The Burden of Surgical Site Infection at Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia and Related Postoperative Outcomes: A Prospective Surveillance Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
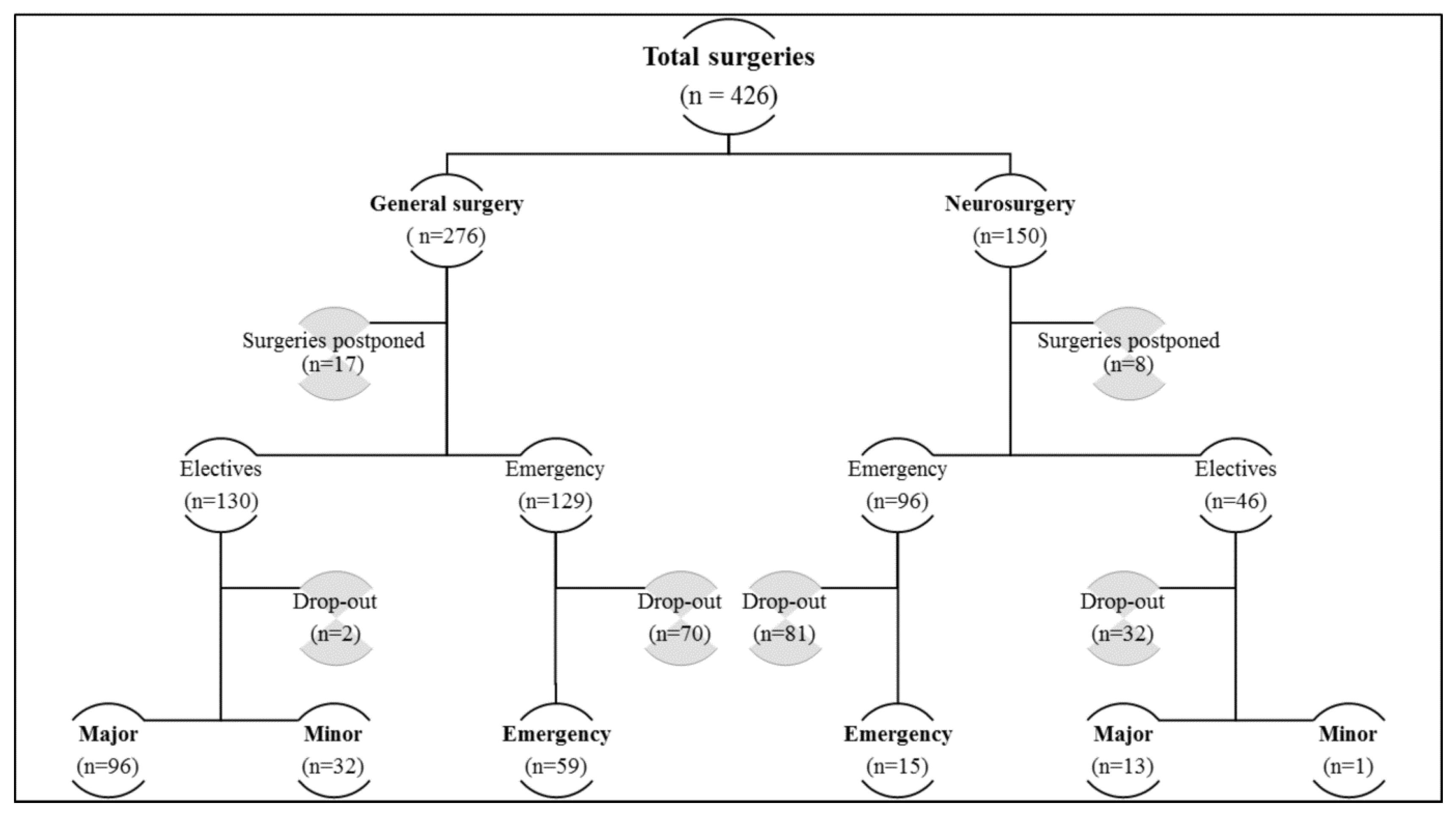
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Predictors of SSI and the Independent Risk Factors of SSI
3.2. Antibiotic Utilization Data
3.3. SSI-Related Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, A.J.; Ariffin, N.; Huat, T.L.; Molok, H.A.; Hashim, S.; Sarijo, J.; Latif, N.H.A.; Hanifah, Y.A.; Kamarulzaman, A. Prevalence of Nosocomial Infection and Antibiotic Use at a University Medical Center in Malaysia. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Healthcare-Associated Infections: Surgical Site Infections—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2017. 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/healthcare-associated-infections-surgical-site-infections-annual-1 (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Herman, T.F.; Bordoni, B. Wound Classification. 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554456 (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Geubbels, E.L.; Mintjes-de Groot, A.J.; van den Berg, J.M.J.; de Boer, A.S. An operating surveillance system of surgical-site infections in The Netherlands: Results of the PREZIES national surveillance network. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2000, 21, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badia, J.M.; Casey, A.L.; Petrosillo, N.; Hudson, P.M.; Mitchell, S.A.; Crosby, C. Impact of surgical site infection on healthcare costs and patient outcomes: A systematic review in six European countries. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Report on the burden of endemic health care-associated infection worldwide clean care is safer care. 2011. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/80135/9789241501507_eng.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Chu, K.; Weiser, T.G. Surgical site infection—The next frontier in global surgery. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.A.; Holloway, S. An observational study of the surgical site infection rate in a General Surgery Department at a General Hospital in Malaysia. Wounds Asia 2019, 2, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fadzwani, B.; Raha, A.R.; Nadia, M.N.; Wan Rahiza, W.M.; Razman, J.; Nordiah, A.J. Surgical antibiotic prophylaxis: Incidence and risk of surgical site infection. IMJM 2020, 19, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques, 3rd ed.; Wiley India Pvt. Limited: New Delhi, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Culver, D.H.; Horan, T.C.; Gaynes, R.P.; Martone, W.J.; Jarvis, W.R.; Emori, T.G.; Banerjee, S.N.; Edwards, J.R.; Tolson, J.S.; Henderson, T.S. Surgical wound infection rates by wound class, operative procedure, and patient risk index. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, 152S–157S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, R.W.; Culver, D.H.; Morgan, W.M.; White, J.W.; Emori, G.; Hooton, T.M. Identifying patients at high risk of surgical wound infection. A simple multivariate index of patient susceptibility and wound contamination. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1985, 121, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren, M.A.; Guaitoli, P.R.; Jansma, E.P.; de Vet, H.C. Nutrition screening tools: Does one size fit all? A systematic review of screening tools for the hospital setting. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrup, J.; Allison, S.P.; Elia, M.; Vellas, B.; Plauth, M. Educational and Clinical Practice Committee, European Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ESPEN). ESPEN guidelines for nutrition screening 2002. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangram, A.J.; Horan, T.C.; Pearson, M.L.; Silver, L.C.; Jarvis, W.R. Guideline for prevention of surgical site infection, 1999. Am. J. Infect. Control 1999, 27, 97–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesbrough, M. District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries Part 2, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mawalla, B.; Mshana, S.E.; Chalya, P.L.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Mahalu, W. Predictors of surgical site infections among patients undergoing major surgery at Bugando Medical Centre in Northwestern Tanzania. BMC Surg. 2011, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raka, L.; Krasniqi, A.; Hoxha, F.; Musa, R.; Mulliqi, G.; Krasniqi, S.; Kurti, A.; Dervishaj, A.; Nuhiu, B.; Kelmendi, B.; et al. Surgical site infections in an abdominal surgical ward at Kosovo Teaching Hospital. J. Infect. Dev. Countr. 2007, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, K.; Ramos, E.; Seas, C.; Henostroza, G.; Gotuzzo, E. Incidence of and risk factors for surgical-site infections in a Peruvian hospital. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliani, K.; L’Heriteau, F.; Astagneau, P.; INCISO Network Study Group. Non-compliance with recommendations for the practice of antibiotic prophylaxis and risk of surgical site infection: Results of a multilevel analysis from the INCISO Surveillance Network. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.Y.; Chen, L.F.; Miller, B.A.; Anderson, D.J. The impact of depth of infection and post discharge surveillance on rate of surgical-site infections in a network of community hospitals. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2012, 33, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, A.L.; Goh, L.M.; Nik Azim, N.A.; Tee, C.S.; Shehab Phung, C.W. Antibiotic usage in surgical prophylaxis: A prospective surveillance of surgical wards at a tertiary hospital in Malaysia. J. Infect. Dev. Countr. 