Ecological Distribution of Virulent Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Livestock, Environment, and Dairy Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus in Examined Samples
2.2. Occurrence and Distribution of Staphylococcus aureus at the Farm Level
2.3. Occurrence and Distribution of MRSA and Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Different Sources
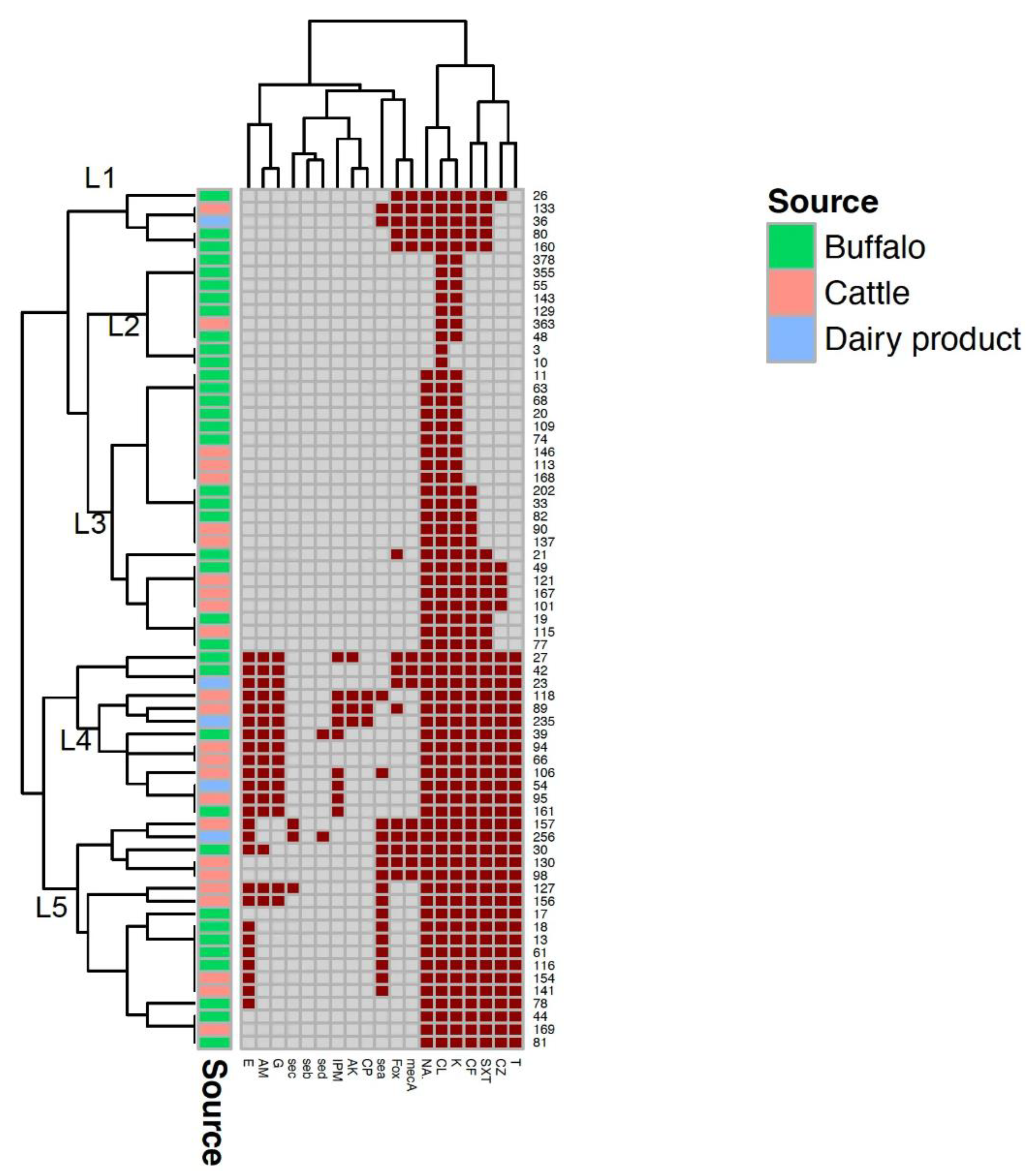
2.4. Antimicrobial Resistence and Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance (MAR) Index of Isolated Staphylococcus aureus Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Samples Collection
4.2. Microbiological and Molecular Characterization of S. aureus
- Isolation and identification of S. aureus
- Molecular characterization
- Amplification of nuc, enterotoxin and mecA genes
4.3. Phenotypic antimicrobial Resistance of Isolated S. aureus (Antibiogram)
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monecke, S.; Kuhnert, P.; Hotzel, H.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Microarray based study on virulence-associated genes and resistance determinants of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 125, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haran, K.P.; Godden, S.M.; Boxrud, D.; Jawahir, S.; Bender, J.B.; Sreevatsan, S. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bulk tank milk from Minnesota dairy farms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hennekinne, J.A.; De Buyser, M.L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, T.C. Livestock-Associated Staphylococcus aureus: The United States Experience. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglam, A.G.; Sahin, M.; Çelik, E.; Çelebi, O.; Akça, D.; Otlu, S. The role of staphylococci in subclinical mastitis of cows and lytic phage isolation against to Staphylococcus aureus. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rainard, P.; Foucras, G.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Watts, J.L.; Koop, G.; Middleton, J.R. Knowledge gaps and research priorities in Staphylococcus aureus mastitis control. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seegers, H.; Fourichon, C.; Beaudeau, F. Production effects related to mastitis and mastitis economics in dairy cattle herds. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peacock, S.J.; Paterson, G.K. Mechanisms of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.; Hetta, H.; Elkelish, A.; Alkhalifah, D.; Hozzein, W.; Batiha, G.; El Nahhas, N.; Mabrok, M.A. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): One health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors, antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M. The continuing threat of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, A.; Shata, R.; Farag, A.; Ramadan, H.; Alkhedaide, A.; Soliman, M.; Elbadawy, M.; Abugomaa, A.; Awad, A. Prevalence and Characterization of PVL-Positive Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Raw Cow’s Milk. Toxins 2022, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelin, J.; Wallin-Carlquist, N.; Cohn, M.T.; Lindqvist, R.; Barker, G.C.; Rådström, P. The formation of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin in food environments and advances in risk assessment. Virulence 2011, 2, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akineden, O.; Annemüller, C.; Hassan, A.A.; Lämmler, C.; Wolter, W.; Zschöck, M. Toxin genes and other characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from milk of cows with mastitis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, D.; Harper, L.; Shopsin, B.