Incidence of Rifampicin Resistance in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Centre Cohort Study on 238 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Has the incidence of PJI caused by rifampicin-resistant bacteria changed over the last 20 years in a single tertiary referral centre in Sweden?
- Is there an association between the rifampicin resistance of the causative bacteria and treatment failure in PJI?
2. Results
2.1. Cohort Characteristics
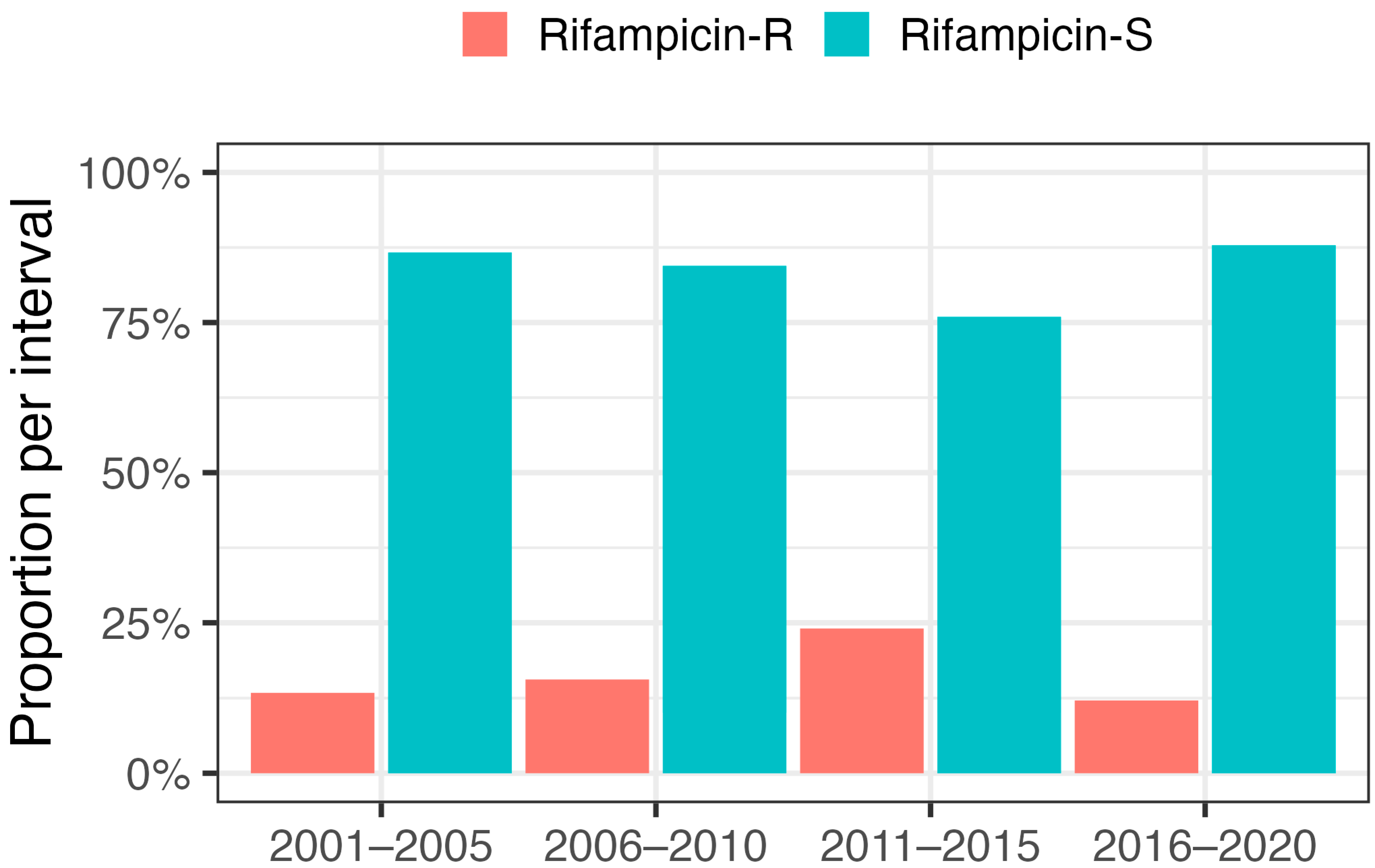
2.2. Incidence of Rifampicin Resistance
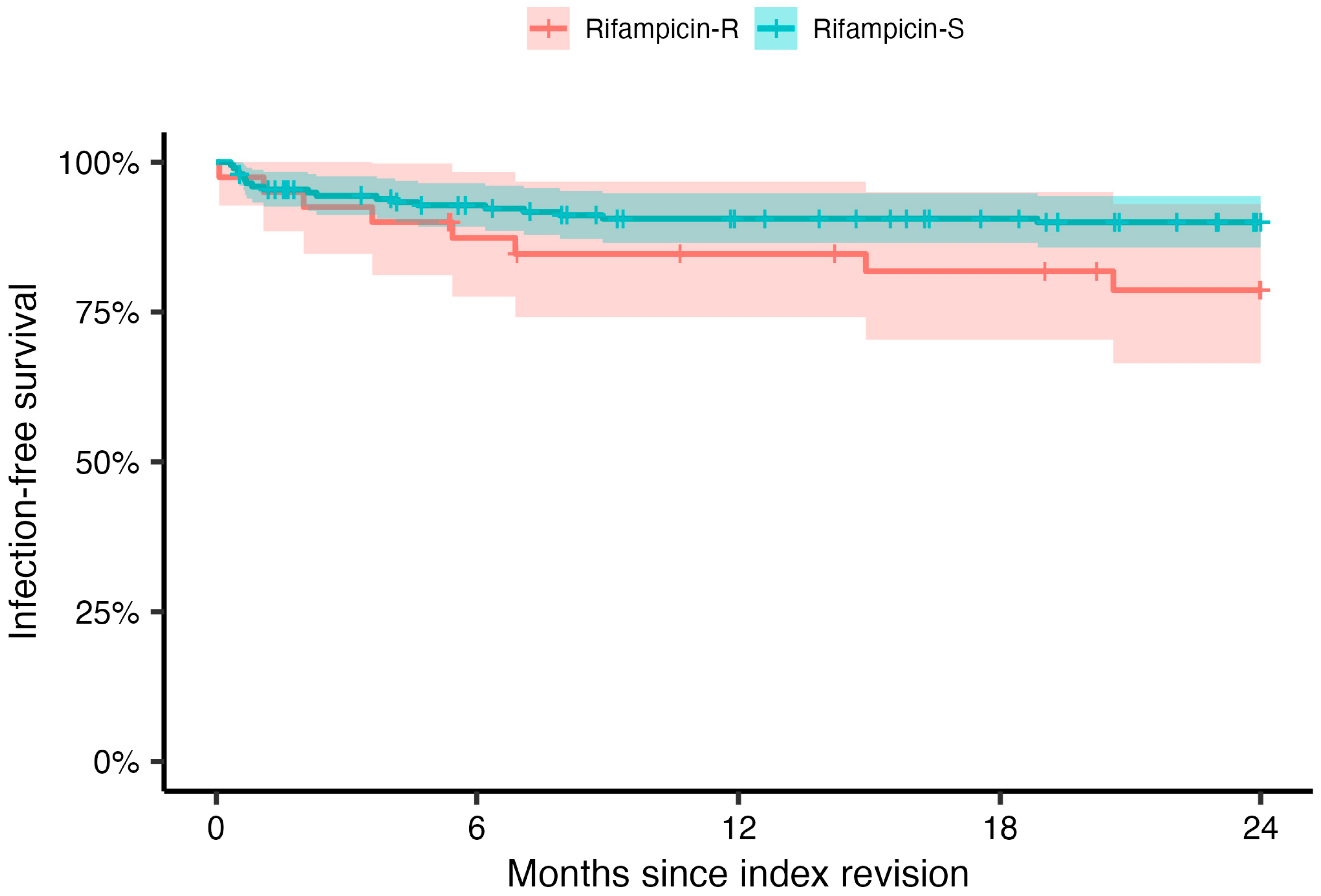
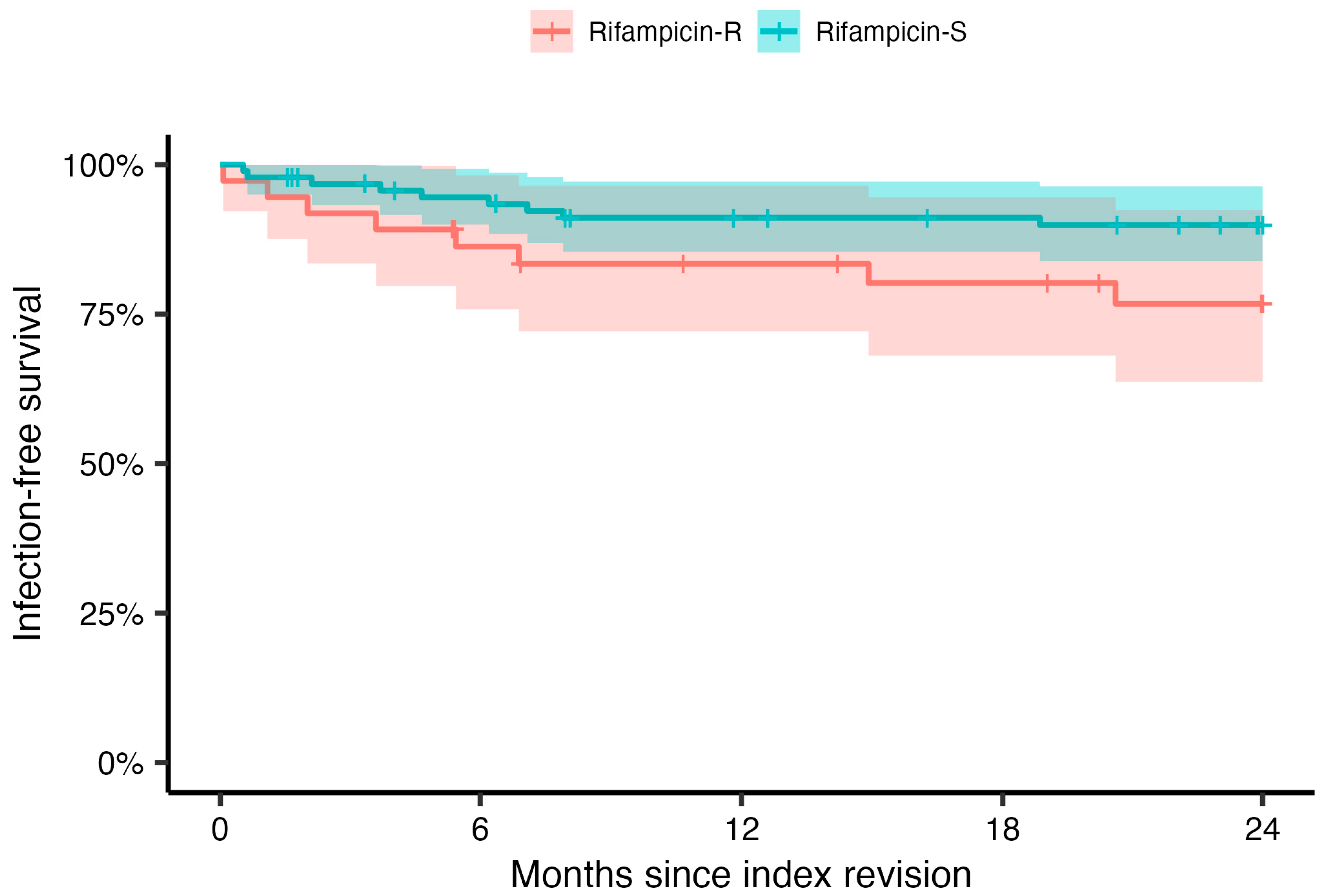
2.3. Treatment Outcomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.S.; Haddad, F.S. Prosthetic joint infection. Bone Joint Res. 2019, 8, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedish Arthroplasty Register 2022. Available online: https://sar.registercentrum.se (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Karachalios, T.; Komnos, G. C. Musculoskeletal Infections. In The EFORT White Book: "Orthopaedics and Traumatology in Europe"; Verhaar, J.A.N., Kjaersgaard-Andersen, P., Limb, D., Gunther, K.P., Karachalios, T., Eds.; Dennis Barber Ltd.: Lowestoft, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, H.; Fenstad, A.M.; Hallan, G.; Overgaard, S.; Pedersen, A.B.; Hailer, N.P.; Karrholm, J.; Rolfson, O.; Eskelinen, A.; Makela, K.T.; et al. Increasing risk of revision due to infection after primary total hip arthroplasty: Results from the Nordic Arthroplasty Register Association. Acta Orthop. 2023, 94, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Luger, M.; Windhager, R.; McNally, M.A. Diagnosing periprosthetic joint infections: A comparison of infection definitions: EBJIS 2021, ICM 2018, and IDSA 2013. Bone Joint Res. 2022, 11, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebse, R. The EBJIS definition of periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, R.; Ribau, A.; Alfaro, P.; Burch, M.A.; Ploegmakers, J.; McNally, M.; Clauss, M.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Soriano, A. The European Bone and Joint Infection Society definition of periprosthetic joint infection is meaningful in clinical practice: A multicentric validation study with comparison with previous definitions. Acta Orthop. 