Early Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) Treated with Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention (DAIR): Inferior Outcomes in Patients with Staphylococci Resistant to Rifampicin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
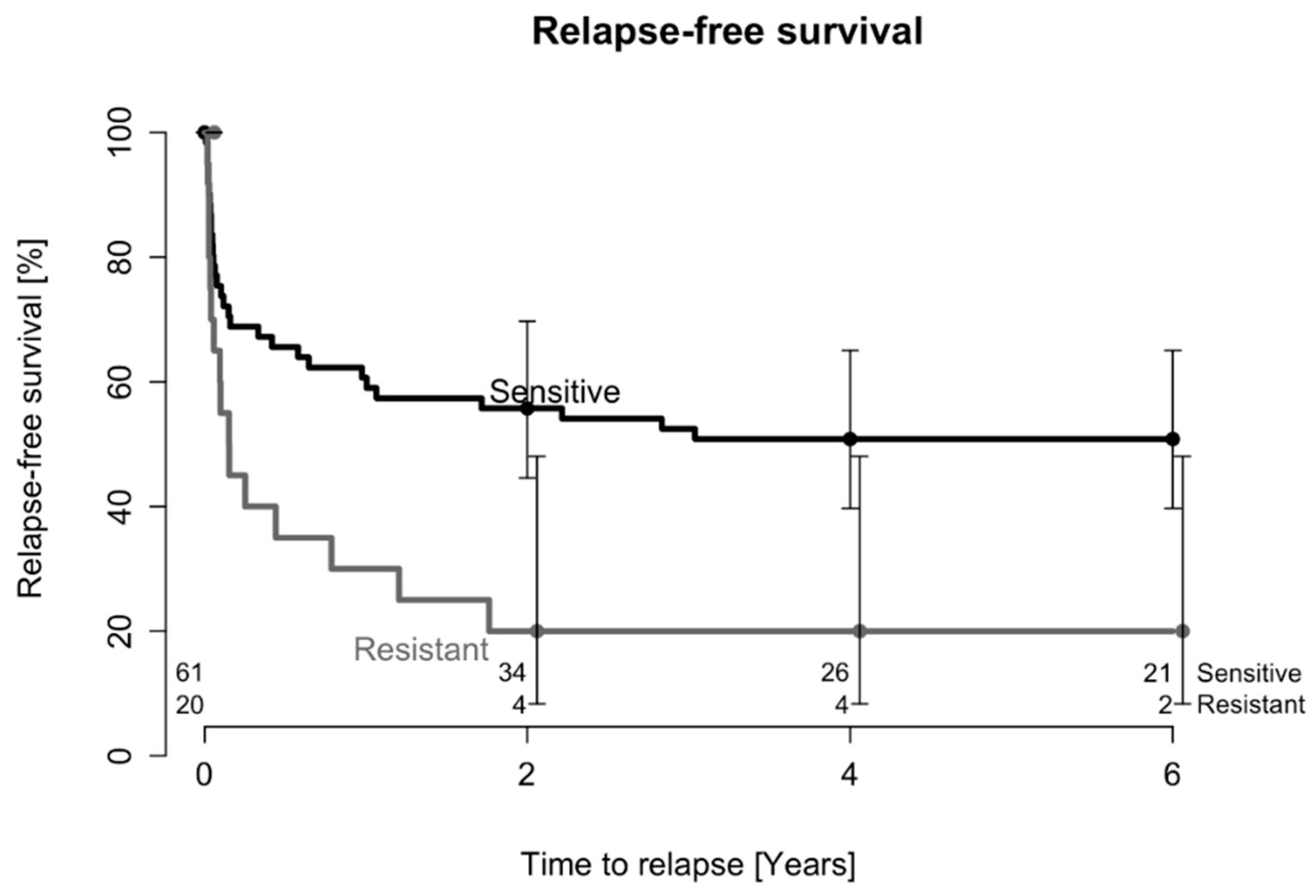
2.1. Treatment Outcome after One DAIR Procedure
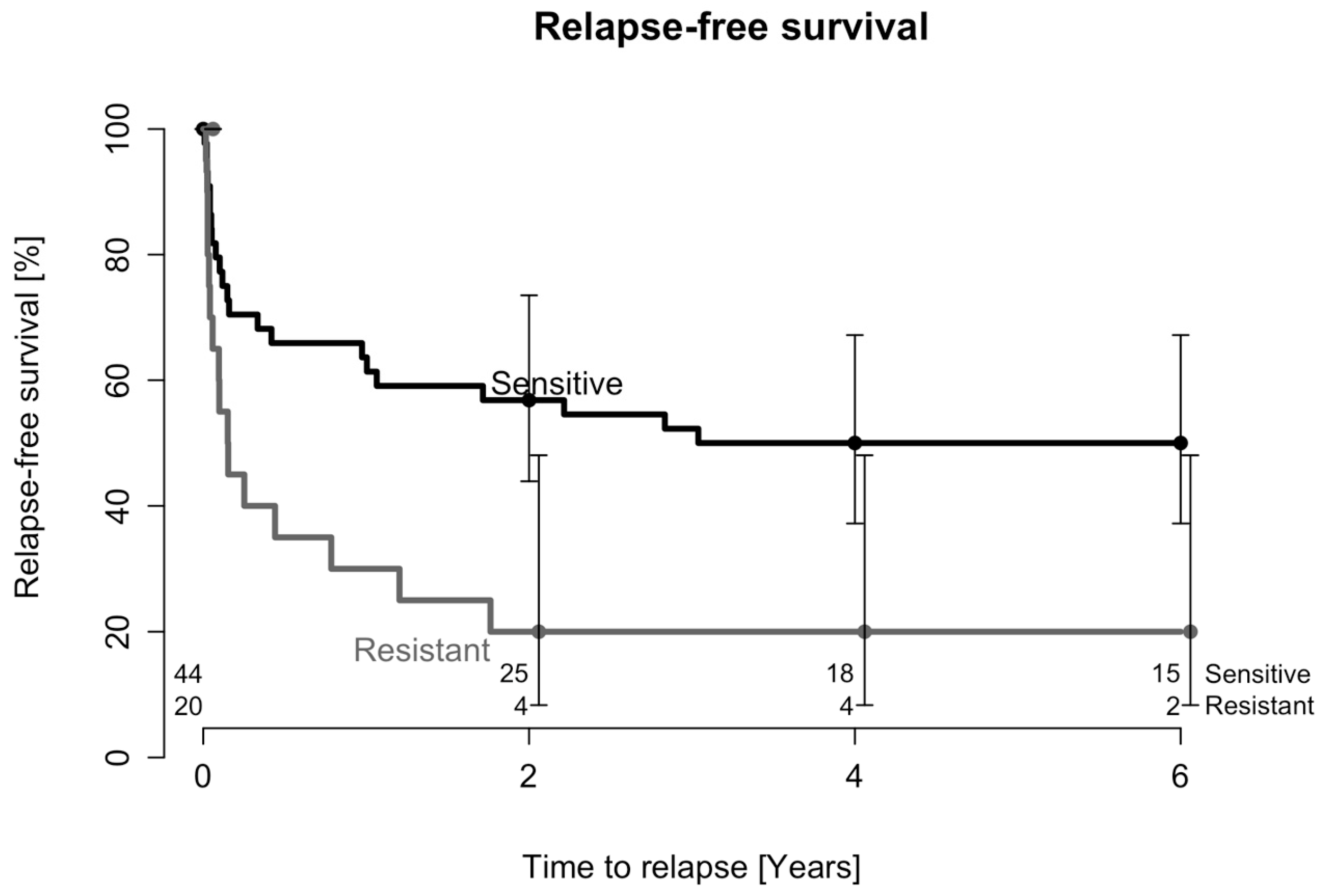
2.2. Treatment Outcome after Two DAIR Procedures
2.3. Analysis of PJI Caused by CoNS
3. Discussion
4. Patients and Methods
Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Schmier, J.; Ong, K.L.; Zhao, K.; Parvizi, J. Infection burden for hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.C.; Son, M.-S.; Chang, E.T.; Zimmerli, W.; Parvizi, J. Are We Winning or Losing the Battle With Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Trends in Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Mortality Risk for the Medicare Population. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 3238–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundtoft, P.; Pedersen, A.; Schønheyder, H.; Møller, J.; Overgaard, S. One-year incidence of prosthetic joint infection in total hip arthroplasty: A cohort study with linkage of the Danish Hip Arthroplasty Register and Danish Microbiology Databases. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundtoft, P.H.; Pedersen, A.B.; Varnum, C.; Overgaard, S. Increased Mortality After Prosthetic Joint Infection in Primary THA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.R.; Pannu, T.S.; Villa, J.M.; Manrique, J.; Riesgo, A.M.; Higuera, C.A. The treatment of periprosthetic joint infection: Safety and efficacy of two stage versus one stage exchange arthroplasty. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozic, K.J.; Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Ong, K.; Vail, T.P.; Berry, D.J. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2009, 91, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, V.; Gordon, M.; Wretenberg, P.; Kärrholm, J.; Garellick, G. Deep infection after total hip replacement: A method for national incidence surveillance. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Ochsner, P.E. Prosthetic-joint infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, I.G.; Berbari, E.F.; Karchmer, A.W. Prosthetic joint infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 19, 885–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbari, E.F.; Osmon, D.R.; Carr, A.; Hanssen, A.D.; Baddour, L.M.; Greene, D.; Kupp, L.I.; Baughan, L.W.; Harmsen, W.S.; Mandrekar, J.N.; et al. Dental procedures as risk factors for prosthetic hip or knee infection: A hospital-based prospective case-control study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, T.N.; Cheng, A.C.; Buising, K.L.; Choong, P.F. Microbiological aetiology, epidemiology, and clinical profile of prosthetic joint infections: Are current antibiotic prophylaxis guidelines effective? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2386–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, C.I.; Lee, J.H.; Joung, M.; Moon, S.; Wi, Y.M.; Chung, D.R.; Ha, C.W.; Song, J.H.; Peck, K.R. Risk factors for treatment failure in patients with prosthetic joint infections. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 75, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, V.V.; Siney, P.D.; Wroblewski, B.M. One-stage revision of infected total hip replacements with discharging sinuses. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1994, 76, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.