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis in diverse host environments. Pathog. Dis 2017, 75, ftx005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mun, S.H.; Kong, R.; Seo, Y.; Zhou, T.; Kan, O.; Shin, D.; Kwon, D.Y. Subinhibitory concentrations of punicalagin reduces expression of virulence-related exoproteins by Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pidwill, G.R.; Gibson, J.F.; Cole, J.; Renshaw, S.A.; Foster, S.J. The Role of Macrophages in Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, V.; Chieffi, D.; Fannelli, F.; Logrieco, A.; Cho, G.; Kabisch, J.; Böhnlein, C.; Franz, C.M. Microbial quality and safety of milk and milk products in the 21st century. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2013–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Jakee, J.K.; Atta, N.; Bakry, M.A.; Elgabry, E.A.; Kandil, M.; El-Said, W.A. Antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from bovine and human sources in Egypt. Glob. Vet. 2011, 7, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Dahshan, H.; Abd-Elall, A.M.M.; Megahed, A.M.; Abd-El-Kader, M.A.; Nabawy, E.E. Veterinary antibiotic resistance, residues, and ecological risks in environmental samples obtained from poultry farms, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess 2015, 187, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.M.; Al Naiemi, N.; Elsohaby, I.; Mahmoud, A.F.; Salem, G.A.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M. Prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales in retail sheep meat from Zagazig city, Egypt. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, B.; Gwida, M.; Sadat, A.; El-Toukhy, M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, M.; Elafify, M. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Virulent Listeria monocytogenes and Cronobacter sakazakii in Dairy Cattle, the Environment, and Dried Milk with the In Vitro Application of Natural Alternative Control. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashker, M.; Gwida, M.; Tomaso, H.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; El-Gohary, F.; Hotzel, H. Staphylococci in cattle and buffaloes with mastitis in Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7450–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awad, A.; Ramadan, H.; Nasr, S.; Ateya, A.; Atwa, S. Genetic characterization, antimicrobial resistance patterns and virulence determinants of staphylococcus aureus isolated form bovine mastitis. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 20, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gwida, M.; Saad, T.; Elgohary, A.; Mohamed, A. Characterization of methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from healthy cattle and buffaloes in a linked community. MVMJ 2021, 22, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmonir, W.; Essa, H.; El-Tras, W.F. Ecology of Staphylococcus aureus and its antibiotic resistance genes in dairy farms: Contributing factors and public health implications. Slov. Vet. Zb. 2019, 55, 747–754. [Google Scholar]
- Algammal, A.M.; Enany, M.E.; El-Tarabili, R.M.; Ghobashy, M.O.I.; Helmy, Y.A. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance profiles, virulence and enterotoxin-determinant genes of MRSA isolated from subclinical bovine mastitis samples in Egypt. Pathogens 2020, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashker, M.; Gwida, M.; Monecke, S.; El-Gohary, F.; Ehricht, R.; Elsayed, M.; Akinduti, P.; El-Fateh, M.; Maurischat, S. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and virulence profile of S. aureus isolated from household cattle and buffalo with mastitis in Egypt. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 240, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberson, J.R.; Fox, L.; Hancock, D.D.; Gay, J.M.; Besser, T.E. Ecology of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Various Sites on Dairy Farms. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, L.Y.W.; Leliso, S.A.; Bulto, A.O.; Ashenafi, D. Isolation, Identification, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Staphylococcus aureus from Clinical Mastitis in Sebeta Town Dairy Farms. Vet. Med. Int. 2021, 2021, 1772658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinini, R.; Cesaris, L.; Dapra, V.; Borromeo, V.; Picozz, C.; Secchi, C.; Zecconi, A. The role of teat skin contamination in the epidemiology of staphylococcus aureus intramammary infections. J. Dairy Res. 2009, 76, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, R.N.; Leeuwen, W.B.; Kreft, D.; Fox, L.K.; Barkema, H.W.; Schukken, Y.H.; Schukken, Y.H.; Van Belkum, A. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine and human skin, milking equipment, and bovine milk by phage typing, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and binary typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3894–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abo-Shama, U.H. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from cattle, buffalo, sheep and goats. Assiut. Vet. Med. J. 2014, 60, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gundogan, N.; Avci, E. Occurrence and antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus in raw milk and dairy products in Turkey. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2014, 67, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, X.; Jiang, T.; Peng, Z.; Xu, J.; Yi, L.; Li, F.; Fanning, S.; Baloch, Z. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus cultured from raw milk taken from dairy cows with mastitis in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, K.; Cai, H.; Huang, S.; Ni, Y.; Luo, B.; Qian, H.; Ji, H.; Wang, X. Prevalence and Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Raw Milk in Northern Xinjiang, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 705947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqib, A.I.; Ijaz, M.; Durrani, A.; Anjum, A.; Hussain, R.; Sana, S.; Farooqi, S.H.; Hussain, K.; Ahmad, S.S. Prevalence and antibiogram of Staphylococcus aureus, a camel mastitogen from Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2017, 49, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mourabit, N.; Arakrak, A.; Bakkali, M.; Zian, Z.; Bakkach, J.; Laglaoui, A. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in farm animals and breeders in north of Morocco. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.J.; Mork, T.; Høgåsen, H.R.; Rørvik, L.M. Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in bulk milk in Norway. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachica, R.V.; Genigeorgis, G.; Hoeprich, P.D. Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 21, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Al-Ashmawy, M.; Elbarbary, A.; Elbaba, H.A. Assessment of microbiological quality in some cheese varieties in Egypt. BVMJ 2019, 36, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.; El-Attar, L.E.; Omran, E. Microbiological Assessment of some Parameters of Kariesh Cheese Sold by Supermarkets and Street Vendors in Alexandria, Egypt. J. High Inst. Public Health 2016, 46, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, D.J.; Donnelly, C.W. Characterization of staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from raw milk utilized in small-scale artisan cheese production. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addis, M.; Pal, M.; Kyule, M.N. Isolation and identification of Staphylococcus species from raw bovine milk in Debre Zeit, Ethiopia. Vet. Res. 2011, 4, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, H.M.; Algammal, A.M.; Elfeil, W.K.; Youssef, F.M.; Harb, S.M.; Abd-Allah, E.M. Prevalence, molecular typing, and antimicrobial resistance of bacterial pathogens isolated from ducks. Vet. World 2019, 12, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enany, M.; Younes, S.; Al Gammal, A.E.; Salem, M.; El Dieb, H. Prevalence of coagulase (coa) gene and mec A gene of S. aureus isolated from bovine clinical mastitis. SCVMJ 2013, 18, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Álvarez, L.; Holden, M.; Lindsay, H.; Webb, C.; Brown, D.; Curran, M.; Walpole, E.; Brooks, K.; Pickard, D.J.; Teale, C.; et al. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a novel mecA homologue in human and bovine populations in the UK and Denmark: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rall, V.L.M.; Vieira, F.P.; Rall, R.; Vieities, R.L.; Fernandes, A.; Candeias, J.M.G.; Cardoso, K.F.G.; Araújo, J.P. PCR detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from raw and pasteurized milk. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asao, T.; Kumeda, Y.; Kawai, T.; Shibata, T.; Oda, H.; Haruki, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Kozaki, S. An extensive outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning due to low-fat milk in Japan: Estimation of enterotoxin A in the incriminated milk and powdered skim milk. Epidemiol. Infect 2003, 130, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Tamate, N.; Yamaguchi, K.; Makino, S.I. Quantitative analysis of Staphylococcus aureus in skimmed milk powder by real-time PCR. J. Vet. Med. Sci 2005, 67, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adame-Gómez, R.; Castro-Alarcón, N.; Vences-Velázquez, A.; Toribio-Jiménez, J.; Pérez-Valdespino, A.; Leyva-Vázquez, M. Genetic Diversity and Virulence Factors of S. aureus Isolated from Food, Humans, and Animals. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1048097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzin, T.; Nazir, K.H.; Zahan, M.N.; Parvej, M.S.; Zesmin, K.; Rahman, M.T. Antibiotic resistance profile of bacteria isolated from raw milk samples of cattle and buffaloes. JAVAR 2016, 3, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphahlele, M.P.; Oguttu, J.W.; Petzer, I.M.; Qekwana, D.N. Prevalence and antimicrobial drug resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from cow milk samples. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimera, Z.I.; Mshana, S.E.; Rweyemamu, M.M.; Mboera, L.E.; Matee, M.I. Antimicrobial use and resistance in food-producing animals and the environment: An African perspective. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haag, A.F.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penadés, J.R. Staphylococcus aureus in Animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Aasbakk, K.; Maeland, J.A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jukes, L.; Mikhail, J.; Bome-Mannathoko, N.; Hadfield, S.J.; Harris, L.G.; El-Bouri, K. Rapid differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and other coagulase-negative staphylococci and meticillin susceptibility testing directly from growth-positive blood cultures by multiplex real-time PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.I.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.D.; Kim, K.S. Detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolates using two-step triplex PCR and conventional methods. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 673–676. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (CLSI, 2020); Thirty Informational Supplement; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, T.; Samir, M.; El-Mekawy, R.; Ariny, E.; El-sayed, S.; Enan, G.; Abdelatif, S.H.; Askora, A.; Merwad, A.M.; Tartor, Y.H. Methicillin- and Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus From Humans and Ready-To-Eat Meat: Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Formation Ability. Front Microbiol. 2022, 12, 735494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Sample | Cattle | Buffalo | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Positive n (%) | No. Examined | Positive n (%) | ||
