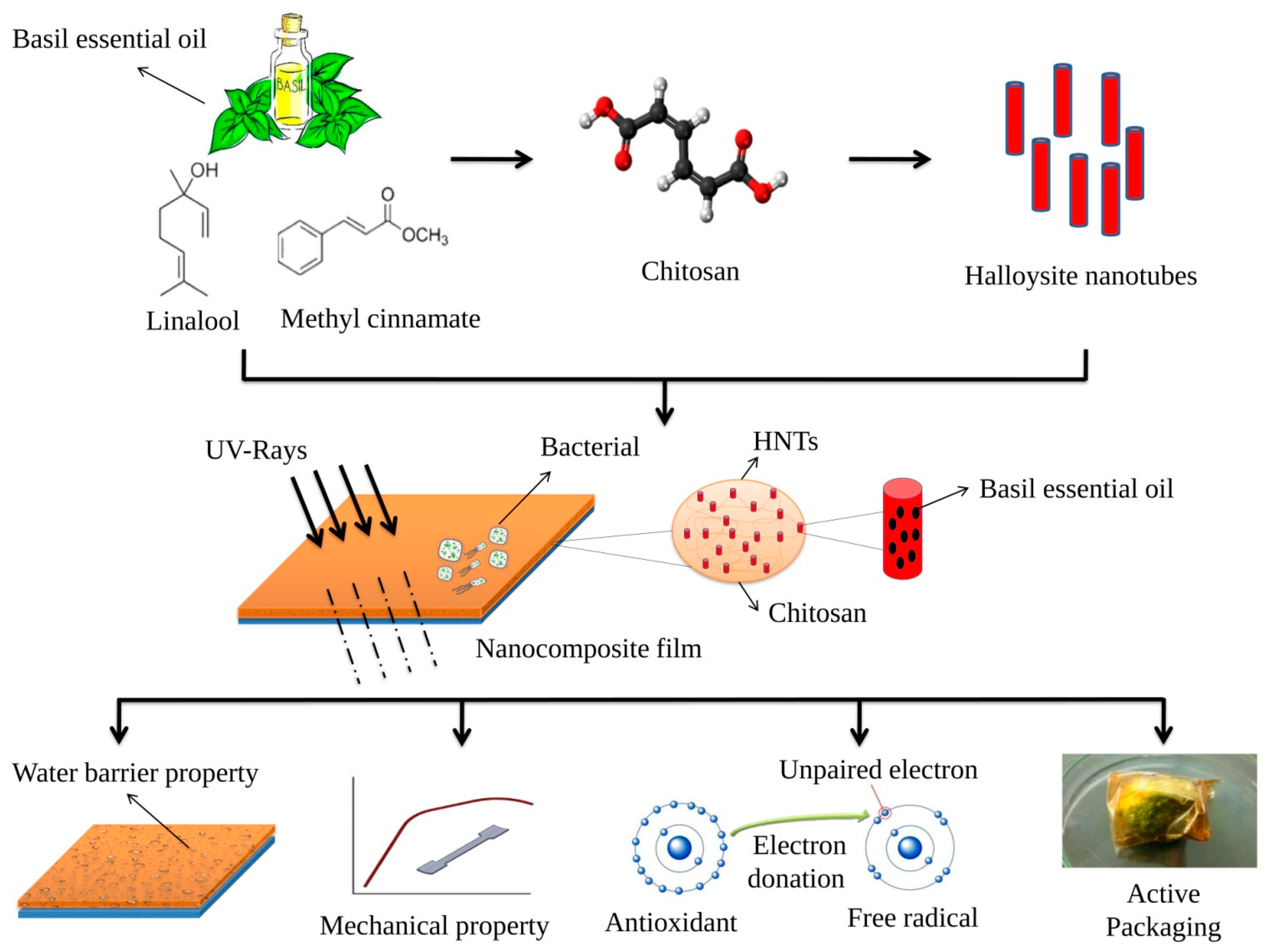
Fabrication and Evaluation of Basil Essential Oil-Loaded Halloysite Nanotubes in Chitosan Nanocomposite Film and Its Application in Food Packaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physical Properties of Film
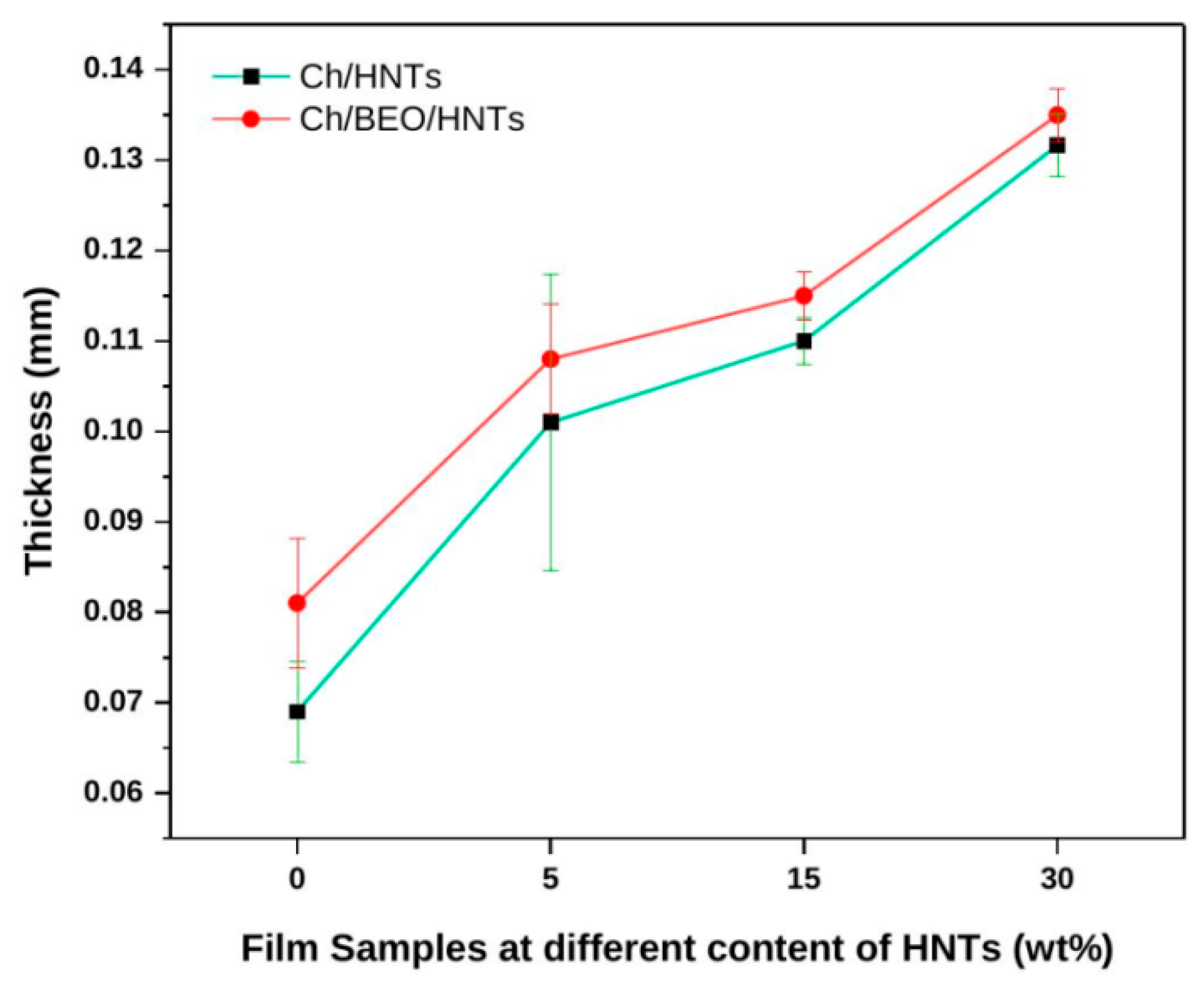
2.1.1. Thickness
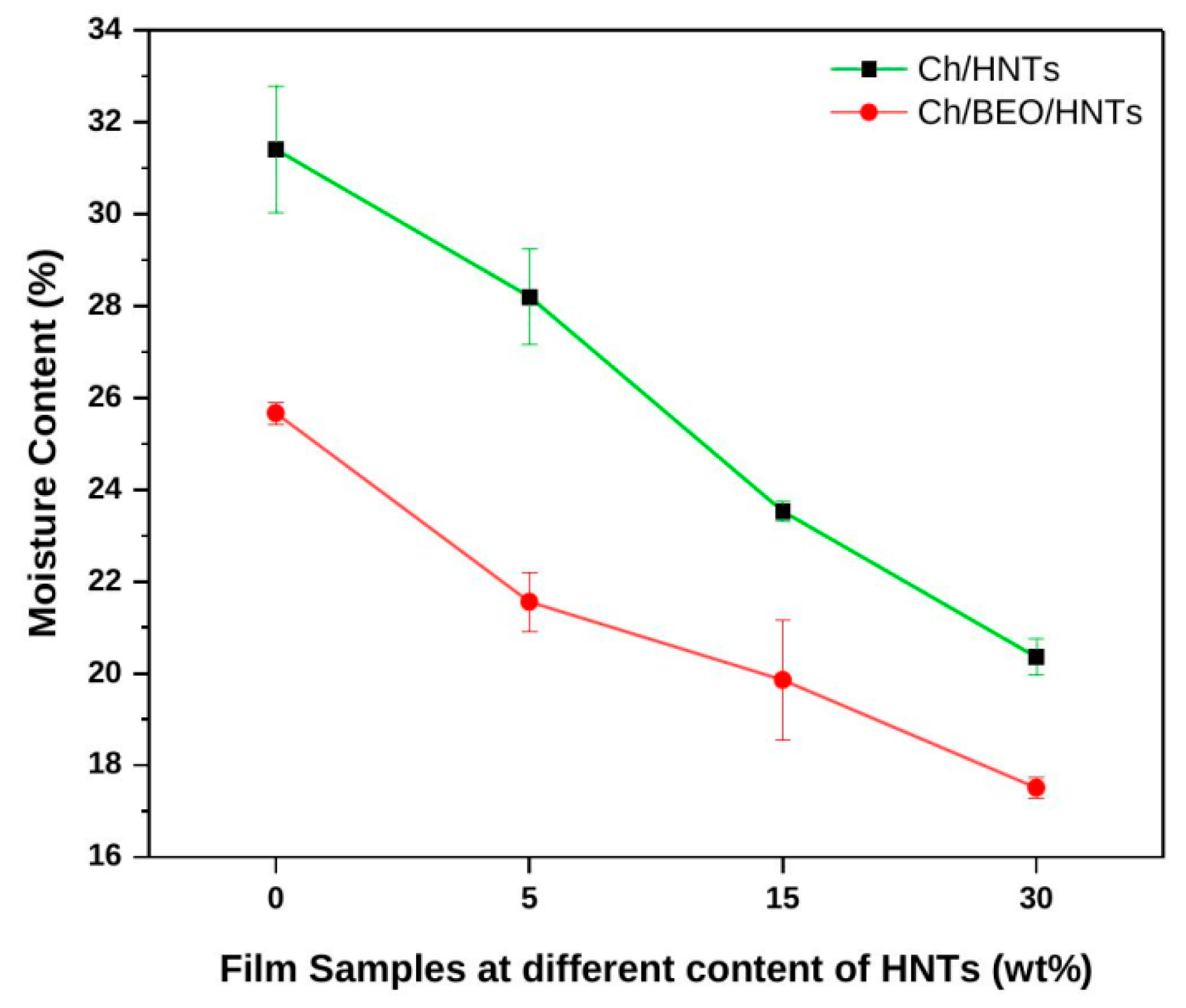
2.1.2. Moisture Content
2.1.3. Water Absorption
2.1.4. Solubility
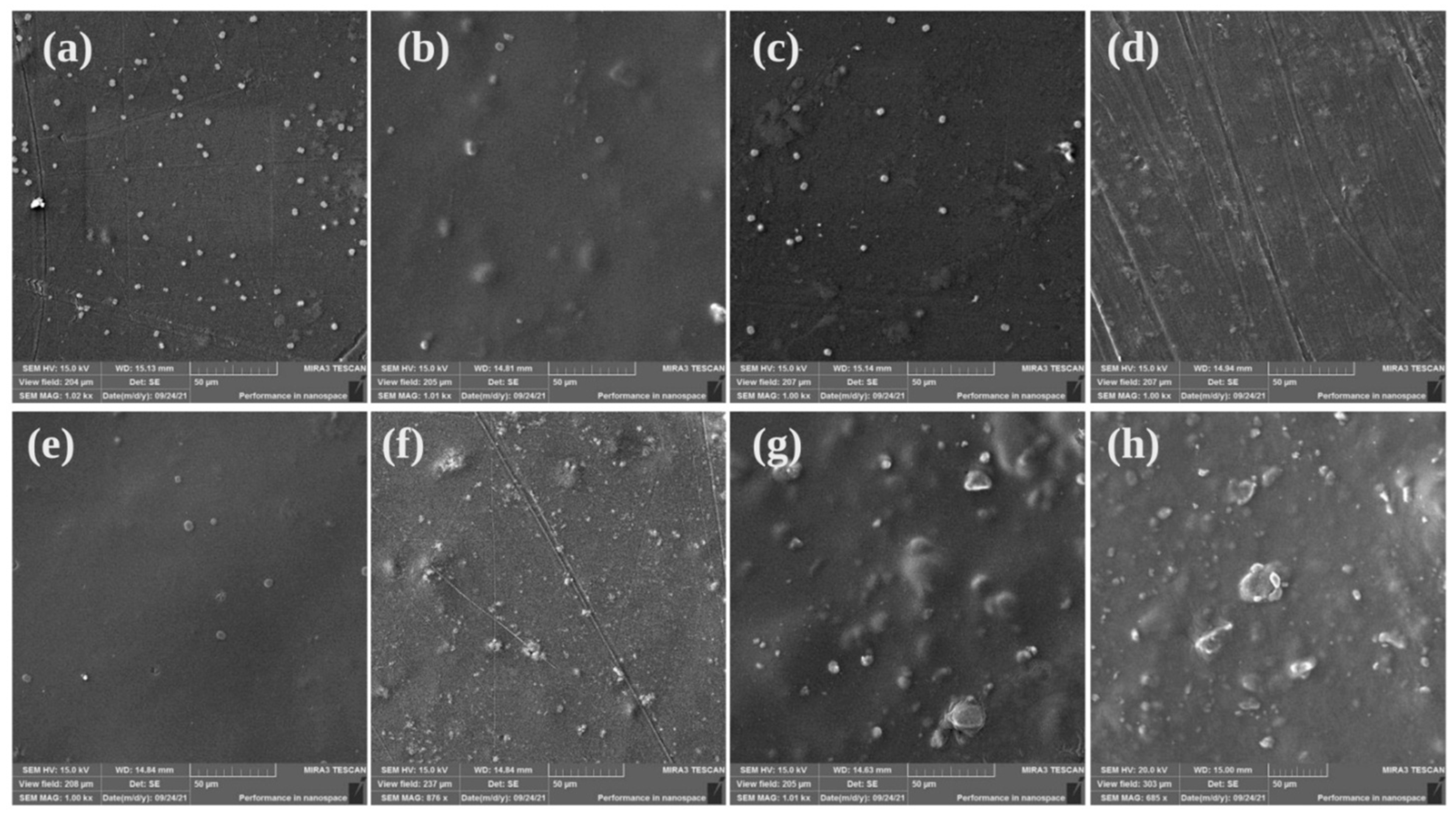
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
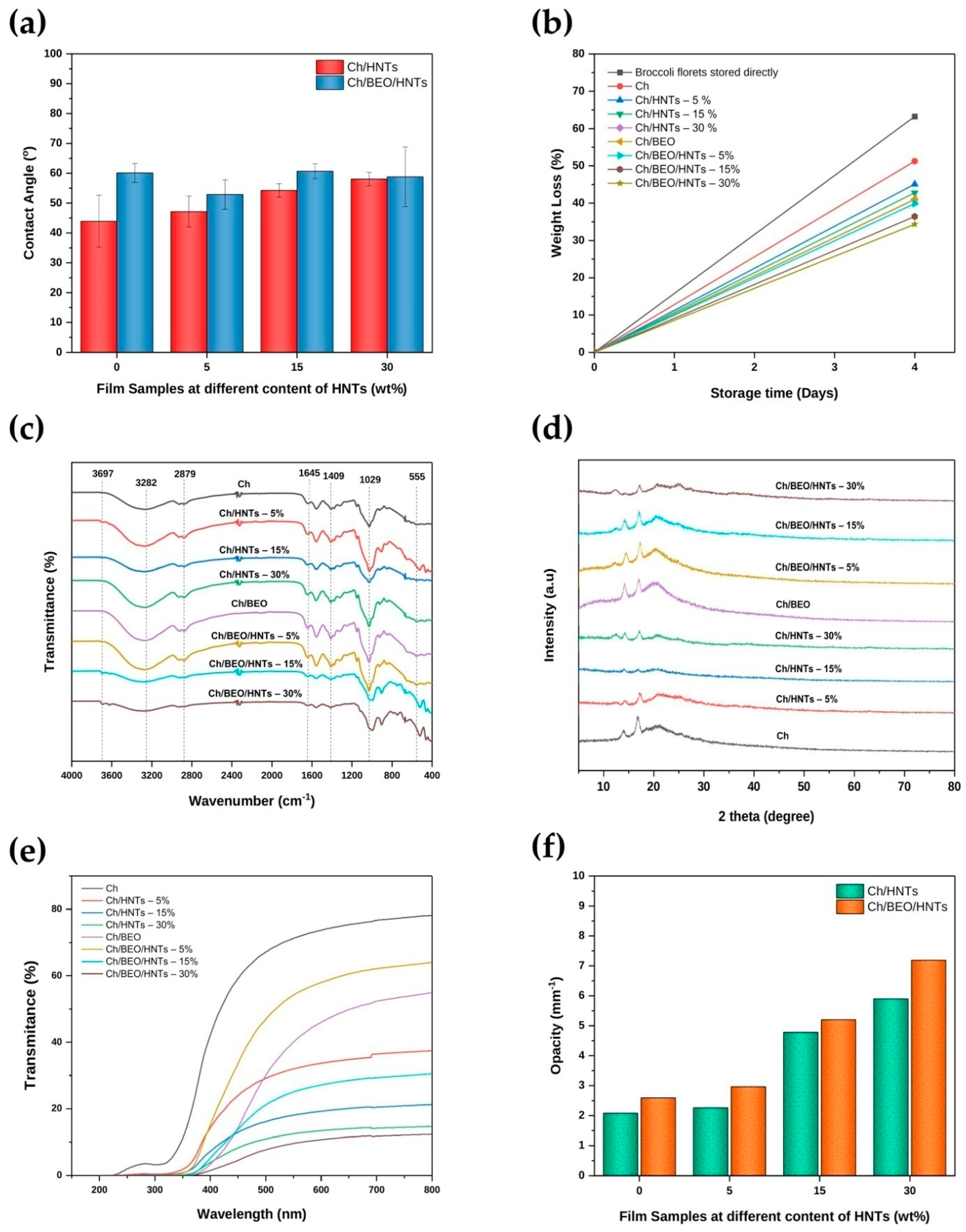
2.3. Contact Angle
2.4. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) Analysis
2.5. Attenuated Total Reflectance–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR–FTIR)
2.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7. Optical Properties of the Films
2.8. Mechanical Properties
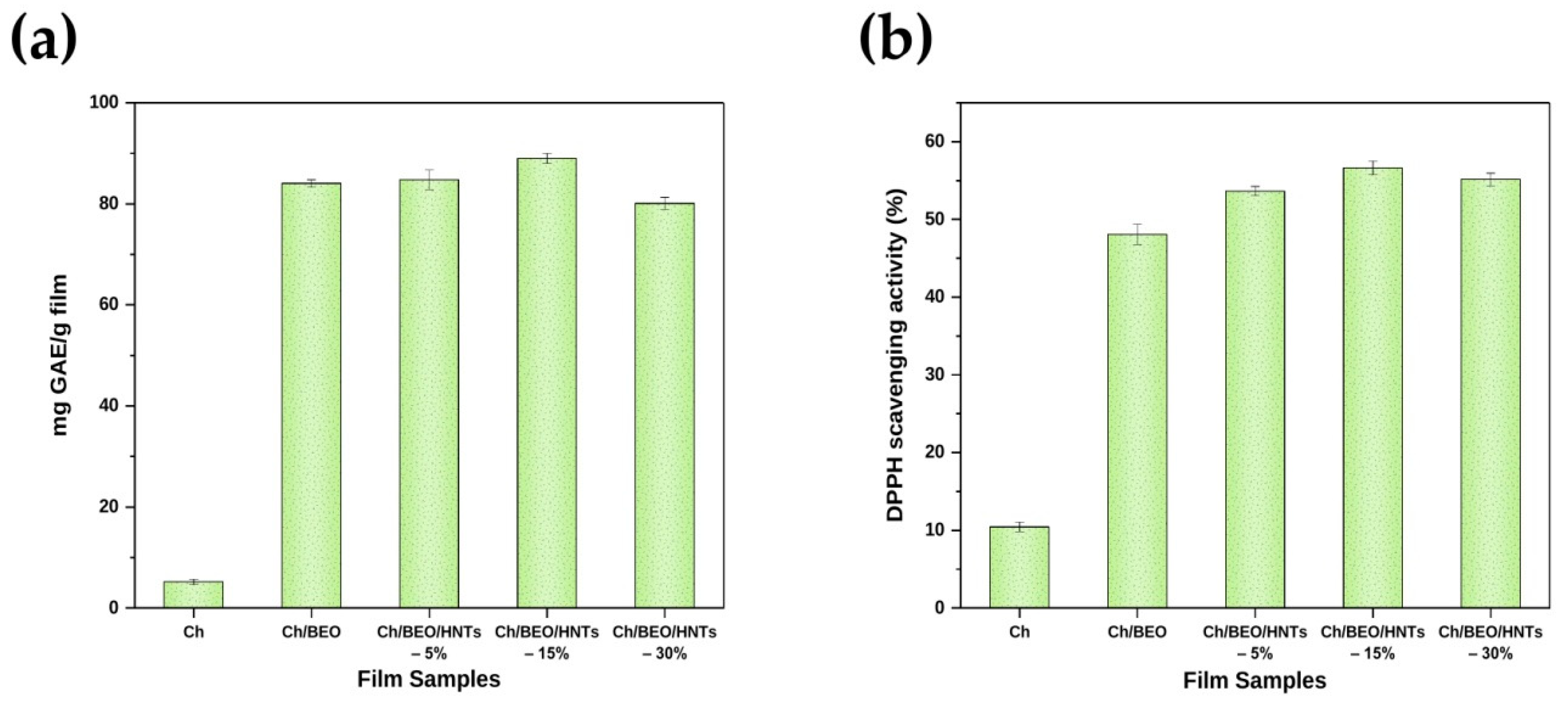
2.9. Antioxidant Properties of the Films
2.10. Storage Test for Food
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Solution Preparation for Ch/BEO/HNTs
3.2.2. Fabrication of Nanocomposite Films
3.3. Characterization of Films
3.3.1. Thickness of the Films
3.3.2. Moisture Content
3.3.3. Water Absorption and Solubility
3.3.4. Contact Angle
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.5. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
3.6. Attenuated Total Reflectance–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR–FTIR)
3.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.8. Optical Properties of the Film
3.9. Mechanical Properties
3.10. Antioxidant Properties
3.10.1. Total Phenolic Content
3.10.2. DPPH (2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) Assay
3.11. Storage Test for Food
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sanuja, S.; Agalya, A.; Umapathy, M.J. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide–neem oil–chitosan bionanocomposite for food packaging application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Z.; Xue, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Li, L. Improving the properties of chitosan films by incorporating shellac nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.L. Food Packaging and Shelf life, a Practical Guide; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Barrera, G.N.; Galimberti, P.I.; Ribotta, P.D.; Igarzabal, C.I.A. Development of edible films prepared by soy protein and the galactomannan fraction extracted from Gleditsia triacanthos (Fabaceae) seed. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.J. Effect of halloysite nanoclay on the physical, mechanical, and antioxidant properties of chitosan films incorporated with clove essential oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.W.; Lin, M.; Mustapha, A. Chitosan/acetylated starch composite films incorporated with essential oils: Physiochemical and antimicrobial properties. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Castro, I.; Martín-Ramos, P.; Matei, P.M.; Fernandes-Correa, M.; Hernánez-Navarro, S.; Martín-Gil, J. Eco-friendly nanocomposites of chitosan with natural extracts, antimicrobial agents, and nanometals. In Handbook of Composites from Renewable Materials; Thakur, V.K., Thakur, M.K., Kessler, M.R., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 8, pp. 35–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojagh, S.M.; Rezaei, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Hosseini, S.M.H. Development and evaluation of a novel biodegradable film made from chitosan and cinnamon essential oil with low affinity toward water. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, S.; Chand, N.; Chaurasia, V. Investigation of water vapor permeability and antimicrobial property of zinc oxide nanoparticles-loaded chitosan-based edible film. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casariego, A.; Souza, B.; Cerqueira, M.; Teixeira, J.; Cruz, L.; Díaz, R.; Vicente, A. Chitosan/clay films’ properties as affected by biopolymer and clay micro/nanoparticles’ concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatt, S.R.; Chander, R.; Sharma, A. Chitosan and mint mixture: A new preservative for meat and meat products. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Navajas, Y.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Sendra, E.; Perez-Alvarez, J.; Fernández-López, J. In vitro antibacterial and antioxidant properties of chitosan edible films incorporated with Thymus moroderi or Thymus piperella essential oils. Food Control 2013, 30, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Santos, R.; Andrade, M.; de Melo, N.R.; Sanches-Silva, A. Use of essential oils in active food packaging: Recent advances and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho, J.I.; Campillo, N.; Viñas, P.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Determination of synthetic phenolic antioxidants in edible oils using microvial insert large volume injection gas-chromatography. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). Title 21: Food and Drugs. ChapterI-Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services, Subchapter B-Food for Human Consumption (Continued), Part 182-Substances Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), Subpart a-General Provisions, Subpart 182.20-Essentialoils, Oleoresins, and Natural Extractives. 2016. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?CFRPart=182 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Alexandre, S.; Vital, A.C.P.; Mottin, C.; do Prado, R.M.; Ornaghi, M.G.; Ramos, T.R.; Guerrero, A.; Pilau, E.J.; do Prado, I.N. Use of alginate edible coating and basil (Ocimum spp.) extracts on beef characteristics during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3835–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amor, G.; Sabbah, M.; Caputo, L.; Idbella, M.; De Feo, V.; Porta, R.; Fechtali, T.; Mauriello, G. Basil essential oil: Composition, antimicrobial properties, and microencapsulation to produce active chitosan films for food packaging. Foods 2021, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Park, H.J. Preparation of halloysite nanotubes coated with Eudragit for a controlled release of thyme essential oil. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, G.; Rathnakar, G.; Santhosh, N. Effect of heat treated HNT on physico-mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Commun. 2019, 13, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Tan, D.; Annabi-Bergaya, F. Properties and applications of halloysite nanotubes: Recent research advances and future prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.J.; Asif, H.M.; Naveed, M. Properties and modification methods of halloysite nanotubes: A state-of-the-art review. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2018, 63, 4109–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrasi, G.; Pantani, R.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA/H alloysite nanocomposite films: Water vapor barrier properties and specific key characteristics. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Pieraccini, S.; Guernelli, S.; Dindo, M.; Francati, S.; Liotta, L.; Colletti, G.; Masiero, S.; Riela, S. Photostability assessment of natural pyrethrins using halloysite nanotube carrier system. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 230, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riela, S.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Clay-based drug-delivery systems: What does the future hold? Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 633–646. [Google Scholar]
- Saadat, S.; Rawtani, D.; Braganza, V. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan film containing nanocomposite of Trachyspermum ammi (ajwain) seed oil loaded Halloysite nanotubes against foodborne pathogenic microorganisms. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 226, 106554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Rawtani, D.; Rao, P.K. Antibacterial activity of chitosan film containing Syzygium aromaticum (clove) oil encapsulated halloysite nanotubes against foodborne pathogenic bacterial strains. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Joshi, A.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lvov, Y. Enlargement of halloysite clay nanotube lumen by selective etching of aluminum oxide. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7216–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. Chitosan/halloysite nanotubes bionanocomposites: Structure, mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benucci, I.; Liburdi, K.; Cacciotti, I.; Lombardelli, C.; Zappino, M.; Nanni, F.; Esti, M. Chitosan/clay nanocomposite films as supports for enzyme immobilization: An innovative green approach for winemaking applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashantha, K.; Lecouvet, B.; Sclavons, M.; Lacrampe, M.F.; Krawczak, P. Poly (lactic acid)/halloysite nanotubes nanocomposites: Structure, thermal, and mechanical properties as a function of halloysite treatment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Pandey, G.; Tharmavaram, M.; Braganza, V.; Rawtani, D. Nano-interfacial decoration of Halloysite Nanotubes for the development of antimicrobial nanocomposites. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Khodaei, D.; Lacroix, M. Effect of chitosan/essential oils/silver nanoparticles composite films packaging and gamma irradiation on shelf life of strawberries. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Kumar, P.; Kardam, S.K.; Gaikwad, K.K. Ethylene scavenging film based on corn starch-gum acacia impregnated with sepiolite clay and its effect on quality of fresh broccoli florets. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y. Combined effects of two kinds of essential oils on physical, mechanical and structural properties of chitosan films. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 36, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Kamdem, D.P. Development and characterization of biodegradable chitosan films containing two essential oils. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atef, M.; Rezaei, M.; Behrooz, R. Characterization of physical, mechanical, and antibacterial properties of agar-cellulose bionanocomposite films incorporated with savory essential oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Enhanced antifouling performance of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) blended poly (vinyl chloride)(PVC/HNTs) ultrafiltration membranes: For water treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 63, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Flux improvement, rejection, surface energy and antibacterial properties of synthesized TiO 2-Mo. HNTs/PVC nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 15049–15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyankson, E.; Aboagye, S.O.; Efavi, J.K.; Agyei-Tuffour, B.; Paemka, L.; Asimeng, B.O.; Balapangu, S.; Arthur, P.K.; Tiburu, E.K. Chitosan-Coated Halloysite Nanotubes As Vehicle for Controlled Drug Delivery to MCF-7 Cancer Cells In Vitro. Materials 2021, 14, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Mukhopadhyay, M. TiO2 decorated functionalized halloysite nanotubes (TiO2@ HNTs) and photocatalytic PVC membranes synthesis, characterization and its application in water treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, M.; Khiabani, M.S.; Mokarram, R.R.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Kafil, H.S. Development and evaluation of chitosan based active nanocomposite films containing bacterial cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sun, J.; Zheng, P.; Kang, X.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Ge, Y.; Hu, Y.; Pang, J. Preparation of an intelligent film based on chitosan/oxidized chitin nanocrystals incorporating black rice bran anthocyanins for seafood spoilage monitoring. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Mashaly, H.; Wilken, R. Nanocomposites based on chitosan/silver/clay for durable multi-functional properties of cotton fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekik, S.B.; Gassara, S.; Bouaziz, J.; Deratani, A.; Baklouti, S. Development and characterization of porous membranes based on kaolin/chitosan composite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, S.; Garcia, M.A.; Pinotti, A. Correlations between structural, barrier, thermal and mechanical properties of plasticized gelatin films. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirvel, P.; Ravi, S. Chemical composition of the essential oil from basil (Ocimum basilicum Linn.) and its in vitro cytotoxicity against HeLa and HEp-2 human cancer cell lines and NIH 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siripatrawan, U.; Vitchayakitti, W. Improving functional properties of chitosan films as active food packaging by incorporating with propolis. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Qin, C. Properties and biological activity of chitosan-coix seed starch films incorporated with nano zinc oxide and Artemisia annua essential oil for pork preservation. LWT 2022, 164, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D-638; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM Int.: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Abdollahi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Farzi, G. Improvement of active chitosan film properties with rosemary essential oil for food packaging. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kwak, S.J.; Yoon, K.S. Efficacy of sodium hypochlorite and acidified sodium chlorite in preventing browning and microbial growth on fresh-cut produce. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, 17, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | wt% HNTs | %Transmission at (200 nm UV-C) | %Transmission at (300 nm UV-B) | %Transmission at (400 nm UV-A) | %Transmission at (600 nm Visible) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ch | 0 | 0 | 3.20 | 42.10 | 73.70 |
| Ch/HNTs | 5 | 0 | 0.40 | 14.30 | 33.70 |
| 15 | 0 | 0.20 | 7.20 | 19.20 | |
| 30 | 0 | 0 | 3.90 | 13.40 | |
| Ch/BEO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.40 | 46.00 |
| Ch/BEO/HNTs | 5 | 0 | 0 | 15.20 | 58.00 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 5.20 | 27.10 | |
| 30 | 0 | 0 | 1.50 | 10.70 |
| Samples | wt% HNTs | Tensile Strength (MPa) | % Elongation at Break |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ch | 0 | 11.37 ± 1.41 | 2.02 ± 0.50 |
| Ch/HNTs | 5 | 13.51 ± 0.83 | 1.56 ± 0.43 |
| 15 | 18.52 ± 1.04 | 1.06 ± 0.38 | |
| 30 | 12.81 ± 0.66 | 1.02 ± 0.58 | |
| Ch/BEO | 0 | 8.56 ± 1.12 | 1.84 ± 0.43 |
