Occurrence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli in Marine Mammals of the North and Baltic Seas: Sentinels for Human Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Species
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Necropsies
2.5. E. coli Isolation and Identification
2.6. Resistance Phenotype
2.7. Resistance Genotype
2.8. Molecular Typing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
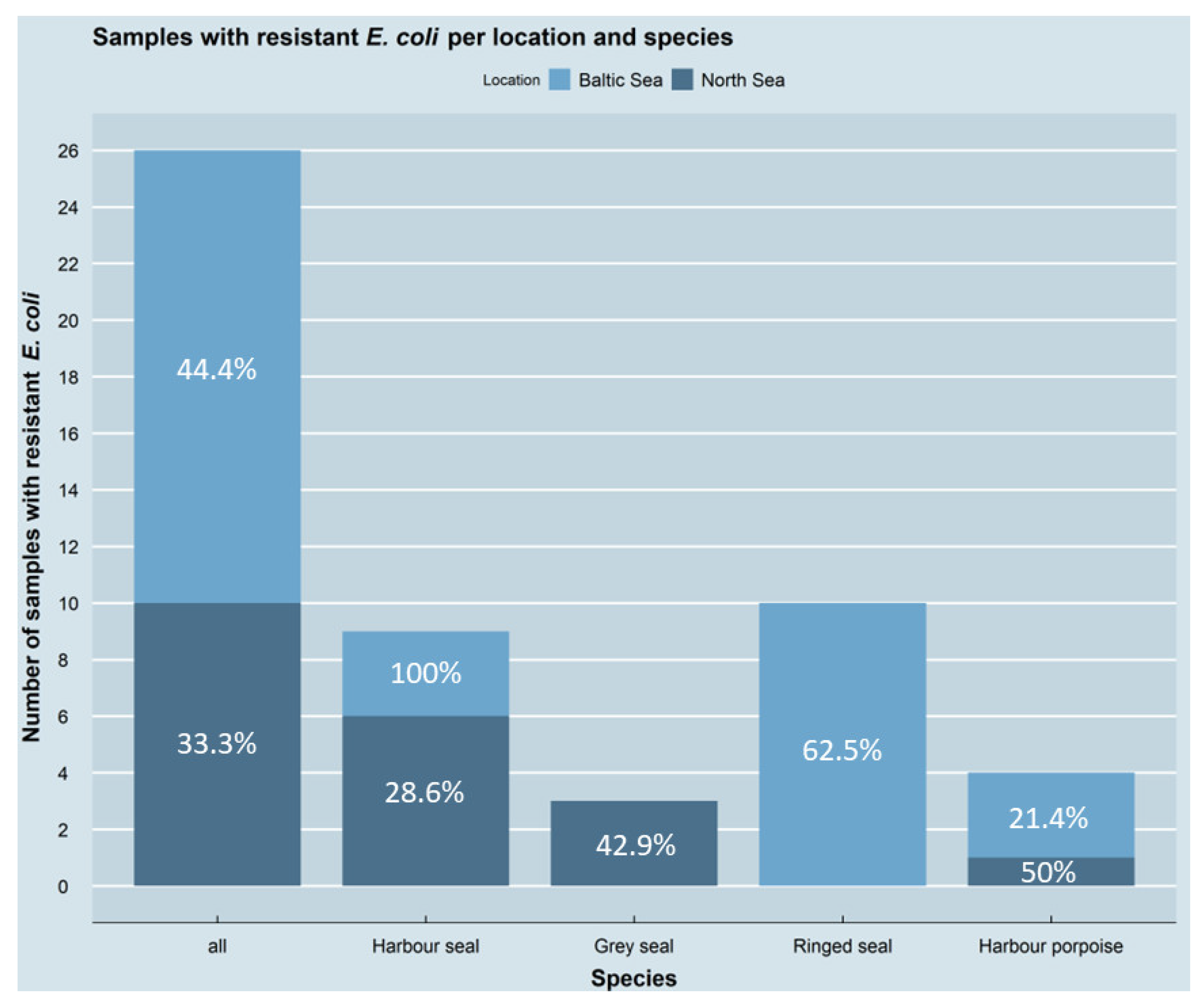
3.1. Occurrence of Antimicrobial-Resistant E. coli Isolates
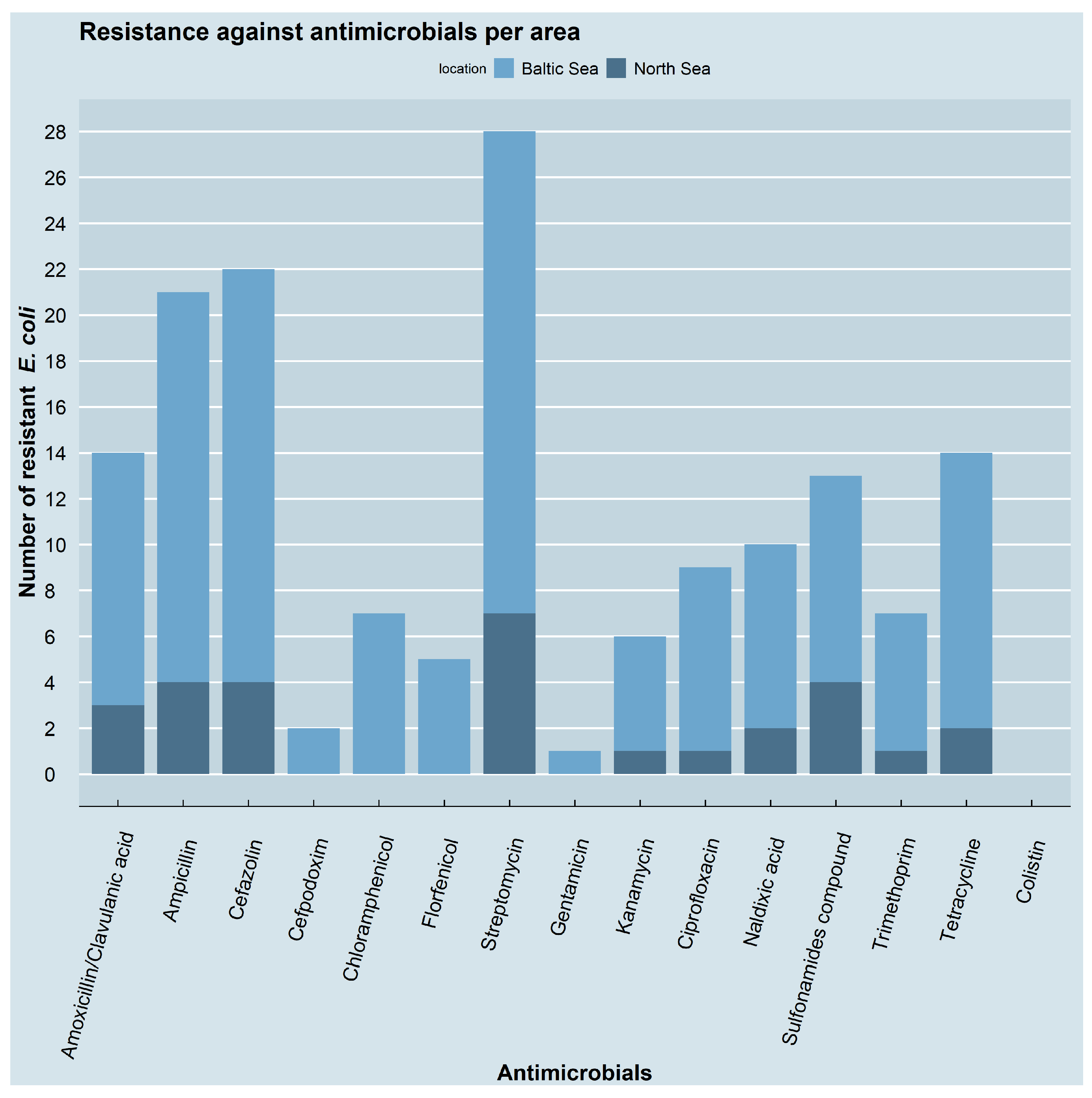
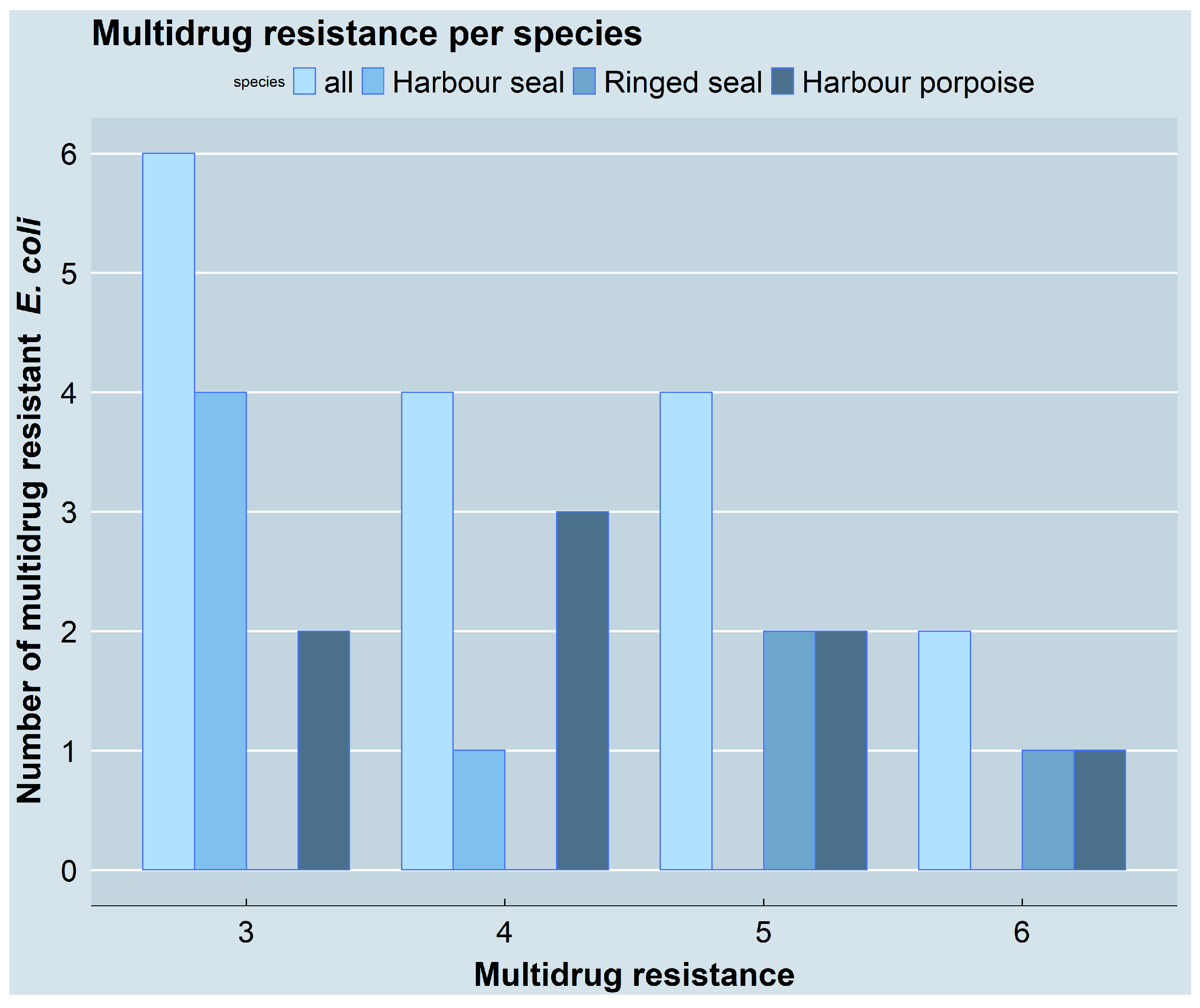
3.2. Resistance Phenotypes and Genotypes
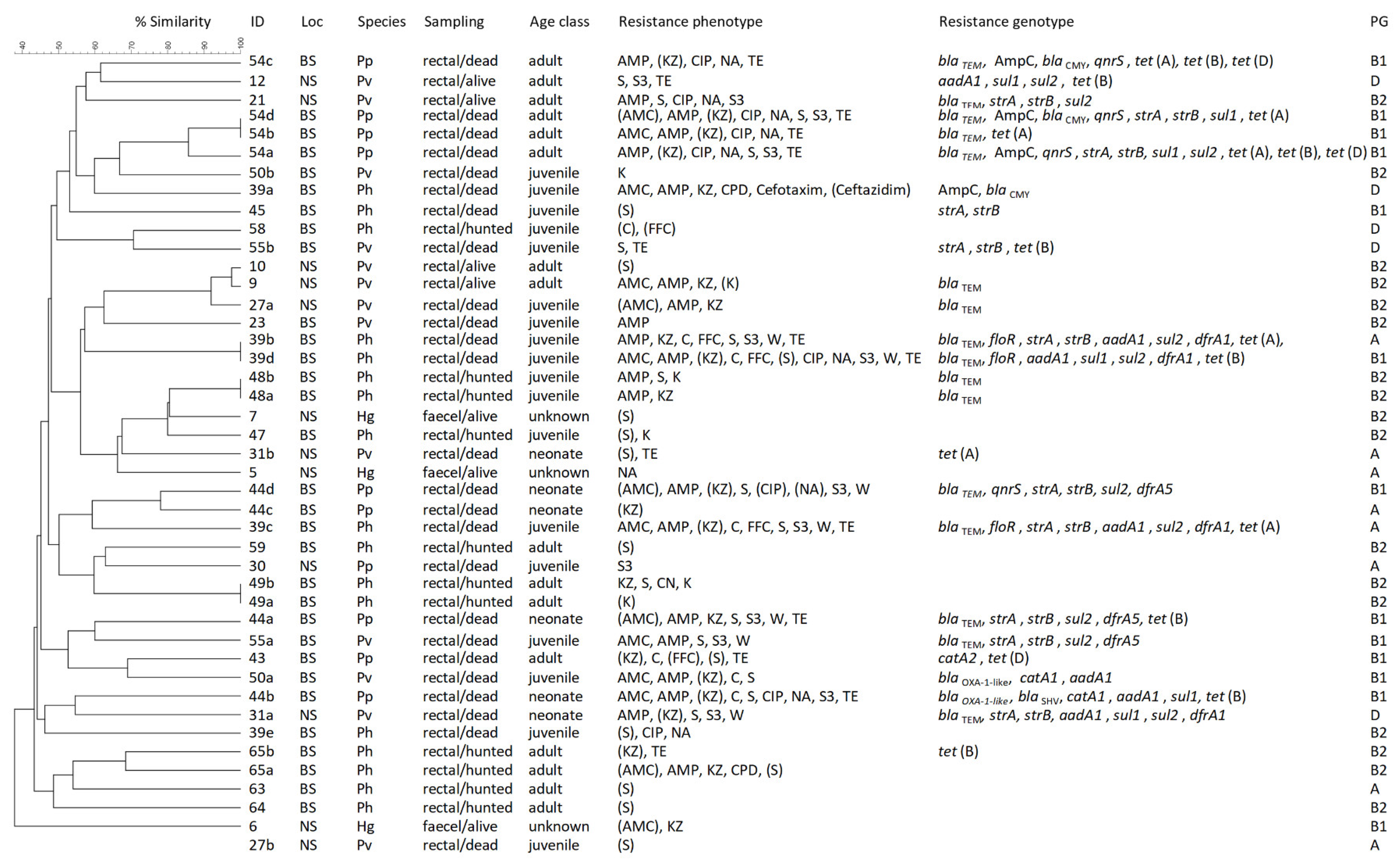
3.3. Molecular Typing
3.4. Health Status and Antimicrobial Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Acar, J.; Davies, J.; Buckley, M. Antibiotic Resistance: An Ecological Perspective on an Old Problem; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Emerging Threat to Public Health Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, A.; Hu, Y.; Bax, R.; Page, C. The Future Challenges Facing the Development of New Antimicrobial Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshland, D.E. The Biological Warfare of the Future. Science 1994, 264, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, C. Reducing the Consumption of Antibiotics: Would That Be Enough to Slow Down the Dissemination of Resistances in the Downstream Environment? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, T.W.; Bemiss, J.A.; Lyon, B.R.; Bossart, G.D.; Fair, P.A. Prevalence and Diversity of Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia coli in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from the Indian River Lagoon, Florida, and Charleston Harbor Area, South Carolina. Aquat. Mamm. 2007, 33, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott Weese, J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Companion Animals. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2008, 9, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Munk, P.; Njage, P.; van Bunnik, B.; McNally, L.; Lukjancenko, O.; Röder, T.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.; Pedersen, S.K.; Kjeldgaard, J.; et al. Global Monitoring of Antimicrobial Resistance Based on Metagenomics Analyses of Urban Sewage. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittecoq, M.; Godreuil, S.; Prugnolle, F.; Durand, P.; Brazier, L.; Renaud, N.; Arnal, A.; Aberkane, S.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Gauthier-Clerc, M.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velhner, M.; Suvajdžić, L.; Petrović, J.; Šepernada, M. Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli in Wild Animals. Arch. Vet. Med. 2012, 5, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, A.M.; Ahlstrom, C.A. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Wildlife: Perspectives on Trends, Acquisition and Dissemination, Data Gaps, and Future Directions. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; et al. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 627821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, S.; Aschenbrenner, K.; Stamm, I.; Bethe, A.; Semmler, T.; Stubbe, A.; Stubbe, M.; Batsajkhan, N.; Glupczynski, Y.; Wieler, L.H.; et al. Comparable High Rates of Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Birds of Prey from Germany and Mongolia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Amábile-Cuevas, C.F. Antibiotic Resistance from, and to the Environment. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Paikin, S.; Rokney, A.; Rubin-Blum, M.; Astrahan, P. Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Coastal Water: An Emerging Threat. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatosy, S.M.; Martiny, A.C. The Ocean as a Global Reservoir of Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7593–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappier, S.P.; Liguori, K.; Ichida, A.M.; Stewart, J.R.; Jones, K.R. Antibiotic Resistance in Recreational Waters: State of the Science. