Raspberry Ketone-Mediated Inhibition of Biofilm Formation in Salmonella enterica Typhimurium—An Assessment of the Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
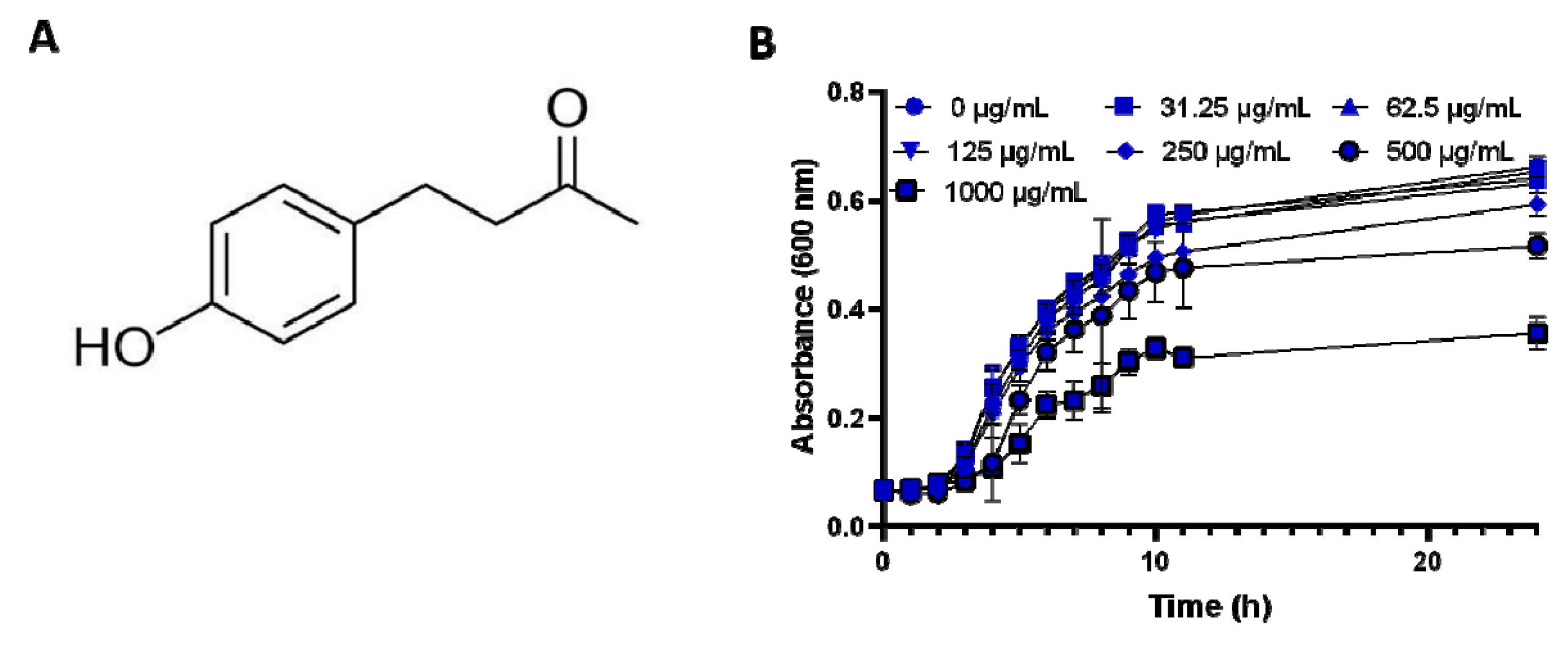
2.1. Anti-Bacterial Effect of RK
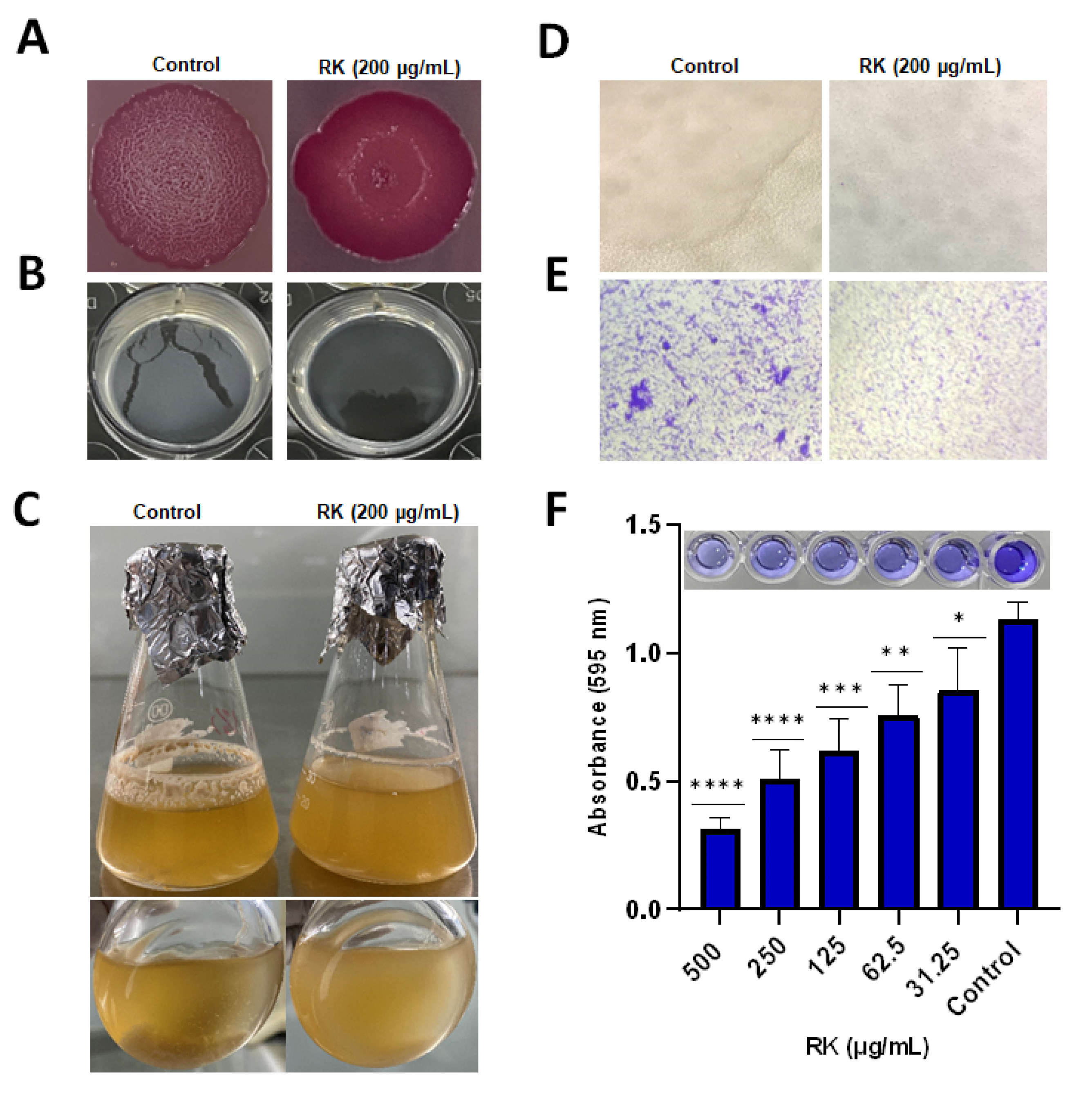
2.2. RK Inhibits Biofilm Formation of S. Typhimurium
2.3. RK Reduces Cellulose Deposition in S. Typhimurium Biofilm
2.4. RK Affects Motility of S. Typhimurium
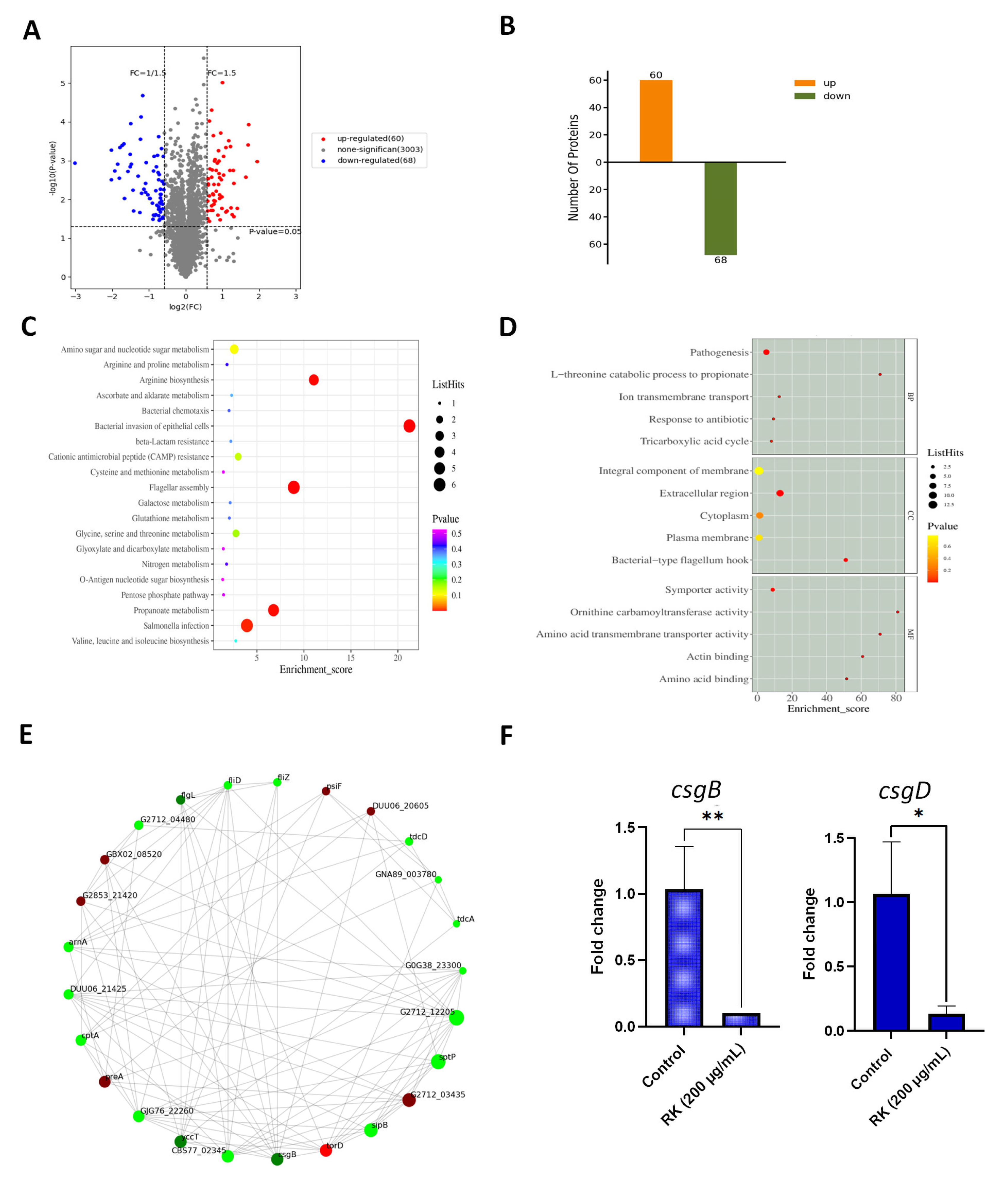
2.5. RK Treatment Inhibits the Expression of Proteins Essential for S. Typhimurium Biofilm Development
2.6. RK Inhibits the Expression of Biofilm-Related Genes in S. Typhimurium
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Determination of MIC
4.3. Growth Curves for Salmonella
4.4. Congo Red Agar Plate Assay
4.5. Calcofluor Staining Assay
4.6. Pellicle Formation Assay
4.7. In Vitro Flask Model Biofilm Development
4.8. Crystal Violet (CV) Staining Assay
4.9. Light Microscopy
4.10. Motility Assay
4.11. TMT-Labeled Quantitative Proteomic Analysis
4.11.1. Protein Extraction and Trypsin Digestion
4.11.2. TMT Labelling and Reversed-Phase Chromatographic Separation
4.11.3. LC-MS Analysis
4.11.4. Data Acquisition and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.12. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription–Quantitative PCR (RT–qPCR)
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eng, S.K.; Pusparajah, P.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Ser, H.L.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Salmonella: A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, J.E.; Hahn, M.M.; D’ Souza, S.J.; Vasicek, E.M.; Sandala, J.L.; Gunn, J.S.; McLachlan, J.B. Salmonella biofilm formation, chronic infection, and immunity within the intestine and hepatobiliary tract. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 624622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trampari, E.; Holden, E.R.; Wickham, G.J.; Ravi, A.; Martins, L.O.; Savva, G.M.; Webber, M.A. Exposure of Salmonella biofilms to antibiotic concentrations rapidly selects resistance with collateral tradeoffs. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotian, A.; Aditya, V.; Jazeela, K.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I.; Deekshit, V.K. Effect of bile on growth and biofilm formation of non-typhoidal Salmonella serovars isolated from seafood and poultry. Res. Microbiol. 