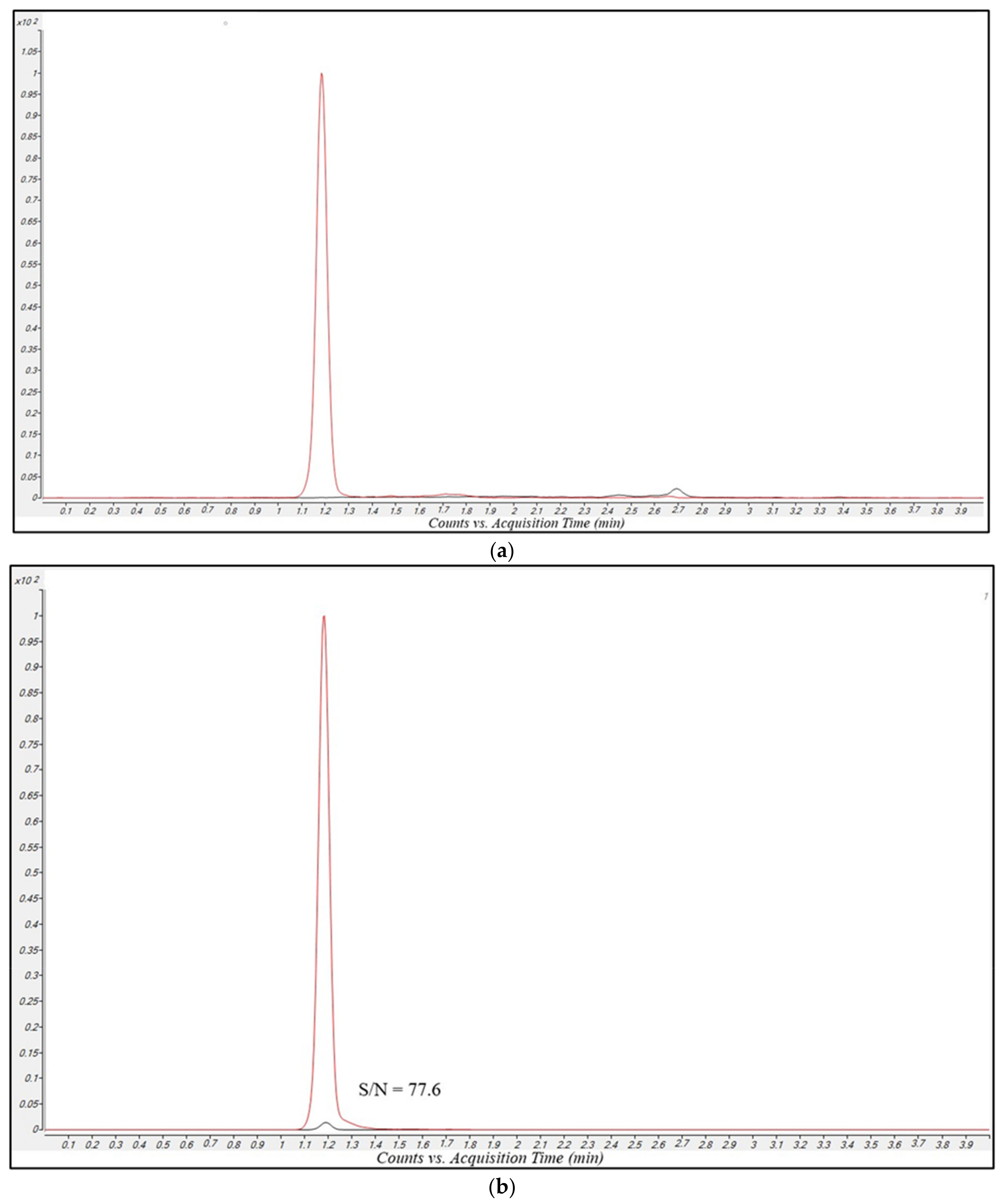
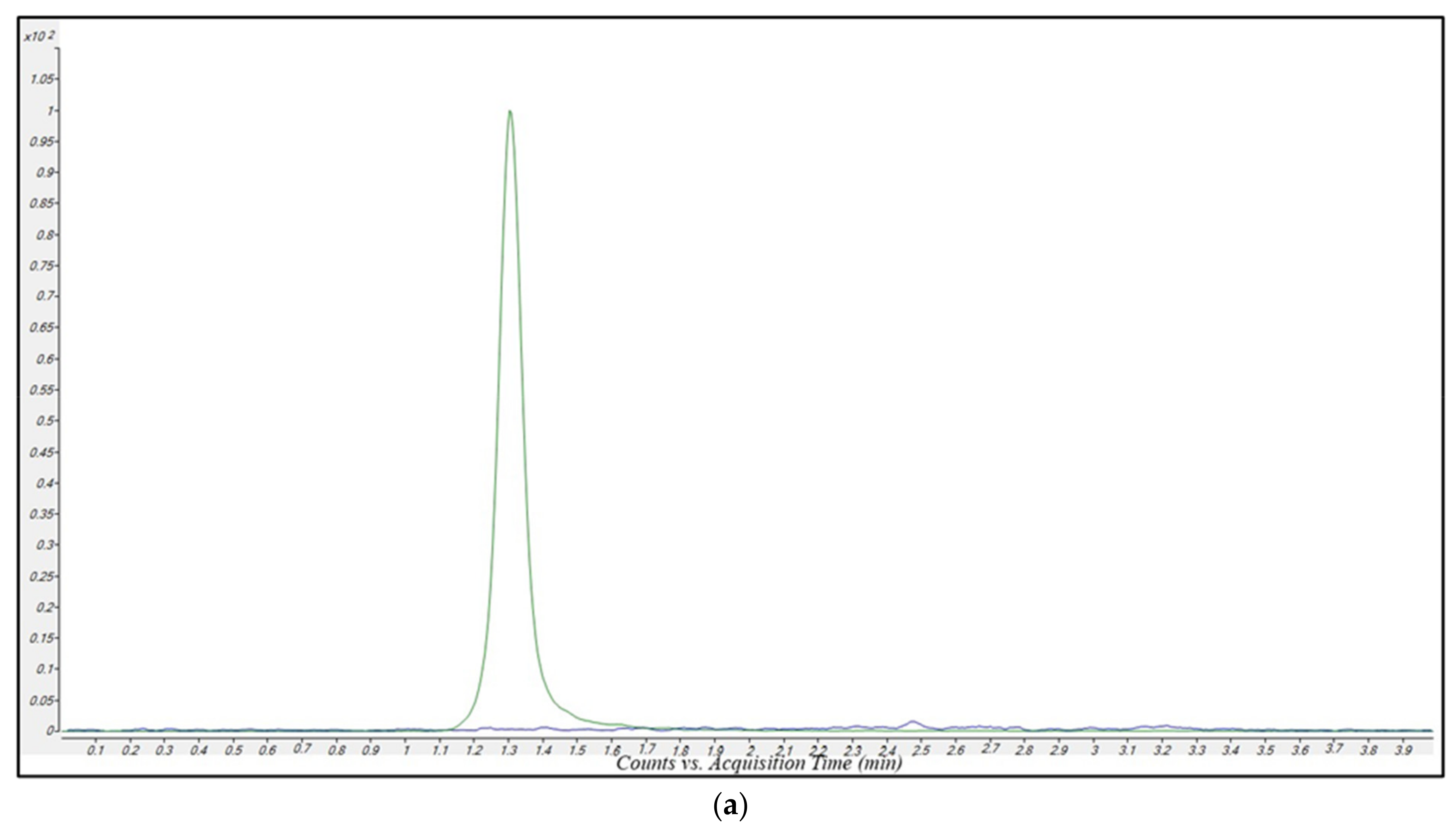
2.2.1. Sensitivity
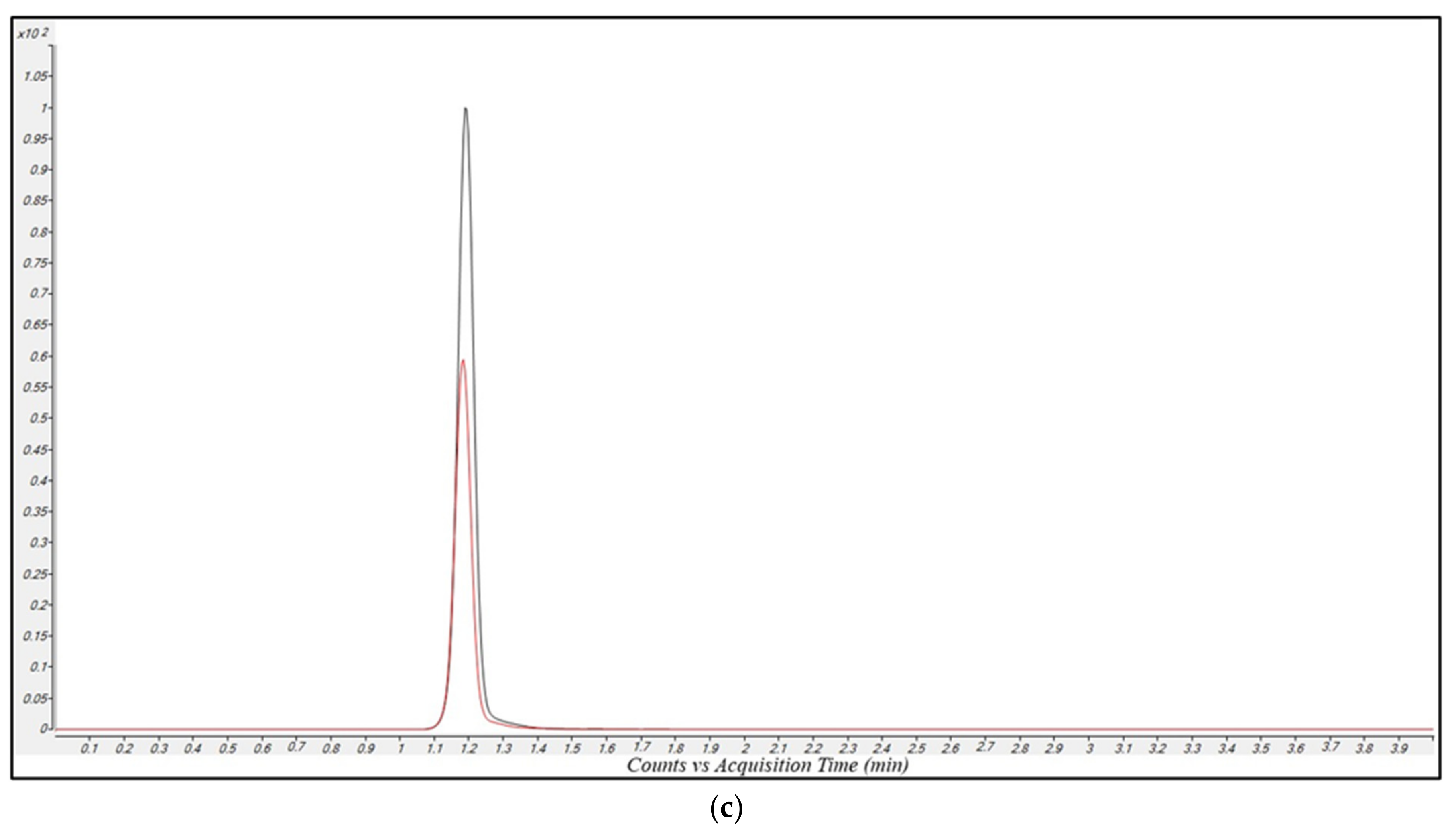
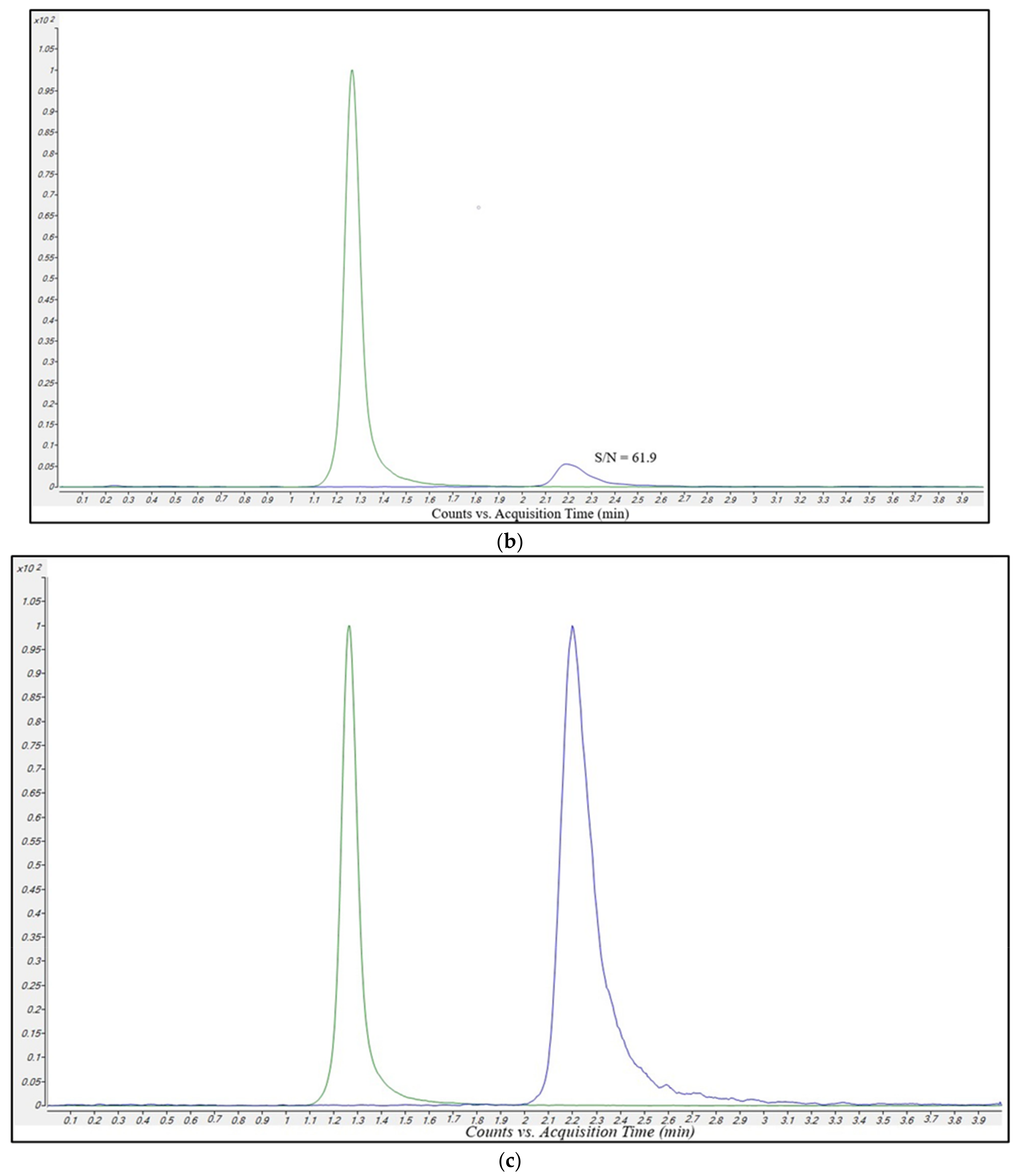
2.2.2. Selectivity and Carry-Over
