Putative Role of an ABC Efflux System in Aliarcobacter butzleri Resistance and Virulence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis of the YbhFSR Efflux System
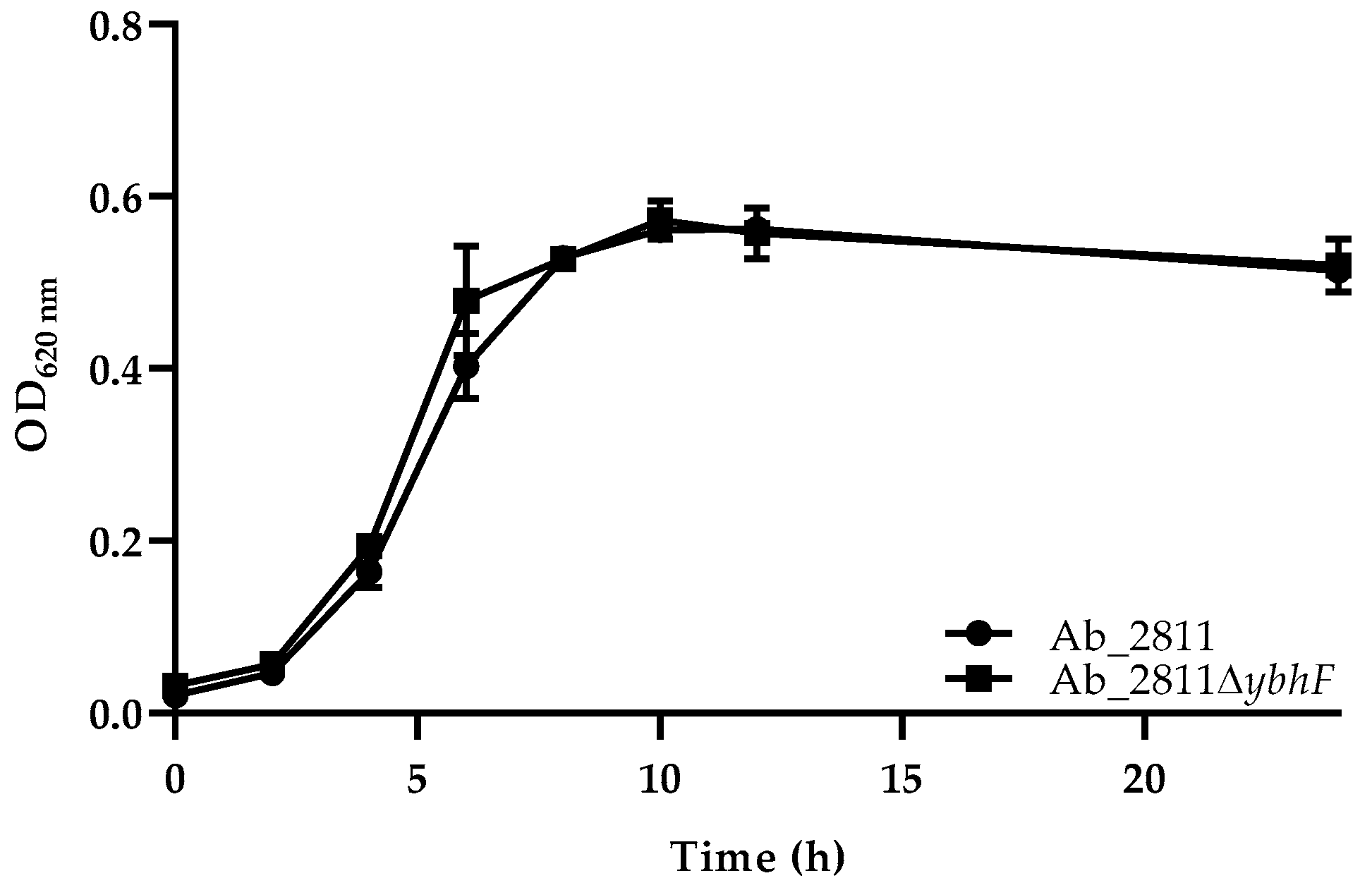
2.2. Influence of Efflux System Disruption in Bacterial Growth
2.3. Impact of the Inactivation of YbhFSR Efflux Pump on Aliarcobacter butzleri Antimicrobial Resistance
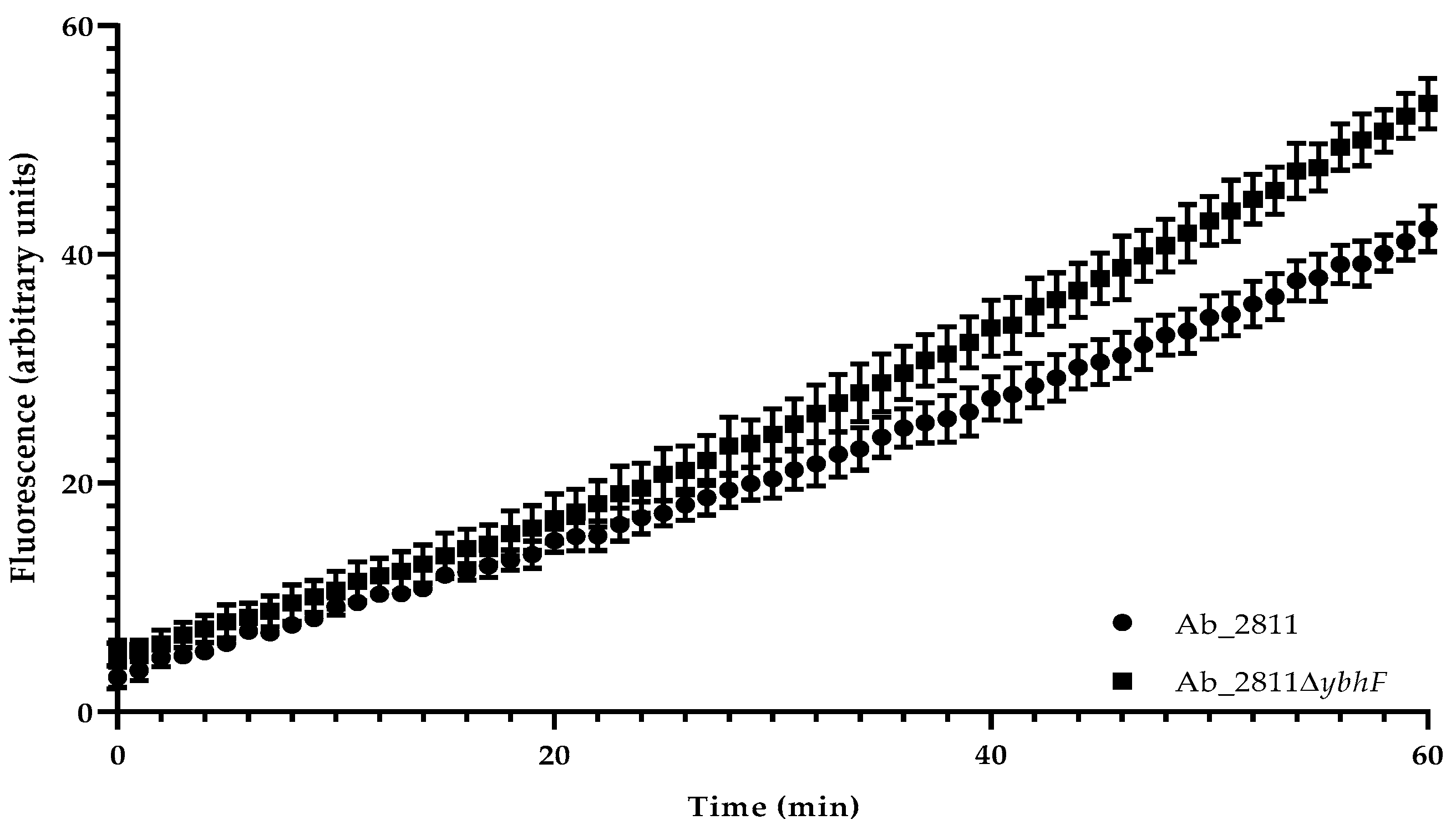
2.4. Effect of the Inactivation of YbhFSR Efflux Pump on Aliarcobacter butzleri Resistance to Oxidative Stress and Virulence
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Bioinformatic Analysis of YbhFSR Efflux Pump
4.3. Construction of Aliarcobacter butzleri Ab_2811ΔybhF Mutant Strain
4.4. Determination of Growth Curves of Parental and Mutant Strains
4.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
4.6. Growth Tests for Compounds Tolerance of Aliarcobacter butzleri
4.7. Ethidium Bromide Accumulation Assay
4.8. Stress Susceptibility Assay
4.9. Motility Assay
4.10. Biofilm Formation Ability
4.11. Serum Susceptibility Assay
4.12. Adhesion and Invasion Assay in a Caco-2 Cell Line
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, S.; Queiroz, J.A.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C. Insights in the Pathogenesis and Resistance of Arcobacter: A Review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 42, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, D.W.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Rinke, C.; Parks, D.H.; Zhang, Y.; Takai, K.; Sievert, S.M.; Simon, J.; Campbell, B.J.; Hanson, T.E.; et al. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Class Epsilonproteobacteria and Proposed Reclassification to Epsilonbacteraeota (phyl. nov.). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, L.; Figueras, M.J. Taxonomy, Epidemiology, and Clinical Relevance of the Genus Arcobacter. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramees, T.P.; Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Rathore, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Saminathan, M.; Tiwari, R.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, R.K. Arcobacter: An Emerging Food-Borne Zoonotic Pathogen, Its Public Health Concerns and Advances in Diagnosis and Control—A Comprehensive Review. Vet. Q. 2017, 37, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieffi, D.; Fanelli, F.; Fusco, V. Arcobacter butzleri: Up-to-Date Taxonomy, Ecology, and Pathogenicity of an Emerging Pathogen. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2071–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, D.; Eibach, D.; Boahen, K.G.; Akenten, C.W.; Pfeifer, Y.; Zautner, A.E.; Mertens, E.; Krumkamp, R.; Jaeger, A.; Flieger, A.; et al. Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella Enterica, Campylobacter Spp., and Arcobacter butzleri from Local and Imported Poultry Meat in Kumasi, Ghana. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidro, J.; Ferreira, S.; Pinto, M.; Domingues, F.; Oleastro, M.; Gomes, J.P.; Borges, V. Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Plasticity of Arcobacter butzleri: Insights on the Genomic Diversity of an Emerging Human Pathogen. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 80, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabeya, H.; Maruyama, S.; Morita, Y.; Ohsuga, T.; Ozawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Abe, M.; Katsube, Y.; Mikami, T. Prevalence of Arcobacter Species in Retail Meats and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of the Isolates in Japan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 90, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathlavath, S.; Kohli, V.; Singh, A.S.; Lekshmi, M.; Tripathi, G.; Kumar, S.; Nayak, B.B. Virulence Genotypes and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Arcobacter butzleri Isolated from Seafood and Its Environment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 263, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Saleha, A.A.; Zunita, Z.; Murugaiyah, M.; Aliyu, A.B.; Jafri, N. Prevalence, Distribution and Antibiotic Resistance of Emergent Arcobacter Spp. from Clinically Healthy Cattle and Goats. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šilha, D.; Pejchalová, M.; Šilhová, L. Susceptibility to 18 Drugs and Multidrug Resistance of Arcobacter Isolates from Different Sources within the Czech Republic. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 9, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Martins, S.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C.; Ferreira, S. Arcobacter Spp. at Retail Food from Portugal: Prevalence, Genotyping and Antibiotics Resistance. Food Control 2018, 85, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Correia, D.R.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C. Arcobacter butzleri Ciprofloxacin Resistance: Point Mutations in DNA Gyrase A and Role on Fitness Cost. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Silva, A.L.; Tomás, J.; Mateus, C.; Domingues, F.; Oleastro, M. Characterization of AreABC, an RND-Type Efflux System Involved in Antimicrobial Resistance of Aliarcobacter butzleri. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e00729-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, C.; Nunes, A.R.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.; Ferreira, S. RND Efflux Systems Contribute to Resistance and Virulence of Aliarcobacter butzleri. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcalde-Rico, M.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Blanco, P.; Martínez, J.L. Multidrug Efflux Pumps at the Crossroad between Antibiotic Resistance and Bacterial Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, V.; Kumar, A. Update on Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pumps in Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e00514-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.F. ABC Transporters: From Microorganisms to Man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1992, 8, 67–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussatova, A.; Kandt, C.; O’Mara, M.L.; Tieleman, D.P. ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orelle, C.; Mathieu, K.; Jault, J.M. Multidrug ABC Transporters in Bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenstein, K.; Dawson, R.J.; Locher, K.P. Structure and Mechanism of ABC Transporter Proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.M.; O’Mara, M.L.; George, A.M. ABC Transporters: A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery inside an Enigma. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, K.J.; Higgins, C.F. Structure and Function of ABC Transporters: The ATP Switch Provides Flexible Control. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2007, 453, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubelski, J.; Konings, W.N.; Driessen, A.J.M. Distribution and Physiology of ABC-Type Transporters Contributing to Multidrug Resistance in Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, H.W.; Venema, K.; Bolhuis, H.; Oussenko, I.; Kok, J.; Poolman, B.; Driessen, A.J.M.; Konings, W.N. Multidrug Resistance Mediated by a Bacterial Homolog of the Human Multidrug Transporter MDR1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10668–10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilfoile, P.G.; Hutchinson, C.R. A Bacterial Analog of the Mdr Gene of Mammalian Tumor Cells Is Present in Streptomyces peucetius, the Producer of Daunorubicin and Doxorubicin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8553–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhuri, B.S.; Bhakta, S.; Barik, R.; Basu, J.; Kundu, M.; Chakrabarti, P. Overexpression and Functional Characterization of an ABC (ATP-Binding Cassette) Transporter Encoded by the Genes drrA and drrB of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem. J. 2002, 367, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocchini, A.E.; Roset, M.S.; Iñó De Iannino, N.; Ugalde, R.A. Membrane Topology Analysis of Cyclic Glucan Synthase, a Virulence Determinant of Brucella Abortus. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7205–7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.T.; Doyle, T.B.; Lynch, A.S. Use of an Efflux-Deficient Streptococcus Pneumoniae Strain Panel to Identify ABC-Class Multidrug Transporters Involved in Intrinsic Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4781–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, Y.; Shimada, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishihama, A. Transcription Factor CecR (YbiH) Regulates a Set of Genes Affecting the Sensitivity of Escherichia coli against Cefoperazone and Chloramphenicol. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Song, B.; Gu, L.; Fan, Z.; Yang, S.; et al. A Putative Efflux Transporter of the ABC Family, YbhFSR, in Escherichia coli Functions in Tetracycline Efflux and Na+(Li+)/H+ Transport. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Holland, I.B. ABC Transporters: Bacterial Exporters-Revisited Five Years On. