Susceptibility Profile and Epidemiological Cut-Off Values Are Influenced by Serotype in Fish Pathogenic Streptococcus agalactiae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
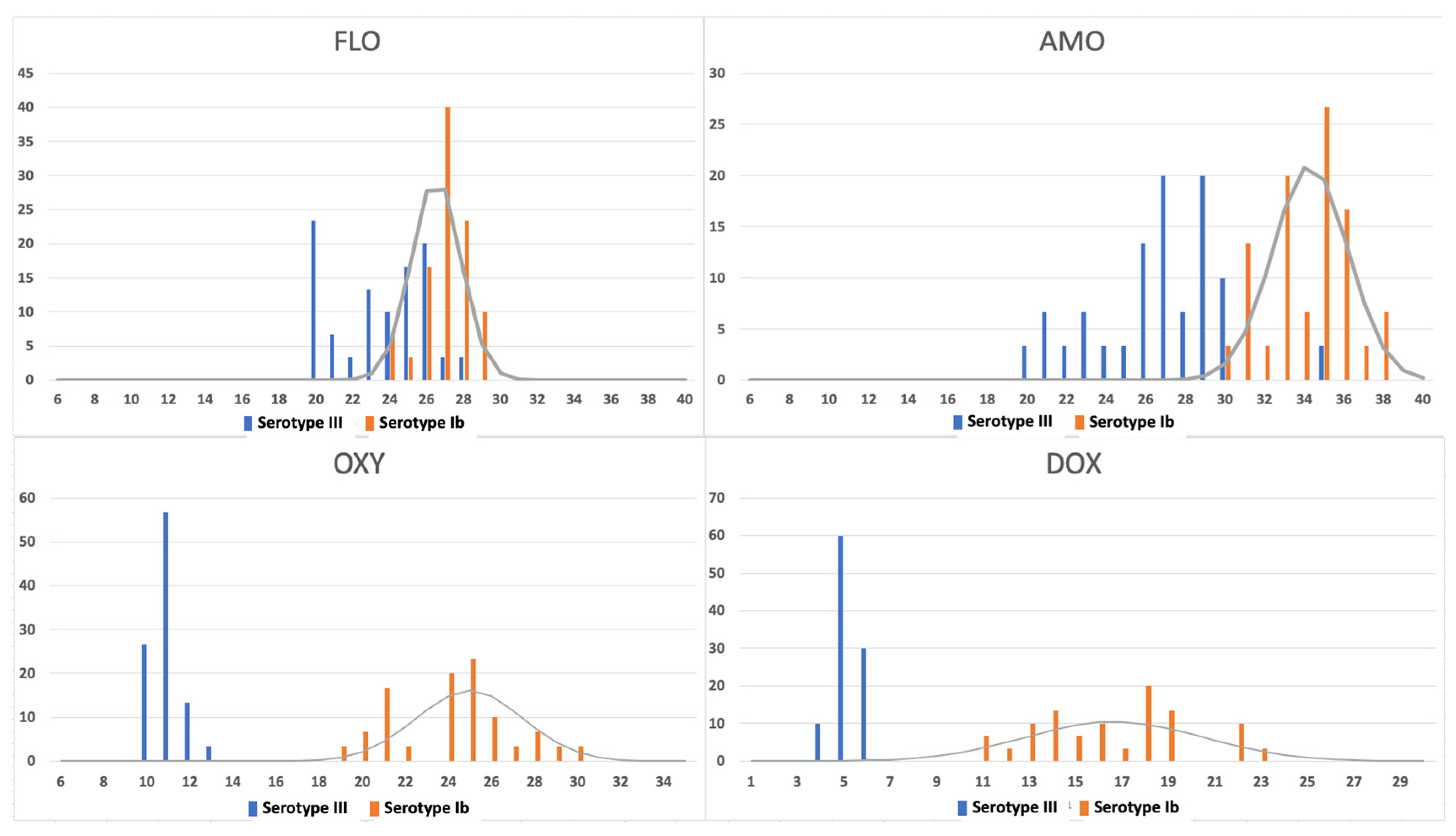
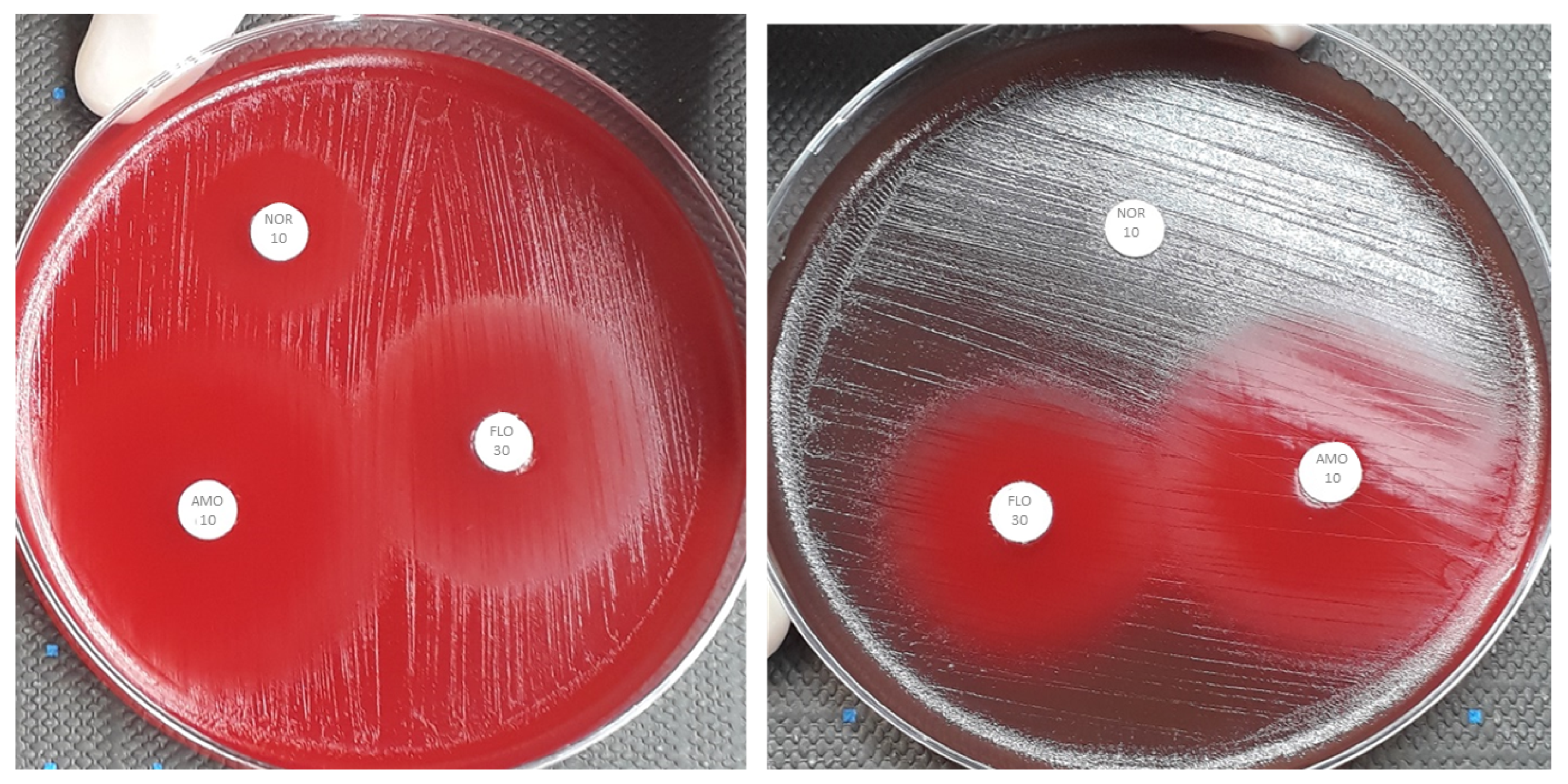
2.1. Sulfamethoxazole 25 and Norfloxacin 10 Disk Studies
2.2. Oxytetracycline 30 and Doxycycline 30 Disk Studies
2.3. Florfenicol 30 and Amoxicillin 10 Disk Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Machado, G.; Barato-Gómez, P.; Iregui-Castro, C. Morphological characterization of the adherence and invasion of Streptococcus agalactiae to the intestinal mucosa of tilapia Oreochromis sp.: An in vitro model. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delphino, M.K.V.C.; Barone, R.S.C.; Leal, C.A.G.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Gardner, I.A.; Gonçalves, V.S.P. Economic appraisal of vaccination against Streptoccocus agalactiae in Nile tilapia farms in Brazil. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 162, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ke, X.; Liu, Z.; Cao, J.; Su, Y.; Lu, M.; Gao, F.; Wang, M.; Yi, M.; Qin, F. Capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus agalactiae is an essential virulence factor for infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linn.). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katholm, J.; Bennedsgaard, T.W.; Koskinen, M.T.; Rattenborg, E. Quality of bulk tank milk samples from Danish dairy herds based on real-time polymerase chain reaction identification of mastitis pathogens. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5702–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, U.P.; Mian, G.F.; Oliveira, I.C.M.; Benchetrit, L.C.; Costa, G.M.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Genotyping of Streptococcus agalactiae strains isolated from fish, human and cattle and their virulence potential in Nile tilapia. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 140, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperi, M.; Pataracchia, M.; Alfarone, G.; Baldassarri, L.; Orefici, G.; Creti, R. A multiplex PCR assay for the direct identification of the capsular type (Ia to IX) of Streptococcus agalactiae. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2010, 80, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobadilla, F.J.; Novosak, M.G.; Cortese, I.J.; Delgado, O.D.; Laczeski, M.E. Prevalence, serotypes and virulence genes of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from pregnant women with 35–37 weeks of gestation. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chideroli, R.T.; Amoroso, N.; Mainardi, R.M.; Suphoronski, S.A.; de Padua, S.B.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A.; Mosela, M.; Moralez, A.T.P.; de Oliveira, A.G.; et al. Emergence of a new multidrug-resistant and highly virulent serotype of Streptococcus agalactiae in fish farms from Brazil. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y.; Zheng, L.; Rehman, T.; Zhao, R.; Wang, K.; OuYang, P.; Chen, D.; Huang, X.; et al. Molecular serotyping and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from fish in China. Aquaculture 2017, 510, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, A.K.; Paoletti, L.C.; Glaser, P.; Dua, M.; Sharma, P.K.; Grandi, G.; Rappuoli, R. Group B Streptococcus: Global incidence and vaccine development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Bowater, R.O.; Walker, M.J.; Beatson, S.