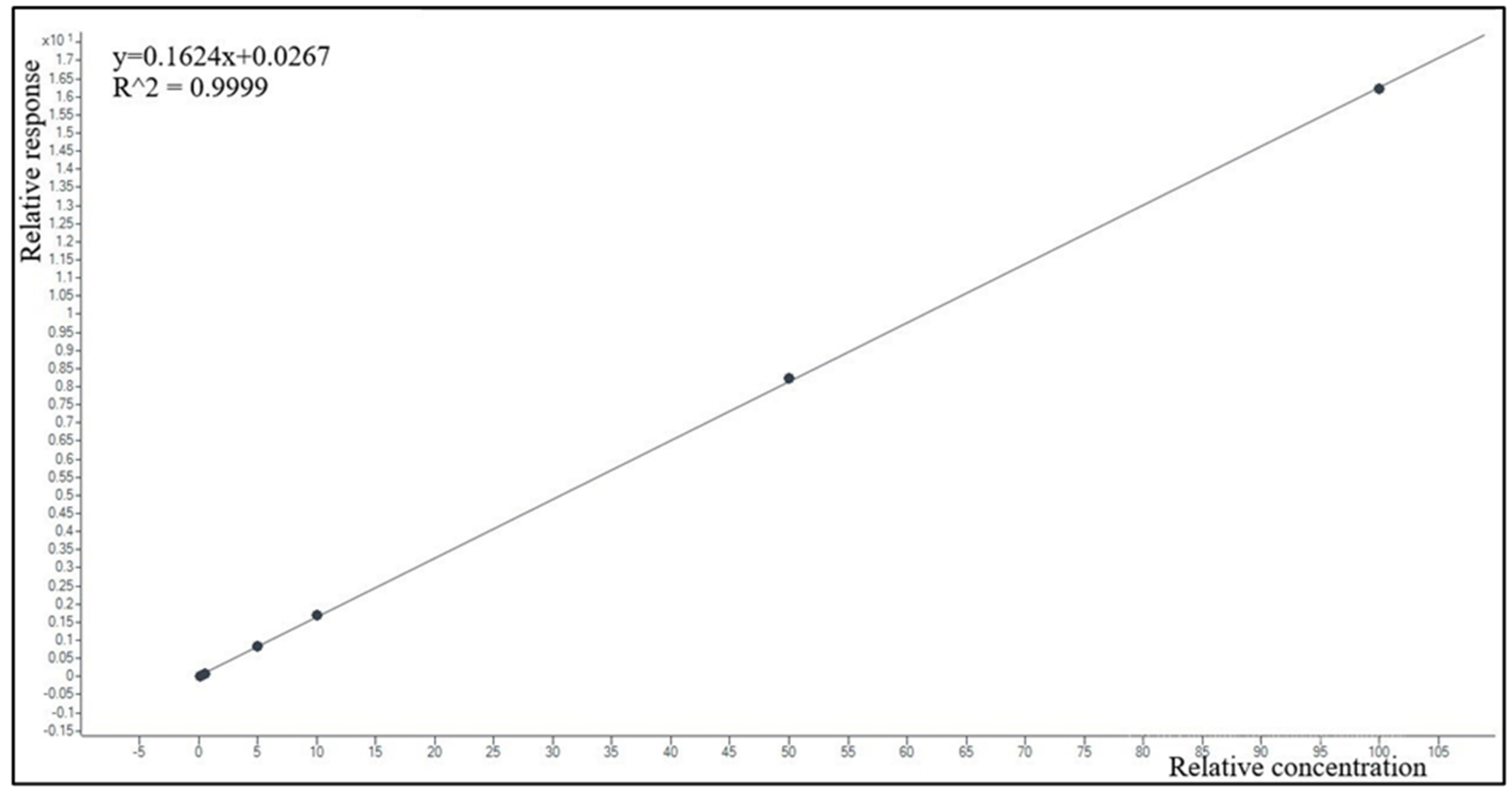
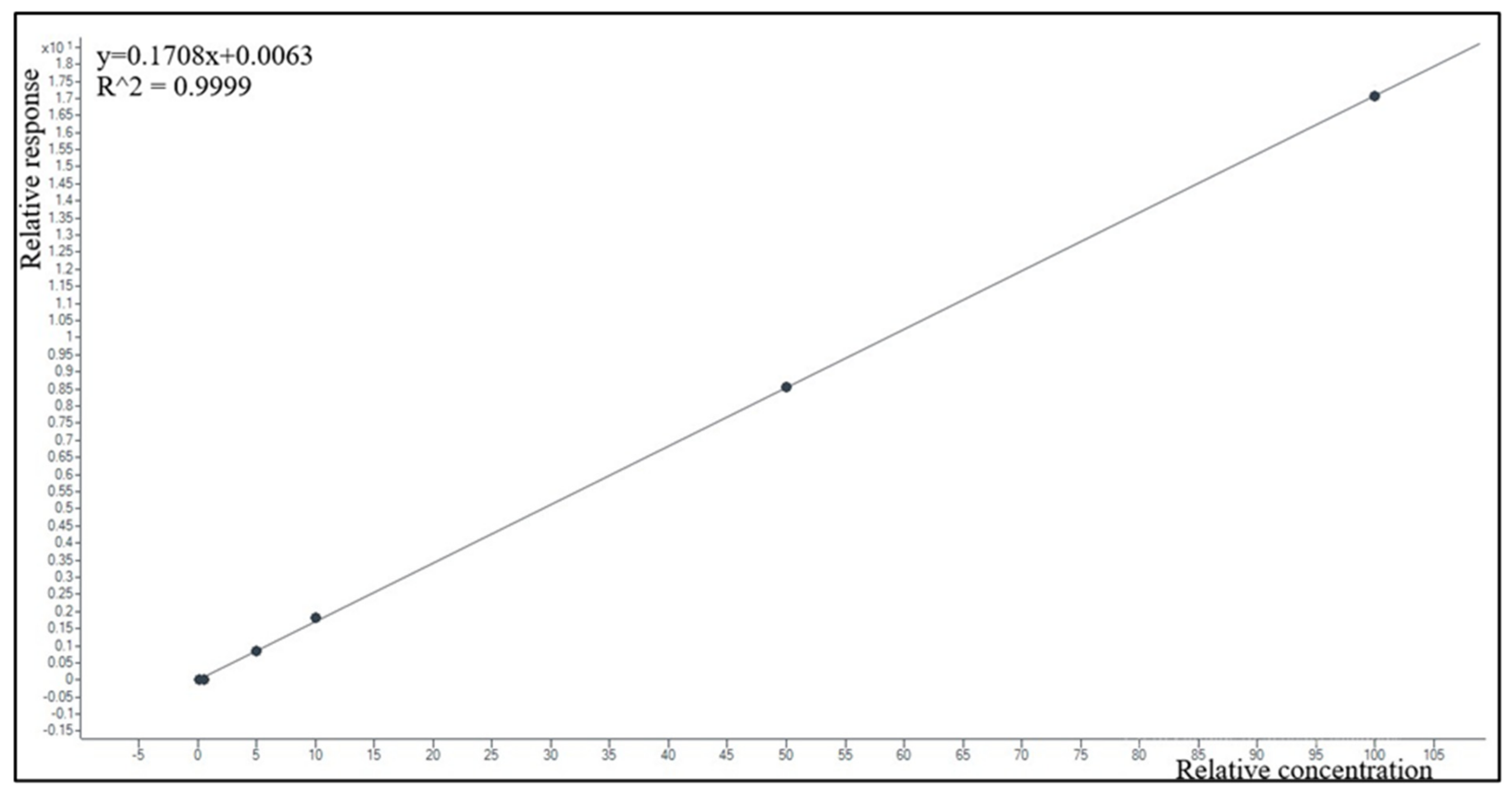
2.2.3. Linearity and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
2.2.4. Dilution Integrity
