Abstract
Enrofloxacin (ENR) is a member of quinolones, which are extensively used in livestock farming and aquaculture to fight various bacterial diseases, but its residues are partially transferred to surface water and affect the local aquatic ecosystem. There are many studies on the effect of ENR on the growth of a single aquatic species, but few on the level of the aquatic community. Epiphytic algae, which are organisms attached to the surface of submerged plants, play an important role in the absorption of nitrogen and phosphorus in the ecological purification pond which are mainly constructed by submerged plants, and are commonly used in aquaculture effluent treatment. Enrofloxacin (ENR) is frequently detected in aquaculture ponds and possibly discharged into the purification pond, thus imposing stress on the pond ecosystem. Here, we performed a microcosm experiment to evaluate the short-term effects of pulsed ENR in different concentrations on the epiphytic algal communities growing on Vallisneria natans. Our results showed an overall pattern of “low-dose-promotion and high-dose-inhibition”, which means under low and median ENR concentrations, the epiphytic algal biomass was promoted, while under high ENR concentrations, the biomass was inhibited. This pattern was mainly attributed to the high tolerance of filamentous green algae and yellow-green algae to ENR. Very low concentrations of ENR also favored the growth of diatoms and cyanobacteria. These results demonstrate a significant alteration of epiphytic algal communities by ENR and also spark further research on the potential use of filamentous green algae for the removal of ENR in contaminated waters because of its high tolerance.
1. Introduction
Enrofloxacin (ENR) is a representative of third-generation quinolones. It is often used in livestock farming and aquaculture to treat animal skin infections, bacterial diseases, and respiratory tract mycoplasma infections due to its broad spectrum of antibacterial activity, low cost, and lack of cross-resistance [1,2,3,4]. It has a long half-life in the water environment, and its metabolite, ciprofloxacin, degrades slowly, which can prolong the metabolic time of enrofloxacin in water [5]. This leads to the long-term exposure of aquatic organisms to low concentrations of ENR [6], enhancing their resistance to ENR and producing resistance genes [7,8], and creating chronic toxic effects in the antioxidant defense system and organ and tissue damage [9]. Furthermore, residual ENR endangers people’s health, reduces food safety, and seriously affects the ecological balance of water bodies through food chain transmission [10]. Therefore, ENR has become one of the most frequently detected emerging pollutants in surface water [11,12,13,14].
Aquatic plants, especially submerged plants, play important roles in the function of ecological purification ponds and are widely used in aquaculture effluent treatments [15,16]. Submerged plants degrade pollutants through the absorption and enrichment of them in the water body and the microbial communities formed around the plants [17]. Epiphytic algae are often attached to the surface of submerged plants. Together with bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and inorganic and organic debris, they make up a tiny ecosystem independent of plants and water [18,19] and make a significant contribution to the absorption and degradation of nutrients. Meanwhile, epiphytic algae have a high sensitivity to water pollutants and are closely related to the pH and nutrients of the surrounding environment [20,21,22], making them a useful indicator for monitoring polluted water [23,24].
Many studies have evaluated the impact of antibiotics on single species of aquatic organisms, and the non-observed effect concentration varies widely depending on the species [1,25,26], but little has been known of the influence of ENR on aquatic systems at the community level thus far. Therefore, we performed mesocosm experiments to assess the short-term effects of pulsed ENR in different concentrations on the epiphytic algal communities growing on Vallisneria natans, a submerged plant that is the most used in ecological restoration and purification. We monitored the cell density and biomass of different groups of algae to evaluate the community alteration under the stress of different concentrations of enrofloxacin (ENR). We hope the outcomes add crucial information to help perform exposure assessments and remove antibiotics from contaminated waters.
2. Results
2.1. Total Algal Density and Biomass
The density and biomass changed roughly synchronously. They were both greater than the control group under low and median ENR concentrations and smaller than the control group under high ENR concentrations, i.e., they exhibited a pattern of “low-dose-promotion and high-dose-inhibition”. The biomass of T3 had the highest value. However, the differences between groups are generally not significant due to the large deviation (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The biomass is more comparable because the cell size varies a lot, so we used biomass in the flowing analysis. A significant relationship was noted between the biomass and ENR concentrations (p < 0.05).