-S. Treatment based on the type of infected tka improves infection control. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klouche, S.; Leonard, P.; Zeller, V.; Lhotellier, L.; Graff, W.; Leclerc, P.; Mamoudy, P.; Sariali, E. Infected total hip arthroplasty revision: One- or two-stage procedure? Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2012, 98, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, N.; Mur, I.; Ribera, A.; Soriano, A.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Sorlí, L.; Cobo, J.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; Del Toro, M.D.; Guío, L.; et al. The Different Microbial Etiology of Prosthetic Joint Infections according to Route of Acquisition and Time after Prosthesis Implantation, Including the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tande, A.J.; Patel, R. Prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 302–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. The significance of infection related to orthopedic devices and issues of antibiotic resistance. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the clinical implications of anti-infective biomaterials and infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8018–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, B.E.; Kourteva, Y.; Kaiser, A.B.; Kernodle, D.S. Inhibition of staphylococcal wound infection and potentiation of antibiotic prophylaxis by a recombinant fragment of the fibronectin-binding protein of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, J.M.; Saini, V.; Ashbaugh, A.G.; Miller, R.J.; Ordonez, A.A.; Ortines, R.V.; Wang, Y.; Sterling, R.S.; Jain, S.K.; Miller, L.S. Oral-Only Linezolid-Rifampin Is Highly Effective Compared with Other Antibiotics for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Study of a Mouse Model. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidlak, D.; Kielian, T. Infectious Dose Dictates the Host Response during Staphylococcus aureus Orthopedic-Implant Biofilm Infection. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovati, A.B.; Bottagisio, M.; de Vecchi, E.; Gallazzi, E.; Drago, L. Animal Models of Implant-Related Low-Grade Infections. A Twenty-Year Review. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 971, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saeed, K.; McLaren, A.C.; Schwarz, E.M.; Antoci, V.; Arnold, W.V.; Chen, A.F.; Clauss, M.; Esteban, J.; Gant, V.; Hendershot, E.; et al. 2018 international consensus meeting on musculoskeletal infection: Summary from the biofilm workgroup and consensus on biofilm related musculoskeletal infections. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implant-associated infection. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, J.; Miguel, L.G.S.; Euba, G.; Rodríguez, D.; García-Lechuz, J.; Riera, M.; Falgueras, L.; Palomino, J.; Benito, N.; del Toro, M.D.; et al. Early prosthetic joint infection: Outcomes with debridement and implant retention followed by antibiotic therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, A.F.; Post, Z.D.; Lutz, R.W.; Orozco, F.R.; Pulido, S.H.; Ong, A.C. Is There Still a Role for Irrigation and Debridement With Liner Exchange in Acute Periprosthetic Total Knee Infection? J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirmengian, C.; Greenbaum, J.; Lotke, P.A.; Booth, R.E.; Lonner, J.H. Limited success with open debridement and retention of components in the treatment of acute Staphylococcus aureus infections after total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2003, 18, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mont, M.A.; Waldman, B.; Banerjee, C.; Pacheco, I.H.; Hungerford, D.S. Multiple