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; McGrann, K.M.; Hughes, D.W.; Right, G.D. Sampling the Antibiotic Resistome. Science 2006, 311, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminov, R.I. The Role of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance in Nature. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2970–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouki, C.; Venieri, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Detection and Fate of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schijven, J.F.; Blaak, H.; Schets, F.M.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Fate of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Faecal Sources in Surface Water and Probability of Human Exposure through Swimming. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11825–11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, B.M.; Brehony, C.; McGrath, E.; Killeen, J.; Cormican, M.; Hickey, P.; Keane, S.; Hanahoe, B.; Dolan, A.; Morris, D. Indistinguishable NDM-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Recreational Waters, Sewage, and a Clinical Specimen in Ireland, 2016 to 2017. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, N.; O’Connor, L.; Mahon, B.; Varley, Á.; McGrath, E.; Ryan, P.; Cormican, M.; Brehony, C.; Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.; et al. Hospital Effluent: A Reservoir for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooban, B.; Fitzhenry, K.; Cahill, N.; Joyce, A.; O’ Connor, L.; Bray, J.E.; Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Abbas Syed, R.; Cormican, M.; et al. A Point Prevalence Survey of Antibiotic Resistance in the Irish Environment, 2018–2019. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, D.; Drum, D.J.V.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Lee, M.D.; Ayers, S.; Sobsey, M.; Maurert, J.J. Free-Living Canada Geese and Antimicrobiai Resistance. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liang, B.; Jiang, B.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Ji, X.; Sun, Y. Migratory Wild Birds Carrying Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli as Potential Transmitters of Antimicrobial Resistance in China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.; Wang, J.; Fanning, S.; McMahon, B.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife: Implications for Public Health. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, X.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Tian, L.; Rao, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, K. Migratory Birds-One Major Source of Environmental Antibiotic Resistance around Qinghai Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarżyńska, M.; Zając, M.; Bomba, A.; Bocian, Ł.; Kozdruń, W.; Polak, M.; Wiącek, J.; Wasyl, D. Antimicrobial Resistance Glides in the Sky—Free-Living Birds as a Reservoir of Resistant Escherichia coli With Zoonotic Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.S.; Rhinehart, H.L.; Hansen, L.J.; Sweeney, J.C.; Townsend, F.I.; Stone, R.; Casper, D.R.; Scott, M.D.; Hohn, A.A.; Rowles, T.K. Bottlenose Dolphins as Marine Ecosystem Sentinels: Developing a Health Monitoring System. Ecohealth 2004, 1, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Tabor, G. Introduction: Marine Vertebrates as Sentinels of Marine Ecosystem Health. Ecohealth 2004, 1, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossart, G.D. Marine Mammals as Sentinel Species for Oceans and Human Health. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A Global Map of Human Impact on Marine Ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, M.L.; Joyce, A.; Duane, S.; Fitzhenry, K.; Hooban, B.; Burke, L.P.; Morris, D. Evaluating the Potential for Exposure to Organisms of Public Health Concern in Naturally Occurring Bathing Waters in Europe: A Scoping Review. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarska, E.; Łuczkiewicz, A.; Pisowacka, M.; Burzyński, A. Antibiotic Resistance and Prevalence of Class 1 and 2 Integrons in Escherichia coli Isolated from Two Wastewater Treatment Plants, and Their Receiving Waters (Gulf of Gdansk, Baltic Sea, Poland). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2018–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.G.H.