Evaluation of Different Strategies to Improve the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection at the Primary Care Level: Training Sessions Increase Prescription Appropriateness of Treatment Regimens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
2.2. Indications
2.3. Prescription Appropriateness
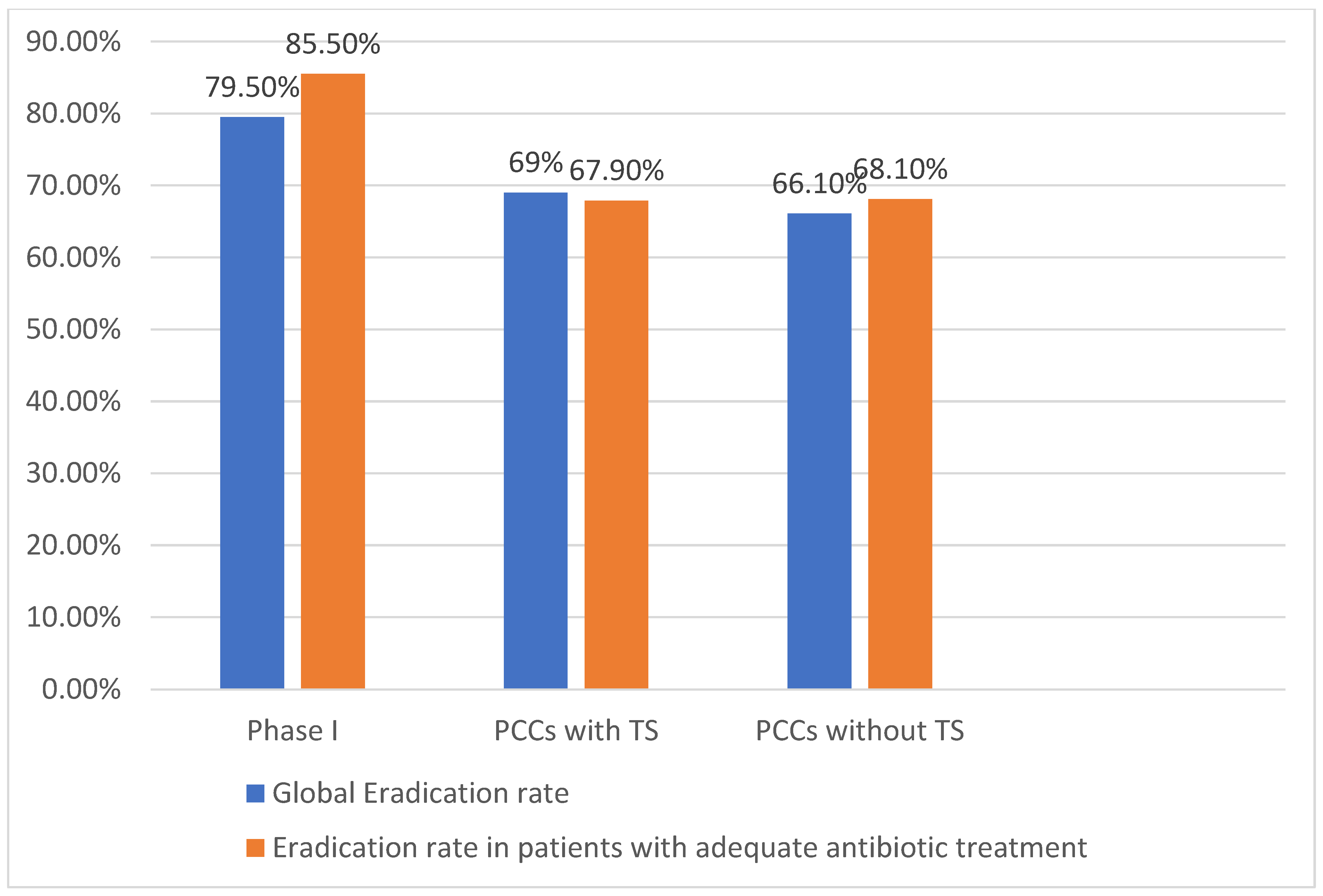
2.4. Eradication Rates
3. Discussion
Strengths and Weaknesses
4. Materials and Methods
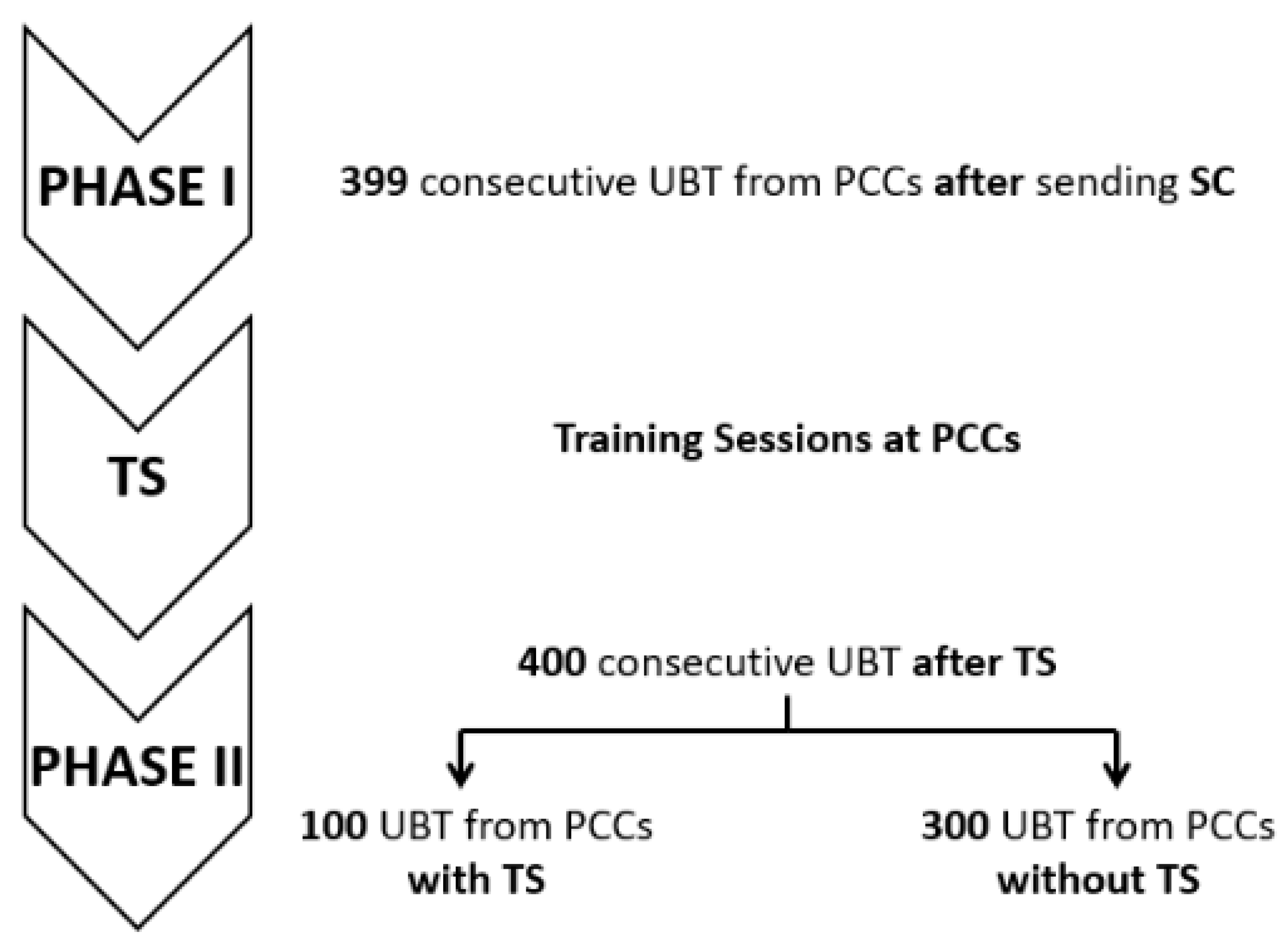
4.1. Study Design
4.1.1. Phase I
4.1.2. Phase II
4.2. Variables
4.3. Statistical Analysis and Ethics Statement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Zagari, R.M.; Bazzoli, F. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burucoa, C.; Axon, A. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leja, M.; Grinberga-Derica, I.; Bilgilier, C.; Steininger, C. Review: Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatila, M.; Thomas, A.S. Current and Future Perspectives in the Diagnosis and Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. J Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milivojevic, V.; Rankovic, I.; Krstic, M.N.; Milosavljevic, T. Dyspepsia Challenge in Primary Care Gastroenterology. Dig. Dis. 2022, 40, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Molina-Infante, J.; Amador, J.; Bermejo, F.; Bujanda, L.; Calvet, X.; Castro-Fernandez, M.; Cuadrado-Lavin, A.; Elizalde, J.I.; Gene, E.; et al. IV Spanish Consensus Conference on Helicobacter pylori infection treatment. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 39, 697–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujanda, L.; Nyssen, O.P.; Vaira, D.; Saracino, I.M.; Fiorini, G.; Lerang, F.; Georgopoulos, S.; Tepes, B.; Heluwaert, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance Prevalence and Trends in Patients Infected with Helicobacter pylori in the Period 2013–2020: Results of the European Registry on H. pylori Management (Hp-EuReg). Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, I.A.; Martinez-Dominguez, S.J.; Almajano, E.A.; Carrera-Lasfuentes, P.; Lanas, A. Management of Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Effectiveness Rates in Daily Clinical Practice in Spain: 2010–2019. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholl, A.G.; Amador, J.; Ricote, M.; Canones-Garzon, P.J.; Gene, E.; Calvet, X.; Gisbert, J.P.; Spanish Primary Care Societies SEMFyC; SEMERGEN and SEMG; the Spanish Association of Gastroenterology; et al. Spanish primary care survey on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection and dyspepsia: Information, attitudes, and decisions. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Contreras, A.D.; Rascon, O.; Amieva-Balmori, M.; Rios-Galvez, S.; Maza, Y.J.; Meixueiro-Daza, A.; Roesch-Dietlen, F.; Remes-Troche, J.M. Approach, attitudes, and knowledge of general practitioners in relation to Helicobacter pylori is inadequate. There is much room for improvement! Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2018, 83, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Qiao, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Wan, M.; Lin, M.J.; Zhang, W.L.; Ding, Y.M.; Kong, Q.Z.; et al. Implementation of WeChat-based patient-doctor interaction in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: A propensity score matching analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2022, 23, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Ji, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zuo, X. Twice daily short-message-based re-education could improve Helicobacter pylori eradication rate in young population: A prospective randomized controlled study. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Qu, J.Y.; Yang, X.X.; Han, Z.X.; Zuo, X. Effects of enhanced education for patients with the Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laredo, V.; Sostres, C.; Alfaro, E.; Arroyo, M.T.; Lanas, A. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection at the primary care level. The implementation of specific counseling improves eradication rates. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.; Feely, J.; Thornton, O.; Dobson, M.; O’Morain, C.A.; O’Connor, H.J. Impact of Helicobacter pylori on the management of dyspepsia in primary care. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Calvet, X.; Bermejo, F.; Boixeda, D.; Bory, F.; Bujanda, L.; Castro-Fernandez, M.; Dominguez-Munoz, E.; Elizalde, J.I.; Forne, M.; et al. III Spanish Consensus Conference on Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 36, 340–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholl, A.G.; Romero, J.A.; Calvo, X.C.; Molina-Infante, J.; Gisbert, J.P. Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de la Infección por Helicobacter Pylori, 2nd ed.; IMC: Madrid, Spain, 2021; Available online: https://www.aegastrum-semfyc.es/require/archivos/infeccion-helicobacter-pylori.