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1461, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifácio, M.; Mateus, C.; Alves, A.R.; Maldonado, E.; Duarte, A.P.; Domingues, F.; Oleastro, M.; Ferreira, S. Natural Transformation as a Mechanism of Horizontal Gene Transfer in Aliarcobacter butzleri. Pathogens 2021, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Fraqueza, M.J.; Queiroz, J.A.; Domingues, F.C.; Oleastro, M. Genetic Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance and Biofilm-Forming Ability of Arcobacter butzleri Isolated from Poultry and Environment from a Portuguese Slaughterhouse. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 162, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Okamoto-Shibayama, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ishihara, K. Characterization of a Novel Potential Peptide Import System in Treponema denticola. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulyayangkul, P.; Heesom, K.J.; Avison, M.B. Novel Mechanisms of Efflux-Mediated Levofloxacin Resistance and Reduced Amikacin Susceptibility in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01284-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M.I.; Piddock, L.J.V. The Efflux Pump Inhibitor Reserpine Selects Multidrug-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Strains That Overexpress the ABC Transporters PatA and PatB. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Liou, R.S.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, T.C. MacABCsm, an ABC-Type Tripartite Efflux Pump of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Involved in Drug Resistance, Oxidative and Envelope Stress Tolerances and Biofilm Formation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 3221–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, R.; Liu, G.; Yao, H.; Pan, Z. Bacitracin Resistance and Enhanced Virulence of Streptococcus suis via a Novel Efflux Pump. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirshikova, T.V.; Sierra-Bakhshi, C.G.; Kamaletdinova, L.K.; Matrosova, L.E.; Khabipova, N.N.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Khilyas, I.V.; Danilova, I.V.; Mardanova, A.M.; Sharipova, M.R.; et al. The ABC-Type Efflux Pump MacAB Is Involved in Protection of Serratia marcescens against Aminoglycoside Antibiotics, Polymyxins, and Oxidative Stress. mSphere 2021, 6, e00033-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Siena, B.; Campolattano, N.; D’Abrosca, G.; Russo, L.; Cantillon, D.; Marasco, R.; Muscariello, L.; Waddell, S.J.; Sacco, M. Characterization of the Mycobacterial MSMEG-3762/63 Efflux Pump in Mycobacterium smegmatis Drug Efflux. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bie, P.; Cheng, J.; Lu, L.; Cui, B.; Wu, Q. The ABC Transporter YejABEF Is Required for Resistance to Antimicrobial Peptides and the Virulence of Brucella melitensis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nies, D.H. Efflux-Mediated Heavy Metal Resistance in Prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrangsu, P.; Rensing, C.; Helmann, J.D. Metal Homeostasis and Resistance in Bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, F.; Di