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Barnes, A.C. Microevolution of Streptococcus agalactiae ST-261 from Australia indicates dissemination via imported tilapia and ongoing adaptation to marine Hosts or Environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 84, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, R.; Liang, W.; Gan, X.; Huang, T.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Chen, M.; Luo, H. Rare serotype occurrence and PFGE genotypic diversity of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from tilapia in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, C.; Ma, H.; Guo, Z.; Feng, J. Molecular typing of Streptococcus agalactiae isolates of serotype Ia from tilapia in southern China. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, D.T.; Carvalho-Castro, G.A.; Leal, C.A.G.; Pereira, U.P.; Leite, R.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Genetic diversity and new genotyping scheme for fish pathogenic Streptococcus agalactiae. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 57, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delannoy, C.M.; Crumlish, M.; Fontaine, M.C.; Pollock, J.; Foster, G.; Dagleish, M.P.; Turnbull, J.F.; Zadoks, R.N. Human Streptococcus agalactiae strains in aquatic mammals and fish. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendram, P.; Mar Kyaw, W.; Leo, Y.S.; Ho, H.; Chen, W.K.; Lin, R.; Pratim, P.; Badaruddin, H.; Ang, B.; Barkham, T.; et al. Group B Streptococcus sequence Type 283 disease linked to consumption of raw Fish, Singapore. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1974–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, C.A.G.; Queiroz, G.A.; Pereira, F.L.; Tavares, G.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Streptococcus agalactiae sequence Type 283 in farmed Fish, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L.; Cantón, R. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefian, M.; Amiri, M.S. A review of the use of prebiotic in aquaculture for fish shrimp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 7313–7318. [Google Scholar]
- Aisyhah, M.A.S.; Amal, M.N.A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Shaqinah, N.N. Streptococcus agalactiae isolates from cultured fishes in Malaysia manifesting low resistance pattern towards selected antibiotics. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, T.F.; Queiroz, G.A.; Teixeira, J.P.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Leal, C.A.G. Recurrent Streptoccoccus agalactiae infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) treated with florfenicol. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.C.; de Queiroz, G.A.; Assis, G.B.N.; Leibowitz, M.P.; Teixeira, J.P.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Leal, C.A.G. Disease outbreaks in farmed Amazon catfish (Leiarius marmoratus × Pseudoplatystoma corruscans) caused by Streptococcus agalactiae, S. iniae, and S. dysgalactiae. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronvall, G. Determination of the real standard distribution of susceptible strains in zone histograms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2003, 22, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Goldsmith, C.E.; Coulter, W.A.; Mason, C.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Lowery, C.J.