2020, 171, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, J.; Kaur, D.; Hambira, C.M.; Sandala, J.L.; Koopman, J.A.; Fuchs, J.R.; Gunn, J.S. Identification of a small molecule anti-biofilm agent against Salmonella enterica. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruteanu, M.; Hernández Lobato, J.I.; Stach, T.; Hengge, R. Common plant flavonoids prevent the assembly of amyloid curli fibres and can interfere with bacterial biofilm formation. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 5280–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, M.M.; Chapman, M.R. Curli biogenesis and function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, S.A.; Puligedda, R.D.; Szabo, P.; Nicastro, L.K.; Miller, A.L.; Qiu, C.; Gallucci, S.; Relkin, N.R.; Buttaro, B.A.; Dessain, S.K.; et al. Salmonella Typhimurium biofilm disruption by a human antibody that binds a pan-amyloid epitope on curli. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, D.O.; Mika, F.; Richter, A.M.; Hengge, R. The green tea polyphenol EGCG inhibits E. coli biofilm formation by impairing amyloid curli fibre assembly and downregulating the biofilm regulator CsgD via the σ(E) -dependent sRNA RybB. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Dos Santos, A.R.; Coelho Trevisan, D.A.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Zanetti Campanerut-Sá, P.A.; Kukolj, C.; de Souza, E.M.; Cardoso, R.F.; Estivalet Svidzinski, T.I.; de Abreu Filho, B.A.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde induces changes in the protein profile of Salmonella Typhimurium biofilm. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girennavar, B.; Cepeda, M.L.; Soni, K.A.; Vikram, A.; Jesudhasan, P.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Grapefruit juice and its furocoumarins inhibits autoinducer signaling and biofilm formation in bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho Trevisan, D.A.; Zanetti Campanerut-Sa, P.A.; da Silva, A.F.; Farias Pereira Batista, A.; Seixas, F.A.V.; Peralta, R.M.; de Sa-Nakanishi, A.B.; de Abreu Filho, B.A.; Junior, M.M.; Graton Mikcha, J.M. Action of carvacrol in Salmonella Typhimurium biofilm: A proteomic study. J. Appl. Biomed. 2020, 18, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabarkapa, I.; Čolović, R.; Đuragić, O.; Popović, S.; Kokić, B.; Milanov, D.; Pezo, L. Anti-biofilm activities of essential oils rich in carvacrol and thymol against Salmonella Enteritidis. Biofouling 2019, 35, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Roy, P.K.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Nahar, S.; Toushik, S.H.; Hossain, M.I.; Rahaman Mizan, M.F.