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Baker-Austin, C. Aquatic Systems: Maintaining, Mixing and Mobilising Antimicrobial Resistance? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.D.; Tello, A.; Keen, P.L. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in Finfish Aquaculture Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 2001–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, J.K.; Mitchell, M.A.; Blackburn, M.-C.H.; Curtis, A.; Thompson, B.A. Evidence of Antibiotic Resistance in Free-Swimming, Top-Level Marine Predatory Fishes. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2010, 41, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Holmes, E.C.; Chen, X.; Tian, J.-H.; Lin, X.-D.; Qin, X.-C.; Gao, W.-H.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.-D.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Diverse and Abundant Resistome in Terrestrial and Aquatic Vertebrates Revealed by Transcriptional Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, D.; Sciortino, S.; Migliore, S.; Galuppo, L.; Puleio, R.; Dara, S.; Vicari, D.; Seminara, S.; Gargano, V. Preliminary Results on the Prevalence of Salmonella spp. in Marine Animals Stranded in Sicilian Coasts: Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile and ARGs Detection in the Isolated Strains. Pathogens 2021, 10, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczkowski, M.; Krawiec, M.; Voslamber, B.; Książczyk, M.; Płoskońska-Bugla, G.; Wieliczko, A. Virulence Genes and the Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Escherichia coli, Isolated from Wild Waterbirds, in the Netherlands and Poland. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marijani, E. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacteria Isolated from Marine and Freshwater Fish in Tanzania. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 4652326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacometti, F.; Pezzi, A.; Galletti, G.; Tamba, M.; Merialdi, G.; Piva, S.; Serraino, A.; Rubini, S. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns in Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica and Escherichia coli Isolated from Bivalve Molluscs and Marine Environment. Food Control 2021, 121, 107590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Bornstein-Forst, S.M.; McLellan, S.L. The Potential for Beach Sand to Serve as a Reservoir for Escherichia coli and the Physical Influences on Cell Die-Off. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.M.; Bossart, G.D.; Mazzoil, M.; Fair, P.A.; Reif, J.S. Risk Factors for Colonization of E. coli in Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida. J. Environ. Public Health 2011, 2011, 597073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ahmed, W.; Sidhu, J.P.S.; Smith, K.; Beale, D.J.; Gyawali, P.; Toze, S. Distributions of Fecal Markers in Wastewater from Different Climatic Zones for Human Fecal Pollution Tracking in Australian Surface Waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, S.; Boire, N.; Carson, K.A.; Vadlamudi, A.; Khuvis, J.; Vadlamudi, V.; Atukorale, V.; Riedel, V.A.A.; Parrish, N.M. A Survey of Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from the Chesapeake Bay and Adjacent Upper Tributaries. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmolka, A.; Nagy, B. Multidrug Resistant Commensal Escherichia coli in Animals and Its Impact for Public Health. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.-Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.-K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekalski, N.; Berthold, T.; Caucci, S.; Egli, A.; Bürgmann, H. Increased Levels of Multiresistant Bacteria and Resistance Genes after Wastewater Treatment and Their Dissemination into Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Elsas, J.D.; Semenov, A.V.; Costa, R.; Trevors, J.T. Survival of Escherichia coli in the Environment: Fundamental and Public Health Aspects. ISME J. 2011, 5, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamborova, I.; Johnston, B.D.; Papousek, I.; Kachlikova, K.; Micenkova, L.; Clabots, C.; Skalova, A.; Chudejova, K.; Dolejska, M.; Literak, I.; et al. Extensive Genetic Commonality among Wildlife, Wastewater, Community, and Nosocomial Isolates of Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 ( H 30R1 and H 30Rx Subclones) That Carry blaCTX-M-27 or blaCTX-M-15. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00519-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbolt, N.J.; Amézquita, A.; Backhaus, T.; Borriello, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Collignon, P.; Coors, A.; Finley, R.; Gaze, W.H.; Heberer, T.; et al. Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA) for Environmental Development and Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemann, A.; Andersen, L.W.; Berggren, P.; Siebert, U.; Benke, H.; Teilmann, J.; Lockyer, C.; Pawliczka, I.; Skóra, K.; Roos, A.; et al. Mitochondrial Control Region and Microsatellite Analyses on Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) Unravel Population Differentiation in the Baltic Sea and Adjacent Waters. Conserv. Genet. 2010, 11, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatius, A.; Kinze, C.C.; Teilmann, J. Population Structure of Harbour Porpoises in the Baltic Region: Evidence of Separation Based on Geometric Morphometric Comparisons. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2012, 92, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lah, L.; Trense, D.; Benke, H.; Berggren, P.; Gunnlaugsson, Þ.; Lockyer, C.; Öztürk, A.; Öztürk, B.; Pawliczka, I.; Roos, A.; et al. Spatially Explicit Analysis of Genome-Wide SNPs Detects Subtle Population Structure in a Mobile Marine Mammal, the Harbor Porpoise. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveegaard, S.; Galatius, A.; Dietz, R.; Kyhn, L.; Koblitz, J.C.; Amundin, M.; Nabe-Nielsen, J.; Sinding, M.-H.S.; Andersen, L.W.; Teilmann, J. Defining Management Units for Cetaceans by Combining Genetics, Morphology, Acoustics and Satellite Tracking. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 3, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härkönen, T.; Brasseur, S.; Teilmann, J.; Vincent, C.; Dietz, R.; Abt, K.; Reijnders, P. Status of Grey Seals along Mainland Europe from the Southwestern Baltic to France. NAMMCO Sci. Publ. 2007, 6, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskovic, R.; Kovacs, K.M.; Hammill, M.O.; White, B.N. Geographic Distribution of Mitochondrial DNA Haplotypes in Grey Seals (Halichoerus grypus). Can. J. Zool. 1996, 74, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.T.; Andersen, L.W.; Dietz, R.; Teilmann, J.; Härkönen, T.; Siegismund, H.R. Integrating Genetic Data and Population Viability Analyses for the Identification of Harbour Seal (Phoca vitulina) Populations and Management Units. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.; Olsen, M.T. Distribution and Population Structure of North Atlantic Harbour Seals (Phoca vitulina). NAMMCO Sci. Publ. 2010, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reeves, R.R. Distribution, Abundance and Biology of Ringed Seals (Phoca hispida): An Overview. NAMMCO Sci. Publ. 1998, 1, 9–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whitehead, P.; Bauchot, L.; Hureau, J.; Nielsen, J.; Tortonese, E. Fishes of the North-Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Benke, H.; Siebert, U.; Lick, R.; Bandomir, B.; Weiss, R. The Current Status of Harbour Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) in German Waters. Arch. Fish. Mar. Res. 1998, 46, 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, U.; Gilles, A.; Lucke, K.; Ludwig, M.; Benke, H.; Kock, K.-H.; Scheidat, M. A Decade of Harbour Porpoise Occurrence in German Waters—Analyses of Aerial Surveys, Incidental Sightings and Strandings. J. Sea Res. 2006, 56, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, U.; Wohlsein, P.; Lehnert, K.; Baumgärtner, W. Pathological Findings in Harbour Seals (Phoca vitulina): 1996–2005. J. Comp. Pathol. 2007, 137, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, U.; Wünschmann, A.; Weiss, R.; Frank, H.; Benke, H.; Frese, K. Post-Mortem Findings in Harbour Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) from the German North and Baltic Seas. J. Comp. Pathol. 