Tamarindus indica Extract as a Promising Antimicrobial and Antivirulence Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antibacterial Effects of T. indica against MDR Bacteria
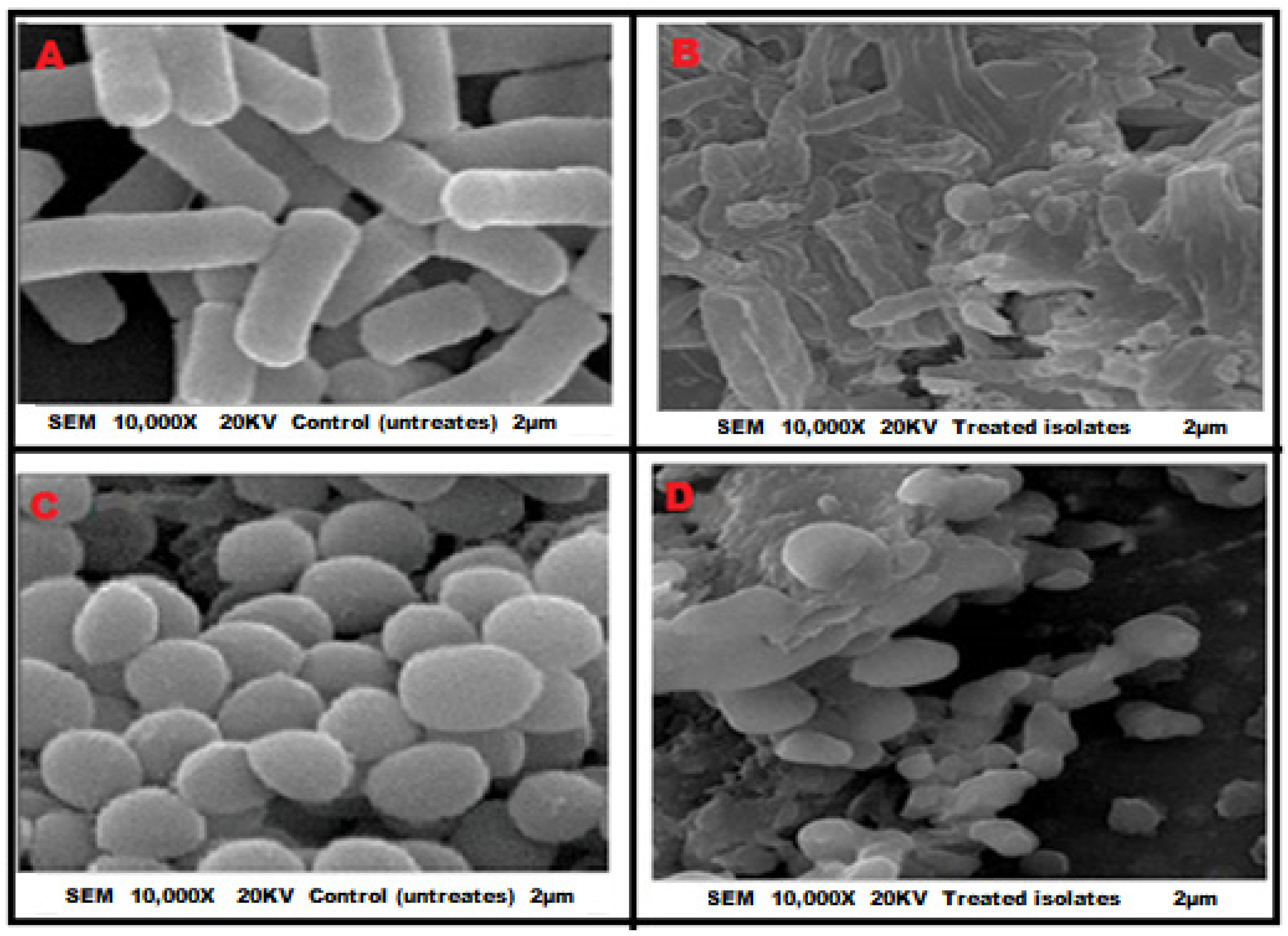
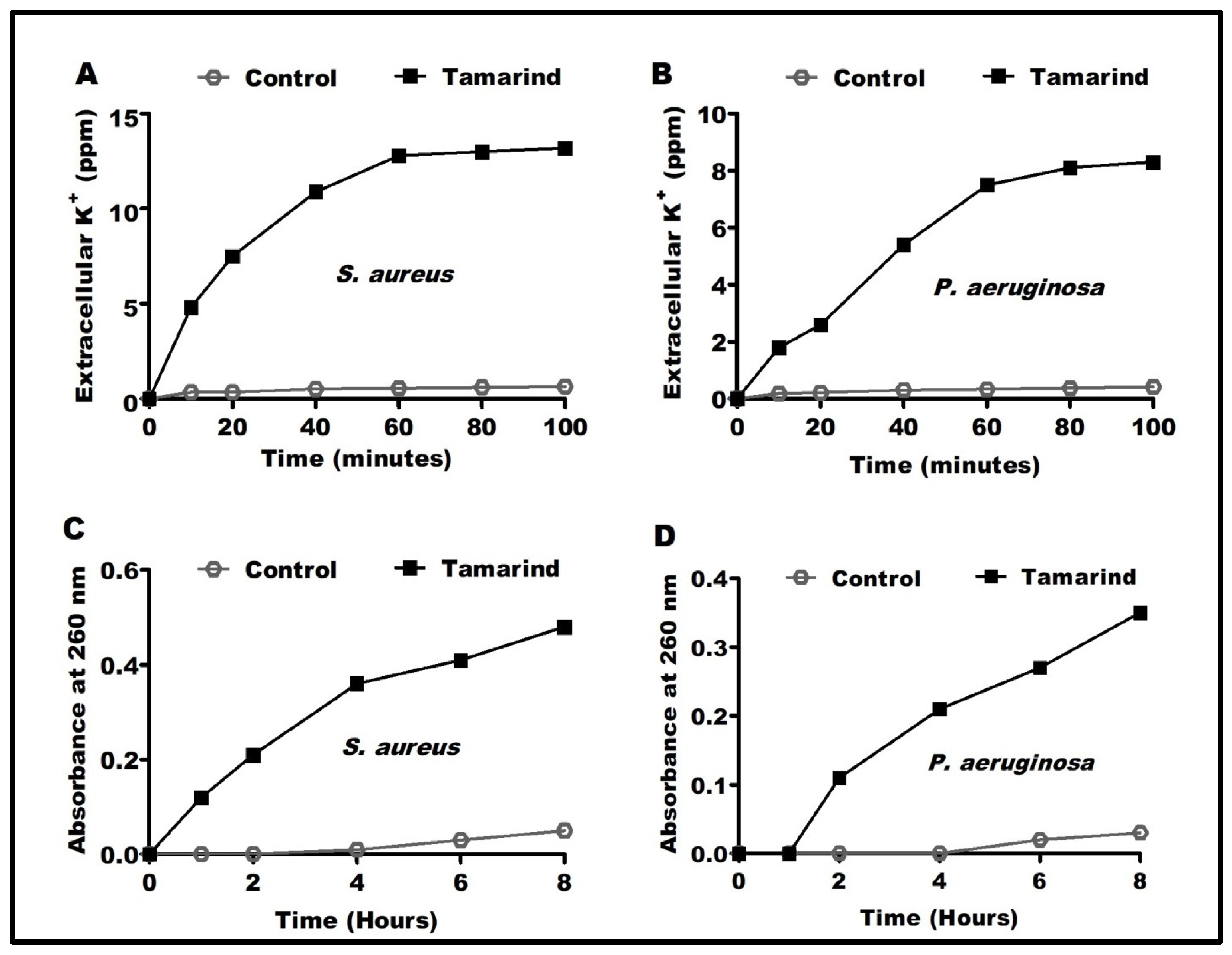
2.2. The Possible Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Actions
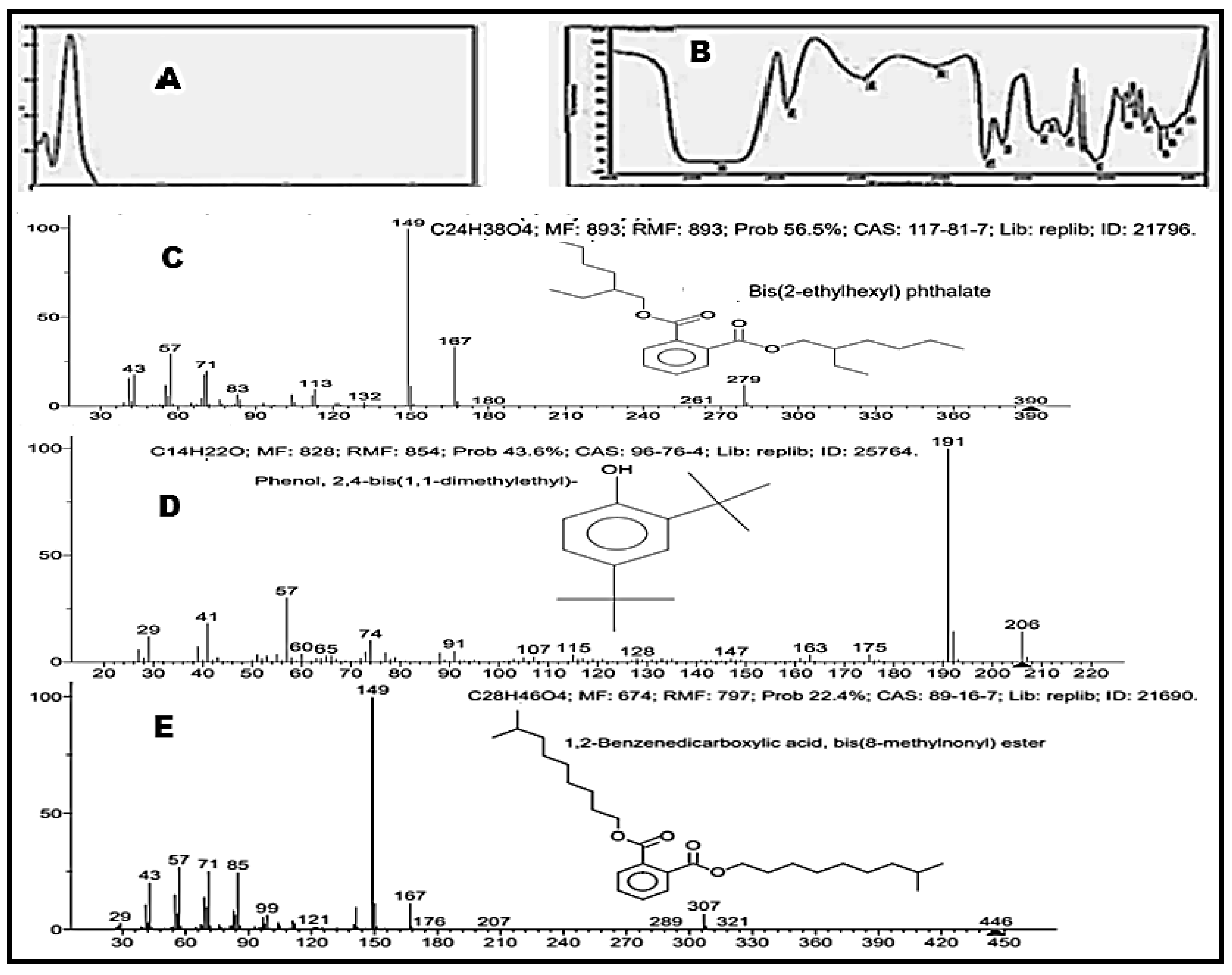
2.3. Phytochemical Analysis of the Bioactive Molecules
2.4. GC-MC Analysis
2.5. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganisms, Plant Materials, and Extraction
4.2. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activities
4.2.1. Agar Diffusion Assay by Filter Paper Disc Method
4.2.2. Estimation of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
4.2.3. Evaluation of Co-Admixture of the Ethanolic Extract from T. indica with the Commonly Used Antibiotics by Checkerboard Method
4.3. Assessment the Possible Antibacterial Mechanisms of T. indica Ethanolic Extract
4.4. Chemical Identification of Bioactive Substances
4.4.1. TLC and Bio-Autographic Assays
4.4.2. Phytochemicals Analysis
4.4.3. GC-MS Analysis
4.5. Molecular Docking Study
4.5.1. Molecular Docking (In Silico) Studies
4.5.2. Preparation of the Investigated Compounds
4.5.3. Preparation of the Proteases of S. aureus and P. aeruginosa
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manandhar, S.; Luitel, S.; Dahal, R.K. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Some Medicinal Plants against Human Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Trop. Med. 2019, 2, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camele, I.; Elshafie, H.S.; Caputo, L.; Sakr, S.H.; De Feo, V. Bacillus mojavensis: Biofilm formation and biochemical investigation of its bioactive metabolites. J. Biol. Res. 2019, 92, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, R.; Coppo, E.; Marchese, A.; Daglia, M.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M. Phytochemicals for human disease: An update on plant-derived compounds antibacterial activity. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 196, 44–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarowska, J.; Futoma-Koloch, B.; Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Frej-Madrzak, M.; Ksiazczyk, M.; Bugla-Ploskonska, G.; Choroszy-Krol, I. Virulence factors, prevalence and potential transmission of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from different sources: Recent reports. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendary, M.M.; Solyman, S.M.; Azab, M.M.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Hanora, A.M. Characterization of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from human and animal samples in Egypt. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Clatworthy, A.E.; Pierson, E.; Hung, D.T. Targeting virulence: A new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellbye, B.; Schuster, M. The sociomicrobiology of antivirulence drug resistance: A proof of concept. mBio 2011, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, M.; Shaheen, A.; Bouhy, A.; Bendary, M. Alternative therapy to manage otitis media caused by multidrug-resistant fungi. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, A.R.; Abdolpour, F.; Monsef-Esfahani, H.R.; Farsam, H. A TLC bioautographic assay for the detection of nitrofurantoin resistance reversal compound. J. Chromatogr. 2007, 850, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadoriya, S.S.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Narwaria, J.; Rai, G.; Jain, A.P. Tamarindus indica: Extent of explored potential. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sudjaroen, Y.; Haubner, R.; Würtele, G.; Hull, W.E.; Erben, G.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Changbumrung, S.; Bartsch, H.; Owen, R.W. Isolation and structure elucidation of phenolic antioxidants from Tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) seeds and pericarp. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, S.I.; Rao, P.C.; Dolecek, C.; Day, N.J.; Stergachis, A.; Lopez, A.D.; Murray, C.L. Measuring and mapping the global burden of antimicrobial resistance. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asowata-Ayodele, A.M.; Otunola, G.A.; Afolayan, A.J. Assessment of the polyphenolic content, free radical scavenging, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities of acetone and aqueous extracts of Lippia javanica (Burm.F.) spreng. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, Z.M.; Da Trindade, L.S.; Santana, G.C.; Padilha, F.F.; Da Costa Mendonça, M.; Da Costa, L.P.; López, J.A.; Macedo, M.L.H. Effect of Tamarindus indica L. and Manihot esculenta extracts on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bendary, M.M.; Solyman, S.M.; Azab, M.M.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Hanora, A.M. Genetic diversity of multidrug resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical and non clinical samples in Egypt. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; Sewid, A.H.; Samir, M.; Hegazy, W.H.; Bahnass, M.M.; Mosbah, R.A.; Ghaith, D.M.; Khalifa, E.; Ramadan, H.; Alshareef, W.A.; et al. Clonal Diversity and Epidemiological Characteristics of ST239-MRSA Strains. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 782045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, W.A.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Nassar, M.S.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bendary, M.M. Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganism 2020, 8, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosallam, F.M.; Helmy, E.A.; Bendary, M.M.; El-Batal, I.A. Potency of a novel synthesized Ag-eugenol nanoemulsion for treating some bacterial and fungal pathogens. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; González-Burgos, E.; Iglesias, I. Current uses and knowledge of medicinal plants in the Autonomous Community of Madrid (Spain): A descriptive cross-sectional study. BMC Complemen. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalona-Arranz, J.; Péres-Roses, R.; Urdaneta-Laffita, I.; Camacho-Pozo, M.; Rodríguez-Amado, J.; Licea-Jiménez, I. Antimicrobial activity of extracts from Tamarindus indica L. leaves. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2010, 6, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwodo, U.U.; Obiiyeke, G.E.; Chigor, V.N.; Okoh, A.I. Assessment of Tamarindus indica extracts for antibacterial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieffe, S.; Williams, L.D.; Reece, S.; Thompson, S.; Knight, G. Antimicrobial Activities of Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) Extracts. J. Plant Sci. Res. 2019, 6, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Mouton, J.W.; Muller, A.E.; Canton, R.; Giske, C.G.; Kahlmeter, G.; Turnidge, J. MIC-based dose adjustment: Facts and fables. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, H.D.; Costa, J.G.; Lima, E.O.; Falcão-Silva, V.S.; Siqueira, J.P. Herbal therapy associated with antibiotic therapy: Potentiation of the antibiotic activity against methicillin–resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Turnera ulmifolia L. BMC Complemen. Altern. Med. 2009, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, M.F.; Nasr, Z.M.; Abousaty, A.I.; Seadawy, H.G.; Shaheen, M.A.; Albogami, S.; Al-Sanea, M.M.; Bendary, M.M. Alternative and Complementary Therapies against Foodborne Salmonella Infections. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendary, M.M.; Ibrahim, D.; Mosbah, R.A.; Mosallam, F.; Hegazy, W.H.; Awad, N.S.; Alshareef, W.A.; Alomar, S.Y.; Zaitone, S.A.; Abd El-Hamid, M.I. Thymol Nanoemulsion: A New Therapeutic Option for Extensively Drug Resistant Foodborne Pathogens. Antibiotics 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddley, J.W.; Pappas, P.G. Antifungal combination therapy: Clinical potential. Drugs 2005, 65, 1461–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasu, N.; Saleem, B.; Nawaz, R. Preliminary screening of four common Plants of family Caesalpiniacae. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 1989, 2, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Padmavathi, A.R.; Abinaya, B.; Pandian, S.K. Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) of marine bacterial origin inhibits quorum sensing mediated biofilm formation in the uropathogen Serratia marcescens. Biofouling 2014, 30, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookying, S.; Duangjai, A.; Saokaew, S.; Phisalprapa, P. Botanical aspects, phytochemicals, and toxicity of Tamarindus indica leaf and a systematic review of antioxidant capacities of T. indica leaf extracts. Front. Nutr. 2022, 20, 977015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumgumjee, N.M. Antimicrobial activities and chemical properties of Tamarindus indica L. leaves extract. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 6172–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.S.; Beswick, T.S. Bacteriology, Virology and Immunity, 10th ed.; The English Language Book Society and Ballierie Tindall: London, UK, 1979; pp. 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.H. Antibacterial activity and action mechanism of the essential oil from enteromorpha linza L. against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Molecules 2016, 21, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, O.A.; Li, L.; Ma, J.B.; Hatab, S.; Xu, L.; Guo, J.W.; Rasulov, B.A.; Liu, Y.H.; Hedlund, B.P.; Li, W.J. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of endophytic bacterial populations from Chinese traditional medicinal plant licorice and characterization of the bioactive secondary metabolites produced by Bacillus atrophaeus Against Verticillium dahliae. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. In CLSI Supplement M100, 30th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Muthu, S.E.; Nandakumar, S.; Rao, U.A. The effect of alcoholic extract of Tamarindus indica Linn. on the growth of clinical isolates of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Indian J. Med. Res. 2005, 122, 525–528. [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino, C.; Labella, C.; Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I.; Musto, M.; Paolino, R.; D’Adamo, C.; Freschi, P. Effects of different heat treatments on lysozyme quantity and antimicrobial activity of jenny milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, S.H.; Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I.; Sadeek, S.A. Synthesis, spectroscopic, and biological studies of mixed ligand complexes of gemifloxacin and glycine with Zn(II), Sn(II), and Ce(III). Molecules 2018, 23, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timurkaynak, F.; Can, F.; Azap, O.K.; Demirbilek, M.; Arslan, H.; Karaman, S.O. In vitro activities of non-traditional antimicrobials alone or in combination against multidrug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from intensive care units. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 7, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbe, R.; Steele-Moor, L.; Goodwin, A.C. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Protocols New York, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultee, A.; Kets, E.P.; Smid, E.J. Mechanisms of action of carvacrol on the food-borne pathogen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4606–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hada, T.; Inoue, Y.; Shiraishi, A.; Hamashima, H. Leakage of K+ ions from Staphylococcus aureus in response to tea tree oil. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 53, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekom, S.E.; Tamokou, J.D.; Kuete, V. Antibacterial and Therapeutic Potentials of the Capsicum annuum Extract against Infected Wound in a Rat Model with Its Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 4, 4303902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sptempack, J.; Ward, R. An improved staining for electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1969, 22, 679–701. [Google Scholar]
- Kawther, F.A. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils of some medicinal plants from Arab Saudi. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 14, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Sakr, S.H.; Sadeek, S.A.; Camele, I. Biological Investigations and Spectroscopic Studies of New Moxifloxacin/Glycine-Metal Complexes. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1800633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harborne, J.B. Phytochemical Methods: A Guide to Modern Techniques of Plant Analysis, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Viggiani, L.; Mostafa, M.S.; El-Hashash, M.A.; Bufo, S.A.; Camele, I. Biological activity and chemical identification of ornithine lipid produced by Burkholderia gladioli pv. agaricicola ICMP 11096 using LC-MS and NMR analyses. J. Biol. Res. 2017, 90, 6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, E.; Camele, I.; Elshafie, H.S.; De Martino, L.; Pellegrino, C.; Grulova, D.; De Feo, V. Chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil of Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum from different areas in the Southern Apennines (Italy). Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlesi, M.; Okiei, W.; Osibote, A.E. Analysis of the essential oil from the leaves of Sesamum radiatum, a potential medication for male infertility factor, by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Inc, C.C.G. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE); Chemical Computing Group Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2016; p. 1010. [Google Scholar]
- Elmaaty, A.A.; Darwish, K.M.; Chrouda, A.; Boseila, A.A.; Tantawy, M.A.; Elhady, S.S.; Shaik, A.B.; Mustafa, M.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. In Silico and In Vitro Studies for Benzimidazole Anthelmintics Repurposing as VEGFR-2 Antagonists: Novel Mebendazole-Loaded Mixed Micelles with Enhanced Dissolution and Anticancer Activity. ACS Omega 2021, 7, 875–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.A.; Elmaaty, A.A.; Hoda, S.E.; Mustafa, M.S.; Salah, M.; Rogy, R.E. Structure based design and synthesis of 3-(7-nitro-3-oxo-3, 4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl) propanehydrazide derivatives as novel bacterial DNA-gyrase inhibitors: In-vitro, In-vivo, In-silico and SAR studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 129, 106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdzalik, M.; Kalinska, M.; Wysocka, M.; Stec-Niemczyk, J.; Cichon, P.; Stach, N.; Gruba, N.; Stennicke, H.R.; Jabaiah, A.; Markiewicz, M.; et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of SplD protease from Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 76812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, M.; Flaherty, K.M.; McKay, D.B. Three-dimensional structure of the elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 1.5-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