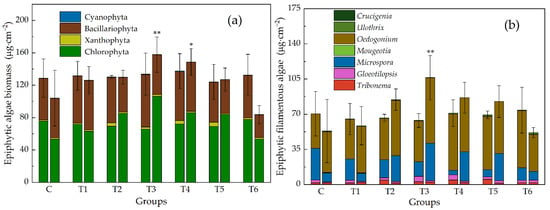
Figure 1.
Biomass of epiphytic algae, (a) at phylum level, (b) epiphytic filamentous algae at genus level. Each group has two histograms (right: Initial; left: 7 d). Groups: C, control group; T1–T6, treatment groups, and the corresponding concentrations of ENR are 0.001, 0.2, 1.13, 6.33, 35.6, and 200 mg · L−1, respectively. Stars above the histogram show significant differences between control group and treatment groups (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).
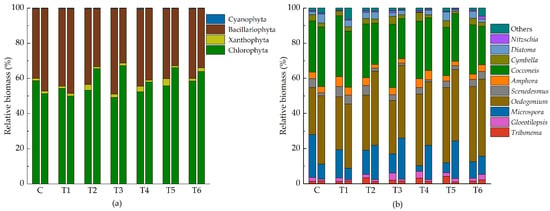
Figure 2.
Community composition of relative biomass of epiphytic algae ((a) at phylum level, (b) at genus level). Each group has two histograms (right: Initial, left: 7 d). Abbreviations for groups are the same as in Figure 1.
2.2. Change in Algal Groups
The biomass of four main groups of algae in this experiment—Chlorophyta, Xanthophyta, Bacillariophyta, and Cyanophyta—changed asynchronously (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Under low ERN concentrations, they were all greater than the control group, but when ENR exceeded 1.13 mg · L−1, diatoms and cyanobacteria decreased along with the increased ENR. In contrast, Chlorophyta and Xanthophyta peaked in T3, and in T5, the recorded biomass was still greater than in the control group. The increase in total biomass was mainly a result of the increase in filamentous algae (Figure 3). The change in the filamentous algal biomass was significantly correlated with the concentration of ENR.
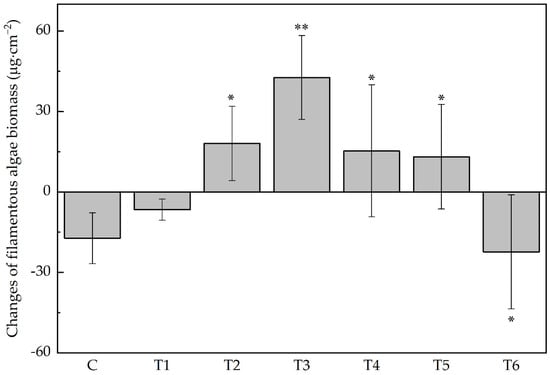
Figure 3.
Changes in the filamentous algal biomass. Abbreviations for groups are the same as in Figure 1. Stars above the histogram show significant difference between control group and treatment groups (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).
2.3. Change of Species
A total of 49 species of epiphytic algae were identified, belonging to 4 phyla and 24 genera (Supplementary Figure S1). Green algae (Chlorophyta) and diatoms (Bacillariophyta) are dominant in the epiphytic algal community, while the relative biomass of the yellow-green algae (Xanthophyta) and blue-green algae (Cyanophyta) was smaller in comparison (Figure 2).