2023, 94, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubb, C.C.; Polkowksi, G.G.; Krause, B. Diagnosis and Prevention of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, e340–e348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Berendt, A.R.; Lew, D.; Zimmerli, W.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Rao, N.; Hanssen, A.; Wilson, W.R.; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, e1–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson Malchau, K.; Tillander, J.; Zaborowska, M.; Hoffman, M.; Lasa, I.; Thomsen, P.; Malchau, H.; Rolfson, O.; Trobos, M. Biofilm properties in relation to treatment outcome in patients with first-time periprosthetic hip or knee joint infection. J. Orthop. Translat. 2021, 30, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, E.; Hanberger, H.; Nilsson, L.E. Pharmacodynamic effects of antibiotics and antibiotic combinations on growing and nongrowing Staphylococcus epidermidis cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrli, W. Rifampin: Mechanisms of action and resistance. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1983, 5 (Suppl. 3), S407–S411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazly Bazzaz, B.S.; Khameneh, B.; Zarei, H.; Golmohammadzadeh, S. Antibacterial efficacy of rifampin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles against Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 93, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beldman, M.; Lowik, C.; Soriano, A.; Albiach, L.; Zijlstra, W.P.; Knobben, B.A.S.; Jutte, P.; Sousa, R.; Carvalho, A.; Goswami, K.; et al. If, When, and How to Use Rifampin in Acute Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infections, a Multicentre Observational Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, C.C.; Ekhtiari, S.; Oral, I.; Selznick, A.; Mundi, R.; Chaudhry, H.; Pincus, D.; Wolfstadt, J.; Kandel, C.E. The Use of Rifampin in Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Kreitmann, L.; Triffaut-Fillit, C.; Valour, F.; Mabrut, E.; Forestier, E.; Lesens, O.; Cazorla, C.; Descamps, S.; Boyer, B.; et al. Duration of rifampin therapy is a key determinant of improved outcomes in early-onset acute prosthetic joint infection due to Staphylococcus treated with a debridement, antibiotics and implant retention (DAIR): A retrospective multicenter study in France. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2020, 5, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roope, L.S.J.; Smith, R.D.; Pouwels, K.B.; Buchanan, J.; Abel, L.; Eibich, P.; Butler, C.C.; Tan, P.S.; Walker, A.S.; Robotham, J.V.; et al. The challenge of antimicrobial resistance: What economics can contribute. Science 2019, 364, eaau4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siljander, M.P.; Sobh, A.H.; Baker, K.C.; Baker, E.A.; Kaplan, L.M. Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in the Setting of Periprosthetic Joint Infection-Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froschen, F.S.; Randau, T.M.; Franz, A.; Molitor, E.; Hoerauf, A.; Hischebeth, G.T.R. Microbiological Trends and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns in Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip or Knee over 6 Years. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STRAMA. Available online: https://strama.se (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Care Program for Joint and Bone Infections. Available online: https://infektion.net/vardprogram/led-och-skelettinfektioner/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Stubbings, W.; Bostock, J.; Ingham, E.; Chopra, I. Mechanisms of the post-antibiotic effects induced by rifampicin and gentamicin in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, S.H.; Haeckl, F.P.J.; Muller, R. Beyond the approved: Target sites and inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase from bacteria and fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 1226–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, W. The Mechanism of Bacterial Resistance and Potential Bacteriostatic Strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Fang, R.; Zhou, B.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Dong, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, T. Evolution of resistance mechanisms and biological characteristics of rifampicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains selected in vitro. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, J.R.; Gould, F.K. Prosthetic joint infections: Single versus combination therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Murillo, O.; Iribarren, J.A.; Soriano, A.; Sanchez-Somolinos, M.; Baraia-Etxaburu, J.M.; Rico, A.; Palomino, J.; Rodriguez-Pardo, D.; Horcajada, J.P.; et al. A large multicenter study of methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections managed with implant retention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendi, P.; Zimmerli, W. The use of rifampin in staphylococcal orthopaedic-device-related infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwich, A.; Dally, F.J.; Bdeir, M.; Kehr, K.; Miethke, T.; Hetjens, S.; Gravius, S.; Assaf, E.; Mohs, E. Delayed Rifampin Administration in the Antibiotic Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections Significantly Reduces the Emergence of Rifampin Resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.H.; Giske, C.G.; Wei, Z.Q.; Shen, P.; Heddini, A.; Li, L.J. Epidemiology and characteristics of antimicrobial resistance in China. Drug Resist. Updates 2011, 14, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, E.; Aithma, N.; Perovic, O.; Oosthuysen, W.F.; Musenge, E.; Duse, A.G. Antimicrobial susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from South Africa. S. Afr. Med. J. 2009, 99, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Stevoska, S.; Himmelbauer, F.; Stiftinger, J.; Stadler, C.; Pisecky, L.; Gotterbarm, T.; Klasan, A. Significant Difference in Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacteria in Septic Revision between Total Knee Arthroplasty and Total Hip Arthroplasty. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, N.S.; Seeber, G.; Soriano, A.; Jutte, P.C.; Westermann, S.; Mithoe, G.; Pirii, L.; Siebers, T.; Have, B.T.; Zijlstra, W.; et al. The Clinical Outcome of Early Periprosthetic Joint Infections Caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis and Managed by Surgical Debridement in an Era of Increasing Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, J.A.; Pust, T.M.; Cappellini, A.J.; Mandell, J.B.; Ma, D.; Shah, N.B.; Brothers, K.M.; Urish, K.L. Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms Have a High Tolerance to Antibiotics in Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Life 2020, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizsan, G.; Sallai, I.; Veres, D.S.; Prinz, G.; Szeker, D.; Skaliczki, G. Rifampicin resistance and risk factors associated with significantly lower recovery rates after two-stage revision in patients with prosthetic joint infection. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 30, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achermann, Y.; Eigenmann, K.; Ledergerber, B.; Derksen, L.; Rafeiner, P.; Clauss, M.; Nuesch, R.; Zellweger, C.; Vogt, M.; Zimmerli, W. Factors associated with rifampin resistance in staphylococcal periprosthetic joint infections (PJI): A matched case-control study. Infection 2013, 41, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, O.E.; Borgen, P.; Bragnes, B.; Figved, W.; Grogaard, B.; Rydinge, J.; Sandberg, L.; Snorrason, F.; Wangen, H.; Witsoe, E.; et al. Rifampin combination therapy in staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections: A randomized controlled trial. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Goto, M.; Nair, R.; Livorsi, D.J.; Sekar, P.; Ohl, M.E.; Diekema, D.J.; Perencevich, E.N.; Alexander, B.; Jones, M.P.; et al. Effectiveness and Optimal Duration of Adjunctive Rifampin Treatment in the Management of Staphylococcus aureus Prosthetic Joint Infections After Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourtet-Hascoet, J.; Bicart-See, A.; Felice, M.P.; Giordano, G.; Bonnet, E. Staphylococcus lugdunensis, a serious pathogen in periprosthetic joint infections: Comparison to Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 51, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajic, I.; Kabic, J.; Kekic, D.; Jovicevic, M.; Milenkovic, M.; Mitic Culafic, D.; Trudic, A.; Ranin, L.; Opavski, N. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: A Comprehensive Review of Currently Used Methods. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedish Reference Group for Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.sls.se/raf/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Nordic Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Available online: https://www.nordicast.org (accessed on 1 August 2023).
