Risk Factors, Genetic Diversity, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus spp. Isolates in Dogs Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit of a Veterinary Hospital
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Staphylococcus spp. Isolation and Identification
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.4. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci
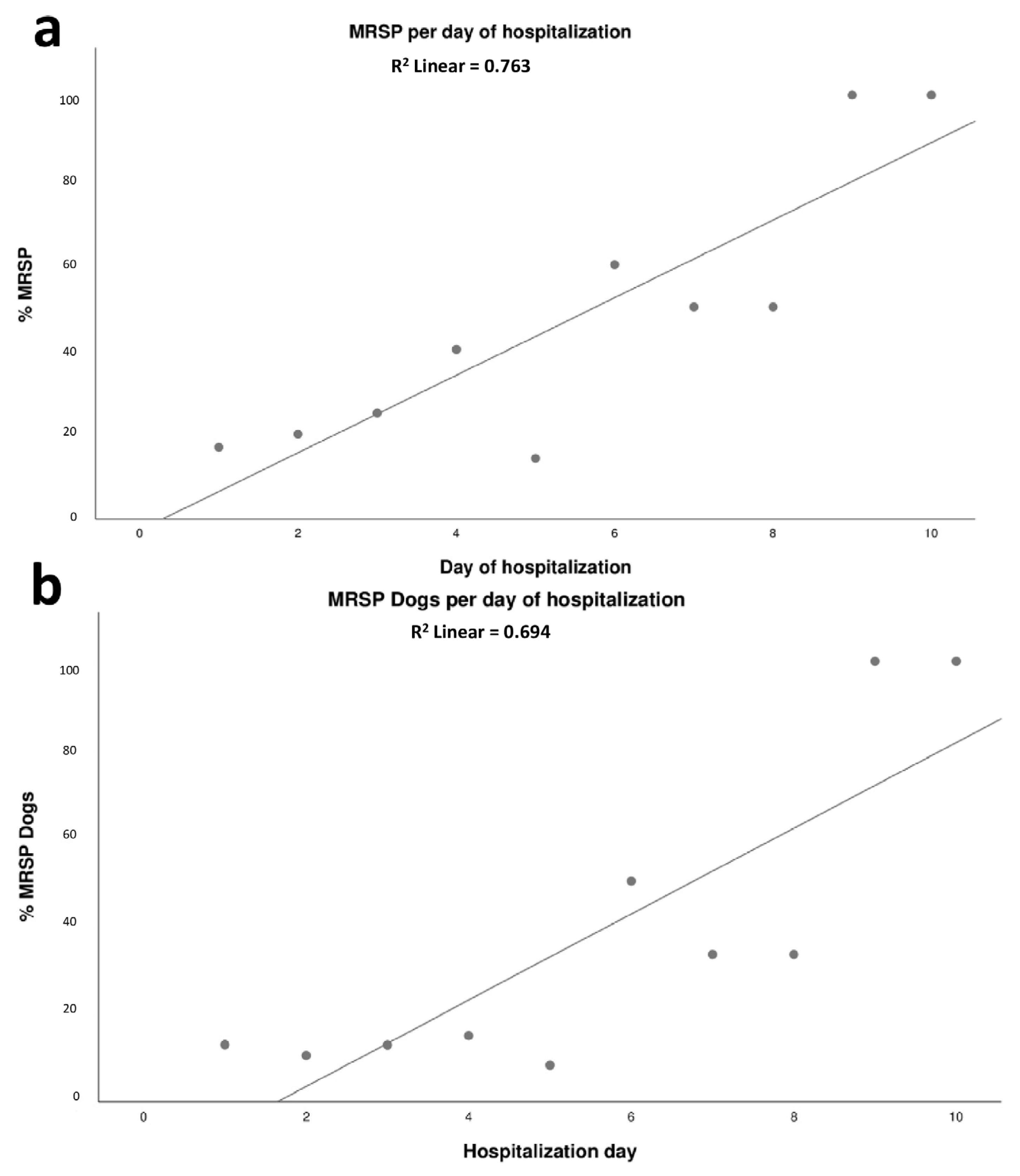
2.5. Dynamics of Colonization of MRSP in Dogs Admitted to the ICU
2.6. Predictors for MRSP in Dogs Admitted to the ICU of HV-UFMG
2.7. Comparison of MRSP Isolates from Infected and Colonized Dogs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strain Collection, Isolation, and Identification
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. DNA Extraction and Detection of mecA
4.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing
4.5. Statistical Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stull, J.W.; Weese, J.S. Hospital-Associated Infections in Small Animal Practice. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 45, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebola, D.C.; Oguttu, J.W.; Kock, M.M.; Qekwana, D.N. Hospital-Acquired and Zoonotic Bacteria from a Veterinary Hospital and Their Associated Antimicrobial-Susceptibility Profiles: A Systematic Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Kamata, S.; Hiramatsu, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in a Veterinary Teaching Hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, K.; Ueno, H.; Muramatsu, Y.; Kadosawa, T.; Yanagisawa, C.; Hanaki, H.; Nakajima, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Tamura, Y. Occurrence and Molecular Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in an Academic Veterinary Hospital. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5165–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienhoff, U.; Kadlec, K.; Chaberny, I.F.; Verspohl, J.; Gerlach, G.-F.; Schwarz, S.; Kreienbrock, L.; Nolte, I.; Simon, D. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius among Cats Admitted to a Veterinary Teaching Hospital. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönthal, T.; Moodley, A.; Nykäsenoja, S.; Junnila, J.; Guardabassi, L.; Thomson, K.; Rantala, M. Large Outbreak Caused by Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius ST71 in a Finnish Veterinary Teaching Hospital–From Outbreak Control to Outbreak Prevention. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, G.; Linek, M.; Bond, R.; Lloyd, D.H.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Thom, N.; Straube, I.; Verheyen, K.; Loeffler, A. Case–Control Risk Factor Study of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius (MRSP) Infection in Dogs and Cats in Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qekwana, D.N.; Oguttu, J.W.; Sithole, F.; Odoi, A. Patterns and Predictors of Antimicrobial Resistance among Staphylococcus Spp. from Canine Clinical Cases Presented at a Veterinary Academic Hospital in South Africa. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoen, H.R.C.; Rose, S.J.; Ramsey, S.A.; de Morais, H.; Bermudez, L.E. Analysis of Staphylococcus Infections in a Veterinary Teaching Hospital from 2012 to 2015. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 66, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Gustafsson, C.; Leander, M.; Fredriksson, M.; Grönlund, U.; Trowald-Wigh, G. Occurrence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci in Surgically Treated Dogs and the Environment in a Swedish Animal Hospital. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 53, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.; Kruger, J.M.; Schall, W.; Beal, M.; Manning, S.D.; Kaneene, J.B. Acquisition and Persistence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Dogs and Cats Admitted to a Veterinary Teaching Hospital. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 243, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somayaji, R.; Priyantha, M.a.R.; Rubin, J.E.; Church, D. Human Infections Due to Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius, an Emerging Zoonosis of Canine Origin: Report of 24 Cases. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, H.; Hisatsune, J.; Ohge, H.; Kutsuno, S.; Hara, T.; Masuda, K.; Aziz, F.; Sugai, M. Implanted Port Catheter System Infection Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius ST71-SCCmec Type III. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 2337–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, J.W.; Bjorvik, E.; Bub, J.; Dvorak, G.; Petersen, C.; Troyer, H.L. 2018 AAHA Infection Control, Prevention, and Biosecurity Guidelines. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2018, 54, 297–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, F.M.; Santana, J.A.; Silva, B.A.; Xavier, R.G.C.; Bonisson, C.T.; Câmara, J.L.S.; Rennó, M.C.; Cunha, J.L.R.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Lobato, F.C.F.; et al. Occurrence and Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Spp. in Diseased Dogs in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL) v4: Recent Updates and New Developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannoehr, J.; Guardabassi, L. Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in the Dog: Taxonomy, Diagnostics, Ecology, Epidemiology and Pathogenicity. Vet. Dermatol. 2012, 23, 253-e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fungwithaya, P.; Brikshavana, P.; Chanchaithong, P.; Prapasarakul, N. Distribution of Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (MRCoPS) in a Surgical Unit and Cystotomy Operation Sites in a Veterinary Teaching Hospital. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.T.; Amador, S.; McGonagle, C.J.; Needle, D.; Gibson, R.; Andam, C.P. Population Genomics of Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in Companion Animals in the United States. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S.; van Duijkeren, E. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in Veterinary Medicine. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Torres, C.; Lozano, C.; Sáenz, Y.; Zarazaga, M. Detection and Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in Healthy Dogs in La Rioja, Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 34, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellman, E.E.; Slettemeås, J.S.; Small, H.; Sunde, M. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius (MRSP) from Healthy Dogs in Norway–Occurrence, Genotypes and Comparison to Clinical MRSP. Microbiologyopen 2015, 4, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocca, G.; Piva, S.; Magno, S.D.; Scarpellini, R.; Giacometti, F.; Serraino, A.; Giunti, M. Prevalence and Patterns of Antimicrobial Resistance among Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Spp. in a Veterinary University Hospital. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.C.; Moodley, A.; Ghibaudo, G.; Guardabassi, L. Carriage of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in Small Animal Veterinarians: Indirect Evidence of Zoonotic Transmission. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, A.V.; Sellon, D.C.; Gay, J.M.; Lofgren, E.T.; Moore, D.A.; Jones, L.P.; Davis, M.A. Prevalence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius on Hand-Contact and Animal-Contact Surfaces in Companion Animal Community Hospitals. Can. Vet. J. 2020, 61, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienhoff, U.; Kadlec, K.; Chaberny, I.F.; Verspohl, J.; Gerlach, G.-F.; Kreienbrock, L.; Schwarz, S.; Simon, D.; Nolte, I. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius among Dogs Admitted to a Small Animal Hospital. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-68440-105-5. [Google Scholar]