| Ch/BEO/HNTs | 5 | 10.28 ± 0.94 | 0.85 ± 0.33 |
| 15 | 13.31 ± 0.74 | 0.62 ± 0.15 | |
| 30 | 9.22 ± 1.04 | 0.52 ± 0.22 |
| Polymer | Nanofiller | Active Agent | Method | UV Light %Trans-mission at (600 nm Visible) | Opacity (mm−1) | Moisture Content (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | Halloysite Nanotubes | Basil oil | Solution casting | 10.17 | 5.20 | 17.51 | Present Study |
| Chitosan | Zinc oxide nanoparticles | Neem oil | Solution Casting | NR | 3.69 | NR | [1] |
| Chitosan | Zinc oxide | Artemisia annua oil | Solution Casting | NR | 1.34 | 8.77 | [49] |
| Chitosan | Silver nanoparticles | Citrus extract | Solution Casting | 17.40 | NR | NR | [33] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhary, N.; Mishra, G.; Yadav, T.; Srivastava, N.; Maurya, V.K.; Saxena, S.K. Fabrication and Evaluation of Basil Essential Oil-Loaded Halloysite Nanotubes in Chitosan Nanocomposite Film and Its Application in Food Packaging. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121820
Chaudhary N, Mishra G, Yadav T, Srivastava N, Maurya VK, Saxena SK. Fabrication and Evaluation of Basil Essential Oil-Loaded Halloysite Nanotubes in Chitosan Nanocomposite Film and Its Application in Food Packaging. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(12):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121820
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhary, Narayan, Gourav Mishra, Tushar Yadav, Nishant Srivastava, Vimal K. Maurya, and Shailendra K. Saxena. 2022. "Fabrication and Evaluation of Basil Essential Oil-Loaded Halloysite Nanotubes in Chitosan Nanocomposite Film and Its Application in Food Packaging" Antibiotics 11, no. 12: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121820
APA StyleChaudhary, N., Mishra, G., Yadav, T., Srivastava, N., Maurya, V. K., & Saxena, S. K. (2022). Fabrication and Evaluation of Basil Essential Oil-Loaded Halloysite Nanotubes in Chitosan Nanocomposite Film and Its Application in Food Packaging. Antibiotics, 11(12), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121820