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.D. Antibiofilm effects of quercetin against Salmonella enterica biofilm formation and virulence, stress response, and quorum-sensing gene expression. Food Control 2022, 137, 108964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgueta, E.; Mena, J.; Orihuela, P.A. Hydroethanolic extracts of Haplopappus baylahuen Remy and Aloysia citriodora Palau have bactericide activity and inhibit the ability of Salmonella Enteritidis to form biofilm and adhere to human intestinal cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 3491831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, C.; Satoh, Y.; Hara, M.; Inoue, S.; Tsujita, T.; Okuda, H. Anti-obese action of raspberry ketone. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Ding, H.Y.; Kuo, S.Y.; Chin, L.W.; Wu, J.Y.; Chang, T.S. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo depigmenting activity of raspberry ketone from Rheum officinale. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4819–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.E.; Abo-Elmatty, D.M.; Mesbah, N.M.; Saleh, S.M.; Ali, A.A.; Sakr, A.T. Raspberry ketone preserved cholinergic activity and antioxidant defense in obesity induced Alzheimer disease in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, K.D.; Palmer, M.B.; Köster, W.L.; White, A.P. Examining the link between biofilm formation and the ability of pathogenic Salmonella strains to colonize multiple host species. Front. Vet Sci. 2017, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano-Félix, J.A.; Chaidez, C.; Mena, K.D.; Soto-Galindo, M.D.S.; Castro-Del Campo, N. Characterization of biofilm formation by Salmonella enterica at the air-liquid interface in aquatic environments. Environ. Monit. Assess 2018, 190, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Kurakula, M.; Mamidipalli, N.; Tiyyagura, P.; Patel, B.; Manne, R. Pharmacological exploration of phenolic compound: Raspberry ketone-update 2020. Plants 2021, 10, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.; Jahan, H.; Shafeeq, S.; Nimtz, M.; Jänsch, L.; Römling, U.; Choudhary, M.I. Clarithromycin exerts an antibiofilm effect against Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium rdar biofilm formation and transforms the physiology towards an apparent oxygen-depleted energy and carbon metabolism. Infect Immun. 