2.2.5. Accuracy and Precision
2.2.6. Matrix Effect and Extraction Recovery
2.2.7. Stability
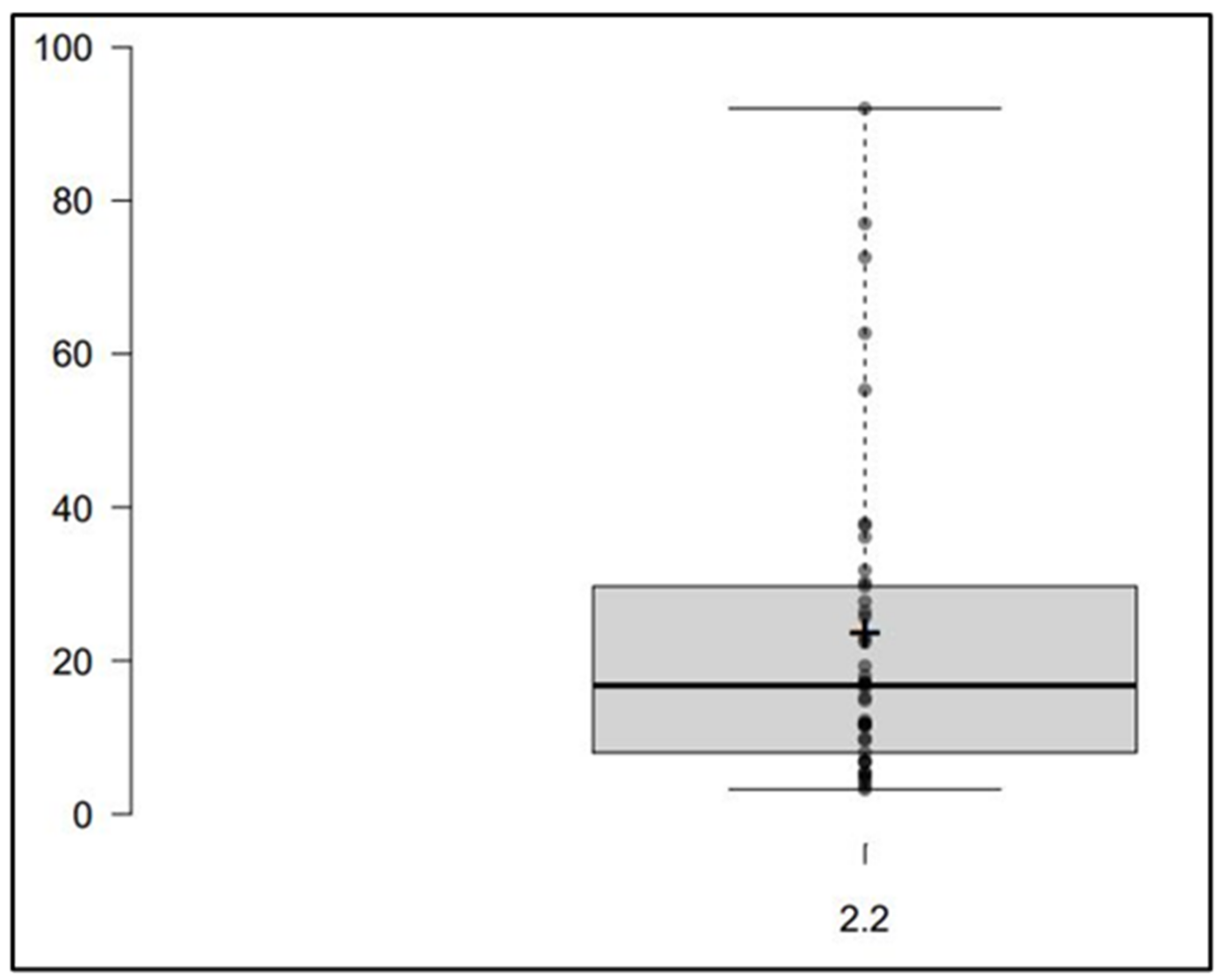
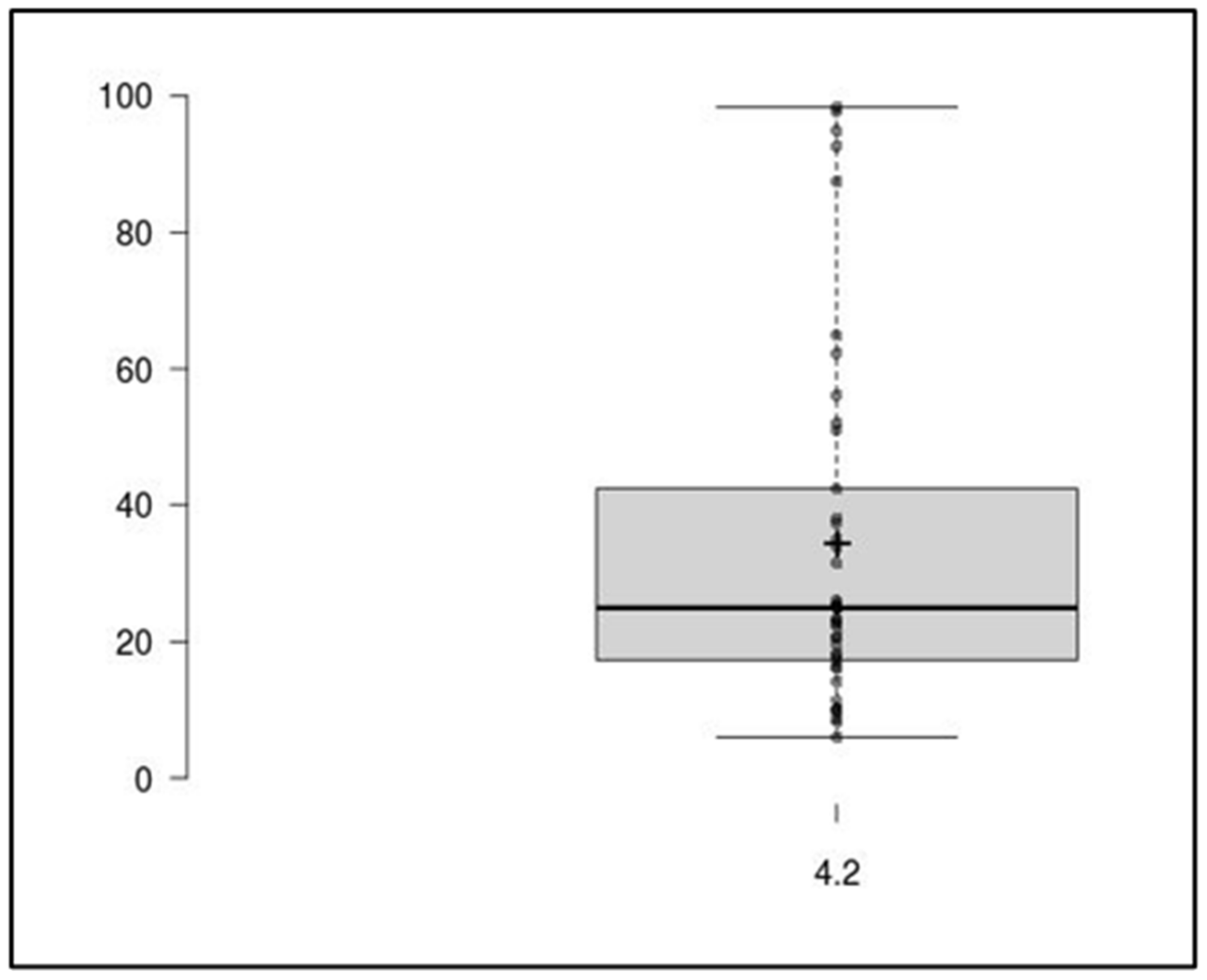
2.3. Clinical Application
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Reagents
4.2. Stock Solutions, Standards, and Quality Controls
4.3. Instrumentation
4.4. Sample Pre-Treatment
4.5. Method Validation
4.5.1. Selectivity and Carry-Over
4.5.2. Linearity and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
4.5.3. Precision and Accuracy
4.5.4. Dilution Integrity
4.5.5. Matrix Effect and Extraction Recovery
4.5.6. Stability
- sample extracts boarded on the autosampler at 10 °C for 24 h;
- sample extracts kept at −20 °C for 24 h;
- matrix samples after three complete freeze and thaw cycles from −80 °C to 25 °C.