Pinto, A.; Mottola, A.; Mule, G.; Chieffi, D.; Baruzzi, F.; Tantillo, G.; Fusco, V. Genomic Characterization of Arcobacter butzleri isolated from Shellfish: Novel Insight into Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Determinants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, E.; Abdel-Glil, M.Y.; Hotzel, H.; Hänel, I.; Tomaso, H. Aliarcobacter Butzleri from Water Poultry: Insights into Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence and Heavy Metal Resistance. Genes 2020, 11, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diggle, S.P.; Song, Z.; Høiby, N.; Cornelis, P.; Williams, P.; Ca, M. The MexGHI-OpmD Multidrug Efflux Pump Controls Growth, Antibiotic Susceptibility and Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa via 4-Quinolone-Dependent Cell-to-Cell Communication. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, P.; Mihasan, M.; Igloi, G.L.; Brandsch, R. A Two-Component Small Multidrug Resistance Pump Functions as a Metabolic Valve during Nicotine Catabolism by Arthrobacter nicotinovorans. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, K.; Latifi, T.; Groisman, E.A. Virulence and Drug Resistance Roles of Multidrug Efflux Systems of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Levy, S.B. Regulation of AcrAB Expression by Cellular Metabolites in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Varela, M.; Corral, J.; Aranda, J.; Barbé, J. Roles of Efflux Pumps from Different Superfamilies in the Surface-Associated Motility and Virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e02190-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, S.; Ekanayaka, A.S.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Webber, M.A. Loss of or Inhibition of All Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pumps of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Results in Impaired Ability to Form a Biofilm. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogomolnaya, L.M.; Andrews, K.D.; Talamantes, M.; Maple, A.; Ragoza, Y.; Vazquez-Torres, A.; Andrews-Polymenis, H. The ABC-Type Efflux Pump MacAB Protects Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium from Oxidative Stress. MBio 2013, 4, e00630-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqumaizi, K.I.; Kumar, S.; Anwer, R.; Mustafa, S. Differential Gene Expression of Efflux Pumps and Porins in Clinical Isolates of MDR Acinetobacter baumannii. Life 2022, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, D.E.; Pico, R.C.; Girardello, R.; Fehlberg, L.C.C.; Gales, A.C. Efflux Pumps Expression and Its Association with Porin Down-Regulation and β-Lactamase Production among Pseudomonas aeruginosa Causing Bloodstream Infections in Brazil. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiku, V. Acinetobacter baumannii: Virulence Strategies and Host Defense Mechanisms. DNA Cell Biol. 2022, 41, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Choi, C.H.; Moon, D.C.; Jin, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, Y.C.; Seol, S.Y.; Cho, D.T.; et al. Serum Resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii through the Binding of Factor H to Outer Membrane Proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 301, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, P.; Ram, S.; Macleod, H.; Wetzler, L.M. The Role of Porins in Neisserial Pathogenesis and Immunity. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, U.; Frosch, M. Mechanisms of Neisserial Serum Resistance. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 32, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 7th ed.; Approved Standard; Document M7-A7; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006; ISBN 1-56238-587-9. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shaughnessy, C.M.; Cunningham, A.F.; MacLennan, C.A. The Stability of Complement-Mediated Bactericidal Activity in Human Serum against Salmonella. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Queiroz, J.A.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C. Genotypic and Phenotypic Features of Arcobacter butzleri Pathogenicity. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 76, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| MIC (µg/mL) (Fold Increase/Decrease) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ab_2811 | Ab_2811∆ybhF | |
| Ampicillin | 64 | 32 (2) |
| Cefotaxime | 32 | 32 (ND) |
| Kanamycin | 2 | 64 (32) |
| Gentamycin | 0.5 | 0.5 (ND) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 16 | 16 (ND) |
| Erythromycin | 32 | 16 (2) |
| Chloramphenicol | 128 | 64 (2) |
| Benzalkonium chloride | 64 | 16 (4) |
| Chlorhexidine | 1 | 1 (ND) |
| Acriflavine | 32 | 16 (2) |
| Ethidium bromide | 64 | 16 (4) |
| MIC (mM) (Fold Decrease) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ab_2811 | Ab_2811∆ybhF | |
| Cadmium | 0.25 | 0.03 (8) |
| Lead | 8 | 8 (ND) |
| Cobalt | 1 | 1 (ND) |
| Copper | 0.5 | 0.25 (2) |
| Chrome | 0.01 | 0.01 (ND) |
| Manganese | 4 | 2 (2) |
| Mercury | 0.003 | 0.003 (ND) |
| Molybdenum | 64 | 64 (ND) |
| Nickel | 1 | 1 (ND) |
| Silver | 0.01 | 0.01 (ND) |
| Zinc | 1 | 0.5 (2) |
| Lithium | 32 | 32 (ND) |
| Sodium | 256 | 128 (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, I.; Mateus, C.; Domingues, F.; Oleastro, M.; Ferreira, S. Putative Role of an ABC Efflux System in Aliarcobacter butzleri Resistance and Virulence. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020339
Martins I, Mateus C, Domingues F, Oleastro M, Ferreira S. Putative Role of an ABC Efflux System in Aliarcobacter butzleri Resistance and Virulence. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020339
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Inês, Cristiana Mateus, Fernanda Domingues, Mónica Oleastro, and Susana Ferreira. 2023. "Putative Role of an ABC Efflux System in Aliarcobacter butzleri Resistance and Virulence" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020339
APA StyleMartins, I., Mateus, C., Domingues, F., Oleastro, M., & Ferreira, S. (2023). Putative Role of an ABC Efflux System in Aliarcobacter butzleri Resistance and Virulence. Antibiotics, 12(2), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020339