2001, 124, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IJsseldijk, L.L.; Brownlow, A.C.; Mazzariol, S. (Eds.) Best Practice on Cetacean Post Mortem Investigation and Tissue Sampling; ASCOBANS/ACCOBAMS: Bonn, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Doumith, M.; Day, M.J.; Hope, R.; Wain, J.; Woodford, N. Improved Multiplex PCR Strategy for Rapid Assignment of the Four Major Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Groups. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3108–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Standard VET01; CLSI Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals. 5th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2018.
- CLSI Supplement VET01S; CLSI Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals. 5th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2020.
- CLSI Supplement M100; CLSI Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 32nd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2022.
- Müller, A.; Jansen, W.; Grabowski, N.T.; Kehrenberg, C. Characterization of Salmonella enterica Serovars Recovered from Meat Products Legally and Illegally Imported into the EU Reveals the Presence of Multiresistant and AmpC-Producing Isolates. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.P.; Cooles, S.W.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Woodward, M.J. Effect of Triclosan or a Phenolic Farm Disinfectant on the Selection of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrenberg, C.; Schwarz, S. Occurrence and Linkage of Genes Coding for Resistance to Sulfonamides, Streptomycin and Chloramphenicol in Bacteria of the Genera Pasteurella and Mannheimia. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 205, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanz, R.; Kuhnert, P.; Boerlin, P. Antimicrobial Resistance and Resistance Gene Determinants in Clinical Escherichia coli from Different Animal Species in Switzerland. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 91, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Agersø, Y.; Ahrens, P.; Jørgensen, J.C.Ø.; Madsen, M.; Jensen, L.B. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Presence of Resistance Genes in Staphylococci from Poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bingen, E. Rapid and Simple Determination of the Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4555–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribot, E.M.; Fair, M.A.; Gautom, R.; Cameron, D.N.; Hunter, S.B.; Swaminathan, B.; Barrett, T.J. Standardization of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Protocols for the Subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2006, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.M.; Gast, R.J.; Bogomolni, A.; Ellis, J.C.; Lentell, B.J.; Touhey, K.; Moore, M. Occurrence and Patterns of Antibiotic Resistance in Vertebrates off the Northeastern United States Coast. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santestevan, N.A.; de Angelis Zvoboda, D.; Prichula, J.; Pereira, R.I.; Wachholz, G.R.; Cardoso, L.A.; de Moura, T.M.; Medeiros, A.W.; de Amorin, D.B.; Tavares, M.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Factor Gene Profiles of Enterococcus spp. Isolates from Wild Arctocephalus australis (South American Fur Seal) and Arctocephalus tropicalis (Subantarctic Fur Seal). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünzweil, O.M.; Palmer, L.; Cabal, A.; Szostak, M.P.; Ruppitsch, W.; Kornschober, C.; Korus, M.; Misic, D.; Bernreiter-Hofer, T.; Korath, A.D.J.; et al. Presence of β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales and Salmonella Isolates in Marine Mammals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, S.A.; Lambourn, D.M.; Huggins, J.L.; Gaydos, J.K.; Dubpernell, S.; Berta, S.; Olson, J.K.; Souze, V.; Evans, A.; Carlson, B.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria in Two Marine Mammal Species, Harbor Seals and Harbor Porpoises, Living in an Urban Marine Ecosystem, the Salish Sea, Washington State, USA. Oceans 2021, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingino, A.; Roberts, M.C.; Wainstein, M.; West, J.; Norman, S.A.; Lambourn, D.; Lahti, J.; Ruiz, R.; D’Angeli, M.; Weissman, S.J.; et al. Surveillance for Antibiotic-Resistant E. coli in the Salish Sea Ecosystem. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R.; Townsend, F.I.; Lane, S.M.; Dyar, E.; Hohn, A.A.; Rowles, T.K.; Staggs, L.A.; Wells, R.S.; Balmer, B.C.; Schwacke, L.H. Survey of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Bottlenose Dolphins Tursiops truncatus in the Southeastern USA. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2014, 108, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, A.P.; Shubin, L.; Cummins, J.; Leonard, F.C.; Barry, G. Detection of BlaOXA-1, BlaTEM-1, and Virulence Factors in E. coli Isolated From Seals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 583759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Nóbrega Carneiro, C.; Villada Rosales, A.M.; Grilo, M.; Ramiro, Y.; Cunha, E.; Nunes, T.; Tavares, L.; Sandi, J.; Oliveira, M. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Enterobacterales Isolated from Two-Finger and Three-Finger Sloths (Choloepus hoffmanni and Bradypus variegatus) of Costa Rica. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Grilo, M.L.; Carneiro, C.; Cunha, E.; Tavares, L.; Patino-Martinez, J.; Oliveira, M. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) of the Island of Maio, Cape Verde. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Monteiro, J.L.; Rana, S.; Vilela, C.L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Positive Bacteria from Timorese River Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Skin Microbiota. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Lepoint, G.; Leroy, Y.; Bouquegneau, J.M. Marine Mammals from the Southern North Sea: Feeding Ecology Data from Δ13C and Δ15N Measurements. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 263, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, O.E.; Aarts, G.M.; Das, K.; Lepoint, G.; Michel, L.; Reijnders, P.J.H. Feeding Ecology of Harbour Porpoises: Stable Isotope Analysis of Carbon and Nitrogen in Muscle and Bone. Mar. Biol. Res. 2012, 8, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinisalo, T.; Valtonen, E.T.; Helle, E.; Jones, R.I. Combining Stable Isotope and Intestinal Parasite Information to Evaluate Dietary Differences between Individual Ringed Seals (Phoca hispida botnica). Can. J. Zool. 2006, 84, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suuronen, P.; Lehtonen, E. The Role of Salmonids in the Diet of Grey and Ringed Seals in the Bothnian Bay, Northern Baltic Sea. Fish. Res. 2012, 125–126, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, B.J.; Fedak, M.A.; Lovell, P.; Hammond, P.S. Movements and Foraging Areas of Grey Seals in the North Sea. J. Appl. Ecol. 1999, 36, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtsheim, D.A.; Viquerat, S.; Ramírez-Martínez, N.C.; Unger, B.; Siebert, U.; Gilles, A. Small Cetacean in a Human High-Use Area: Trends in Harbor Porpoise Abundance in the North Sea Over Two Decades. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 606609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, S.K.; Chovan, J.L.; Gaydos, J.K. Aerobic Bacterial Isolations from Harbor Seals (Phoca vitulina) Stranded in Washington: 1992–2003. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2006, 37, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, A.M.; Goldstein, J.D.; Reif, J.S.; Fair, P.A.; Bossart, G.D. Antibiotic-Resistant Organisms Cultured from Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Inhabiting Estuarine Waters of Charleston, SC and Indian River Lagoon, FL. Ecohealth 2009, 6, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.P.; Nolan, S.; Gulland, F.M.D. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bacteria Isolated from Pinnipeds Stranded in Central and Northern California. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1998, 29, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Bundesamt für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit. Paul-Ehrlich-Gesellschaft für Chemotherapie e.V. In GERMAP 2015—Bericht Über Den Antibiotikaverbrauch und die Verbreitung Von Antibiotikaresistenzen in der Human- und Veterinärmedizin in Deutschland; Antiinfectives Intelligence: Rheinbach, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Access, Watch, Reserve (AWaRe) Classification of Antibiotics for Evaluation and Monitoring of Use. 2021. (WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.04); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Ramirez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E. Aminoglycoside Modifying Enzymes. Drug Resist. Update 2010, 13, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Mechanisms of Drug Resistance: Quinolone Resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, B.F.; de Campos, P.A.; Royer, S.; Ferreira, M.L.; Gonçalves, I.R.; da Fonseca Batistão, D.W.; Resende, D.S.; de Brito, C.S.; Gontijo-Filho, P.P.; Ribas, R.M. High Frequency of the Combined Presence of QRDR Mutations and PMQR Determinants in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli Isolates from Nosocomial and Community-Acquired Infections. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, D.N.; Mahdy, W.K.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Khairy, R.M.M. Impact of Co-Existence of PMQR Genes and QRDR Mutations on Fluoroquinolones Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Strains Isolated from Community and Hospital Acquired UTIs. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.A. The Importance of Efflux Pumps in Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Reales-Calderon, J.; Corona, F.; Lira, F.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Bernardini, A.; Sanchez, M.; Martinez, J. Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps: Much More Than Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzer, P.J.; Inouye, S.; Inouye, M.; Whittam, T.S. Phylogenetic Distribution of Branched RNA-Linked Multicopy Single-Stranded DNA among Natural Isolates of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 6175–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingen, E.; Picard, B.; Brahimi, N.; Mathy, S.; Desjardins, P.; Elion, J.; Denamur, E. Phylogenetic Analysis of Escherichia coli Strains Causing Neonatal Meningitis Suggests Horizontal Gene Transfer from a Predominant Pool of Highly Virulent B2 Group Strains. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, E.F.; Hartl, D.L. Chromosomal Regions Specific to Pathogenic Isolates of Escherichia coli Have a Phylogenetically Clustered Distribution. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, B.; Garcia, J.S.; Gouriou, S.; Duriez, P.; Brahimi, N.; Bingen, E.; Elion, J.; Denamur, E. The Link between Phylogeny and Virulence in Escherichia coli Extraintestinal Infection. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, T.; Clermont, O.; Gouriou, S.; Picard, B.; Nassif, X.; Denamur, E.; Tenaillon, O. Extraintestinal Virulence Is a Coincidental By-Product of Commensalism in B2 Phylogenetic Group Escherichia coli Strains. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, T.C.; Harcourt, R.G.; Beaumont, L.J.; Webster, K.N.; Power, M.L. Molecular Detection of Antibiotic-Resistance Determinants in Escherichia coli Isolated from the Endangered Australian Sea Lion (Neophoca cinerea). J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulham, M.; Power, M.; Gray, R. Diversity and Distribution of Escherichia coli in Three Species of Free-Ranging Australian Pinniped Pups. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 571171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Páramo, P.; Le Menac’h, A.; Le Gall, T.; Amorin, C.; Gouriou, S.; Picard, B.; Skurnik, D.; Denamur, E. Identification of Forces Shaping the Commensal Escherichia coli Genetic Structure by Comparing Animal and Human Isolates. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppe, N.D.C.; Silva, J.S.; Carlos, C.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Saraiva, A.M.; Ottoboni, L.M.M.; Torres, T.T. Worldwide Phylogenetic Group Patterns of Escherichia coli from Commensal Human and Wastewater Treatment Plant Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.M.; Cowling, A. The Distribution and Genetic Structure of Escherichia coli in Australian Vertebrates: Host and Geographic Effects. Microbiology 2003, 149, 3575–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufler, K.