irrigation, debridement, and retention of components in infected total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 1997, 12, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Tharani, R.; Schmalzried, T.P. Results of direct exchange or debridement of the infected total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 404, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, A.; Thórhallsdóttir, V.G.; Robertsson, O.; W-Dahl, A.; Stefánsdóttir, A. 75% success rate after open debridement, exchange of tibial insert, and antibiotics in knee prosthetic joint infections. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, J.W.; Vos, S.J.; Saouti, R.; Vergroesen, D.A.; Graat, H.C.; Debets-Ossenkopp, Y.J.; Peters, E.J.; Nolte, P.A. Prosthetic joint-associated infections treated with DAIR (debridement, antibiotics, irrigation, and retention): Analysis of risk factors and local antibiotic carriers in 91 patients. Acta Orthop. 2013, 84, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buller, L.T.; Sabry, F.Y.; Easton, R.W.; Klika, A.K.; Barsoum, W.K. The preoperative prediction of success following irrigation and debridement with polyethylene exchange for hip and knee prosthetic joint infections. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 857–864.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboltins, C.A.; Page, M.A.; Buising, K.L.; Jenney, A.W.J.; Daffy, J.R.; Choong, P.F.M.; Stanley, P.A. Treatment of staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections with debridement, prosthesis retention and oral rifampicin and fusidic acid. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byren, I.; Bejon, P.; Atkins, B.L.; Angus, B.; Masters, S.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Gundle, R.; Berendt, A. One hundred and twelve infected arthroplasties treated with ‘DAIR’ (debridement, antibiotics and implant retention): Antibiotic duration and outcome. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, C.M.; Sistrunk, W.W.; Duffy, M.C.; Hanssen, A.D.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Ilstrup, D.M.; Osmon, D.R. Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infection treated with debridement and prosthesis retention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marculescu, C.E.; Berbari, E.F.; Hanssen, A.D.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Harmsen, S.W.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Osmon, D.R. Outcome of prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement and retention of components. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyonos, L.; Zmistowski, B.; Della Valle, C.J.; Parvizi, J. Infection control rate of irrigation and débridement for periprosthetic joint infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3043–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helou, O.C.; Berbari, E.F.; Lahr, B.D.; Eckel-Passow, J.E.; Razonable, R.R.; Sia, I.G.; Virk, A.; Walker, R.C.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Wilson, W.R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rifampin containing regimen for staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement and retention. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, K.A.; Seeley, M.; Ghanem, E.; Austin, M.S.; Purtill, J.J.; Parvizi, J. Irrigation and Debridement in the Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection: Traditional Indications Revisited. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Berendt, A.R.; Lew, D.; Zimmerli, W.