2014, 8, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misha, G.; Chelkeba, L.; Melaku, T. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of surgical site infections among patients admitted to Jimma Medical Center, South West Ethiopia: Prospective cohort study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 65, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totty, J.P.; Moss, J.W.E.; Barker, E.; Mealing, S.J.; Posnett, J.W.; Chetter, I.C.; Smith, G.E. The impact of surgical site infection on hospitalisation, treatment costs, and health-related quality of life after vascular surgery. Int. Wound J. 2021, 18, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenny, A.P.; Asante, F.A.; Otieku, E.; Bediako-Bowan, A.; Enemark, U. Attributable cost and extra length of stay of surgical site infection at a Ghanaian teaching hospital. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2020, 2, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimlichman, E.; Henderson, D.; Tamir, O.; Franz, C.; Song, P.; Yamin, C.K.; Keohane, C.; Denham, C.R.; Bates, D.W.; Health Care-Associated Infections. A Meta-analysis of Costs and Financial Impact on the US Health Care System. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, K.A. American College of Surgeons and Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Site Infection Guidelines, 2016 Update. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 224, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkland, K.B.; Briggs, J.P.; Trivette, S.L.; Wilkinson, W.E.; Sexton, D.J. The impact of surgical-site infections in the 1990s: Attributable mortality, excess length of hospitalization, and extra costs. Hosp. Epidemiol. 1999, 20, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lissovoy, G.; Fraeman, K.; Hutchins, V.; Murphy, D.; Song, D.; Vaughn, B.B. Surgical site infection: Incidence and impact on hospital utilization and treatment costs. Am. J. Infect. Control 2009, 37, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehouse, J.D.; Friedman, N.D.; Kirkland, K.B.; Richardson, W.J.; Sexton, D.J. The Impact of Surgical-Site Infections Following Orthopedic Surgery at a Community Hospital and a University Hospital Adverse Quality of Life, Excess Length of Stay, and Extra Cost. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2002, 23, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buang, S.S.; Haspani, M.S. Risk factors for neurosurgical site infections after a neurosurgical procedure: A prospective observational study at Hospital Kuala Lumpur. Med. J. Malays. 2012, 67, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Haines, S.J.; Walters, B.C. Antibiotic prophylaxis for cerebrospinal fluid shunts: A metanalysis. Neurosurgery 1994, 34, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, L.A.; Gout, B.S.; Crowe, T.C. Hospital malnutrition: Prevalence, identification and impact on patients and the healthcare system. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, T.; Akin, M.; Topaloglu, S.; Berkem, H.; Yüksel, B.; Hengirmen, S.; Yildiz, Y.; Tez, M. External Validation of SENIC and NNIS Scores for Predicting Wound Infection in Colorectal Surgery. Surg. Sci. 2011, 2, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Gómez-Ortega, A.; Sillero-Arenas, M.; Llorca, J. Epidemiology of Surgical-Site Infections Diagnosed After Hospital Discharge A Prospective Cohort Study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2001, 22, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, C.H.; Escobar, R.M.; Villegas, M.I.; Castaño, A.; Trujillo, J. Surgical site infection in abdominal trauma patients: Risk prediction and performance of the NNIS and SENIC indexes. Can. J. Surg. 2011, 54, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruse, P.J.; Foord, R. A five-year prospective study of 23,649 surgical wounds. Arch. Surg. 1973, 107, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, R.W. Nosocomial infections in surgical patients: Developing valid measures of intrinsic patient risk. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, S145–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; MacLeod, W.B.; Phung, D.C.; Cong, Q.T.; Nguy, V.H.; Van Nguyen, H.; Hamer, H.D. Incidence and predictors of surgical-site infections in Vietnam. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2001, 22, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, J.; Ward, W.; Milstone, A.; Carlson, T.; Frederick, J.; Hadhazy, E.; Perl, T. Financial impact of surgical site infections on hospitals: The hospital management perspective. JAMA Surg. 2013, 148, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adisa, A.O.; Lawal, O.O.; Adejuyigbe, O. Evaluation of two methods of preoperative hair removal and their relationship to postoperative wound infection. J. Infect. Dev. Countr. 2011, 5, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthazar, E.R.; Colt, J.D.; Nichols, R. Preoperative hair removal: A random prospective study of shaving versus clipping. South Med. J. 1982, 75, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenberg, M.W.; De Wit, G.A.; Bonten, M.J. Cost-effectiveness of preoperative screening and eradication of Staphylococcus aureus carriage. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratzler, D.W.; Houck, P.M.; Richards, C.; Steele, L.; Dellinger, E.P.; Fry, D.E.; Wright, C.; Ma, A.; Carr, K.; Red, L. Use of antimicrobial prophylaxis for major surgery: Baseline results from the National Surgical Infection Prevention Project. Arch. Surg. 2005, 140, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourmousoglou, C.E.; Yiannakopoulou, E.C.; Kalapothaki, V.; Bramis, J.; Papadopoulos, J.S. Adherence to guidelines for antibiotic prophylaxis in general surgery: A critical appraisal. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabrah, A.; Bahwerth, F.; Alghamdi, S.; Alkhotani, A.; Alahmadi, A.; Alhuzali, M.; Aljerary, I.; Alsulami, A. Antibiotics Usage and Resistance among Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in the Intensive Care Unit in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhomoud, F.; Aljamea, Z.; Almahasnah, R.; Alkhalifah, K.; Basalelah, L.; Alhomoud, F.K. Self-medication and self-prescription with antibiotics in the Middle East—Do they really happen? A systematic review of the prevalence, possible reasons, and outcomes. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 57, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, R.R.; Rabie, A.S.I.; Bin Shaman, M.; Shaaban, A.H.; Fahmy, A.M.; Sofy, M.R.; Lattyak, E.A.; Abuelhana, A.; Naguib, I.A.; Ashour, A.M.; et al. Antibiotic consumption in hospitals during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparative study. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsugoor, M.H.; Alsuhaymi, N.; Alshahrani, Y.; Alsagoor, Y.H.; Alghamdi, A.M.; Alalawi, S.M.; Alalawi, S.B.; Alothayqi, F.A.; Alamri, M.M.; Ewis, A.A. Prevalence of self-medication among students of Umm Al-Qura and AlBaha Universities in Saudi Arabia. Med. Sci. 2022, 26, ms388e2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, M.H.; Siddiqui, M.I.; Jokhdar, H.A.; Hassan-Hussein, A.; Garout, M.A.; Hafiz, S.M.; Alshareef, M.M.; Falemban, A.M.; Neveen, A.A.; Nermeen, A.A. Prescribing patterns for acute respiratory infections in children in primary health care centers, Makkah Al Mukarramah, Saudi Arabia. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2018, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.S.; Chong, C.P. Surgeons’ adherence to guidelines for surgical antimicrobial prophylaxis—A review. Australas. Med. J. 2012, 5, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, Y.M.; Alharbi, R.H.; Aljabri, A.K.; Alofi, F.S.; Alshaalani, O.A.; Alssdi, B.H. Adherence to the guidelines for surgical antimicrobial prophylaxis in a Saudi tertiary care hospital. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2020, 15, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Balaha, M.; Haseeb, A.; Khan, A. Antibiotic Usage in Surgical Prophylaxis: A Retrospective Study in the Surgical Ward of a Governmental Hospital in Riyadh Region. Healthcare 2022, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, A.; El-Menyar, A.; Al-Thani, H.; Zarour, A.; Parchani, A.; Asim, M.; El-Enany, R.; Al-Tamimi, H.; Latifi, R. Adherence of surgeons to antimicrobial prophylaxis guidelines in a tertiary general hospital in a rapidly developing country. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 2013, 842593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvêa, M.; Novaes, C.D.O.; Pereira, D.M.T.; Iglesias, A.C. Adherence to guidelines for surgical antibiotic prophylaxis: A review. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 19, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.J.; Almalki, Z.S.; Alfaifi, A.A.; Alshehri, A.M.; Alahmari, A.K.; Elazab, E.; Almansour, A.; Haseeb, A.; Balaha, M.F.; Khan, A.H. Implementing an Antimicrobial Stewardship Programme to Improve Adherence to a Perioperative Prophylaxis Guideline. Healthcare 2022, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 48 (17–75) * |