- Adiguzel, M.C.; Schaefer, K.; Rodriguez, T.; Ortiz, J.; Sahin, O. Prevalence, Mechanism, Genetic Diversity, and Cross-Resistance Patterns of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Isolated from Companion Animal Clinical Samples Submitted to a Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory in the Midwestern United States. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, B.; Tedin, K.; Lübke-Becker, A. Multidrug-Resistant Opportunistic Pathogens Challenging Veterinary Infection Control. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.; Valério-Bolas, A.; Saraiva-Marques, C.; Alexandre-Pires, G.; Pereira da Fonseca, I.; Santos-Gomes, G. Development of Dog Immune System: From in Uterus to Elderly. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.C.; Nelson, R.W. Canine and Feline Endocrinology and Reproduction; Elsevier Science Health Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; ISBN 978-1-4557-3456-6. [Google Scholar]
- Holst, B.S.; Gustavsson, M.H.; Johannisson, A.; Hillström, A.; Strage, E.; Olsson, U.; Axnér, E.; Lilliehöök, I. Inflammatory Changes during Canine Pregnancy. Theriogenology 2019, 125, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, N.C.; Bärgman, S.C.; Moodley, A.; Nielsen, S.S.; Guardabassi, L. Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius Colonization Patterns and Strain Diversity in Healthy Dogs: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Study. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duim, B.; Verstappen, K.M.; Broens, E.M.; Laarhoven, L.M.; van Duijkeren, E.; Hordijk, J.; de Heus, P.; Spaninks, M.; Timmerman, A.J.; Wagenaar, J.A. Changes in the Population of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius and Dissemination of Antimicrobial-Resistant Phenotypes in the Netherlands. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, A.; Damborg, P.; Guardabassi, L.; Moodley, A.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Broens, E.M. Specific Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Mec (SCCmec) Types and Clonal Complexes Are Associated with Low-Level Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid and Cefalotin Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.S.; Kuster, S.P.; Nigg, A.; Dazio, V.; Brilhante, M.; Rohrbach, H.; Bernasconi, O.J.; Büdel, T.; Campos-Madueno, E.I.; Gobeli Brawand, S.; et al. Poor Infection Prevention and Control Standards Are Associated with Environmental Contamination with Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales and Other Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Swiss Companion Animal Clinics. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Working Group on the Classification of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Elements (IWG-SCC). Classification of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Mec (SCCmec): Guidelines for Reporting Novel SCCmec Elements. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4961–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.C.; Solyman, S.M.; Eberlein, L.C.; Bemis, D.A.; Woron, A.M.; Kania, S.A. Identification of a Predominant Multilocus Sequence Type, Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Cluster, and Novel Staphylococcal Chromosomal Cassette in Clinical Isolates of MecA-Containing, Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchaithong, P.; Prapasarakul, N.; Perreten, V.; Schwendener, S. Characterization of a Novel Composite Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Mec in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius from Thailand. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, T.; Saegusa, S.; Shirai, M.; Murakami, M.; Kato, Y. New Categories Designated as Healthcare-Associated and Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius in Dogs. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthing, K.A.; Schwendener, S.; Perreten, V.; Saputra, S.; Coombs, G.W.; Pang, S.; Davies, M.R.; Abraham, S.; Trott, D.J.; Norris, J.M. Characterization of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Mec Elements from Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius Infections in Australian Animals. mSphere 2018, 3, e00491-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, G.B.N.; Pereira, F.L.; Zegarra, A.U.; Tavares, G.C.; Leal, C.A.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Use of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry for the Fast Identification of Gram-Positive Fish Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Tsubakishita, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakusabe, A.; Ohtsuka, M.; Hirotaki, S.; Kawakami, T.; Fukata, T.; Hiramatsu, K. Multiplex-PCR Method for Species Identification of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Ge, Z.; Whary, M.T.; Erdman, S.E.; Horwitz, B.H. Helicobacter Hepaticus Infection in Mice: Models for Understanding Lower Bowel Inflammation and Cancer. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated From Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI supplement VET01S; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-68440-093-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, M.T.; Lubbers, B.V.; Schwarz, S.; Watts, J.L. Applying Definitions for Multidrug Resistance, Extensive Drug Resistance and Pandrug Resistance to Clinically Significant Livestock and Companion Animal Bacterial Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, D.G.; Saunders, N.A.; Owen, R.J. Rapid Extraction of Bacterial Genomic DNA with Guanidium Thiocyanate. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1989, 8, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Minamide, W.; Wada, K.; Nakamura, E.; Teraoka, H.; Watanabe, S. Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Strains of Staphylococci by Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Bankevich, A.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Pyshkin, A.; Sirotkin, A.; Sirotkin, Y.; et al. Assembling Single-Cell Genomes and Mini-Metagenomes from Chimeric MDA Products. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 714–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Allesøe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A Novel Web Tool for WGS-Based Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Associated with Chromosomal Point Mutations in Bacterial Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Ito, T.; Ma, X.X.; Watanabe, S.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Etienne, J.; Hiramatsu, K. Combination of Multiplex PCRs for Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Mec Type Assignment: Rapid Identification System for Mec, Ccr, and Major Differences in Junkyard Regions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, T.; Falush, D.; Lan, R.; Colles, F.; Mensa, P.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H.; Reeves, P.R.