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Comparison of minimum inhibitory concentration by broth microdilution testing versus standard disc diffusion testing in the detection of penicillin erythromycin ciprofloxacin resistance in viridans group streptococci. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Espinel-Ingroff, A.; Turnidge, J. The role of epidemiological cutoff values (ECVs/ECOFFs) in antifungal susceptibility testing and interpretation for uncommon yeasts and moulds. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2016, 33, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronvall, G.; Kahlmeter, G.; Myhre, E.; Galas, M.F. A new method for normalized interpretation of antimicrobial resistance from disk test results for comparative purposes. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barony, G.M.; Tavares, G.C.; Pereira, F.L.; Carvalho, A.F.; Dorella, F.A.; Leal, C.A.G.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Large-scale genomic analyses reveal the population structure and evolutionary trends of Streptococcus agalactiae strains in Brazilian fish farms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, G.F.; Godoy, D.T.; Leal, C.A.G.; Yuhara, T.Y.; Costa, G.M.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Aspects of the natural history and virulence of S. agalactiae infection in Nile tilapia. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 136, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.J.; Pasnik, D.J.; Klesius, P.H.; Al-Ablani, S. First report of Streptococcus agalactiae and Lactococcus garvieae from a wild bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, F.C.; Leal, C.A.G.; Carvalho-Castro, G.A.; Leite, R.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Carrier state induced by oxytetracycline therapy against streptococcosis in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sapugahawatte, D.N.; Yang, Y.; Wong, K.T.; Lo, N.W.S.; Ip, M. Multidrug-resistant Streptococcus agalactiae Strains Found in human and fish with high penicillin and cefotaxime non-susceptibilities. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Huang, P.Y.; Chen, H.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Tsai, I.A.; Lu, C.C.; Chen, C.C. Genetic and pathogenic difference between Streptococcus agalactiae serotype Ia fish and human isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadbad, M.A.; Kafil, H.S.; Rezaee, M.A.; Farzami, M.R.; Dehkharghani, A.D.; Sadeghi, J.; Gholizadeh, P.; Khodaei, F.; Aghazadeh, M. Streptococcus agalactiae clinical isolates in Northwest Iran: Antibiotic susceptibility, molecular typing, and biofilm formation. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. 2020, 15, Doc23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangwetngam, M.; Suanyuk, N.; Kong, F.; Phromkunthong, W. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibilities of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from infected cultured tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Thailand: Nine-year perspective. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.H.; Garcia, F.; Gozi, K.S.; Romera, D.M.; Francisco, J.G.; Moura-Andrade, G.C.R.; Tornisielo, V.L. Relationship between antibiotic residues and occurrence of resistant bacteria in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in cage-farm. J. Environ. Sci. Health B. 2016, 51, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergal, A.; Loucif, L.; Benouareth, D.E.; Bentorki, A.A.; Abat, C.; Rolain, J.M. Molecular epidemiology and distribution of serotypes, genotypes, and antibiotic resistance genes of Streptococcus agalactiae clinical isolates from Guelma, Algeria and Marseille, France. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanetti, E.; Brenciani, A.; Lupidi, R.; Roberts, M.C.; Varaldo, P.E. Presence of the tet(O) gene in erythromycin- and tetracycline-resistant strains of Streptococcus pyogenes and linkage with either the mef(A) or the erm(A) gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2844–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, A.B.; Oliveira, I.C.; Pinto Tde, C.; Mattos, M.C.; Benchetrit, L.C. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, virulence determinants and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of type Ia group B streptococci isolated from humans in Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2009, 104, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Duarte, R.S.; Bellei, B.C.; Miranda, O.P.; Brito, M.A.V.P.; Teixeira, L.M. Distribution of antimicrobial resistance and virulence-related genes among Brazilian Group B streptococci recovered from bovine and human sources. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.C.M.; de Mattos, M.C.; Areal, M.F.T.; Ferreira-Carvalho, B.T.; Figuiredo, A.M.S.; Benchetrit, L.C. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of human Group B streptococci isolated in Brazil. J. Chemother. 2005, 17, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, A.; Bejerano, Y.; Bercovier, H. Streptococcus shiloi and Streptococcus difficile: Two new streptococcal species causing a meningoencephalitis in fish. Curr. Microbiol. 1994, 28, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, P.; Devriese, L.A.; Pot, B.; Kersters, K.; Melin, P. Streptococcus difficile is a nonhemolytic Group B, type Ib Streptococcus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cooper, K.E. The Theory of Antibiotic Inhibition Zones. In Analytical Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1963; pp. 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Ruane, N.M.; Douglas, I.; Carroll, C.; Kronvall, G.; Fleming, G.T.A. Impact of inter-lab variation on the estimation of epidemiological cut-off values for disc diffusion susceptibility test data for Aeromonas salmonicida. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoff, R.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Wooster, G.A.; Getchell, R.G.; Bowser, P.R.; Clifford, A.; Craig, J.L.; Lim, P.; Wetzlich, S.E.; Craigmill, A.L.; et al. Florfenicol residues in three species of fish after 10-day oral dosing in feed. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2009, 21, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, J.F.; Moulin, G.; Page, S.W.; Pastoret, P.P. Antimicrobial resistance in animal and public health: Introduction and classification of antimicrobial agents. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2012, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannika, K.; Pisuttharachai, D.; Srisapoome, P.; Wongtavatchai, J.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I.; Unajak, S.; Areechon, N. Molecular serotyping, virulence gene profiling and pathogenicity of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from tilapia farms in Thailand by multiplex PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clsi. Methods for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated From Aquatic Animals, 2nd ed.; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Eucast. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters; Eucast: Växjö, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
