Serum and Prostatic Tissue Concentrations of Cefazolin, Ciprofloxacin and Fosfomycin after Prophylactic Use for Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
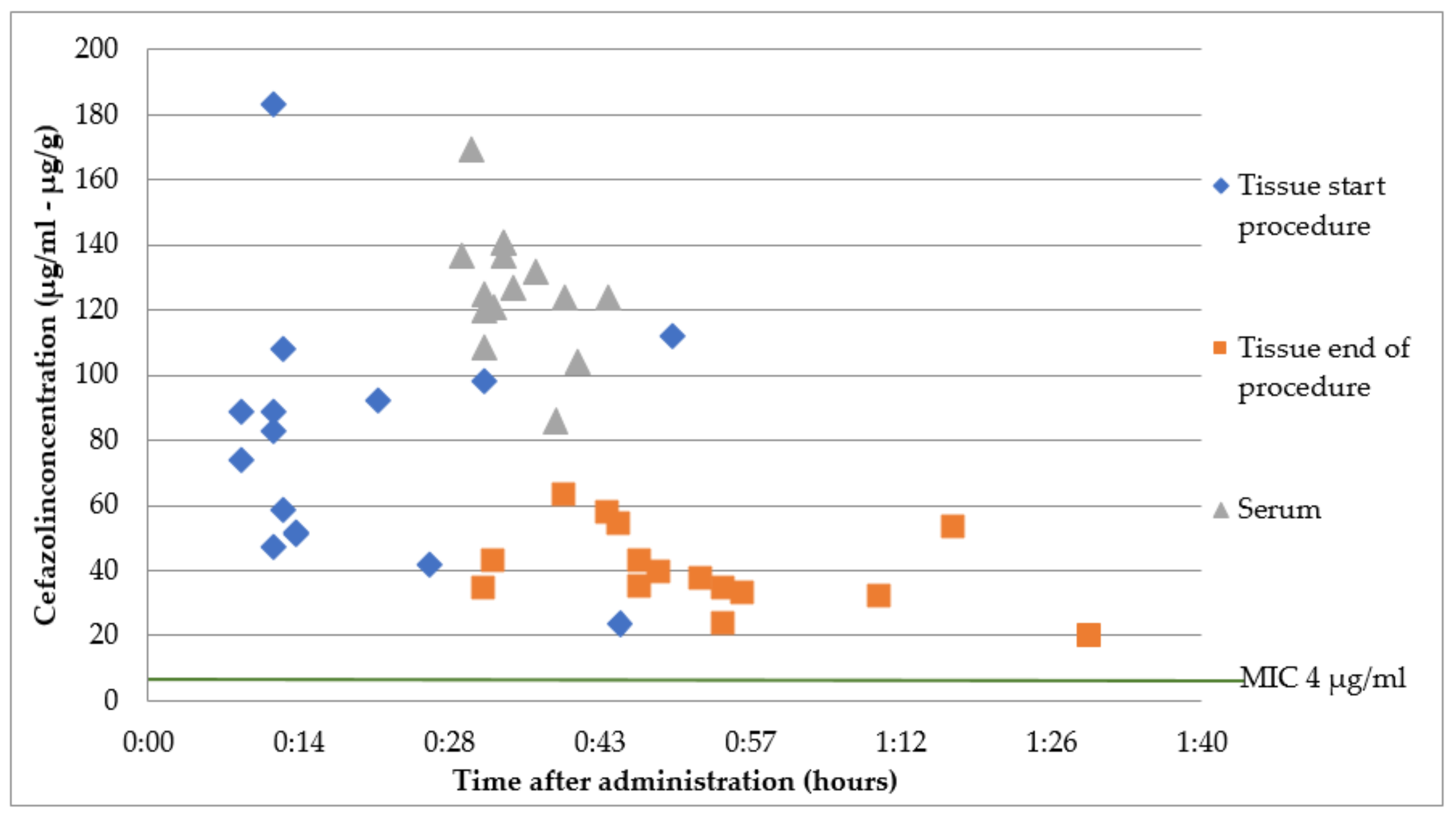
2.1. Group A: Intravenous Cefazolin 2 g Immediately before Surgery
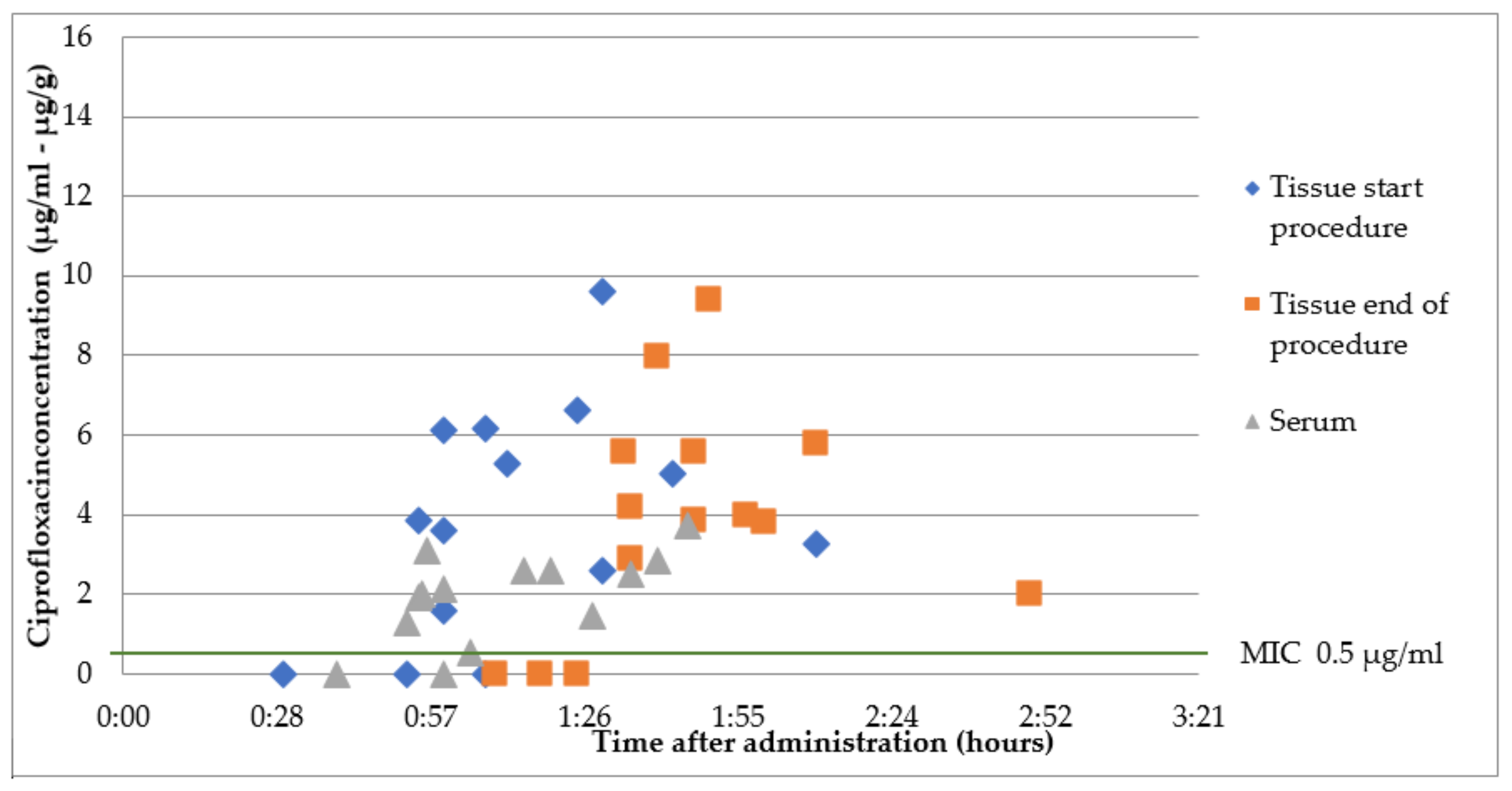
2.2. Group B1: Oral Ciprofloxacin 500 mg 1 h Prior to Surgery
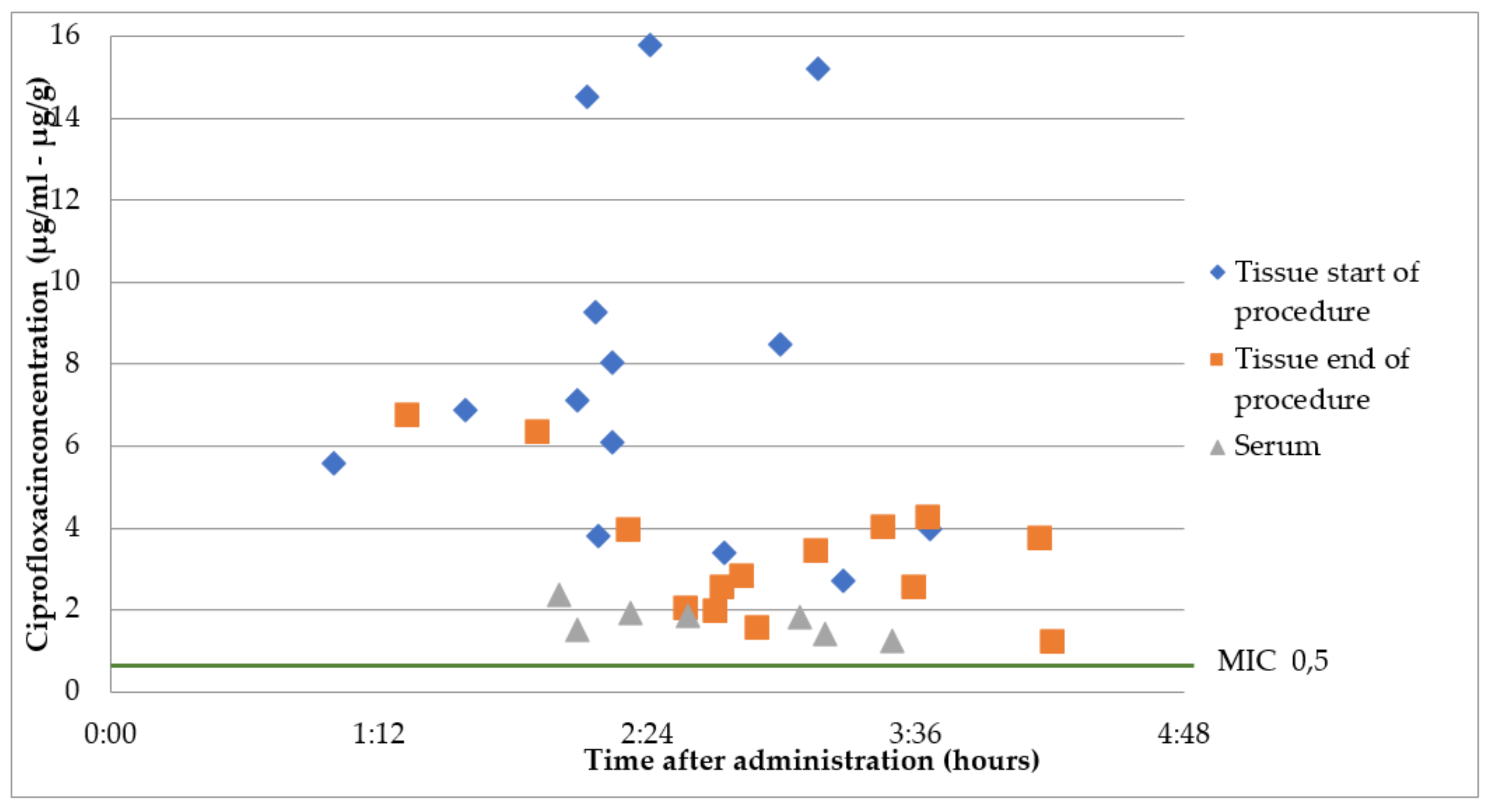
2.3. Group B2: Oral Ciprofloxacin 500 mg 2 h Prior to Surgery
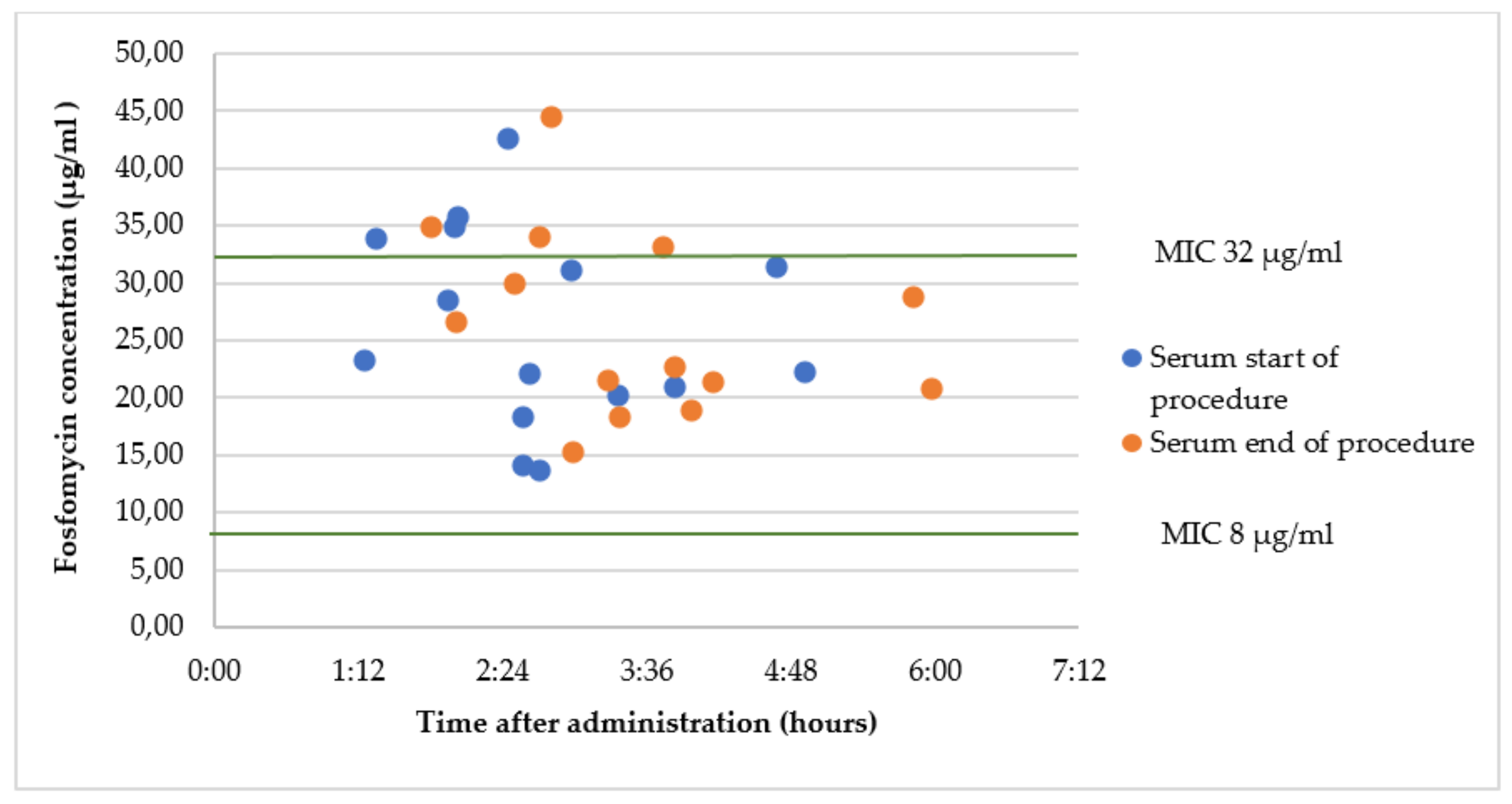
2.4. Group C1: Oral Fosfomycin 3 g 2 h Prior to Surgery
2.5. Group C2: Intravenous Fosfomycin 2 g Immediately before Surgery
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiang, W.; Jianchen, W.; MacDonald, R.; Monga, M.; Wilt, T.J. Antibiotic prophylaxis for transurethral prostatic resection in men with preoperative urine containing less than 100.000 bacteria per mL: A systematic review. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, P.O.; Graversen, P.H. Antimicrobial prophylaxis in transurethral surgery. Infection 1986, 14, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, A.; Barratt, A. Prophylactic antibiotic use in transurethral prostatic resection: A meta-analysis. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmied, S.; Thurmann, P.A.; Roth, S. Antibiotikaprophylaxe bei transurethraler resection der prostate. Urologe 2009, 48, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kastoris, A.C.; Kapaskelis, A.M.; Karageorgopoulos, D.E. Fosfomycin