| Gender | |
| Male | 113 (52.3) |
| Female | 103 (47.7) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |
| ≥30 (Obese) | 36 (16.7) |
| 25.0–29.9 | 51 (23.6) |
| 18.5–24.9 | 97 (44.9) |
| <18.5 | 32 (14.8) |
| Race | |
| Malay | 199 (92.1) |
| Chinese | 14 (6.5) |
| Others | 3 (1.4) |
| Smoker | |
| No | 150 (69.4) |
| Yes | 66 (30.6) |
| Drinks Alcohol | |
| No | 213 (98.6) |
| Yes | 3 (1.4) |
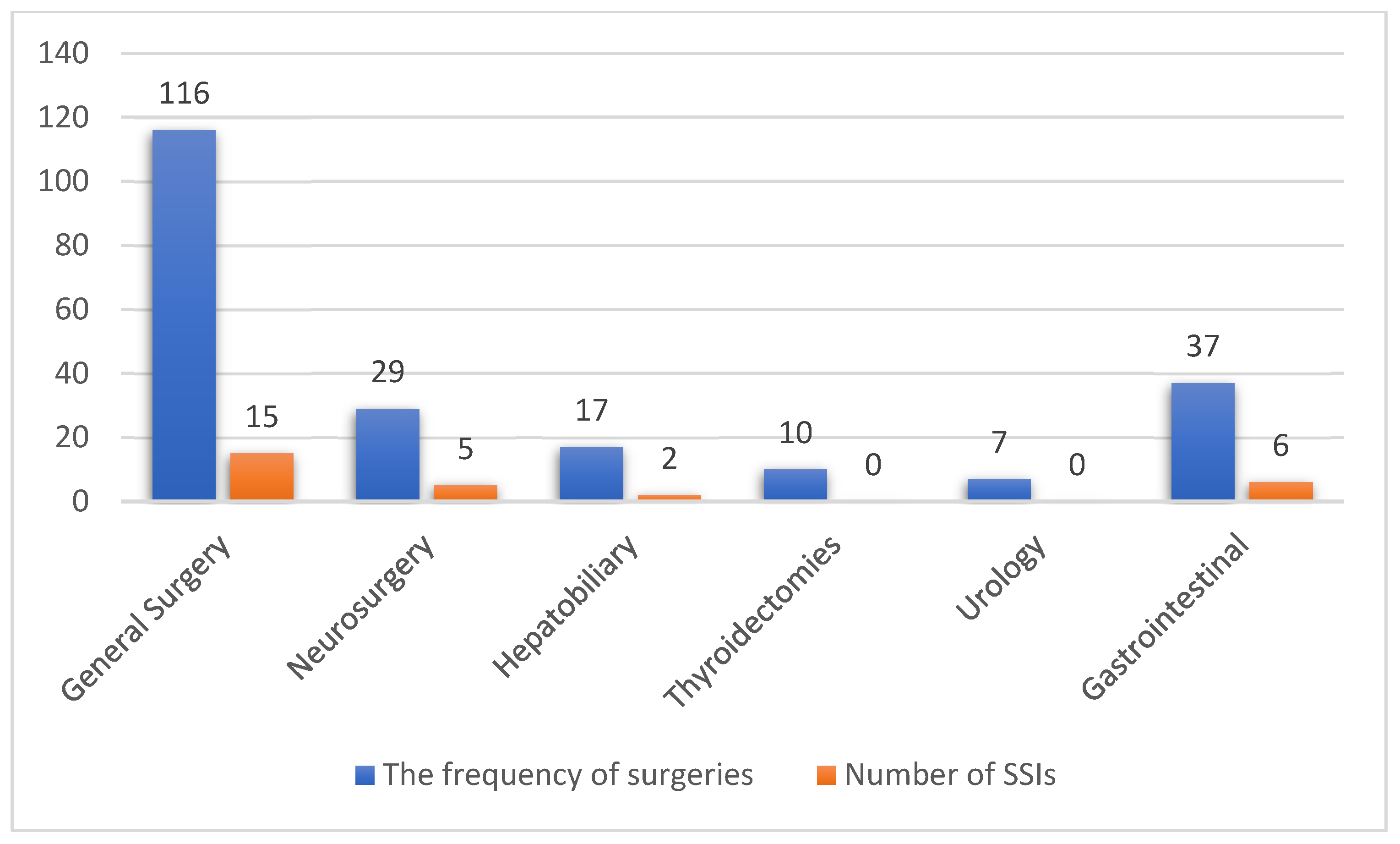
| Surgical Category | The Numbers and Percentages of Surgeries N (%) |
|---|---|
| General surgery | 116 (53.7) |
| Appendectomy | 37 (17.1) |
| Wound surgeries * | 36 (16.7) |
| Herniorrhaphy | 21 (9.7) |
| Exploratory laparotomy | 5 (2.3) |
| Splenectomy | 3 (1.4) |
| Mastectomy | 14 (6.5) |
| Neurosurgery † | 29 (13.4) |
| Hepatobiliary | 17 (7.8) |
| Cholecystectomy | 15 (6.9) |
| Biliary surgeries | 2 (0.9) |
| Thyroidectomies | 10 (4.6) |
| Urology ‡ | 7 (3.2) |
| Gastrointestinal | 37 (17.1) |
| Colectomies | 19 (8.8) |
| Gastrectomy | 6 (2.8) |
| Others § | 12 (5.6) |
| Total | N = 216 |
| Description | Distribution between Cohorts Median (Range) | p-Value † | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSI | Non-SSI | ||
| Pre-operative length of stay (days) | 1 (1–17) | 1 (1–16) | 0.107 |
| Post-operative length of stay (days) | 10 (1–79) | 2 (1–79) | <0.001 |
| Total length of stay (days) | 13 (2–80) | 4 (1–95) | <0.001 |
| Variables | N | Surgical Site Infections (%) | Univariate p-Value | Multivariate p-Value | Adjusted Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 28) | No (n = 188) | Upper | Lower | |||||
| Age | 216 | 49 ± 14.6 * | 44.7 ± 16.8 * | 0.201 | 0.886 | 0.997 | 0.961 | 1.035 |
| Gender (female) | 103 | 39.3 | 48.9 | 0.342 | 0.965 | 0.978 | 0.361 | 2.646 |
| Comorbidity | 104 | 71.4 | 44.7 | 0.011 | 0.121 | 2.571 | 0.780 | 8.480 |
| Co-existing infection | 111 | 71.4 | 48.4 | 0.027 | 0.036 | 3.127 | 1.080 | 9.050 |
| Emergency procedures | 74 | 53.6 | 31.4 | 0.024 | - | - | - | - |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 54 | 57.1 | 20.2 | 0.001 | - | - | - | - |
| Intraoperative serum glucose ≥ 10 mmol/L | 17 | 21.4 | 5.9 | 0.008 | - | - | - | - |
| Operations by junior surgeon | 96 | 42.9 | 44.7 | 0.856 | 0.059 | 3.228 | 0.955 | 10.912 |
| High risk of malnutrition (using MUST) | 46 | 50 | 17 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 3.764 | 1.339 | 10.582 |
| Patients at risk with NNIS | 99 | 85.7 | 39.3 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 5.975 | 1.813 | 19.698 |