| Wild-type (WT) Mean | Wild-type (WT) SD | COWT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| III | Ib | Comb | III | Ib | Comb | III | Ib | Comb | |
| DOX | 10 | 22 | 22 | 0.74 | 3.79 | 3.79 | 8 | 12 | 12 |
| OXY | 10 | 25 | 25 | 0.56 | 2.47 | 2.47 | 10 | 19 | 19 |
| FLO | 25 | 27 | 27 | 1.4 | 1.11 | 1.3 | 21 | 24 | 23 |
| AMO | 28 | 34 | 35 | 1.96 | 1.91 | 1.88 | 23 | 30 | 30 |
| Strain | Serotype III | Strain | Serotype Ib | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXY | DOX | AMO | FLO | OXY | DOX | AMO | FLO | ||
| 492/19 | 11 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 27 (WT) | 25 (WT) | 189/17 | 26 (WT) | 27 (WT) | 33 (WT) | 27 (WT) |
| 118/17 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 29 (WT) | 20 (NWT) | 58/17 | 30 (WT) | 26 (WT) | 30 (WT) | 26 (WT) |
| 149/17 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 39 (WT) | 26 (WT) | 86/17 | 22 (WT) | 18 (WT) | 34 (WT) | 27 (WT) |
| 294/18 | 10 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 22 (NWT) | 21 (WT) | 68/17 | 24 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 30 (WT) | 26 (WT) |
| 237/18 | 11 (NWT) | 9 (NWT) | 24 (WT) | 21 (WT) | 311/18 | 25 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 33 (WT) | 29 (WT) |
| 325/18 | 11 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 22 (NWT) | 21 (WT) | 366/18 | 25 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 34 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 328/18 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 25 (WT) | 21 (WT) | 310/18 | 26 (WT) | 22 (WT) | 32 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 27/17 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 26 (WT) | 21 (WT) | 365/18 | 25 (WT) | 19 (WT) | 35 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 215/18 | 11 (NWT) | 9 (NWT) | 22 (NWT) | 20 (NWT) | 251/18 | 22 (WT) | 24 (WT) | 31 (WT) | 25 (WT) |
| 117/17 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 22 (NWT) | 20 (NWT) | 393/18 | 23 (WT) | 22 (WT) | 35 (WT) | 26 (WT) |
| 327/18 | 10 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 29 (WT) | 24 (WT) | 339/18 | 23 (WT) | 21 (WT) | 29 (WT) | 25 (WT) |
| 239/18 | 10 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 30 (WT) | 27 (WT) | 421/18 | 28 (WT) | 26 (WT) | 32 (WT) | 26 (WT) |
| 306/18 | 10 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 31 (WT) | 26 (WT) | 496/19 | 25 (WT) | 22 (WT) | 31 (WT) | 24 (WT) |
| 399/18 | 10 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 33 (WT) | 24 (WT) | 472/19 | 27 (WT) | 28 (WT) | 40 (WT) | 27 (WT) |
| 330/18 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 32 (WT) | 28 (WT) | 495/19 | 28 (WT) | 25 (WT) | 34 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 400/18 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 31 (WT) | 27 (WT) | 482/19 | 27 (WT) | 24 (WT) | 32 (WT) | 29 (WT) |
| 487/19 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 34 (WT) | 27 (WT) | 514/19 | 28 (WT) | 26 (WT) | 35 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 488/19 | 12 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 34 (WT) | 29 (WT) | 502/19 | 26 (WT) | 28 (WT) | 40 (WT) | 29 (WT) |