2020, 88, e00510–e00520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Rouf, S.F.; Sun, L.; Cimdins, A.; Shafeeq, S.; Le Guyon, S.; Schottkowski, M.; Rhen, M.; Römling, U. BcsZ inhibits biofilm phenotypes and promotes virulence by blocking cellulose production in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb. Cell Fact 2016, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberg, J.A.; Le Breton, Y.; Harro, J.M.; Allison, D.L.; McIver, K.S.; Shirtliff, M.E. The arginine deiminase pathway impacts antibiotic tolerance during biofilm-mediated Streptococcus pyogenes infections. mBio 2020, 11, e00919–e00920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, J.; Groisman, E.A.; Kang, D.H.; Shin, D.; Ryu, S. Expression of STM4467-encoded arginine deiminase controlled by the STM4463 regulator contributes to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium virulence. Infect Immun. 2012, 80, 4291–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Liao, S.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wu, G.; Dai, G.; Chen, L. Quantitative proteomics reveals the mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J. Proteome. Res. 2020, 19, 3109–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, N.; Rouf, S.F.; Römling, U.; Rhen, M. Modulation of biofilm-formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by the periplasmic DsbA/DsbB oxidoreductase system requires the GGDEF-EAL domain protein STM3615. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Deng, L.; Huang, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Xu, C. Flagellar motility is critical for Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium biofilm development. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenackers, H.; Hermans, K.; Vanderleyden, J.; De Keersmaecke, S.C.J. Salmonella biofilms: An overview on occurrence, structure, regulation and eradication. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 502–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attmannspacher, U.; Scharf, B.E.; Harshey, R.M. FliL is essential for swarming: Motor rotation in absence of FliL fractures the flagellar rod in swarmer cells of Salmonella enterica. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.C.; Brown, N.F.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium effectors SopB, SopE, SopE2 and SipA disrupt tight junction structure and function. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourlin, C.; Simon, G.; Pommier, J.; Chippaux, M.; Méjean, V. The periplasmic TorT protein is required for trimethylamine N-oxide reductase gene induction in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Wang, G.; Liang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Xu, X. Preliminary transcriptome analysis of mature biofilm and planktonic cells of Salmonella Enteritidis exposure to acid stress. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Insights into the transcriptome profile of mature biofilm of Salmonella Typhimurium on stainless steels surface. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grows Aerobically: Approved Standard, 9th ed.; CLSI Document MO7- A9; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 32, pp. 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Ahmad, I.; Blanka, A.; Schottkowski, M.; Cimdins, A.; Galperin, M.Y.; Römling, U.; Gomelsky, M. GIL, a new c-di-GMP-binding protein domain involved in regulation of cellulose synthesis in Enterobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.; Papenfort, K.; Hentrich, K.; Ahmad, I.; Le Guyon, S.; Reimann, R.; Grantcharova, N.; Römling, U. Hfq and Hfq-dependent small RNAs are major contributors to multicellular development in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, Y.; Guo, D.; Jin, T.; Guan, N.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liang, S.; Xia, X.; et al. Antibiofilm activity of coenzyme Q0 against Salmonella Typhimurium and its effect on adhesion-invasion and survival-replication. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8545–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farha, A.K.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Raspberry Ketone-Mediated Inhibition of Biofilm Formation in Salmonella enterica Typhimurium—An Assessment of the Mechanisms of Action. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020239
Farha AK, Sui Z, Corke H. Raspberry Ketone-Mediated Inhibition of Biofilm Formation in Salmonella enterica Typhimurium—An Assessment of the Mechanisms of Action. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020239
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarha, Arakkaveettil Kabeer, Zhongquan Sui, and Harold Corke. 2023. "Raspberry Ketone-Mediated Inhibition of Biofilm Formation in Salmonella enterica Typhimurium—An Assessment of the Mechanisms of Action" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020239
APA StyleFarha, A. K., Sui, Z., & Corke, H. (2023). Raspberry Ketone-Mediated Inhibition of Biofilm Formation in Salmonella enterica Typhimurium—An Assessment of the Mechanisms of Action. Antibiotics, 12(2), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020239