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Wöhrmann, M.; Baddam, R.; Ahmed, N.; Müller, K.; Kola, A.; Fruth, A.; Ewers, C.; et al. Clonal Spread and Interspecies Transmission of Clinically Relevant ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli of ST410—Another Successful Pandemic Clone? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiv155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Resistance Gene | All | Harbour Seal | Ringed Seal | Harbour Porpoise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaTEM | 16 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| blaSHV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| blaOXA-1-like | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| blaCMY | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| strA | 11 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| strB | 11 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| aadA1 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| catA1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| catA2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| floR | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| tet(A) | 7 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| tet(B) | 8 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| tet(D) | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| sul1 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| sul2 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| dfrA1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| dfrA5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| qnrS | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Phylogenetic Group | A | B1 | B2 | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 8 (18.6%) | 13 (30.2%) | 17 (39.5%) | 5 (11.6%) |
| Harbour seal | 2 (15.4%) | 2 (15.4%) | 6 (46.2%) | 3 (23.1%) |
| Grey seal | 1 (33.3%) | 1 (33.3%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0 |
| Ringed seal | 3 (17.6%) | 2 (11.8%) | 10 (58.8%) | 2 (11.8%) |
| Harbour porpoise | 2 (20.0%) | 8 (80.0%) | 0 | 0 |
| Antimicrobial-Resistant Isolates | Yes | No | |
|---|---|---|---|
| overall health | good | 2 | 3 |
| moderate | 10 | 11 | |
| poor | 8 | 7 | |
| body condition | good | 6 | 12 |
| moderate | 6 | 5 | |
| poor | 4 | 3 | |
| sex | male | 11 | 10 |
| female | 9 | 11 | |
| age | neonate | 2 | 1 |
| juvenile | 11 | 13 | |
| adult | 7 | 6 | |
| (broncho)pneumonia | yes | 6 | 6 |
| no | 14 | 15 | |
| sepsis | yes | 8 | 10 |
| no | 12 | 11 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gross, S.; Müller, A.; Seinige, D.; Wohlsein, P.; Oliveira, M.; Steinhagen, D.; Kehrenberg, C.; Siebert, U. Occurrence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli in Marine Mammals of the North and Baltic Seas: Sentinels for Human Health. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091248
Gross S, Müller A, Seinige D, Wohlsein P, Oliveira M, Steinhagen D, Kehrenberg C, Siebert U. Occurrence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli in Marine Mammals of the North and Baltic Seas: Sentinels for Human Health. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(9):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091248
Chicago/Turabian StyleGross, Stephanie, Anja Müller, Diana Seinige, Peter Wohlsein, Manuela Oliveira, Dieter Steinhagen, Corinna Kehrenberg, and Ursula Siebert. 2022. "Occurrence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli in Marine Mammals of the North and Baltic Seas: Sentinels for Human Health" Antibiotics 11, no. 9: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091248
APA StyleGross, S., Müller, A., Seinige, D., Wohlsein, P., Oliveira, M., Steinhagen, D., Kehrenberg, C., & Siebert, U. (2022). Occurrence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli in Marine Mammals of the North and Baltic Seas: Sentinels for Human Health. Antibiotics, 11(9), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091248