for the treatment of multidrug resistant, including extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Enterobacteriaceae infections: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteo, J.; Bautista, V.; Lara, N.; Cuevas, O.; Arroyo, M.; Fernández, S.; Lázaro, E.; de Abajo, F.J.; Campos, J. Spanish ESBL-EARS-Net Study Group. Parallel increase in community use of fosfomycin and resistance to fosfomycin in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- John, D. Turnidge on behalf of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Cefazolin and Enterobacteriaceae: Rationale for revised susceptibility testing breakpoints. CID 2011, 52, 917–924. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, M.; Koca, O.; Kaya, C.; Karaman, M.I. A prospective randomized and placebo-controlled study for the evaluation of antibiotic prophylaxis in transurethral resection of the prostate. Urol. Int. 2007, 79, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugg, J.; Lettieri, J.; Stass, H.; Agarwal, V. Determination of the concentration of ciprofloxacin in prostate tissue following administration of a single, 1000mg, extended-release dose. J. Chemother. 2008, 20, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Fei, X.; Shi, H. Contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasound for assessing vascularisation of hypoechoic BPH nodules in the transition and peripheral zones: Comparison with pathological examination. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, S.G.; Dijkmans, A.C.; Wilms, E.B.; Kamerling, I.M.C.; Burggraaf, J.; Stevens, J.; van Nieuwkoop, C. Pharmacokinetics of fosfomycin in patients with prophylactic treatment for recurrent Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz Zacarías, N.V.; Dijkmans, A.C.; Burggraaf, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Wilms, E.B.; van Nieuwkoop, C.; Touw, D.J.; Kamerling, I.M.C.; Stevens, J. Fosfomycin as a potential therapy for the treatment of systemic infections: A population pharmacokinetic model to simulate multiple dosing regimens. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2018, 6, e00378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, B.J.; Mahony, A.A.; Ellis, A.G.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Bolton, D.M.; Zeglinski, P.T.; Frauman, A.G.; Grayson, M.L. Is fosfomycin a potential treatment alternative for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative prostatitis? Clin. Infect. Dis. OffPubl Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2014, 58, e101–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, N.; Ra, S.; Okada, S.; Sakakibara, T.; Tonami, H.; Kitagawa, Y.; Miyazaki, S. Transference of antibiotics into prostatic tissues: Sampling method by transurethral resection for the measurement of the concentration of antibiotics in prostatic tissue. Hinyokika Kiyo 1986, 32, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pilatz, A.; Veeratterapillay, R.