4.6. Clinical Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.; Cheon, E. Meropenem-Vaborbactam for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infections Including Acute Pyelonephritis. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2018, 19, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, A.; Del Giacomo, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; Tumbarello, M. Meropenem/Vaborbactam: A next Generation β-Lactam β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combination. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2020, 18, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackley, R.; Roshdy, D.; Meredith, J.; Minor, S.; Anderson, W.E.; Capraro, G.A.; Polk, C. Meropenem-Vaborbactam versus Ceftazidime-Avibactam for Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02313–e02319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alosaimy, S.; Jorgensen, S.C.J.; Lagnf, A.M.; Melvin, S.; Mynatt, R.P.; Carlson, T.J.; Garey, K.W.; Allen, D.; Venugopalan, V.; Veve, M.; et al. Real-World Multicenter Analysis of Clinical Outcomes and Safety of Meropenem-Vaborbactam in Patients Treated for Serious Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alosaimy, S.; Lagnf, A.M.; Morrisette, T.; Scipione, M.R.; Zhao, J.J.; Jorgensen, S.C.J.; Mynatt, R.; Carlson, T.J.; Jo, J.; Garey, K.W.; et al. Real-World, Multicenter Experience With Meropenem-Vaborbactam for Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections Including Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaibani, P.; Lombardo, D.; Bussini, L.; Bovo, F.; Munari, B.; Giannella, M.; Bartoletti, M.; Viale, P.; Lazzarotto, T.; Ambretti, S. Epidemiology of Meropenem/Vaborbactam Resistance in KPC-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Causing Bloodstream Infections in Northern Italy, 2018. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, M.; Pea, F. Jumping into the Future: Overcoming Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Hurdles to Optimize the Treatment of Severe Difficult to Treat-Gram-Negative Infections with Novel Beta-Lactams. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, C.M.; Bhavnani, S.M.; Loutit, J.S.; Morgan, E.E.; White, D.; Dudley, M.N.; Griffith, D.C. Phase 1 Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Vaborbactam and Meropenem Alone and in Combination Following Single and Multiple Doses in Healthy Adult Subjects. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02228-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, A.; Bahmany, S.; Wijma, R.A.; van der Nagel, B.C.H.; Koch, B.C.P. Simultaneous Determination of Nine β-Lactam Antibiotics in Human Plasma by an Ultrafast Hydrophilic-Interaction Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1060, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briscoe, S.E.; McWhinney, B.C.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A.; Ungerer, J.P.J. A Method for Determining the Free (Unbound) Concentration of Ten Beta-Lactam Antibiotics in Human Plasma Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Ultraviolet Detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 907, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlier, M.; Stove, V.; De Waele, J.J.; Verstraete, A.G. Ultrafast Quantification of β-Lactam Antibiotics in Human Plasma Using UPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 978–979, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paal, M.; Zoller, M.; Schuster, C.; Vogeser, M.; Schütze, G. Simultaneous Quantification of Cefepime, Meropenem, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Linezolid and Piperacillin in Human Serum Using an Isotope-Dilution HPLC-MS/MS Method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 152, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigo-Bonnin, R.; Juvany-Roig, R.; Leiva-Badosa, E.; Sabater-Riera, J.; Pérez-Fernández, X.L.; Cárdenas-Campos, P.; Sospedra-Martínez, E.; Colom, H.; Alía, P. Measurement of Meropenem Concentration in Different Human Biological Fluids by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4997–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, T.; Fiedler, S.; Mihai, S.; Parsch, H. Determination of Meropenem Levels in Human Serum by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Ultraviolet Detection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, J.; Maier, B.; Suhr, A.; Zoller, M.; Frey, L.; Teupser, D.; Vogeser, M. Quantification of Piperacillin, Tazobactam, Cefepime, Meropenem, Ciprofloxacin and Linezolid in Serum Using an Isotope Dilution UHPLC-MS/MS Method with Semi-Automated Sample Preparation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, C.A.; Nicolau, D.P. Development of an HPLC Method for the Determination of Meropenem/Vaborbactam in Biological and Aqueous Matrixes. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2020, 58, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthiban, C.; Dixit, C.; Siddartha, B. Analytical Method Development and Validation for Simultaneous Estimation of Meropenem and Vaborbactam in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form by RP-HPLC. WJPS 2022, 10, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.L.; Pandey, S.; Sime, F.B.