| 03/17 | 10 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 32 (WT) | 27 (WT) | 516/19 | 26 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 33 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 26/17 | 10 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 34 (WT) | 28 (WT) | 505/19 | 25 (WT) | 20 (WT) | 37 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 212/18 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 26 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 506/19 | 21 (WT) | 18 (WT) | 32 (WT) | 28 (WT) |
| 334/18 | 10 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 27 (WT) | 22 (WT) | 265/18 | 24 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 35 (WT) | 29 (WT) |
| 240/18 | 11 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 28 (WT) | 24 (WT) | 523/19 | 22 (WT) | 19 (WT) | 33 (WT) | 26 (WT) |
| 491/19 | 11 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 29 (WT) | 25 (WT) | 513/19 | 25 (WT) | 24 (WT) | 28 (WT) | 24 (WT) |
| 219/18 | 12 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 29 (WT) | 27 (WT) | 390/18 | 29 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 33 (WT) | 30 (WT) |
| 322/18 | 10 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 26 (WT) | 26 (WT) | 88/17 | 21 (WT) | 18 (WT) | 35 (WT) | 26 (WT) |
| 137/17 | 12 (NWT) | 11 (NWT) | 30 (WT) | 26 (WT) | 246/18 | 23 (WT) | 18 (WT) | 31 (WT) | 29 (WT) |
| 213/19 | 12 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 27 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 253/18 | 25 (WT) | 23 (WT) | 37 (WT) | 27 (WT) |
| 397/18 | 12 (NWT) | 9 (NWT) | 25 (WT) | 24 (WT) | 164/17 | 22 (WT) | 17 (WT) | 34 (WT) | 27 (WT) |
| 223/18 | 13 (NWT) | 10 (NWT) | 34 (WT) | 27 (WT) | 160/17 | 22 (WT) | 19 (WT) | 34 (WT) | 29 (WT) |
| Species | Agent | Source | Wild-type Mean | Wild-type SD | COWT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. agalactiae | DOX | III + Ib (Present study) | 22 | 3.79 | 12 |
| OXY | 25 | 2.45 | 19 | ||
| TET | EUCAST ** | 22 | 2.19 | 20 | |
| MIN | 25 | 2.47 | 19 | ||
| S. dysgalactiae | TET | 27 | 2.03 | 21 |
| Strain | Year | Serotype | State | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA 189/17 | 2017 | Ib | Pernambuco | Jatobá |
| SA 58/17 | 2017 | Ib | Pernambuco | Jatobá |
| SA 86/17 | 2017 | Ib | Ceará | Fortaleza |
| SA 68/17 | 2017 | Ib | Pernambuco | Jatobá |
| SA 88/17 | 2017 | Ib | Ceará | Fortaleza |
| SA 164/17 | 2017 | Ib | São Paulo | Rifaina |
| SA 160/17 | 2017 | Ib | São Paulo | Rifaina |
| SA 311/18 | 2018 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 366/18 | 2018 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 310/18 | 2018 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 365/18 | 2018 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 251/18 | 2018 | Ib | São Paulo | Rio Grandinho |
| SA 393/18 | 2018 | Ib | Minas Gerais | Carmo do Rio Claro |
| SA 339/18 | 2018 | Ib | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 421/18 | 2018 | Ib | Minas Gerais | Uberlandia |
| SA 265/18 | 2018 | Ib | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 390/18 | 2018 | Ib | Minas Gerais | Carmo do Rio Claro |