| Total Cohort (n = 238), n (%) | Rifampicin-Sensitive (n = 198), n (%, 95%CI) | Rifampicin-Resistant (n = 40), n (%, 95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 137 (58) | 118 (60, 52–66) | 19 (48, 32–64) |
| Female | 101 (42) | 80 (40, 34–48) | 21 (52, 36–68) |
| Joint | |||
| Hip | 154 (65) | 129 (65, 58–72) | 25 (63, 46–77) |
| Knee | 84 (35) | 69 (35, 28–42) | 15 (38, 23–54) |
| Age | |||
| 16–64 years | 67 (28) | 58 (29, 23–36) | 9 (23, 11–39) |
| 65–74 years | 76 (32) | 59 (30, 24–37) | 17 (43, 27–59) |
| 75–84 years | 62 (26) | 50 (25, 19–32) | 12 (30, 17–47) |
| ≥85 years | 33 (14) | 31 (16, 11–22) | 2 (5, 1–18) |
| Surgery prior to index surgery | |||
| Primary arthroplasty | 149 (63) | 134 (68, 61–74) | 15 (38, 23–54) |
| Revision arthroplasty | 34 (14) | 29 (15, 10–21) | 5 (13, 5–28) |
| DAIR 1 | 40 (17) | 24 (12, 8–18) | 16 (40, 25–57) |
| Other | 15 (6) | 11 (6, 3–10) | 4 (10, 3–25) |
| Index surgery | |||
| DAIR 1 | 159 (67) | 144 (73, 66–79) | 15 (38, 23–54) |
| 2-stage | 63 (26) | 40 (20, 15–27) | 23 (58, 41–73) |
| 1-stage | 16 (7) | 14 (7, 4–12) | 2 (5, 1–18) |
| Causative bacteria | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus | 107 (43) | 104 (53, 45–60) | 3 (7, 2–21) |
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci | 131 (53) | 94 (47, 40–55) | 37 (93, 79–98) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazarinis, S.; Hailer, N.P.; Järhult, J.D.; Brüggemann, A. Incidence of Rifampicin Resistance in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Centre Cohort Study on 238 Patients. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101499
Lazarinis S, Hailer NP, Järhult JD, Brüggemann A. Incidence of Rifampicin Resistance in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Centre Cohort Study on 238 Patients. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(10):1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101499
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazarinis, Stergios, Nils P. Hailer, Josef D. Järhult, and Anders Brüggemann. 2023. "Incidence of Rifampicin Resistance in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Centre Cohort Study on 238 Patients" Antibiotics 12, no. 10: 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101499
APA StyleLazarinis, S., Hailer, N. P., Järhult, J. D., & Brüggemann, A. (2023). Incidence of Rifampicin Resistance in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Centre Cohort Study on 238 Patients. Antibiotics, 12(10), 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101499