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A.; Wallis, S.C. A Validated LC-MSMS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Meropenem and Vaborbactam in Human Plasma and Renal Replacement Therapy Effluent and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7831–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammoun, A.K.; Khedr, A.; Khayyat, A.N.; Hegazy, M.A. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometric Method for Quantitation of the Recently Food and Drug Administration Approved Combination of Vaborbactam and Meropenem in Human Plasma. R Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Bioanalytical Method Validation; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, F.; Deprez, G.; Seyler, L.; Taccone, F.; Hites, M.; Gulbis, B.; Vincent, J.-L.; Jacobs, F.; Cotton, F. Rapid Quantification of Six β-Lactams to Optimize Dosage Regimens in Severely Septic Patients. Talanta 2013, 103, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analyte | Retention Time (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Production (m/z) | Dwell Time (ms) | Fragmentator (V) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRP | 1.21 | 384.2 | 141.0 | 20 | 166 | 16 |
| MRP-d6 | 1.20 | 390.2 | 147.1 | 20 | 166 | 16 |
| VBR | 2.35 | 296.0 | 234.1 | 20 | 166 | 20 |
| AVI-C13 | 1.16 | 269.0 | 96.0 | 20 | 166 | 29 |
| Time (min) | A (%) | B (%) | Flow (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 95 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 5 | 95 | 0.5 |
| 3.5 | 5 | 95 | 0.5 |
| 3.51 | 95 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 95 | 5 | 0.5 |
| QC Levels | Nominal Conc. (mg/L) | Intraday (n = 5) | Inter-Day (n = 3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg Conc. (mg/L) | Avg Precision (CV%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | Avg Conc. (>mg/L) | Avg Precision (CV%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | ||
| LLOQ | 0.1 | 0.06 | 14.5 | 10.8 | 0.06 | 15.9 | 19.2 |
| LQC | 0.25 | 0.27 | 10.5 | 9.5 | 0.28 | 10.6 | 10.3 |
| MQC | 25 | 23.8 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 25.4 | 9.8 | 6.7 |
| HQC | 75 | 76.9 | 9.8 | 8.7 | 73.9 | 10.2 | 4.1 |
| QC Levels | Nominal Conc. (mg/L) | Intraday (n = 5) | Inter-Day (n = 3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg Conc. (mg/L) | Avg Precision (CV%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | Avg Conc. (mg/L) | Avg Precision (CV%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | ||
| LLOQ | 0.1 | 0.04 | 17.5 | 19.8 | 0.04 | 17.9 | 19.1 |
| LQC | 0.25 | 0.24 | 12.5 | 9.5 | 0.23 | 10.4 | 13.3 |
| MQC | 25 | 26.8 | 10.9 | 9.9 | 26.4 | 9.5 | 9.7 |
| HQC | 75 | 77.5 | 10.8 | 7.5 | 76.9 | 8.2 | 7.1 |
| Quality Control Level | N° | Avg Me (%) | Avg IS-Normalized Me (%) | Avg ER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LQC | 30 | 121.8 | 102.2 | 86.3 |
| MQC | 30 | 115.5 | 104.1 | 88.5 |
| HQC | 30 | 117.2 | 100.3 | 91.4 |
| Quality Control Level | N° | Avg Me (%) | Avg IS-Normalized Me (%) | Avg ER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LQC | 30 | 181.9 | 104.2 | 76.3 |
| MQC | 30 | 185.7 | 105.1 | 83.5 |
| HQC | 30 | 187.2 | 98.3 | 87.4 |
| Quality Control | LQC | MQC | HQC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types of Sample | Tested Conditions | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) |
| extracts | autosampler post 2 h | −20.1 | −19.5 | −24.2 |
| freezer post 24 h | −19.5 | −19.7 | −21.8 | |
| plasma samples | freeze-thaw stability | |||
| 1 cycle | −15.2 | −15.6 | −15.8 | |
| 2 cycle | −35.6 | −29.2 | −22.5 | |
| 3 cycle | −67.1 | −65.2 | −56.1 | |
| Quality Control | LQC | MQC | HQC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types of Sample | Tested Conditions | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) | Avg Accuracy (Bias%) |
| extracts | autosampler post 2 h | −12.1 | −19.2 | −14.6 |
| freezer post 24 h | −9.5 | −8.7 | −9.1 | |
| plasma samples | freeze-thaw stability | |||
| 1 cycle | −8.8 | −9.1 | −9.4 | |
| 2 cycle | −15.1 | −19.2 | −12.6 | |
| 3 cycle | −27.4 | −25.1 | −26.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barone, R.; Conti, M.; Giorgi, B.; Gatti, M.; Cojutti, P.G.; Viale, P.; Pea, F. Fast and Sensitive Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Meropenem and Vaborbactam in Human Plasma Microsamples by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040719
Barone R, Conti M, Giorgi B, Gatti M, Cojutti PG, Viale P, Pea F. Fast and Sensitive Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Meropenem and Vaborbactam in Human Plasma Microsamples by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(4):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040719
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarone, Rossella, Matteo Conti, Beatrice Giorgi, Milo Gatti, Pier Giorgio Cojutti, Pierluigi Viale, and Federico Pea. 2023. "Fast and Sensitive Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Meropenem and Vaborbactam in Human Plasma Microsamples by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring" Antibiotics 12, no. 4: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040719
APA StyleBarone, R., Conti, M., Giorgi, B., Gatti, M., Cojutti, P. G., Viale, P., & Pea, F. (2023). Fast and Sensitive Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Meropenem and Vaborbactam in Human Plasma Microsamples by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Antibiotics, 12(4), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040719