At the end of the experiment, the dominant species slightly varied in the experimental groups (Figure 4). Cocconeis placentula, Microspora sp1, and Oedocladium spp. were commonly dominant in all the samples. In the control group, the higher or highest recorded biomass was for the species Oedocladium sp1, Oedocladium sp2, Oedocladium sp5, Microspora sp1, and C. placentula. In treatment group T1, the highest values were recorded for the species Oedocladium sp1, Oedocladium sp4, Oedocladium sp3, C. placentula, etc. In treatment group T2, the highest values were recorded for the species Oedocladium sp1, Oedocladium sp2, Oedocladium sp4, Oedocladium sp5 Microspora sp1, and C. placentula. Microspora sp1, C. placentula, Oedogonium sp1, Oedogonium sp2, and Oedogonium sp4 had the highest recorded biomass in treatment group T3. The biomass of C. placentula, Oedogonium sp1, Oedogonium sp2, and Oedogonium sp3 was dominant in terms of the biomass in treatment groups T4 and T5. In treatment group T6, the biomass of C. placentula, Oedogonium sp1, Oedogonium sp2, and Gloeotilopsis sp1 was relatively high. The relative biomass of Scenedesmus quadricauda under the ENR concentration of 200 mg∙L−1 was also high.
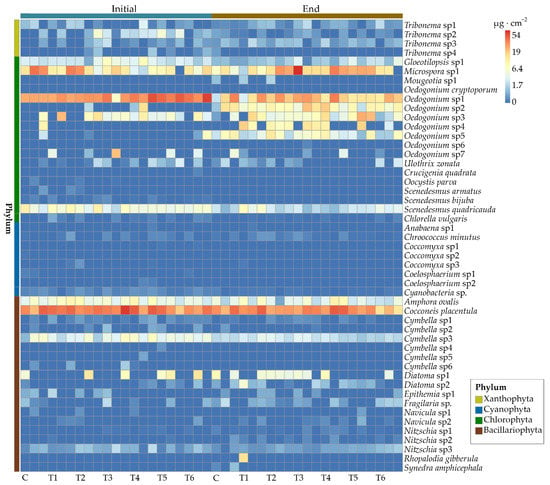
Figure 4.
Heatmap of epiphytic algal species biomass. The color of the square indicates the level of the biomass. Each group has three replications. Abbreviations for groups are the same as in Figure 1.
2.4. Community Diversity
Overall, the variation range of the epiphytic algal diversity measured by the Shannon index was 1.21–1.74 (Figure 5). Compared with control group C, treatment group T4 had the lowest Shannon diversity index while treatment group T2 had the highest, but the difference was not significant (p > 0.05).
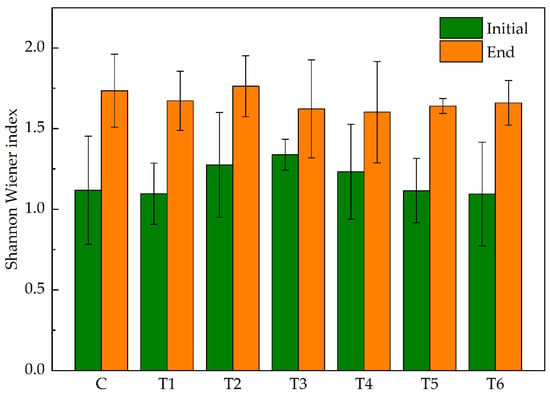
Figure 5.
Shannon Wiener index of epiphytic algae at the initial and end of the experiment. Abbreviations for groups are the same as in Figure 1.
PCA plot revealed the responses of the main epiphytic algal species (relative biomass > 10%) on the surface of V. natans to different concentrations of ENR (Figure 6). Overall, the green algal species, Oedocladium spp. and Microspora sp1, occurred more at the end of experiments in the treatment groups. They gained their highest biomass under moderate ENR concentrations and decreased under the highest concentrations of ENR.
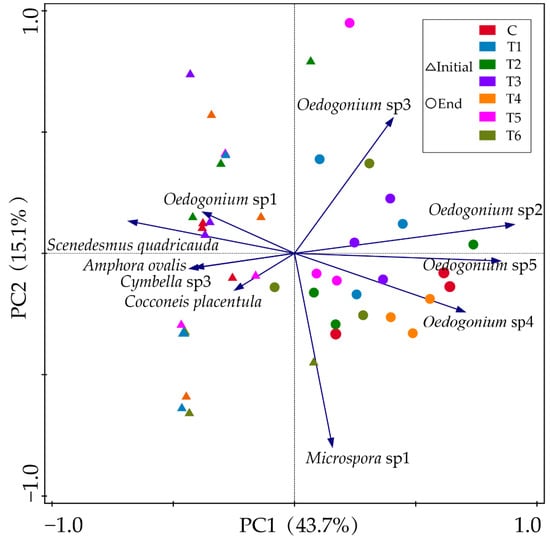
Figure 6.