| Pre-operative LOS (days) | 216 | 3.9 ± 5.0 * | 1.9 ± 2.0 * | 0.002 | - | - | - | - |
| Post-operative LOS (days) | 216 | 15.9 ± 18 * | 5.23 ± 8.44 * | 0.000 | 0.038 | 1.040 | 1.002 | 1.079 |
| Surgery duration > 120 min | 80 | 57.1 | 34 | 0.007 | 0.027 | 3.571 | 1.156 | 11.035 |
| Surgical Category | The Recommended Antibiotics |
|---|---|
| Obstetrics and gynecology surgeries Head and neck surgeries Plastic surgeries Vascular surgeries Gastrointestinal surgeries Orthopedic surgeries Urological surgeries Neurological surgeries Cardiac surgeries Hepatobiliary surgeries | Cephalosporin alone or with metronidazole Cephalosporin alone or with metronidazole Cephalosporin aloneAmpicillin/sulbactam or amoxi cillin/clavulanic acid Cephalosporin alone or with metronidazole Cephalosporin alone Cephalosporin alone or with metronidazole Ampicillin/sulbactam, or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid Cephalosporin alone or with metronidazole Cephalosporin alone Cephalosporin alone Cephalosporin and gentamicin |
| Item | Number of the Patients | SSIs Number | Rate of SSIs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients who received antibiotics at the appropriate time | 141 | 18 | 12.8% |
| Patients who received antibiotics at an inappropriate time | 19 | 4 | 21.1% |
| Total | 160 | 22 | 13.75% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, O.H.; Zakaria, A.D.; Hashim, M.N.; Khan, A.H.; AlQarni, A.; AlGethamy, M.; Mahboob, M.; Aljoaid, A.M.; Ahmed, N.J.; Haseeb, A. The Burden of Surgical Site Infection at Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia and Related Postoperative Outcomes: A Prospective Surveillance Study. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020208
Khan OH, Zakaria AD, Hashim MN, Khan AH, AlQarni A, AlGethamy M, Mahboob M, Aljoaid AM, Ahmed NJ, Haseeb A. The Burden of Surgical Site Infection at Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia and Related Postoperative Outcomes: A Prospective Surveillance Study. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020208
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Omaid Hayat, Andee Dzulkarnaen Zakaria, Mohd Nizam Hashim, Amer Hayat Khan, Abdullmoin AlQarni, Manal AlGethamy, Mohammed Mahboob, Anas Mohammed Aljoaid, Nehad Jaser Ahmed, and Abdul Haseeb. 2023. "The Burden of Surgical Site Infection at Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia and Related Postoperative Outcomes: A Prospective Surveillance Study" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020208
APA StyleKhan, O. H., Zakaria, A. D., Hashim, M. N., Khan, A. H., AlQarni, A., AlGethamy, M., Mahboob, M., Aljoaid, A. M., Ahmed, N. J., & Haseeb, A. (2023). The Burden of Surgical Site Infection at Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia and Related Postoperative Outcomes: A Prospective Surveillance Study. Antibiotics, 12(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020208