| SA 246/18 | 2018 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 253/18 | 2018 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 496/19 | 2019 | Ib | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 472/19 | 2019 | Ib | São Paulo | Jau |
| SA 495/19 | 2019 | Ib | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 482/19 | 2019 | Ib | Minas Gerais | Alfenas |
| SA 514/19 | 2019 | Ib | Mato Grosso | Chapada dos Guimaraes |
| SA 502/19 | 2019 | Ib | Mato Grosso do Sul | Selvíria |
| SA 516/19 | 2019 | Ib | Paraná | Toledo |
| SA 505/19 | 2019 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 506/19 | 2019 | Ib | São Paulo | Santa Fé do Sul |
| SA 523/19 | 2019 | Ib | Minas Gerais | Carmo do Rio Claro |
| SA 513/19 | 2019 | Ib | Mato Grosso | Chapada dos Guimaraes |
| SA 118/17 | 2017 | III | Bahia | Valença |
| SA 149/17 | 2017 | III | Bahia | Valença |
| SA 27/17 | 2017 | III | Bahia | Gloria |
| SA 117/17 | 2017 | III | Bahia | Valença |
| SA 03/17 | 2017 | III | Pernambuco | Itacarube |
| SA 26/17 | 2017 | III | Bahia | Gloria |
| SA 137/17 | 2017 | III | Bahia | Valença |
| SA 294/18 | 2018 | III | Pernambuco | Jatobá |
| SA 237/18 | 2018 | III | Pernambuco | Santo Antonio |
| SA 325/18 | 2018 | III | Piaui | Guadalupe |
| SA 328/18 | 2018 | III | Piaui | Guadalupe |
| SA 215/18 | 2018 | III | Bahia | Valença |
| SA 327/18 | 2018 | III | Piaui | Guadalupe |
| SA 239/18 | 2018 | III | Pernambuco | Santo Antonio |
| SA 306/18 | 2018 | III | Bahia | Gloria |
| SA 399/18 | 2018 | III | Maranhao | São Joao do Maranhão |
| SA 330/18 | 2018 | III | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 400/18 | 2018 | III | Maranhao | São Joao do Maranhão |
| SA 212/18 | 2018 | III | Bahia | Valença |
| SA 334/18 | 2018 | III | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 240/18 | 2018 | III | Pernambuco | Santo Antonio |
| SA 219/18 | 2018 | III | Alagoas | Coruripe |
| SA 322/18 | 2018 | III | Piaui | Guadalupe |
| SA 397/18 | 2018 | III | Ceará | Fortaleza |
| SA 223/18 | 2018 | III | Alagoas | Coruripe |
| SA 492/19 | 2019 | III | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 487/19 | 2019 | III | Alagoas | Piranhas |
| SA 488/19 | 2019 | III | Alagoas | Piranhas |
| SA 491/19 | 2019 | III | Bahia | Paulo Afonso |
| SA 213/19 | 2019 | III | Bahia | Valença |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leal, C.A.G.; Silva, B.A.; Colombo, S.A. Susceptibility Profile and Epidemiological Cut-Off Values Are Influenced by Serotype in Fish Pathogenic Streptococcus agalactiae. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121726
Leal CAG, Silva BA, Colombo SA. Susceptibility Profile and Epidemiological Cut-Off Values Are Influenced by Serotype in Fish Pathogenic Streptococcus agalactiae. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(12):1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121726
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeal, Carlos Augusto Gomes, Brendhal Almeida Silva, and Salene Angelini Colombo. 2023. "Susceptibility Profile and Epidemiological Cut-Off Values Are Influenced by Serotype in Fish Pathogenic Streptococcus agalactiae" Antibiotics 12, no. 12: 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121726
APA StyleLeal, C. A. G., Silva, B. A., & Colombo, S. A. (2023). Susceptibility Profile and Epidemiological Cut-Off Values Are Influenced by Serotype in Fish Pathogenic Streptococcus agalactiae. Antibiotics, 12(12), 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121726