PCA plots of main epiphytic algal species at the initial (triangles) and end (circles) of the experiment. Colors represent different groups. Abbreviations for groups are the same as in Figure 1.
3. Discussion
Different algal species responded differently to antibiotics depending on their cell structure and evolutionary status. Our results showed that ENR, when in concentrations less than 0.2 mg∙L−1, stimulated most of the algae to demonstrate growth, while cyanobacteria and diatoms were inhibited when the ENR concentration was higher than 1.13 mg∙L−1. When the ENR concentration was less than 6.33 mg∙L−1, the dominant species in the treatment groups were mainly Oedocladium sp1, Oedocladium sp2, and C. placentula, and the Cyanophyta and Bacillariophyta species, such as Chroococcus minutus, also grew well. However, with the increase in the ENR concentration, when it was higher than 6.33 mg·L−1, the dominant species changed to Microspora sp1, Oedocladium sp1, and Oedocladium sp3, and the Cyanophyta almost disappeared. Additionally, according to the PCA analysis, ENR concentrations had less of a negative effect on the density of filamentous algae, such as Oedocladium and Gloeotilopsis, which means that smaller epiphytic algae exhibit higher sensitivity when contaminated with antibiotics. Smaller cell groups of algae are conducive to increasing the surface-to-volume ratio, improving the absorption efficiency of nutrients, and promoting growth [27].
Studies have shown that Scenedesmus is a typical alga with an inducible defense ability, and S. quadricauda can induce the degradation of antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin, through biotransformation or biocatalysis by means of decarboxylation and demethylation [28,29], so the relative abundance of S. quadricauda in the ENR concentration of the 200 mg∙L−1 treatment group is relatively high compared with the other treatment groups.
The cyanobacterial biomass decreased significantly in most of the treated groups. It has been shown that the cellular structure and metabolic pathways of cyanobacteria are similar to those of bacteria, and most antibiotics can find the corresponding sites of action in cyanobacterial cells, which leads to cyanobacteria’s high sensitivity to antibiotics [30]. On the contrary, there are fundamental differences between green algae and prokaryotes in the cellular structure and composition, so green algae have a low sensitivity to antibiotics [31]. This can explain why Chlorophyta was still the dominant population under different concentrations of ENR and contributed a lot to the total algal biomass. Consequently, the biomass of Chlorophyta determined the changes in the total biomass in each treated group.
There was a pattern of “low-dose-promotion and high-dose-inhibition” because the low concentration of ENR stimulated the increase in the intracellular reactive oxygen of algal cells and consequently stimulated a series of physiological reactions, which had a promoting effect on the growth of epiphytic algae. However, as the ENR concentration continued to increase, the growth inhibition effect of epiphytic algae was more obvious after being stressed to a certain extent [32], and as a whole, the biomass of epiphytic algae rose first and then declined with the increased concentration of ENR. ENR has excitatory toxicity (Hormesis) on the epiphytic algae, which refers to the dose–response relationship in which an agent stimulates the growth of the test species at low doses and inhibits its growth at higher doses [33], that is, the toxic effect of low concentrations of ENR on epiphytic algae is small, which can slightly benefit the growth and reproduction of epiphytic algae [34]. On the contrary, high concentrations of ENR obviously inhibited epiphytic algae, which is not conducive to the growth and reproduction of attached algae. Since ENR promotes algal growth at low concentrations, in the results of the present study, the inflection points of this effect may be depended on a threshold of 1.13 mg∙L−1 for Cyanophyta and above 35.6 for filamentous Chlorophyta. Under the threshold, ENR slightly promoted the total biomass and total density of epiphytic algae, while above the threshold, ENR inhibited growth.