| Rectal swabs | 20 | 5 (25.0) | 30 | 4 (13.3) | 0.292 |
| Udder swabs | 20 | 5 (25.0) | 30 | 5 (16.7) | 0.470 |
| Milk | 20 | 3 (15.0) | 30 | 7 (23.3) | 0.470 |
| subtotal | 60 | 13 (21.7) | 90 | 16 (17.8) | 0.554 |
| Bedding material | 20 | 4 (20.0) | 30 | 4 (13.3) | 0.528 |
| Boot swabs | 20 | 3 (15.0) | 30 | 5 (16.7) | 0.874 |
| Feed | 20 | 2 (10.0) | 30 | 10 (33.3) | 0.058 |
| Water | 20 | 3 (15.0) | 30 | 2 (6.7) | 0.335 |
| subtotal | 80 | 12 (15.0) | 120 | 21 (17.5) | 0.640 |
| Total | 140 | 25 (17.9) | 210 | 37 (17.6) | 0.954 |
| Type of Samples | Cattle | Buffalo | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm I | Farm II | p Value | Farm III | Farm IV | p Value | |||||
| n | Positive n (%) | n | Positive n (%) | n | Positive n (%) | n | Positive n (%) | |||
| Rectal swabs | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 10 | 3 (30.0) | 0.606 | 15 | 2 (13.3) | 15 | 2 (13.3) | 1.0 |
| Udder swabs | 10 | 3 (30.0) | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 0.606 | 15 | 2 (13.3) | 15 | 3 (20.0) | 0.624 |
| Milk | 10 | 1 (10.0) | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 0.531 | 15 | 0(0.0) | 15 | 7 (40.0) | 0.003 * |
| Subtotal | 30 | 6 (20.0) | 30 | 7 (23.3) | 0.754 | 45 | 4 (8.9) | 45 | 12 (26.8) | 0.027 * |
| Bedding | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 1.0 | 15 | 1 (6.7) | 15 | 3 (20.0) | 0.598 |
| Boot swabs | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 10 | 1 (10.0) | 0.531 | 15 | 1 (6.7) | 15 | 4 (26.7) | 0.330 |
| Feed | 10 | 0 (0.0) | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 0.136 | 15 | 0 (0.0) | 15 | 10 (66.7) | ≤0.001 * |
| Water | 10 | 0 (0.0) | 10 | 3 (30.0) | 0.06 | 15 | 0 (0.0) | 15 | 2 (13.3) | 0.483 |
| Subtotal | 40 | 4 (10.0) | 40 | 8 (20.0) | 0.21 | 60 | 2 (3.3) | 60 | 19 (31.7) | ≤0.001 * |
| Total | 70 | 10 (14.3) | 70 | 15 (21.4) | 0.269 | 105 | 6 (5.7) | 105 | 31 (29.5) | ≤0.001 * |
| Gene Function | Target Genes | Positive Samples n/Tested n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Buffalo | Karish Cheese | Total | ||
| Virulence genes | sea | 10/25 (40.0) | 6/37 (16.2) | 2/5 (40.0) | 18/67 (26.9) |
| seb | 0/25 (0.0) | 0/37 (0.0) | 0/5 (0.0) | 0/67 (0.0) | |
| sec | 2/25 (8.0) | 0/37 (0.0) | 1/5 (20.0) | 3/67 (4.5) | |
| sed | 0/25 (0.0) | 1/37 (2.7) | 1/5 (20.0) | 2/67 (3.0) | |
| Total | 12/25 (48.0) | 7/37 (18.9) | 4/5 (80.0) | 23/67 (34.3) | |
| Resistance gene | mecA | 4/25 (16.0) | 6/37 (16.2) | 3/5 (60.0) | 13/67 (19.4) |
| Antimicrobial Agents | Concentration (µg) | Resistant n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Clindamycin (CL) | 10 | 67 (100.0) |
| Kanamycin (K) | 30 | 65 (97.0) |
| Nalidixic acid (NA) | 30 | 58 (86.6) |
| Cefotaxime (CF) | 30 | 49 (73.1) |
| Sulphamethazole—trimethoprim (SXT) | 25 | 44 (65.7) |
| Cefazolin (CZ) | 30 | 36 (53.7) |
| Tetracycline (T) | 30 | 31 (46.3) |
| Erythromycin (E) | 15 | 25 (37.3) |
| Ampicillin (AM) | 10 | 16 (23.9) |
| Gentamicin (G) | 10 | 15 (22.3) |
| Imipenem (IPM) | 10 | 9 (13.4) |
| Amikacin (AK) | 30 | 4 (6.0) |
| Ciprofloxacin (CP) | 5 | 3 (4.5) |
| Cefoxitin (FOX) | 30 | 15 (22.3) |
| Cattle (n = 25) | Buffalo (n = 37) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | Range | |
| 0.519 ± 0.235 | 0.14–1.0 | 0.382 ± 0.225 | 0.07–0.93 | 0.024 * |