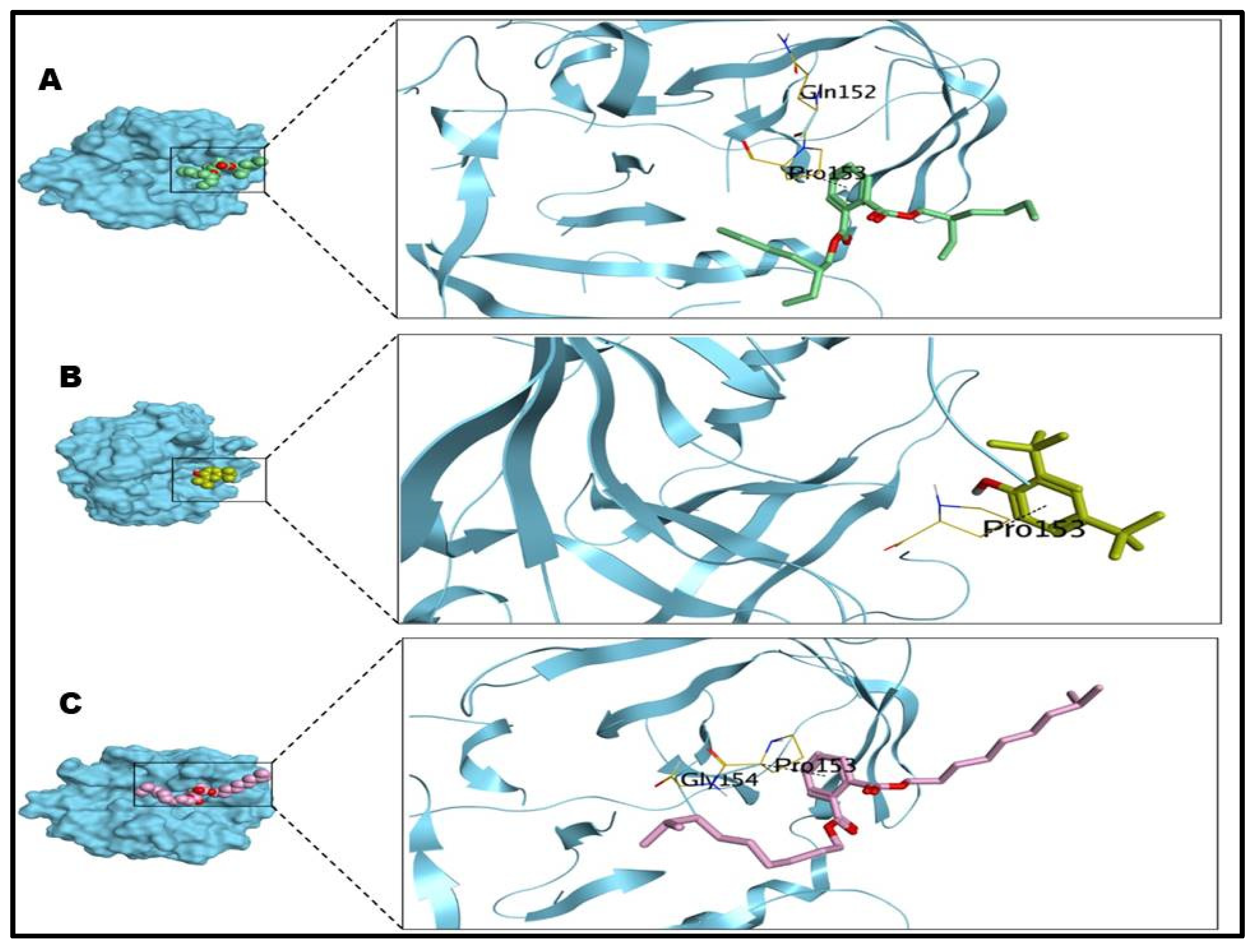
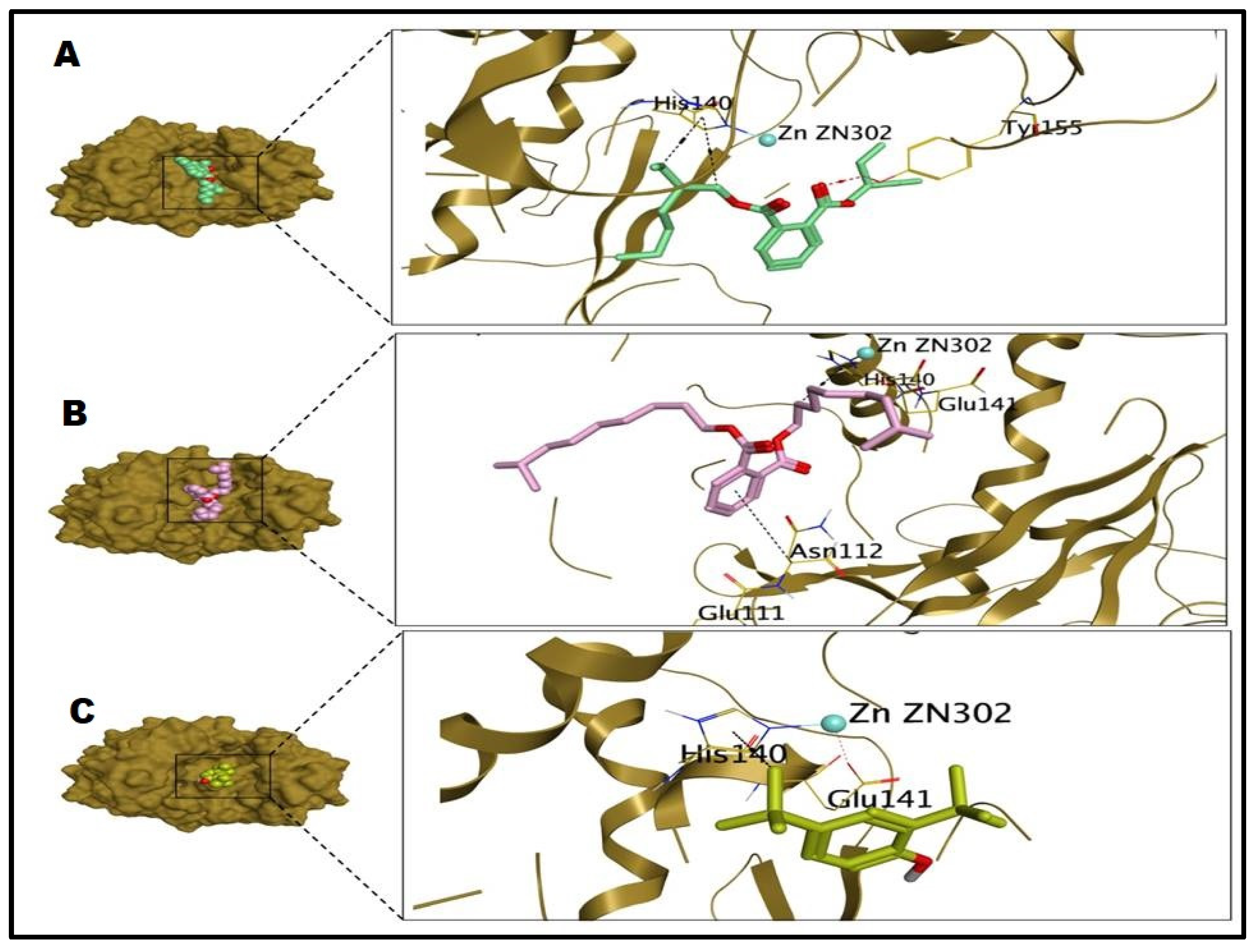
| Tested Microbes | Comp. No | S Score (Kcal/mol) | RMSD (Å) | Interactions | Distances (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | 1 | −6.52 | 1.74 | PRO153/pi-H | 3.83 |
| 2 | −4.46 | 1.52 | PRO153/pi-H | 3.89 | |
| 3 | −7.36 | 1.58 | PRO153/pi-H | 3.77 | |
| P. aeruginosa | 1 | −7.47 | 2.38 | TYR155/H-acceptor GLU141/Metal HIS140/H-pi HIS140/H-pi | 2.85 1.72 4.40 3.70 |
| 2 | −4.74 | 0.98 | GLU141/Metal HIS140/H-pi | 1.72 4.25 | |
| 3 | −7.45 | 1.90 | GLU141/Metal HIS140/H-pi ASN112/pi-H | 1.72 4.43 4.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghaly, M.F.; Albalawi, M.A.; Bendary, M.M.; Shahin, A.; Shaheen, M.A.; Abu Eleneen, A.F.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Elmaaty, A.A.; Elrefai, M.F.M.; Zaitone, S.A.; et al. Tamarindus indica Extract as a Promising Antimicrobial and Antivirulence Therapy. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030464
Ghaly MF, Albalawi MA, Bendary MM, Shahin A, Shaheen MA, Abu Eleneen AF, Ghoneim MM, Elmaaty AA, Elrefai MFM, Zaitone SA, et al. Tamarindus indica Extract as a Promising Antimicrobial and Antivirulence Therapy. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030464
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhaly, Mohamed F., Marzough Aziz Albalawi, Mahmoud M. Bendary, Ahmed Shahin, Mohamed A. Shaheen, Abeer F. Abu Eleneen, Mohammed M. Ghoneim, Ayman Abo Elmaaty, Mohamed F. M. Elrefai, Sawsan A. Zaitone, and et al. 2023. "Tamarindus indica Extract as a Promising Antimicrobial and Antivirulence Therapy" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030464
APA StyleGhaly, M. F., Albalawi, M. A., Bendary, M. M., Shahin, A., Shaheen, M. A., Abu Eleneen, A. F., Ghoneim, M. M., Elmaaty, A. A., Elrefai, M. F. M., Zaitone, S. A., & Abousaty, A. I. (2023). Tamarindus indica Extract as a Promising Antimicrobial and Antivirulence Therapy. Antibiotics, 12(3), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030464