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Rao, N.; Hanssen, A.; Wilson, W.R.; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, e1–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmark, B.; Unemo, M.; Nilsdotter-Augustinsson, Å.; Söderquist, B. Antibiotic susceptibility among Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from prosthetic joint infections with special focus on rifampicin and variability of the rpoB gene. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, W.; Widmer, A.F.; Blatter, M.; Frei, R.; Ochsner, P.E.; for the Foreign-Body Infection (FBI) Study Group. Role of rifampin for treatment of orthopedic implant–related staphylococcal infections a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998, 279, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drancourt, M.; Stein, A.; Argenson, J.N.; Roiron, R.; Groulier, P.; Raoult, D. Oral treatment of Staphylococcus spp. infected orthopaedic implants with fusidic acid or ofloxacin in combination with rifampicin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 39, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdal, J.-E.; Skråmm, I.; Mowinckel, P.; Gulbrandsen, P.; Bjørnholt, J.V. Use of rifampicin and ciprofloxacin combination therapy after surgical debridement in the treatment of early manifestation prosthetic joint infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soriano, A.; García, S.; Bori, G.; Almela, M.; Gallart, X.; Macule, F.; Sierra, J.; Martínez, J.; Suso, S.; Mensa, J. Treatment of acute post-surgical infection of joint arthroplasty. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Renz, N.; Trampuz, A.; Ojeda-Thies, C. Twenty common errors in the diagnosis and treatment of periprosthetic joint infection. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, A.F.; Gaechter, A.; Ochsner, P.E.; Zimmerli, W. Antimicrobial treatment of orthopedic implant-related Infections with rifampin combinations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 14, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, A.G.; Costerton, J.W. Bacterial adherence to biomaterials and tissue. The significance of its role in clinical sepsis. Minerva Anestesiol. 1985, 67, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbejuade, H.O.; Lovering, A.M.; Webb, J.C. The role of microbial biofilms in prosthetic joint infections. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvori, C.; Frontali, L.; Leoni, L.; Tecce, G. Effect of rifamycin on protein synthesis. Nature 1965, 207, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, G.N.; Tamura, K. Rifampin combination therapy for nonmycobacterial infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizsan, G.; Sallai, I.; Veres, D.S.; Prinz, G.; Szeker, D.; Skaliczki, G. Rifampicin resistance and risk factors associated with significantly lower recovery rates after two-stage revision in patients with prosthetic joint infection. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 30, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trobos, M.; Firdaus, R.; Malchau, K.S.; Tillander, J.; Arnellos, D.; Rolfson, O.; Thomsen, P.; Lasa, I. Genomics of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis from Periprosthetic Joint Infections and Correlation to Clinical Outcome. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0218121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatopoulos, G.; Kendrick, B.; McNally, M.; Athanasou, N.A.; Atkins, B.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Taylor, A.; Gundle, R. Outcome Following Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention in Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection-An 18-Year Experience. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Nurjadi, D.; Eigenbrod, T.; Bode, K.A. Evaluation of antibiotic resistance to orally administrable antibiotics in staphylococcal bone and joint infections in one of the largest university hospitals in Germany: Is there a role for fusidic acid? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Eiff, C.P.G.; Heilmann, C. Pathogenesis of infections due to coagulase-negative staphylococci. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widerström, M.; Wiström, J.; Edebro, H.; Marklund, E.; Backman, M.; Lindqvist, P.; Monsen, T. Colonization of patients, healthcare workers, and the environment with healthcare-associated Staphylococcus epidermidis genotypes in an intensive care unit: A prospective observational cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stefani, S.; Varaldo, P. Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant staphylococci in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.A.; Pust, T.M.; Cappellini, A.J.; Mandell, J.B.; Ma, D.; Shah, N.B.; Brothers, K.M.; Urish, K.L. Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms Have a High Tolerance to Antibiotics in Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Life 2020, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, S.H.; Haeckl, F.P.J.; Müller, R. Beyond the approved: Target sites and inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase from bacteria and fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 1226–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, W. The Mechanism of Bacterial Resistance and Potential Bacteriostatic Strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Fang, R.; Zhou, B.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Dong, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, T. Evolution of resistance mechanisms and biological characteristics of rifampicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains selected in vitro. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.T.; Andam, C.P. Extensive Horizontal Gene Transfer within and between Species of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantosti, A.; Sanchini, A.; Monaco, M. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Futur. Microbiol. 2007, 2, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmark, B.; Söderquist, B.; Unemo, M. Simultaneous species identification and detection of rifampicin resistance in staphylococci by sequencing of the rpoB gene. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarinis, S.; Hailer, N.P.; Järhult, J.D.; Brüggemann, A. Incidence of Rifampicin Resistance in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Centre Cohort Study on 238 Patients. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, Ø.; Borgen, P.; Bragnes, B.; Figved, W.; Grøgaard, B.; Rydinge, J.; Sandberg, L.; Snorrason, F.; Wangen, H.; Witsøe, E.; et al. Rifampin combination therapy in staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections: A randomized controlled trial. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roope, L.S.J.; Smith, R.D.; Pouwels, K.B.; Buchanan, J.; Abel, L.; Eibich, P.; Butler, C.C.; Tan, P.S.; Walker, A.S.; Robotham, J.V.; et al. The challenge of antimicrobial resistance: What economics can contribute. Science 2019, 364, eaau4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröschen, F.S.; Randau, T.M.; Franz, A.; Molitor, E.; Hoerauf, A.; Hischebeth, G.T.R. Microbiological Trends and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns in Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip or Knee over 6 Years. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beldman, M.; Löwik, C.; Soriano, A.; Albiach, L.; Zijlstra, W.P.; Knobben, B.A.S.; Jutte, P.; Sousa, R.; Carvalho, A.; Goswami, K.; et al. If, When, and How to Use Rifampin in Acute Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infections, a Multicentre Observational Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendi, P.; Zimmerli, W. The use of rifampin in staphylococcal orthopaedic-device-related infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic joint infection: Current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urish, K.L.; Bullock, A.G.; Kreger, A.M.; Shah, N.B.; Jeong, K.; Rothenberger, S.D.; The Infected Implant Consortium. A Multicenter Study of Irrigation and Debridement in Total Knee Arthroplasty Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Treatment Failure Is High. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T.; Aiyer, A.; Battenberg, A.; Brown, S.A.; Callaghan, J.J.; Citak, M.; Egol, K.; Garrigues, G.E.; et al. 2018 International Consensus Meeting on Musculoskeletal Infection: Research Priorities from the General Assembly Questions. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedish Reference Group for Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.sls.se/raf/ (accessed on 22 October 2023).
- Nordic Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Available online: https://www.nordicast.org (accessed on 22 October 2023).

| Rifampicin-Sensitive | Rifampicin-Resistant | |
|---|---|---|
| Variable | ||
| Sex | ||
| Female (n = 42) | 30 | 12 |
| Male (n = 39) | 31 | 8 |
| Age | ||
| ˂70 (n = 34) | 26 | 8 |
| ≥70 (n = 47) | 35 | 12 |
| Joint | ||
| Hip (n = 51) | 35 | 16 |
| Knee (n = 30) | 26 | 4 |
| Index surgery | ||
| Primary (n = 63) | 49 | 14 |
| Revision (n = 18) | 12 | 6 |
| Staphylococcus spp. | ||
| Coagulase-negative staphylococcus (n = 64) | 44 | 20 |
| Staphylococcus aureus (n = 17) | 17 | 0 |
| Duration from index surgery to first DAIR procedure (mean days (range)) | 24 (7–42) | 25 (8–42) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eriksson, H.K.; Lazarinis, S.; Järhult, J.D.; Hailer, N.P. Early Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) Treated with Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention (DAIR): Inferior Outcomes in Patients with Staphylococci Resistant to Rifampicin. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111589
Eriksson HK, Lazarinis S, Järhult JD, Hailer NP. Early Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) Treated with Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention (DAIR): Inferior Outcomes in Patients with Staphylococci Resistant to Rifampicin. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(11):1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111589
Chicago/Turabian StyleEriksson, Hannah K., Stergios Lazarinis, Josef D. Järhult, and Nils P. Hailer. 2023. "Early Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) Treated with Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention (DAIR): Inferior Outcomes in Patients with Staphylococci Resistant to Rifampicin" Antibiotics 12, no. 11: 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111589
APA StyleEriksson, H. K., Lazarinis, S., Järhult, J. D., & Hailer, N. P. (2023). Early Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) Treated with Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention (DAIR): Inferior Outcomes in Patients with Staphylococci Resistant to Rifampicin. Antibiotics, 12(11), 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111589