It has been suggested that antibiotics affect the algae by affecting the photosynthesis of algae and reducing chlorophyll content, thereby affecting the biomass of algae [35]. For autotrophic algae, chlorophyll plays an important role in the absorption, transmission, and conversion of light energy, and changes in its content directly affect whether algal photosynthesis can be carried out normally, which, in turn, affects the synthesis of organic matter (such as proteins) in algal cells [36]. It has also been found that, on the one hand, ciprofloxacin, ENR, and ofloxacin all affect the photosynthetic pigment content in Scenedesmus obliquus, and as the concentration of antibiotics increases, the color of the algae becomes lighter, and the photosynthetic pigment content gradually decreases. On the other hand, when subjected to antibiotic stress, the antioxidant system of the algal cells is affected, which induces a large number of free radicals and a sharp increase in their accumulation in the algal cells. In turn, this causes oxidative stress in the cell and produces peroxidation reactions in the membrane lipids [37], breaking the cell membrane, increasing the permeability of the algal cell membrane, reacting with macromolecular substances in the cell, and affecting the normal metabolic function of the cell [38], and when the ambient antibiotic concentration exceeds the threshold, the antioxidant system of the algal cells can no longer maintain the homeostatic balance of free radical production and scavenging, so oxidative damage occurs, and the algal cells die. Furthermore, antibiotics also affect the transportation of some algal proteins, the replication and transcription of enzyme genes, and the encoding of photosynthetic genes [39].
The growth or culture of microalga-based technology is a potential method for antibiotic removal. Microalgae are autotrophic organisms that can use light energy to grow and can tolerate higher concentrations of antibiotics compared with bacteria [40]. They can make full use of nitrogen, phosphorus, and small organic particles in wastewater. This method can reduce the supply of nutrients in wastewater treatment, and the treated algal biomass can be extracted to obtain valuable by-products, forming a virtuous cycle that has attracted the attention of researchers. A large number of studies have shown that microalgae can effectively remove pollutants from municipal wastewater, industrial wastewater, surface water, domestic wastewater, aquaculture effluents, and medical wastewater [41,42,43,44,45]. Microalgae are not the target organism of antibiotics. A certain concentration of antibiotics has a low effect on the growth and reproduction of microalgae [46]. Our results showed that antibiotics could promote the growth of algae in the presence of low concentrations, and high concentrations of antibiotics may also seriously inhibit the growth of algae, which is consistent with another study [47]. ENR can be removed by micro-green algae, Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus obliquus [48]. The filamentous algae have a high tolerance to antibiotics, sparking further research on whether they can be used to remove antibiotics.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cultivation of Epiphytic Algae
Vallisneria natans was used as the substrate of epiphytic algae. The plants were collected in a wild pond. We selected plants in good growing conditions and then cleaned and removed the withered and rotten leaves. However, we kept epiphytic algae on the leaves and cultured them in 72 L glass tanks with transparent glass beads in the bottom to fix the roots. The planting density in each tank was about 1200 plants∙m−2, and the corresponding weight was 390.4 ± 1.5 g. This density was similar to a wild pond. In order to make the photoperiod and diurnal temperature fluctuation close to natural water conditions, the glass tank was placed in a greenhouse with a shading net. Temperature and light were monitored every day to prevent the adverse effects of intense light and high temperatures. An optical and temperature recorder MX2202 (Onset HOBO, Bourne, MA, USA) was used to record the light intensity at the top of V. natans and water temperature, and the underwater quantum meter MQ-210 (Apogee Instruments, Inc., Logan, UT, USA) was used to measure the photosynthetically active radiation at noon.
During the cultivation periods, the water temperature was 26 ± 2.5 °C, and the maximum photosynthetically active radiation on the water surface did not exceed the light saturation point of V. natans by 200 μmol∙m−2∙s−1. All the tanks were connected and circulated by water pipes to ensure that the initial biological community and water quality of each tank were homogeneous. After two weeks of culture, V. natans grew well, and epiphytic algae on the leaves were visible to the naked eye.