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- O’Brien, M.A.; Rogers, S.; Jamtvedt, G.; Oxman, A.D.; Odgaard-Jensen, J.; Kristoffersen, D.T.; Forsetlund, L.; Bainbridge, D.; Freemantle, N.; Davis, D.A.; et al. Educational outreach visits: Effects on professional practice and health care outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 4, CD000409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giguere, A.; Legare, F.; Grimshaw, J.; Turcotte, S.; Fiander, M.; Grudniewicz, A.; Makosso-Kallyth, S.; Wolf, F.M.; Farmer, A.P.; Gagnon, M.P. Printed educational materials: Effects on professional practice and healthcare outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 10, CD004398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltin, D.; Dotan, I.; Birkenfeld, S. Improvement in the implementation of Helicobacter pylori management guidelines among primary care physicians following a targeted educational intervention. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2019, 32, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crankshaw, S.; Butt, J.; Gierisch, J.M.; Barrett, N.J.; Mervin-Blake, S.; Oeffinger, K.; Patierno, S.; Worthy, V.; Godbee, R.; Epplein, M. The Durham Initiative for Stomach Health (DISH): A pilot community-based Helicobacter pylori education and screening study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Salih, M.; Jafri, W.; Ali Shah, H.; Hamid, S. Helicobacter pylori infection: Approach of primary care physicians in a developing country. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene, E.; Sanchez-Delgado, J.; Calvet, X.; Azagra, R. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection in primary care in Spain. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 31, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltin, D.; Kimchi, N.; Dickman, R.; Gingold-Belfer, R.; Niv, Y.; Birkenfeld, S. Attitudes and practice related to Helicobacter pylori infection among primary care physicians. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.G.; Kim, J.W.; Jeong, J.B.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, K.L.; Park, Y.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, J.U.; Kim, N.Y.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Discrepancies between primary physician practice and treatment guidelines for Helicobacter pylori infection in Korea. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshibangu-Kabamba, E.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and antibiotic resistance—From biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phase I n = 399 | Phase II n = 400 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adequate indications, n (%) | 229 (57.5) | PCCs with TS n = 100 | PCCs without TS n = 300 |
| 67 (67) | 188 (62.7) | ||
| Dyspepsia | 140 (61.1) | 44 (65.7) | 128 (68.1) |
| Eradication control | 83 (36.2) | 17 (25.4) | 50 (26.6) |
| Gastric or duodenal ulcer | 2 (0.9) | 3 (4.5) | 5 (2.7) |