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Ochman, H.; et al. Sex and Virulence in Escherichia Coli: An Evolutionary Perspective. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaureguy, F.; Landraud, L.; Passet, V.; Diancourt, L.; Frapy, E.; Guigon, G.; Carbonnelle, E.; Lortholary, O.; Clermont, O.; Denamur, E.; et al. Phylogenetic and Genomic Diversity of Human Bacteremic Escherichia Coli Strains. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Total-Genome-Sequenced Bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyman, S.M.; Black, C.C.; Duim, B.; Perreten, V.; van Duijkeren, E.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Eberlein, L.C.; Sadeghi, L.N.; Videla, R.; Bemis, D.A.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing for Characterization of Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.D. How Old Is My Dog? Identification of Rational Age Groupings in Pet Dogs Based Upon Normative Age-Linked Processes. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 643085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Reference | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (n = 53) | Male | 19 (35.8%) |
| Female | 34 (64.2%) | |
| Dog size (n = 53) | Large breed | 17 (32.1%) |
| Medium breed | 20 (37.7%) | |
| Small breed | 16 (30.2%) | |
| Household with other animals (n = 43) | Yes | 30 (69.8%) |
| No | 13 (30.2%) | |
| Comorbidity (n = 53) | Yes | 25 (47.2%) |
| No | 28 (52.8%) | |
| Age (months; n = 46) 1 | Puppies (<12) | 6 (13%) |
| Adults (≥12 and <84) | 17 (37%) | |
| Elderly (≥84) | 23 (50%) | |
| Length of ICU stay (n = 54) | 1 to 2 days | 23 (42.6%) |
| 3 to 4 days | 18 (33.3%) | |
| >4 days | 13 (24.1%) | |
| Previous use of antimicrobial (n = 41) | Yes | 20 (48.8%) |
| No | 21 (51.2%) | |
| Antimicrobial use during ICU stay (n = 53) | Yes | 41 (77.4%) |
| No | 12 (22.6%) | |
| Clinical outcome (n = 53) | Release from ICU | 33 (62.3%) |
| Death | 20 (37.7%) |
| Day of Hospitalization | Staphylococcus sp. | S. pseudintermedius | MRSP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolates (%) | Dogs (%) | Isolates (%) | Dogs (%) | Isolates (%) | Dogs (%) | |
| 1 | 97/162 (59.9) | 45/54 (83.3) | 65/97 (67) | 37/45 (82.2) | 11/97 (11.3) | 7/45 (15.6) |
| 2 | 37/114 (32.5) | 23/38 (60.5) | 25/37 (67.6) | 19/23 (82.6) | 5/37 (13.5) | 4/23 (17.4) |
| 3 | 29/93 (31.2) | 19/31 (61.3) | 20/29 (69) | 15/19 (78.9) | 5/29 (17.2) | 4/19 (21) |
| 4 | 25/60 (41.7) | 14/20 (70) | 20/25 (80) | 11/14 (78.6) | 8/14 (32) | 3/14 (21.4) |
| 5 | 8/36 (22.2) | 6/12 (50) | 7/8 (87.5) | 5/6 (83.3) | 1/8 (12) | 1/6 (16.7) |
| 6 | 6/12 (50) | 4/4 (100) | 5/6 (83.3) | 4/4 (100) | 3/6 (50) | 2/4 (50) |
| 7 | 2/9 (22.2) | 2/3 (66.7) | 2/2 (100) | 2/2 (100) | 1/2 (50) | 1/2 (50) |
| 8 | 5/9 (55.6) | 3/3 (100) | 4/5 (80) | 3/3 (100) | 2/5 (40) | 1/3 (33.3) |
| 9 | 1/3 (33.3) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) |
| 10 | 1/3 (33.3) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) | 1/1 (100) |
| Total | 211/501 (42.1) | 51/54 (94.4) | 150/211 (71) | 45/51 (88.2) | 38/211 (18) | 11/51 (21.6) |
| Staphylococcus sp. | Isolates | Animals | Nasal Isolates | Rectal Isolates | Axillary Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. pseudintermedius | 150/211 (71.1%) | 45/51 (88.2%) | 59/150 (39.3%) d | 57/150 (38%) d | 34/150 (22.7%) e |
| S. aureus | 27/211 (12.8%) | 13/51 (25.5%) | 19/27 (70.4%) f | 2/27 (7.4%) g | 6/27 (22.2%) g |
| S. haemolyticus | 13/211 (6.2%) | 9/51 (17.6%) | 5/13 (38.5%) | 4/13 (30.8%) | 4/13 (30.8%) |
| S. devriese | 4/211 (1.9%) | 2/51 (3.9%) | 0/4 (0%) | 1/4 (25%) | 3/4 (75%) |
| S. felis | 3/211 (1.4%) | 3/51 (5.9%) | 0/3 (0%) | 3/3 (100%) | 0/3 (0%) |