4.2. Experimental Design
The experiment included a control group (C) and six treatment groups (T1~T6), with three replicates in each group. According to the common containment concentration, water solubility, and minimum effective concentration of various aquatic organisms of ENR [1,49], the ENR concentrations in T1~T6 were set as 0.001, 0.2, 1.13, 6.33, 35.6, and 200 mg∙L−1, respectively. ENR was dissolved in the culture solution of V. natans to make a stock solution.
Before the addition of ENR, TN and TP concentrations in the tanks were adjusted to 0.16 mg∙L−1 and 4 mg∙L−1, respectively, simulating the nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in aquaculture ponds and also providing nutrients for plant growth during the experiment. Distilled water was supplemented regularly without changing water to ensure that the volume of water in each tank was 55 L. ENR was added once at the beginning of the experiment to simulate the pulse of aquaculture effluent.
4.3. Epiphytic Algal Sampling and Measurement
Before and 7 days after the addition of ENR, 15 V. natans were randomly selected from each tank, the leaf surface was carefully cleaned with a soft brush, and the total leaf surface area was recorded. The solution with scrubbed algae was collected and fixed to a constant volume. Then, a 50 mL subsample was taken, and we added 0.75 mL of Lugol’s iodine solution and 2 mL of formalin and sedimented it for more than 96 h. After the algae were completely settled, discarding the supernatant, they were concentrated to a volume of 25 mL.
For unicell or small colony algal species, we used a 0.1 mL counting chamber (20 mm × 20 mm), counted the samples under the optical microscope (Nikon CX21, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) with a magnification of 400×, and counted more than 400 algal cells per sample.
For the filamentous algae, it was easy to make a large deviation since the 0.1 mL counting chamber is too small, and the measurement error is unacceptable according to our practice. Therefore, we use a 1 mL counting chamber to count and identify the filamentous algae. Counting was completed with a magnification of 200×, and more than 400 filamentous algal cells per sample were recorded. A total of more than 40,000 cells was observed during the experiment. Algal taxa were identified according to a series of books on freshwater algal flora and an online database [50,51,52,53,54,55,56].
To calculate the biomass of algae, 30 cells of each species were randomly selected and measured. Then, the cell volumes were calculated based on the most approximate geometric shapes. Fresh biomass (wet weight) was estimated by assuming the specific gravity of algal cells of 1 (106 µm3 is roughly equivalent to 1 µg fresh algal weight).
4.4. Statistical Analyses
According to the counting results, the cell density and fresh biomass of epiphytic algae (cells · cm−2, μg · cm−2) per unit area of V. natans leaves were calculated.
In the present study, species with a relative abundance of Pi > 10% were considered the dominant species in the community. We used Shannon–Wiener index (H) to analyze species diversity characteristics of the epiphyte community by the following formula:
where is the proportion of the entire community made up of species I, and S is the total number of unique species.
At the significance level of p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA was used to compare the differences between six treatment groups (T1~T6) and one control group (C). The vegan package in R3.2.5 was used for PCA analysis and heat map illustrating to compare the similarity and differences of algal community structure.