| Livestock (n = 29) and dairy products (n = 5) (n = 34) | Environment (n = 33) | p Value | ||
| 0.519 ± 0.260 | 0.14–1.0 | 0.394 ± 0.211 | 0.07–0.79 | 0.035 * |
| Sample | MAR Index | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Median | Range | ||
| Rectal swabs | 0.452 ± 0.319 | 0.357 | 0.14–1.0 | 0.027 * |
| Udder swabs | 0.386 ± 0.241 ef | 0.286 | 0.14–0.79 | |
| Milk | 0.621 ± 0.161 adf | 0.607 | 0.36–0.93 | |
| Karish | 0.700 ± 0.216 bce | 0.786 | 0.36–0.93 | |
| Bedding material | 0.499 ± 0.174 | 0.535 | 0.29–0.71 | |
| Boot swabs | 0.321 ± 0.100 ab | 0.357 | 0.14–0.43 | |
| Feed | 0.363 ± 0.216 cd | 0.321 | 0.07–0.79 | |
| Water | 0.414 ± 0.347 | 0.286 | 0.07–0.79 | |
| Herd ID | Animal Species | Number of Animals/Herds | Samples Type and Number | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectal Swabs | Udder Swabs | Milk | Bedding Materials | Boot Swabs | Feed | Water | Total | |||
| I | Cattle | 37 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 70 |
| II | Cattle | 28 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 70 |
| Subtotal | 65 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 140 | |
| III | Buffaloes | 38 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 105 |
| IV | Buffaloes | 39 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 105 |
| Subtotal | 77 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 210 | |
| Total | 142 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 350 | |
| Karish cheese | 30 samples of Karish cheese were collected from 10 different markets (three/market) | 380 | ||||||||
| Target Gene | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′→3′) | Product Size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| nuc (F) | GCGATTGATGGTGATACGGTT | 270 | [55] |
| nuc (R) | AGCCAAGCCTTGACGAACTAAAGC | ||
| mecA (F) | TAGAAATGACTGAAC GTCCG | 533 | [56] |
| mecA (R) | TTGCGATCA ATGTTACCGTAG | ||
| sea (F) | TTGGAAACGGTTAAAACGAA | 120 | [47] |
| sea (R) | GAACCTTCCCATCAAAAACA | ||
| seb (F) | TCGCATCAAACTGACAAACG | 478 | |
| seb (R) | GCGGTACTCTATAAGTGCC | ||
| sec (F) | GACATAAAAGCTAGGAATTT | 257 | |
| sec (R) | AAATCGGATTAACATTATCC | ||
| sed (F) | CTAGTTTGGTAATATCTCCT | 317 | |
| sed (R) | TAATGCTATATCTTATAGGG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badawy, B.; Elafify, M.; Farag, A.M.M.; Moustafa, S.M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.Z.; Moawad, A.A.; Algammal, A.M.; Ramadan, H.; Eltholth, M. Ecological Distribution of Virulent Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Livestock, Environment, and Dairy Products. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111651
Badawy B, Elafify M, Farag AMM, Moustafa SM, Sayed-Ahmed MZ, Moawad AA, Algammal AM, Ramadan H, Eltholth M. Ecological Distribution of Virulent Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Livestock, Environment, and Dairy Products. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111651
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadawy, Basma, Mahmoud Elafify, Alshimaa M. M. Farag, Samar M. Moustafa, Mohamed Z. Sayed-Ahmed, Amira A. Moawad, Abdelazeem M. Algammal, Hazem Ramadan, and Mahmoud Eltholth. 2022. "Ecological Distribution of Virulent Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Livestock, Environment, and Dairy Products" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111651
APA StyleBadawy, B., Elafify, M., Farag, A. M. M., Moustafa, S. M., Sayed-Ahmed, M. Z., Moawad, A. A., Algammal, A. M., Ramadan, H., & Eltholth, M. (2022). Ecological Distribution of Virulent Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Livestock, Environment, and Dairy Products. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111651