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Omar, M.I.; Pradere, B.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, T.; Mezei, T.; Devlies, W.; Bruyère, F.; et al. European Association of Urology Position Paper on the Prevention of Infectious Complications Following Prostate Biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonkat, G.; Wagenlehner, F. In the Line of Fire: Should Urologists Stop Prescribing Fluoroquinolones as Default? Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Gallelli, L.; Cocci, A.; Tiscione, D.; Verze, P.; Lanciotti, M.; Vanacore, D.; Rizzo, M.; Gacci, M.; Saleh, O.; et al. Antimicrobial prophylaxis for transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy: Fosfomycin trometamol, an attractive alternative. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijma, R.A.; Bahmany, S.; Wilms, E.; van Gelder, T.; Mouton, J.W.; Koch, B.C. A fast and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of fosfomycin in human urine and plasma using one sample preparation method and HILIC chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1061–1062, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group A (n = 15) | Group B1 (n = 14) | Group B2 (n = 16) | Group C1 (n = 15) | Group C2 (n = 15) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median, years (range) | 69 (55–76) | 76 (54–93) | 73 (58–88) | 67 (61–84) | 72 (57–88) |
| Weight, mean, kg (SD) | 88 (±8) | 84 (±16) | 80 (±11) | 80 (±16) | 79 (±22) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2, MDRD, mean (SD) | 82 (±18) | 66 (±17) | 76 (±13) | 92 (±42) | 87 (±24) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobels, A.; Lentjes, K.J.; Froeling, F.M.J.A.; van Nieuwkoop, C.; Wilms, E.B. Serum and Prostatic Tissue Concentrations of Cefazolin, Ciprofloxacin and Fosfomycin after Prophylactic Use for Transurethral Resection of the Prostate. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010022
Sobels A, Lentjes KJ, Froeling FMJA, van Nieuwkoop C, Wilms EB. Serum and Prostatic Tissue Concentrations of Cefazolin, Ciprofloxacin and Fosfomycin after Prophylactic Use for Transurethral Resection of the Prostate. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobels, Annemieke, Koen J. Lentjes, Frank M. J. A. Froeling, Cees van Nieuwkoop, and Erik B. Wilms. 2023. "Serum and Prostatic Tissue Concentrations of Cefazolin, Ciprofloxacin and Fosfomycin after Prophylactic Use for Transurethral Resection of the Prostate" Antibiotics 12, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010022
APA StyleSobels, A., Lentjes, K. J., Froeling, F. M. J. A., van Nieuwkoop, C., & Wilms, E. B. (2023). Serum and Prostatic Tissue Concentrations of Cefazolin, Ciprofloxacin and Fosfomycin after Prophylactic Use for Transurethral Resection of the Prostate. Antibiotics, 12(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010022