5. Conclusions
The effects of different concentrations of enrofloxacin on the epitope community are different, showing the pattern of “low-dose-promotion and high-dose-inhibition”, but the thresholds are different in regard to different algal groups and species. The tolerance of filamentous Chlorophyta to ENR in epiphytic algae is higher than that of Bacillariophyta and Cyanophyta, sparking further research on the potential use of filamentous green algae for the removal of ENR in contaminated waters because of its high tolerance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics11081020/s1, Figure S1: epiphytic algae observed in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.J.; data curation, L.J. and G.J.; formal analysis, Q.C., L.J. and Y.Z.; investigation, L.J.; methodology, L.J.; project administration, G.J.; resources, G.J.; visualization, Q.C. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft, L.J. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, Q.C. and G.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by The Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (19050501900), The Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2017ZX07207002), and Shanghai Ocean University (A2-2006-21-200301).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Hongbo Pan, Wei Zhang, and Ruilei Zhang for their kind help in the experiment. Thanks also give to the anonymous reviews.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ebert, I.; Bachmann, J.; Kühnen, U.; Küster, A.; Kussatz, C.; Maletzki, D.; Schlüter, C. Toxicity of the fluoroquinolone antibiotics enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin to photoautotrophic aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, L.; Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Díaz, E.; Ordóñez, S. A review of the adsorption-biological hybrid processes for the abatement of emerging pollutants: Removal efficiencies, physicochemical analysis, and economic evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intorre, L.; Cecchini, S.; Bertini, S.; Cognetti Varriale, A.M.; Soldani, G.; Mengozzi, G. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin in the seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 2000, 182, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S. Fluoroquinolones in animal health. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, G.; Li, T.; Song, C.; Chen, J. Dynamic elimination of enrofloxacin under varying temperature and pH in aquaculture water: An orthogonal study. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecko, N.; Pokludova, L.; Blahova, J.; Svobodova, Z.; Literak, I. Implications of fluoroquinolone contamination for the aquatic environment—A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, C.; Qiu, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, W. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its effluent-receiving river. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.X.; Cheng, X.R.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Fu, J. Pharmaceuticals pollution of aquaculture and its management in China. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Bona, M.; Zounková, R.; Merlanti, R.; Blaha, L.; de Liguoro, M. Effects of enrofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim on two generations of Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, C.; Kamira, B.; Qiu, L.; Fan, L.; Wu, W.; Meng, S.; Hu, G.; Chen, J. Occurrence and human dietary assessment of fluoroquinolones antibiotics in cultured fish around Tai Lake, China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2899–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-J.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Liu, S. Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrignanò, E.; Kannan, A.M.; Proctor, K.; Petrie, B.; Hodgen, S.; Feil, E.J.; Lewis, S.E.; Lopardo, L.; Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Rice, J.; et al. (Fluoro)quinolones and quinolone resistance genes in the aquatic environment: A river catchment perspective. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, M.; Rico, A.; Phu, T.M.; Huong, D.T.T.; Phuong, N.T.; van den Brink, P.J. Ecological risk assessment of the antibiotic enrofloxacin applied to Pangasius catfish farms in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; He, Q.; Hong, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. Effects of water quality adjusted by submerged macrophytes on the richness of the epiphytic algal community. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xia, Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, Y.; Lou, C.; Wang, H.; Han, J. The influence of flow rates and water depth gradients on the growth process of submerged macrophytes and the biomass composition of the phytoplankton assemblage in eutrophic water: An analysis based on submerged macrophytes photosynthesis parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 31477–31488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khellaf, N.; Djelal, H.; Amrane, A. An overview of the valorization of aquatic plants in effluent depuration through phytoremediation processes. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugaste, R.; Reunanen, M. The composition and density of epiphyton on some macrophyte species in the partly meromictic Lake Verevi. In Lake Verevi, Estonia—A Highly Stratified Hypertrophic Lake; Ott, I., Kõiv, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Periphyton: Functions and Application in Environmental Remediation; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Han, R.; Wang, G.; Cao, X. O2, pH, and redox potential microprofiles around Potamogeton malaianus measured using microsensors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K. The role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow freshwater aquatic systems. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carignan, R.; Kalff, J. Phosphorus release by submerged macrophytes: Significance to epiphyton and phytoplankton 1,1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ács, É.; Reskóné, N.M.; Szabó, K.; Taba, G.; Kiss, K.T. Application of epiphytic diatoms in water quality monitoring of Lake Velence—Recommendations and assignments. Acta Bot. Hung. 2005, 47, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riato, L.; Leira, M. Heterogeneity of epiphytic diatoms in shallow lakes: Implications for lake monitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 105988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; He, D.; Chang, F.; Dang, C.Y.; Fu, J. Combined effects of sulfamethoxazole and erythromycin on a freshwater microalga, Raphidocelis subcapitata: Toxicity and Oxidative Stress. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carusso, S.; Juárez, A.B.; Moretton, J.; Magdaleno, A. Effects of three veterinary antibiotics and their binary mixtures on two green alga species. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raven, J.A.; Kübler, J.E. New light on the scaling of metabolic rate with the size of algae. J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fang, H.; Lin, X.; Dai, X.; Liu, H. Photosynthetic toxicity of enrofloxacin on Scenedesmus obliquus in an aquatic environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Chen, L.; Lu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X. Toxic effects of enrofloxacin on Scenedesmus obliquus. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, A.B.; Kolpin, D.W.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Tolls, J. Are veterinary medicines causing environmental risks? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 286a–294a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.Q.; Guo, R.X. Access the toxic effect of the antibiotic cefradine and its UV light degradation products on two freshwater algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ma, Z.; Peng, J.; Mo, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Yang, F. Transcriptomic analysis of Raphidocelis subcapitata exposed to erythromycin: The role of DNA replication in hormesis and growth inhibition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedergreen, N.; Streibig, J.C.; Kudsk, P.; Mathiassen, S.K.; Duke, S.O. The occurrence of hormesis in plants and algae. Dose Response 2006, 5, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Gao, B. Stimulation effects of ciprofloxacin and sulphamethoxazole in Microcystis aeruginosa and isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation-based screening of antibiotic targets. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Min, Z.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Han, J.; Li, P. Interactive effects of roxithromycin and freshwater microalgae, Chlorella pyrenoidosa: Toxicity and removal mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-Y.; Nie, X.-P.; Liu, W.-Q.; Snoeijs, P.; Guan, C.; Tsui, M.T.K. Toxic effects of erythromycin, ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole on photosynthetic apparatus in Selenastrum capricornutum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Sun, S.; Jia, R.; Xu, L.; Hou, W.; Lu, N.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Hou, L.A. Effects of sulfamethoxazole exposure on the growth, antioxidant system of Chlorella vulgaris and Microcystis aeruginosa. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q. Antioxidant responses and degradation of two antibiotic contaminants in Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 86, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B. Cellular and transcriptional responses in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to two antibiotic contaminants. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yeap, T.S.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Ng, H.Y. Pretreatment of saline antibiotic wastewater using marine microalga. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ummalyma, S.B.; Sahoo, D. Bioremediation and biomass production of microalgae cultivation in river water contaminated with pharmaceutical effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Saiyin, H.; Zheng, Z. The collaborative effect of Chlorella vulgaris-Bacillus licheniformis consortia on the treatment of municipal water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ho, S.-H.; Cheng, C.-L.; Guo, W.-Q.; Nagarajan, D.; Ren, N.-Q.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Perspectives on the feasibility of using microalgae for industrial wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Liu, Q.; Nan, F.; Xie, S. Nutrients removal from undiluted cattle farm wastewater by the two-stage process of microalgae-based wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Hu, L.-X.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L.; He, L.-Y.; Ying, G.-G. Microalgae-based technology for antibiotics removal: From mechanisms to application of innovational hybrid systems. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Gonzalo, S.; Rodea-Palomares, I.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Boltes, K.; Marco, E.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: Implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ye, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Microstructure and antioxidative capacity of the microalgae mutant Chlorella PY-ZU1 during tilmicosin removal from wastewater under 15% CO2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Fang, J.; Wang, H. Degradation and metabolic pathways of sulfamethazine and enrofloxacin in Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus obliquus treatment systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28198–28208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; He, J.T.; He, B.N.; Lao, T.Y.; Liu, F.; Guan, X.Y. Sensitivity assessment of denitrifying bacteria against typical antibiotics in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2019, 21, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wei, Y. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger, E.G.; Sigee, D.C. Freshwater Algae: Identification, Enumeration and Use as Bioindicators, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jao, C.C. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis, (Tomus I): Zygnemataceae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Bi, L. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Tomus V): Ulothricales Ulvales Chaetophorales Trentepohliales Sphaeropleales; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Li, J. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Tomus X): Bacillariophyta, Pennatae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Tomus XI): Xanthophyta; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase; World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).