| Others | 4 (1.8) | 3 (4.5) | 5 (2.7) |
| Inadequate indications | 170 (42.5) | 33 (33) | 112 (37.3) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | 39 (23.1) | 8 (24.2) | 39 (35.1) |
| Dyspepsia in >55 years | 36 (21.3) | 8 (24.2) | 21 (18.9) |
| Abdominal pain | 22 (13) | 4 (12.1) | 13 (11.7) |
| Others | 73 (42.6) | 13 (39.5) | 39 (35.1) |
| Peptic Ulcer |
|---|
| Non-investigated dyspepsia in patients <55 years old and without alarm symptoms * (Test and Treat strategy) |
| Functional dyspepsia |
| History of peptic ulcer and long-term treatment with NSAID or aspirin |
| Low-grade gastric MALT lymphoma |
| Gastric cancer |
| First-degree family history of gastric cancer |
| Atrophic gastritis or intestinal metaplasia |
| Iron deficiency anaemia of uncertain aetiology |
| Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura |
| Vitamin B deficiency of uncertain aetiology |
| Offer treatment to all patients with confirmed H. pylori infection |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfaro, E.; Martínez-Domínguez, S.J.; Laredo, V.; Lanas, Á.; Sostres, C. Evaluation of Different Strategies to Improve the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection at the Primary Care Level: Training Sessions Increase Prescription Appropriateness of Treatment Regimens. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121746
Alfaro E, Martínez-Domínguez SJ, Laredo V, Lanas Á, Sostres C. Evaluation of Different Strategies to Improve the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection at the Primary Care Level: Training Sessions Increase Prescription Appropriateness of Treatment Regimens. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(12):1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121746
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfaro, Enrique, Samuel J. Martínez-Domínguez, Viviana Laredo, Ángel Lanas, and Carlos Sostres. 2022. "Evaluation of Different Strategies to Improve the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection at the Primary Care Level: Training Sessions Increase Prescription Appropriateness of Treatment Regimens" Antibiotics 11, no. 12: 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121746
APA StyleAlfaro, E., Martínez-Domínguez, S. J., Laredo, V., Lanas, Á., & Sostres, C. (2022). Evaluation of Different Strategies to Improve the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection at the Primary Care Level: Training Sessions Increase Prescription Appropriateness of Treatment Regimens. Antibiotics, 11(12), 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121746