| S. epidermidis | 3/211 (1.4%) | 2/51 (3.9%) | 0/3 (0%) | 1/3 (33.3%) | 2/3 (66.7%) |
| S. hominis | 3/211 (1.4%) | 3/51 (5.9%) | 1/3 (33.3%) | 1/3 (33.3%) | 1/3 (33.3%) |
| S. simulans | 3/211 (1.4%) | 3/51 (5.9%) | 0/3 (0%) | 2/3 (66.7%) | 1/3 (33.3%) |
| S. saprophyticus | 2/211 (1.0%) | 2/51 (3.9%) | 1/2 (50%) | 0/2 (0%) | 1/2 (50%) |
| S. delphini | 1/211 (0.5%) | 1/51 (1.9%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| S. schleiferi | 1/211 (0.5%) | 1/51 (1.9%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| S. equorum | 1/211 (0.5%) | 1/51 (1.9%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| Total ** | 211 (100%) | 51 (100%) | 85/211 (50.9%) a | 72/211 (43.1%) ab | 54/211 (32.3%) b |
| Variable | MRSP Isolates | p-Value | OR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 4/84 (5%) | <0.001 | 7.31 |
| Female | 34/127 (27%) | ||
| Size | |||
| Small (S) | 14/79 (18%) | S × M = 0.52; S × L = 0.66; M × L = 0.18 | NA |
| Medium (M) | 14/60 (23%) | ||
| Large (L) | 10/72 (14%) | ||
| Age | |||
| Young (≤12 months) (Y) | 4/24 (17%) | (Y + A) × E = 0.016 | 2.64 |
| Adult (>12 e ≥ 84 months) (A) | 7/56 (13%) | ||
| Elderly (>84 months) (E) | 27/91 (30%) | ||
| Contact with other animals | |||
| Yes | 31/119 (26%) | 0.27 | NA |
| No | 6/37 (16%) | ||
| Comorbidity | |||
| Yes | 22/123 (18%) | 1.0 | NA |
| No | 16/88 (18%) | ||
| Prior use of antimicrobials | |||
| Yes | 24/74 (32%) | 0.017 | 2.53 |
| No | 11/69 (16%) | ||
| Antimicrobial use during hospitalization | |||
| Yes | 26/155 (17%) | 0.43 | NA |
| No | 12/56 (21%) | ||
| Beta-lactams use during hospitalization | |||
| Yes | 26/129 (20%) | 0.71 | NA |
| No | 12/71 (17%) | ||
| Death | |||
| Yes | 1/20 (5%) | 0.14 | NA |
| No | 37/191 (19%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santana, J.A.; Paraguassu, A.O.; Santana, R.S.T.; Xavier, R.G.C.; Freitas, P.M.C.; Aburjaile, F.F.; Azevedo, V.A.d.C.; Brenig, B.; Bojesen, A.M.; Silva, R.O.S. Risk Factors, Genetic Diversity, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus spp. Isolates in Dogs Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit of a Veterinary Hospital. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030621
Santana JA, Paraguassu AO, Santana RST, Xavier RGC, Freitas PMC, Aburjaile FF, Azevedo VAdC, Brenig B, Bojesen AM, Silva ROS. Risk Factors, Genetic Diversity, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus spp. Isolates in Dogs Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit of a Veterinary Hospital. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030621
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantana, Jordana Almeida, Amanda Oliveira Paraguassu, Ranielle Stephanie Toledo Santana, Rafael Gariglio Clark Xavier, Patricia Maria Colleto Freitas, Flavia Figueira Aburjaile, Vasco Ariston de Carvalho Azevedo, Bertram Brenig, Anders Miki Bojesen, and Rodrigo Otávio Silveira Silva. 2023. "Risk Factors, Genetic Diversity, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus spp. Isolates in Dogs Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit of a Veterinary Hospital" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030621
APA StyleSantana, J. A., Paraguassu, A. O., Santana, R. S. T., Xavier, R. G. C., Freitas, P. M. C., Aburjaile, F. F., Azevedo, V. A. d. C., Brenig, B., Bojesen, A. M., & Silva, R. O. S. (2023). Risk Factors, Genetic Diversity, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus spp. Isolates in Dogs Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit of a Veterinary Hospital. Antibiotics, 12(3), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030621








